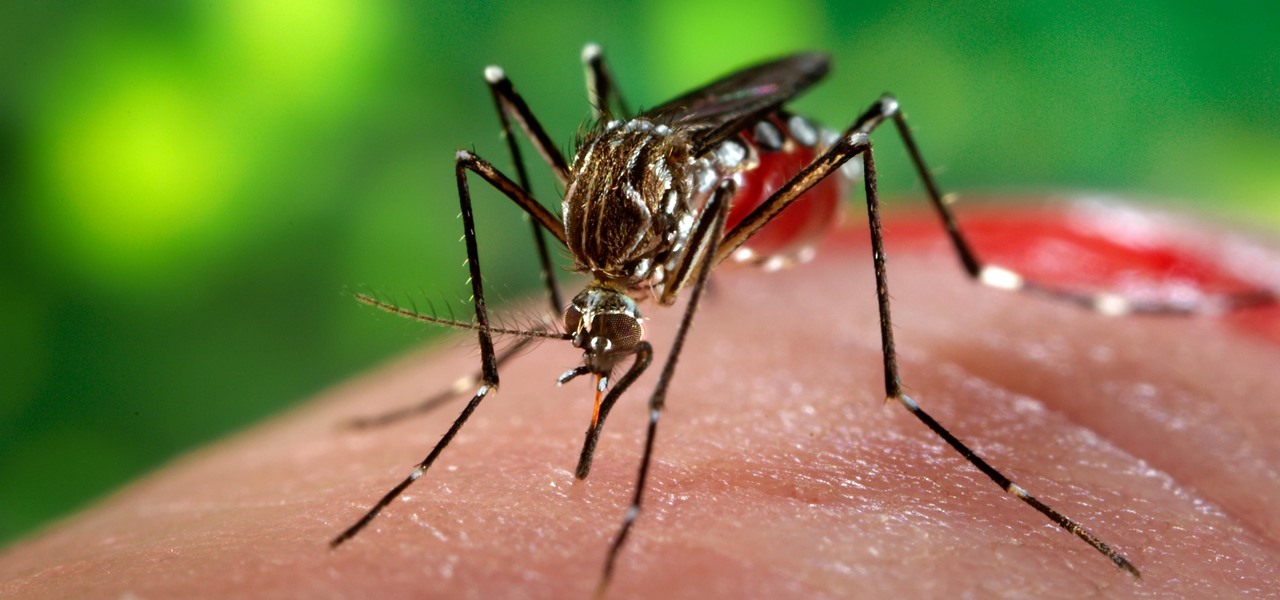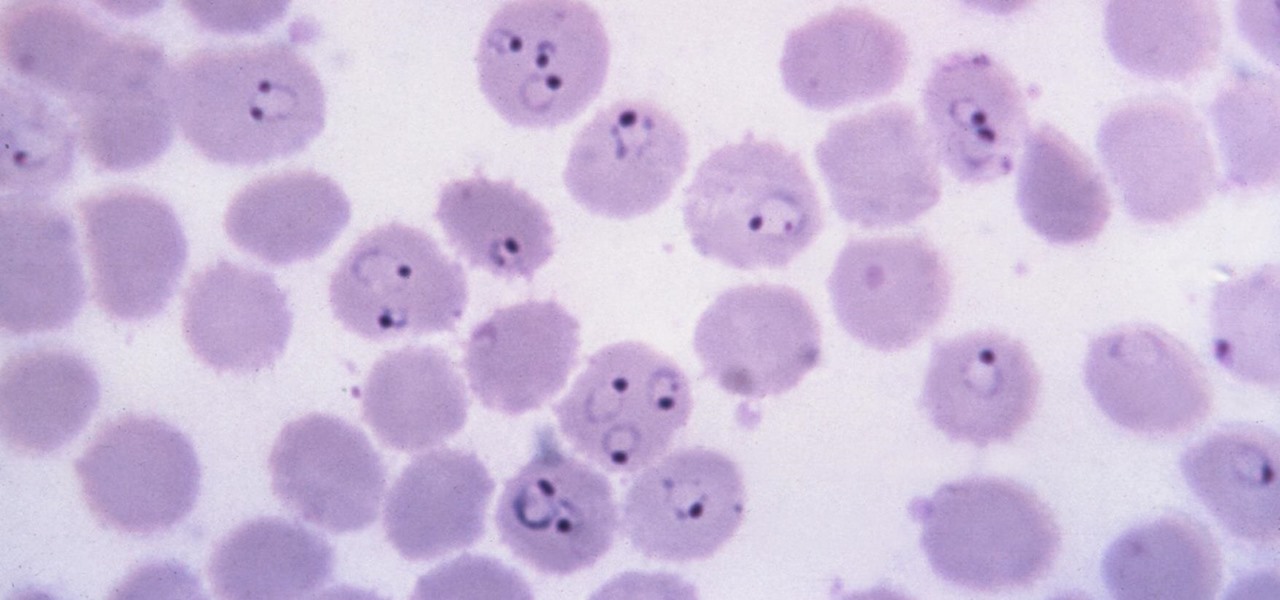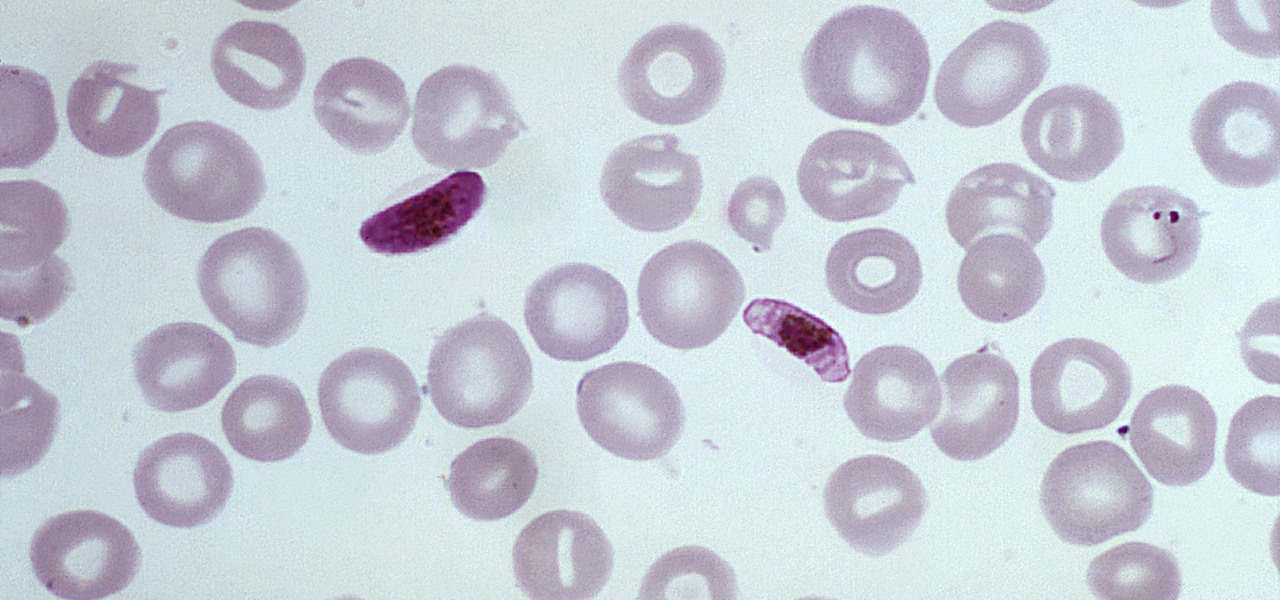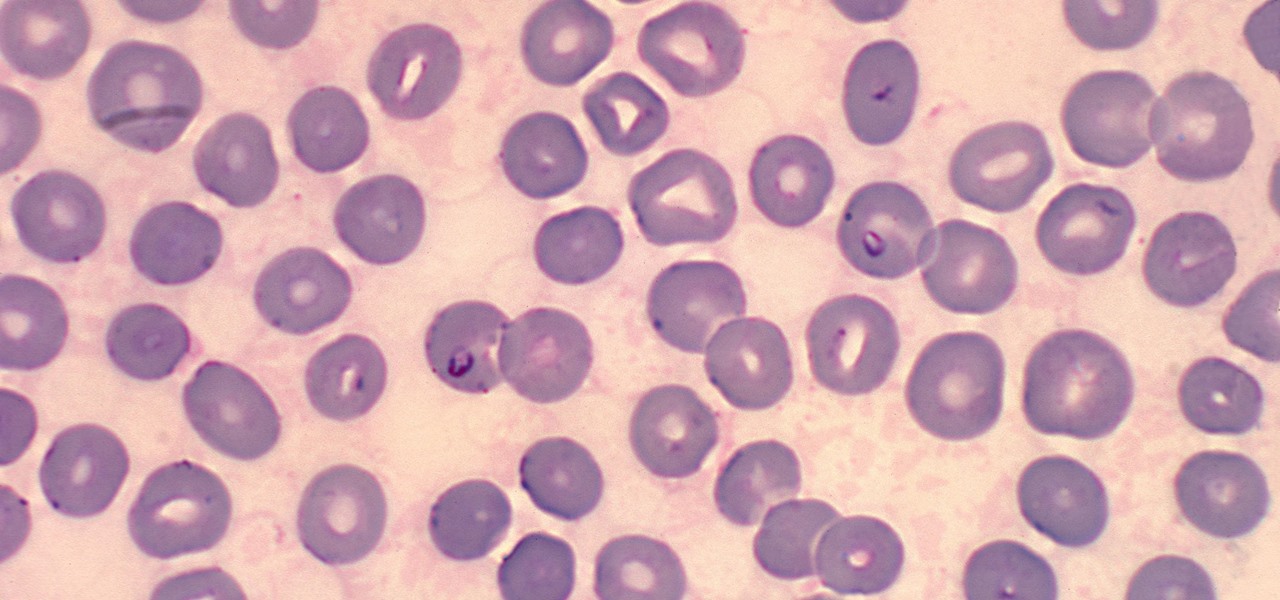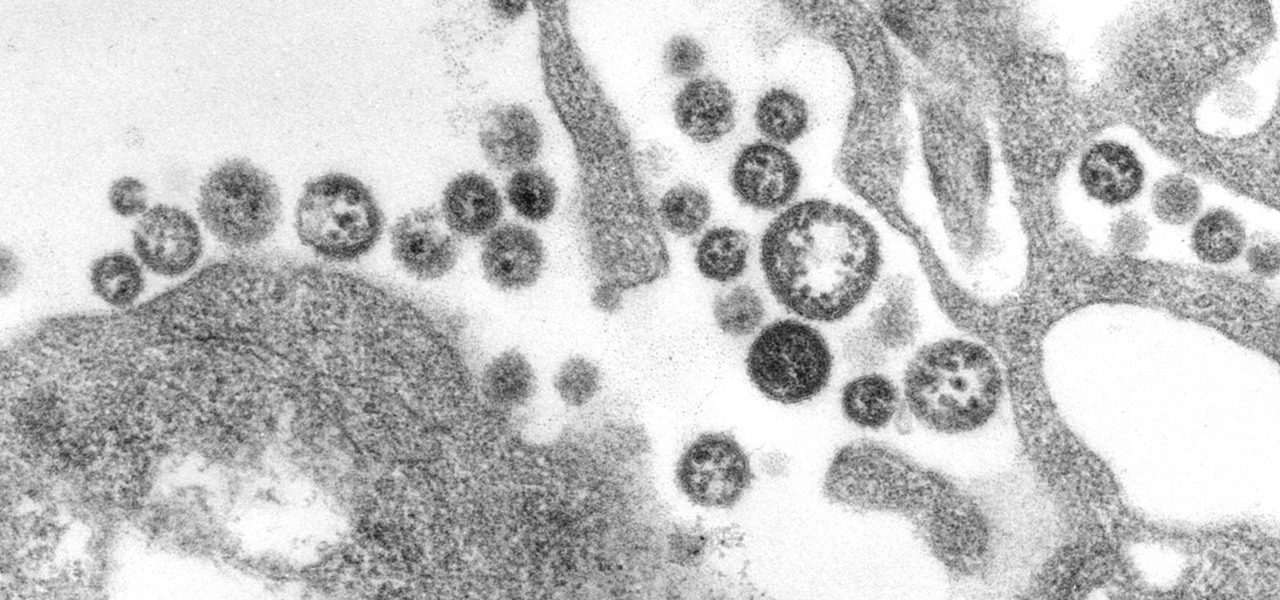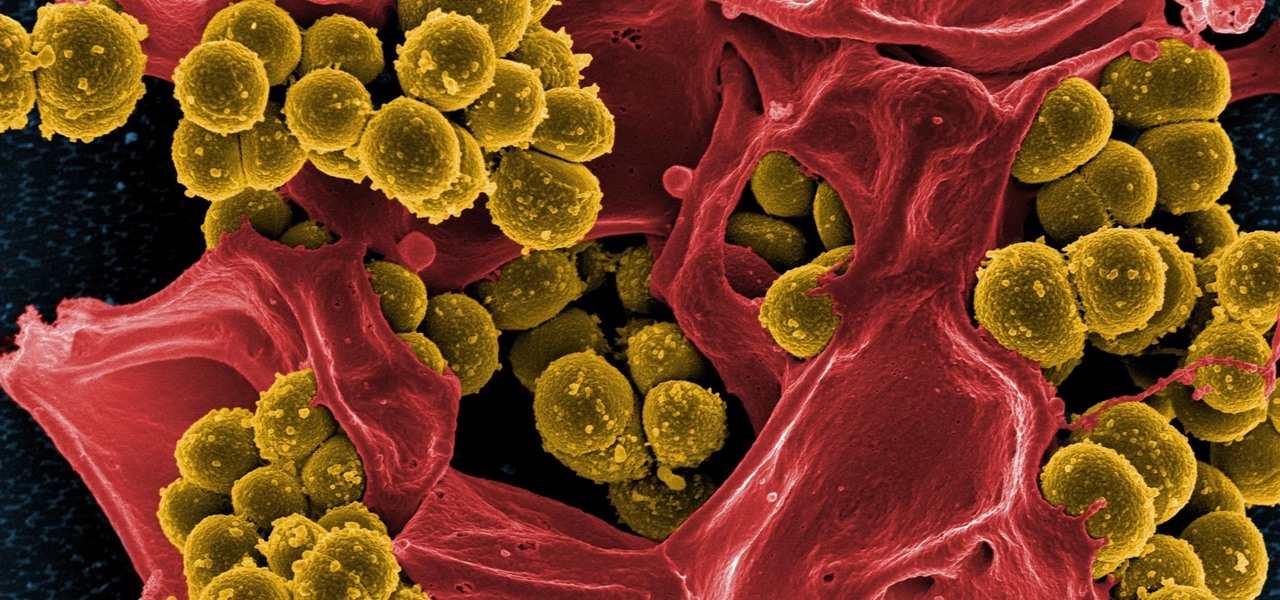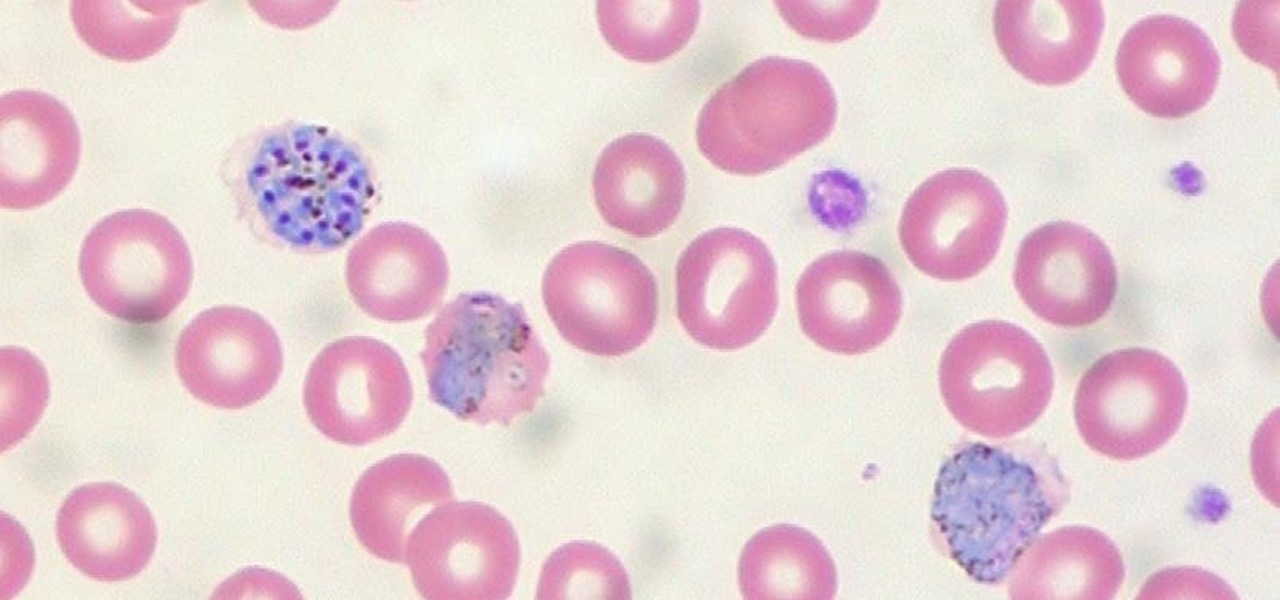
When the mosquito that carries the malaria parasite (Plasmodium falciparum) bites someone, the parasite must travel to the liver where it undergoes part of its lifecycle before infecting red blood cells and spreading to its next host. Until now, the first step of how the parasite gets to the liver hasn't been clear.

Deadly rat lungworm parasites have found their way into Florida. The parasitic worm relies on snails and rats to complete its life cycle, but don't let this nematode's name fool you. This worm can cause meningitis and death in humans who inadvertently consume snails, frogs, or crustaceans harboring the infective parasite.
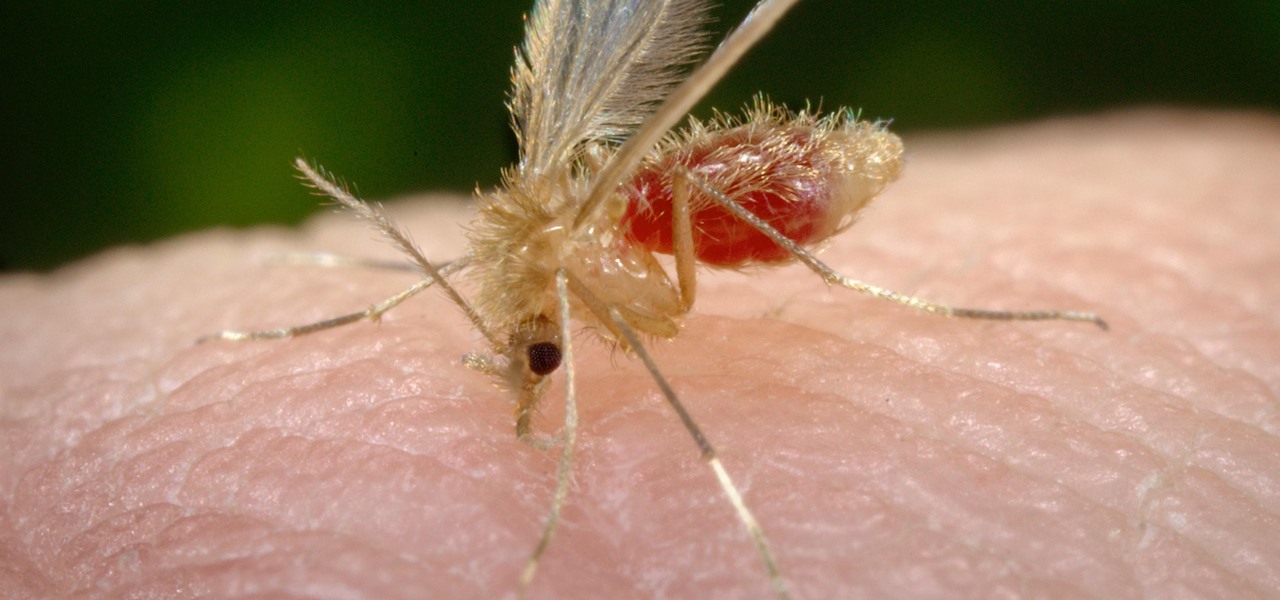

Transmitted by a sandfly one-third the size of a mosquito, parasitic Leishmania protozoa are responsible for a flesh-destroying disease that kills an estimated 20,000 people per year. Two new studies offer understanding of how the parasite provides immunity through persistence and why some people suffer more virulent forms of the disease.
For the first time, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved medication to treat children with a serious infection called Chagas disease, which stealthily infects and damages the hearts of millions of victims a year.

Warning: If you are eating and for some reason still decided to click on this article, turn around now. Maui, Hawaii health officials have reported finding at least six cases of angiostrongyliasis, a parasitic lungworm that infects humans. Colloquially, it's known as rat lungworm disease. And if you think that name is awful, just wait until you hear what it does to the human body.
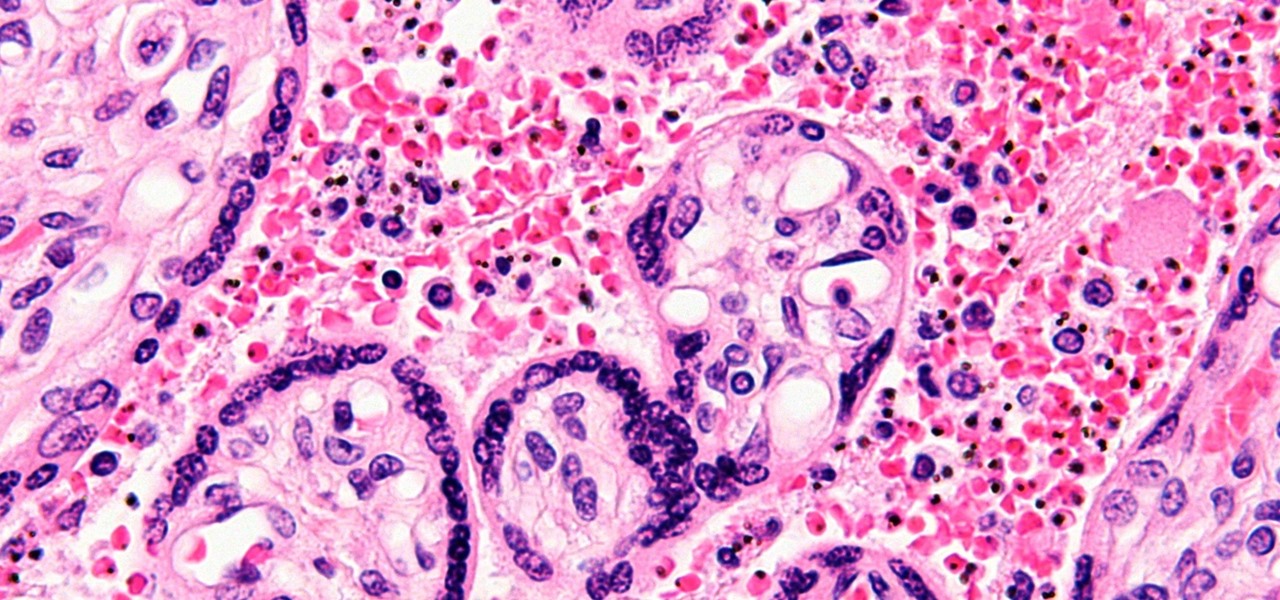
You might feel the bite, you might not, but an infected mosquito has injected you with a parasite named Plasmodium falciparum, a single-cell protozoa that quickly takes up residence in your body.

Somewhere around 600–800 million people in the world are infected with whipworm (Trichuris trichiura), an infection they got from ingesting soil or water contaminated with feces of infected animals or people containing the parasite's eggs.

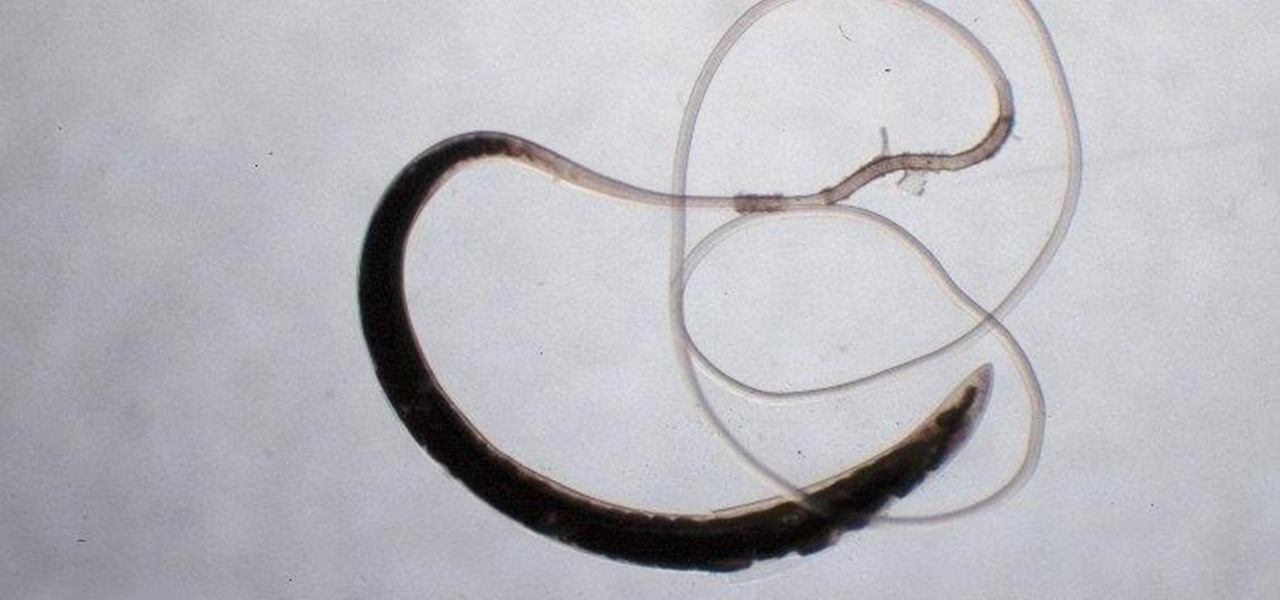
After California college student Luis Ortiz blacked out and was taken to the hospital in 2015, doctors were startled to discover the reason his brain was swelling—a one-centimeter long, wriggling tapeworm living within a ventricle in the middle of his brain.

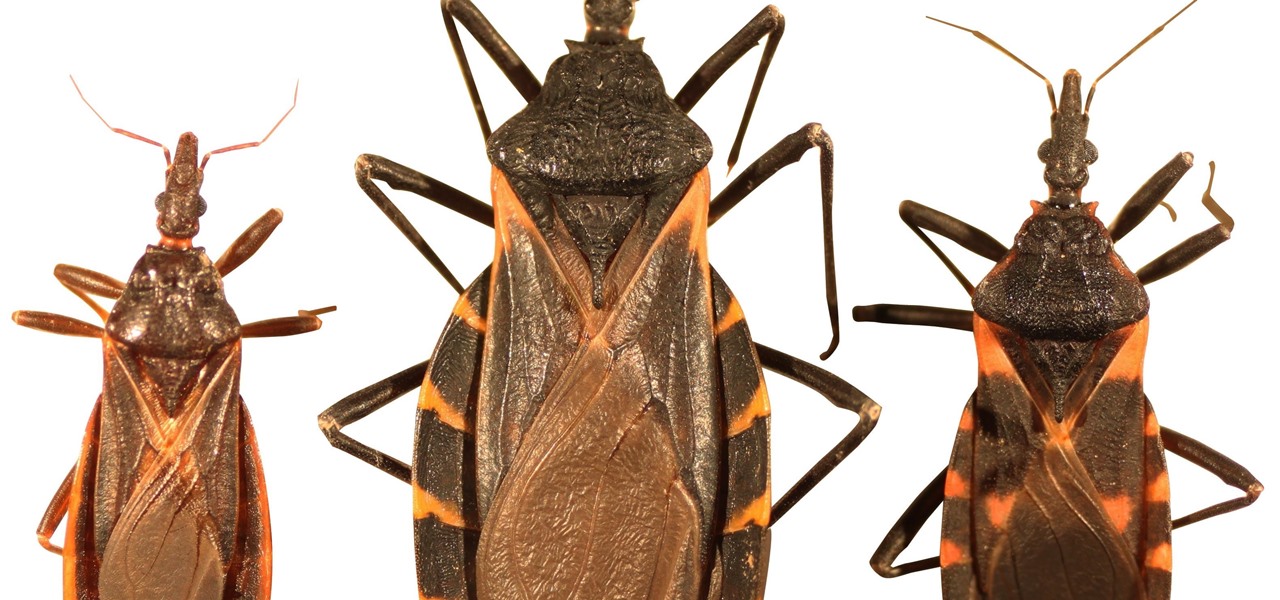
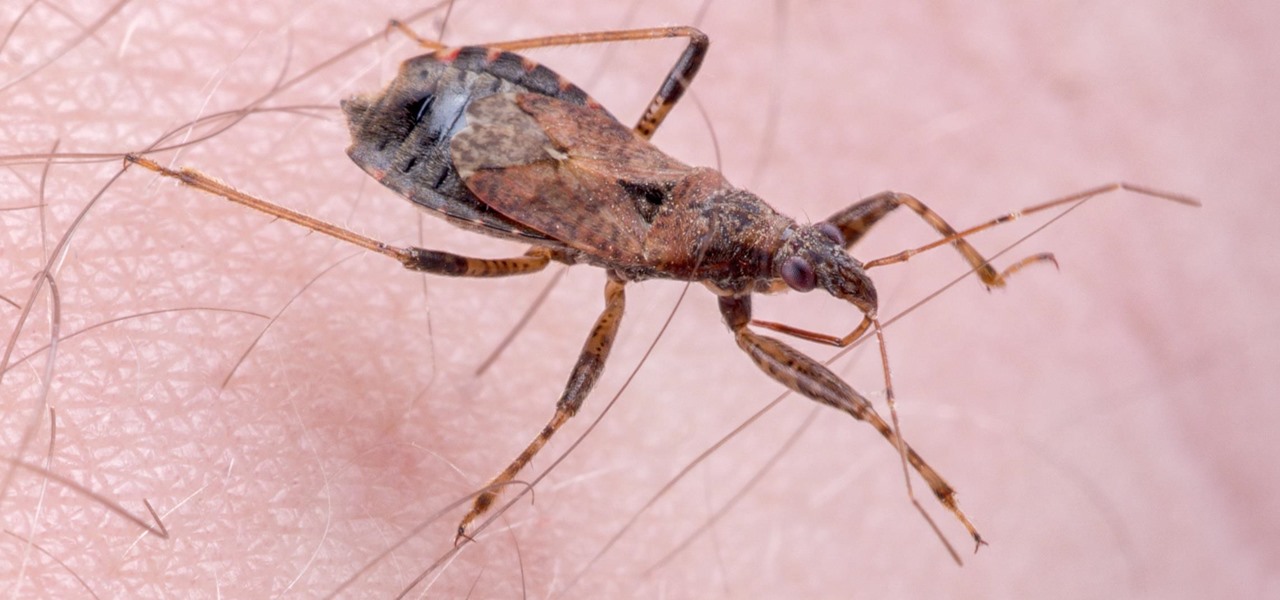
Take a close look at the image above. These bugs spread a deadly parasite that infects thousands of people each year. They also live in the US, and it's important to know where they are and whether you need to worry that they're carrying a dangerous infection.

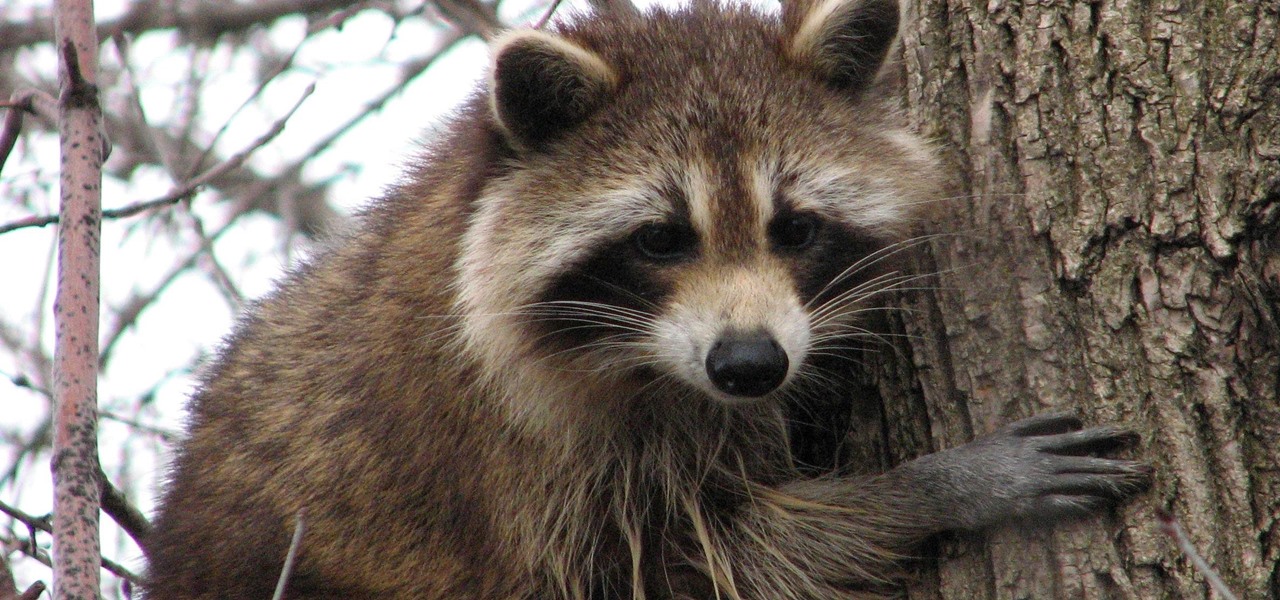
So cute, so furry, and so chock full of parasites. While raccoons are fun to watch, they are neither friendly nor clean — and they can make you sick in more ways than one.

Learn how to identify the major parasite that destroys Monarch caterpillars and butterflies. A quick magnified look at their scales can reveal this most dangerous butterfly plague.

Computer viruses are terrifying. They are undetectable, dangerous, and operate constantly right under your nose. For the average computer user, there are only a few repair options. You could buy expensive antivirus software that causes more problems than it fixes, you can wipe your hard drive clean and lose all of your important data, or if all else fails—just switch to Linux.

In this excellent informative yet entertaining video Sara from petside.com invites you to join here in the war to end flea and tick infestation. You'll learn why they love to attack your pet and how exactly to combat these pesky little parasite. So gear up for battle and make sure you end up on top and not defeated by these annoying little blood suckers.

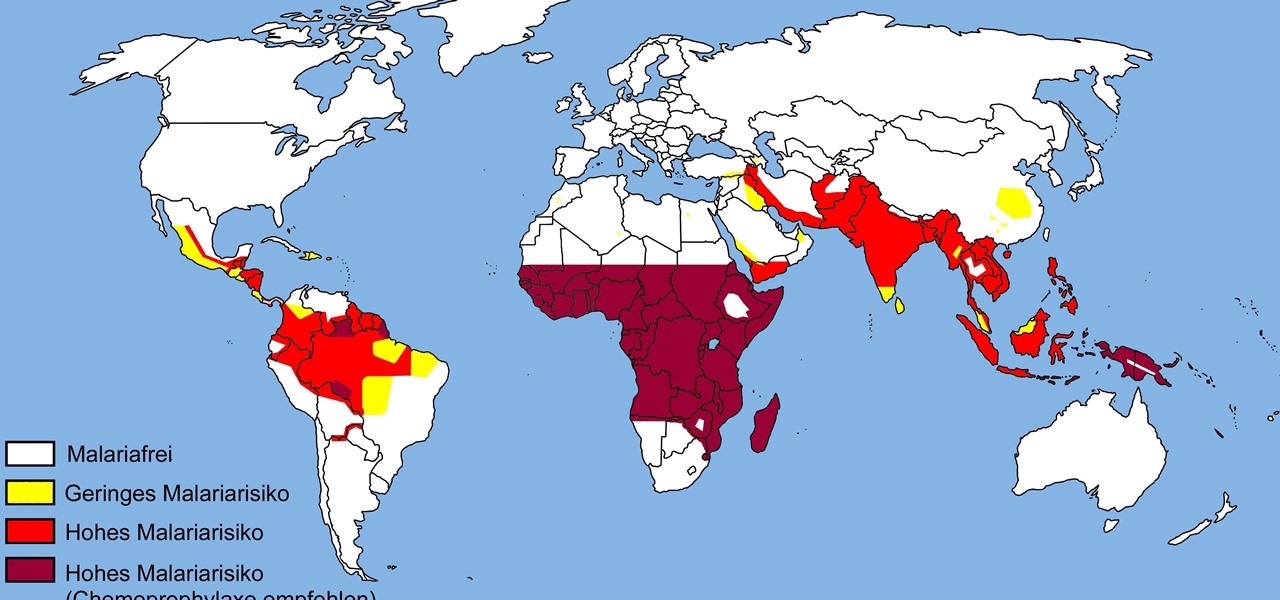
Malaria is a massive worldwide health problem. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate that 212 million cases of malaria occurred worldwide in 2015 and 429,000 of the infected people died.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimated that there were 212 million cases of malaria across the world in 2015, and 429,000 of those people died — mostly children living in Africa. Preventing and treating those infections has been a challenging world priority. That makes a new malaria drug discovery — published in Science Translational Medicine — incredibly important.

The intestinal parasite Cyclospora cayetanensis has a dramatically increased infection rate this summer, and the source is still unknown, the CDC advised today. 2017 is a good year for Cyclospora looking for homes to start their families and a bad year for those of us who don't like food-stealing tenants living in our bodies.

Giardia -- ever hear of it? Probably not, but you'd more than likely be surprised to know that it is the most common nonbacterial cause of diarrhea in the United States. Learn how to care for your pet with help from VetVid. See how to prevent and treat giardia in pets with this video tutorial.

You may not have heard of visceral leishmaniasis, onchocerciasis, or lymphatic filariasis, and there is a reason for that. These diseases, part of a group of infections called neglected tropical diseases (NTDs), impact more than a billion people on the planet in countries other than ours. Despite the consolation that these often grotesque illnesses are "out of sight, out of mind," some of these infections are quietly taking their toll in some southern communities of the US.

Looking to learn how to bake delectable pork chops? Follow these steps and you will soon be enjoying a delicious and easy pork chop dish that will please any palate.

Even if your cat drives you a little nuts, don't worry, because a new study says that cats pose no risk to your mental health.

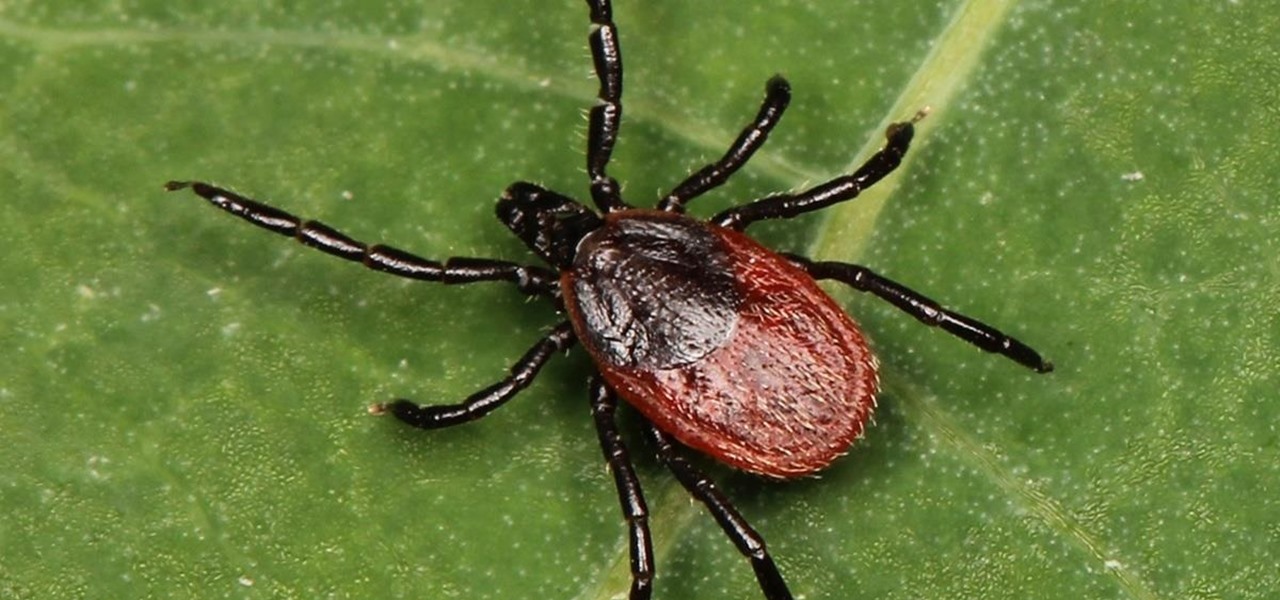
As a part of the already crowded field of diseases transmitted by ticks, you may not know the disease babesiosis, a dangerous infection caused by a parasite that infiltrates blood cells.

While no longer native to the United States, hospitalization from malaria occurs in this country more than most would believe. Why is that, and what can you do to protect yourself when you travel abroad to regions where malaria is active?

The number of households in the US that go hungry because they lack money for food hit a high of almost 15% in 2011. While that number continues to decline, nearly 13% of American households still go hungry.

The theme for 2017's World Malaria Day, which is today, April 25, is "End Malaria for Good." For many Americans, this might seem like an odd plea. Especially since Malaria is seemingly an obsolete problem here. However, on World Malaria Day, it's important to remember the danger of malaria is still very much present in the US. And around the world, the disease is at the epicenter of a global crisis.

A robust appetite for imported foods is leading to increased disease outbreak in the US. Despite the locovore and slow food movements, America's demand for foreign foods is picking up. According to a study published in the journal of Emerging Infectious Diseases, demand for imported fresh fruits, vegetables, and seafoods has jumped in recent years.

Like humans, cats can suffer infections caused by ticks, and too often, the disease is fatal. Learn about tickborne diseases that affect cats and what you can do to protect Fluffy from an untimely demise.

Whether you like it or not, certain songs get stuck in your head. You might be driving to work or school when suddenly Cher's 1998 lead single "Believe" plays on the radio.

It is not just a bad summer for ticks — it has been a bad decade for the spread of tick-borne infections. New surveillance from the CDC reports rapid expansion and increase in cases of babesiosis, a sometimes life-threatening disease, in Wisconsin.

With summer just ahead, you, or your children, may be looking forward to some pool time or the water park. When planning water-based fun this year, keep a heads-up for microbes.

If you live with pets, you know where their tongue has been, yet you let them kiss and lick you all they want without even thinking twice about it. I've heard people say that a dog's mouth is very clean, and that their saliva, delivered by licking, can help heal wounds, but is that really true?

Researchers have been studying the blood meals of flies to understand the flow of infectious pathogens in wild animals.

All fields of study have their own language. For people interested in learning about microbes, the language can sometimes be downright difficult — but it doesn't need to be. From antibiotics to xerophiles, we have you covered in an easy-to-understand glossary.

Four million Americans misused prescription opioid painkillers in 2014. Those who do are 40 times more likely to inject heroin or other drugs than other people. Now, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) are blaming that misuse for a 12-fold increase in endocarditis, an infection of the heart valves.

When the climate changes, so do all the things that rely on the climate, including people, plants, and pathogens. A European study recently took a broad look at what kind of microorganisms are most likely to be affected as climate change heats, cools, dries, and wets the world around us.

A recent study offers information that might help combat a deadly virus that affects an estimated 300,000 people each year in West Africa.

Rising on the world stage, dengue fever is transmitted by mosquitoes — and apparently air travel too.

Citrus greening disease — caused by a bacteria spread by psyllid insects — is threatening to wipe out Florida's citrus crop. Researchers have identified a small protein found in a second bacteria living in the insects that helps bacteria causing citrus greening disease survive and spread. They believe the discovery could result in a spray that could potentially help save the trees from the bacterial invasion.

Mosquitoes are a big problem, and citronella candles are not the solution. There are a lot of mosquito species. The American Mosquito Control Association reports there are more than 3000 mosquito species in the world, and about 200 of those occur in the US. The most common are the Aedes, Anopheles, and Culex species. These are also the three mosquito species most likely to transmit serious illness, and all of them live in the US.

Drug-resistant bacteria have made curing some infections challenging, if not nearly impossible. By 2050, it's estimated that 10 million people will be dying annually from infections with antibiotic-resistant organisms.

Lyme is a growing threat as we move into warmer weather in the US. Researchers have said this year could be one of the worst for this tick-borne disease, as a skyrocketing mouse population and warmer temperatures increase the risk.