
News: 'Useless' Antibiotics Work When Matched Up in Threes
The search is on to find antibiotics that will work against superbugs — bacteria that are rapidly becoming resistant to many drugs in our antibiotic arsenal.


The search is on to find antibiotics that will work against superbugs — bacteria that are rapidly becoming resistant to many drugs in our antibiotic arsenal.
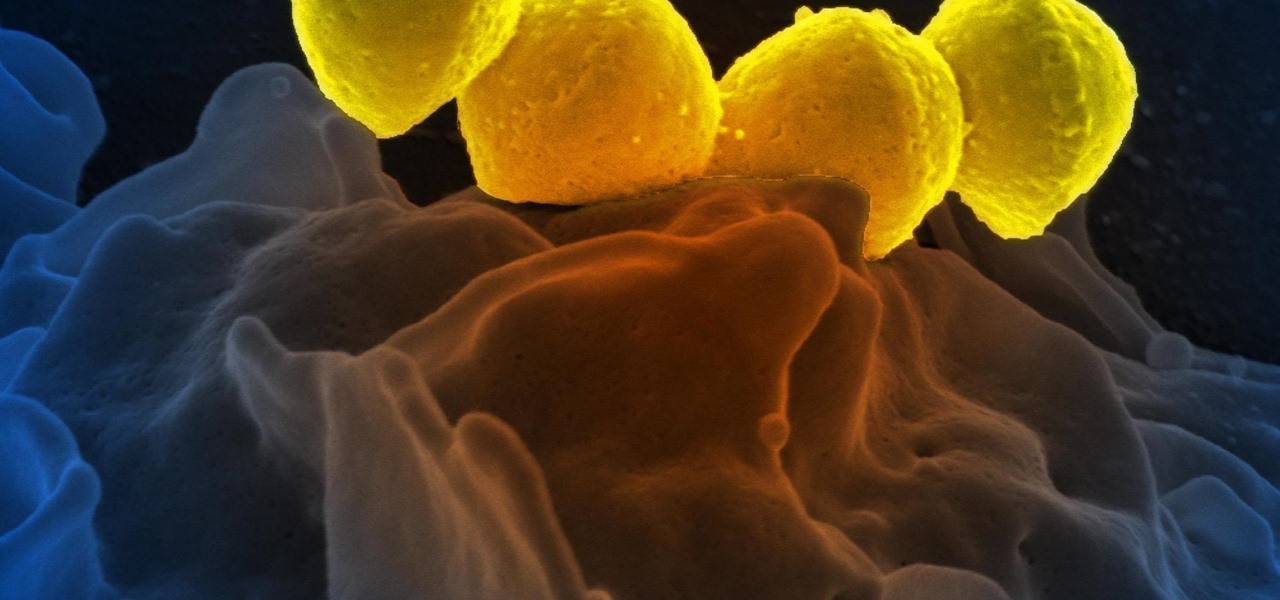
Significant strides have been in the race to find antibiotics to treat superbug infections — those caused by bacteria resistant to the antibiotics used to treat them. Now, an international team of scientists has discovered a new antibiotic produced by a microbe found in Italian soil.

Citrus greening disease — caused by a bacteria spread by psyllid insects — is threatening to wipe out Florida's citrus crop. Researchers have identified a small protein found in a second bacteria living in the insects that helps bacteria causing citrus greening disease survive and spread. They believe the discovery could result in a spray that could potentially help save the trees from the bacterial invasion.
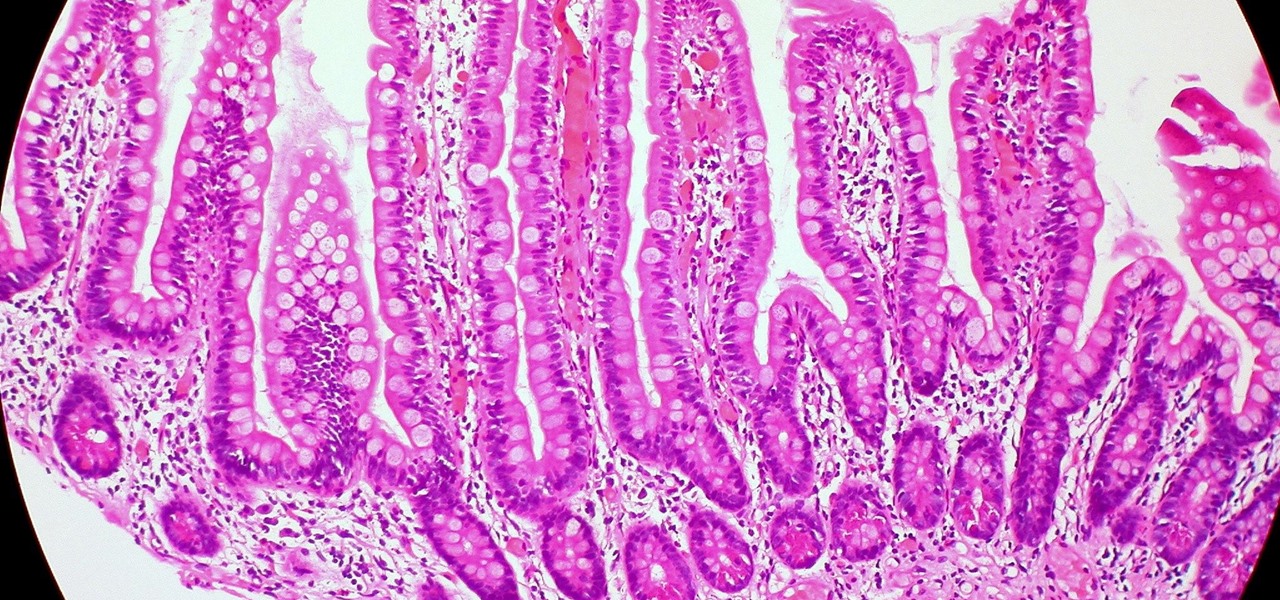
Several recent research studies have pointed to the importance of the microbes that live in our gut to many aspects of our health. A recent finding shows how bacteria that penetrate the mucus lining of the colon could play a significant role in diabetes.

Listeria monocytogenes bacteria don't play fair. Healthy people can usually handle the food-borne infection, but the bacterial infection hits pregnant women, fetuses and cancer patients very hard. Interestingly, a new study found that other bacteria may help prevent Listeria infections in those people.
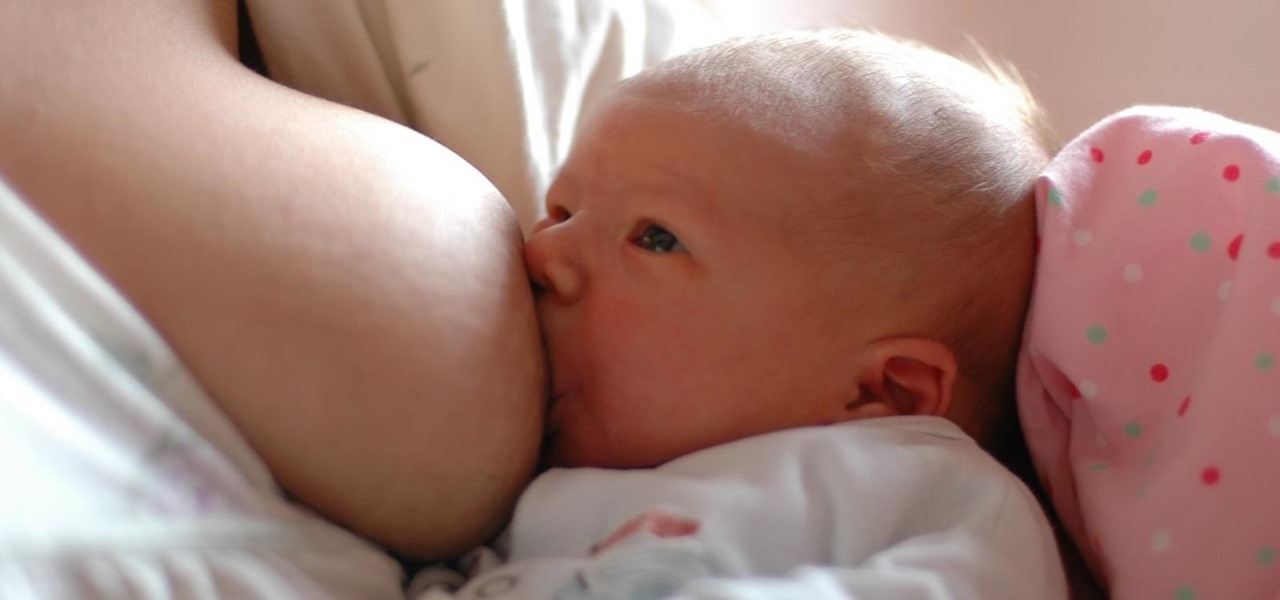

Breastfeeding is the ultimate in farm-to-table dining. It is sustenance prepared just for the baby and delivered with a very personal touch. Along with bonding, breastfeeding provides powerful protection to infants and young children in the form of beneficial bacteria, hormones, vitamins, protein, sugar, and antibodies manufactured on site to support infant health.
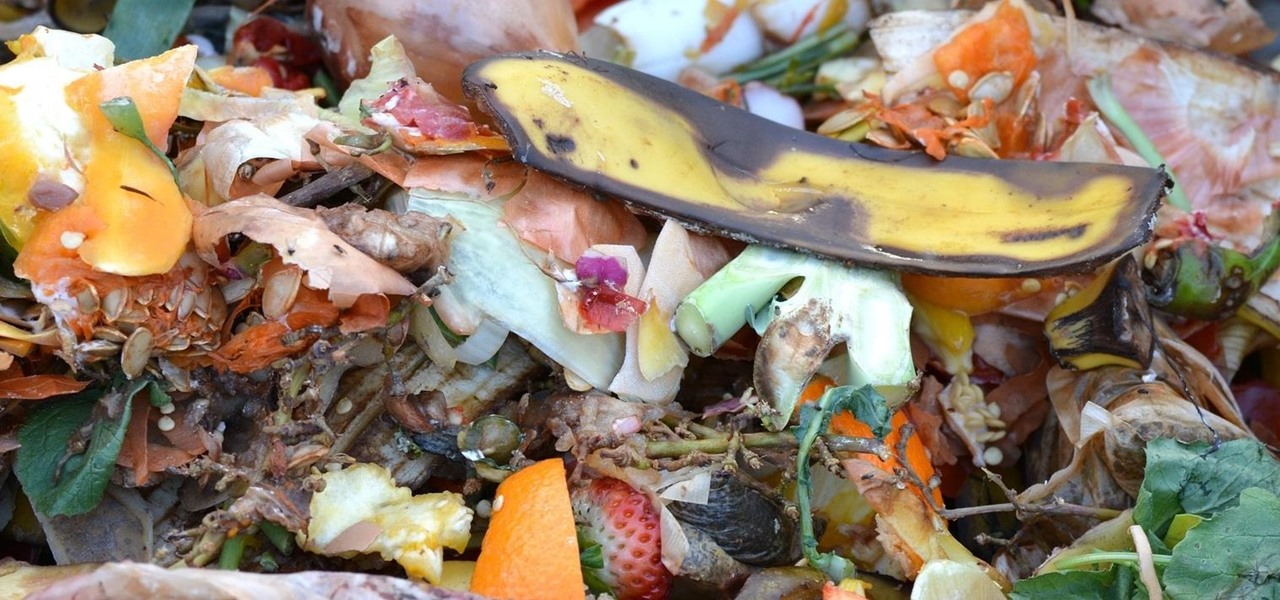

Are you looking for a little microbe magic? Think composting. Composting is a great way to reuse food and plant waste that you would otherwise throw into the trash, which would just end up in a landfill somewhere. During the composting cycle, microbes reduce this organic waste until it can be fed back into the soil as rich, crumbly compost. When returned to the soil, compost feeds plants and improves the nature of life underground. Sound like a great idea? It is — and it's easy.

In the ongoing search to find better ways to use antibiotics, an extract made from maple syrup has some surprisingly important medical benefits.

Overweight kids often become overweight adults. New research suggests a couple reasons why and suggested that there may be ways to intercept that fate.
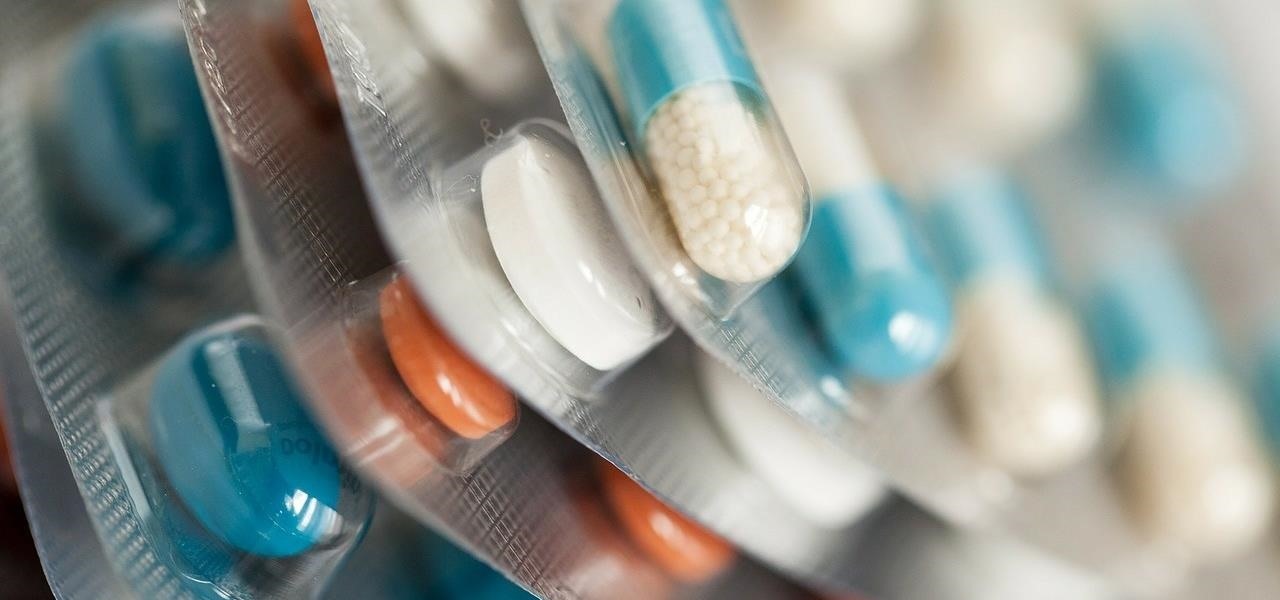
Although their effectiveness is waning, antibiotics remain a front-line defense against many infections. However, new science reveals using the wrong antibiotic for an infection could makes things much worse.
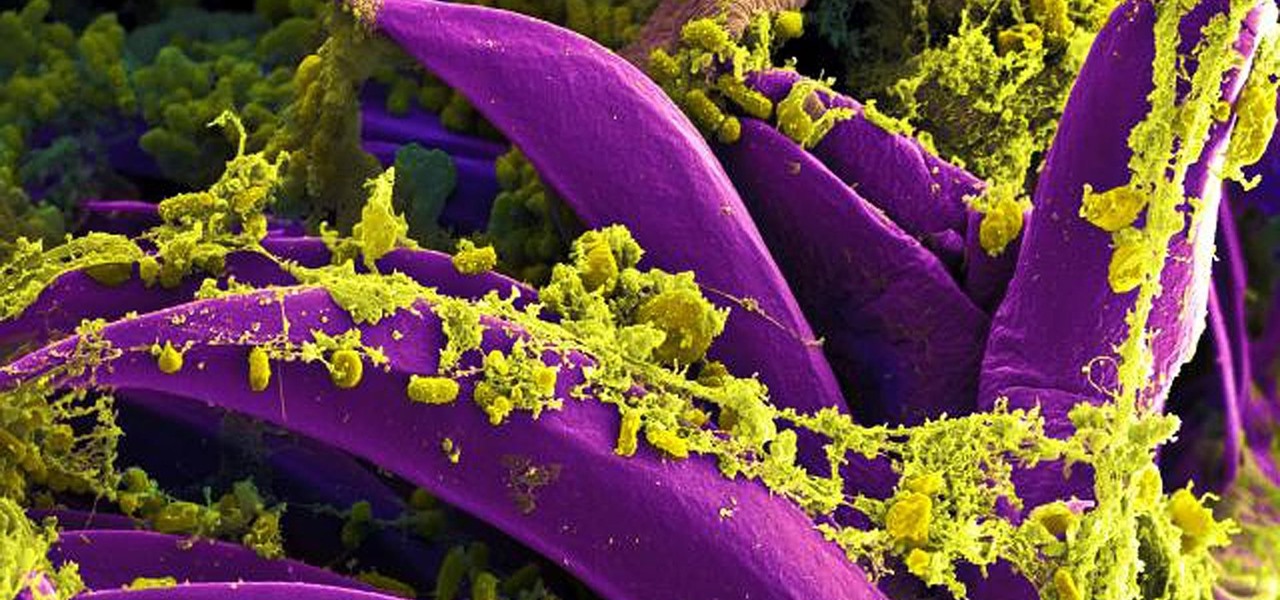
Antibiotics are one of our main weapons against infections. The problem is that many bacteria are becoming resistant to most of the antibiotics we use to treat them, and those 'superbugs' have created an urgent threat to our global health. A research group found a new way to hit a well known bacterial target and have developed a drug to hit it.

Legionnaires' disease is named after 1976 outbreak in Philadelphia that sickened 221 people and killed 34. More often striking adults over the age of 50, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently reported two cases where newborns contracted the often fatal disease — at their moment of birth.
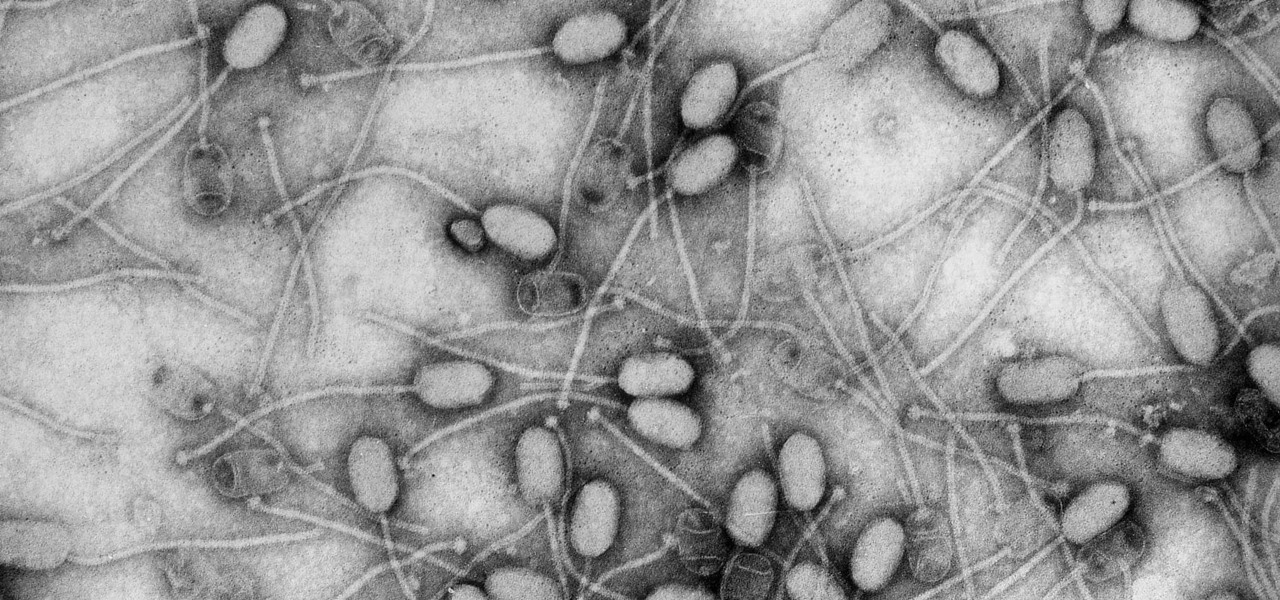
Fighting fire with fire, scientists are harnessing the adaptability of helpful microbes to challenge the adaptability of deadly microbes. What are we talking about? Hunting with phages — viruses that attack and kill bacteria.
The body's usual response to a bacterial infection in the blood — called sepsis — takes time. It requires a carefully orchestrated sequence of events that gets the body's immune system ramped up to deal with the invading bacteria.

A disease called "citrus greening" has devastated and permanently altered citrus production in the United States, but a vaccine that could protect orange trees may be part of a winning strategy to beat the bacteria that is killing the trees.
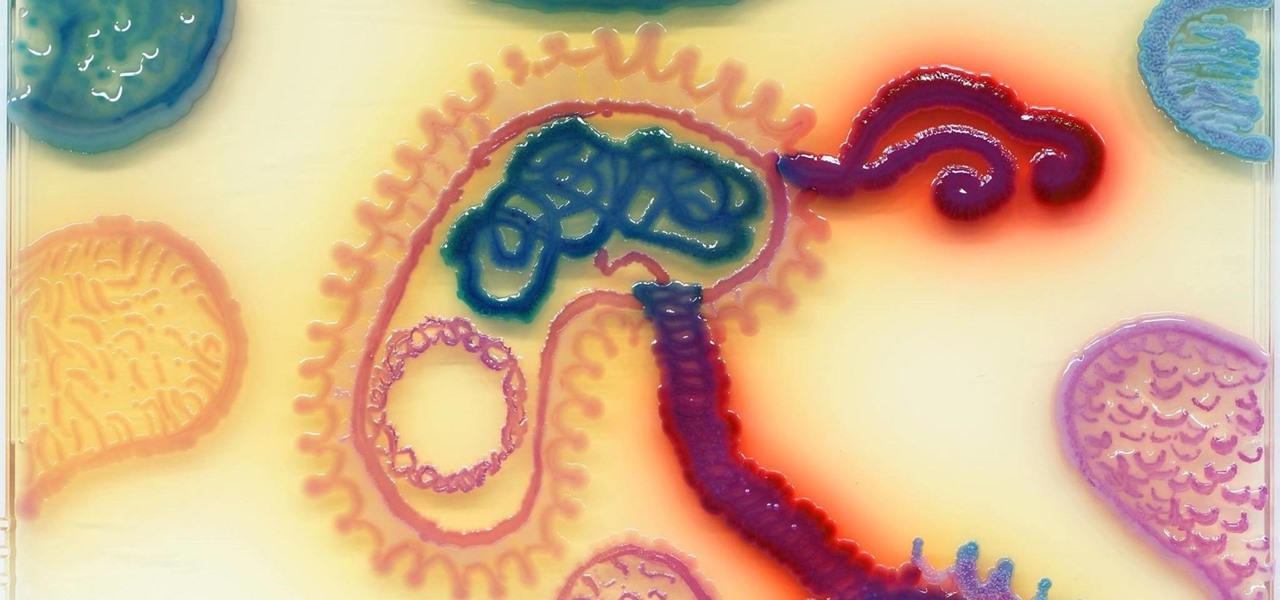
Think of the coolest, most unique way to create art that you can. Got it? Now think about creating that art out of living things.
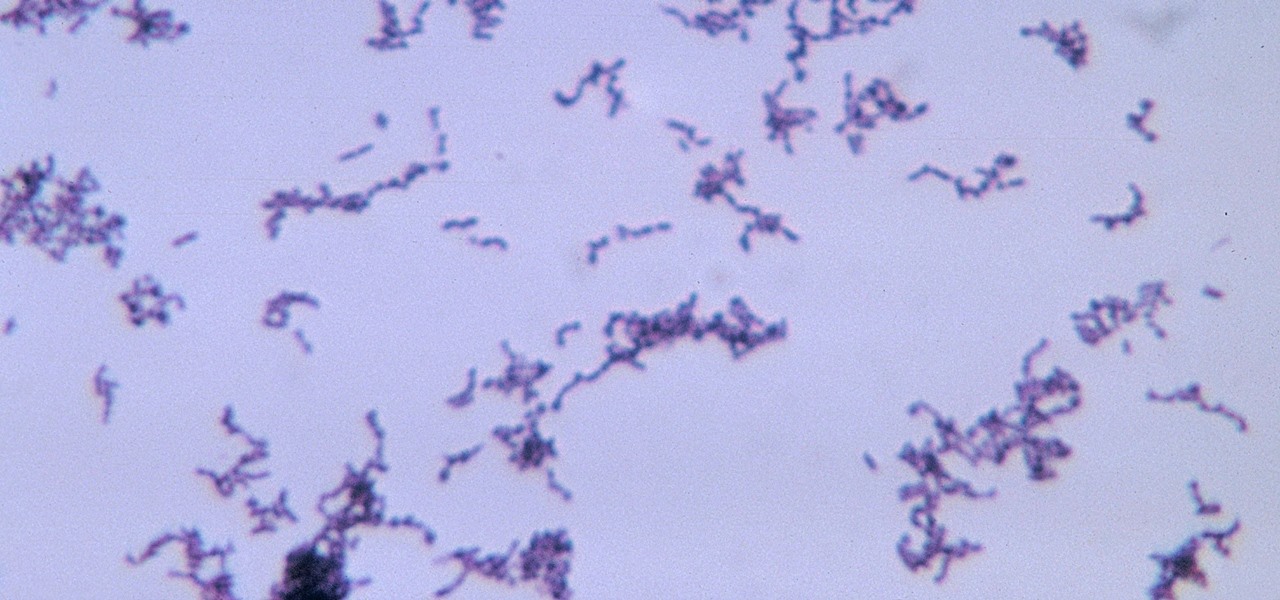
The squiggly guys in this article's cover image are Propionibacterium acnes. These bacteria live in low-oxygen conditions at the base of hair follicles all over your body. They mind their own business, eating cellular debris and sebum, the oily stuff secreted by sebaceous glands that help keep things moisturized. Everybody has P. acnes bacteria—which are commonly blamed for causing acne—but researchers took a bigger view and discovered P. acnes may also play a part in keeping your skin clear.
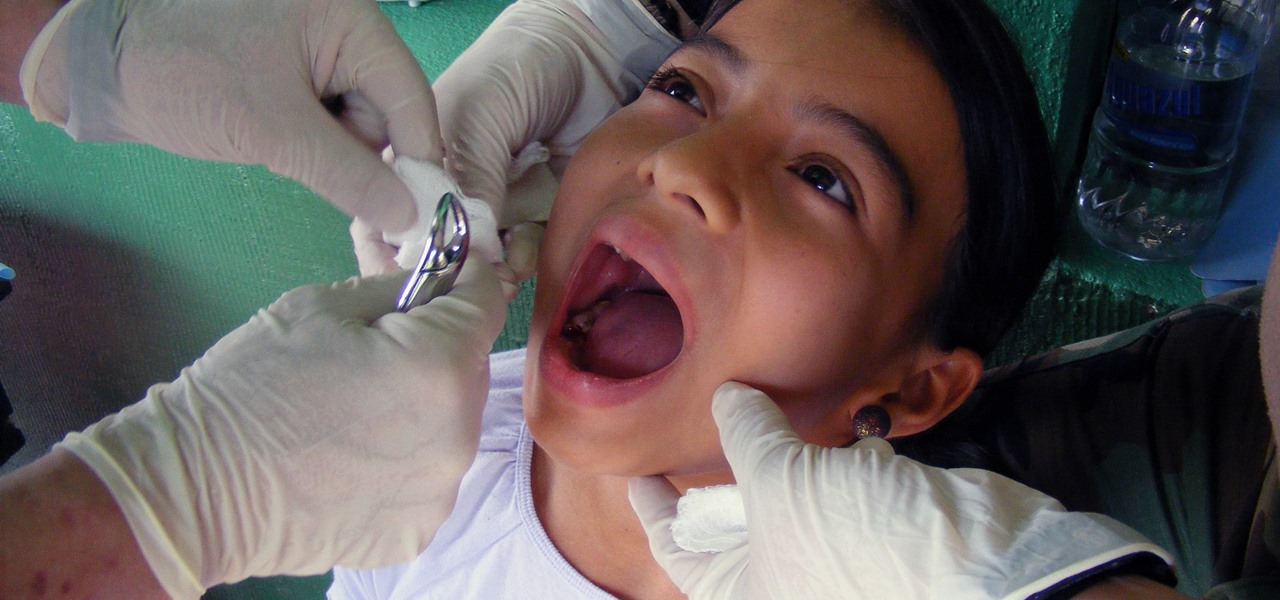
As many as 700 species of bacteria live on our teeth and in our mouth, and just like the microbiomes inhabiting other parts of our bodies, they change in response to diseases and other health conditions.
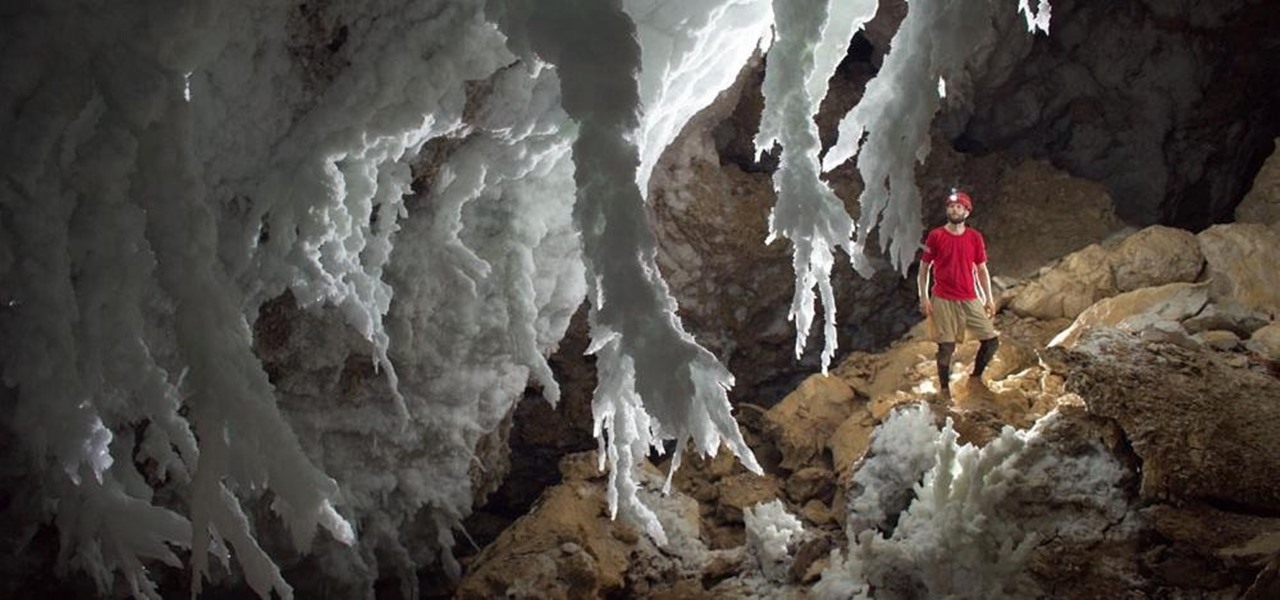

One thousand feet under the ground, extremophile microbes that have not seen the light of day for four million years are giving up some fascinating facts to scientists who go the distance.
Both professional and home cooks have been rinsing raw chicken and turkey before cooking it for what seems like forever. It's one of those divisive practices—either you do it or you don't, and people tend to be rather opinionated on their stances.
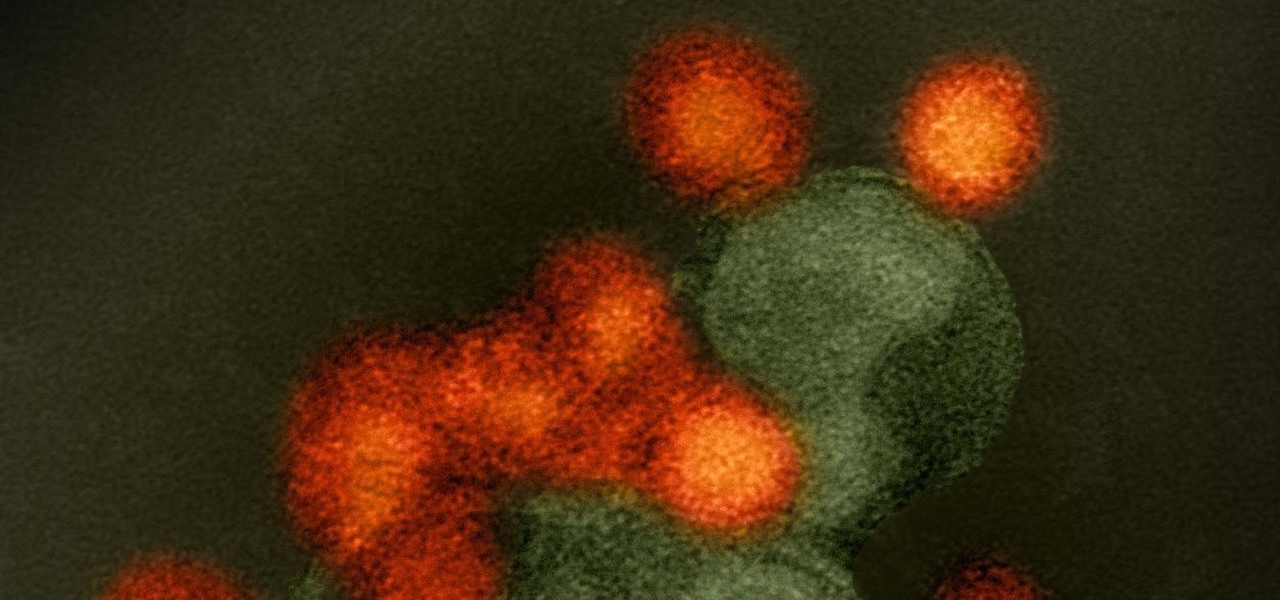
We might think of Zika as a mosquito-borne virus that effects developing fetuses, but, it also can be passed through sex by either a man or a woman, just like herpes and other STD viruses. New research has shown that vaginal bacteria can inhibit sexually transmitted Zika virus and Herpes Simplex Virus-2 in women.
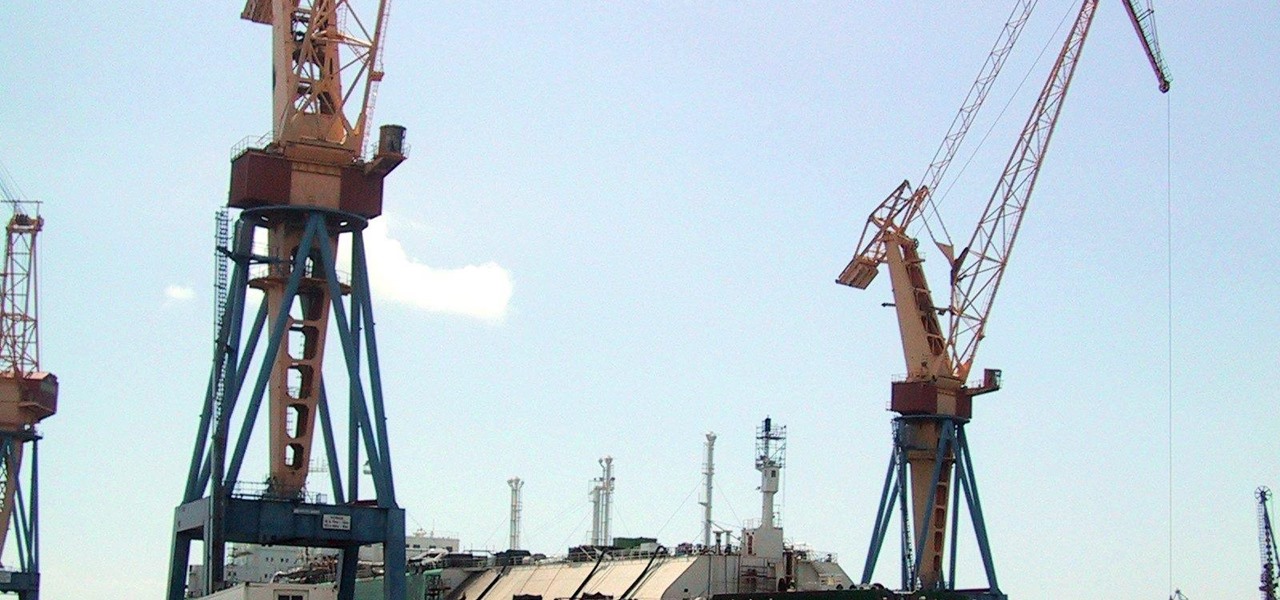

About a third of the methane released into the environment comes from the production and transport of natural gas. The gas leaks as it moves along the transport chain from gas wellheads to market.
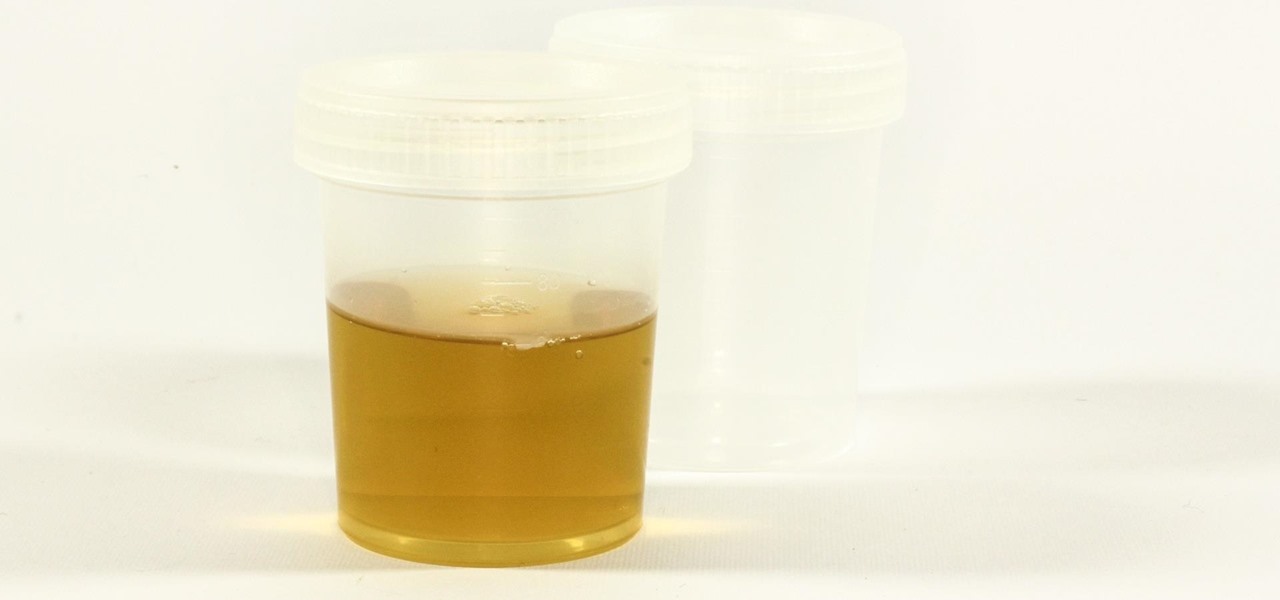

Have you ever had a burning sensation when you urinate? Low fever, back pain, and maybe cloudy urine? Male or female, it could have been a urinary tract infection. If it lasted long enough, the chances are good you went to the doctor for help. For about 20% of women, standard testing for a UTI does not reveal the presence of infection-causing bacteria, even though bacteria may be causing their symptoms. Well, a new test may provide better answers.
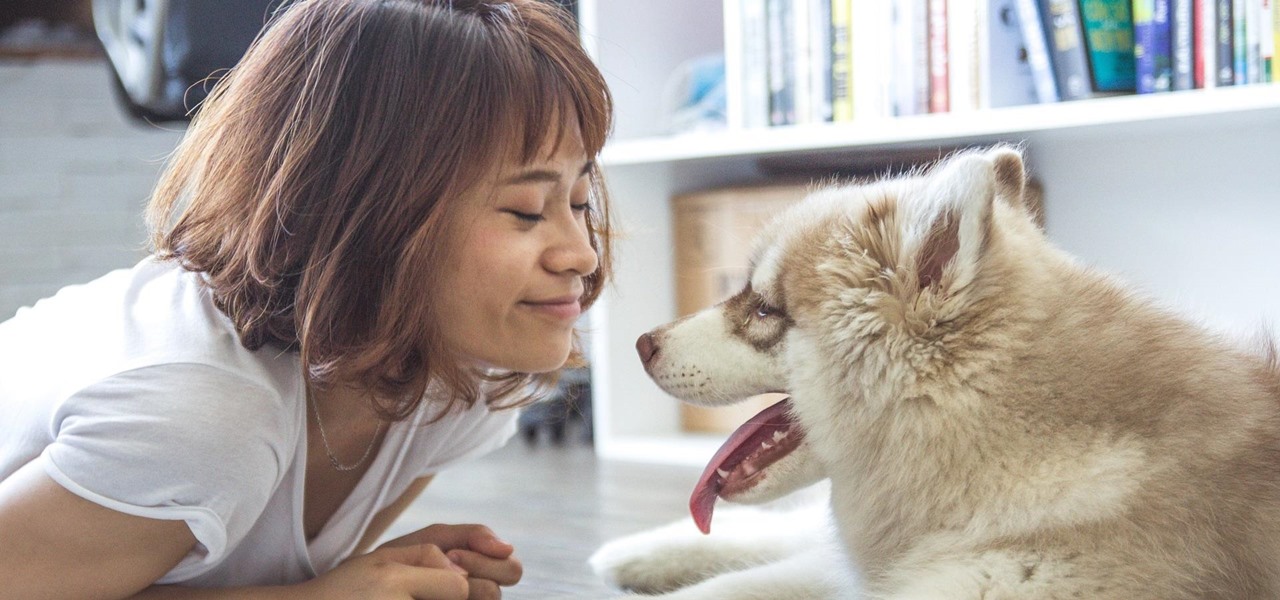

Our canine best friends could spread our bacterial worst nightmare, according to a recent study. The problem with drug-resistant bacteria is well known. Overused, poorly used, and naturally adaptive bacteria clearly have us outnumbered. As science drives hard to find alternative drugs, therapies, and options to treat increasingly resistant infections, humans are treading water, hoping our drugs of last resort work until we figure out better strategies.
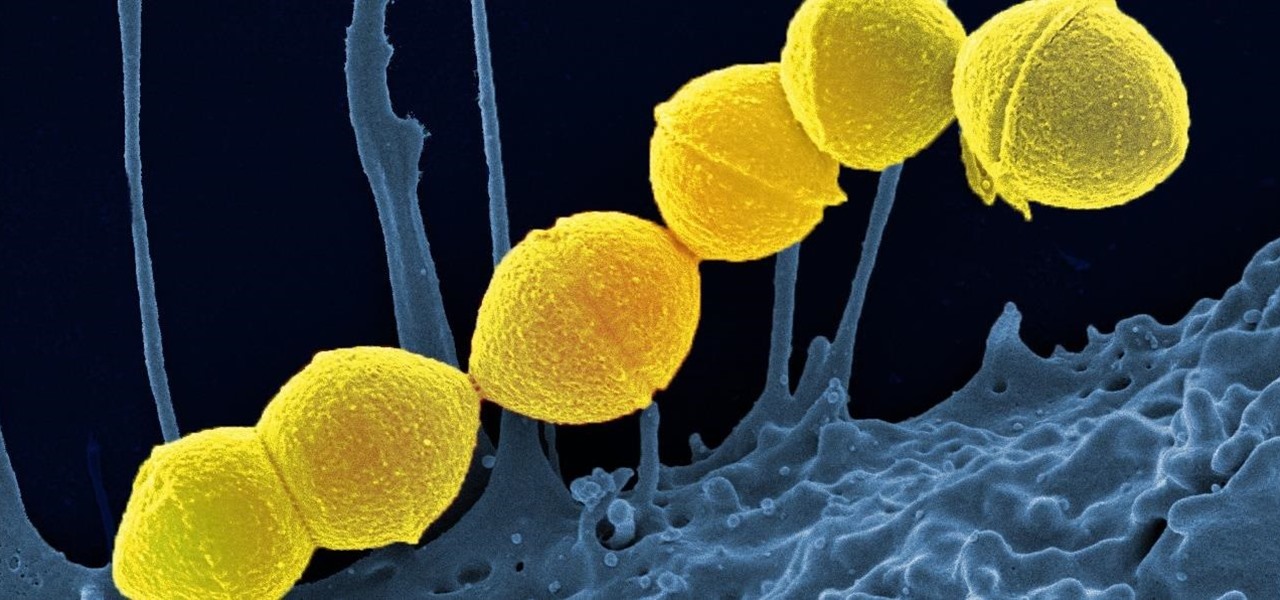
It's not the bacteria itself that takes lives and limbs during invasive flesh-eating bacteria infections. It's the toxins secreted by the group A Streptococcus bacteria invading the body that causes the most damage.

Potbellies don't have to happen as we age, according to two studies done on twins published online in the International Journal of Obesity.
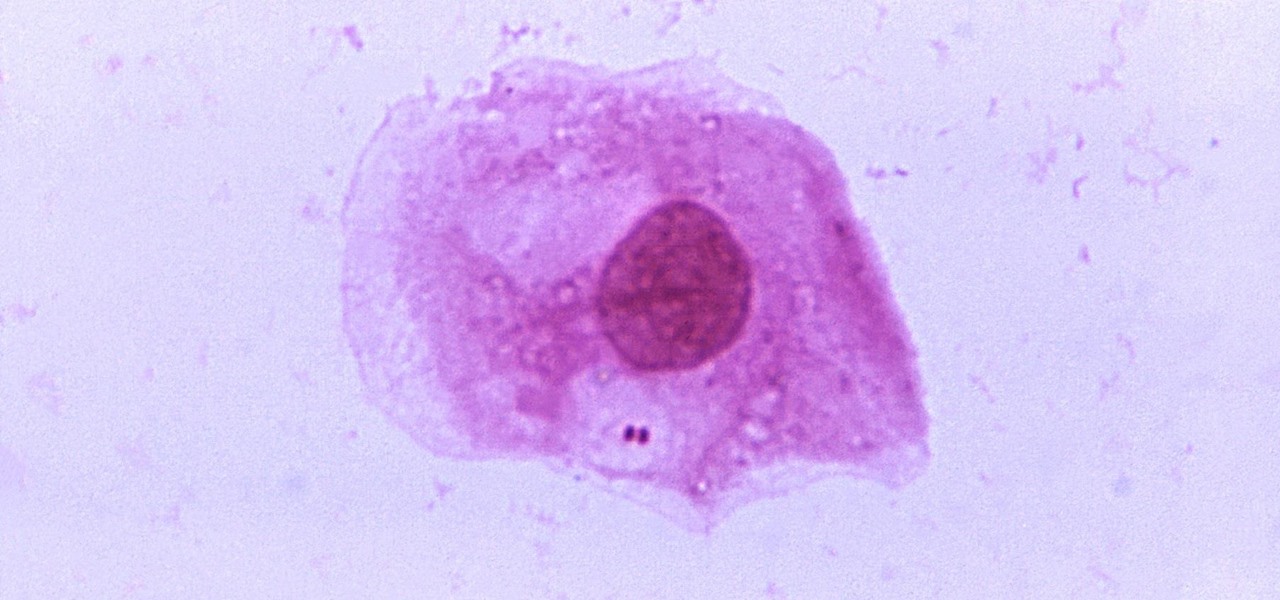
How can bacteria that lives in the throat of 10%–35% of people—without causing an infection—cause life-threatening meningitis and sepsis in others?

Antibiotic-resistant infections that usually occur only in hospital settings are spreading in communities, increasing hospital stays—and danger—for young children.
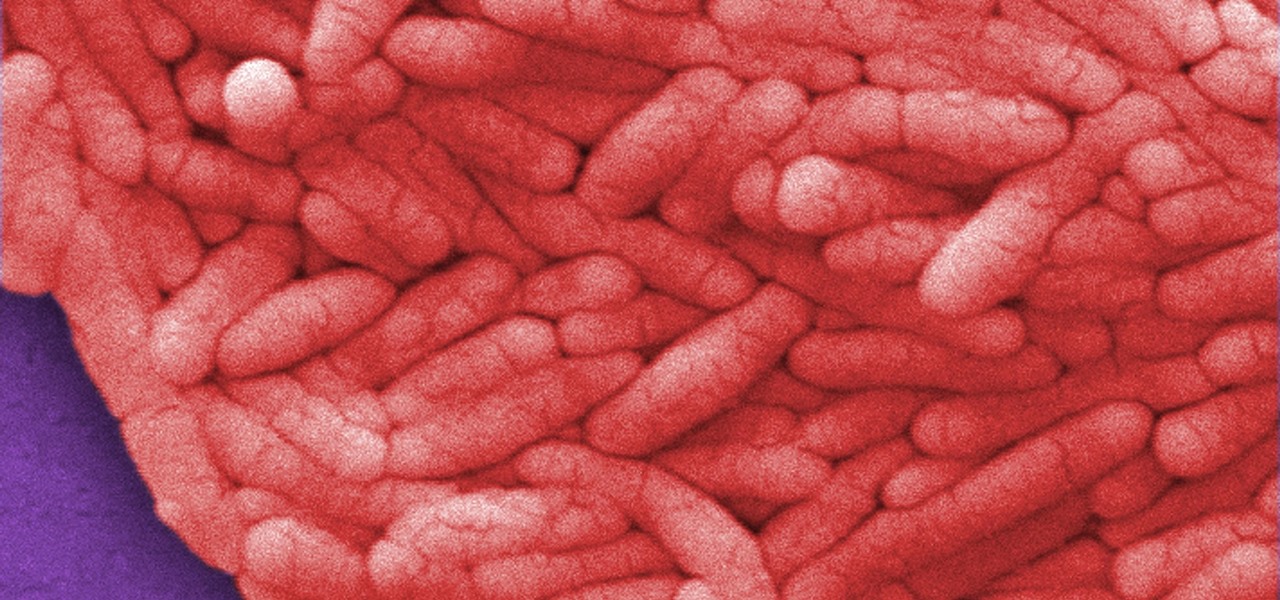
We usually associate Salmonella bacteria with a dangerous type of food poisoning, but they actually are pretty good at seeking out tumors. That trait made the bacteria a great candidate to deliver a protein that would help knock tumors out.
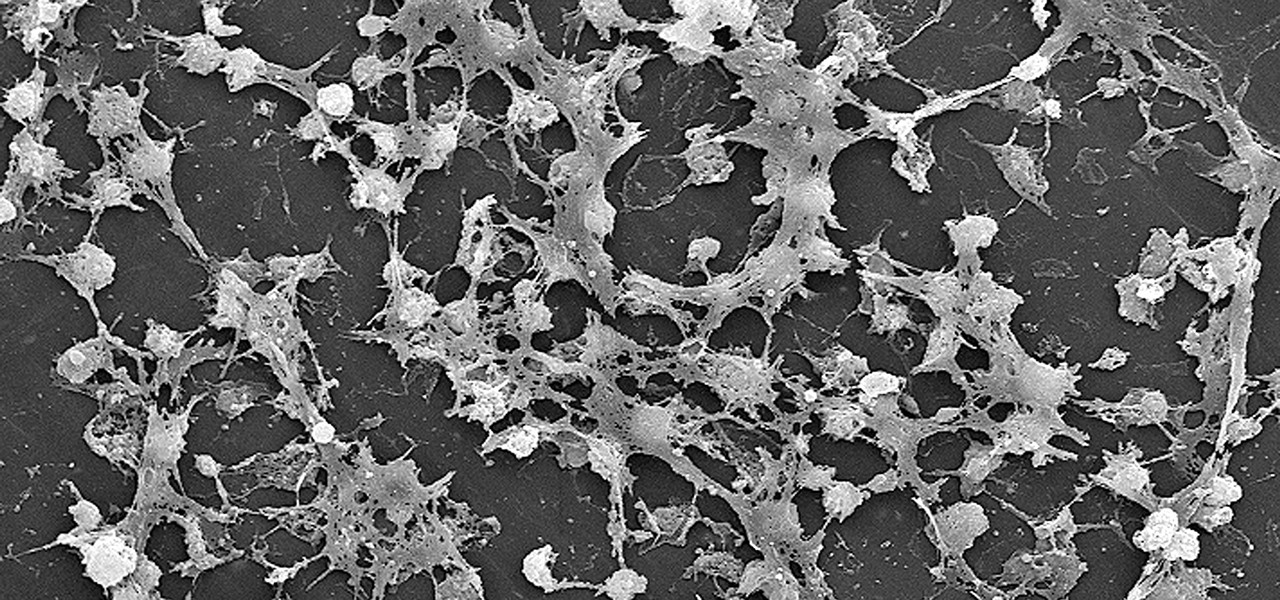
Lighthouses and signal fires may have been the first social media. Without the ability to share language, a distant light meant "humans here." A new study from the University of California, San Diego, finds that bacteria can also send out a universal sign to attract the attention of their own, and other bacterial species.
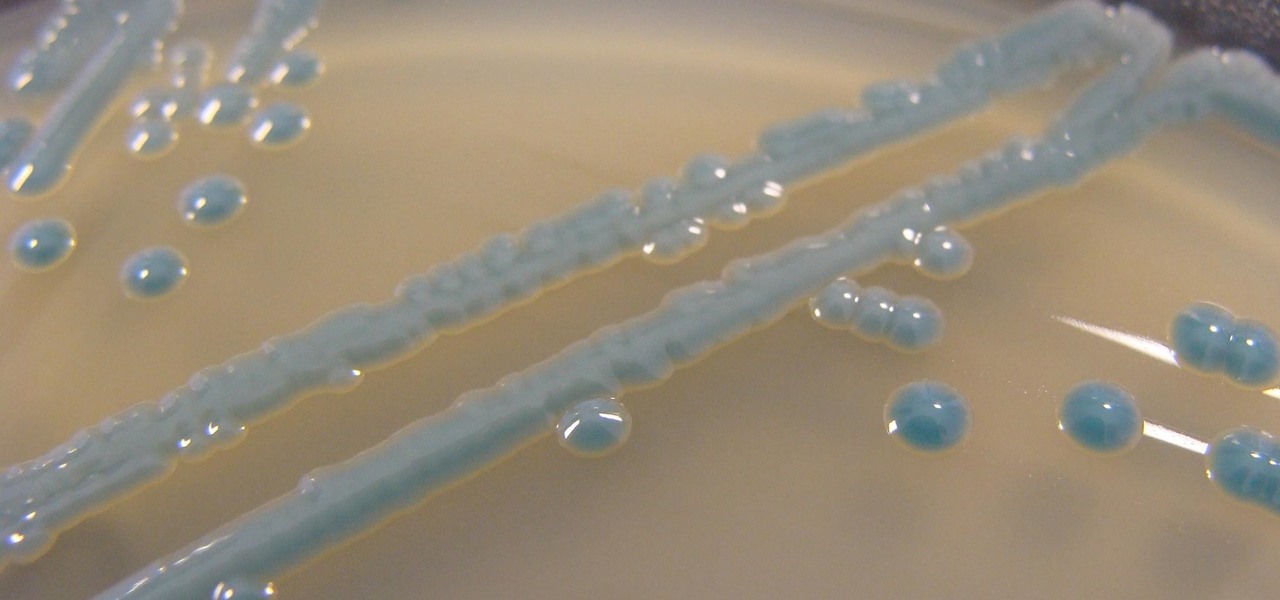
The growing list of dangerous antibiotic resistant organisms has just acquired three new members. Researchers have discovered three new species of Klebsiella bacteria, all of which can cause life-threatening infections and have genes that make them resistant to commonly used antibiotics.

New research explores how the bacteria on the penis can leave men more susceptible to infection with HIV.
The evidence is mounting and is becoming indisputable: Gut bacteria play a role in strokes and heart attacks. The link may seem a little far-fetched, but cardiovascular disease may have less to do with what we eat and more to do with what chemicals gut bacteria make from the food we eat.

We know that healthcare-related facilities can be fertile ground for antibiotic-resistant bacteria, but recent research suggests your produce aisle might be too.
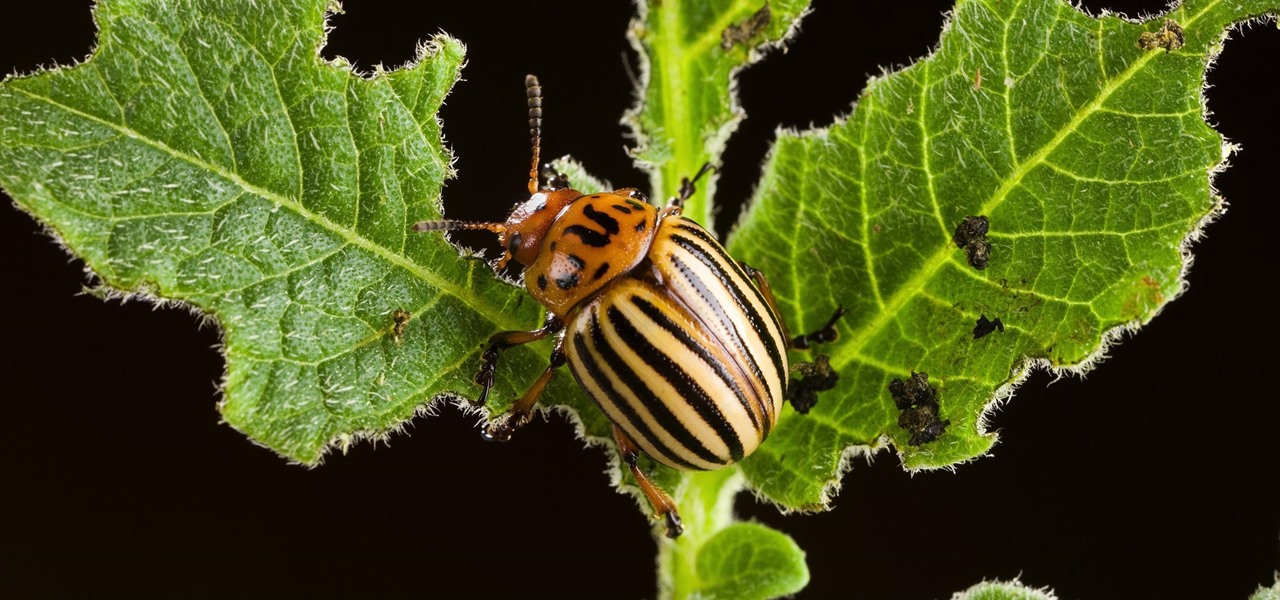

Before you bite into that beautiful tomato in your garden, the tomato fruitworm, or the Colorado potato beetle, might have beat you to it.
Bacteriotherapy sounds a lot more amenable of a term than "fecal transplant," yet they're both treatments that use bacteria itself to cure or treat infections. Fecal transplants, specifically, are an up-and-coming treatment option for a potentially deadly and difficult-to-treat diarrheal infection called Clostridium difficile.

Learn how to remove pet stains and odors quickly and easily so you no longer have to worry about occasional accidents. These are the items you are going to need: some clean old towels, paper towels,
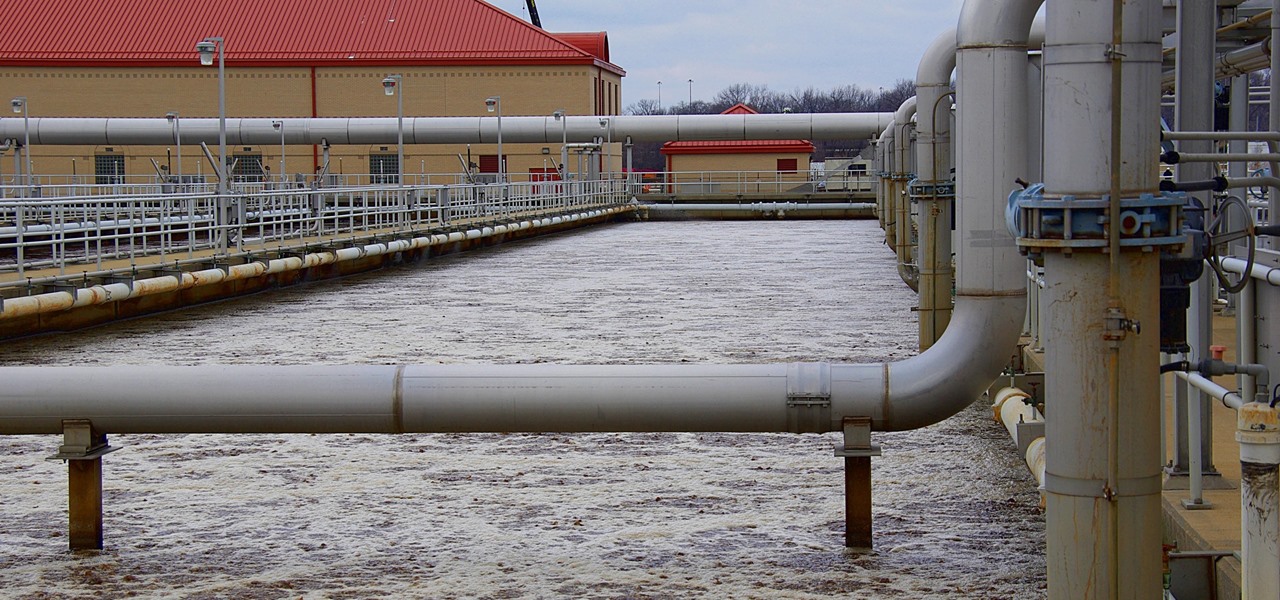

Everything from disposed of drugs to hormones and disease-causing bacteria — anything that is rinsed or flushed down the drain — can contaminate wastewater.

Joe McKenna died when he was 30 years old. A young married man with his future ahead of him, he was cleaning up the station where he worked as a fireman. Struck by a piece of equipment fallen from a shelf, Joe complained of a sore shoulder. Over the next week, Joe worsened and ended up in the hospital. Chilled, feverish, and delirious, his organs shut down from an infection we'd now call septic shock.
The story of Helicobacter pylori is a real testament to the tenacity of medical researchers to prove their hypothesis. It took decades before the scientific world would accept that the bacteria H. pylori caused ulcers.