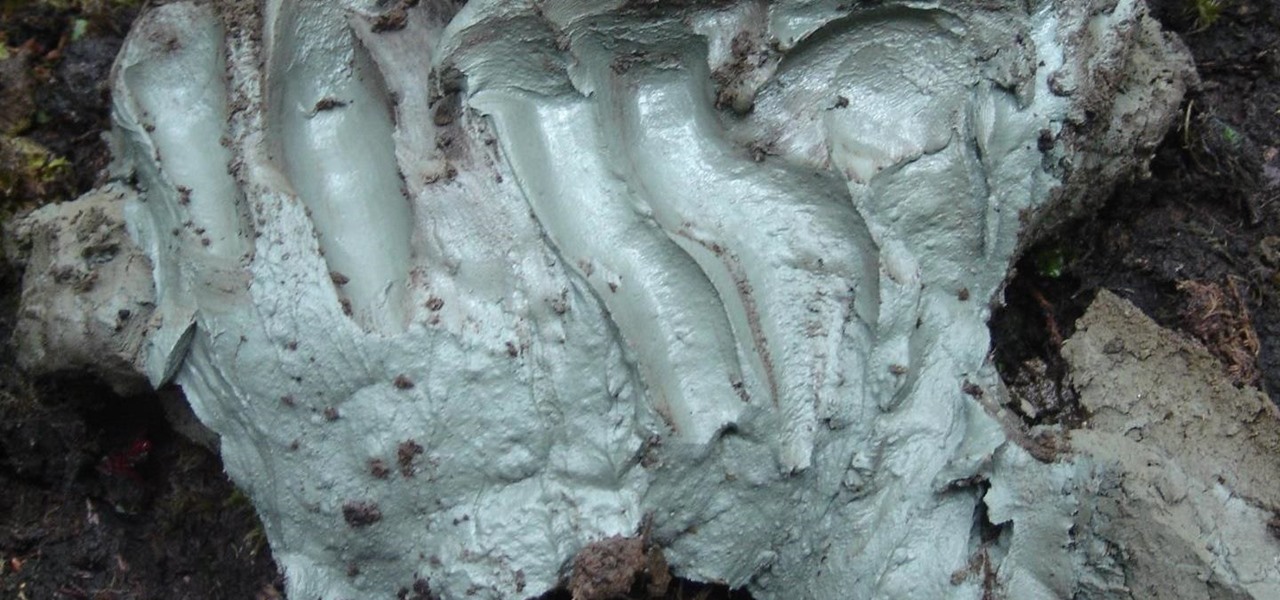
For as long as 14,000 years, the First Nations people of the Heitsuk Nation have made their home along the Central Coast of the Canadian province of British Columbia. Among the territory's inlets, islands, rivers, and valleys lie a clay deposit on the north side of Kisameet Bay, near King Island. For as long as most can remember, the tribe has used the clay as medicine. Now science says microbes that live in that clay may have important antibacterial properties.
The growing list of dangerous antibiotic resistant organisms has just acquired three new members. Researchers have discovered three new species of Klebsiella bacteria, all of which can cause life-threatening infections and have genes that make them resistant to commonly used antibiotics.
Once we recover from the respiratory infection pneumonia, our lungs are better equipped to deal with the next infection — thanks to some special cells that take up residence there.

Foodborne infections often occur through the contamination of equipment, food-prep tools, and unsanitary surfaces. A recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reminds us that breast pump parts are part of the food-delivery chain — and they can become contaminated too.

For younger children, a day at the playground is not complete without some sandbox time. Long a favorite of children and parents, sandboxes could also be sheltering dangerous pathogens.
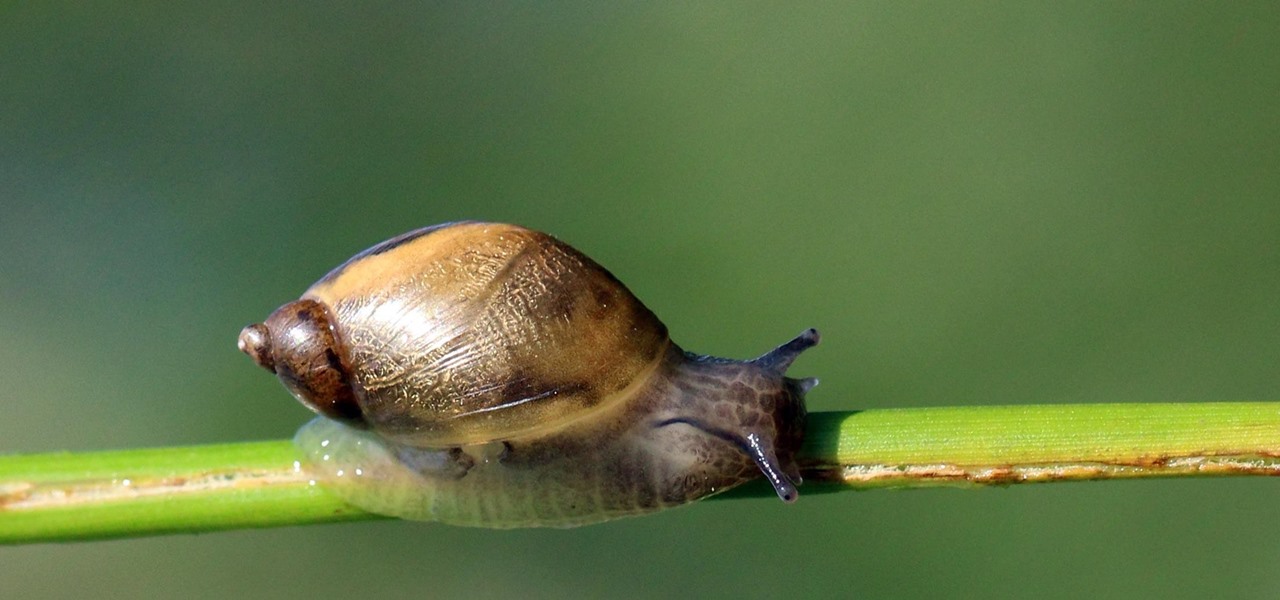

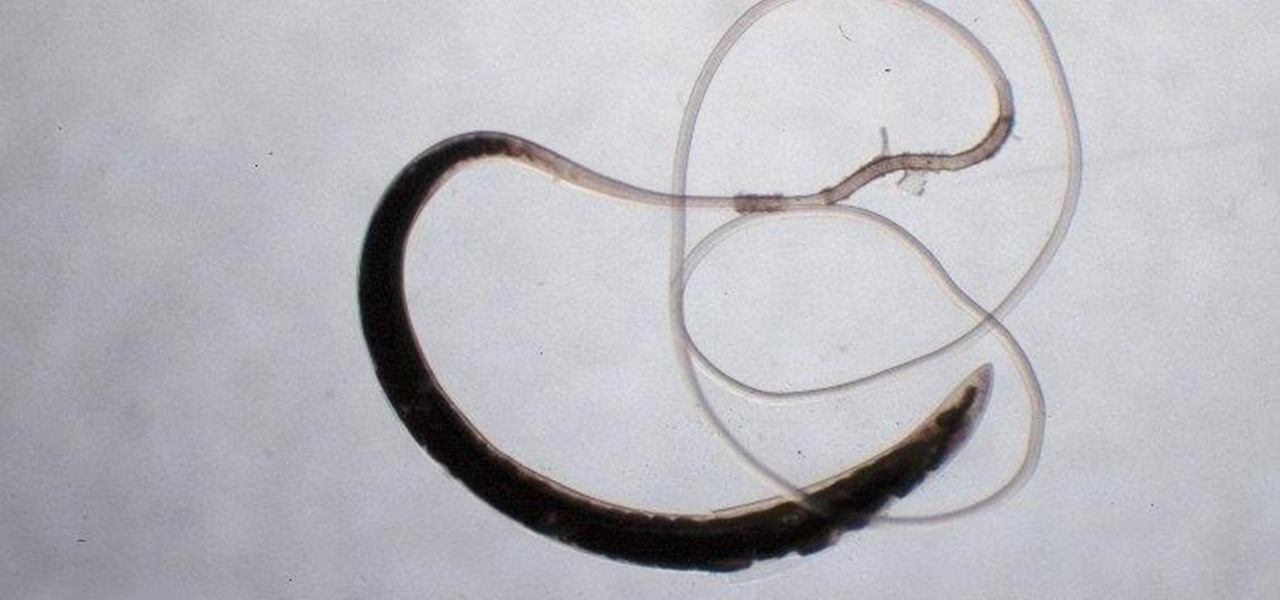
Deadly rat lungworm parasites have found their way into Florida. The parasitic worm relies on snails and rats to complete its life cycle, but don't let this nematode's name fool you. This worm can cause meningitis and death in humans who inadvertently consume snails, frogs, or crustaceans harboring the infective parasite.

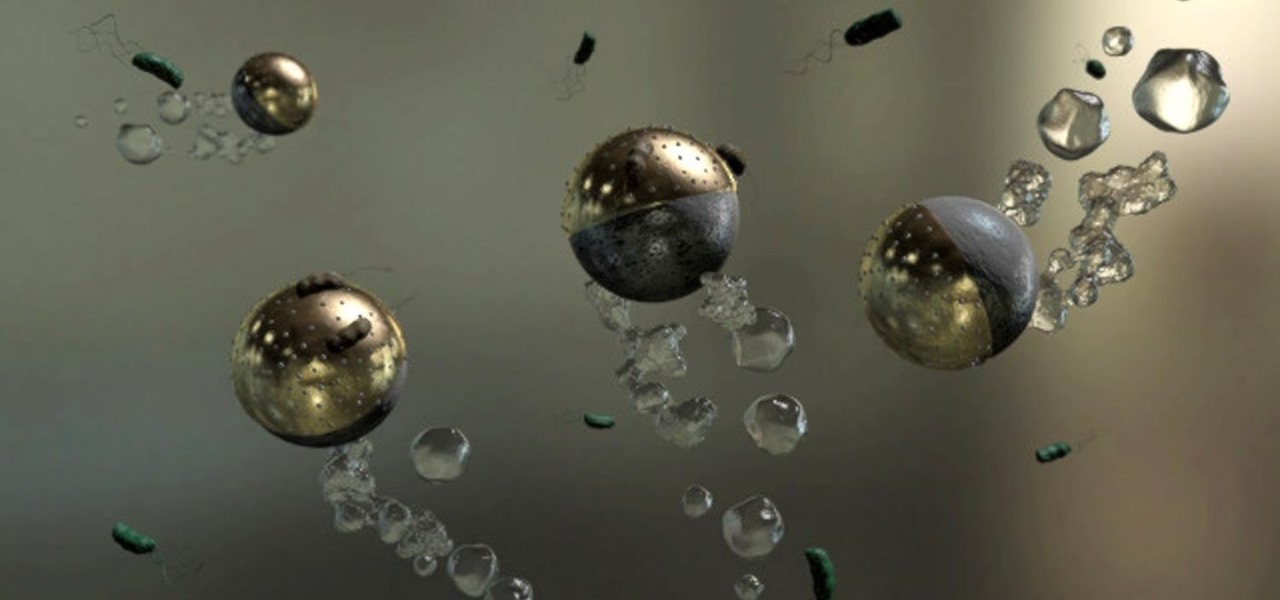
Look no further than Flint, Michigan, to discover the serious consequences of contaminated drinking water. Around the world, water polluted by pathogens and toxins sickens people or cuts them off from safe drinking water. Looking for a solution, researchers created tiny, swimming robots that pack a powerful punch against waterborne pathogens.

Even before we are born, our immune system is hard at work. New research shows how the developing fetal immune system takes advantage of the time and opportunity of gestation — in the presence of mom's cells and tissues — to develop a sense of self.

Zika is a threat to unborn babies — the virus can cause neurological damage if it infects a mother during pregnancy. But as with many things, our solutions to the problem aren't always all that much better than the problem itself.

Intense exercise can cause problems with our digestive tract. It even has a name — "Exercise-induced Gastrointestinal Syndrome." Simply put, strenuous exercise can damage the gut and let the bacteria that reside there potentially pass into the bloodstream.

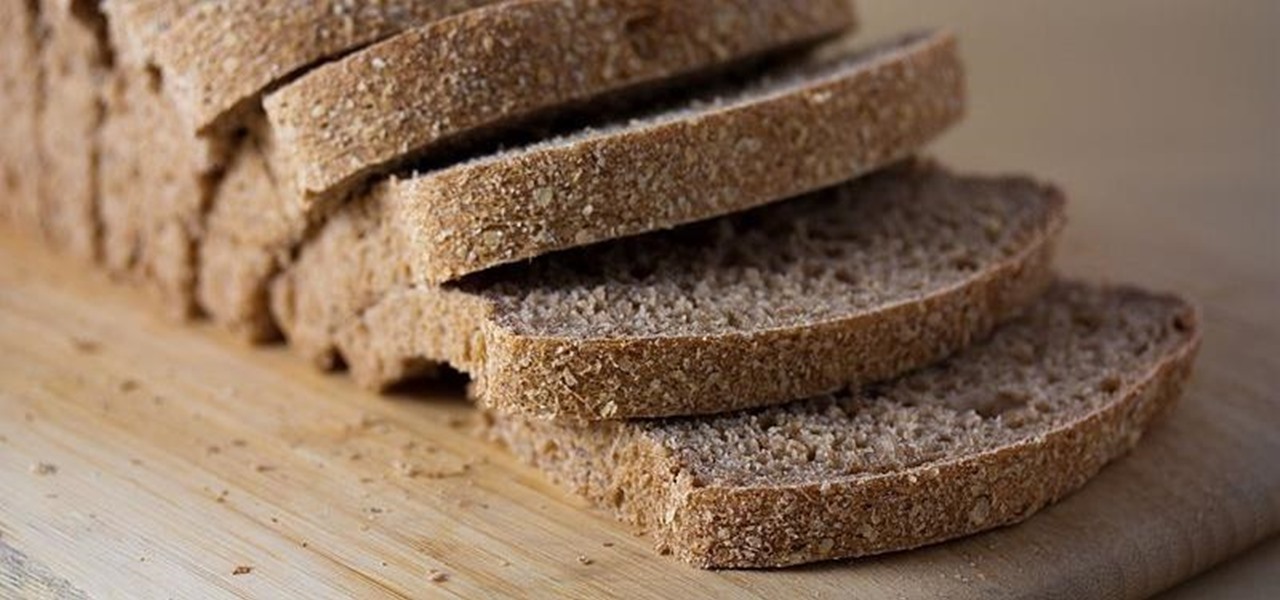
Move over whole wheat — white bread may be back in style after a new study shows that it may be your gut microbes that decide what kind of bread is best for you.

Drug-resistant bacteria have made curing some infections challenging, if not nearly impossible. By 2050, it's estimated that 10 million people will be dying annually from infections with antibiotic-resistant organisms.

We've worked hard to reduce the flow of toxic chemicals into our waterways, which means no more DDT and other bad actors to pollute or destroy wildlife and our health. But one observation has been plaguing scientists for decades: Why are large quantities of one toxic chemical still found in the world's oceans?

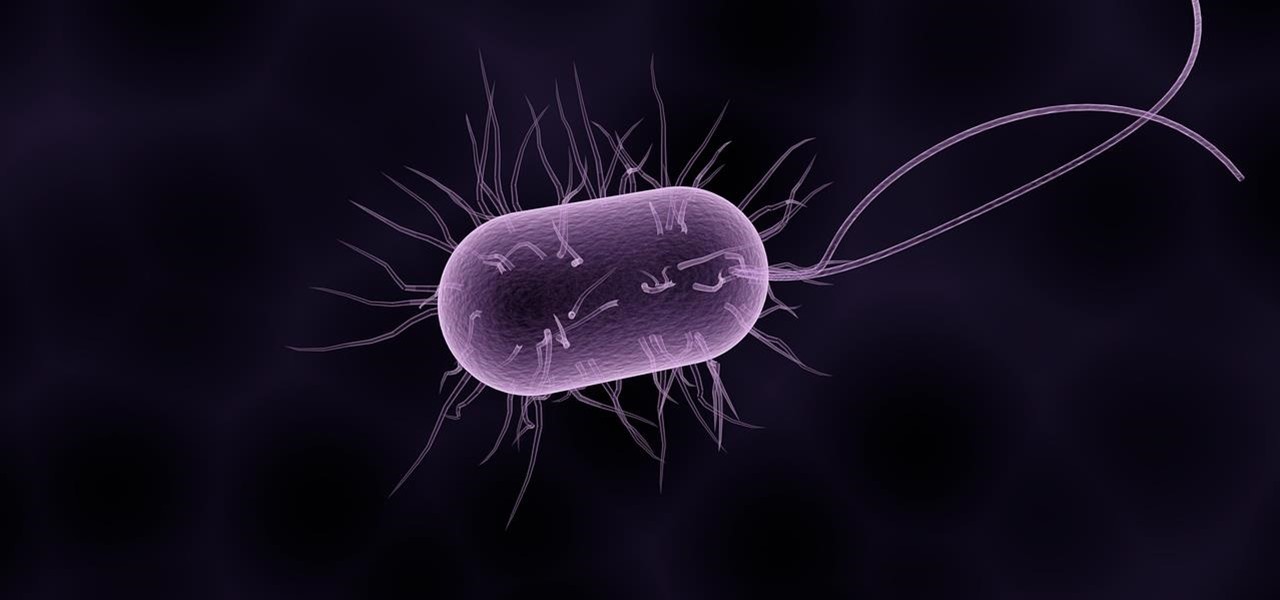
The bacteria Klebsiella pneumoniae is a bad actor known for being antibiotic-resistant and causing a variety of serious infections in hospitals, including pneumonia, surgical site wounds, and meningitis. K. pneumoniae is something you do not want to encounter if you have a compromised immune system.

We fight cancer in a variety of ways, but no matter whether drugs, biologics, or our immune cells are part of the battle, they can do a better job fighting back cancer if we can help them find the tumors.

Fighting fire with fire, scientists are harnessing the adaptability of helpful microbes to challenge the adaptability of deadly microbes. What are we talking about? Hunting with phages — viruses that attack and kill bacteria.

The evolution of our infection-fighting systems may have something to teach modern scientists. That's what a group from the University of Granada in Spain found when they studied a protein that's been around for over four billion years. Their work, by senior author José Sánchez-Ruiz and colleagues in the Department of Physical Chemistry, was published in the journal Cell Reports.

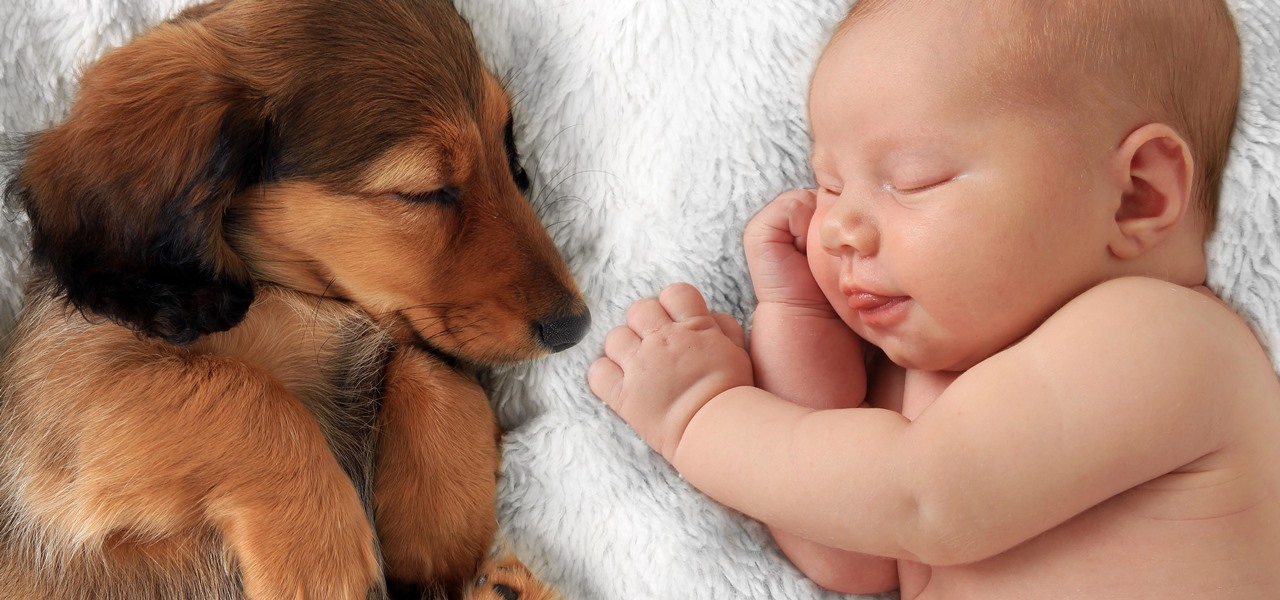
For many of us, pets are important family members. They give us loyalty, companionship, and comfort. Now, researchers have given us another reason to welcome them into the family: Babies from families with furry pets — the majority of which were dogs — had higher levels of two types of beneficial gut bacteria.

The noses of kids who live in areas of intense pig farming may harbor antibiotic-resistant bacteria, presumably acquired from the animals, according to a new study by scientists at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, UNC Gillings School of Global Public Health, and Statens Serum Institut in Denmark, published in Environmental Health Perspectives.

On October 17, 1943, a story in the New York Herald Tribune read "Many laymen — husbands, wives, parents, brothers, sisters, friends — beg Dr. Keefer for penicillin," according to the American Chemical Society. Dr. Chester Keefer of Boston was responsible for rationing the new miracle drug, penicillin.

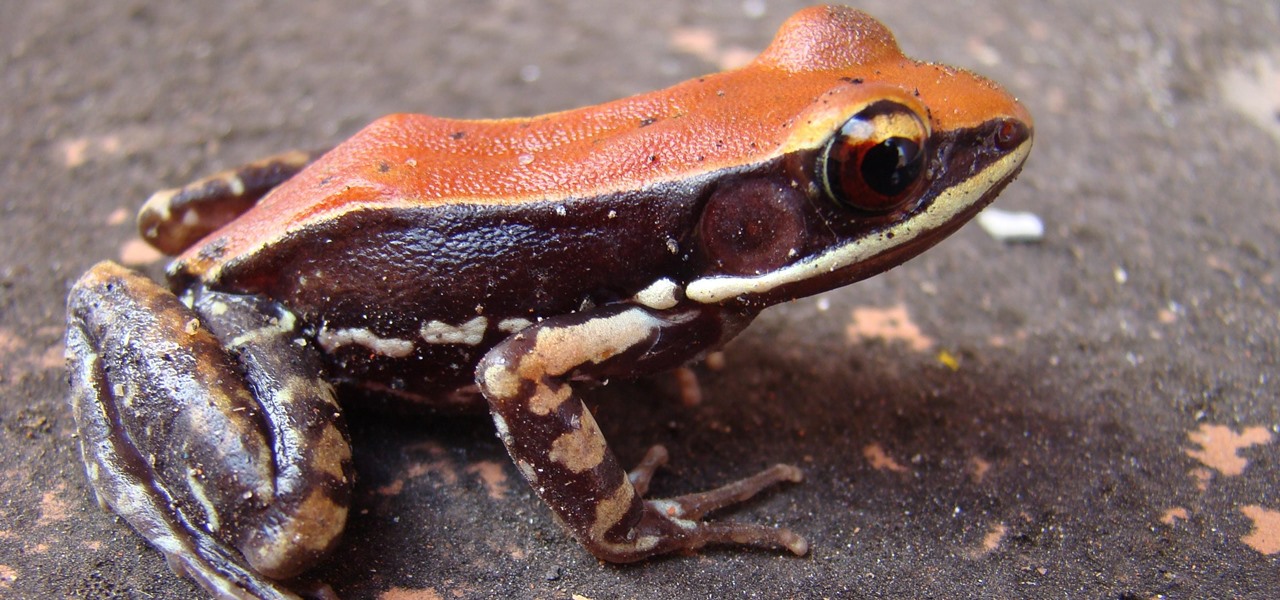
Our quest to find novel compounds in nature that we can use against human diseases —a process called bioprospecting — has led a research team to a small frog found in India. From the skin slime of the colorful Hydrophylax bahuvistara, researchers reported finding a peptide — a small piece of protein — that can destroy many strains of human flu and can even protect mice against the flu.

Potbellies don't have to happen as we age, according to two studies done on twins published online in the International Journal of Obesity.

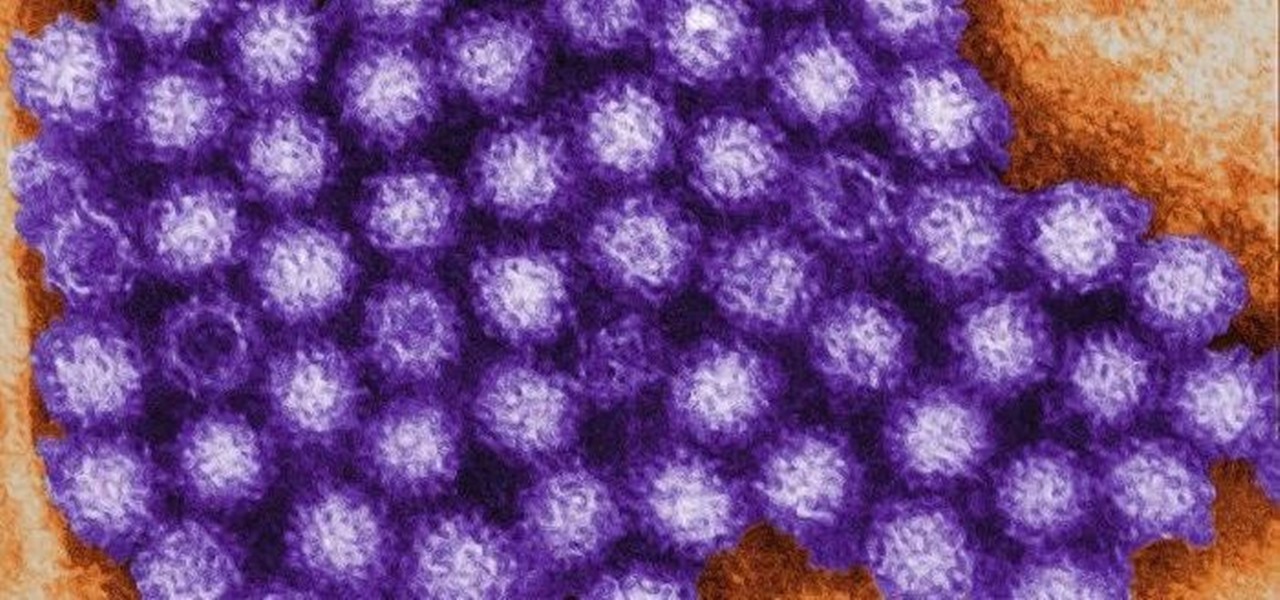
Have you ever had the stomach flu, aka the 24-hour flu? Well, chances are high that you never had influenza, but an intestinal infection called gastroenteritis.

Hospitals are places we go to get well, and we don't expect to get sick or sicker there. But a study from researchers at the Cleveland Clinic, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, and Cleveland VA Medical Center in Ohio found that hospital floors in patient rooms were frequently contaminated with healthcare-associated pathogens—often dangerous multi-drug resistant bacteria.

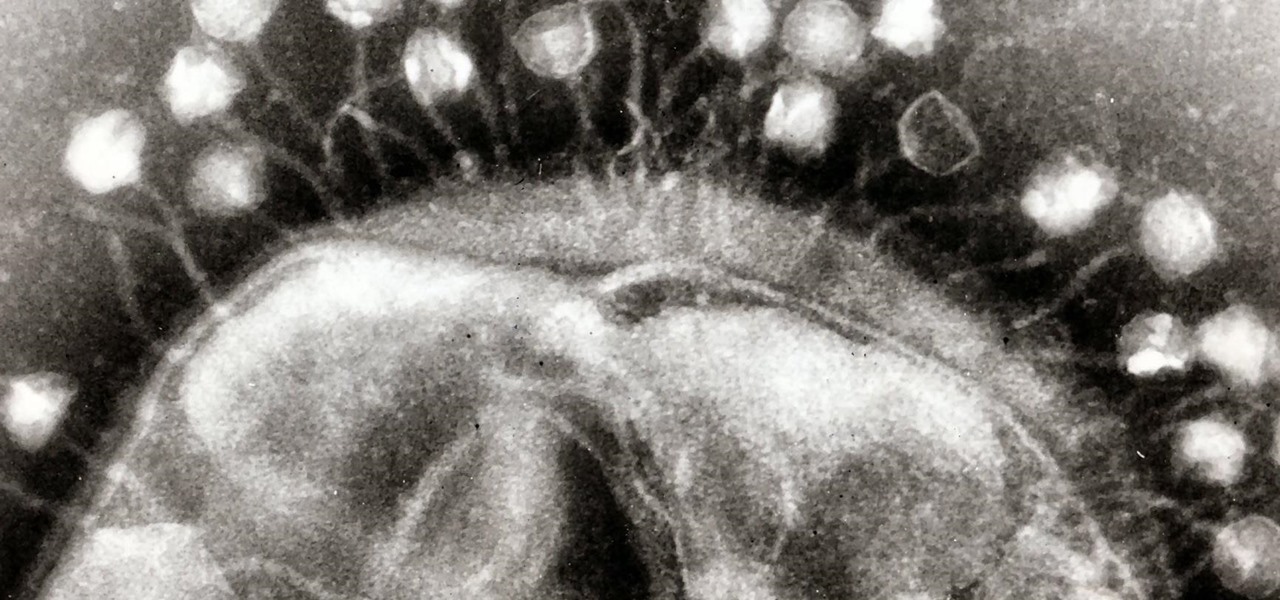
Somewhere around 600–800 million people in the world are infected with whipworm (Trichuris trichiura), an infection they got from ingesting soil or water contaminated with feces of infected animals or people containing the parasite's eggs.

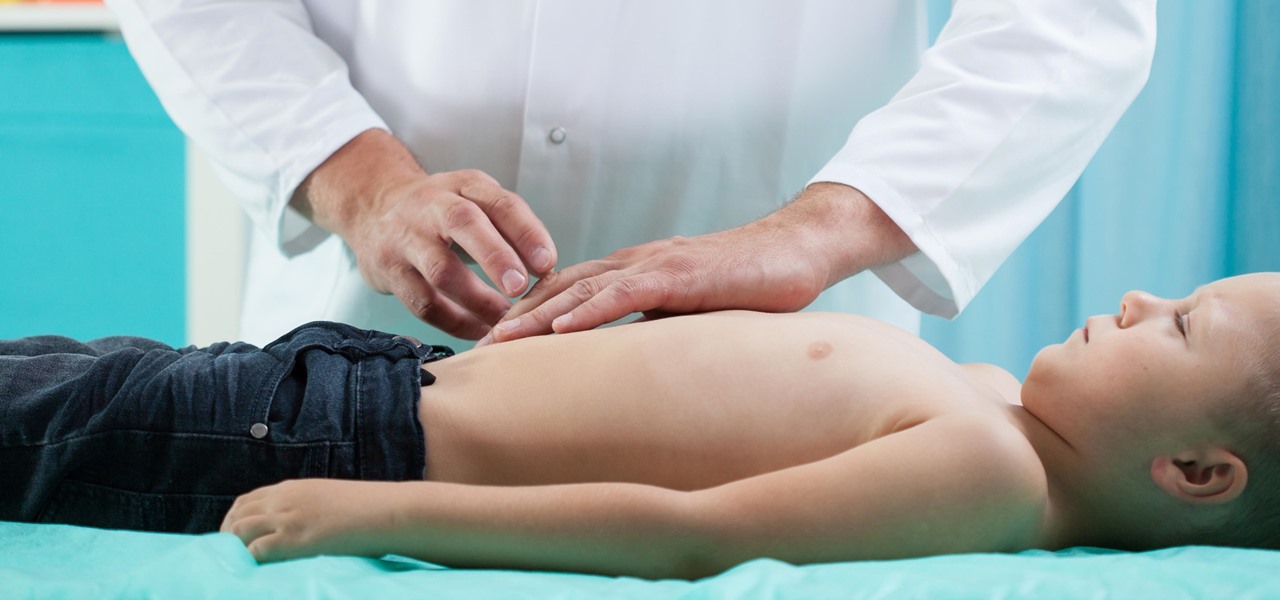
A new study confirms that antibiotics can prevent surgical intervention if your child's appendix becomes inflamed, potentially saving his or her life.

A rose by any other name may smell as sweet, but one annoying invasive weed may hold the answer to treating the superbug MRSA. Researchers from Emory University have found that the red berries of the Brazilian peppertree contain a compound that turns off a gene vital to the drug-resistance process.

Even if your cat drives you a little nuts, don't worry, because a new study says that cats pose no risk to your mental health.

New research suggests the bacteria that causes listeriosis may be a bigger threat in early pregnancy than previously thought. Usually considered a danger to late pregnancy, scientists suggest early undiagnosed miscarriages could be caused, in some cases, by infection with Listeria.

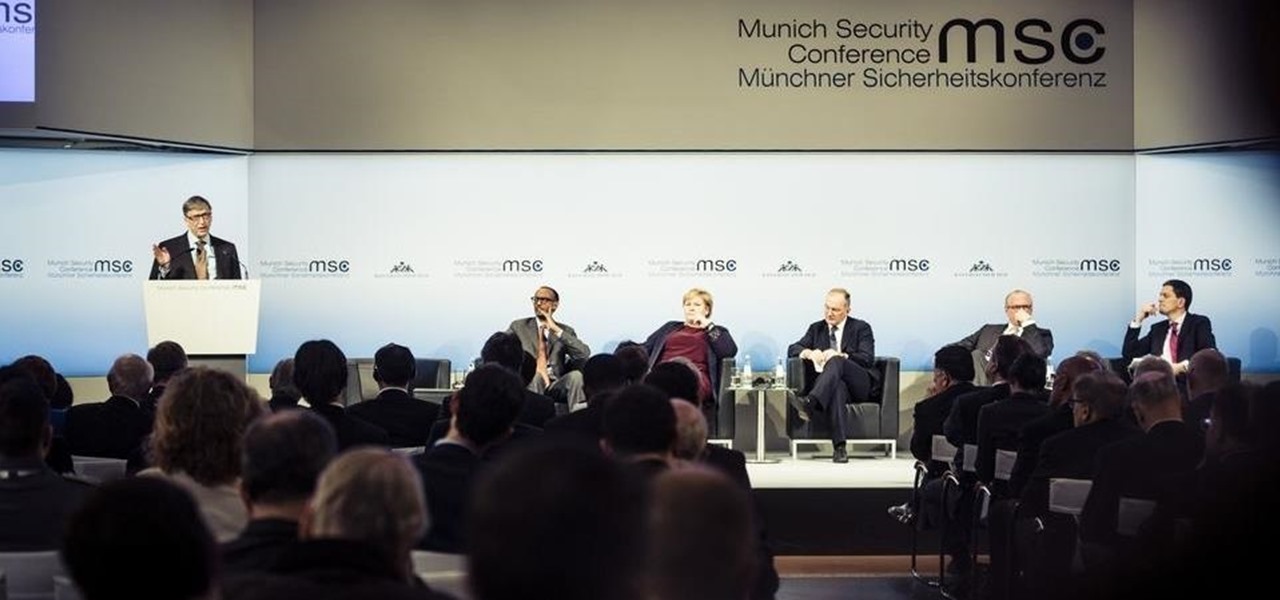
At a global security conference in Munich, philanthropist and businessman Bill Gates spoke about the next pandemic and a dire lack of global readiness. Here's how his statement could come true—and how to be ready when it does.

Have the sniffles? Yes. Does your head hurt? Yes. Coughing? Yes. Could you have influenza? Yes. How do you know the difference? With these symptoms, you could also have a cold.

Seagrass may help your favorite beach stay a little less toxic. A new study, led by Joleah Lamb, a postdoctoral researcher in the Harvell Lab at Cornell University, found that coastal seagrasses reduce levels of pathogens dangerous to humans and marine organisms in near-shore waters.

A recent pathogen outbreak in Illinois is just one of many outbreaks of an underappreciated, but serious, viral infection passed from rodents to humans. These hantaviruses have been cropping up more frequently in the last decade or so, giving us more reason to clean out our dusty attics, basements, and garages.

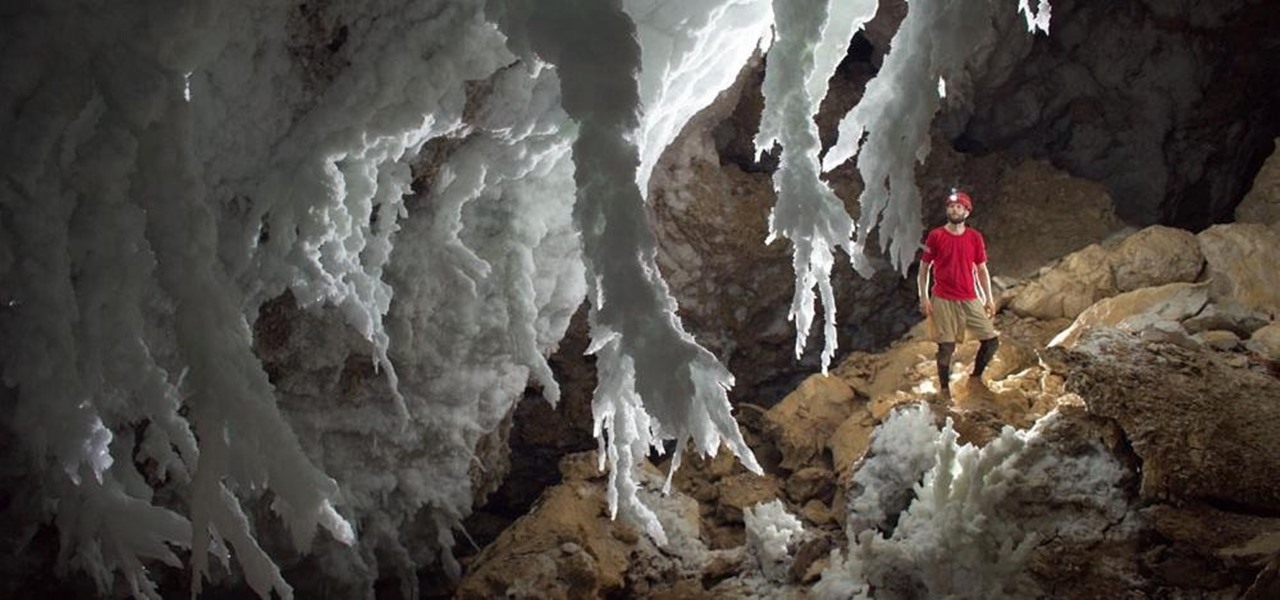
One thousand feet under the ground, extremophile microbes that have not seen the light of day for four million years are giving up some fascinating facts to scientists who go the distance.

The story of Helicobacter pylori is a real testament to the tenacity of medical researchers to prove their hypothesis. It took decades before the scientific world would accept that the bacteria H. pylori caused ulcers.

If you're grossed out by anything creepy, crawly, and with more than 4 legs... then stop being so close-minded and eat some bugs already, dammit.

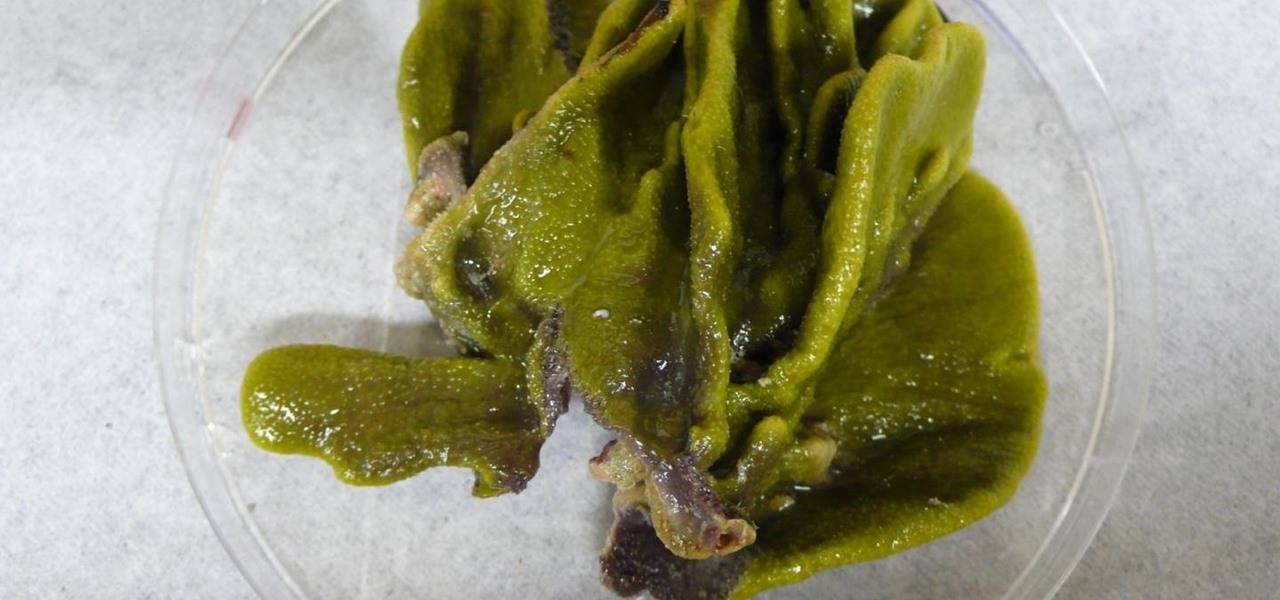
Seaweed isn't just for rolling sushi anymore. The food science world is introducing chefs and home cooks to dulse (rhymes with pulse), kale's wacky seaweed cousin that tastes surprisingly like bacon and may even be the next big superfood.

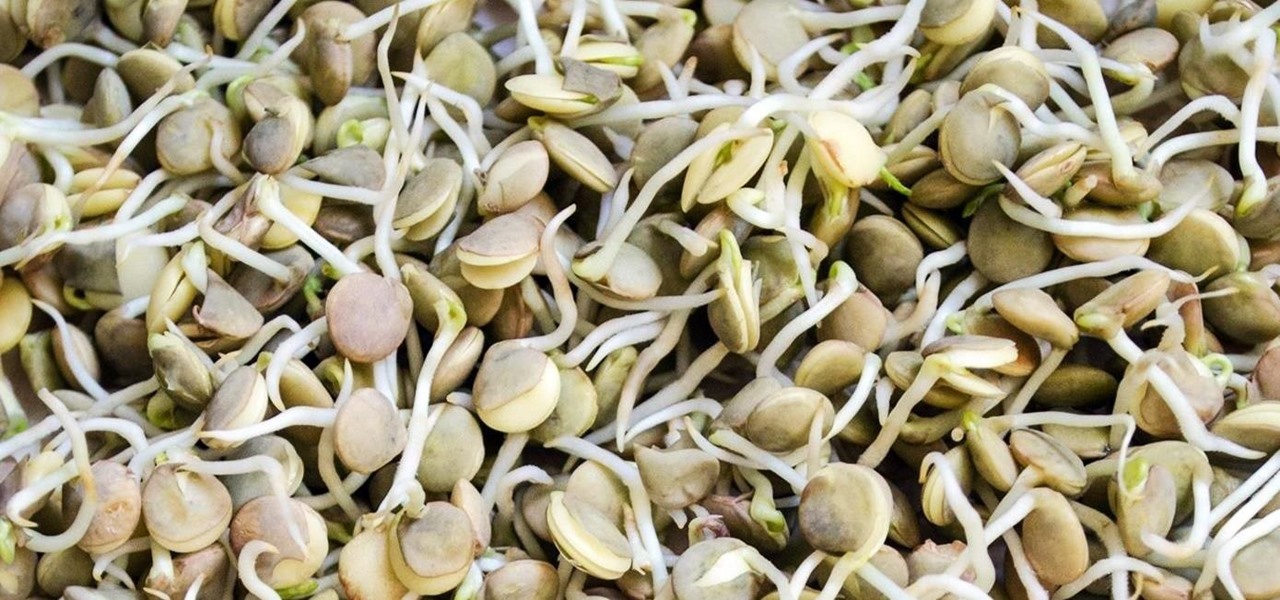
The sprouts, they're alive! Alive, I tell you—aaaaaaliiiiiive! (Cue dramatic music.) It's true: sprouts are a living food, and they're packed with more nutritional benefits than some raw vegetables. It's easy and fun to grow your own sprouts from seeds, legumes, and grains. Plus, watching them grow is incredibly satisfying—you're bringing new life into the world (and onto your plate)!

It should come as no surprise that, according to Details Magazine, nearly half of all people who make New Year's resolutions pledge to lose weight, eat healthier, and/or get fit. There are innumerable companies out there that are ready and willing to take advantage of this momentum: from those hocking "magic bullet" pills that will increase your energy or reduce your belly fat to the myriad shake- and juice-based diets that put you at a near-starvation calorie input—and will probably have you...

You might be familiar with the use of zucchini blossoms in cooking and maybe even know how to make herbal simple syrups. But if you really want to show off as someone who knows how to use flowering plants in food, try adding some flower water to your cooking/baking repertoire.