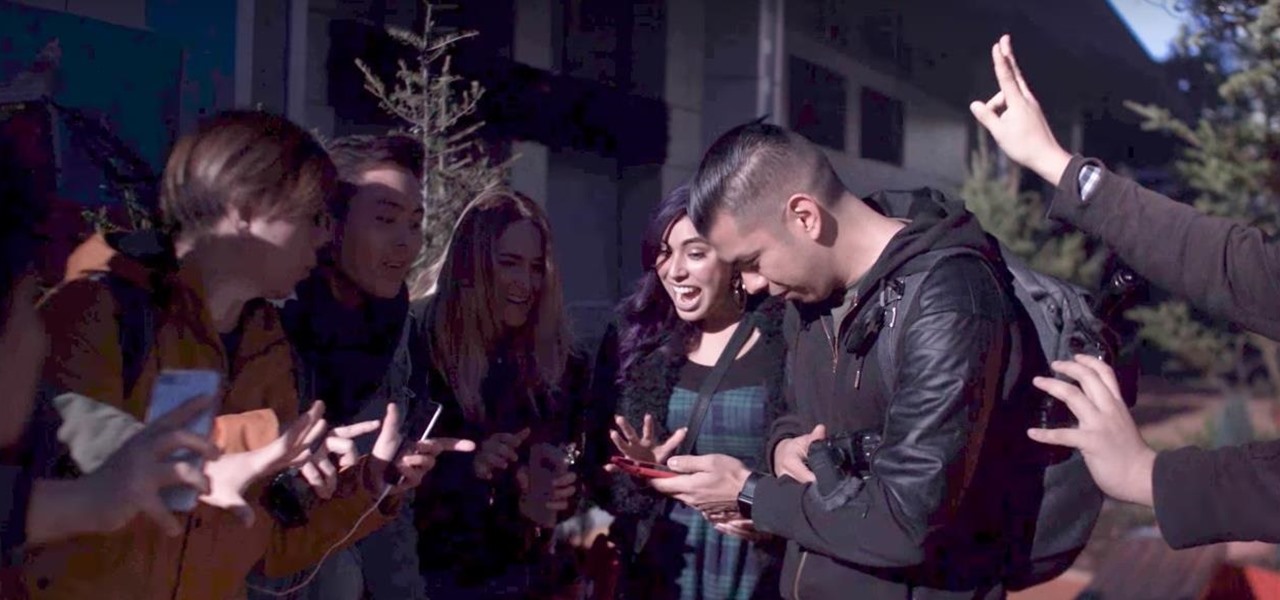
A new study published by American University demonstrates how Pokémon GO and other augmented reality games can help city governments bring communities closer together.

Any internet user will need to download files eventually, and most simply have faith that what they are downloading is trustworthy. This doesn't give much clarity into the contents of the file, but if the file's author published the original checksum, comparing it to the SHA-256 hash of the downloaded file can ensure nothing was tampered with.

As the fish farming industry struggles to become more environmentally friendly, it just gained another problem. Fish food loaded with antibiotic-resistant genes.
Whether or not a microbe is successful at establishing an infection depends both on the microbe and the host. Scientists from Duke found that a single DNA change can allow Salmonella typhi, the bacteria that causes typhoid fever, to invade cells. That single genetic variation increased the amount of cholesterol on cell membranes that Salmonella and other bacteria use as a docking station to attach to a cell to invade it. They also found that common cholesterol-lowering drugs protected zebrafi...

Regarding foodborne pathogens, eating fish is not as hazardous as it was a few years ago — but if fins are on the menu, it's good to have a heads-up about what's good and what's bad these days.

Whether your palate runs to domestic or imported, a piece of cheese can be a real treat for the senses. Its smell, taste, and texture are all parts of its appeal. A big part of what makes that savory wonderfulness comes from the microbes in and on the cheese. Thanks to a team of researchers dedicated to studying those microbes, we have a better understanding of their importance to cheese and us.

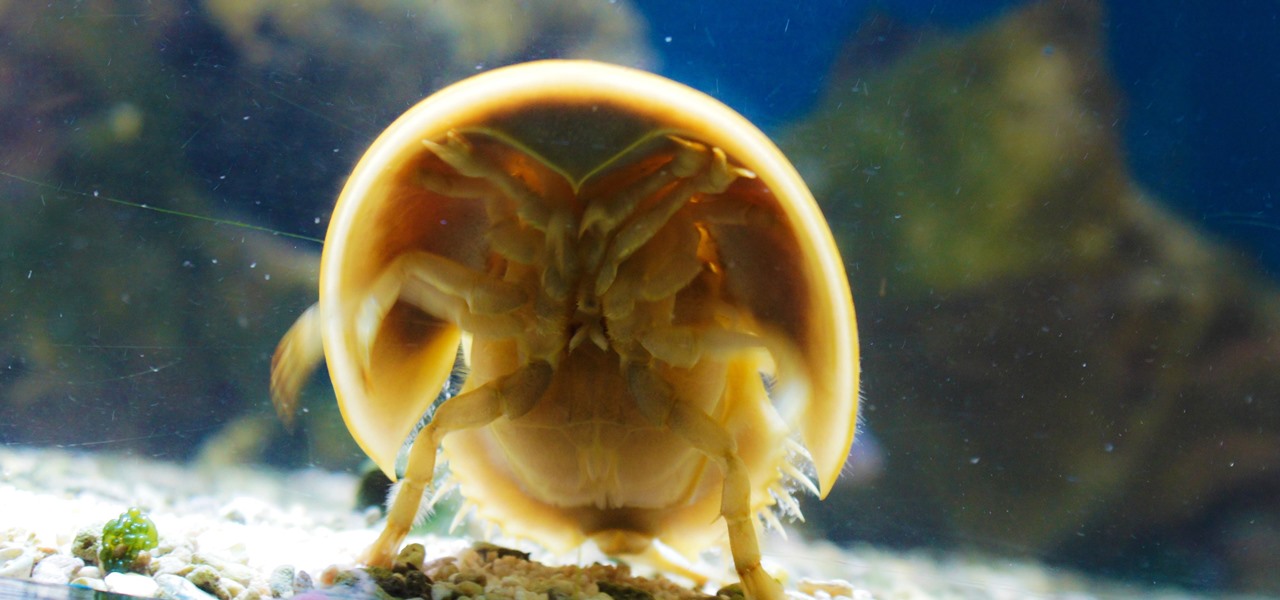
During the millions of years they've been on earth horseshoe crabs have developed a trick that can save our lives even now — and may be especially useful in the fight against healthcare-associated infections.

The next time you suffer a cut or abrasion, think twice before you reach for the Neosporin. It's time, and mom, tested — you get a cut, you wash it carefully, then apply some triple-threat antimicrobial ointment. You may or may not slap on a band-aid. We won't cover it here, but so that you know, covering the wound with a sterile dressing or band-aid is a good idea.

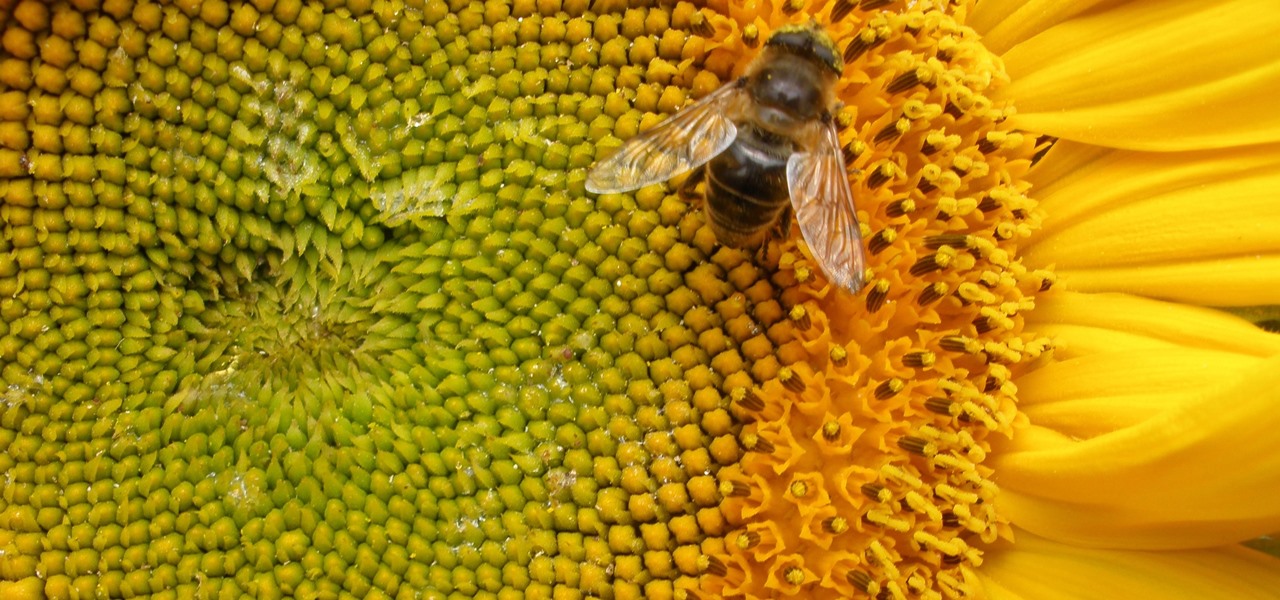
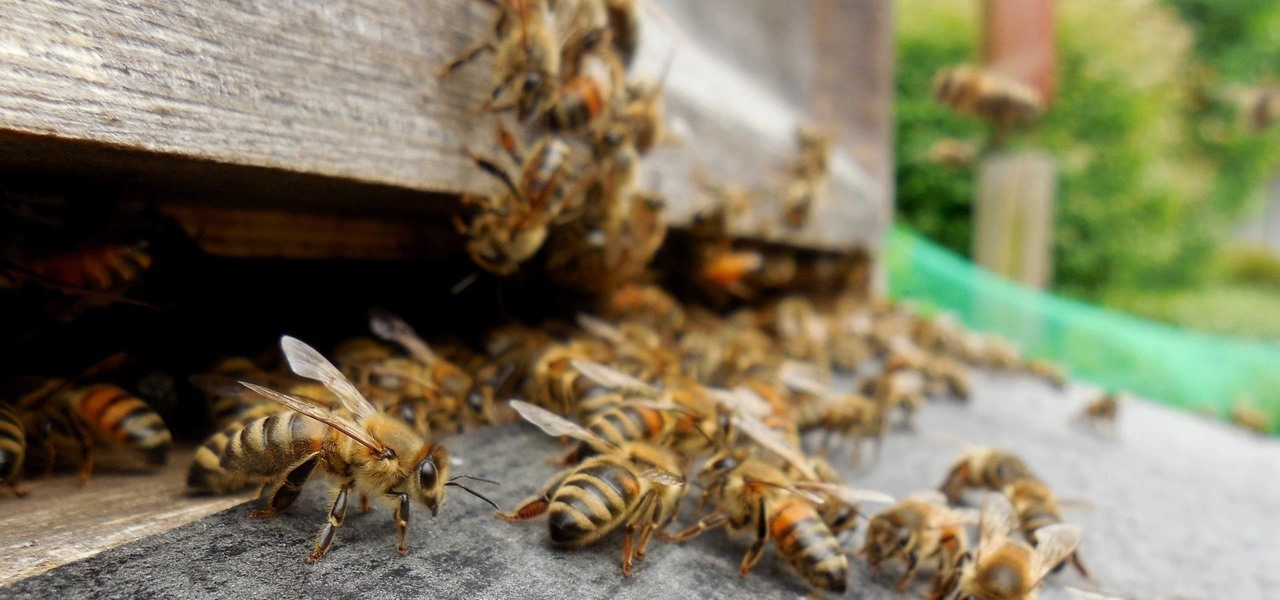
By connecting the dots between theory and real-life effect, two new studies offer more proof that neonicotinoid insecticides are causing extensive damage to honeybee colonies.

Tell the truth. The bat picture creeps you out. You are not alone. But in reality, bats truly are some of our best friends. They gobble thousands of disease-spreading bugs a night. But they also carry viruses that can be deadly to humans. So, bats — friend or foe?

When building anything of a social nature, be it a local roller derby or softball team, a club dance night for chiptune, or building new technology markets, the community around those ideas are an important factor in helping these things not only come into existence but to grow into something that enlightens everyone involved. The community around an idea can actually make or break these new ventures — and this applies to augmented and mixed reality as well.

If you have encountered bed bugs lately, you are not alone. While the pesticides used to fight these pests are losing effectiveness, a fungus shows promise in knocking the bugs out of beds everywhere.

Add antibiotics to the possible list of culprits responsible for honeybee decline around the world. While it may come as a surprise, antibiotics are commonly mixed into feed used by commercial beekeepers to maintain their hives. In a recent study published in PLOS Biology, researchers from the University of Texas at Austin found antibiotics used to treat honeybees may be a contributing factor in individual bee death and colony collapse.

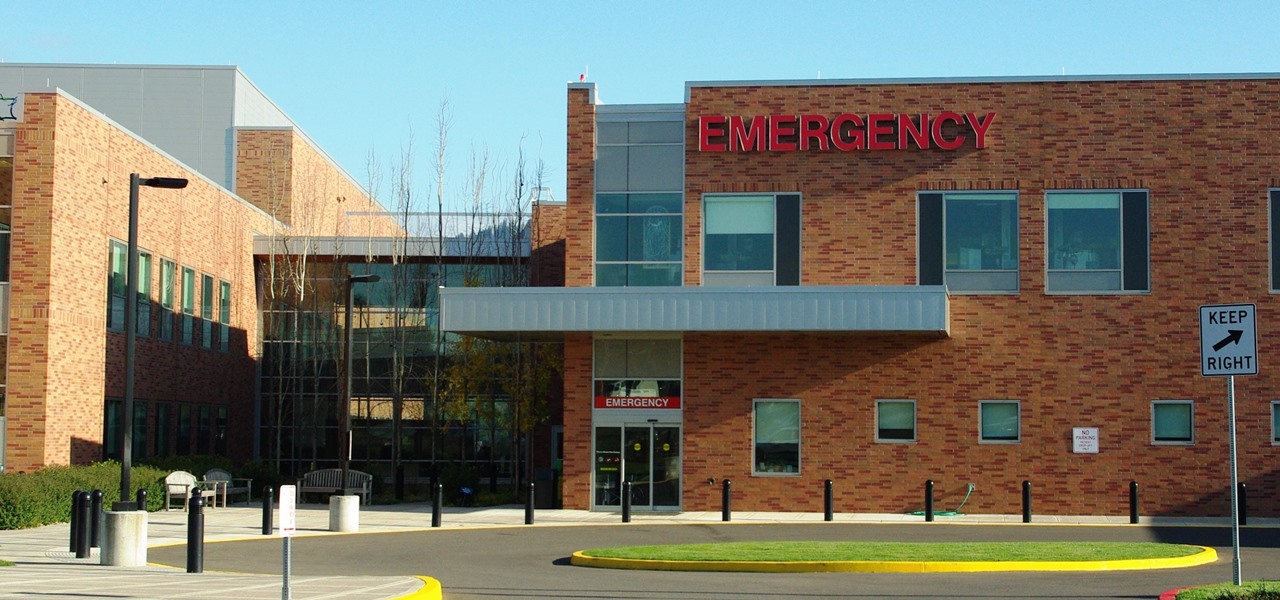
It feels like someone reached into your chest and squeezed. Your head throbs in unison with your heartbeat. Clammy dread coats your body in sweat. Whether you call 911 or someone does it for you, the ER is your next stop.

Joe McKenna died when he was 30 years old. A young married man with his future ahead of him, he was cleaning up the station where he worked as a fireman. Struck by a piece of equipment fallen from a shelf, Joe complained of a sore shoulder. Over the next week, Joe worsened and ended up in the hospital. Chilled, feverish, and delirious, his organs shut down from an infection we'd now call septic shock.

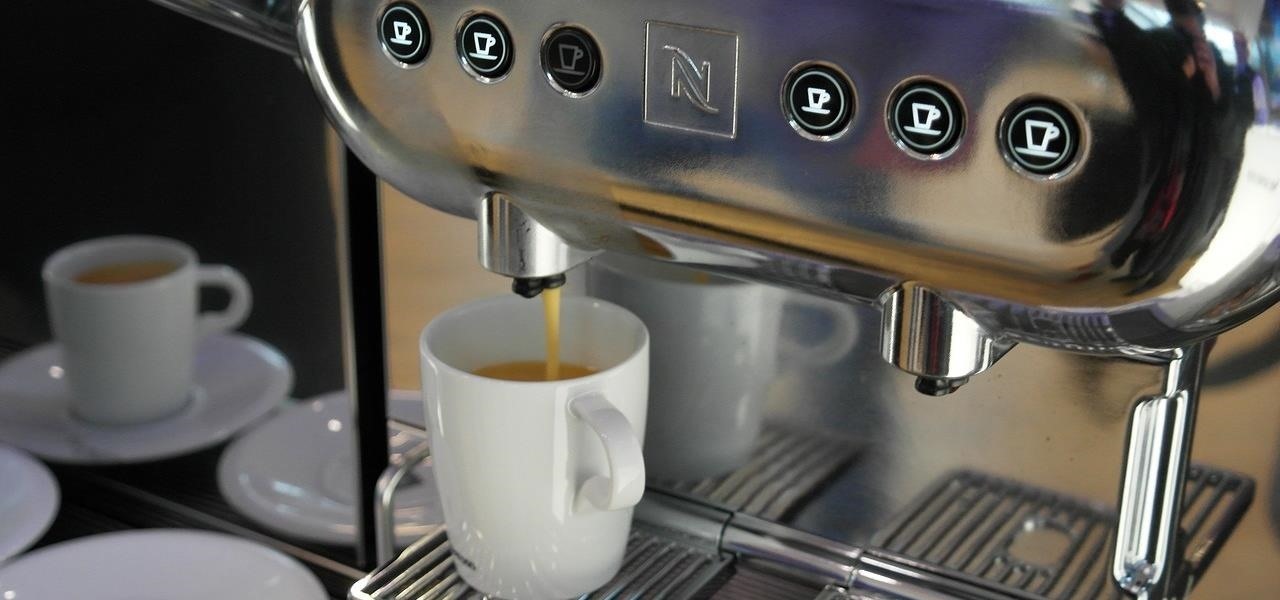
You just sat down, coffee in hand, and the day is ready to start. Now that you have taken a few sips, let me pose a question: What is living in that coffeemaker of yours? The answer might make you dump that coffee down the drain pronto.

NOTICE: Ciuffy will be answering questions related to my articles on my behalf as I am very busy. Hope You Have Fun !!!

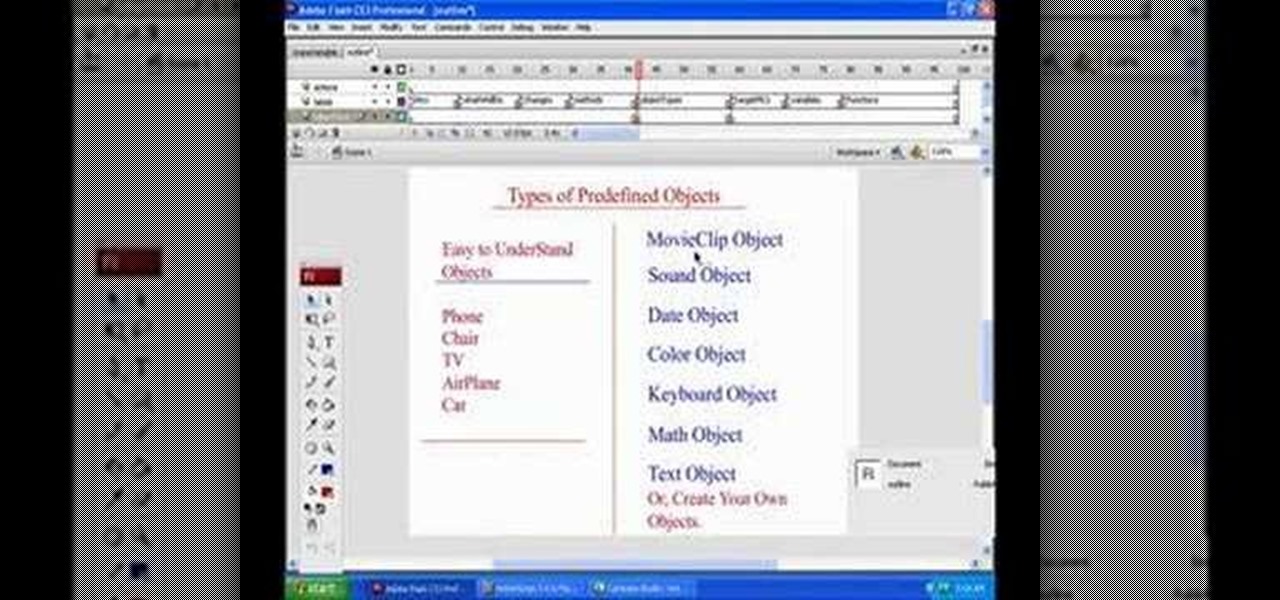
An Object within Flash CS3 is a thing - a thing that has attributes and can perform actions. That thing may be a ball bouncing in your animation or a dog barking. In this short tutorial, author Bill Dallas Lewis presents the concept of Objects within ActionScript 3 and Flash CS3 as well as how to interact with objects within your presentation.

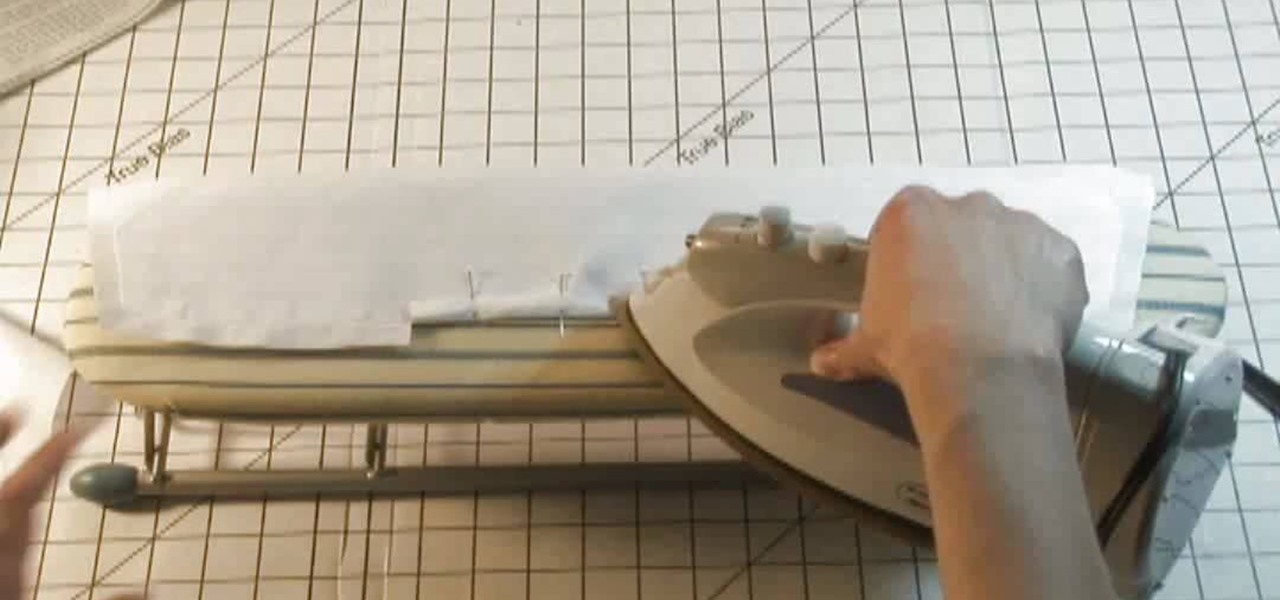
By using sewing pattern Simplicity 4670, the author of this tutorial video takes you through the steps needed to produce a great shirt collar. First you should attach interfacing to one piece of the shirt collar. Here you will be using fusible interfacing and taking the facing to the shirt collar iron the interfacing to the wrong side of the fabric. Sew a guide line that is 5/8ths of an inch wide along the notched edge of the shirt collar's facing piece. At the dot markings of the collar clip...

Charades is a word-guessing game that's acted out in pantomime by players at parties or other gatherings.

Rich Dad, Poor Dad author presents commentary on how money can manipulate or be manipulated. Make money work for you.

When learning Wi-Fi hacking, picking a compatible Wi-Fi network adapter is the first step to learning to crack Wi-Fi passwords.

For anyone using open source information to conduct an investigation, a balance between powerful tools and privacy controls are a must. Buscador is a virtual machine packed full of useful OSINT tools and streamlined for online research. This program can easily be set up in VirtualBox, and once that's done, we'll walk you through some of the most useful tools included in it.

This is a tale about microbes, a man who became a hermit, and the parchment that carries both of their stories.

A virus easily spread among trout and salmon could make it harder to keep your favorite fish on the menu.

Urinary tract infections (UTIs) drive over eight million people to seek medical attention every year. Almost all — as many as 90% — of those infections are caused by Escherichia coli. Copper can kill bacteria, but E. coli has found a way to capture the copper, preventing its antibacterial action. Now, researchers have found that, in a cruel irony, the bacteria use the copper it grabs as a nutrient to feed its growth.

Bacteria, viruses and other germs sometimes set off the immune system to overreact, producing a severe condition called sepsis. Sepsis is so dangerous that it is the leading cause of death of children across the world, killing a million kids every year, mostly in developing countries. Probiotic bacteria might be able to prevent sepsis and infections, but no large research studies have been done to find out whether that actually works. Until now.

For as long as 14,000 years, the First Nations people of the Heitsuk Nation have made their home along the Central Coast of the Canadian province of British Columbia. Among the territory's inlets, islands, rivers, and valleys lie a clay deposit on the north side of Kisameet Bay, near King Island. For as long as most can remember, the tribe has used the clay as medicine. Now science says microbes that live in that clay may have important antibacterial properties.

Crusty, itchy, red eyes? There is a decent chance you could have conjunctivitis, or pink eye, an infection of the thin lining around the eye and the eyelid, caused by bacteria, an allergen, virus, or even your contact lenses. Whatever the cause — you call up your doctor to get a prescription to clear it up, right? Not really.

Love is the spice of life — it is also the microbes that couples share through sickness and in health, through the bathroom and in a hallway.

Not all bacteria in the eyes cause infection. A group of researchers from the National Eye Institue has shown that not only is there a population of bacteria on the eyes that reside there but they perform an important function. They help activate the immune system to get rid of bad, potentially infection-causing — pathogenic — bacteria there.

Forget the rise of the machines. Tardigrades are set to outlive everything — even the bots. When the last echo of a whisper in a cell phone has long dissipated into space, the water bears will still be hanging out.

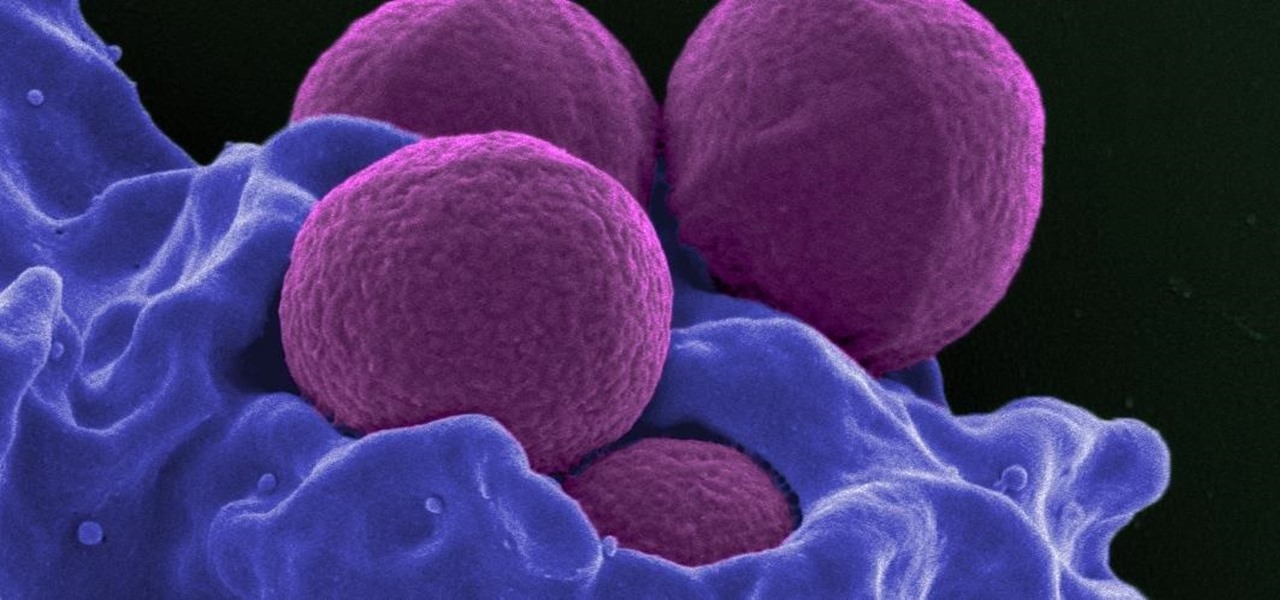
Staphylococcus aureus is a widespread bacteria — about a third of us have it on our body right now — usually in our nose or on our skin. And it probably isn't causing an infection. But, about 1% of people who have Staphylococcus aureus present have a type that is resistant to the antibiotic methicillin.

Flu vaccines can help prevent us from getting or suffering the most severe effects of the flu. But, each vaccine only protects us from three different strains of the flu. If we don't have a vaccine against all types of flu, it leaves us open for an epidemic with a flu virus we didn't expect.

Twelve-year old Rory Staunton took a dive for a basketball during gym class and came up with a cut on his arm. The school nurse applied a couple of band-aids, without cleaning the cut, and off he went. In approximately three days, hospital physicians told his parents there was nothing else that they could do for their son; he was dead.

With a death rate of one in five, sepsis is a fast-moving medical nightmare. New testing methods might improve your odds of survival if this infection ever hits you.

Sex makes the world go 'round, and when it does, so does gonorrhea. Finally some good news on the growing menace of drug-resistant gonorrhea — a large, long-term study shows a vaccine may work in reducing the incidence of an increasingly dangerous infection.

The search is on to find antibiotics that will work against superbugs — bacteria that are rapidly becoming resistant to many drugs in our antibiotic arsenal.

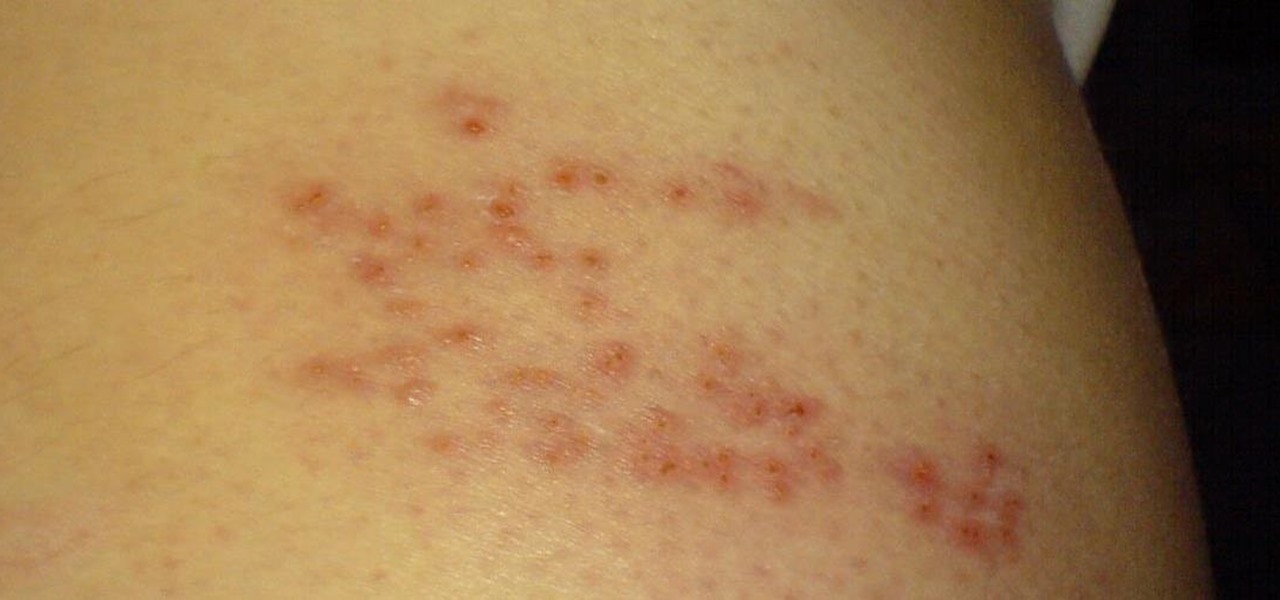
People who have heart disease get shingles more often than others, and the reason has eluded scientists since they first discovered the link. A new study has found a connection, and it lies in a defective white cell with a sweet tooth.

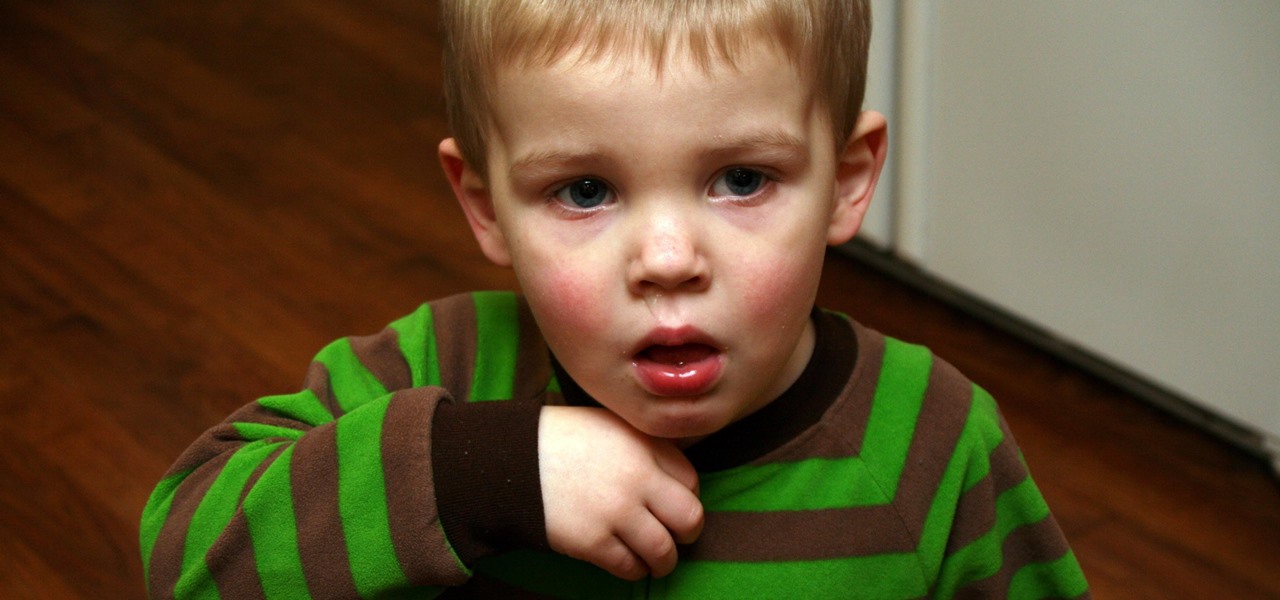
It's not always easy to get to the root of an infection outbreak. Epidemiologists study infected people, contacts, and carefully examine where the infections happened and when. In the case of a 2012 outbreak of pertussis — whooping cough — in Oregon, scientists just published an analysis of how vaccination status affected when a child became infected during the outbreak.