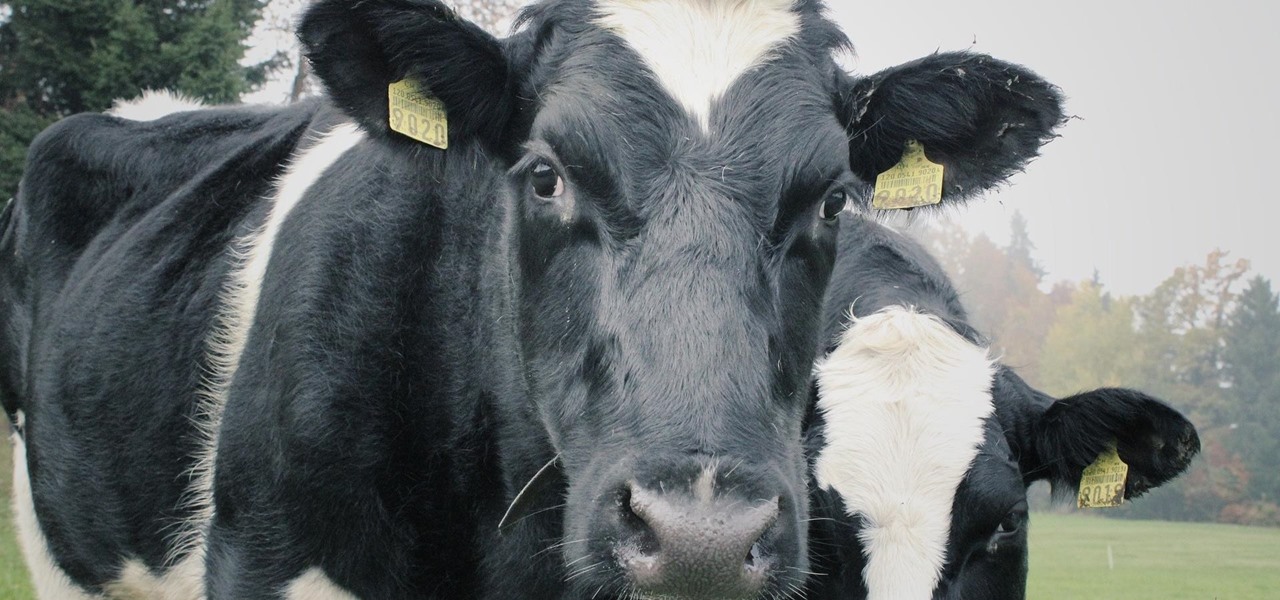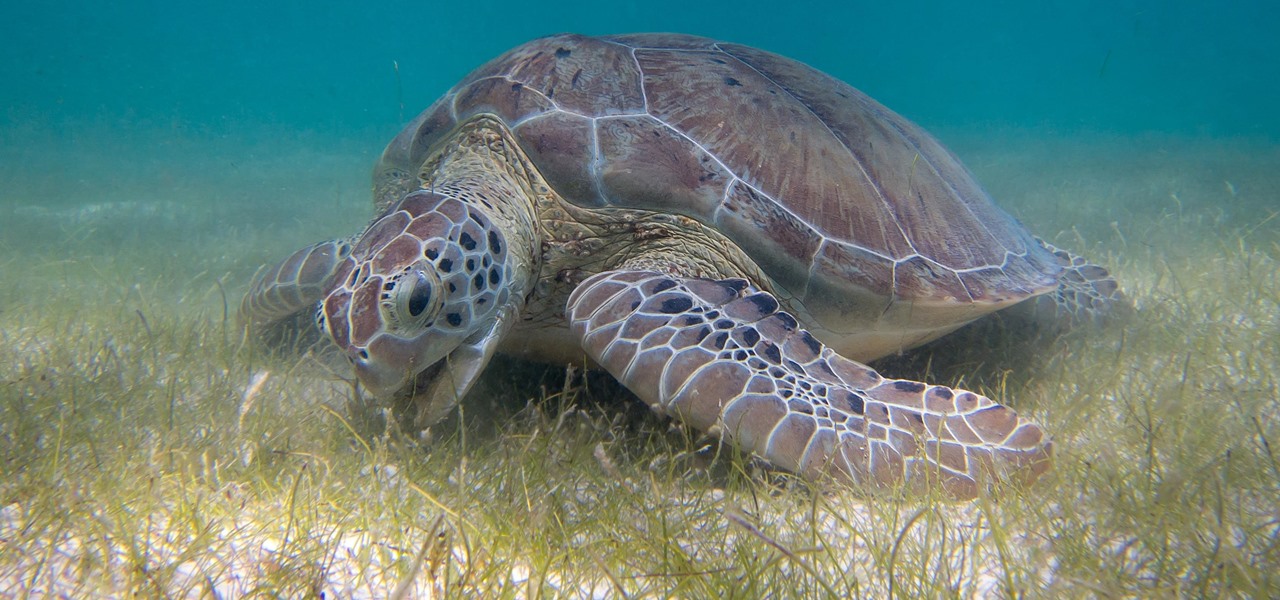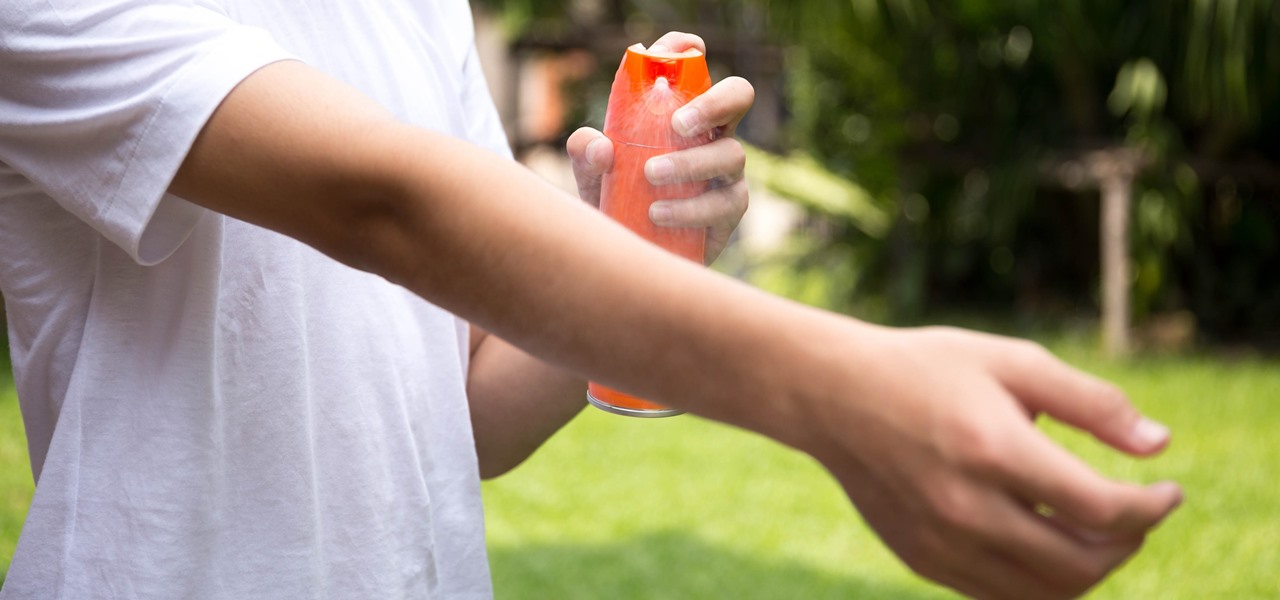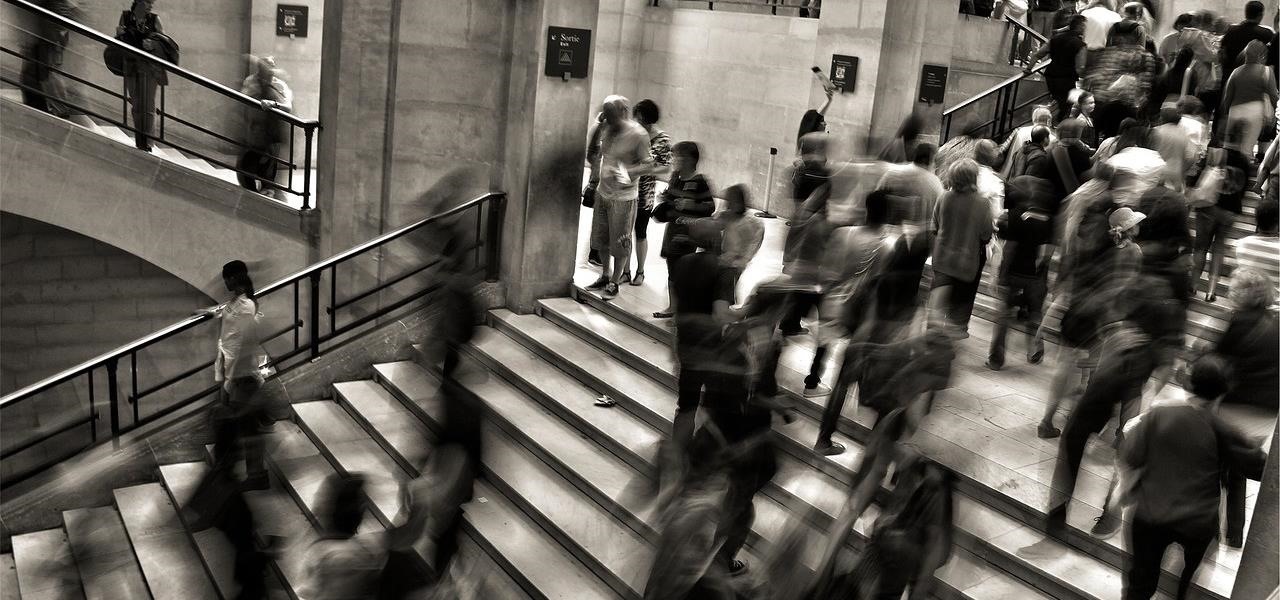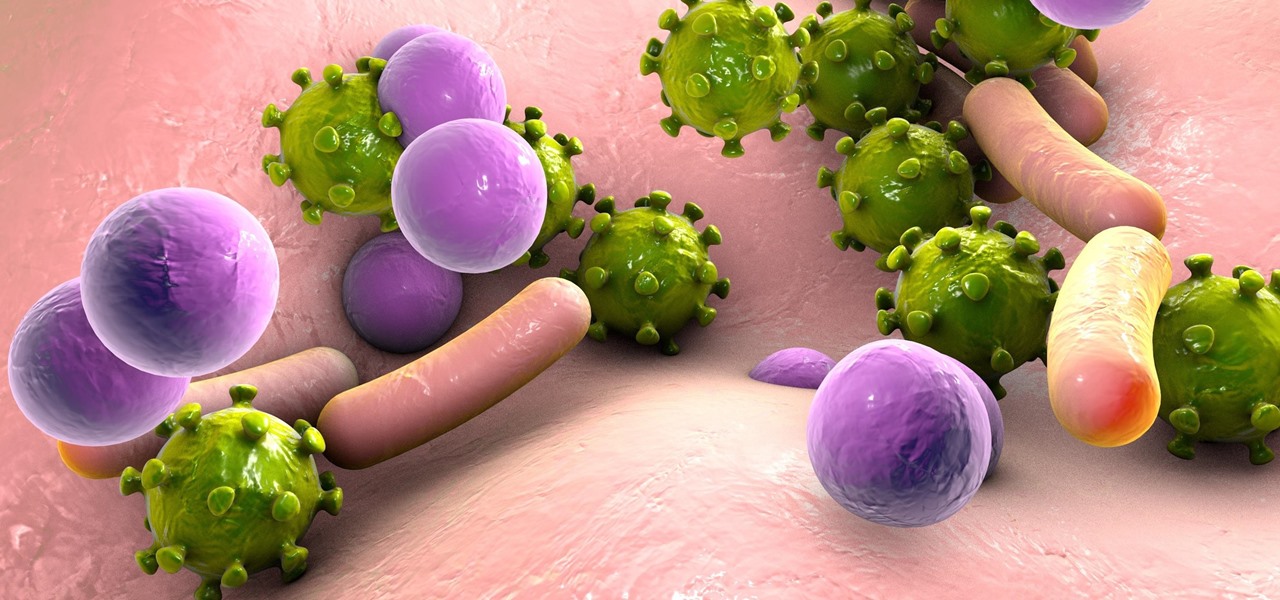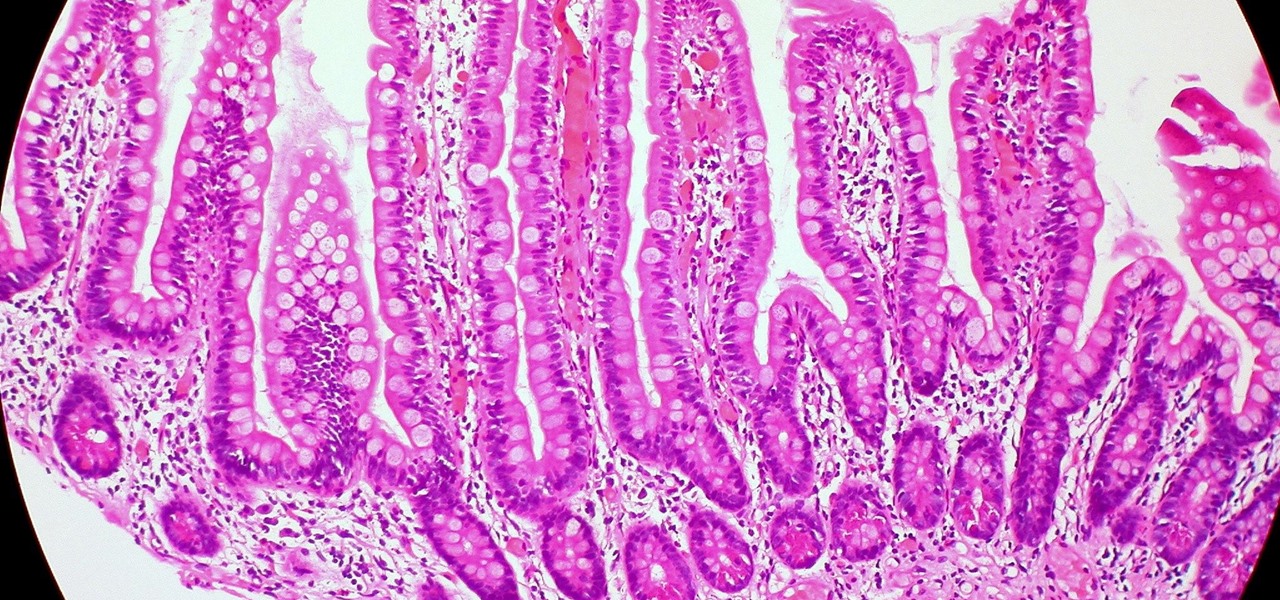
Several recent research studies have pointed to the importance of the microbes that live in our gut to many aspects of our health. A recent finding shows how bacteria that penetrate the mucus lining of the colon could play a significant role in diabetes.

Listeria monocytogenes bacteria don't play fair. Healthy people can usually handle the food-borne infection, but the bacterial infection hits pregnant women, fetuses and cancer patients very hard. Interestingly, a new study found that other bacteria may help prevent Listeria infections in those people.
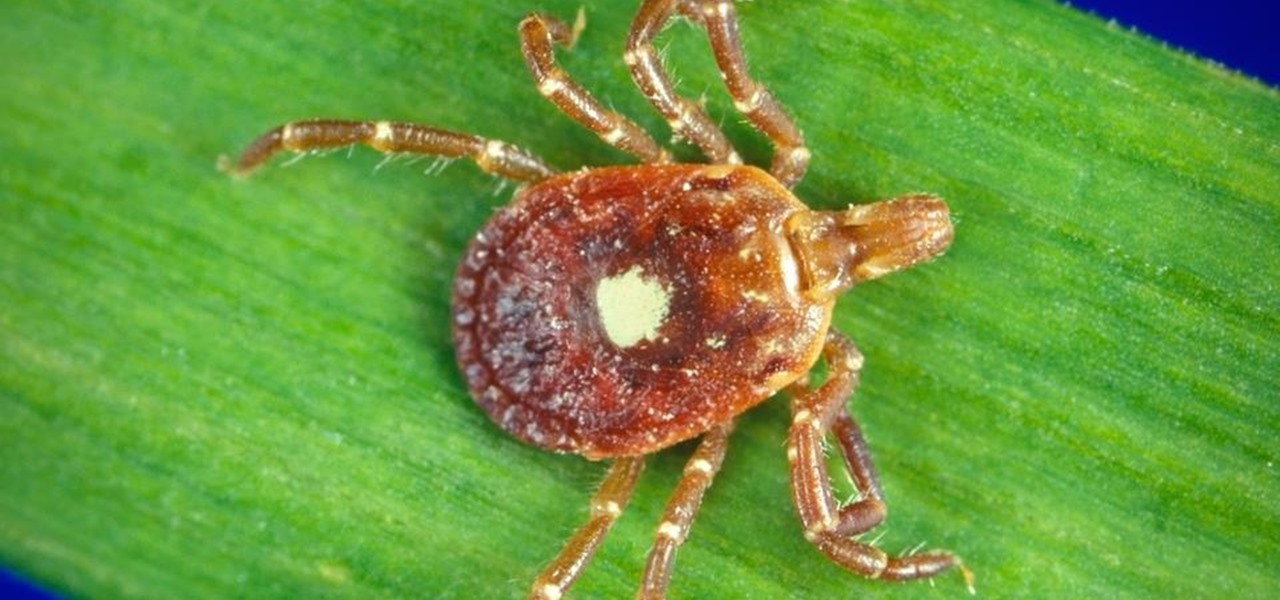

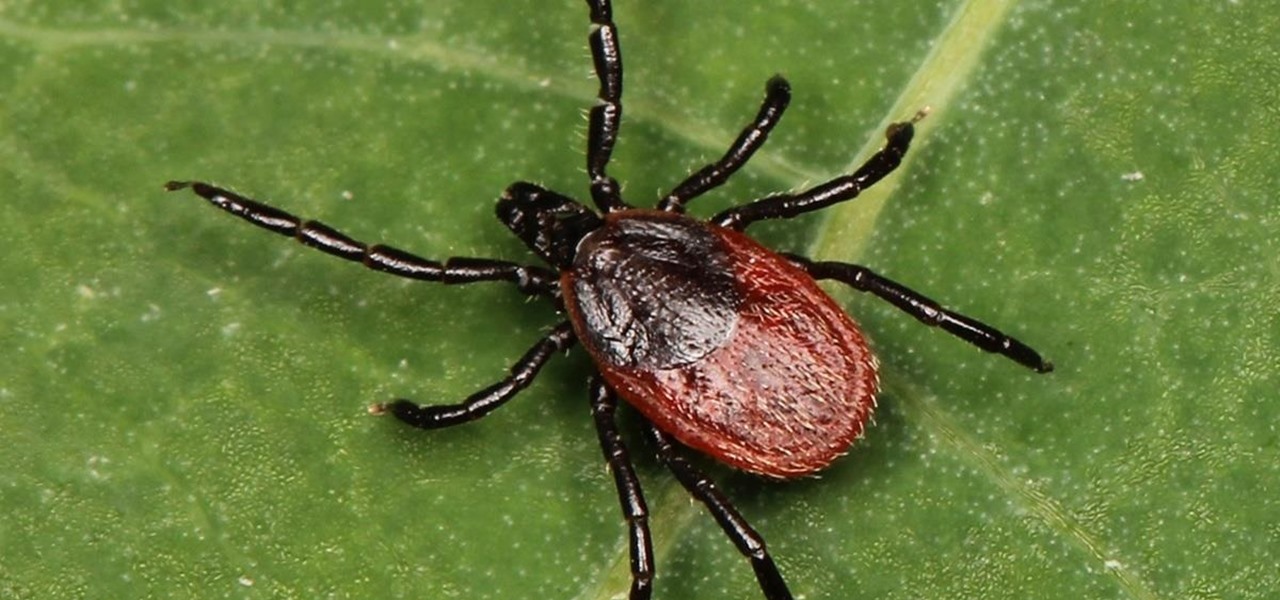
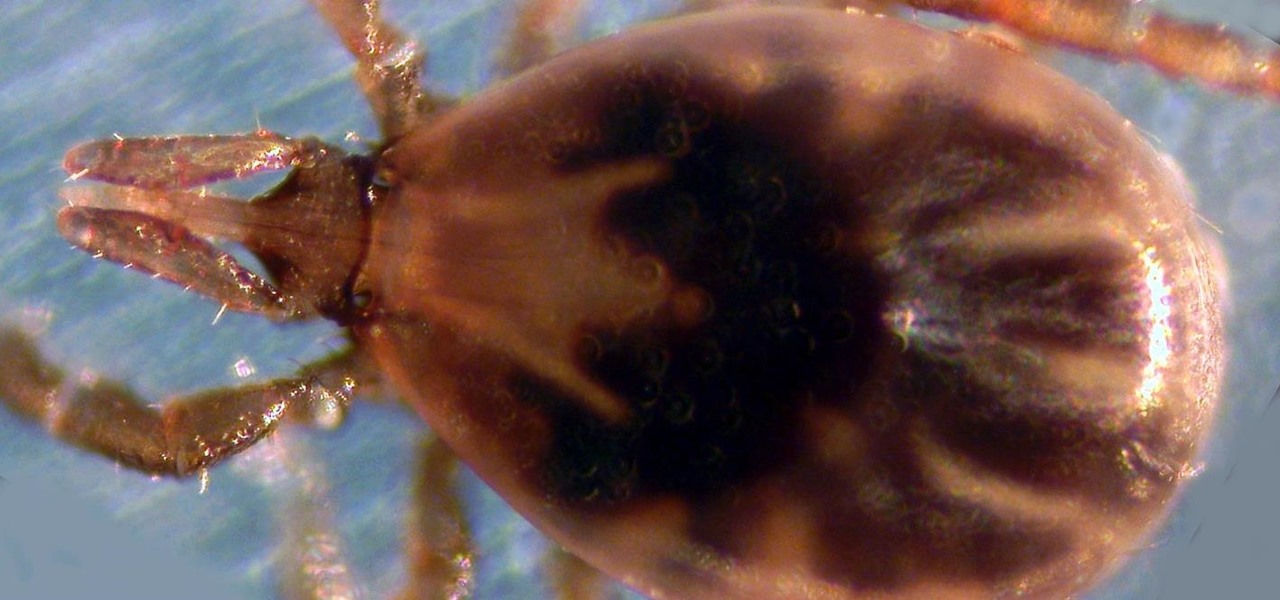
The possibility of severe tickborne illness is increasing as an aggressive tick from the American southeast moves up the Atlantic Coast.
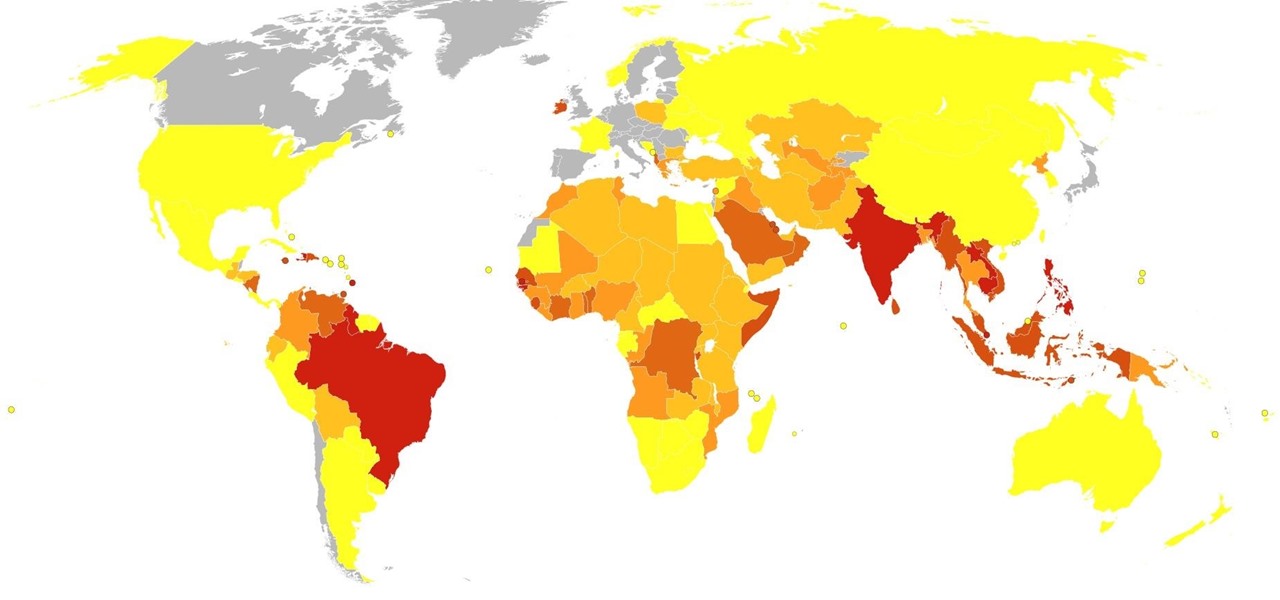
Dengue fever is a danger to anyone living or visiting tropical or subtropical regions. It can be hard to detect the infection in its earliest and most treatable phase, especially in children. Luckily, new research highlights better techniques for triaging the disease in infected children with more severe symptoms, potentially saving lives.
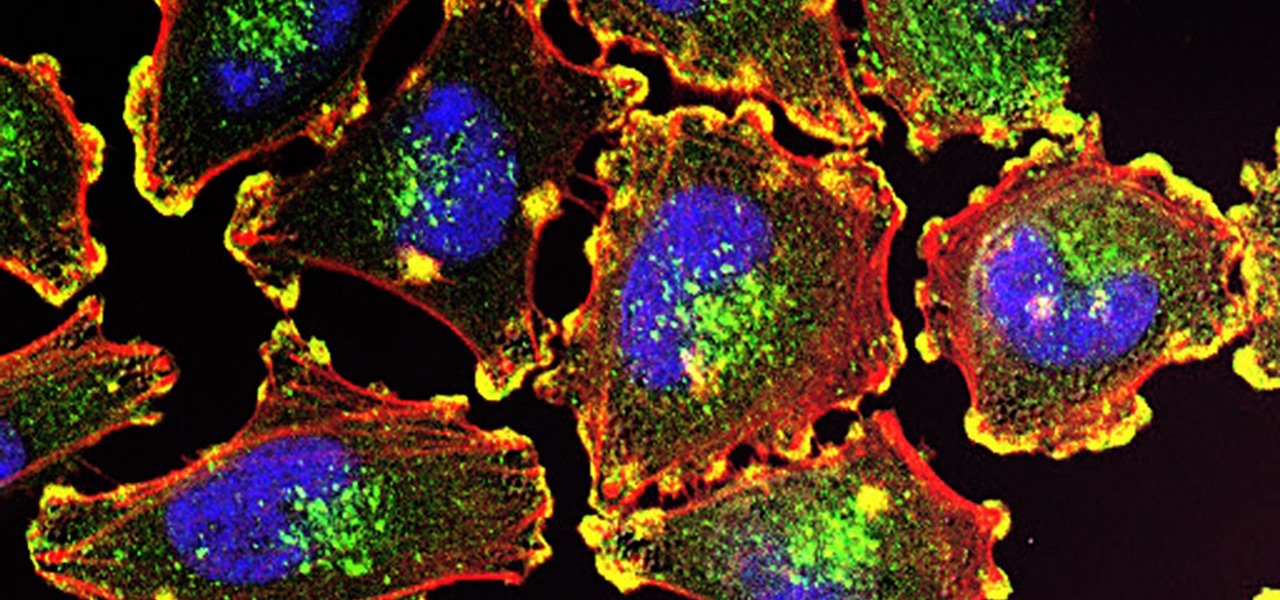
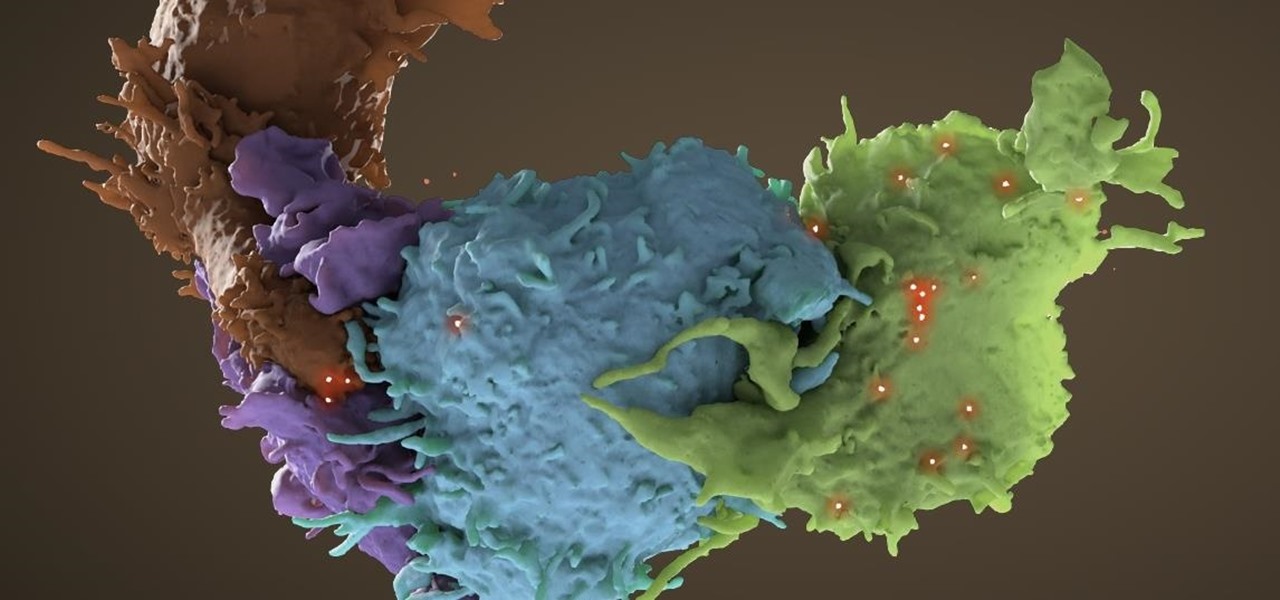
Activating the body's own immune system to fight cancer is the goal of immunotherapy. It's less toxic than chemotherapy and works with our body's natural defenses. The trouble is, it doesn't work for most patients — only about 40% of cancer patients get a good response from immunotherapy. But coupling it with another type of cancer therapy just might deliver the punch that's needed to knock out cancer.

As headlines focus on melting glaciers and rising water levels caused by global warming, climate change is quietly taking its toll on the nearly invisible occupants of this planet, the microbes.

We've worked hard to reduce the flow of toxic chemicals into our waterways, which means no more DDT and other bad actors to pollute or destroy wildlife and our health. But one observation has been plaguing scientists for decades: Why are large quantities of one toxic chemical still found in the world's oceans?

Lyme is a growing threat as we move into warmer weather in the US. Researchers have said this year could be one of the worst for this tick-borne disease, as a skyrocketing mouse population and warmer temperatures increase the risk.

Water makes up about 60% of your body weight. Whether you like it plain, flavored, bubbly, or in beverages or food, we all need water daily to avoid dehydration and stay healthy. For communities in need of clean drinking water, new research using bacteria may offer a simplified, lower-cost method for boosting potable water supplies.

The evolution of our infection-fighting systems may have something to teach modern scientists. That's what a group from the University of Granada in Spain found when they studied a protein that's been around for over four billion years. Their work, by senior author José Sánchez-Ruiz and colleagues in the Department of Physical Chemistry, was published in the journal Cell Reports.

In order for software developers to do their jobs as new hardware reaches the market, they will need the right tools to get their projects off the ground and into augmented and mixed reality devices. There have been completely new approaches to development when it comes to AR and MR, and these are some of the faces behind them.

Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a highly contagious disease that can be life-threatening for young children. New research backs a recommendation that all pregnant women receive a pertussis booster with each pregnancy, as it can help their infants fight off the infection.

Facebook really wants us to use Messenger. For the most part, they've succeeded; theirs is one of the most popular messaging apps right now. And with yesterday's announcement of new features, Facebook is only going to make their flagship chat application better.

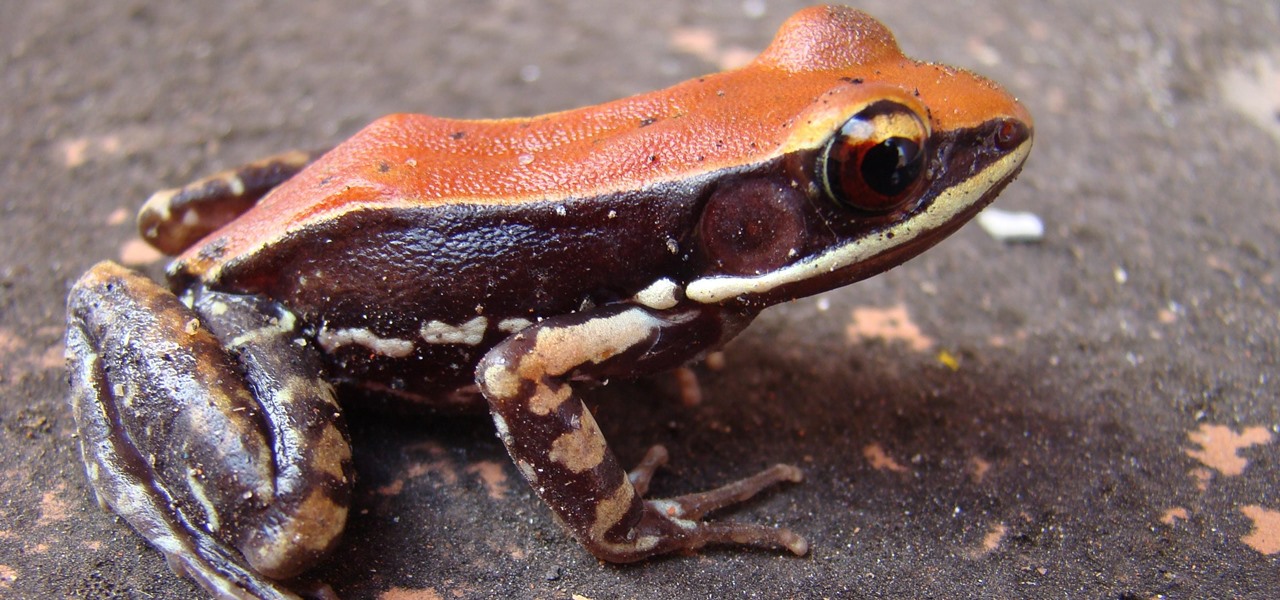
Our quest to find novel compounds in nature that we can use against human diseases —a process called bioprospecting — has led a research team to a small frog found in India. From the skin slime of the colorful Hydrophylax bahuvistara, researchers reported finding a peptide — a small piece of protein — that can destroy many strains of human flu and can even protect mice against the flu.

Antibiotics used to prevent diseases in livestock are creating a world of hurt for humans and the soil we depend on for food. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a global health issue. The overuse, underuse, and poor use of these life-saving drugs is rapidly removing them as a treatment option for serious infections in humans—plus bacteria are naturally adaptive.

Viral infections have been the focus of attention in the development of autoimmune diseases—diseases where the body's immune system reacts to the body's own cells—because they trigger the immune system into action.

Two viral liver diseases could help us find the path toward the cause of Parkinson's disease. Researchers from the University of Oxford and UCL Institute of Neurology in London have reported an association between hepatitis B and C infections and an increased risk of Parkinson's disease. Their findings were published early online in the journal Neurology.

To keep fungal pathogens at bay in their crowded homes, wood ants mix potions to create powerful protection for their nest and their young.

Most females have had at least one urinary tract infection in their lifetimes. Recurrent UTIs are particularly problematic in young, sexually active women, where about 80% of the infections are caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli, better known as E. coli.

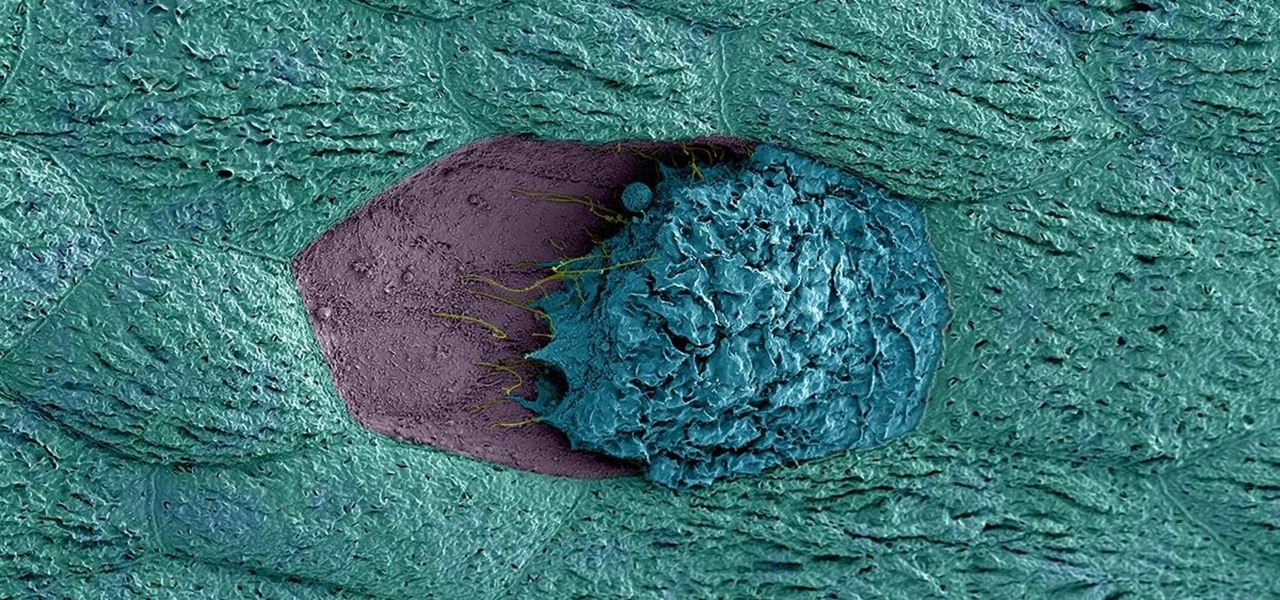
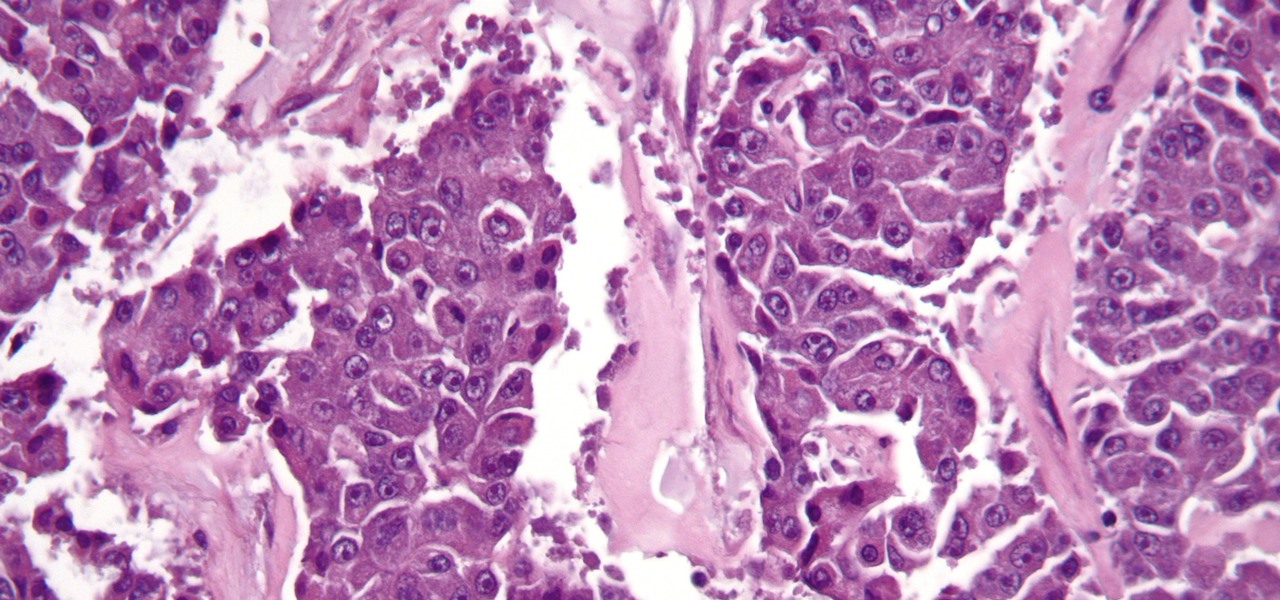
The search for a cancer treatment that selectively finds and kills only the cancerous cells has just made a giant leap forward.

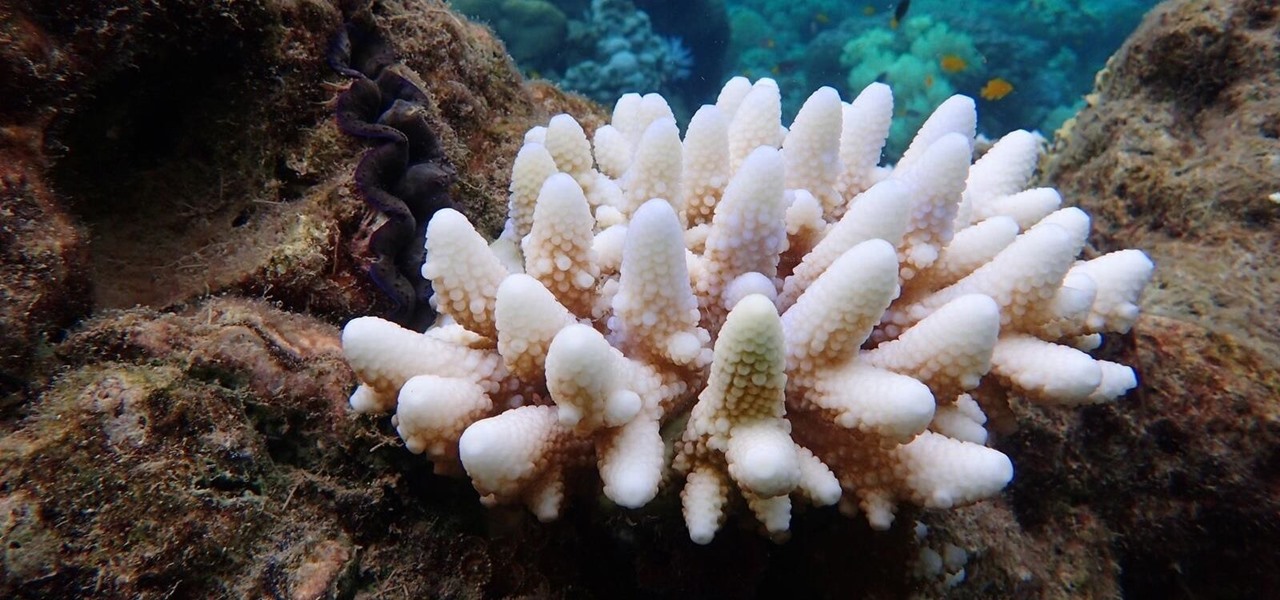
The Great Barrier Reef in Australia is the largest living system on the planet. Yet more than 90% of the reef is bleaching because of the loss of a tiny algae that lives within the coral.

Tremendous strides have been made in the treatment and outlook for patients infected with HIV, the human immunodeficiency virus. Treatment with a combination of antiretroviral drugs can keep patients with HIV alive for decades, without symptoms of the infection. The trouble is, if HIV-infected people stop taking their medications, the virus takes over in full force again—because the virus hides out quietly in cells of the immune system, kept in check, but not killed by the treatment.

In a world increasingly regulated by computers, bugs are like real-life cheat codes. They give you the power to break the rules and do good or bad without ever leaving your seat. And government agencies around the world are discovering and stockpiling unreported bugs as cyberweapons to use against anybody they see fit.

In the past, infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) commonly led to dementia as the virus made its way to the brain. Even in effectively treated people, HIV can hide out and replicate in places like the brain, where it's tough to detect. That's why it's very concerning that half of all HIV-infected patients still report cognitive problems.

Arsenic occurs naturally in the environment, but it is also one of the most commonly found heavy metals in wastewater, deposited there by inappropriate disposal and arsenical pesticides, for example.

Hospitals are places we go to get well, and we don't expect to get sick or sicker there. But a study from researchers at the Cleveland Clinic, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, and Cleveland VA Medical Center in Ohio found that hospital floors in patient rooms were frequently contaminated with healthcare-associated pathogens—often dangerous multi-drug resistant bacteria.

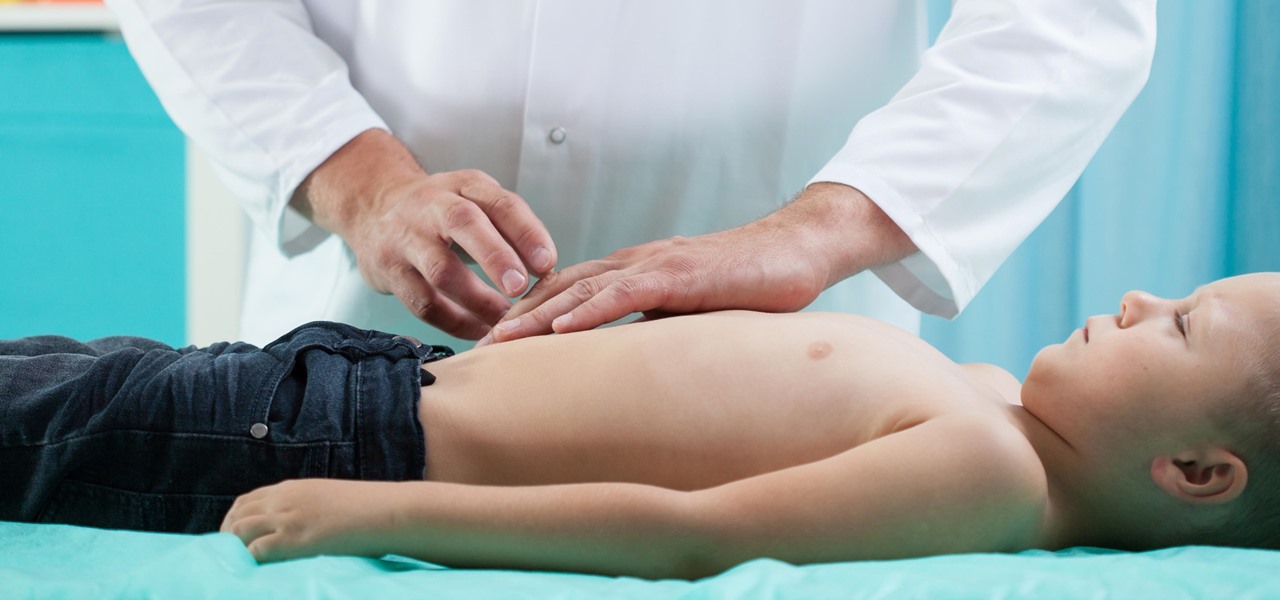
A new study confirms that antibiotics can prevent surgical intervention if your child's appendix becomes inflamed, potentially saving his or her life.

As drug-resistant bacteria become more commonplace, researchers are looking for new antibacterial strategies to disrupt disease-causing microbes. Some scientists are working to create new drugs, while others are trying out drug combinations. Another group, however, are ditching pharmaceuticals altogether and experimenting with non-drug alternatives.

Ecosystem changes caused by agricultural choices in Brazil are creating a dangerous microbe mix in exploding populations of vampire bats and feral pigs.

In the past, to see a pre-constructed state of the house that you would one day live in, you had to be able to read blueprints or hire an artist to sketch it out. Later came the ability to have a 3D rendering of that house on a screen, but you'd still have to work hard to envision it in real life.

A new study just out reveals that HIV takes hold in the human body with the help of cells that usually work to heal, not kill.

Seagrass may help your favorite beach stay a little less toxic. A new study, led by Joleah Lamb, a postdoctoral researcher in the Harvell Lab at Cornell University, found that coastal seagrasses reduce levels of pathogens dangerous to humans and marine organisms in near-shore waters.

Responding to the emergence of Zika in the US, researchers investigated what type of repellent works best to reduce your odds of a mosquito bite from Aedes aegypti, the mosquito species that spreads the Zika virus.

The pathogen referred to as a "nightmare bacteria" is quietly adapting and spreading faster than anticipated.

You know the signs—sneezing, fever, nagging cough, no energy, no appetite. It's the flu, but this time, it's your dog who's down and out. Yes, dogs get the flu, too. However, a team from the University of Rochester Medical Center and their collaborators have developed a new vaccine that may make the doggy flu a thing of the past.

As fun as it is to see Fido's face light up when you feed him table scraps, American dogs are getting fat. The good news is that research is homing in on nutritional strategies to boost canine capabilities to maintain a healthy weight.

Over 1.2 million people in the US are infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)—and one out of eight of them don't know it. Even after decades of intense research into the virus, there's still no cure for it. One of the big problems is that the virus hides out in certain cells of the body, resisting treatments that kill it.

Transmitted by ticks, Lyme disease is a serious infection that is probably headed your way. A recent study confirms the pathogen that causes Lyme disease is now established in nine national parks in the East, including Acadia and Shenandoah National Parks.

If you're grossed out by anything creepy, crawly, and with more than 4 legs... then stop being so close-minded and eat some bugs already, dammit.

I'm sure I'm not the only one on here that has googled "Why am I always tired?"... and I'm definitely not alone when I say that all of the advice I've found so far is useless: