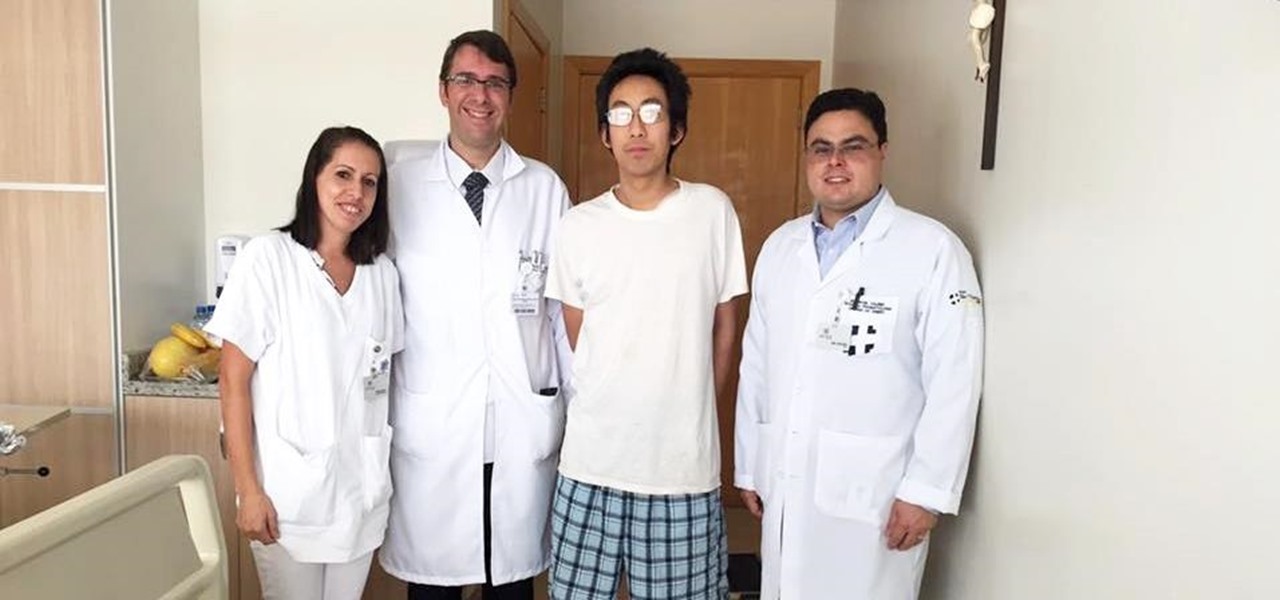
Late last year, two surgeons from the Instituto de Ortopedia e Traumatologia de Jaraguá do Sul in Brazil started using a combination of 3D printing and the Microsoft HoloLens to help plan spinal surgeries. And now, with the rest of their team, they've successfully performed a surgical procedure on their first international patient using their 3D impression planning and augmented reality process.

When computers have vision but people don't, why not have the former help the latter? That's the gist behind the Cognitive Augmented Reality Assistant (CARA), a new HoloLens app developed by the California Institute of Technology.
Streptococcus and staphylococcus bacteria produce toxins that can cause toxic shock syndrome.
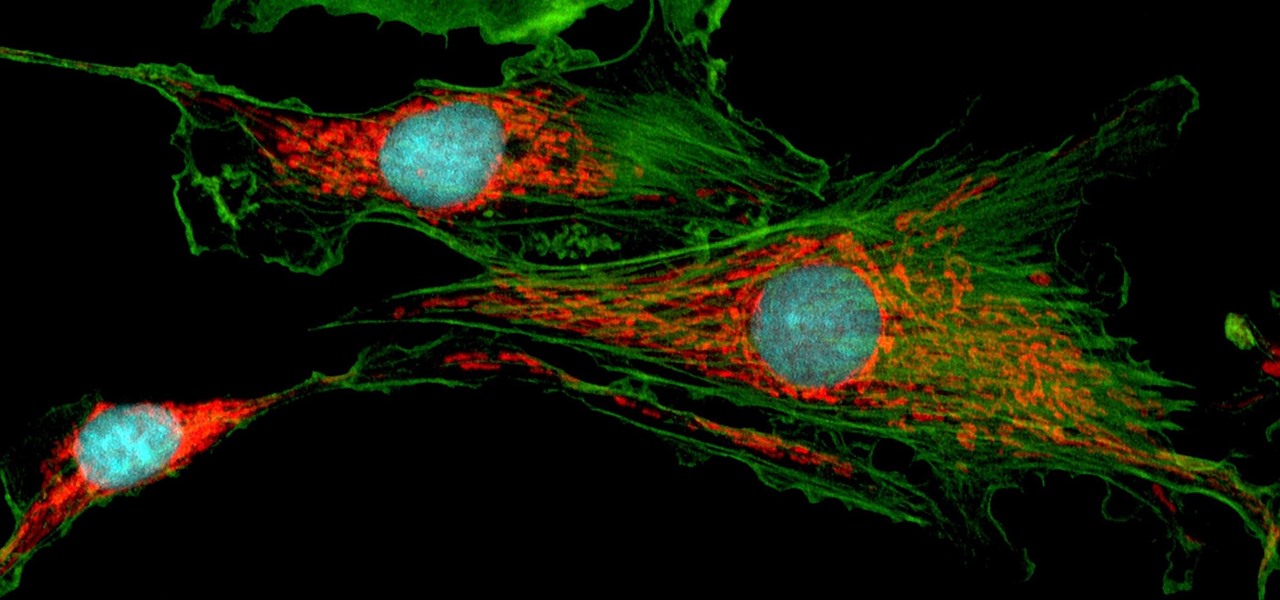
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of our cells because they generate energy to power them. But they also play a key role in the death of cells when they're damaged, infected, stressed, no longer needed, or at the end of their life.
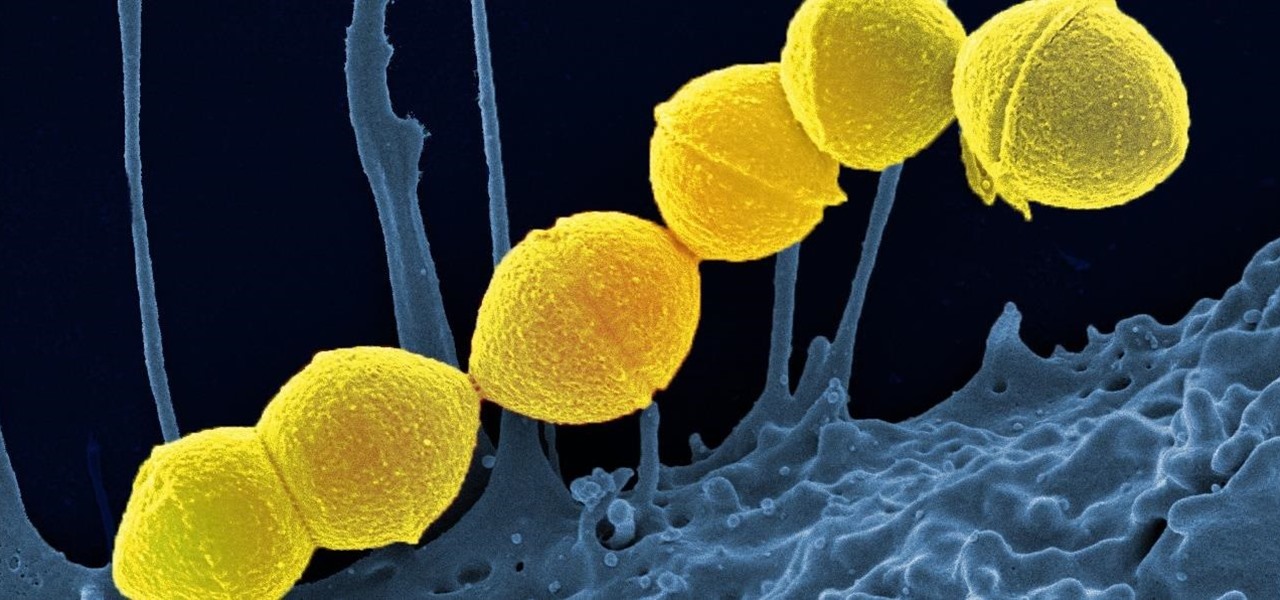
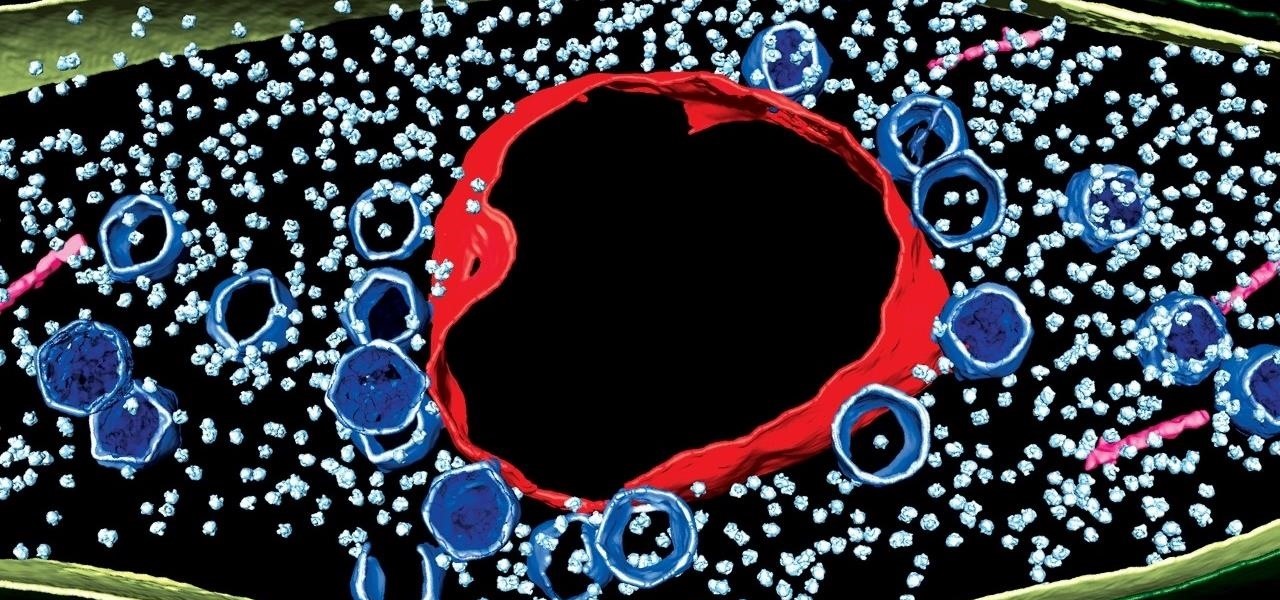
It's not the bacteria itself that takes lives and limbs during invasive flesh-eating bacteria infections. It's the toxins secreted by the group A Streptococcus bacteria invading the body that causes the most damage.

Usually, the mucus lining of the female genital tract presents a barrier that helps prevent infections. But, somehow, the bacteria that causes gonorrhea gets around and through that barrier to invade the female genital tract.

No one can dispute the evolutionary success of bugs. The oldest insect fossils were found encased in crystallized mineral silica in Scotland in 1926, and they're between 396 and 407 million years old.

In the Western world, the only time you'd associate food with cockroaches is health code violations. And while other cultures and countries are more open to cooking with and eating these and other little buggers, insects are probably not a food trend that will be adopted by the West anytime soon.

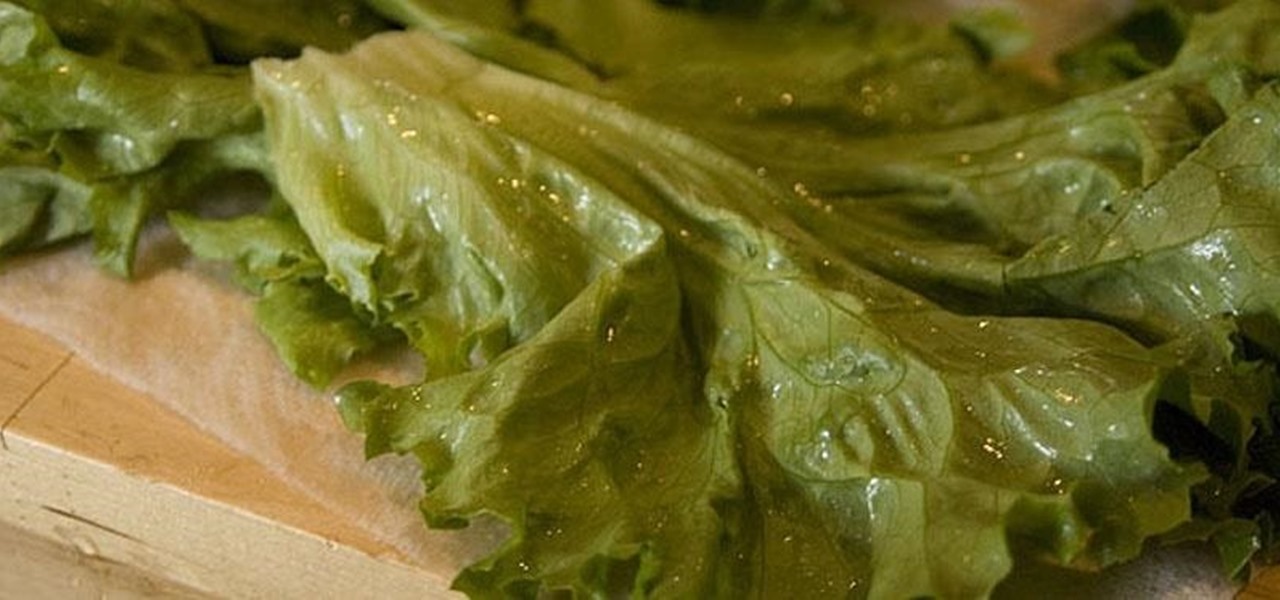
Sometimes you've got a head of lettuce that you want to eat but it lacks a certain youth. In other words, it's wilted and browning at the edges. Other times, you get to the grocery store near the end of day and the only lettuce or greens available look a little on the sad side. Never fear. You're not doomed to a meal of fast food or mouthfuls of soggy salad. You can easily revive those leaves and have something crisp, green, and delicious for your next meal, so don't dump it in the trash.

You need a break from gloomy coronavirus updates. We all do. The unrelenting stream of doom and negative news is both helpful in terms of keeping ourselves and our families safe, but it also has the unfortunate effect of increasing our anxiety. When will this end? How bad will it get? Is there reason to be hopeful?

Urinary tract infections (UTIs) drive over eight million people to seek medical attention every year. Almost all — as many as 90% — of those infections are caused by Escherichia coli. Copper can kill bacteria, but E. coli has found a way to capture the copper, preventing its antibacterial action. Now, researchers have found that, in a cruel irony, the bacteria use the copper it grabs as a nutrient to feed its growth.

The incidence of tuberculosis (TB) is dropping in the US, but the World Health Organization (WHO) considers it to be epidemic in the rest of the world — there were over 10 million new cases in 2016.

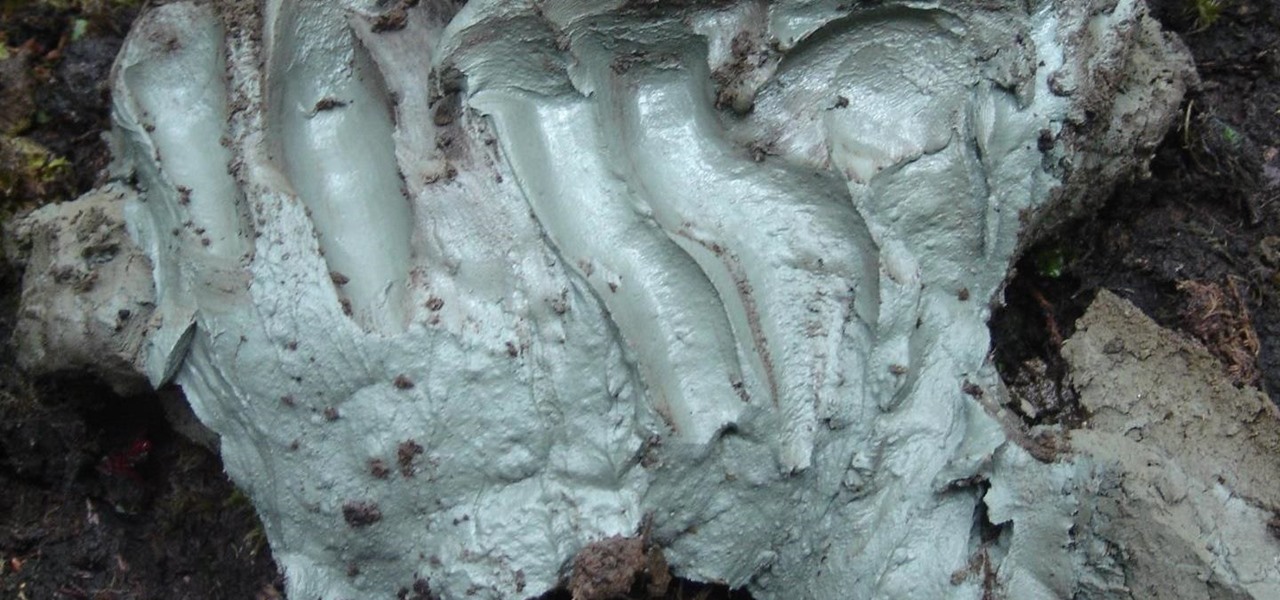
For as long as 14,000 years, the First Nations people of the Heitsuk Nation have made their home along the Central Coast of the Canadian province of British Columbia. Among the territory's inlets, islands, rivers, and valleys lie a clay deposit on the north side of Kisameet Bay, near King Island. For as long as most can remember, the tribe has used the clay as medicine. Now science says microbes that live in that clay may have important antibacterial properties.

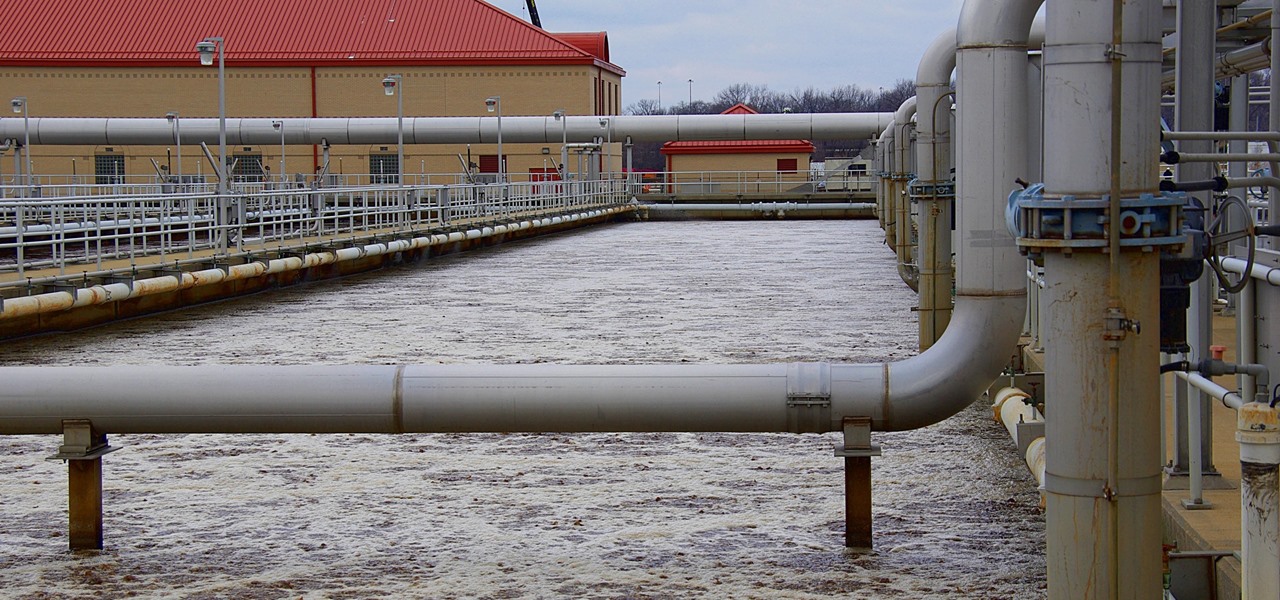
Everything from disposed of drugs to hormones and disease-causing bacteria — anything that is rinsed or flushed down the drain — can contaminate wastewater.

We've worked hard to reduce the flow of toxic chemicals into our waterways, which means no more DDT and other bad actors to pollute or destroy wildlife and our health. But one observation has been plaguing scientists for decades: Why are large quantities of one toxic chemical still found in the world's oceans?

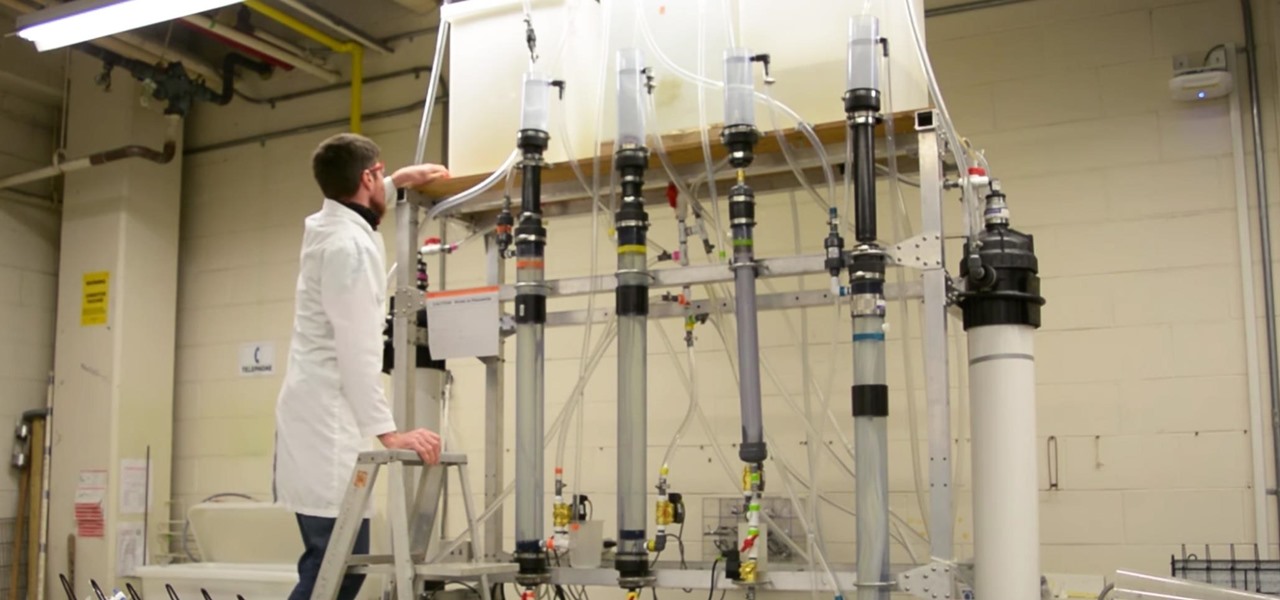
Water makes up about 60% of your body weight. Whether you like it plain, flavored, bubbly, or in beverages or food, we all need water daily to avoid dehydration and stay healthy. For communities in need of clean drinking water, new research using bacteria may offer a simplified, lower-cost method for boosting potable water supplies.

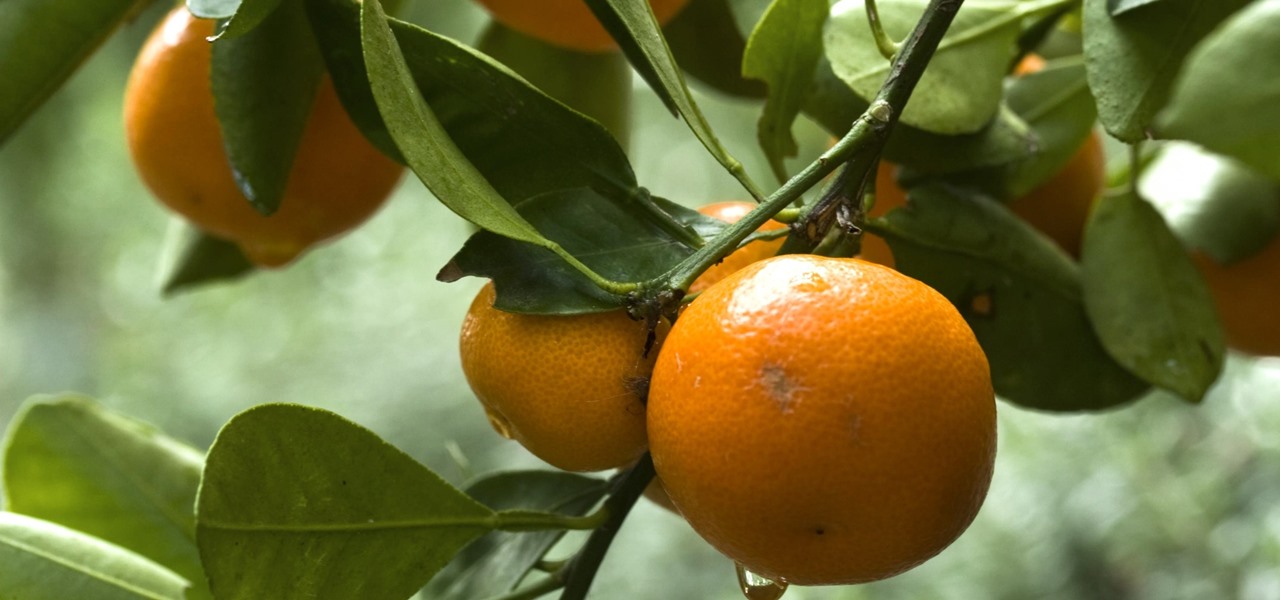
A disease called "citrus greening" has devastated and permanently altered citrus production in the United States, but a vaccine that could protect orange trees may be part of a winning strategy to beat the bacteria that is killing the trees.

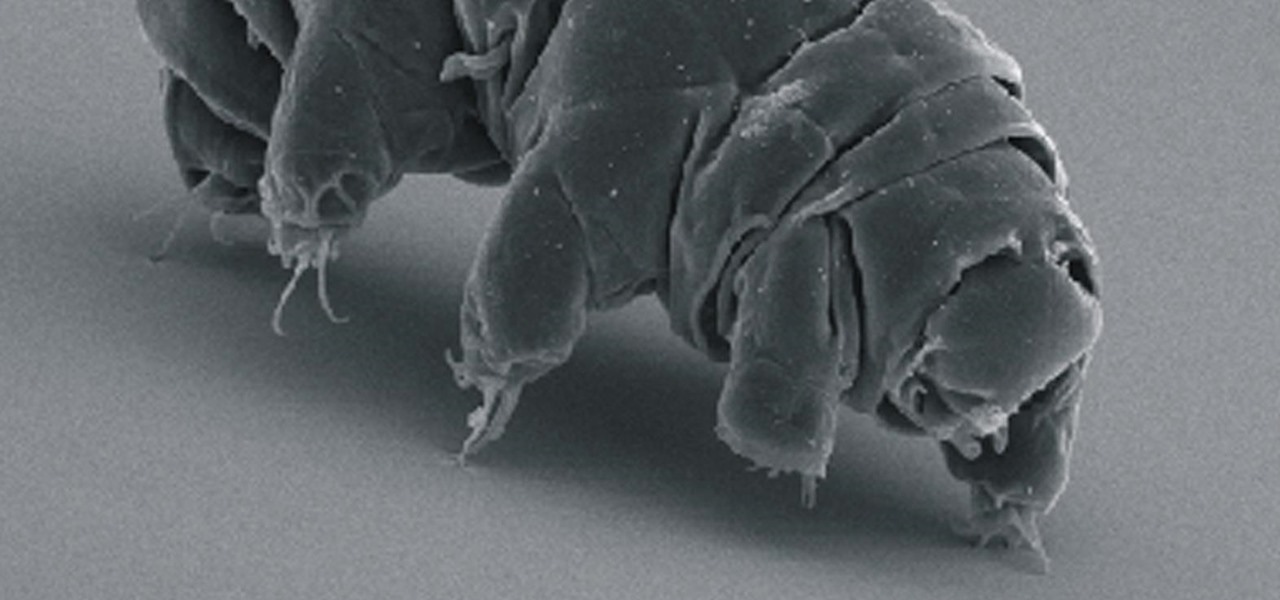
Call them what you will—moss piglets, water bears, or by their real name, tardigrade—but these intriguing tiny creatures can come back from the brink of death. They can survive boiling, deep freezing, UV radiation, completely drying out, and even a trip to space—without the benefit of being in a spacecraft.

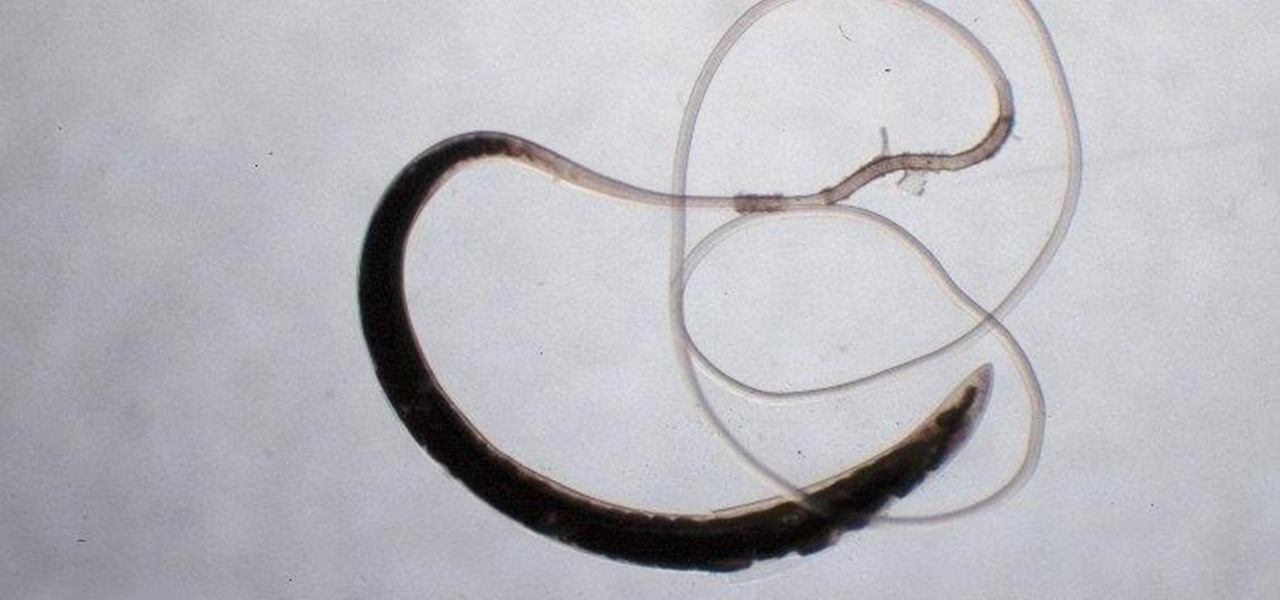
Somewhere around 600–800 million people in the world are infected with whipworm (Trichuris trichiura), an infection they got from ingesting soil or water contaminated with feces of infected animals or people containing the parasite's eggs.

Ecosystem changes caused by agricultural choices in Brazil are creating a dangerous microbe mix in exploding populations of vampire bats and feral pigs.

Seagrass may help your favorite beach stay a little less toxic. A new study, led by Joleah Lamb, a postdoctoral researcher in the Harvell Lab at Cornell University, found that coastal seagrasses reduce levels of pathogens dangerous to humans and marine organisms in near-shore waters.

Responding to the emergence of Zika in the US, researchers investigated what type of repellent works best to reduce your odds of a mosquito bite from Aedes aegypti, the mosquito species that spreads the Zika virus.

If you want to appreciate the value of microbes, look no further than a chunk of cheese. Because cheese roughly traces back to the Neolithic Era, we might say the earliest cheesemakers were the first humans to manipulate microbes—without even knowing it. Now, thanks to microbiologists and the long tradition of cheesemaking, we know a lot more about the microbes that make our favorite types of cheese possible.

Scientists are constantly on the search for new organisms, species, and other types of life. A special group of these researchers, calling themselves "bioprospectors," dive deep into mines to find unique lifeforms with special properties not found anywhere else.

Although their effectiveness is waning, antibiotics remain a front-line defense against many infections. However, new science reveals using the wrong antibiotic for an infection could makes things much worse.

Lighthouses and signal fires may have been the first social media. Without the ability to share language, a distant light meant "humans here." A new study from the University of California, San Diego, finds that bacteria can also send out a universal sign to attract the attention of their own, and other bacterial species.

Using extreme time-lapse microscopy, scientists watched a virus take over a bacteria to create a cell that looked and functioned more like a plant or animal cell. True story.

Cholera may be rare in the US, but cases of the disease have increased worldwide since 2005, particularly in Africa, southeast Asia, and Haiti. An estimated 3 to 5 million people are infected, and more than 100,000 die from the disease globally each year, mostly from dehydration.

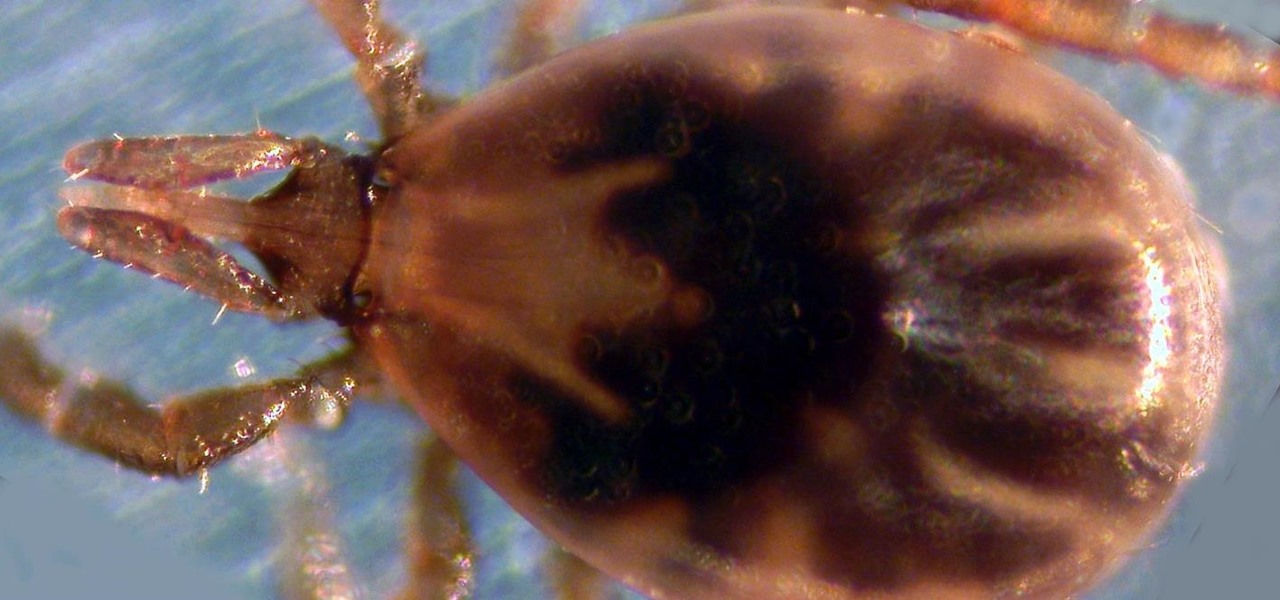
Transmitted by ticks, Lyme disease is a serious infection that is probably headed your way. A recent study confirms the pathogen that causes Lyme disease is now established in nine national parks in the East, including Acadia and Shenandoah National Parks.

What do Leo Tolstoy (writer), Beethoven (composer), Paul Gaugin (artist), and Adolf Hitler (politician) have in common? They are all considered to have suffered from the sexually transmitted disease syphilis.

The future of forests looks dreary in the face of a warming climate, but scientists are exploring the relationship between soil microbes and the ability of trees to move to higher altitudes, a key component of their survival.

It won't come as a surprise to hear that your cell phone, tablet, and laptop are loaded with bacteria and other organic material. While most of these bacteria are harmless, there are good reasons to reduce the capability of your mobile devices to infect you—or other people.

Jostled in the airport, someone is coughing in line. The air looks empty but it is loaded with microbes that make their way into your body. You get sick. You give it to your family, and that's pretty much it. But what if you were so contagious that you spread it to your entire community and beyond?

Exposed to hormones, pharmaceuticals, and other chemicals, the beautiful wild fish in Canada's Grand River have taken on some pretty odd characteristics—they're turning into females. A long-term study suggests using bacteria to manage polluted water could turn the tide for feminized fish.

Whenever I went to the grocery store on a mission for blueberries, I'd inevitably find myself staring at these weird little tomato-looking berries... and wondering what the hell they really were. Tomatoes? Berries? A weird science experiment? Then, I'd set a pint of blueberries in my cart and carry on, forgetting about them for the time being.

Smartphones have been a hot button issue around school campuses for several years now—some schools allow them, others confiscate them on sight. But the fact of the matter is, when used correctly, a smartphone can be just as much of a learning tool as a textbook or school-issued laptop.

Does TikTok scare you? Trust me, I get it. It's a strange, unfamiliar place to those of us not accustomed to its ways, populated by teenagers and college students with their own subcultures, memes, and humor. But here's the thing: TikTok has something for everyone, you included.

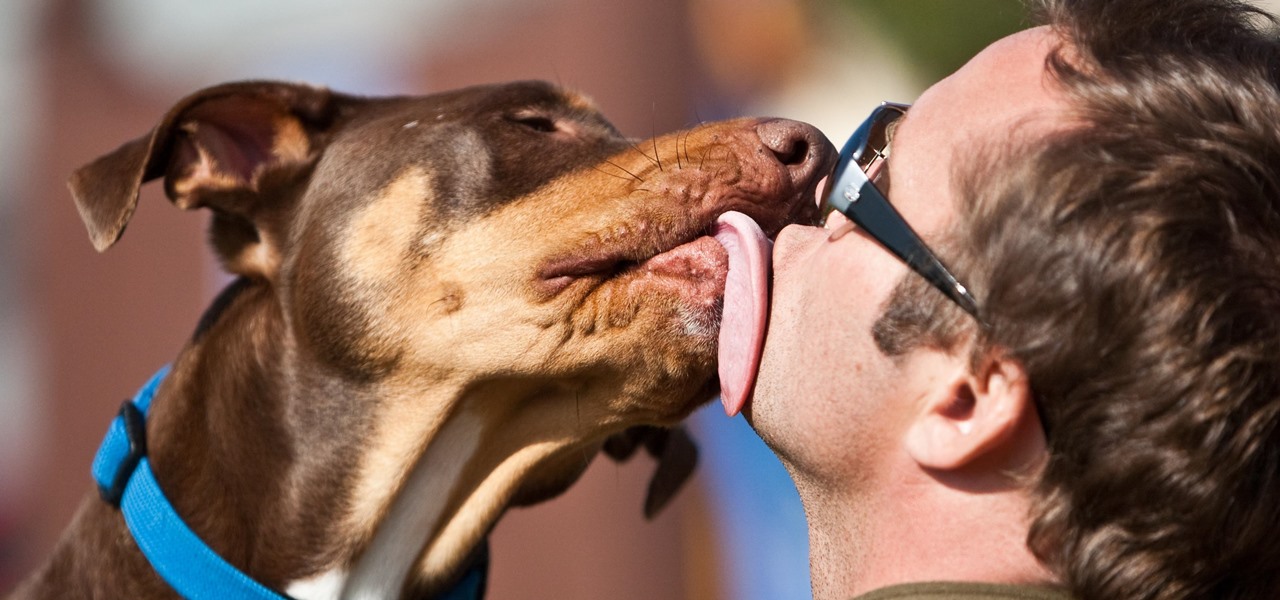
If you live with pets, you know where their tongue has been, yet you let them kiss and lick you all they want without even thinking twice about it. I've heard people say that a dog's mouth is very clean, and that their saliva, delivered by licking, can help heal wounds, but is that really true?

All fields of study have their own language. For people interested in learning about microbes, the language can sometimes be downright difficult — but it doesn't need to be. From antibiotics to xerophiles, we have you covered in an easy-to-understand glossary.

Lidar, a technology first used by meteorologists and aerospace engineers and then adopted in self-driving vehicles, has slowly crept into consumer electronics over the last five years. If you have a Pro model iPhone or iPad, there's a good chance it has a lidar sensor, and you're likely using it whether you know it or not.