
How To: Get your body bikini ready
Learn how to get your body bikini ready. Try these proven methods to get an awesome bathing suit bod.


Learn how to get your body bikini ready. Try these proven methods to get an awesome bathing suit bod.

Facebook recently hit a snag in its quest to take augmented reality face effects to its millions of users.
Smartphones are like high tech buckets that collect our personal information through constant use. This has some obvious benefits, like getting a more personalized experience with our devices. On the other hand, this data is a tempting target for bad actors looking to make a buck at the expense of your privacy.

If you're like me, then you're rarely just watching TV. You're probably also simultaneously following reactions on Twitter during a live airing of The Walking Dead. Or perhaps you're checking your fantasy football scores while a real game is in progress. Or you might just have the TV on in the background while you're writing an article about a new augmented reality app.

An older man dies of Zika. A younger man who cares for him catches Zika — but doctors cannot pinpoint how the disease was transmitted. While proximity to the patient is sufficient explanation for the rest of us, for microbe hunters, it is a medical mystery. Why? Zika is not known to transmit from person-to-person casually.
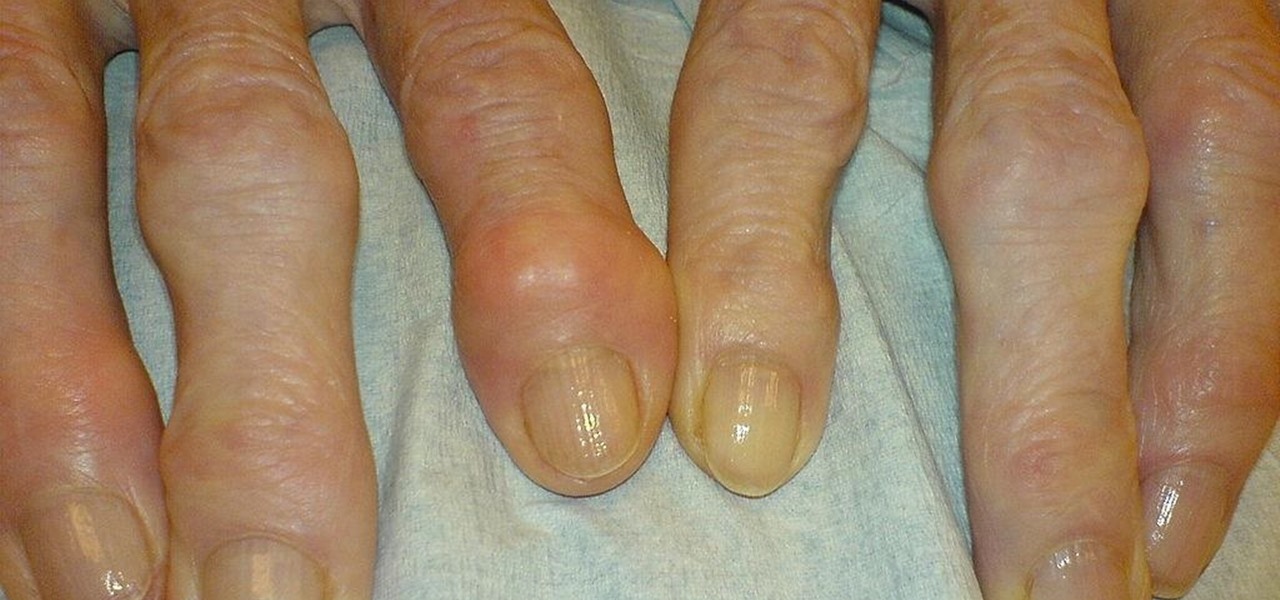
As if the swollen, painful joints of rheumatoid arthritis weren't enough, the disease is the result of our immune system turning against cells of our own body. Ever since this realization, scientists have worked to find the trigger that sets the immune system off. Scientists believe that gut bacteria may have a role in initiating the abnormal immune response. Now, a team of researchers from Boston has figured out how that might occur.
Once we recover from the respiratory infection pneumonia, our lungs are better equipped to deal with the next infection — thanks to some special cells that take up residence there.
Cancer cells do a pretty good job of flying under the radar of our immune system. They don't raise the alarm bells signaling they are a foreign invader the way viruses do. That might be something scientists can change, though.
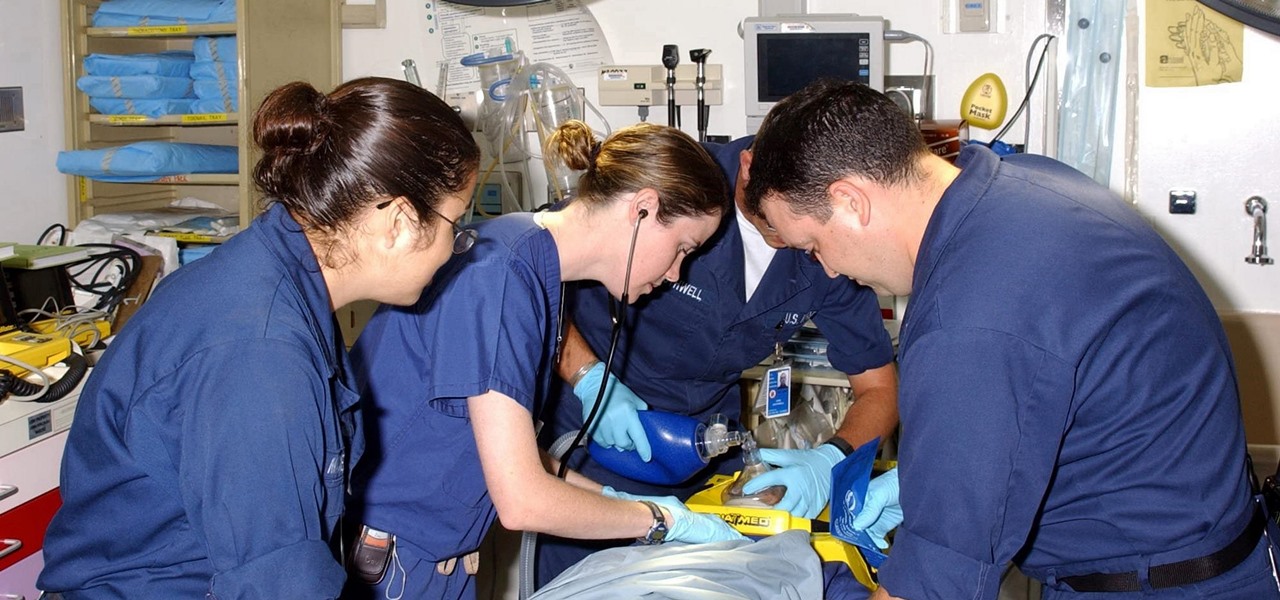
With a death rate of one in five, sepsis is a fast-moving medical nightmare. New testing methods might improve your odds of survival if this infection ever hits you.

Colorectal cancer — cancer of the colon or rectum — is the third most commonly diagnosed cancer in the US. To reduce the chances of a diagnosis we are all urged to stop smoking, keep our weight down, decrease our intake of alcohol and red meat, keep active, and get screened for colon cancer. But, new research has found something that participates in the development of colorectal cancer that might not be as easy to control: A strep bacteria that promotes tumor growth.

Despite longer live spans, almost half a million people die of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) each year, many of them preventable.
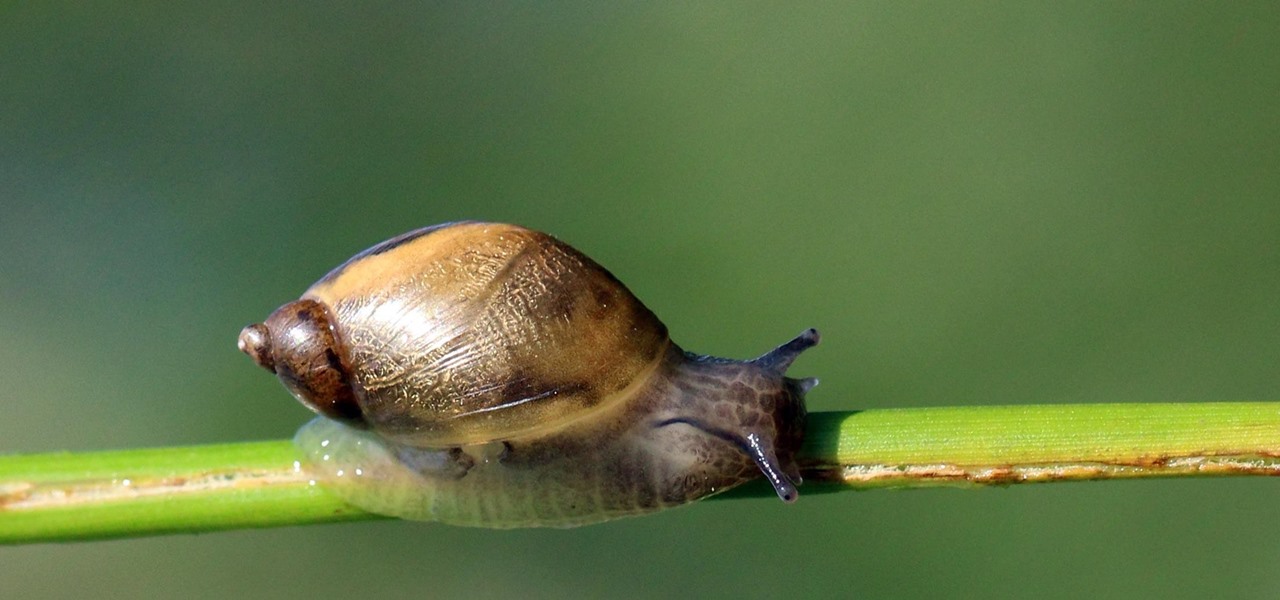

Deadly rat lungworm parasites have found their way into Florida. The parasitic worm relies on snails and rats to complete its life cycle, but don't let this nematode's name fool you. This worm can cause meningitis and death in humans who inadvertently consume snails, frogs, or crustaceans harboring the infective parasite.

Bone loss and belly fat may no longer be certain fates of menopause, thanks to new research from an international team of scientists.
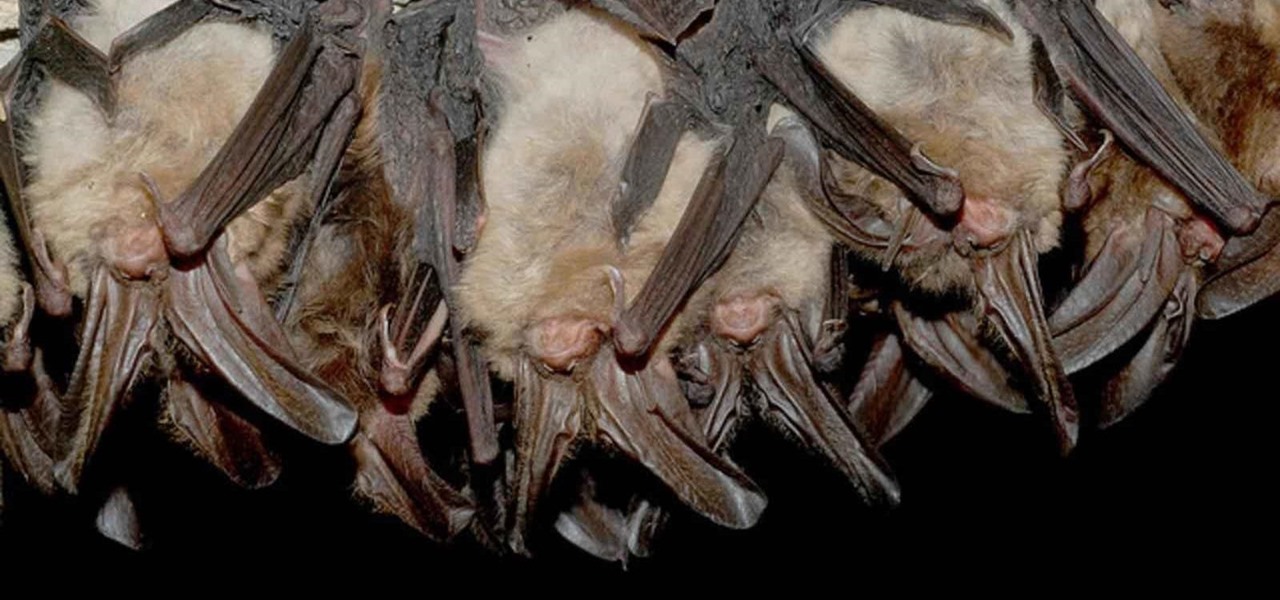
Tell the truth. The bat picture creeps you out. You are not alone. But in reality, bats truly are some of our best friends. They gobble thousands of disease-spreading bugs a night. But they also carry viruses that can be deadly to humans. So, bats — friend or foe?
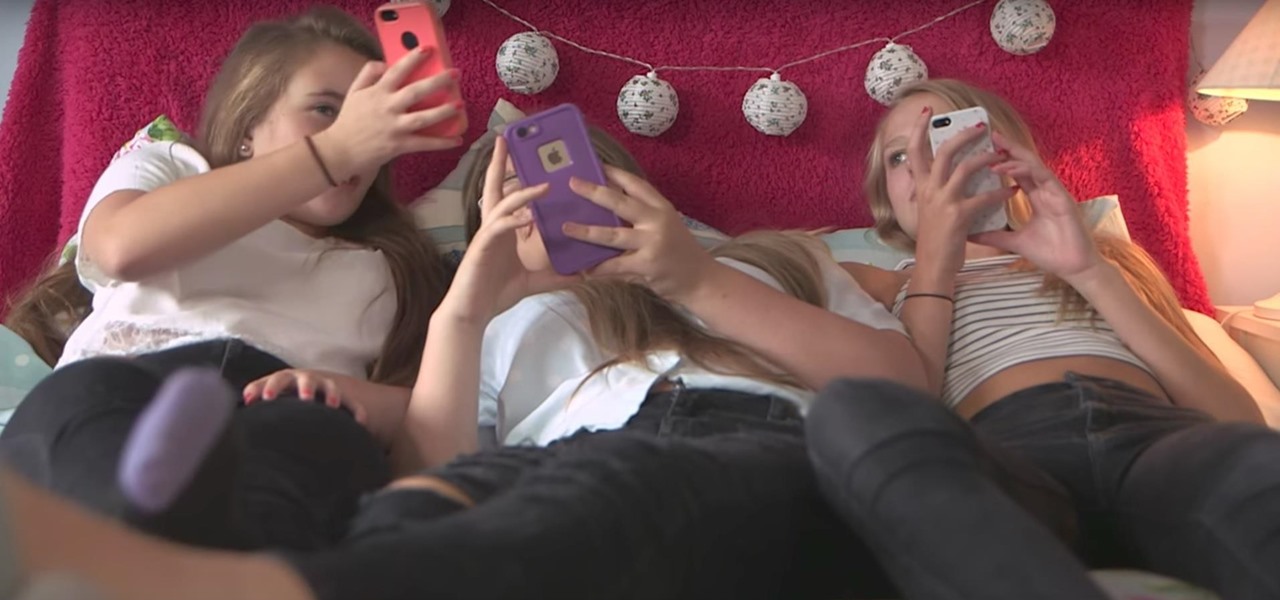

While restaurants and classrooms have enacted policies banning cell phones, one father has had enough of his kids' obsessive phone habits. Dr. Tim Farnum is now seeking to ban the sale of smartphones to children under 13.
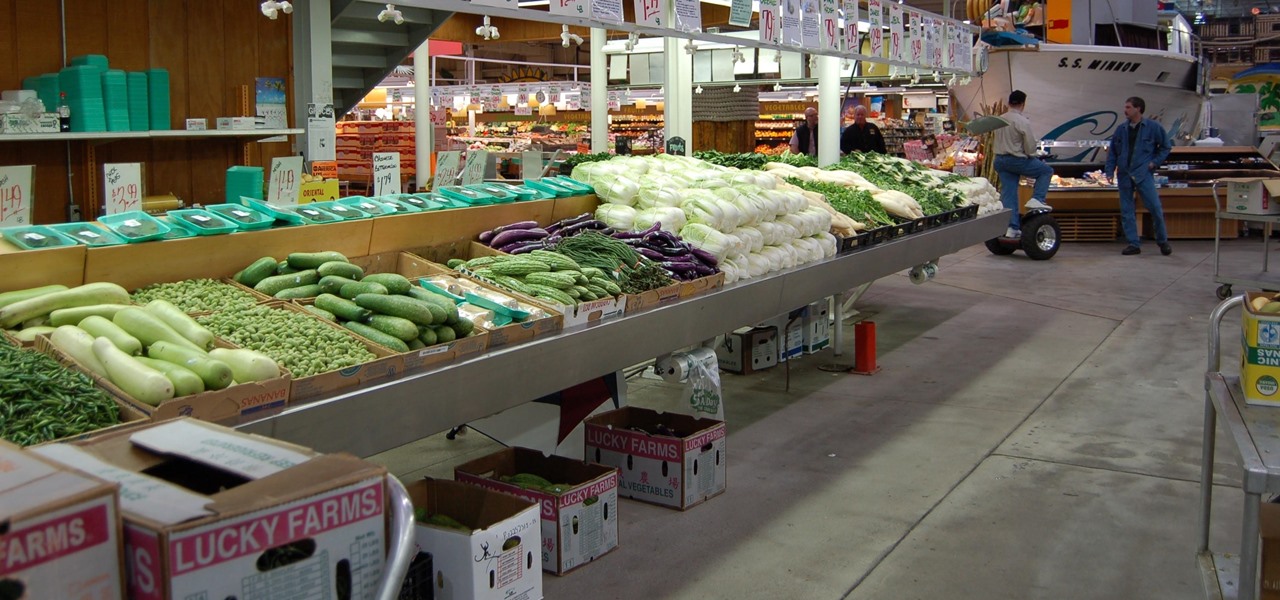

We know that healthcare-related facilities can be fertile ground for antibiotic-resistant bacteria, but recent research suggests your produce aisle might be too.
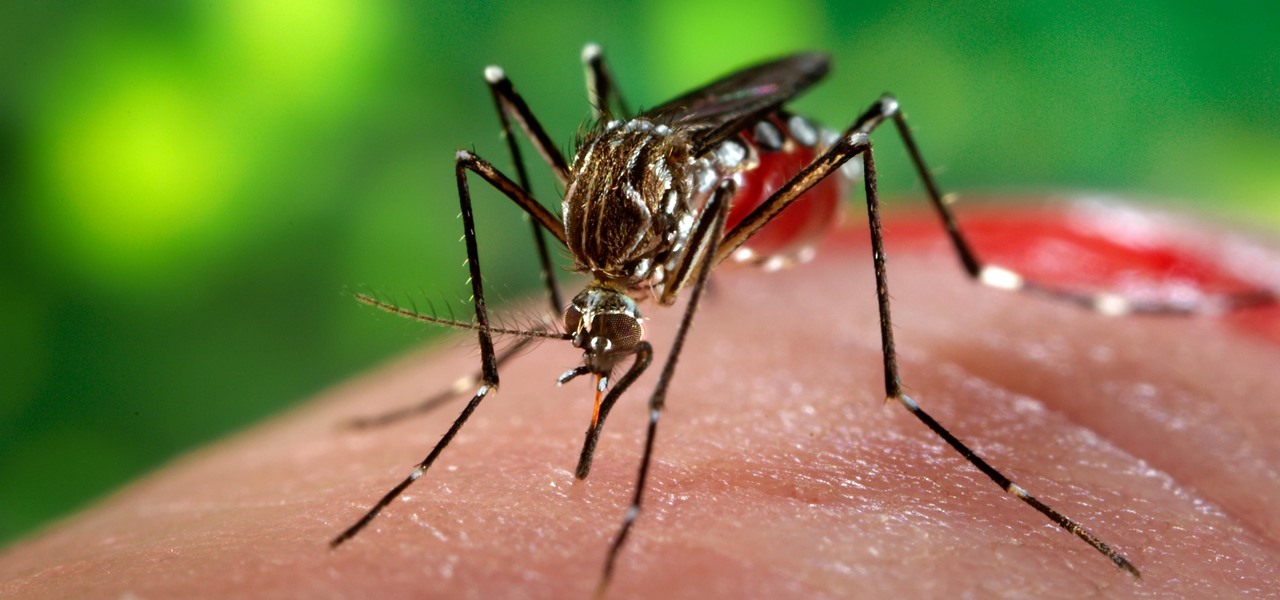

Mosquitoes are a big problem, and citronella candles are not the solution. There are a lot of mosquito species. The American Mosquito Control Association reports there are more than 3000 mosquito species in the world, and about 200 of those occur in the US. The most common are the Aedes, Anopheles, and Culex species. These are also the three mosquito species most likely to transmit serious illness, and all of them live in the US.
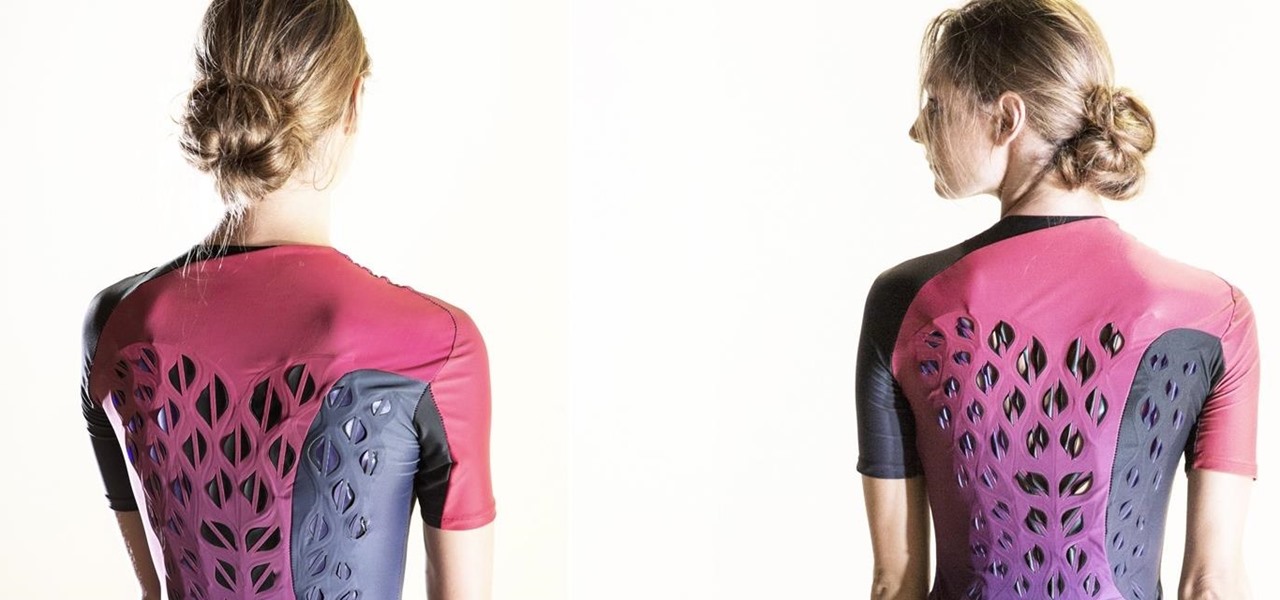

Microbial cells can improve the functionality of clothes in creative and useful ways, including cooling us down during a workout or making clothing glow for better visibility.
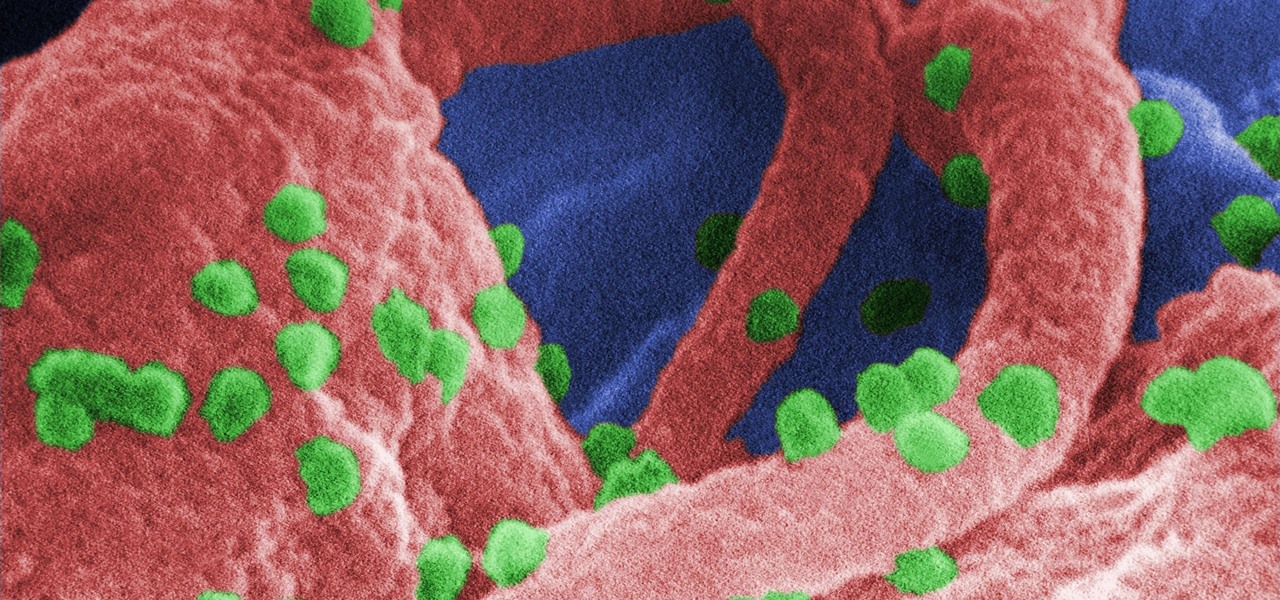
The problem with HIV is that it attacks and kills the very cells of the immune system that are supposed to protect us from infections — white blood cells. But a new technique, developed by scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) in La Jolla, California, offers a distinct HIV-killing advantage.
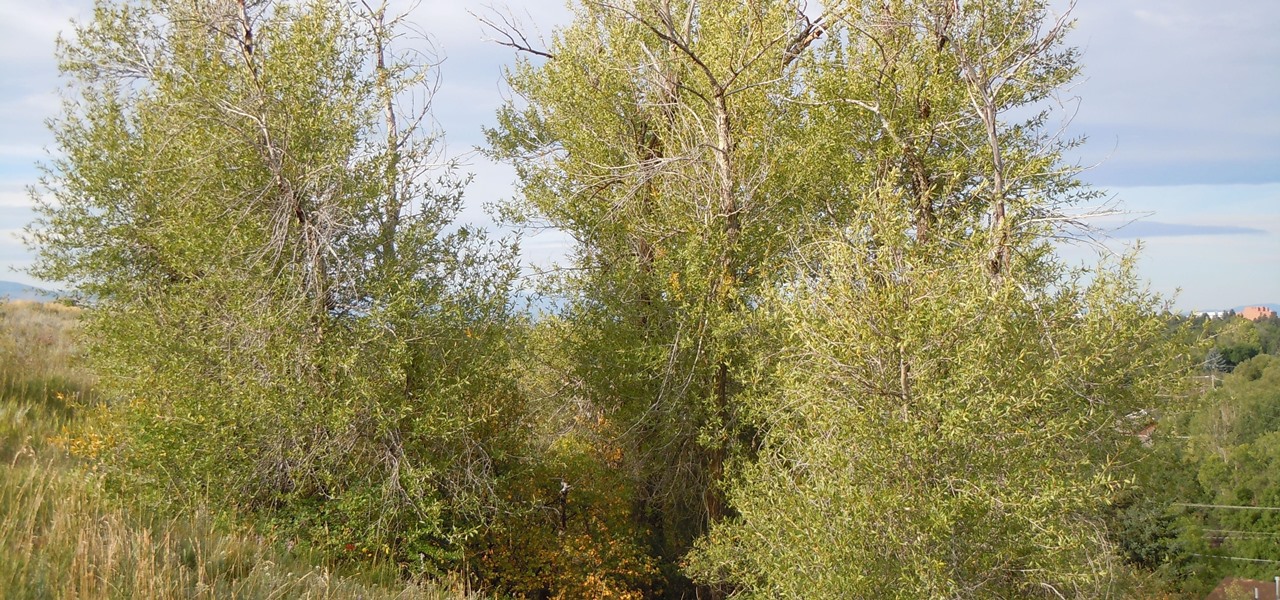

The future of forests looks dreary in the face of a warming climate, but scientists are exploring the relationship between soil microbes and the ability of trees to move to higher altitudes, a key component of their survival.
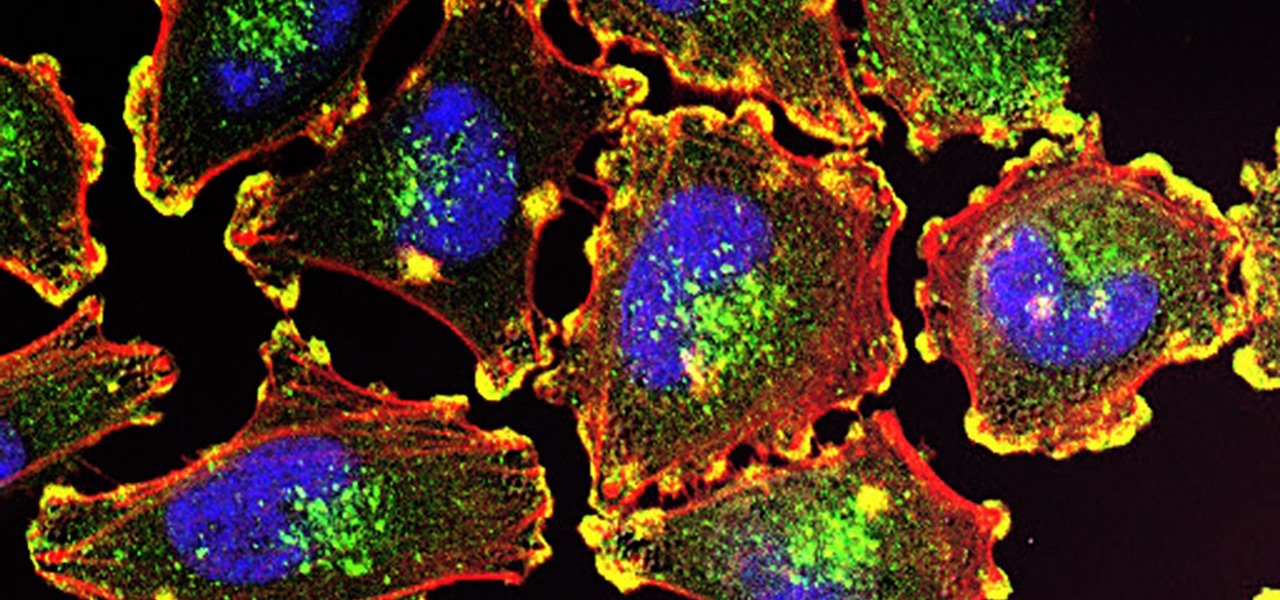
Activating the body's own immune system to fight cancer is the goal of immunotherapy. It's less toxic than chemotherapy and works with our body's natural defenses. The trouble is, it doesn't work for most patients — only about 40% of cancer patients get a good response from immunotherapy. But coupling it with another type of cancer therapy just might deliver the punch that's needed to knock out cancer.
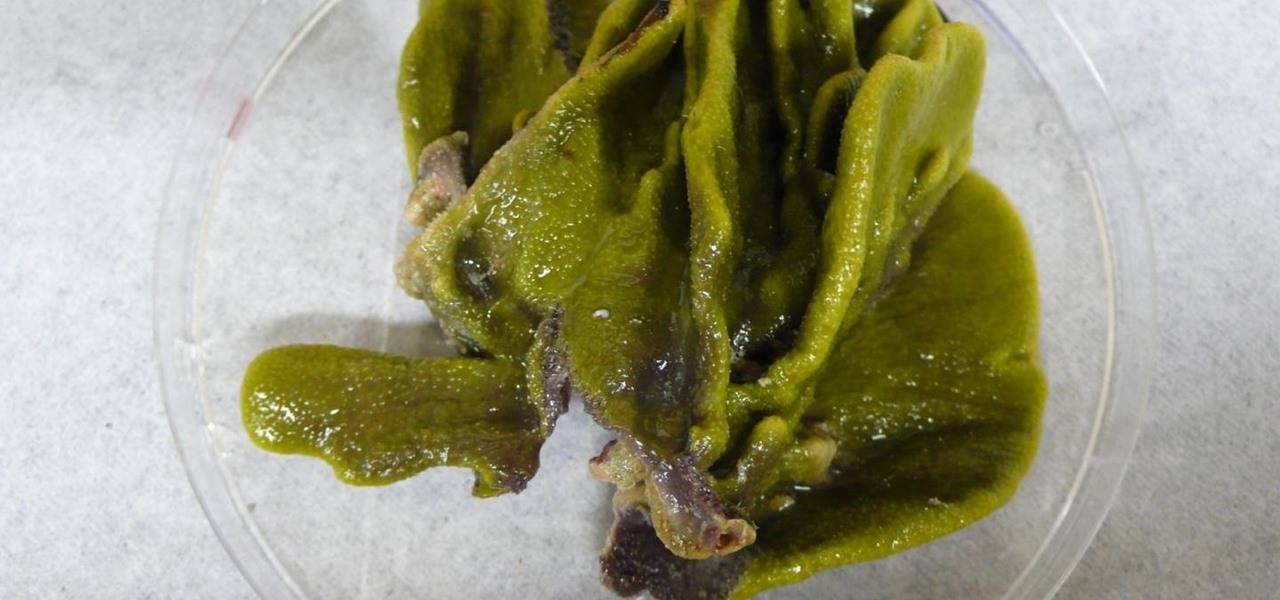

We've worked hard to reduce the flow of toxic chemicals into our waterways, which means no more DDT and other bad actors to pollute or destroy wildlife and our health. But one observation has been plaguing scientists for decades: Why are large quantities of one toxic chemical still found in the world's oceans?
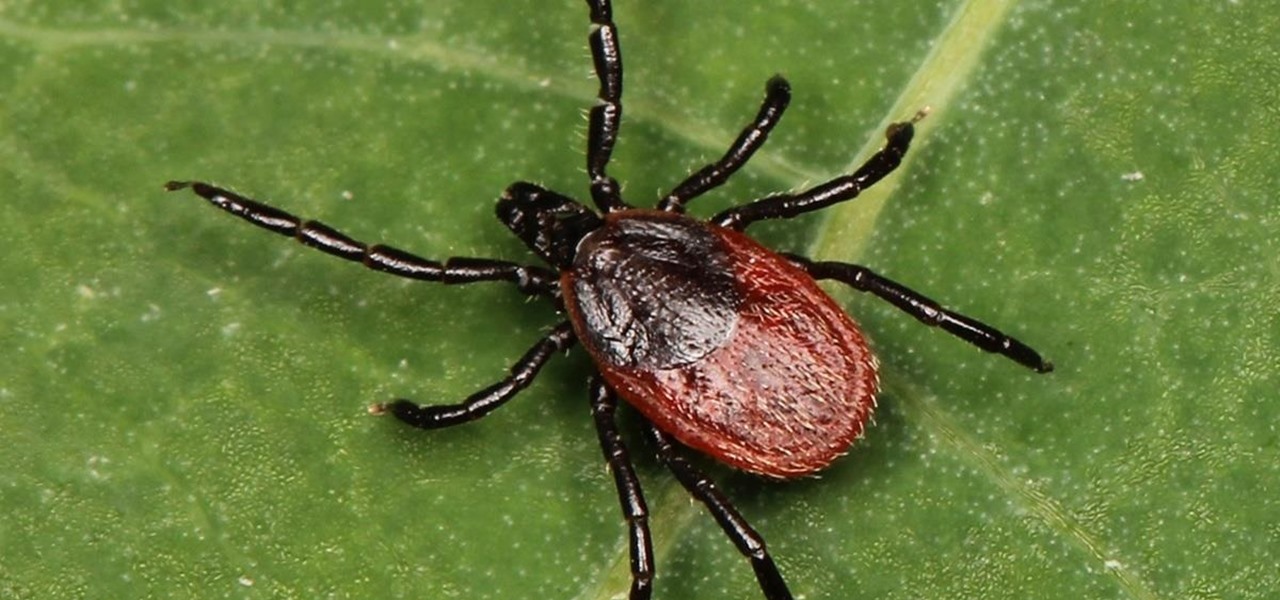

Lyme is a growing threat as we move into warmer weather in the US. Researchers have said this year could be one of the worst for this tick-borne disease, as a skyrocketing mouse population and warmer temperatures increase the risk.

We fight cancer in a variety of ways, but no matter whether drugs, biologics, or our immune cells are part of the battle, they can do a better job fighting back cancer if we can help them find the tumors.
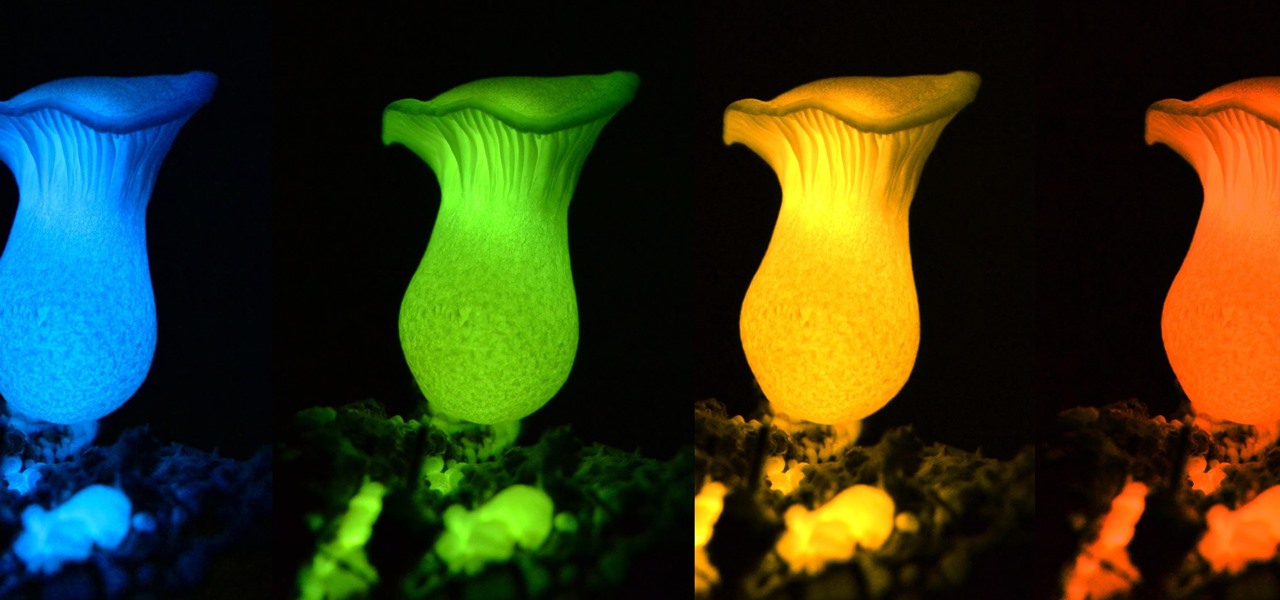
Bioluminescence — the ability of an organism to produce and emit light — is nature's light show. Plants, insects, fish, and bacteria do it, and scientists understand how. Until now, though, we didn't know how fungi glow.
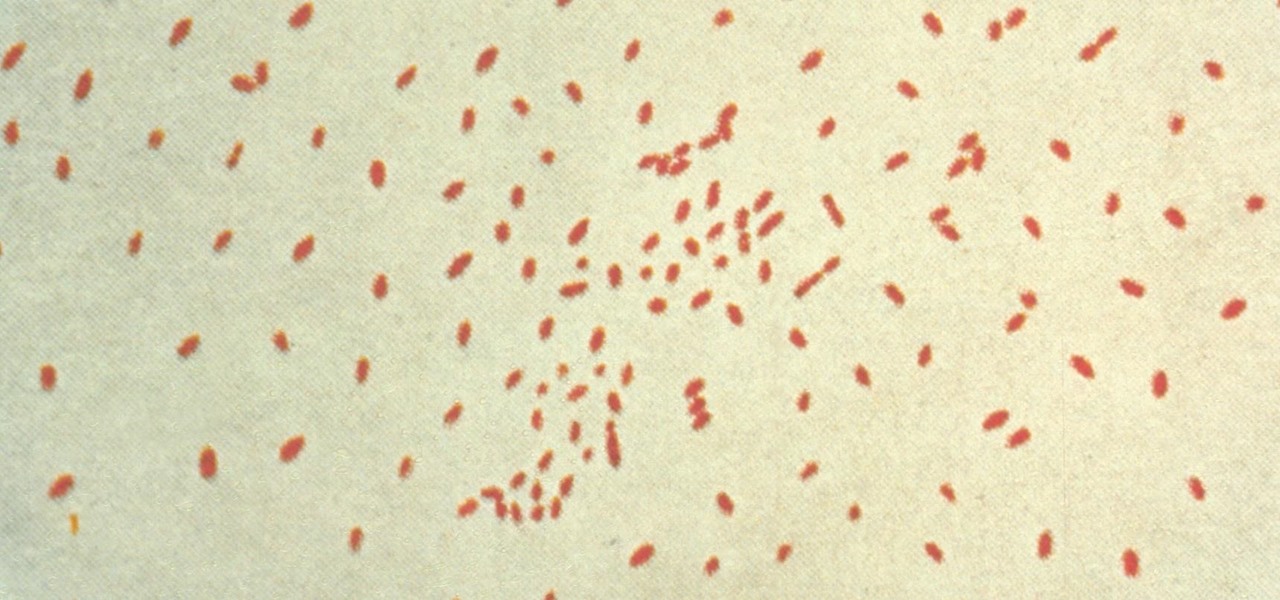
Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a highly contagious disease that can be life-threatening for young children. New research backs a recommendation that all pregnant women receive a pertussis booster with each pregnancy, as it can help their infants fight off the infection.
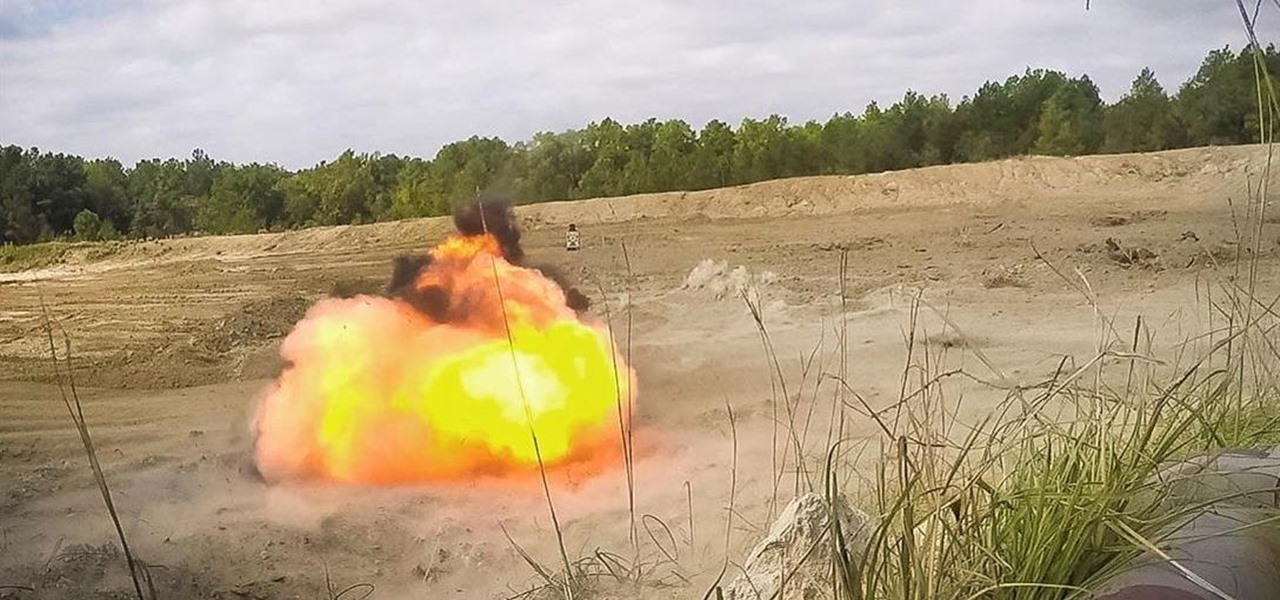

Devastating and deadly, land mines are a persistent threat in many areas of the world. Funding to clear regions of land mines has been decreasing, but new research may offer a less dangerous method of locating hidden, underground explosives by using glowing bacteria.
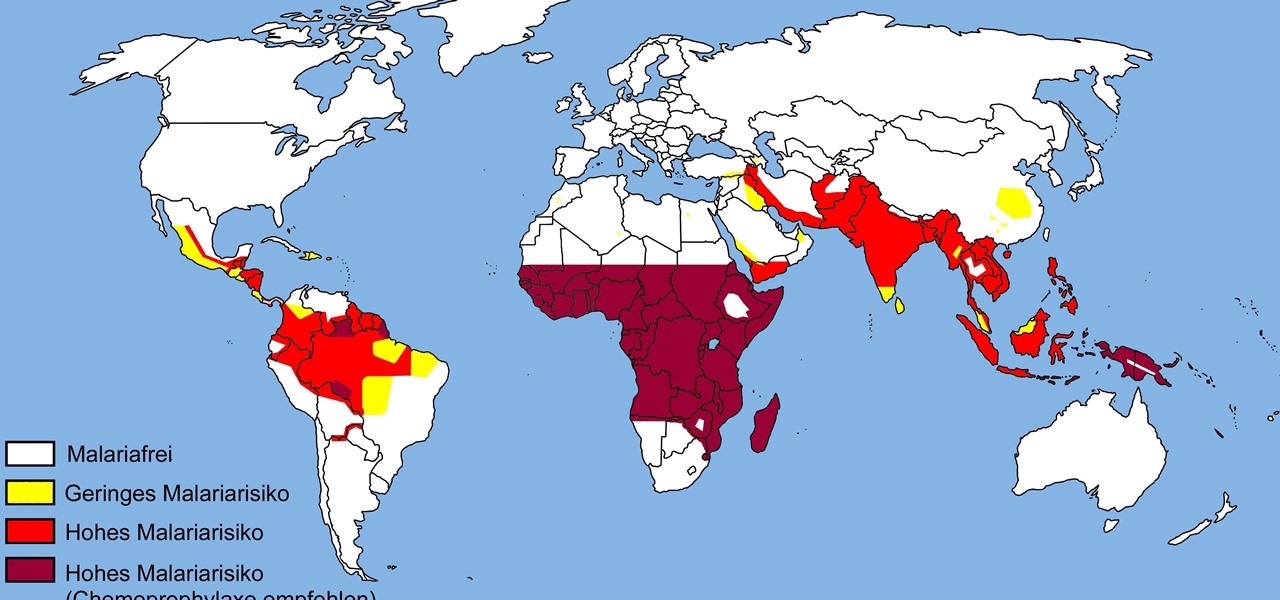
The theme for 2017's World Malaria Day, which is today, April 25, is "End Malaria for Good." For many Americans, this might seem like an odd plea. Especially since Malaria is seemingly an obsolete problem here. However, on World Malaria Day, it's important to remember the danger of malaria is still very much present in the US. And around the world, the disease is at the epicenter of a global crisis.
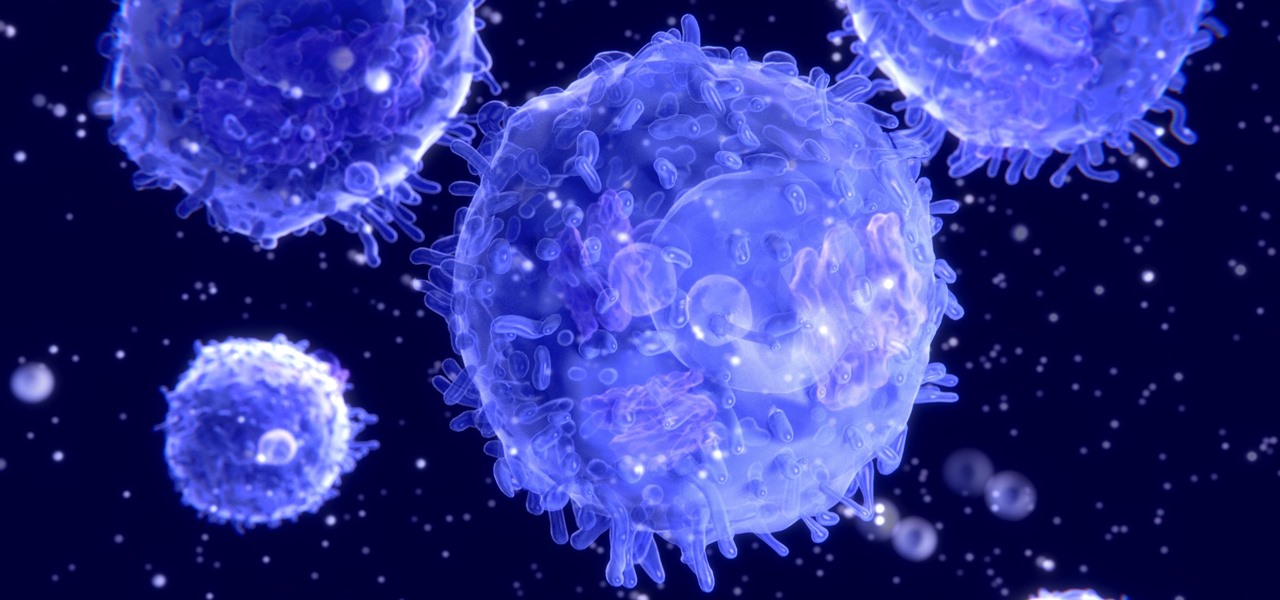
HIV-infected people who are treated long-term with antiviral drugs may have no detectable virus in their body, but scientists know there are pools of the virus hiding there, awaiting the chance to emerge and wreak havoc again. Since scientists discovered these latent pools, they have been trying to figure out if the remaining HIV is the cause of or caused by increased activation of the immune system.

Our quest to find new antibiotics has taken a turn — a turn down the road, that is. A team of scientists from the University of Oklahoma is scooping up roadkill and searching for bacteria on them that might yield the world's next antibiotic.
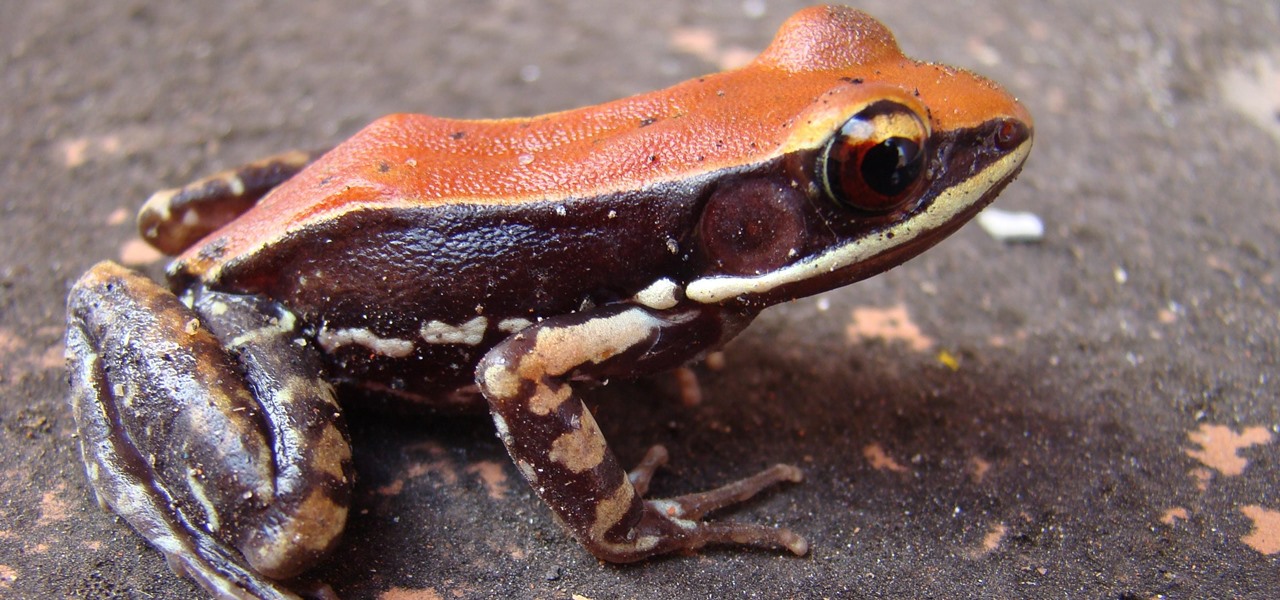

Our quest to find novel compounds in nature that we can use against human diseases —a process called bioprospecting — has led a research team to a small frog found in India. From the skin slime of the colorful Hydrophylax bahuvistara, researchers reported finding a peptide — a small piece of protein — that can destroy many strains of human flu and can even protect mice against the flu.

When it comes to global warming, most of us think of carbon dioxide emissions. While carbon dioxide is the most important greenhouse gas, carbon dioxide emissions have stayed constant for the last three years. On the other hand, methane, the second most important gas, has been steadily rising since 2007.
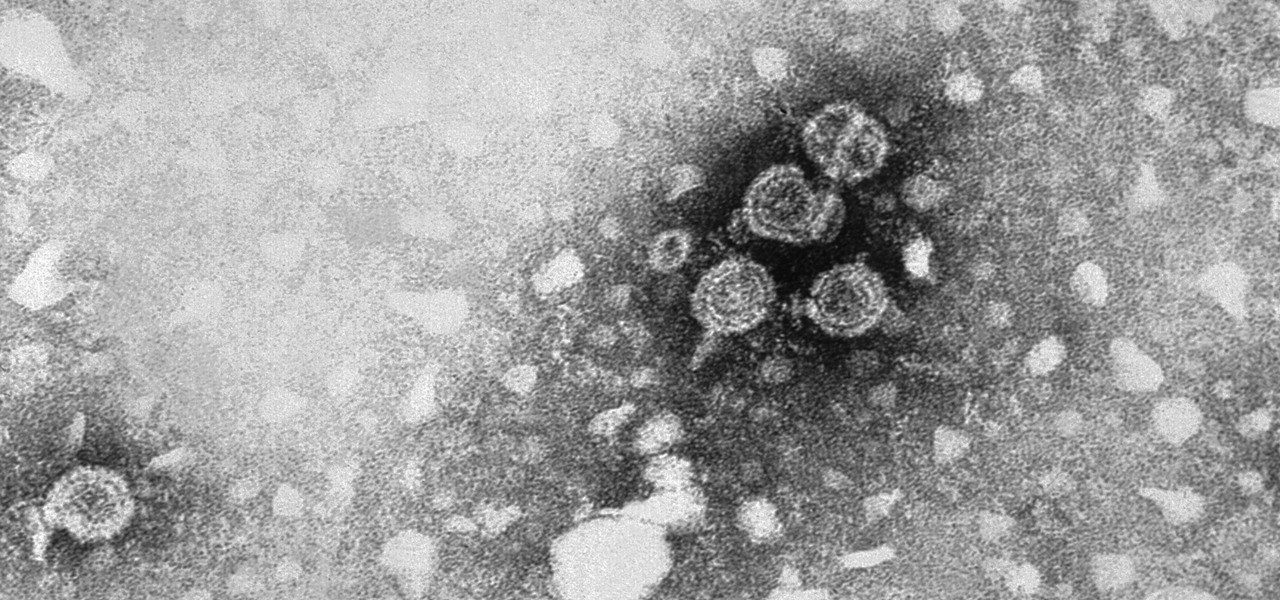
Two viral liver diseases could help us find the path toward the cause of Parkinson's disease. Researchers from the University of Oxford and UCL Institute of Neurology in London have reported an association between hepatitis B and C infections and an increased risk of Parkinson's disease. Their findings were published early online in the journal Neurology.
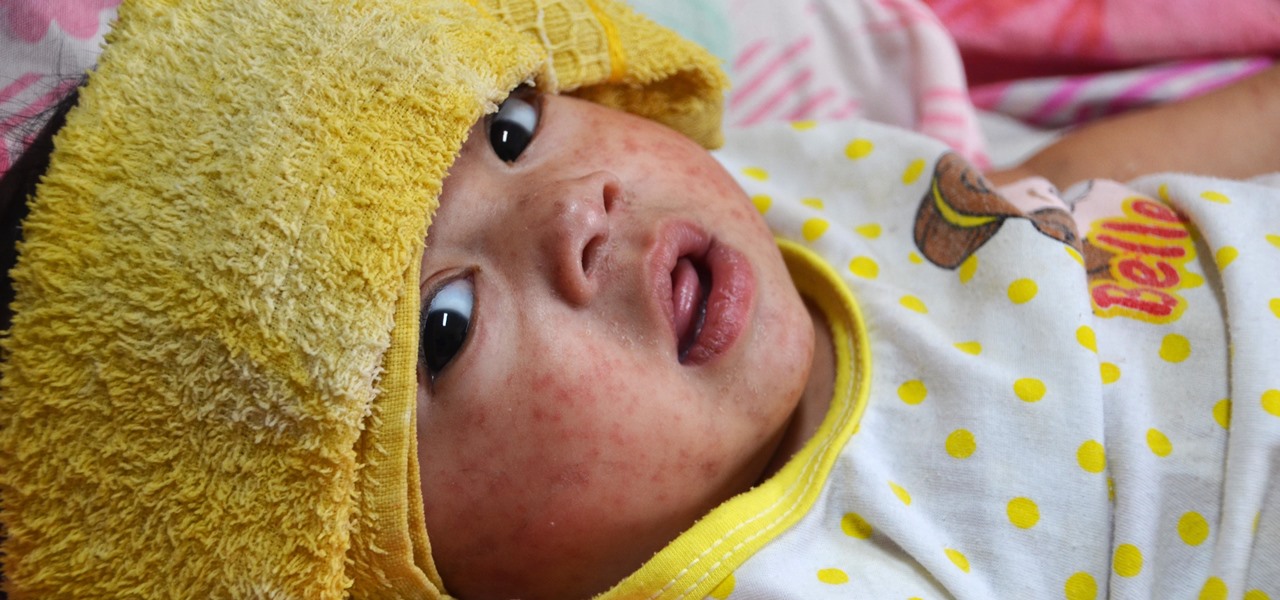
Nineteen days ago, several hundred people could have been exposed by a traveler with measles in Nova Scotia, Canada. The next day, someone flying from Minnesota to Nebraska may have spread the measles to other passengers. A couple weeks ago, it's possible that a man and his six-month old child spread the measles in several Seattle-based locations. Authorities are trying to locate persons who may have been in contact with these people. None of the persons with measles were vaccinated. Why?

For regions that experienced a boom in mouse populations last year, scientists say 2017 could see a surge in cases of Lyme disease.

Marijuana is legal to use for medical purposes in 28 states and the District of Columbia, but the quick development of this new industry could have left some regulation issues in the lurch.

Ecosystem changes caused by agricultural choices in Brazil are creating a dangerous microbe mix in exploding populations of vampire bats and feral pigs.
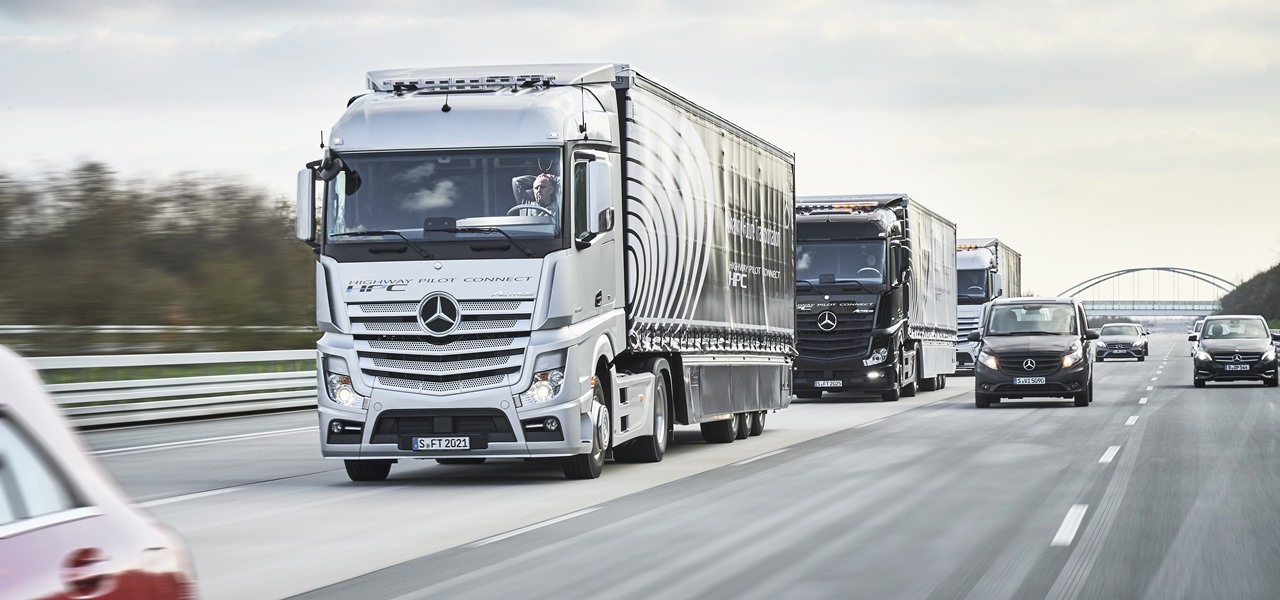

Japan is in the process of curbing its aging population and mature workforce. According to The Diplomat, the country's population has been declining at a steady rate. To meet future productivity demands in commercial and industrial sectors, local officials are turning to self-driving technology, including truck platooning, where three or five vehicles travel autonomously in a string formation. This practice, according to a study by MIT, can reduce fuel consumption by up to 20% (more about thi...
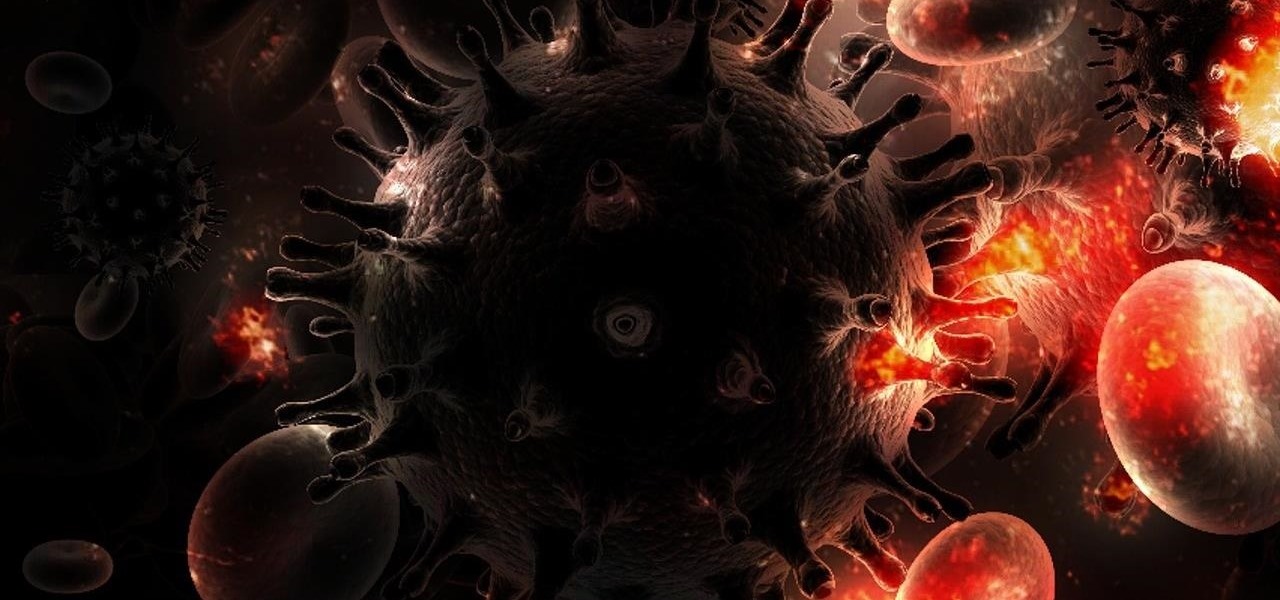
Over 1.2 million people in the US are infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)—and one out of eight of them don't know it. Even after decades of intense research into the virus, there's still no cure for it. One of the big problems is that the virus hides out in certain cells of the body, resisting treatments that kill it.

After California college student Luis Ortiz blacked out and was taken to the hospital in 2015, doctors were startled to discover the reason his brain was swelling—a one-centimeter long, wriggling tapeworm living within a ventricle in the middle of his brain.