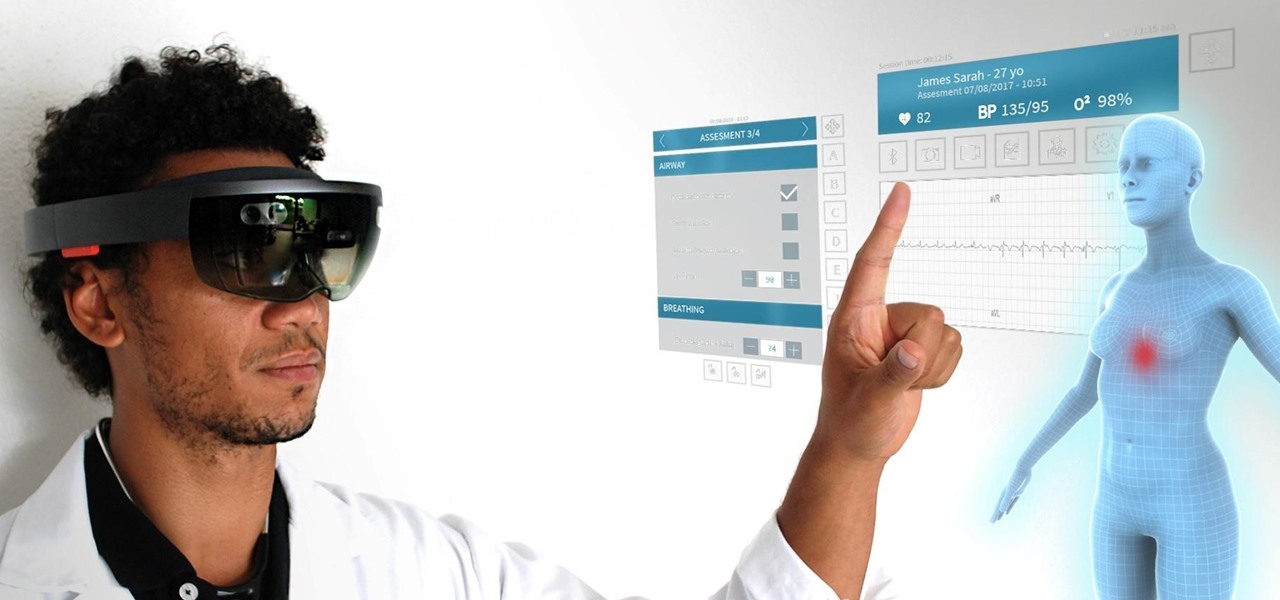
A new telemedicine application for the Microsoft HoloLens is promising paramedics and EMTs a new tool for diagnosis and treatment of patients in the field.

Aura, a highly rated app for mindfulness and mental health, just became available on Android and is currently on sale.
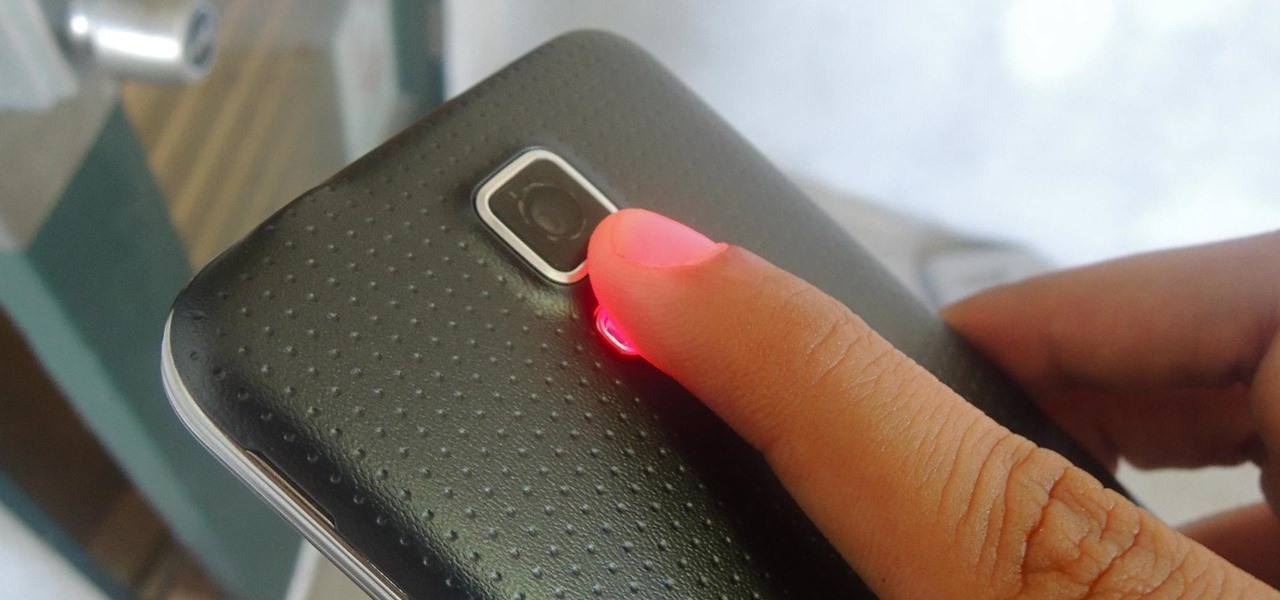

While it can't do anything to alleviate stress, a recent update to S Health will let you monitor your stress levels using nothing but your Samsung Galaxy S5. If you're feeling stressed, just place your fingertip on the heart-rate sensor and S Health will tell you roughly how stressed out you are (or aren't).
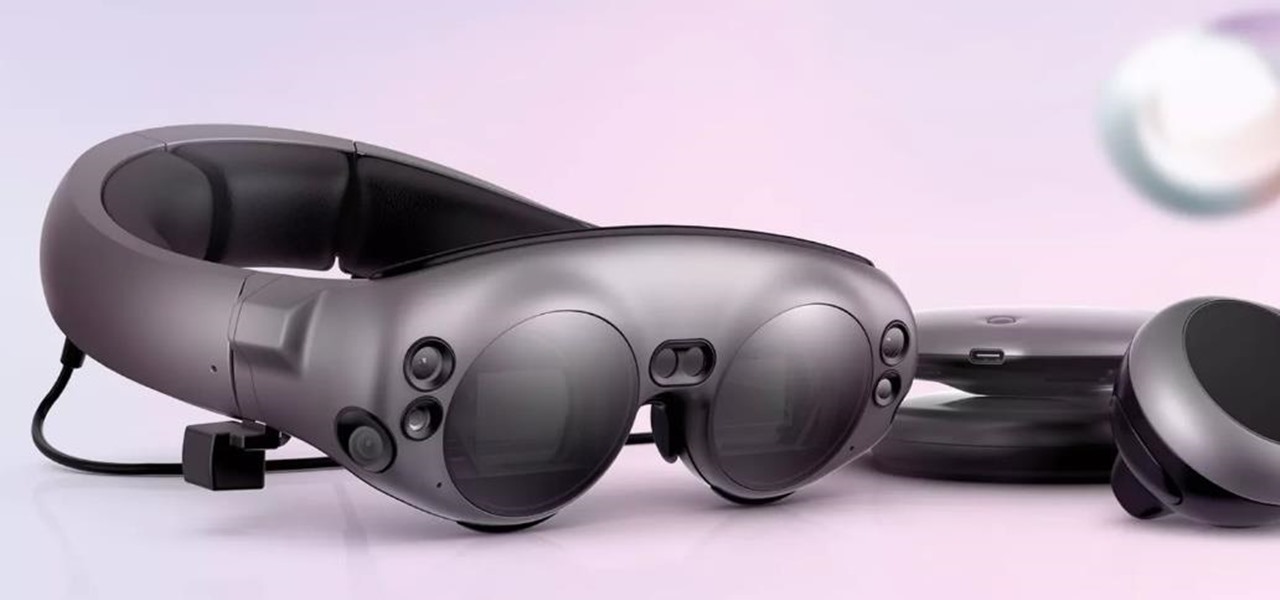

While many of the latest content partnerships announced by Magic Leap appear to lean towards entertainment and gaming, a new partnership with medical technology provider Brainlab has Magic Leap getting down to more serious business.

Autism affects 1 in 68 children in the US, and that means it affects at least 1 in every 68 families. More boys than girls are diagnosed as being on the autism spectrum, and it's estimated that almost 60,000 12-year-olds in the US have autism. That is a 37-fold increase from the 1 in 2,500 children diagnosed just 30 years ago.

We live in world where it is hard to stay positive all of the time. I know at times it gets hard to see the bright side of things and sometimes you just want to give up and let life pass you by. This kind of thinking is usually indicative of a deeper psychological problem which requires professional help, but what about when you can't go see a therapist?

If you're an AirPods user, things are a lot better with iOS 18 and iPadOS 18. If you're not, it may finally be time to grab yourself a set of AirPods, especially if you're into privacy and gaming.

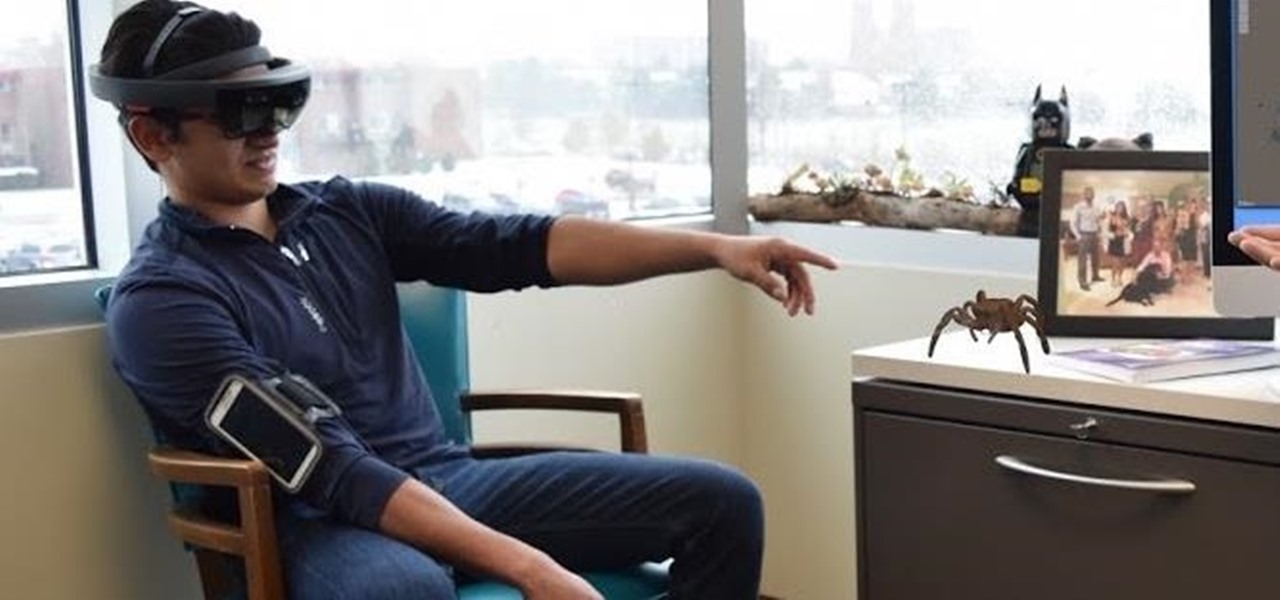
Halloween may be finished, but the augmented reality chills are not over yet for some people. Arachnophobes are bravely facing their fears by cozying up to augmented reality spiders for a university study.

For the first time, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved medication to treat children with a serious infection called Chagas disease, which stealthily infects and damages the hearts of millions of victims a year.

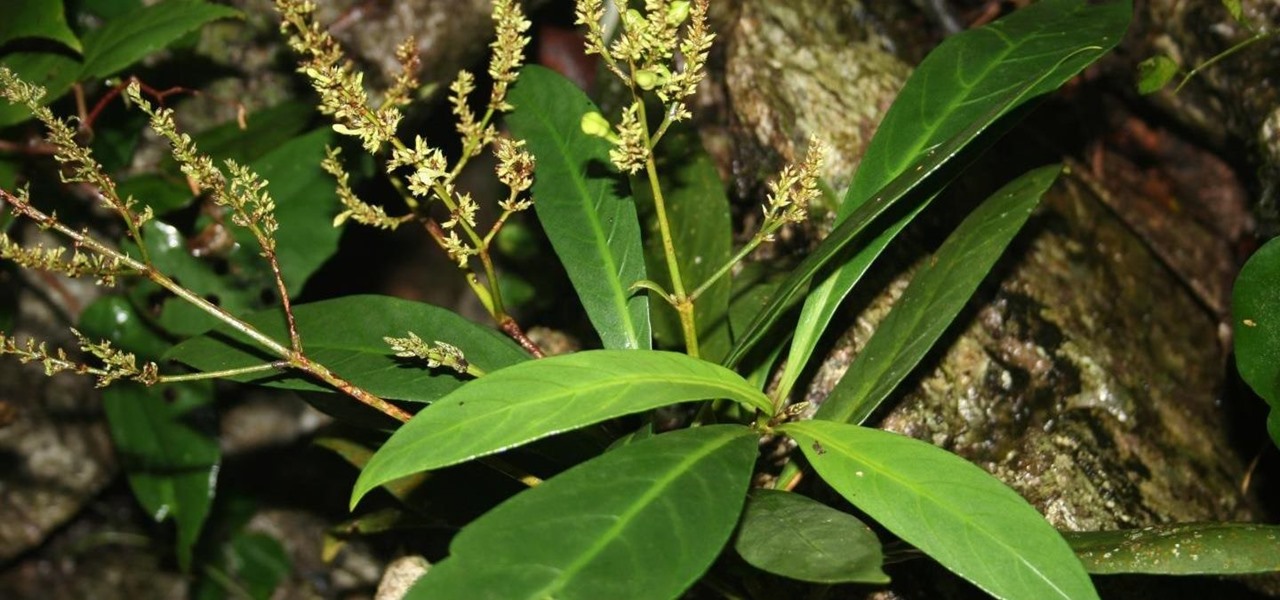
Natural remedies used through the ages abound, especially in Asian medicine. The willow-leaved justicia plant, found throughout Southeast Asia, has traditionally been used to treat arthritis, but scientists have just discovered it contains an anti-HIVcompound more potent than AZT. AZT was the first drug approved to treat HIV, and is still used in HIV combination therapy today.

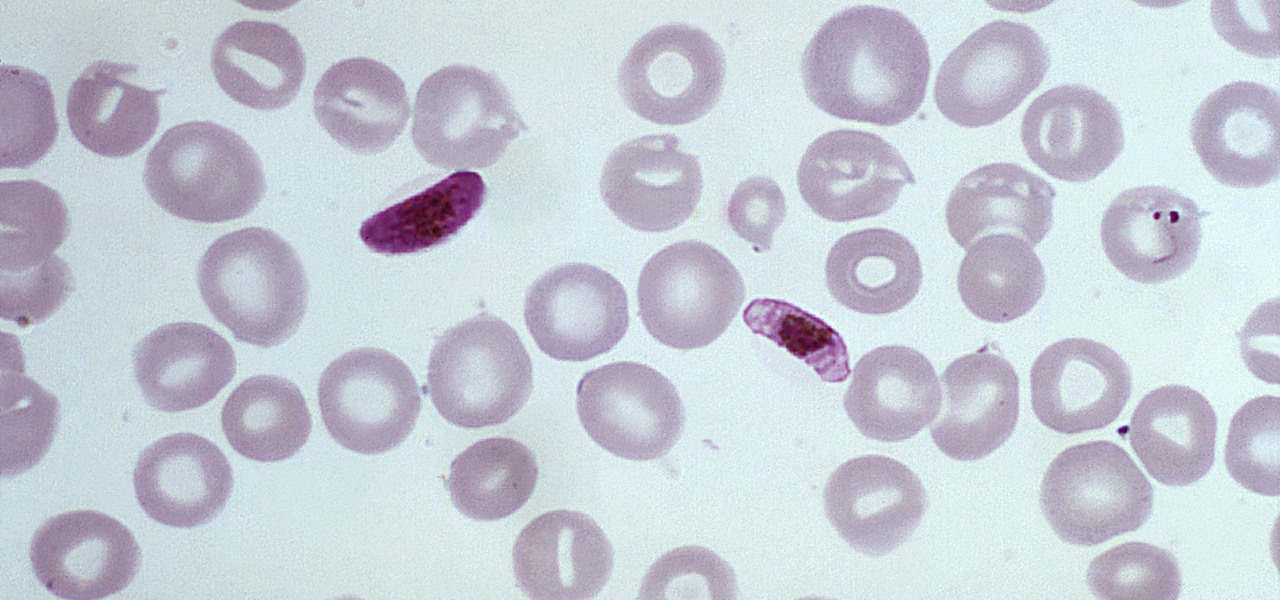
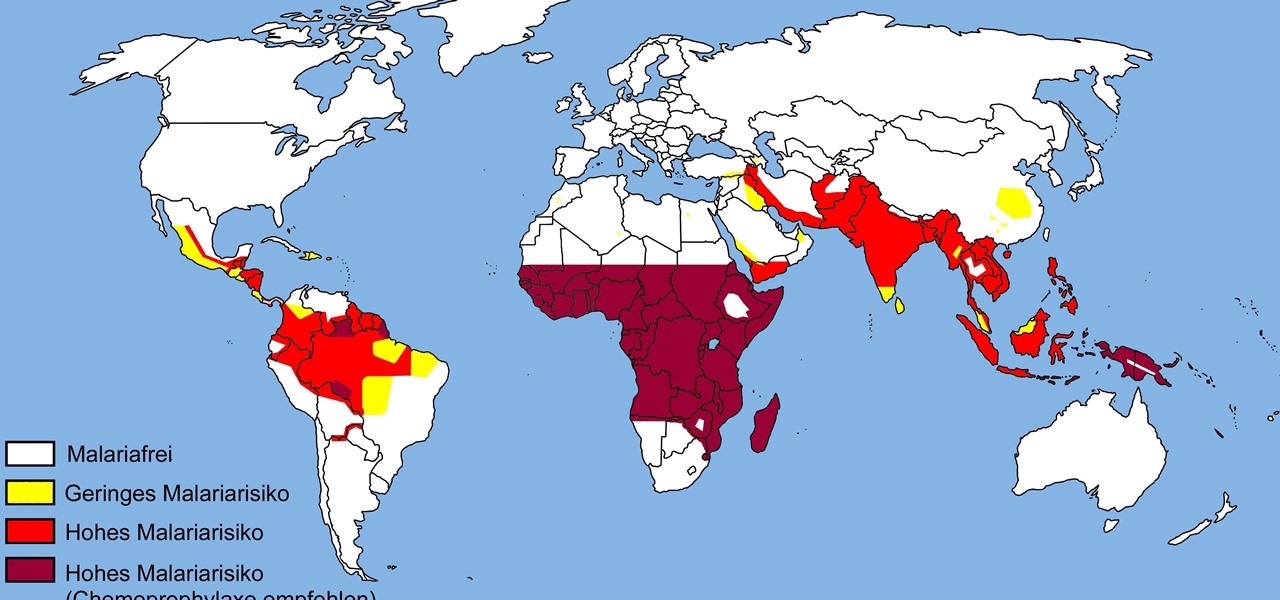
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimated that there were 212 million cases of malaria across the world in 2015, and 429,000 of those people died — mostly children living in Africa. Preventing and treating those infections has been a challenging world priority. That makes a new malaria drug discovery — published in Science Translational Medicine — incredibly important.

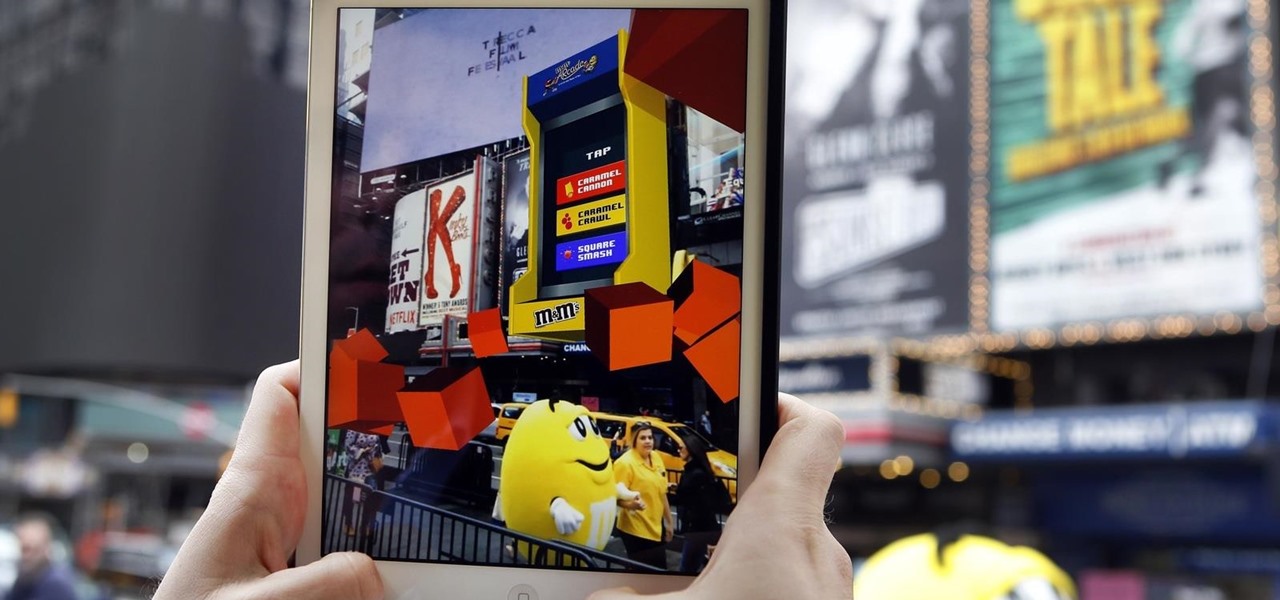
Marketing and healthcare, two of the leading industries in the adoption of augmented reality, continue to demonstrate applications for the technology in their businesses. Meanwhile, improvements to augmented reality devices are just around the corner with new developments from two display makers.

We usually associate Salmonella bacteria with a dangerous type of food poisoning, but they actually are pretty good at seeking out tumors. That trait made the bacteria a great candidate to deliver a protein that would help knock tumors out.

It's a rare person who enjoys swallowing pills—and equally rare to find those who can toss a pill back easily and effortlessly without gulps of water and coughs. The transition from liquid medicine to pills, tablets, and capsules can be a rough one, and some of us still struggle well into our adult lives. Yet the reason your pills are getting caught in your throat may not be the medication's fault—it's all in how you swallow.

True story: a friend of mine regularly started a fight with her boyfriend everyday at 4 p.m. Every day. This went on for years until he finally got the bright idea of shoving a granola bar at her the minute she came home from work. Shazam! The fights were a thing of the past.

Hey, you, still stuck at home? Cheer up, today is the first day of spring. Yes, really. And since you're probably locked in on TV, we're guessing you need a break from some of the less than sunshiney news reports rolling in. Well, no worries, because there's actually some good news to report.

You need a break from gloomy coronavirus updates. We all do. The unrelenting stream of doom and negative news is both helpful in terms of keeping ourselves and our families safe, but it also has the unfortunate effect of increasing our anxiety. When will this end? How bad will it get? Is there reason to be hopeful?

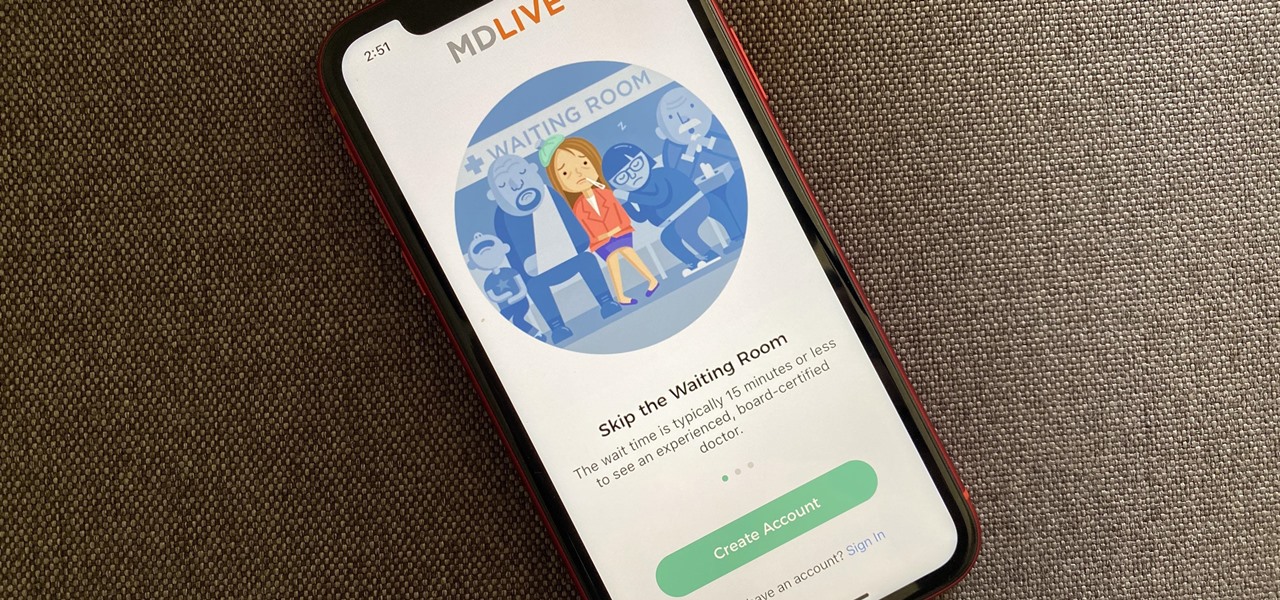
The World Health Organization has declared the new coronavirus a pandemic, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends video visits with a healthcare professional to reduce the risk of being exposed to the coronavirus that causes COVID-19. If you are experiencing mild flu-like symptoms, virtual doctor visits may also prevent you from endangering others.

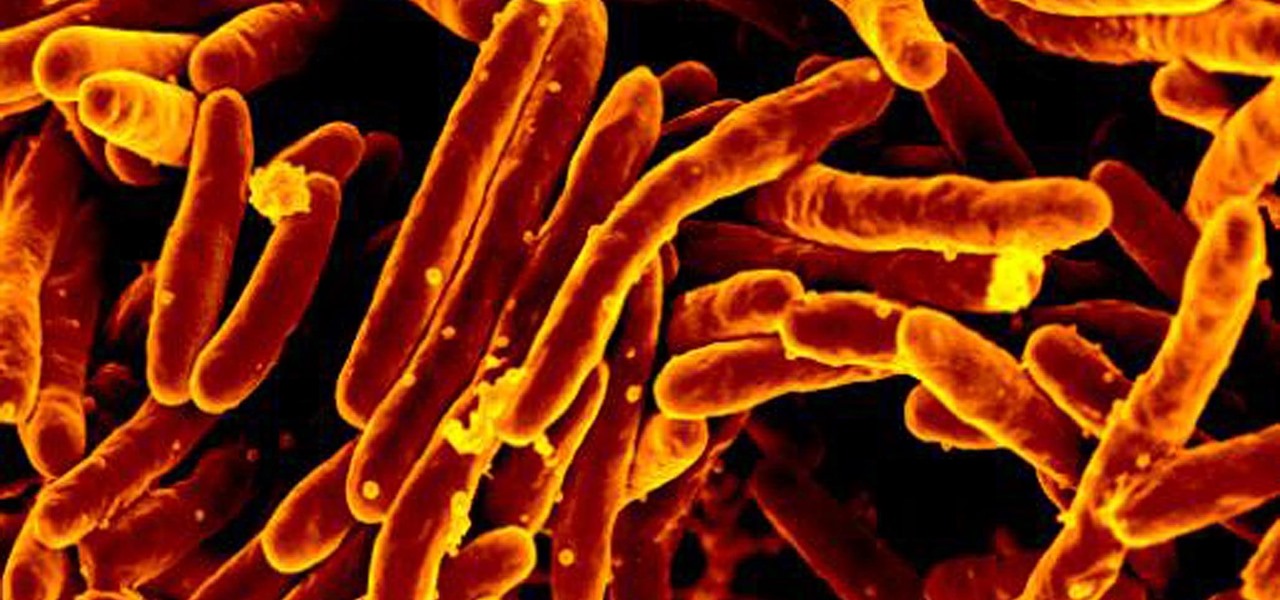
The incidence of tuberculosis (TB) is dropping in the US, but the World Health Organization (WHO) considers it to be epidemic in the rest of the world — there were over 10 million new cases in 2016.

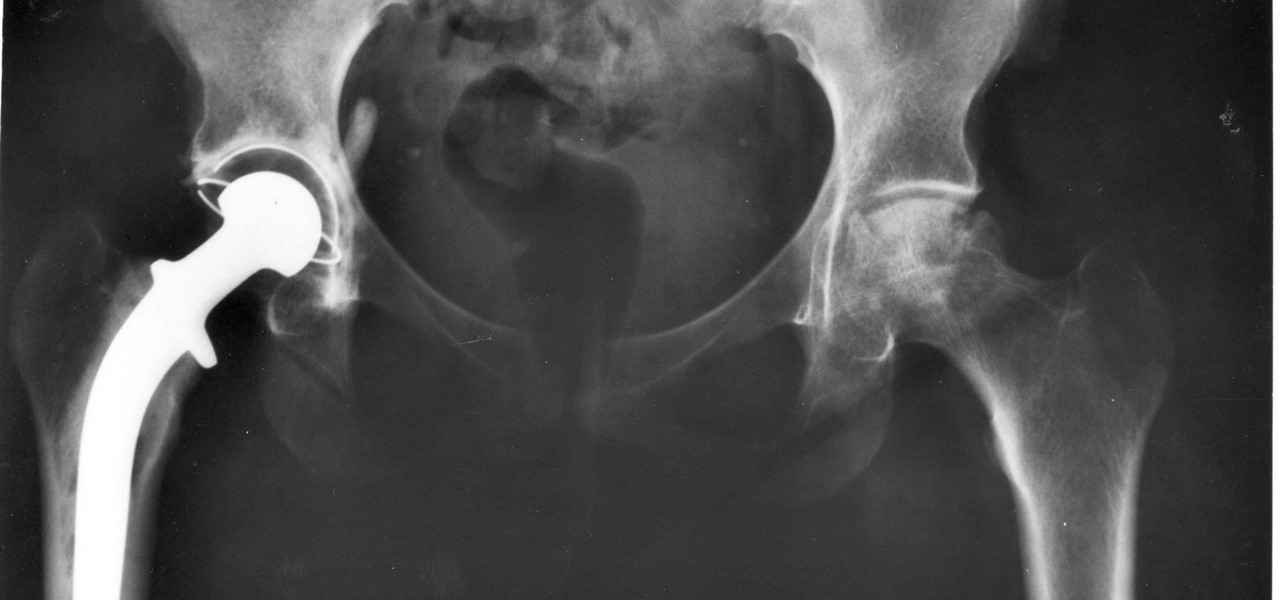
For about a million Americans each year, a joint replacement brings relief from pain and restored mobility. But, 5–10% of those people have to endure another surgery within seven years, and most of those are due to an infection in their new joint. If doctors could treat infections more effectively, patients could avoid a second surgery, more pain, and another rehabilitation.

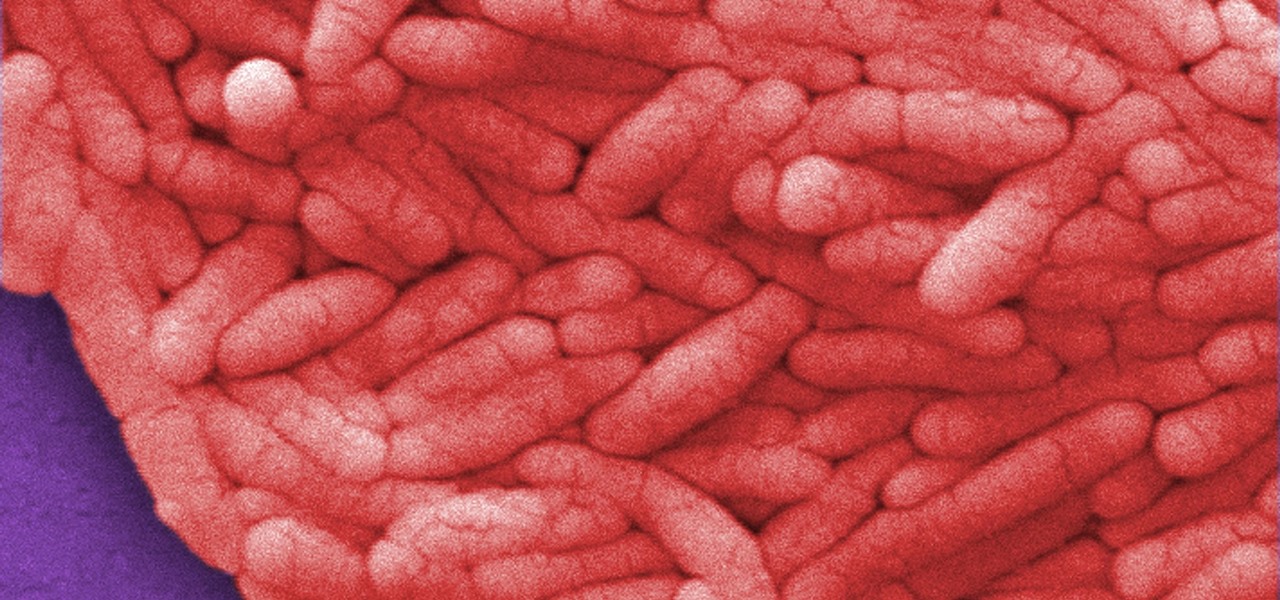
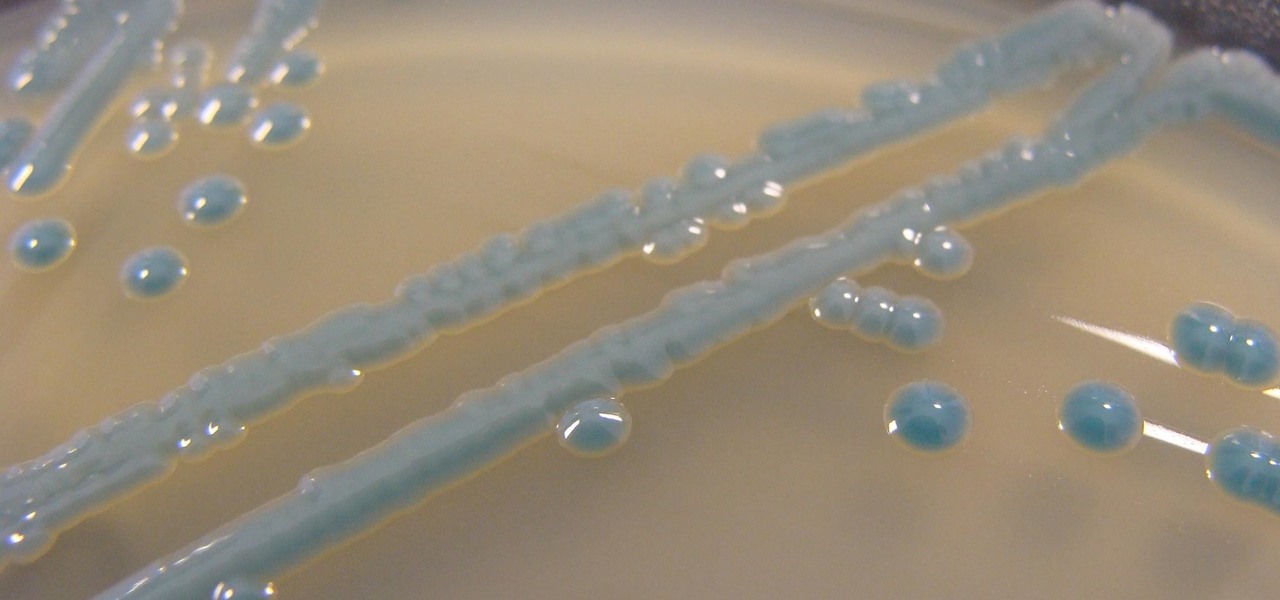
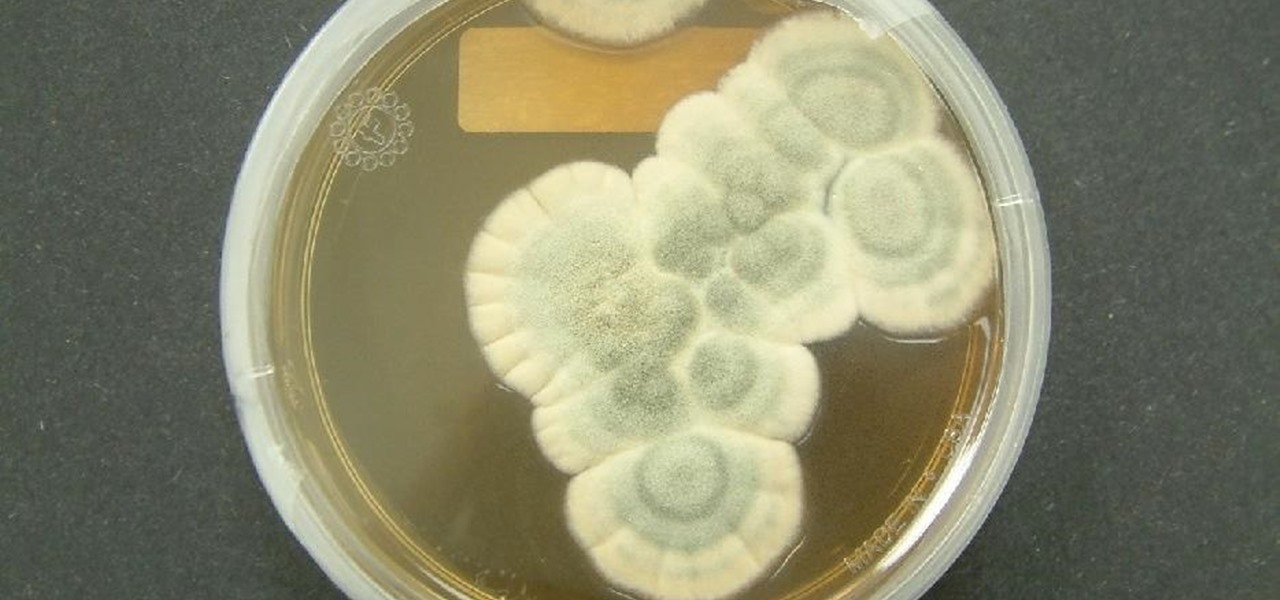
The growing list of dangerous antibiotic resistant organisms has just acquired three new members. Researchers have discovered three new species of Klebsiella bacteria, all of which can cause life-threatening infections and have genes that make them resistant to commonly used antibiotics.

An older man dies of Zika. A younger man who cares for him catches Zika — but doctors cannot pinpoint how the disease was transmitted. While proximity to the patient is sufficient explanation for the rest of us, for microbe hunters, it is a medical mystery. Why? Zika is not known to transmit from person-to-person casually.

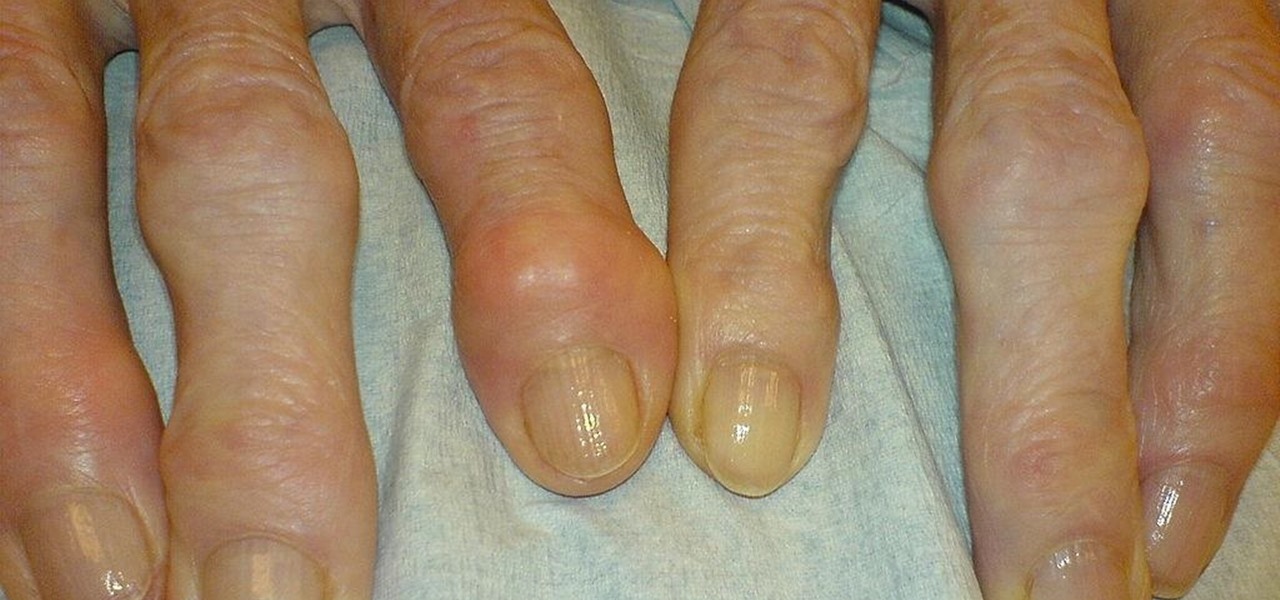
As if the swollen, painful joints of rheumatoid arthritis weren't enough, the disease is the result of our immune system turning against cells of our own body. Ever since this realization, scientists have worked to find the trigger that sets the immune system off. Scientists believe that gut bacteria may have a role in initiating the abnormal immune response. Now, a team of researchers from Boston has figured out how that might occur.

After years of telling patients to finish any prescribed course of antibiotics completely, a group of researchers in the UK say it is no longer necessary, and could even be harmful if we want to preserve the antibiotics we can still use.

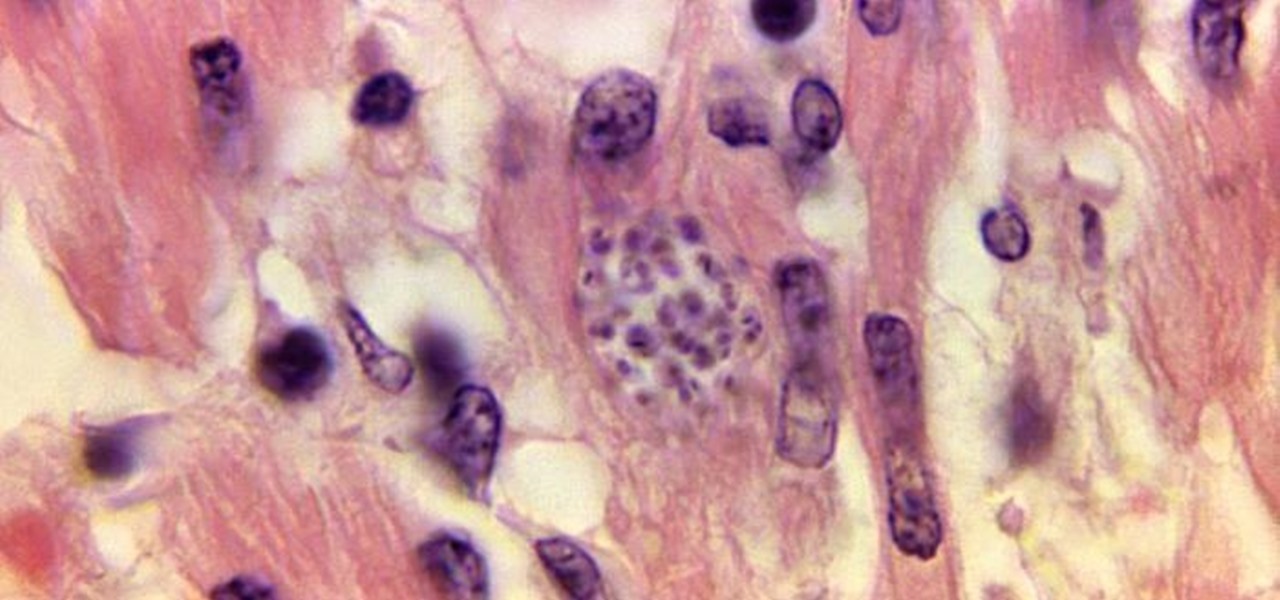
Colorectal cancer — cancer of the colon or rectum — is the third most commonly diagnosed cancer in the US. To reduce the chances of a diagnosis we are all urged to stop smoking, keep our weight down, decrease our intake of alcohol and red meat, keep active, and get screened for colon cancer. But, new research has found something that participates in the development of colorectal cancer that might not be as easy to control: A strep bacteria that promotes tumor growth.

Sex makes the world go 'round, and when it does, so does gonorrhea. Finally some good news on the growing menace of drug-resistant gonorrhea — a large, long-term study shows a vaccine may work in reducing the incidence of an increasingly dangerous infection.

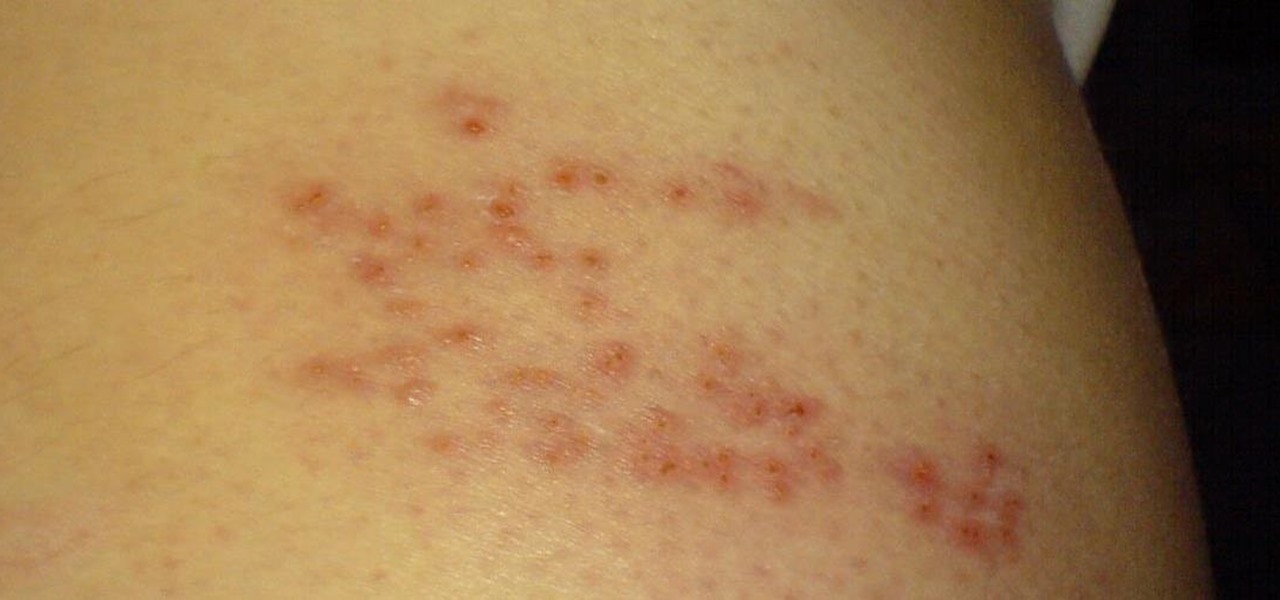
People who have heart disease get shingles more often than others, and the reason has eluded scientists since they first discovered the link. A new study has found a connection, and it lies in a defective white cell with a sweet tooth.

Alzheimer's disease — an irreversible, progressive brain disorder — is the sixth leading cause of death in the US and more than afflicts 5 million Americans. As if those numbers aren't scary enough, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention expect that number to nearly triple by 2050.

Move over whole wheat — white bread may be back in style after a new study shows that it may be your gut microbes that decide what kind of bread is best for you.

Dengue fever is a danger to anyone living or visiting tropical or subtropical regions. It can be hard to detect the infection in its earliest and most treatable phase, especially in children. Luckily, new research highlights better techniques for triaging the disease in infected children with more severe symptoms, potentially saving lives.

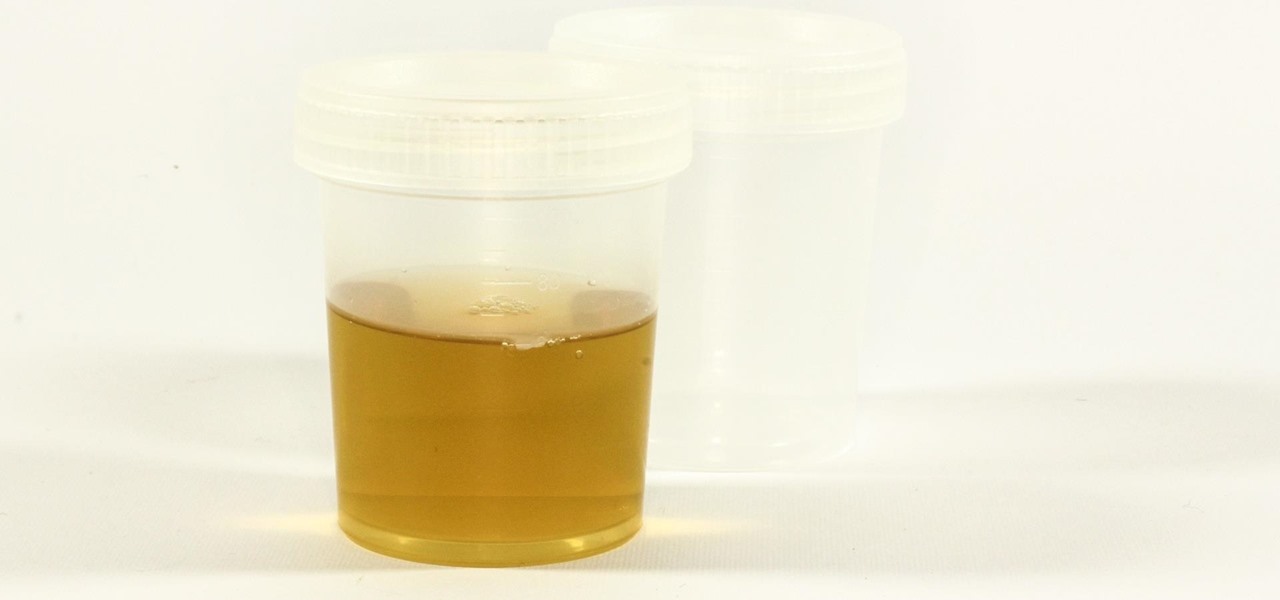
Have you ever had a burning sensation when you urinate? Low fever, back pain, and maybe cloudy urine? Male or female, it could have been a urinary tract infection. If it lasted long enough, the chances are good you went to the doctor for help. For about 20% of women, standard testing for a UTI does not reveal the presence of infection-causing bacteria, even though bacteria may be causing their symptoms. Well, a new test may provide better answers.

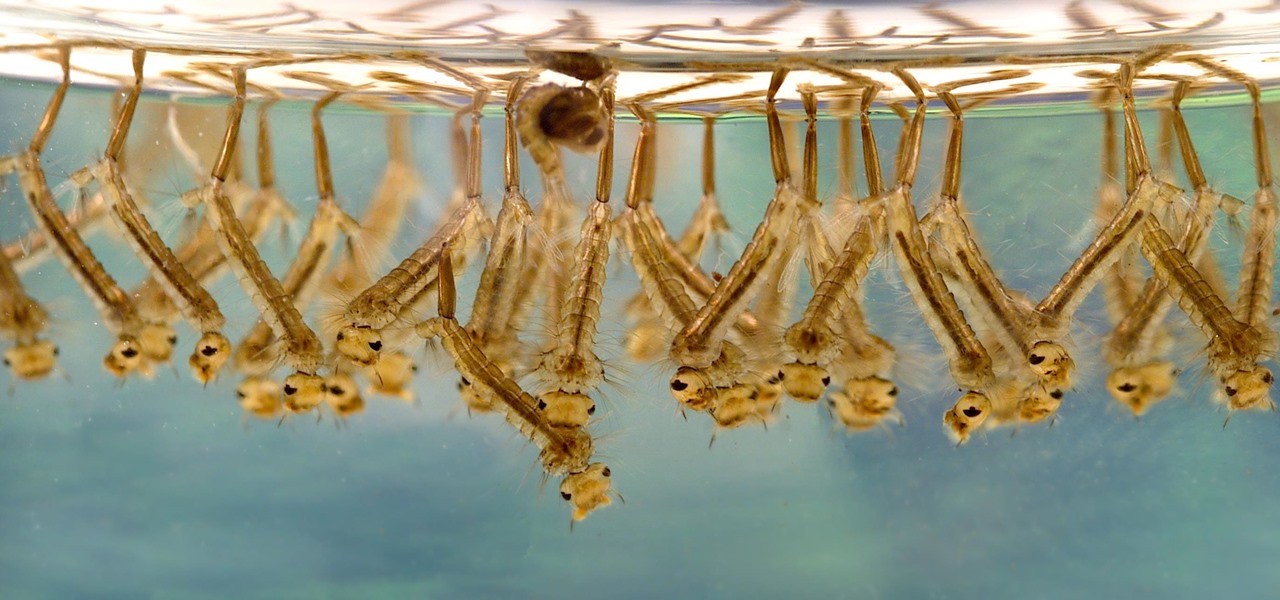
When just floating peacefully in the water with their brood mates, the Culex mosquito larvae in the image above does not look very frightening. But in their adult form, they are the prime vector for spreading West Nile virus — a sometimes mild, sometimes fatal disease.

The theme for 2017's World Malaria Day, which is today, April 25, is "End Malaria for Good." For many Americans, this might seem like an odd plea. Especially since Malaria is seemingly an obsolete problem here. However, on World Malaria Day, it's important to remember the danger of malaria is still very much present in the US. And around the world, the disease is at the epicenter of a global crisis.

As summer mosquito season approaches, researchers are warning people with previous exposure to West Nile virus to take extra precautions against Zika. A new study found that animals with antibodies to West Nile in their blood have more dangerous infections with Zika than they would normally.

It has become hard to decipher where your digital imprint ends and your true self begins in today's tech-dominated world. Scrolling through news feeds and endless updates is not conducive to a good night's sleep, nor does it help you lead a well-balanced life.

The culprit probably wasn't what doctors were expecting when a 57-year-old man in Hong Kong came to the hospital. The patient was admitted to the intensive care unit in critical condition. A clue to the cause of the infection would lie in the man's profession—he was a butcher.

A new study has found that up to half of people who think they have a penicillin "allergy" can still receive the drug, and other antibiotics with similar structures, without any negative reactions to the meds. Why? Because they're not really allergic, doctors say.

In the past, infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) commonly led to dementia as the virus made its way to the brain. Even in effectively treated people, HIV can hide out and replicate in places like the brain, where it's tough to detect. That's why it's very concerning that half of all HIV-infected patients still report cognitive problems.

Although their effectiveness is waning, antibiotics remain a front-line defense against many infections. However, new science reveals using the wrong antibiotic for an infection could makes things much worse.

You know the signs—sneezing, fever, nagging cough, no energy, no appetite. It's the flu, but this time, it's your dog who's down and out. Yes, dogs get the flu, too. However, a team from the University of Rochester Medical Center and their collaborators have developed a new vaccine that may make the doggy flu a thing of the past.