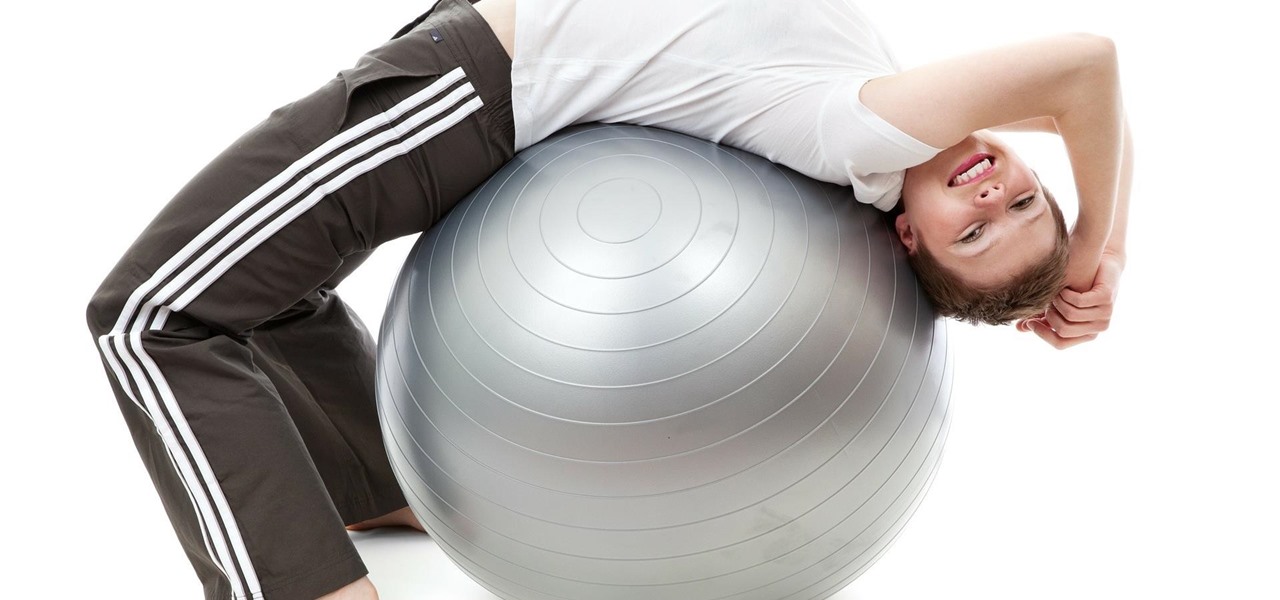
A week into my internship, I experienced pretty serious back pain and slight difficulty breathing. I scheduled a doctor's appointment to make sure nothing was wrong, and I got a surprising diagnosis: bad posture.

About a third of the methane released into the environment comes from the production and transport of natural gas. The gas leaks as it moves along the transport chain from gas wellheads to market.

The launch of the Audi A8 marks the world's first Level 3 car on offer in retail channels, except there is one catch: it can only take full control of driving at speeds of 37.3 mph or less.
The community of bacteria that lives in our gut has a lot to tell us. It can give clues to what we eat, the environment we live in, and diseases and disorders we may have. Now, scientists have linked these bacterial species to how we feel. A new research study found an association between women's gut bacteria and their emotions.

Montezuma's revenge, the runs, the trots, or just diarrhea — everyone gets it sooner or later. What exactly is diarrhea good for, if anything?
A new medical development is going to change the way many of us look at getting the flu vaccine. A painless flu vaccine skin patch is making needles and vials a thing of the past. Researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University have shown that a flu vaccine can be administered safely and comfortably with this new patch, which delivers the vaccine through a matrix of tiny dissolving microneedles.

Look no further than Flint, Michigan, to discover the serious consequences of contaminated drinking water. Around the world, water polluted by pathogens and toxins sickens people or cuts them off from safe drinking water. Looking for a solution, researchers created tiny, swimming robots that pack a powerful punch against waterborne pathogens.

Legionnaires' disease is named after 1976 outbreak in Philadelphia that sickened 221 people and killed 34. More often striking adults over the age of 50, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently reported two cases where newborns contracted the often fatal disease — at their moment of birth.

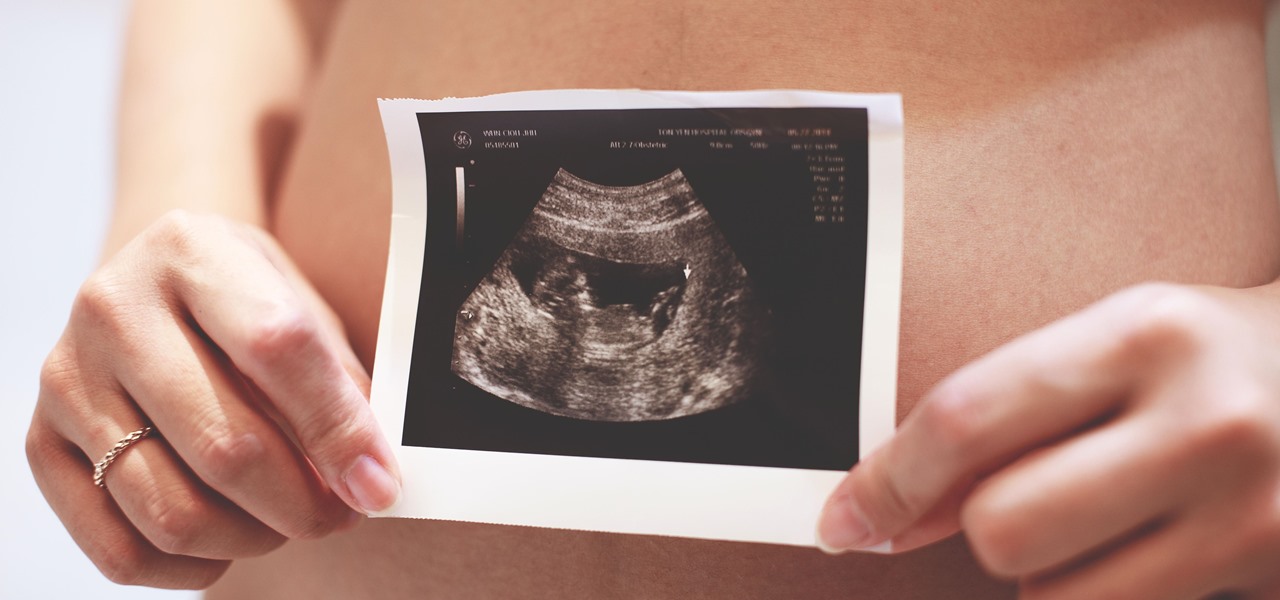
Even before we are born, our immune system is hard at work. New research shows how the developing fetal immune system takes advantage of the time and opportunity of gestation — in the presence of mom's cells and tissues — to develop a sense of self.

I haven't bought into Apple Pay just yet, but I do love the idea of having quick access to passes like loyalty programs, boarding passes, and my Starbucks card. However, for some users, it's impossible to open these passes stored in Apple Wallet on the iPhone's lock screen. While it's not totally obvious, or even ideal, there is a way to get those Wallet passes back on your lock screen in iOS 9 or iOS 10.

As headlines focus on melting glaciers and rising water levels caused by global warming, climate change is quietly taking its toll on the nearly invisible occupants of this planet, the microbes.

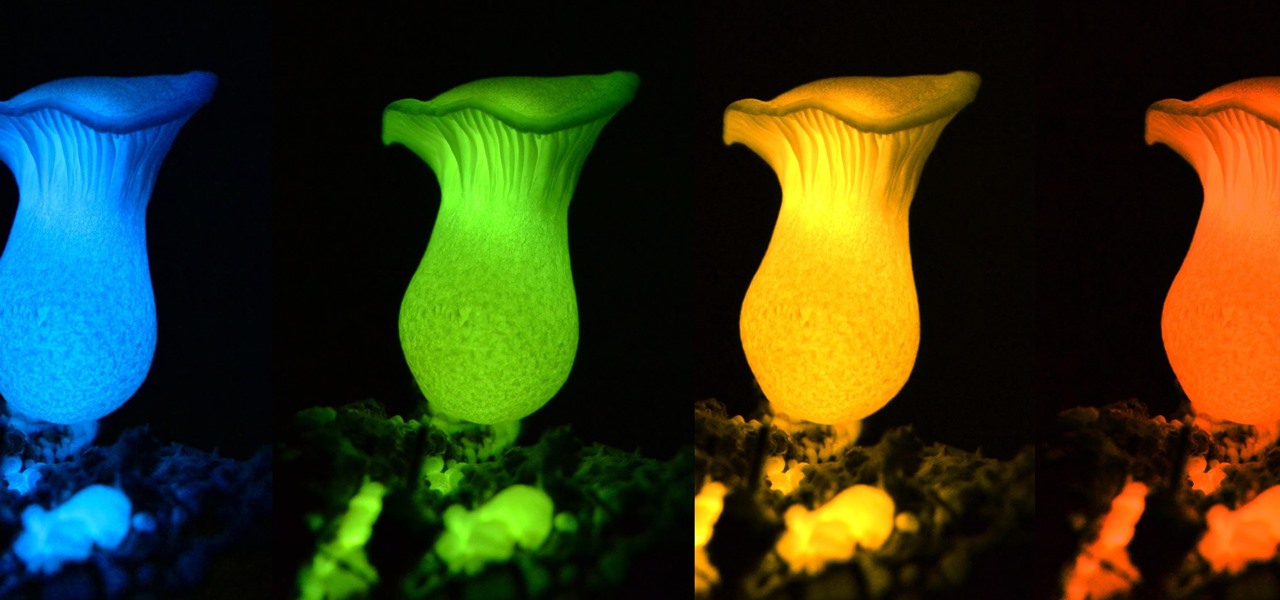
Bioluminescence — the ability of an organism to produce and emit light — is nature's light show. Plants, insects, fish, and bacteria do it, and scientists understand how. Until now, though, we didn't know how fungi glow.

Water makes up about 60% of your body weight. Whether you like it plain, flavored, bubbly, or in beverages or food, we all need water daily to avoid dehydration and stay healthy. For communities in need of clean drinking water, new research using bacteria may offer a simplified, lower-cost method for boosting potable water supplies.

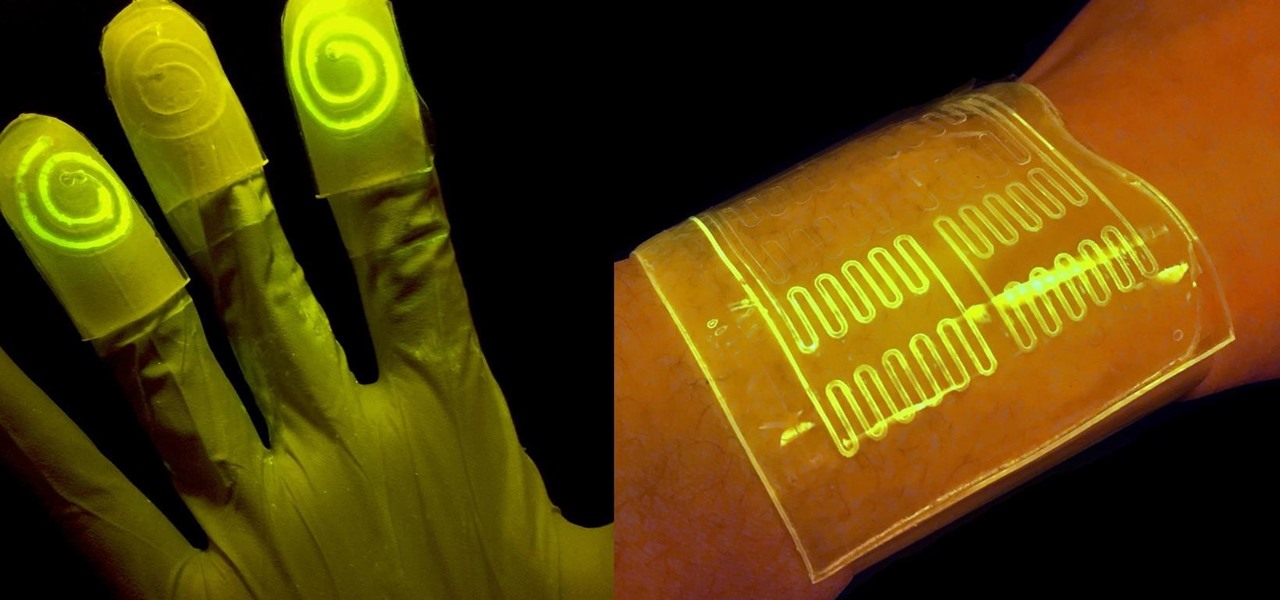
While at work, you notice your gloves changing color, and you know immediately that you've come in contact with dangerous chemicals. Bandages on a patient signal the presence of unseen, drug-resistant microbes. These are ideas that might have once seemed futuristic but are becoming a reality as researchers move forward with technology to use living bacteria in cloth to detect pathogens, pollutants, and particulates that endanger our lives.

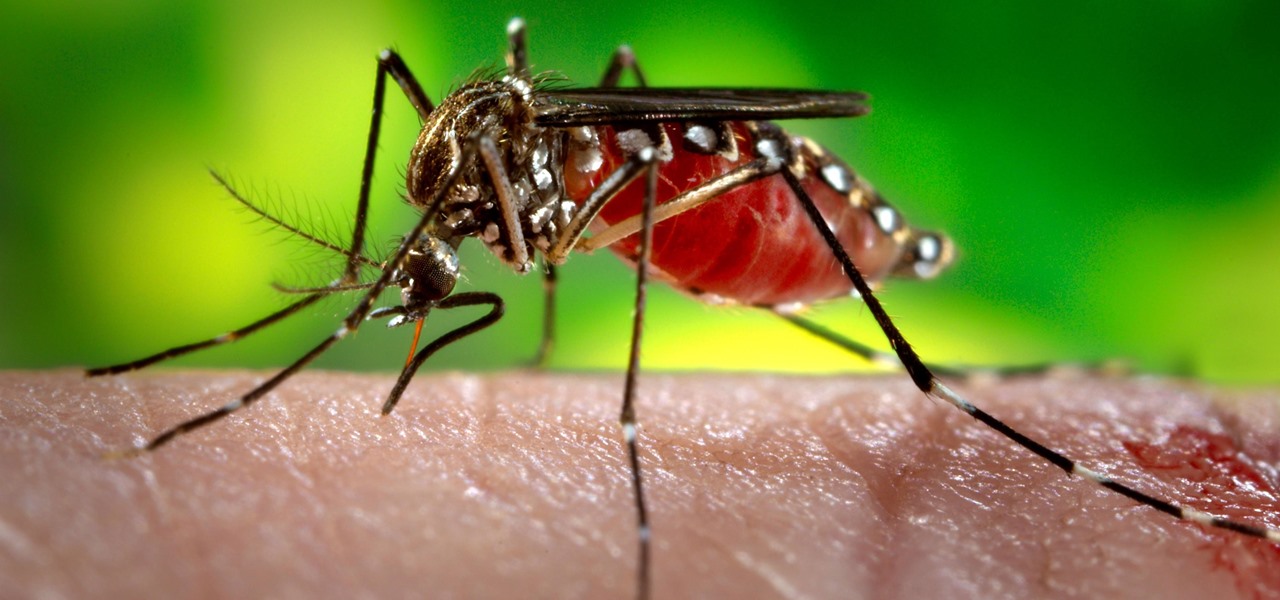
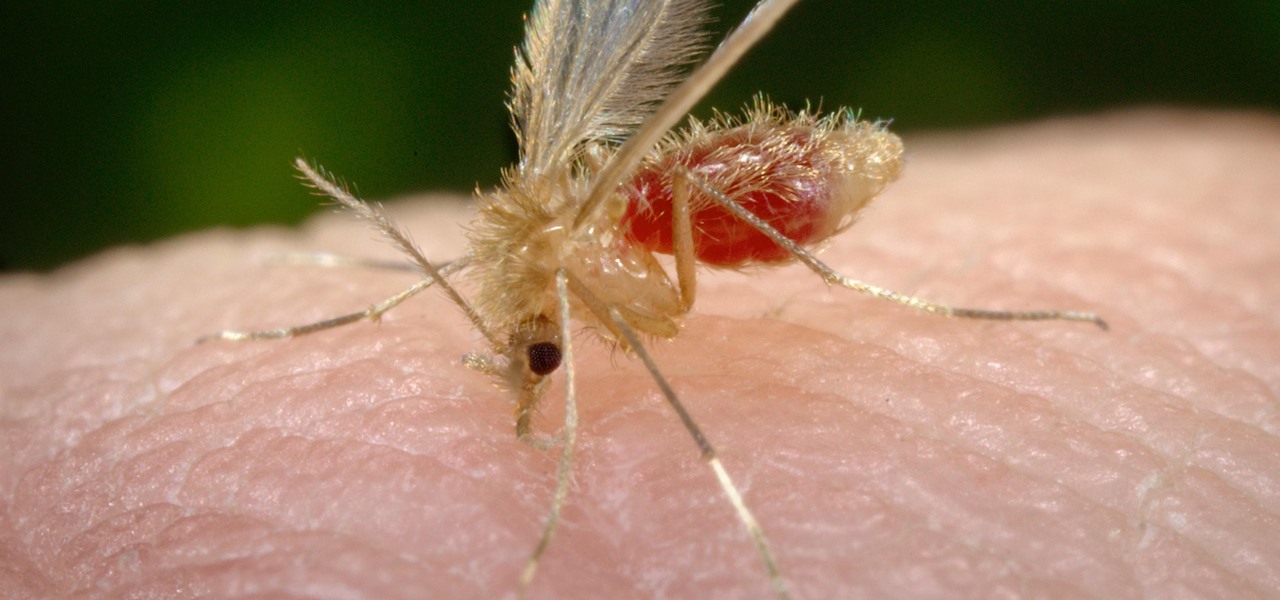
As summer mosquito season approaches, researchers are warning people with previous exposure to West Nile virus to take extra precautions against Zika. A new study found that animals with antibodies to West Nile in their blood have more dangerous infections with Zika than they would normally.

Antibiotics used to prevent diseases in livestock are creating a world of hurt for humans and the soil we depend on for food. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a global health issue. The overuse, underuse, and poor use of these life-saving drugs is rapidly removing them as a treatment option for serious infections in humans—plus bacteria are naturally adaptive.

In the ongoing search to find better ways to use antibiotics, an extract made from maple syrup has some surprisingly important medical benefits.

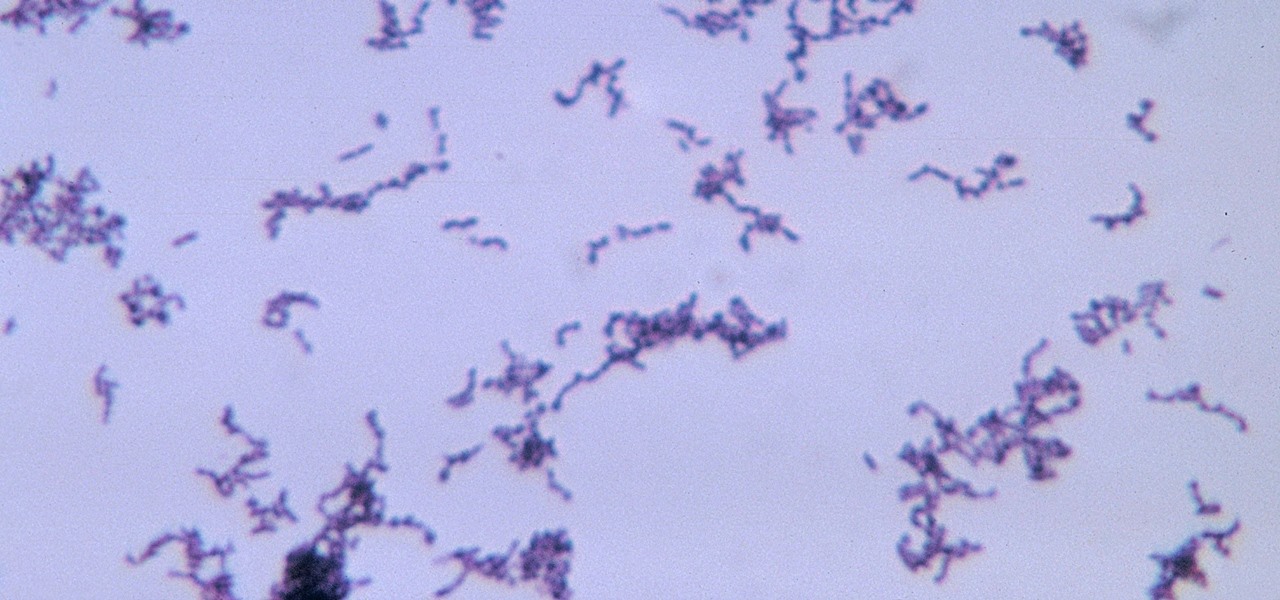
The squiggly guys in this article's cover image are Propionibacterium acnes. These bacteria live in low-oxygen conditions at the base of hair follicles all over your body. They mind their own business, eating cellular debris and sebum, the oily stuff secreted by sebaceous glands that help keep things moisturized. Everybody has P. acnes bacteria—which are commonly blamed for causing acne—but researchers took a bigger view and discovered P. acnes may also play a part in keeping your skin clear.

Growing populations and higher temperatures put pressure on world food supplies. Naturally occurring soil bacteria may save crops in drought-stressed areas, put more land into crop production, and produce more food.

Two viral liver diseases could help us find the path toward the cause of Parkinson's disease. Researchers from the University of Oxford and UCL Institute of Neurology in London have reported an association between hepatitis B and C infections and an increased risk of Parkinson's disease. Their findings were published early online in the journal Neurology.

Most females have had at least one urinary tract infection in their lifetimes. Recurrent UTIs are particularly problematic in young, sexually active women, where about 80% of the infections are caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli, better known as E. coli.

There could be a fresh outbreak of the Zika virus in the Americas as the weather heats up and the mosquito population blooms.

An outbreak of anthrax from contaminated meat in Tanzania sickened dozens of people and moves the danger of this deadly bacteria back into focus.

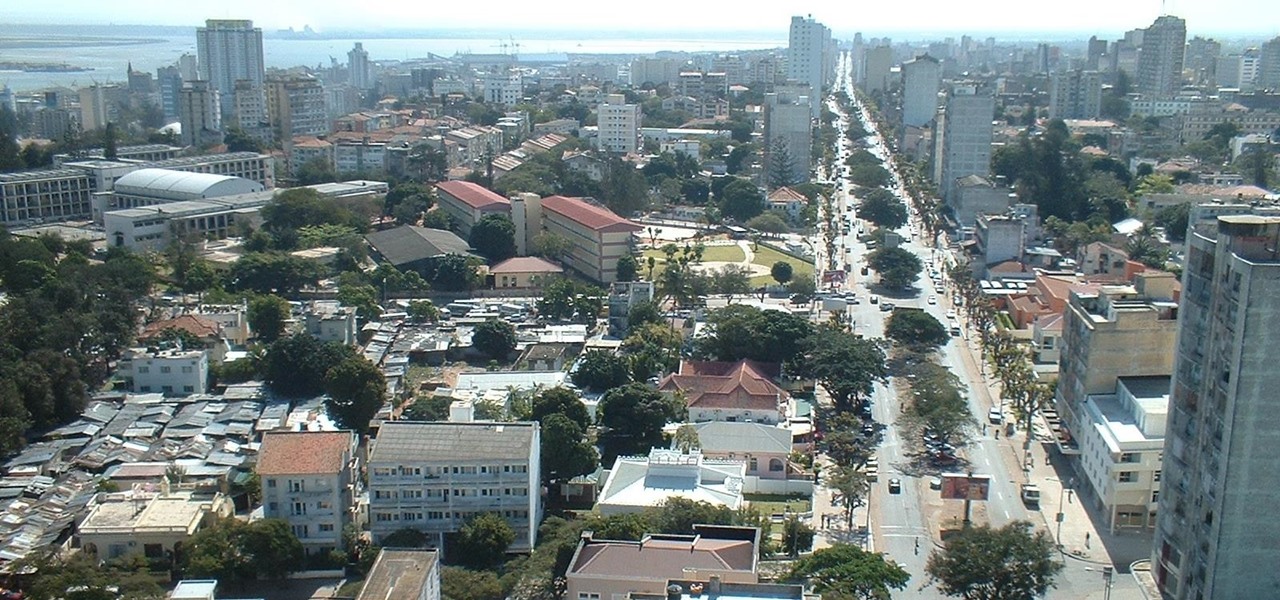
Cholera is rapidly spreading in Mozambique, with over 1,200 people infected. Since the outset of 2017, cholera has spread from the capital city of Maputo (pictured above) to three of its ten provinces. Health officials report other areas in the country are seeing case counts rise, and two deaths have been logged so far.

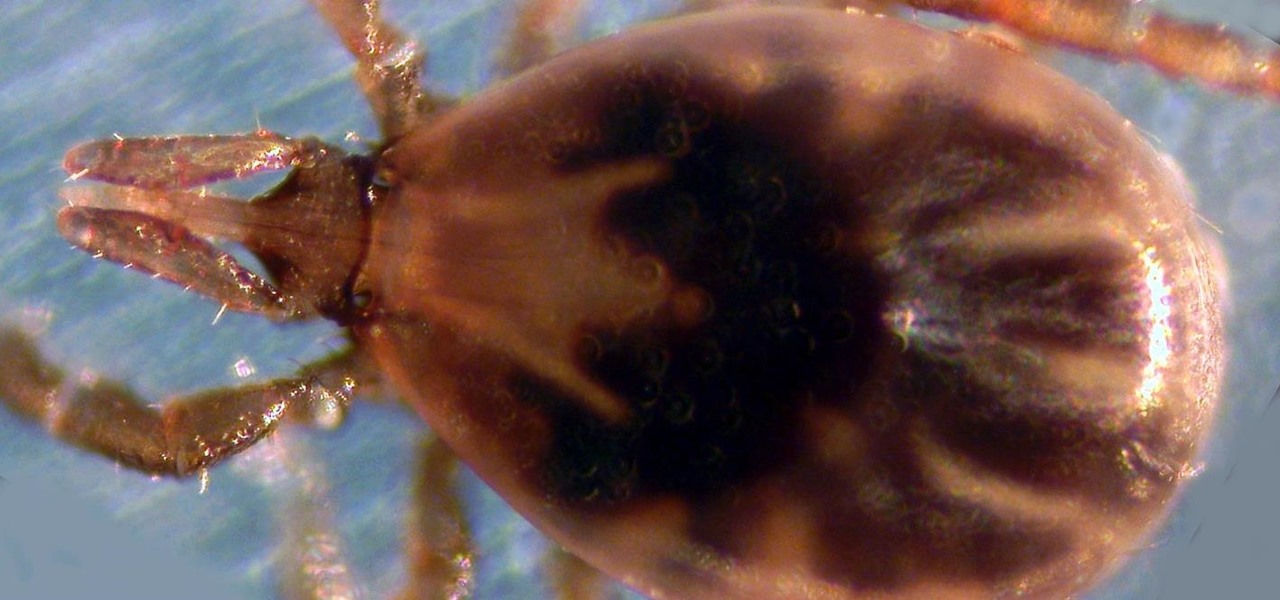
For regions that experienced a boom in mouse populations last year, scientists say 2017 could see a surge in cases of Lyme disease.

We may not fully appreciate all the important roles wheat plays in our lives until it's gone—or at least, when it's in very short supply. What would a world be like without bread, cakes, cereal, pasta, or wheat beer? If the dire warnings about an impending stem rust fungus come to pass, we may know all too soon.

Maternal infection with genital herpes, or other pathogens, during early pregnancy could increase risk of autism, or other neurodevelopmental disorders, says a new study.

Even if your cat drives you a little nuts, don't worry, because a new study says that cats pose no risk to your mental health.

New research suggests the bacteria that causes listeriosis may be a bigger threat in early pregnancy than previously thought. Usually considered a danger to late pregnancy, scientists suggest early undiagnosed miscarriages could be caused, in some cases, by infection with Listeria.

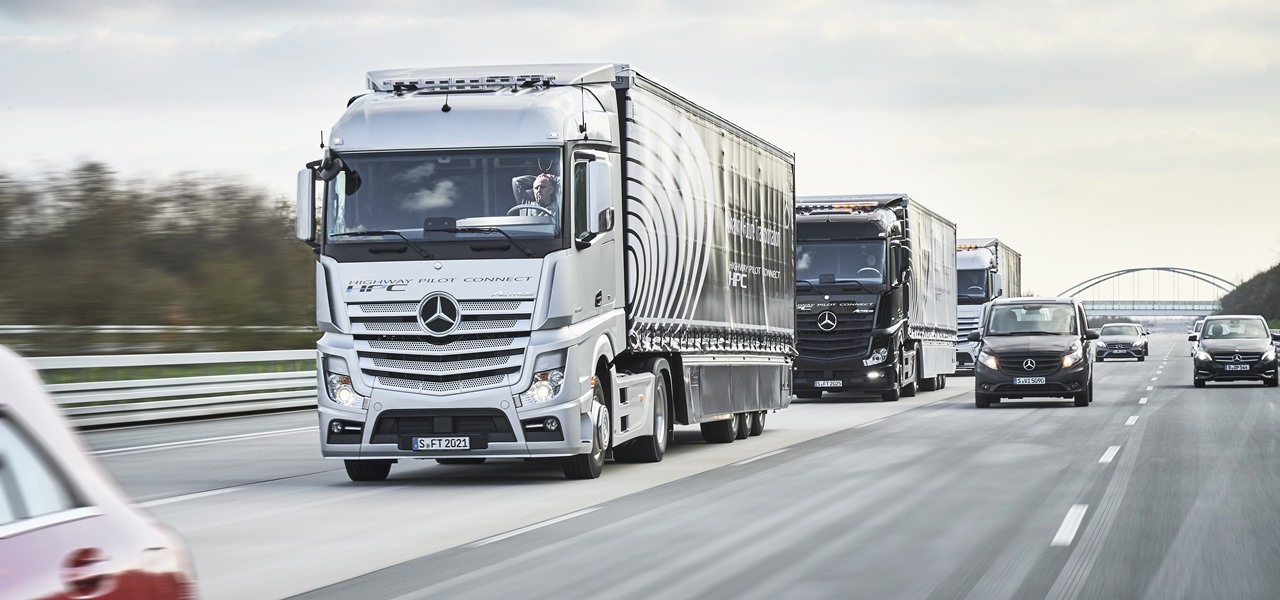
Japan is in the process of curbing its aging population and mature workforce. According to The Diplomat, the country's population has been declining at a steady rate. To meet future productivity demands in commercial and industrial sectors, local officials are turning to self-driving technology, including truck platooning, where three or five vehicles travel autonomously in a string formation. This practice, according to a study by MIT, can reduce fuel consumption by up to 20% (more about thi...

A new study just out reveals that HIV takes hold in the human body with the help of cells that usually work to heal, not kill.

Seagrass may help your favorite beach stay a little less toxic. A new study, led by Joleah Lamb, a postdoctoral researcher in the Harvell Lab at Cornell University, found that coastal seagrasses reduce levels of pathogens dangerous to humans and marine organisms in near-shore waters.

Although their effectiveness is waning, antibiotics remain a front-line defense against many infections. However, new science reveals using the wrong antibiotic for an infection could makes things much worse.

Transmitted by a sandfly one-third the size of a mosquito, parasitic Leishmania protozoa are responsible for a flesh-destroying disease that kills an estimated 20,000 people per year. Two new studies offer understanding of how the parasite provides immunity through persistence and why some people suffer more virulent forms of the disease.

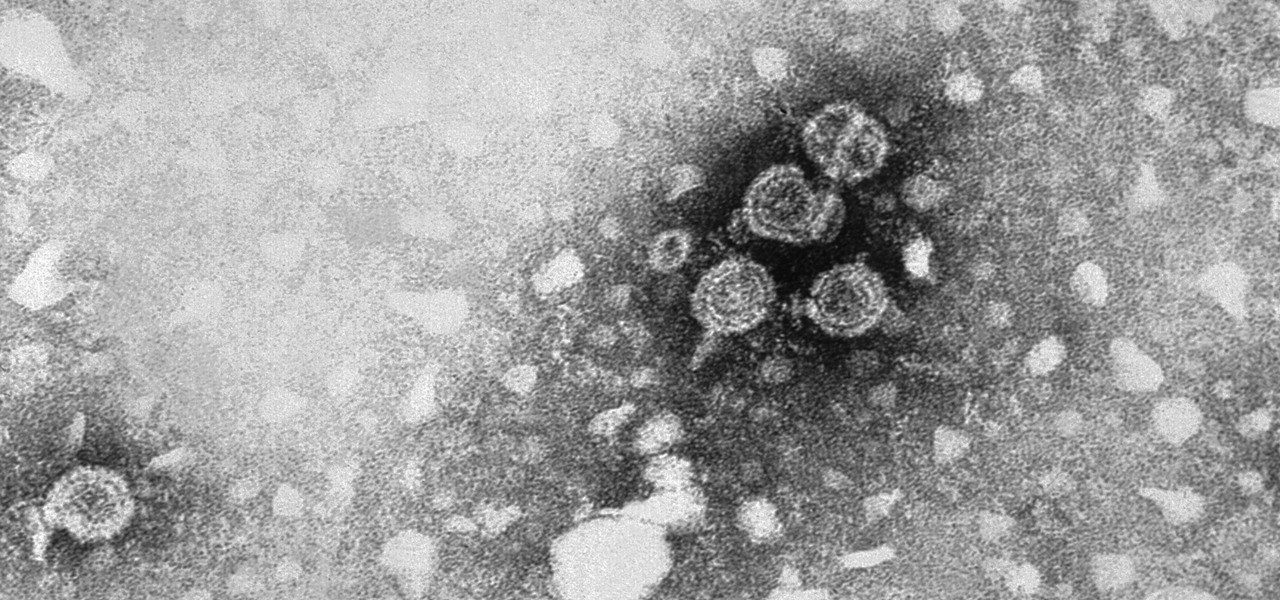
In the summer of 1976, 4,000 American Legionnaires descended upon the Bellevue-Stratford Hotel in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, for a four-day convention. Several days later, many of the attendees experienced symptoms of severe pneumonia. By the beginning of August, 22 people had died. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimate that about 180 people were sickened and 29 people died before this mysterious outbreak burnt out.

A recent pathogen outbreak in Illinois is just one of many outbreaks of an underappreciated, but serious, viral infection passed from rodents to humans. These hantaviruses have been cropping up more frequently in the last decade or so, giving us more reason to clean out our dusty attics, basements, and garages.

Transmitted by ticks, Lyme disease is a serious infection that is probably headed your way. A recent study confirms the pathogen that causes Lyme disease is now established in nine national parks in the East, including Acadia and Shenandoah National Parks.

If you have a mobility impairment that affects your hands, arms, or manual dexterity, a smartphone's touch-based interface can almost be a barrier between you and the mobile internet. Eye-tracking software requires too much computing power for today's smartphones to handle, so it might seem as though there's no good way to interact with an Android device.

The story of Helicobacter pylori is a real testament to the tenacity of medical researchers to prove their hypothesis. It took decades before the scientific world would accept that the bacteria H. pylori caused ulcers.

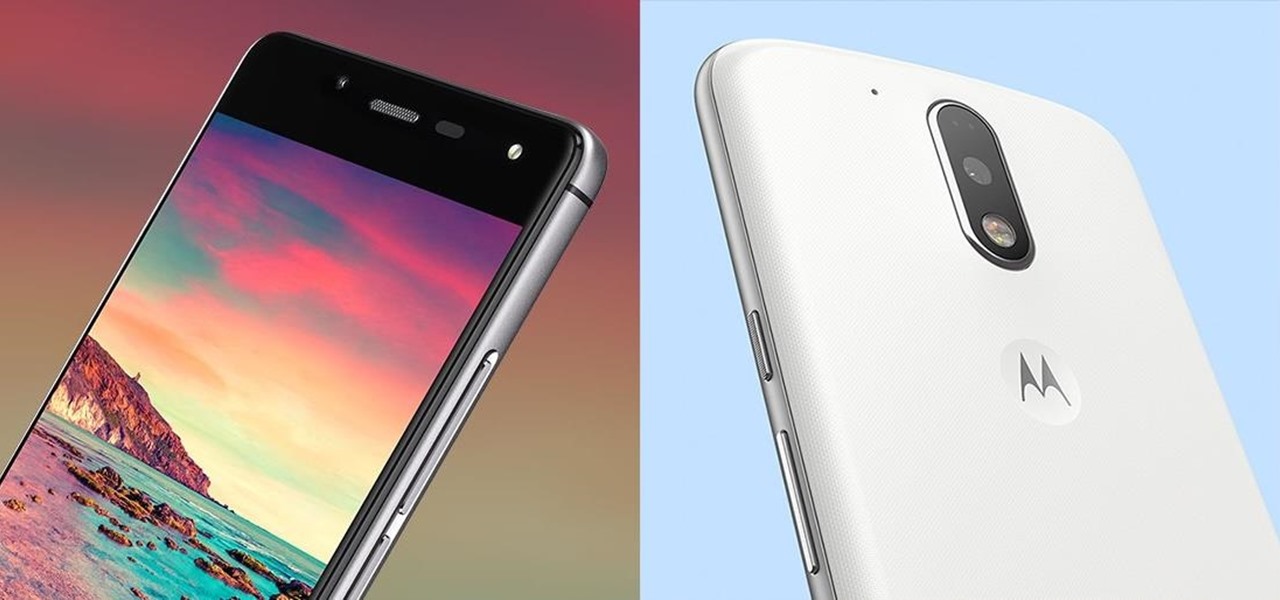
Amazon is running a pre-sale deal on a few unlocked smartphones by BLU and Motorola, which will be released on July 12, 2016. The 8 GB BLU R1 HD is on sale for just $49.99, and the 16 GB version is available for $59.99, for a savings of $50 off either phone. You can also grab the 16 GB Motorola Moto G4 for $149.99, or the 32 GB variant for $179.99, again a $50 discount on each.