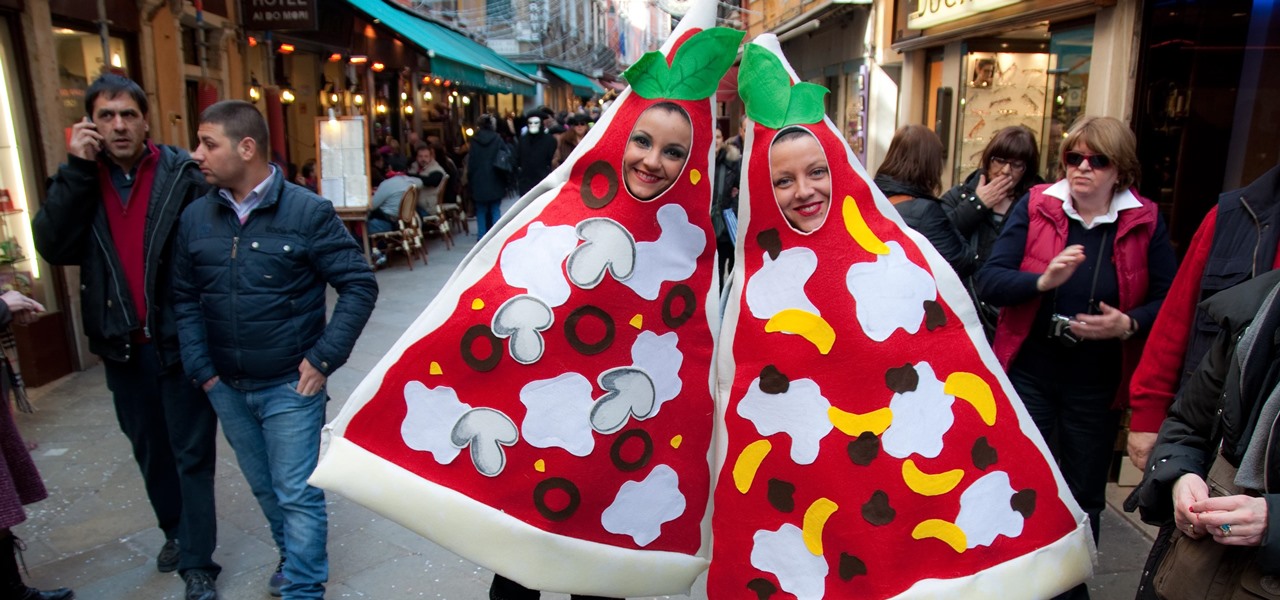

How To: 13 Food Costumes That Let You Be What You Eat This Halloween
No one ever said you had to be a culturally-relevant pun for Halloween, you know—or a scantily-dressed version of the inmates from Orange is the New Black.


No one ever said you had to be a culturally-relevant pun for Halloween, you know—or a scantily-dressed version of the inmates from Orange is the New Black.
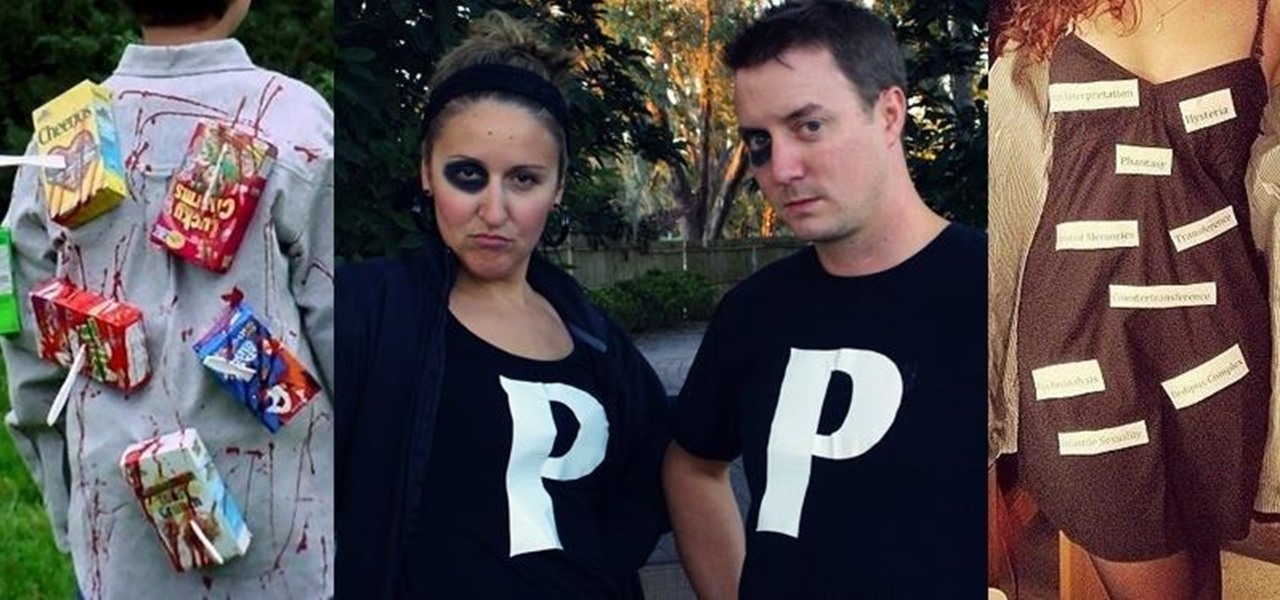

If you haven't come up with a funny, innovative costume yet for Halloween, you're running out of time. While all your friends are busy perfecting their month-long DIY costume project, you're still being lazy about it and have just now started to search online for ideas.
Samsung created quite a buzz when it debuted a built-in heart rate sensor on the Galaxy S5 back in 2014, but amazingly, not many other manufacturers decided to follow suit. It's really a shame, too, since data from a heart rate sensor would go perfectly hand in hand with the increasing fitness- and activity-tracking features that most smartphones sport these days.

Most mobile games have moved to an online-only format, meaning you need to be connected to the Internet in order to get any kind of multiplayer action going. This is great when you're at home on Wi-Fi, but when you're out and about, slow and inconsistent data speeds can cause serious lag. Or worse yet, you may be nearing your monthly data cap!

Before I start this tutorial, no, this is not that "Effective. Power." text that is going around. With that being said, let's talk about this attack.

Whether it's terrorism or brain-hungry zombies you're neutralizing, first-person shooters are an awesome way to immerse yourself within a new world and kill some time with your iPad or iPhone. And with so many games available in this genre, we wanted to show off ten of our absolute favorites.
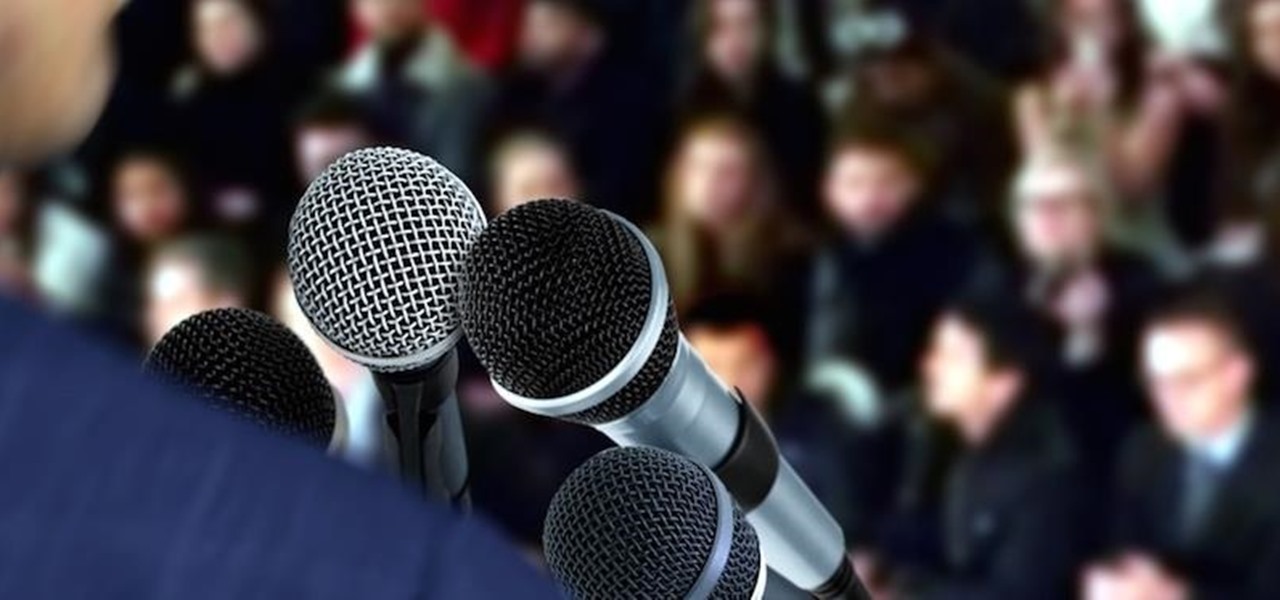

Sweaty palms, stuttered speech, and terror blackouts: if you're someone who absolutely despises speaking before audiences, you've probably experienced side effects like these. No matter how well prepared we are, or how familiar our audience is, giving a presentation can be an experience more terrifying than death, according to psychologists. Unfortunately, it's impossible to avoid public speeches, but you can make these events less frightening with a few simple hacks.
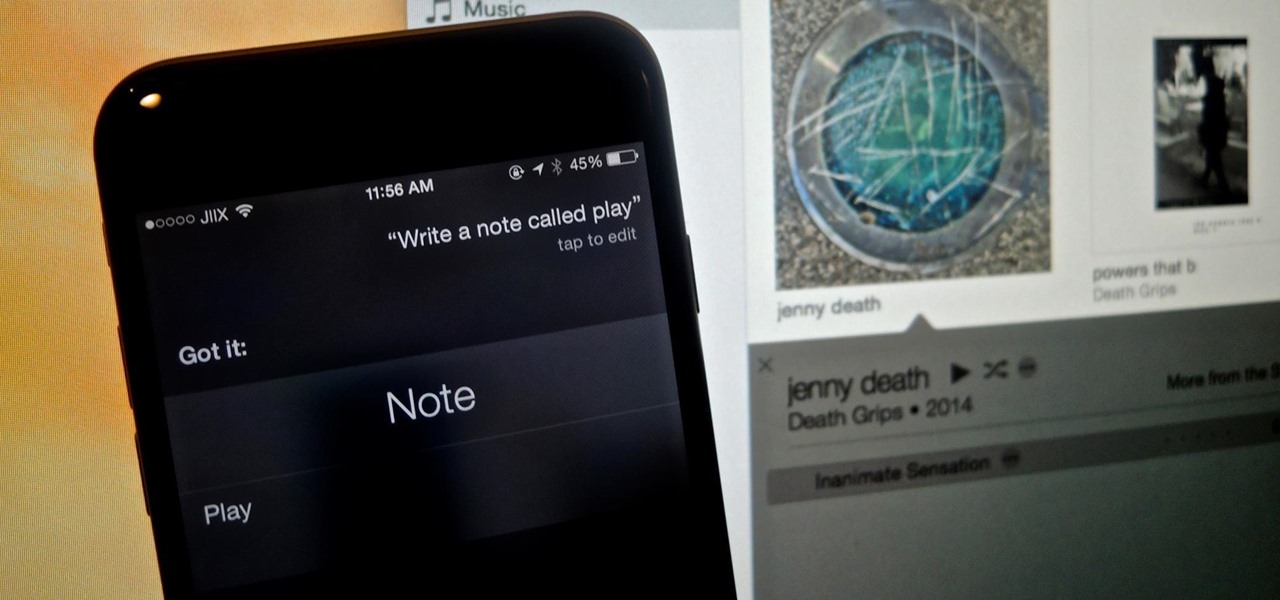
While Apple's Continuity feature has certainly impressed me, I can't help but feel like it could be used to create a better connection between my iPhone and Mac. Sure, Handoff allows me to pick up where I left off in certain applications between the two devices, and it lets me pick up calls and send text messages on my Mac, but I want even more functionality.
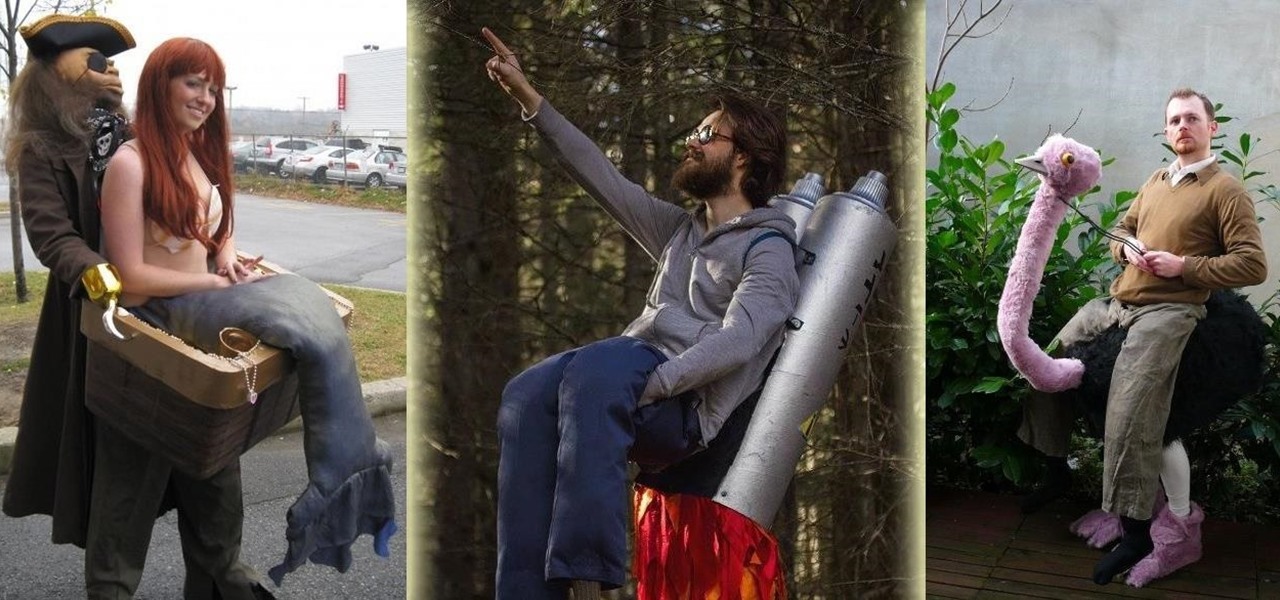

Every year, some overly ambitious neighbor down the street amazes the crowds with his DIY illusion costume. While these costumes certainly require more work than pulling a mask over your head, they do have that wow factor that others lack.
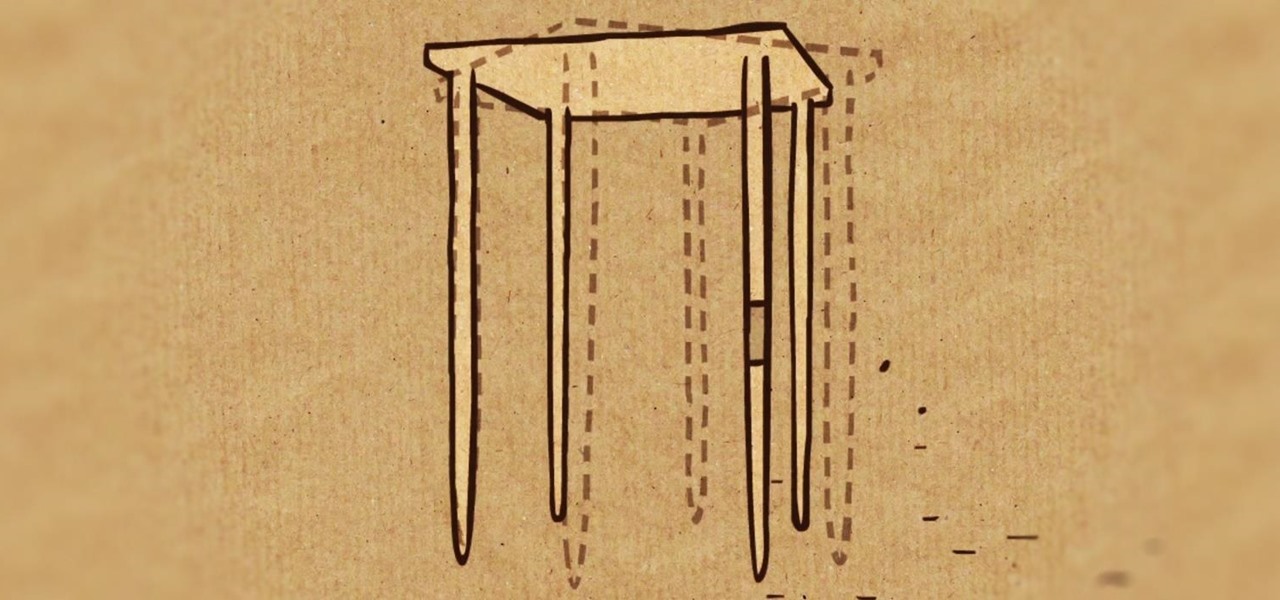
As sure as death and taxes, sitting at a wobbly table at one time or another is inescapable. With your weight on it, the table shifts from one end to the other, lifting one leg in the air and then the other; a parade of seesaws, especially if you have someone sitting on the other end.
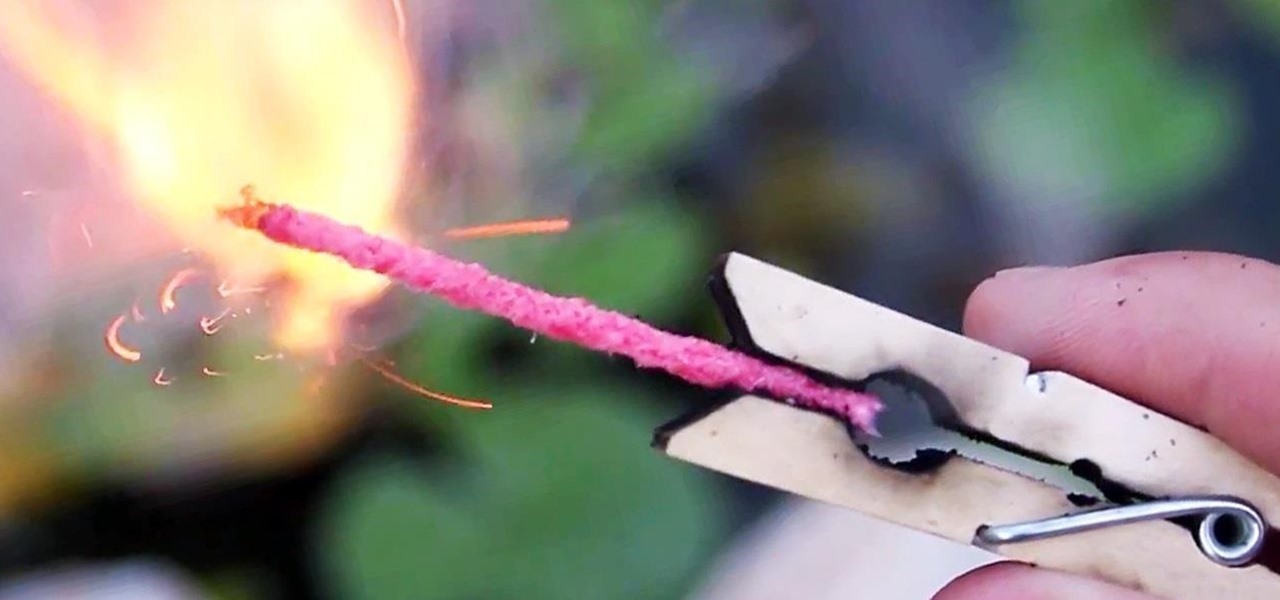

The big fireworks day is almost here, but most of you are limited in what you can do when it comes to celebrating the Fourth of July with a bang. Unless you live in a dry area prone to wildfires, one type of fireworks you can probably still legally buy are sparklers.
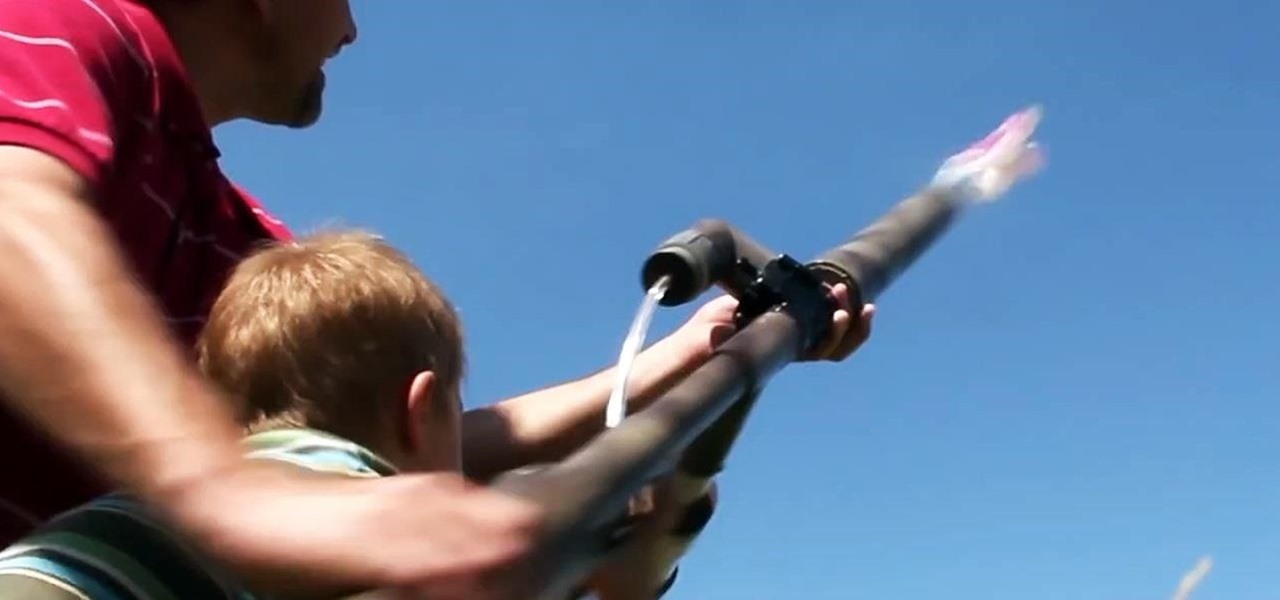

This summer's going to be a hot one, so skip the water pistol this year and break out the big guns! In this project, I'll be showing you how to build a water balloon shotgun—a high-powered water balloon launcher that's capable of firing 17 water balloons at the same time!
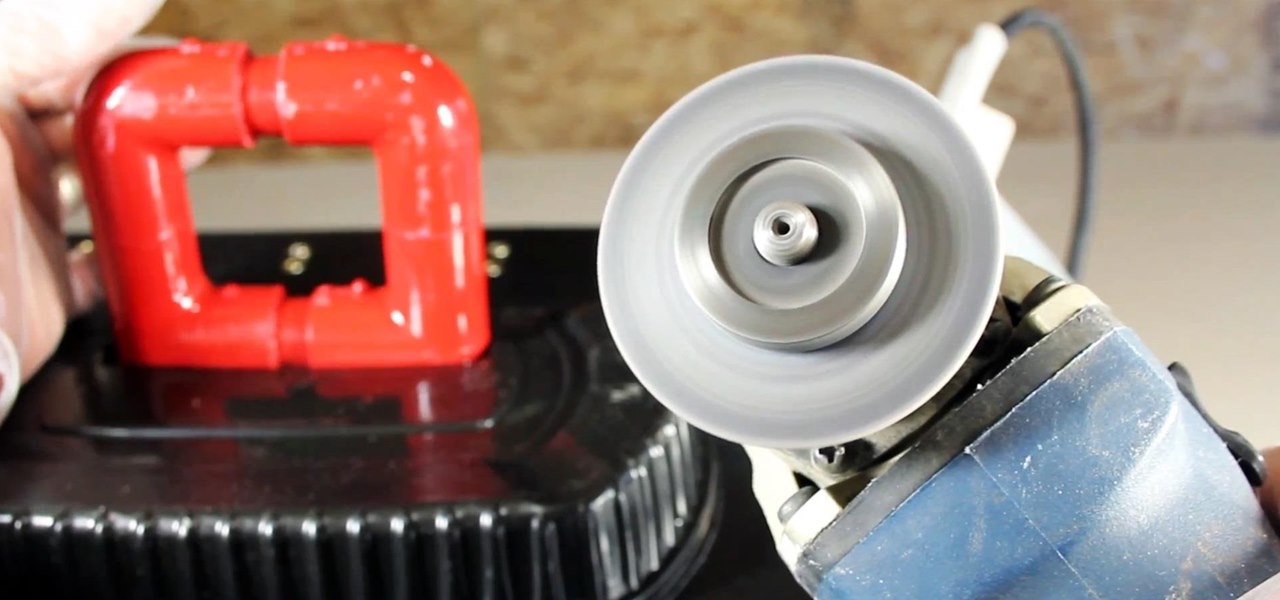

Mixing water and electricity is extremely risky and potentially lethal, yet that's exactly what I did with the Scariac. In its simplest form, the Scariac is just a glorified version of two wires in a bucket of water, but it's actually one of the cheapest power controllers you can make.
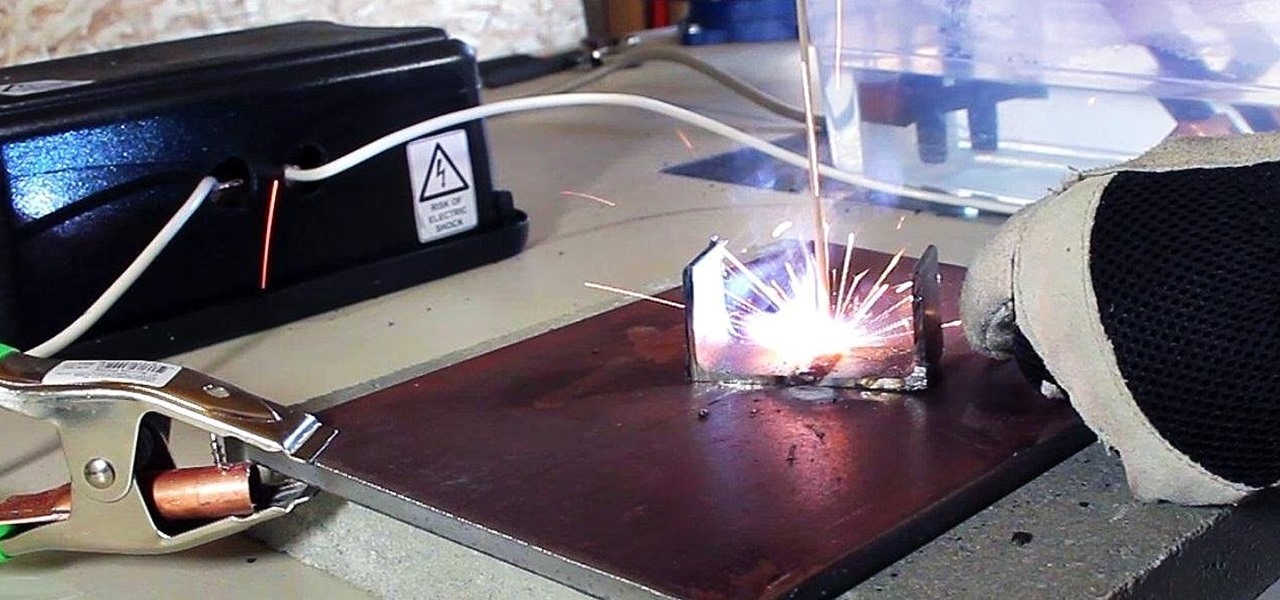
In a previous article, I demonstrated an Arc Welder made using parts from old microwave ovens. Video: .
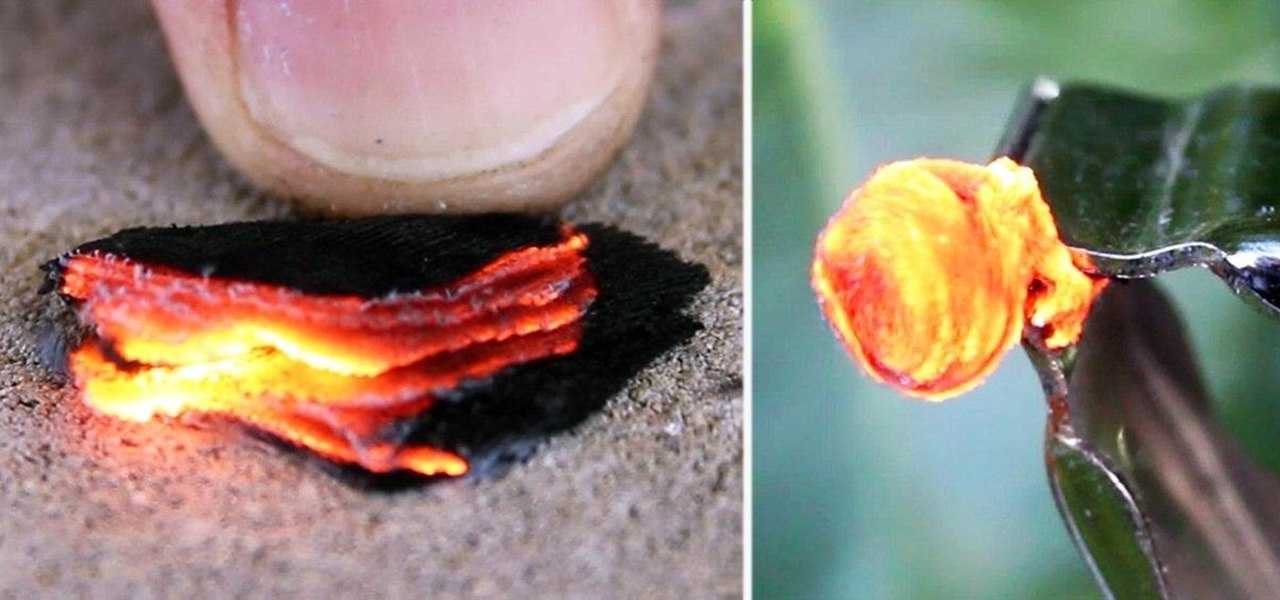

For this project, I sacrificed some of my kids' clothes and a can of tuna to make some high-quality fire starter! Here's how to make a great batch of char cloth to add to your emergency survival kit.
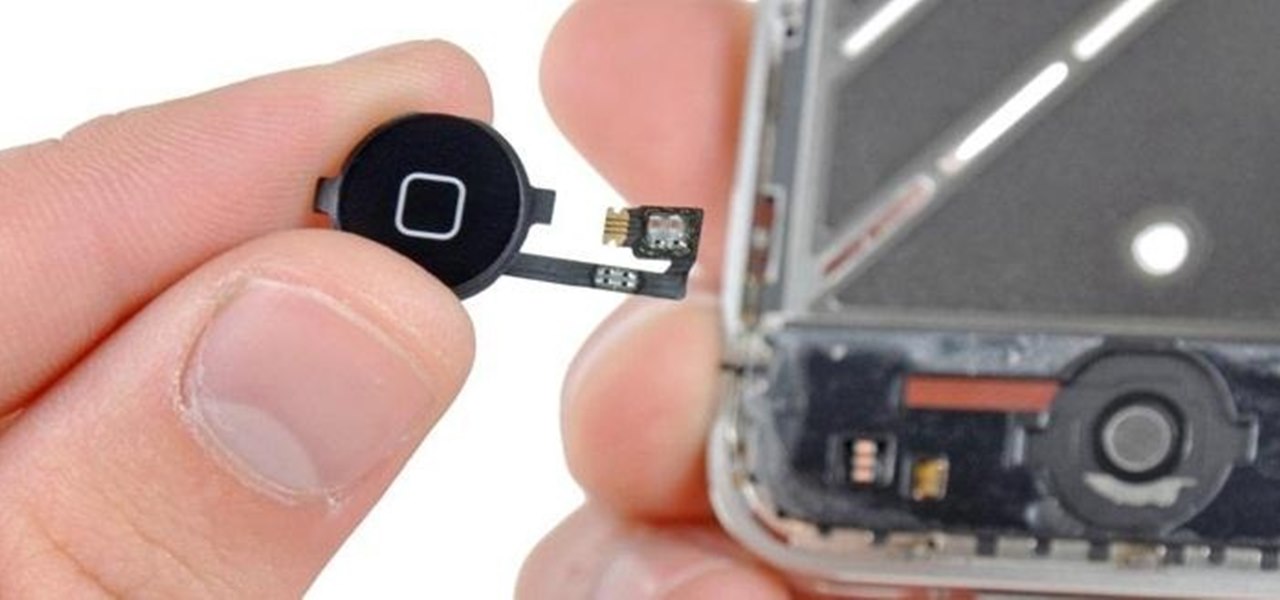

When a phone has only one main button, it can be pretty frustrating when that one button doesn't really work anymore. If you have an iPhone 4 or 4S, you know exactly what I'm talking about. Yep, the Home button, which is prone to unresponsiveness and lag. Most users blame the Home button issues on either dirt, moisture, or misalignment. No matter what the reason, having a busted Home button sucks, especially for those of you no longer under warranty. But that's okay, because there are a few t...
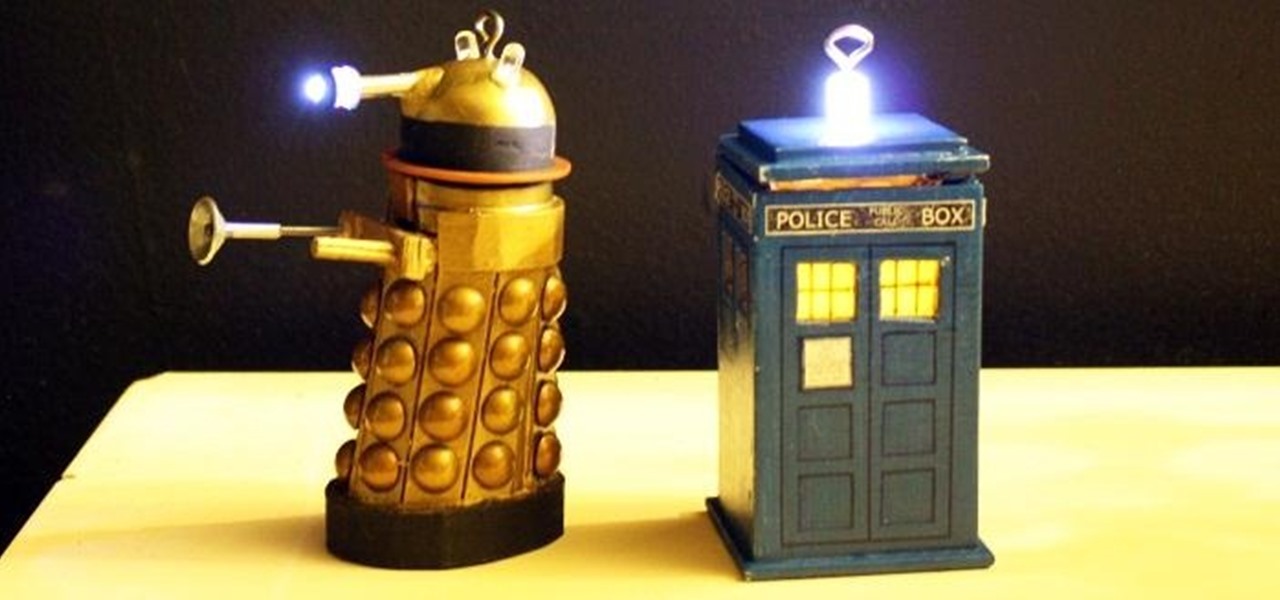

One of the more enjoyable parts of Christmas (other than opening gifts of course) is going out to find the perfect tree, struggle bringing it into the house, and decorating it. As the years went by, I realized that our tree looked exactly like every other tree in the neighborhood: the same lights, the same angel at the top, and the same red, green and white ornaments.
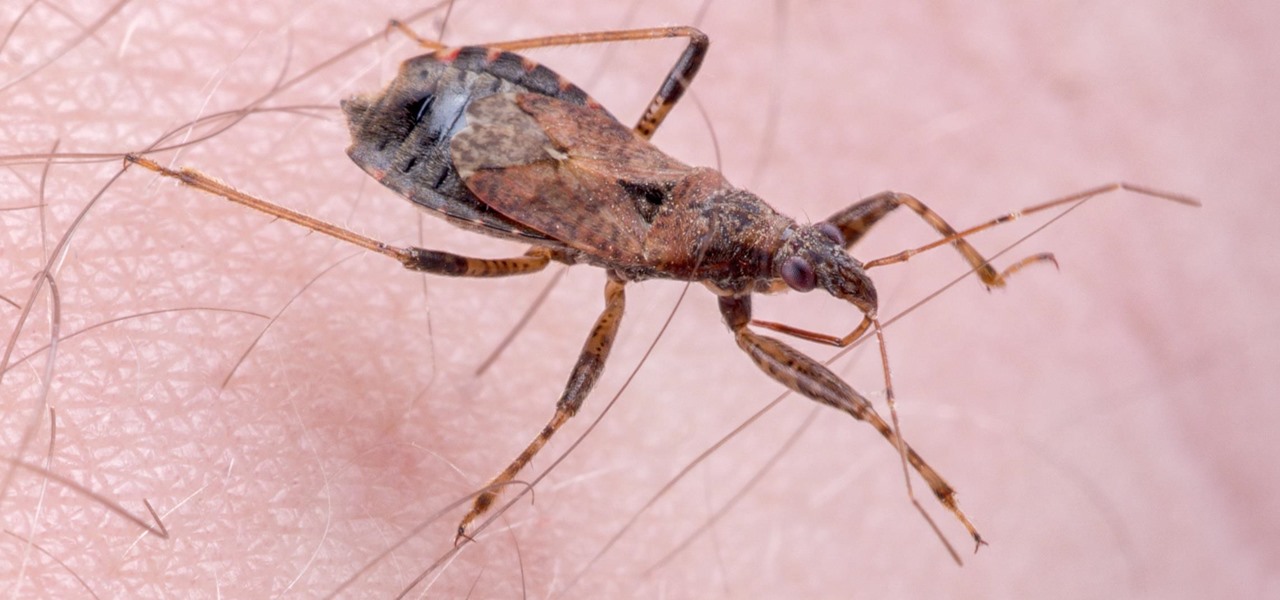

You may not have heard of visceral leishmaniasis, onchocerciasis, or lymphatic filariasis, and there is a reason for that. These diseases, part of a group of infections called neglected tropical diseases (NTDs), impact more than a billion people on the planet in countries other than ours. Despite the consolation that these often grotesque illnesses are "out of sight, out of mind," some of these infections are quietly taking their toll in some southern communities of the US.

While the Apple Watch does have up to 18 hours of battery life each day on a full charge, your results will vary depending on how often you use it and what you're actually doing with it.
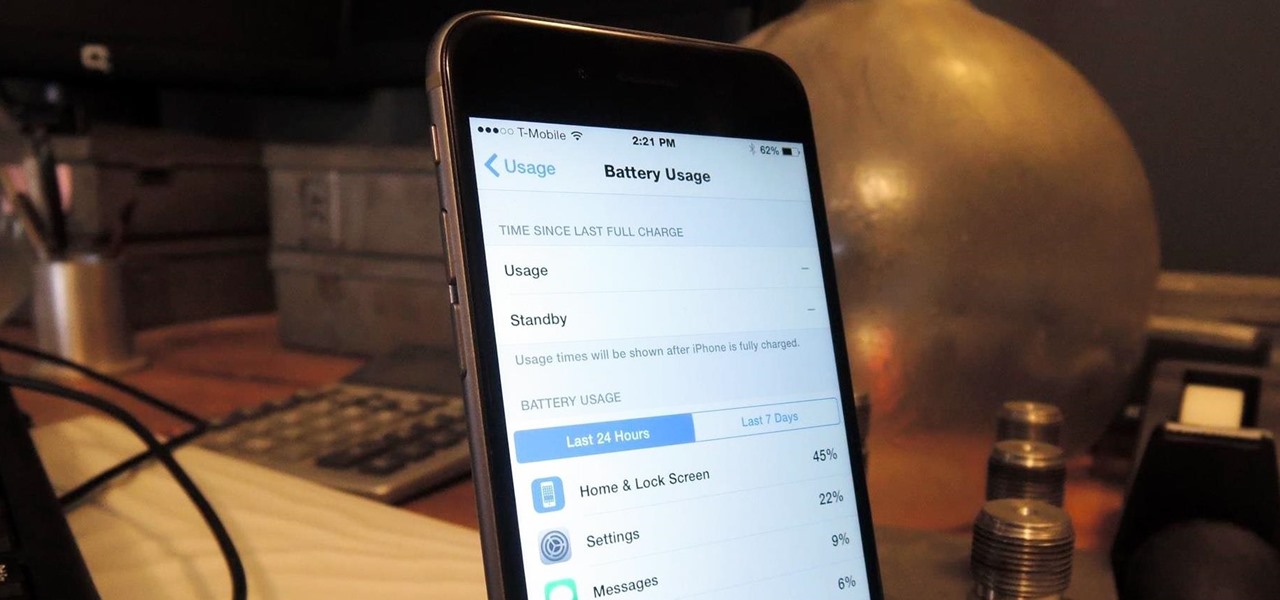
The new iPhone 6 and 6 Plus are supposed to last a lot longer in your pocket with improved battery life, but that doesn't mean that iOS 8 will be that friendly on your older iPhone model. All of those awesome new features could be killing your battery, but with some simple tweaking, your battery life concerns will be a mere afterthought.

Wireless emergency alerts help warn mobile phone users of imminent threats to life or property, such as extreme weather and natural disasters. These alerts target affected geographic areas and come with a loud sound scary enough to make you want to turn off emergency alerts altogether on your iPhone, but there's a way to keep emergency alerts without the ear-splitting, intrusive sound.
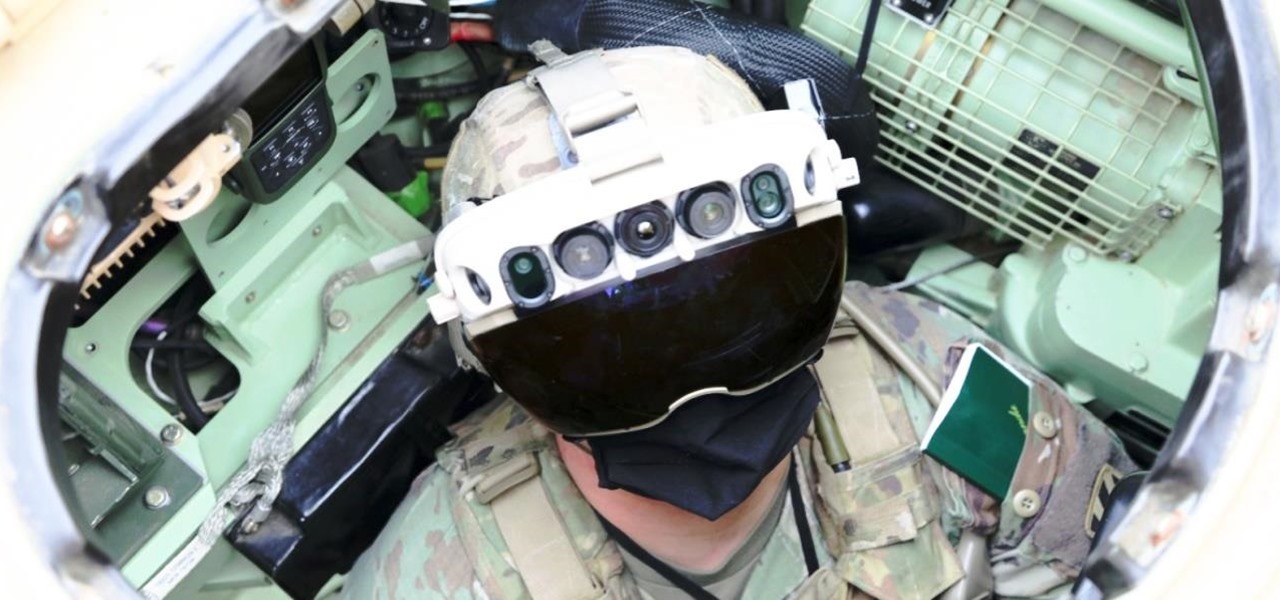

It's all fun and games until the technology is actually put into use and you realize augmented reality is now part of Death Star.
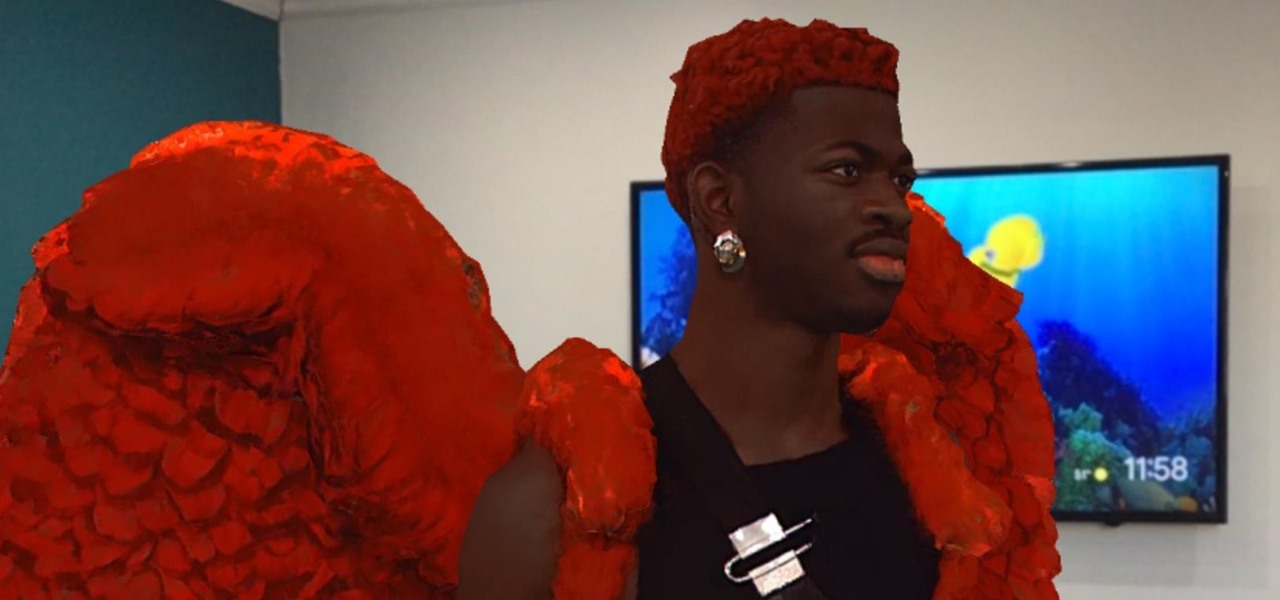

Who had Lil Nas X, blood-drop Nikes, and satan worship on your 2021 bingo card? In a story that's stranger than fiction, the "Old Town Road" rapper has ruffled some feathers with the video for his new single, "MONTERO (Call Me By Your Name)" filled with demonic imagery usually reserved for death metal bands.
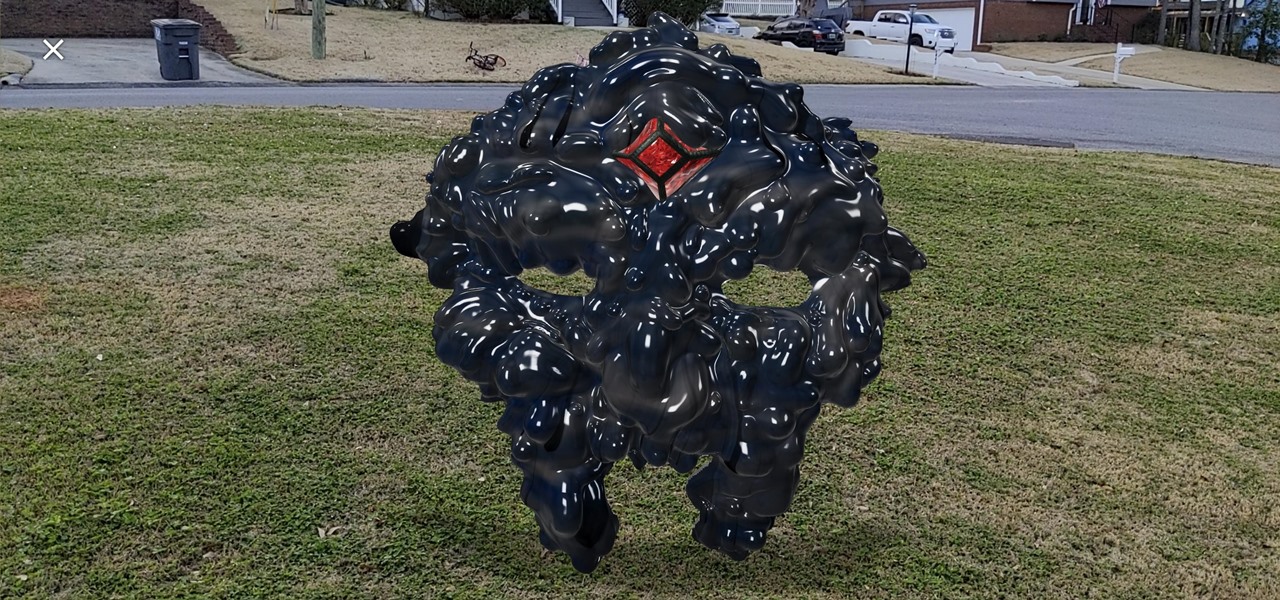

The hype surrounding non-fungible tokens (NFTs) has reached astronomical levels over the past few weeks, and now the technology has intersected with augmented reality's orbit in a fantastic way.

GameGuru was created for game enthusiasts who are not programmers or designers. By offering catalogs with thousands of royalty-free assets, GameGuru lets design novices bring their visions to life.

Staying inside during the coronavirus pandemic isn't easy for most of us. As important as it is to keep away from others, it can be challenging to keep to ourselves day after day. That's why mobile game developers are stepping in to help; many are making their games free for a limited time, to provide some much-needed fun during scary times.
There are times when leadership is tested. This is one of those times. As government and business leaders around the world are grappling with the unfolding coronavirus pandemic, the real-time responses to the crisis from many leaders have been great and, at times, less-than-optimal.

So you've been playing Call of Duty Mobile for some time but can't seem to get MVP at the end of the battle. Well, since the game is a competition of players and bots, you're in an uphill battle. But you don't have to languish at the bottom. With the help of these tips, you might just nab your first MVP.

With the announcement of ARKit 2.0 at WWDC 2018, Apple is bringing some powerful new capabilities to mobile augmented reality apps this fall.
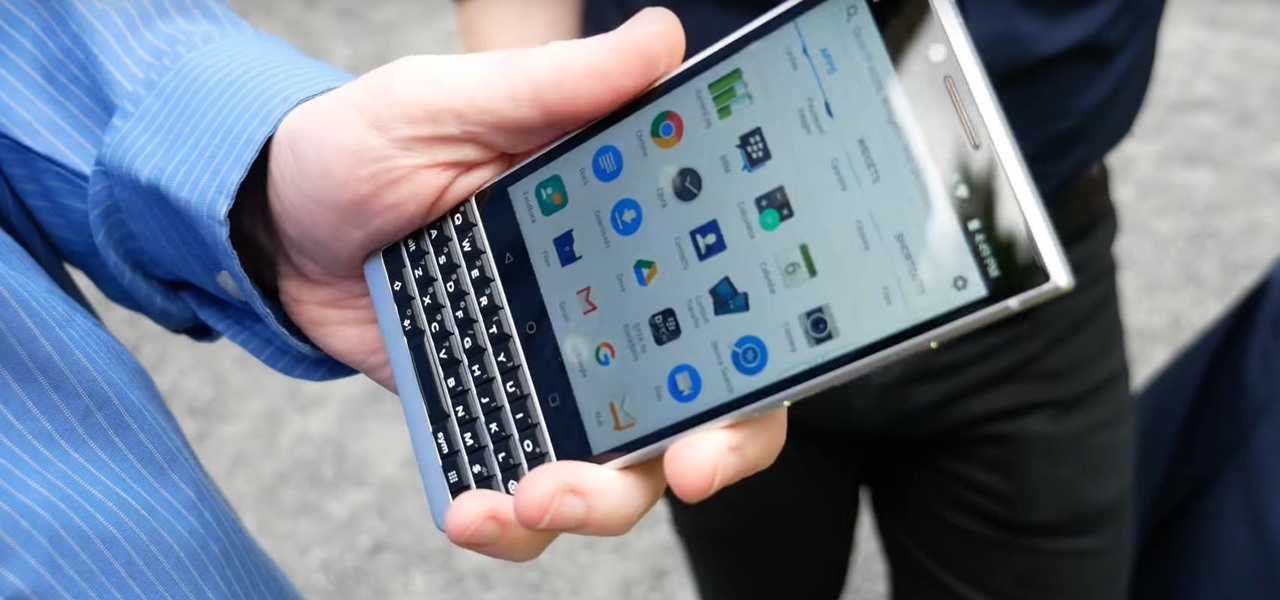

After years of struggling, it appears BlackBerry has finally figured out how to update its iconic design for modern times. The BlackBerry KEY2 pays homage to past devices such as the Bold 9000 while adapting to modern times with the Android OS. The result is a device that might be the best BlackBerry to date.
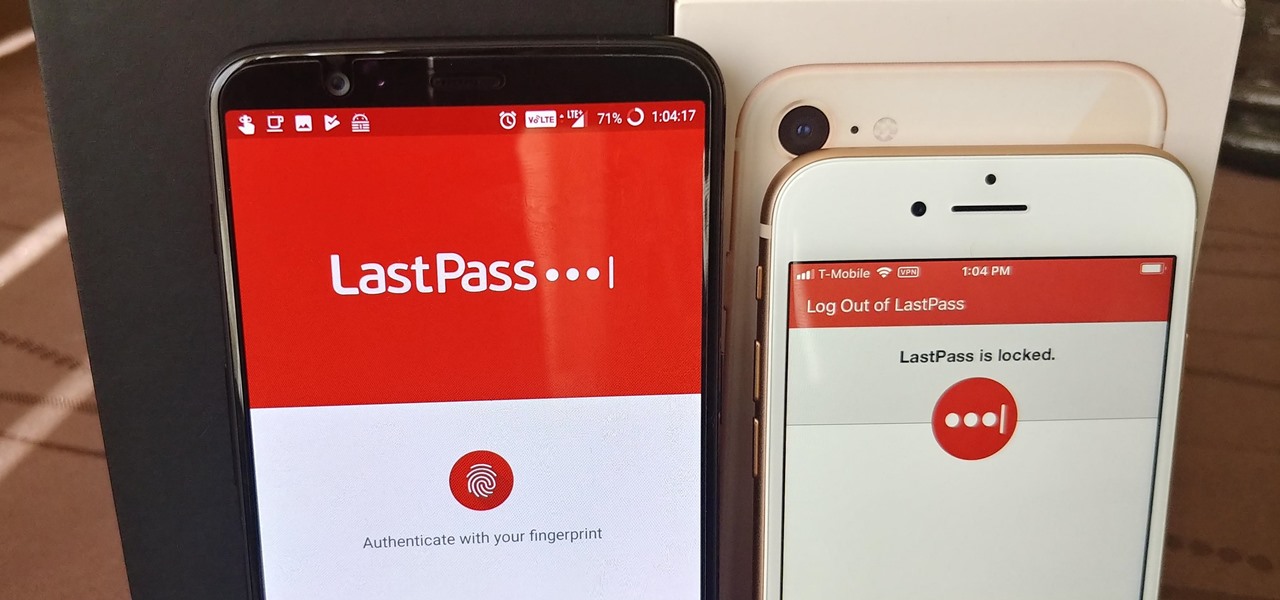
When traversing the web, you'll regularly come across websites that require you to create an account. With the majority of these accounts, protection is limited to a simple password. Despite this, many people are still using weak passwords such "123456." For these reasons, you really need a password manager, and our research has shown that LastPass is still your best bet.
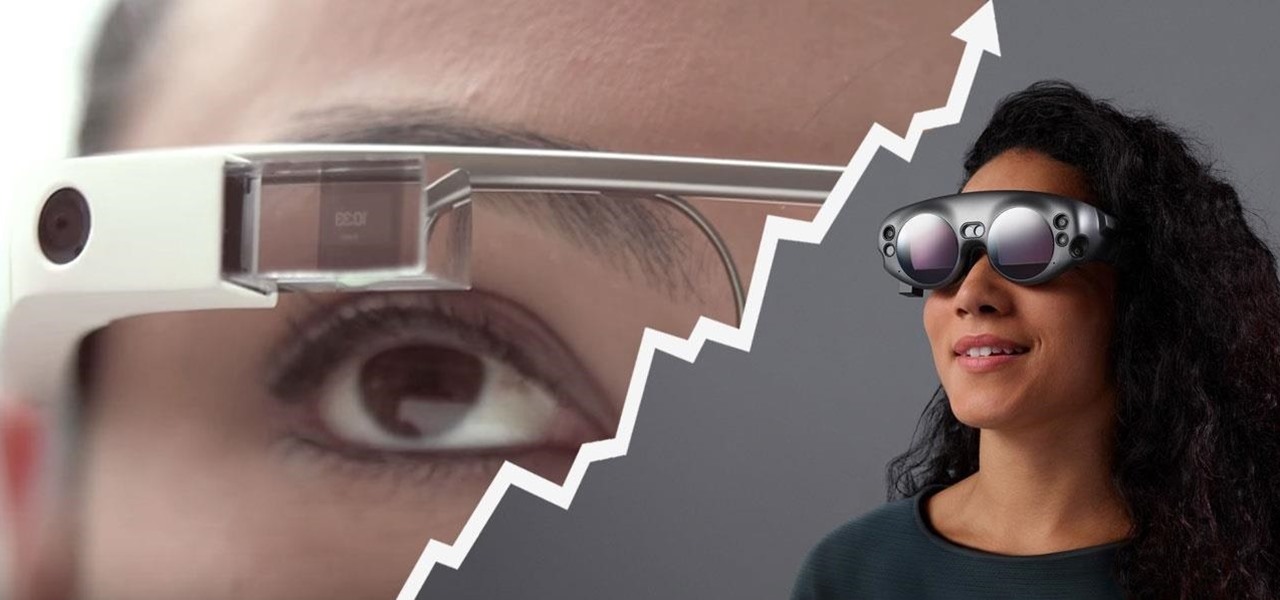

The reveal of Magic Leap One: Creator Edition brought with it some insight into the path the device took from prototype to "final" design.
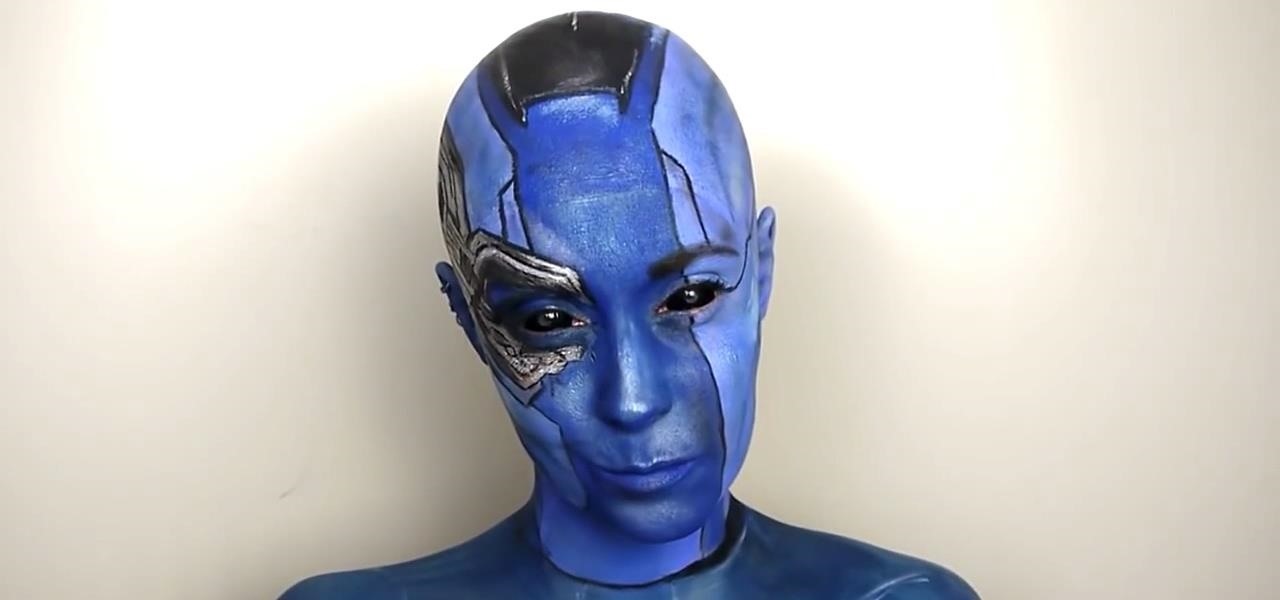

Karen Gillan must have had an absolute blast chewing the scenery as Nebula in Guardians of the Galaxy Vol. 2, seeing as how Nebula is a ball of pure, seething fury pretty much 24/7. Combine that larger-than-life personality with her iconic blue and silver cyborg look, and you have a guaranteed hit for cosplay or Halloween.

If you have a taste for sweets, you have at least one thing in common with mosquitoes. While too much sugar is unhealthy for humans, a new product makes sweets deadly to mosquitoes.
Whether or not a microbe is successful at establishing an infection depends both on the microbe and the host. Scientists from Duke found that a single DNA change can allow Salmonella typhi, the bacteria that causes typhoid fever, to invade cells. That single genetic variation increased the amount of cholesterol on cell membranes that Salmonella and other bacteria use as a docking station to attach to a cell to invade it. They also found that common cholesterol-lowering drugs protected zebrafi...
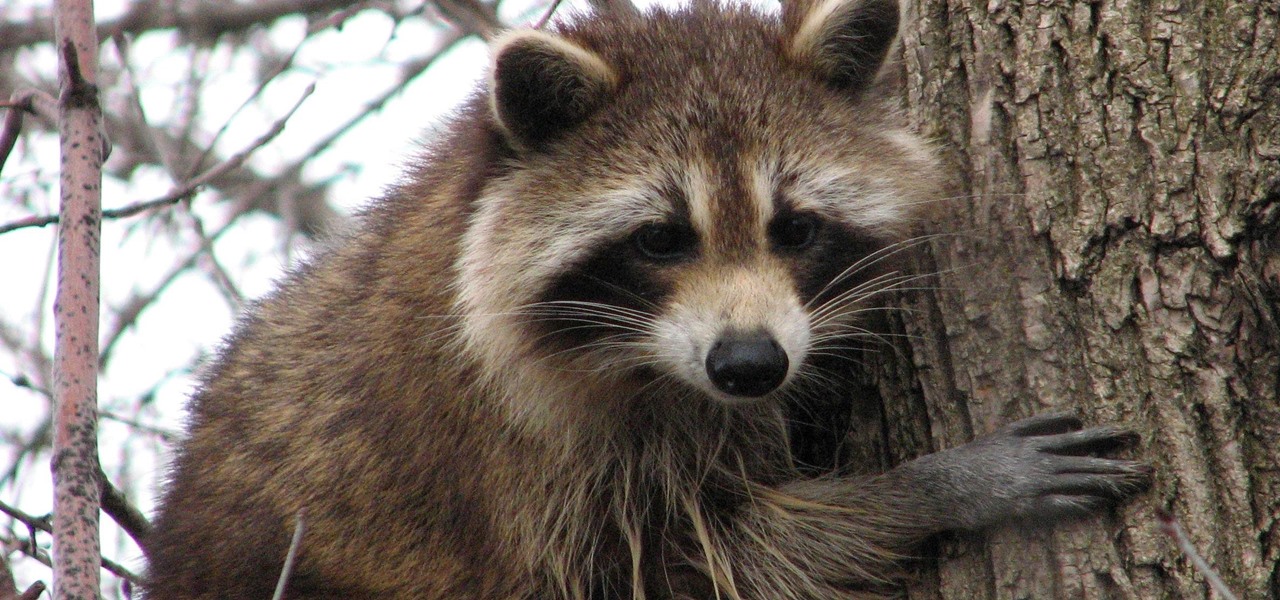

So cute, so furry, and so chock full of parasites. While raccoons are fun to watch, they are neither friendly nor clean — and they can make you sick in more ways than one.
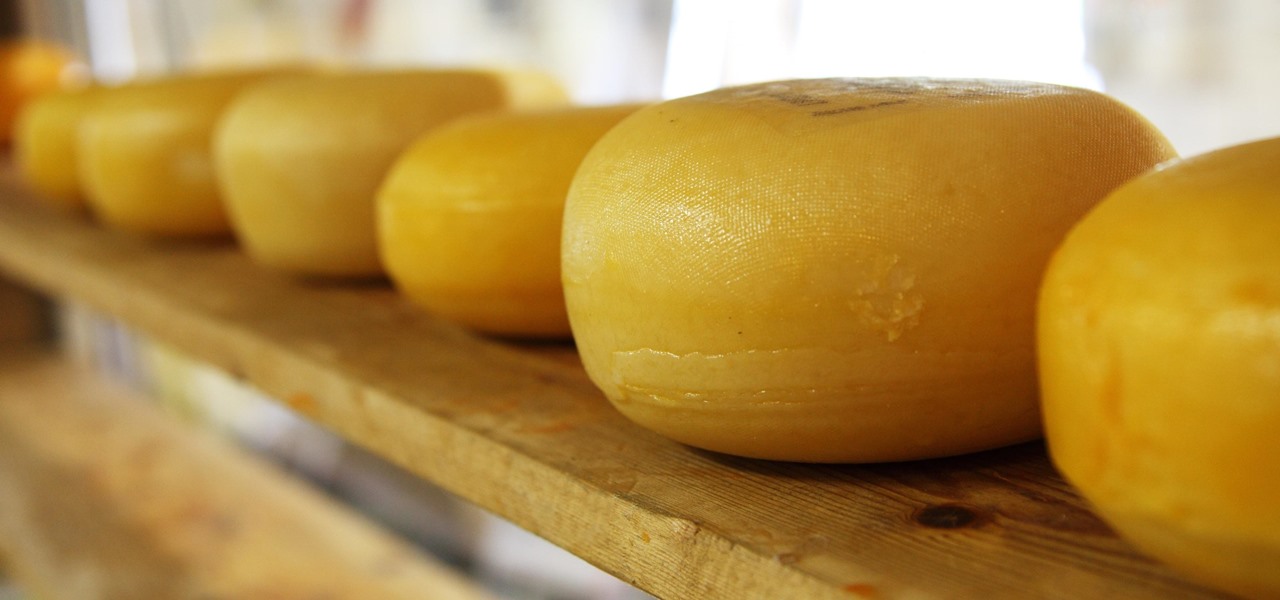

Whether your palate runs to domestic or imported, a piece of cheese can be a real treat for the senses. Its smell, taste, and texture are all parts of its appeal. A big part of what makes that savory wonderfulness comes from the microbes in and on the cheese. Thanks to a team of researchers dedicated to studying those microbes, we have a better understanding of their importance to cheese and us.
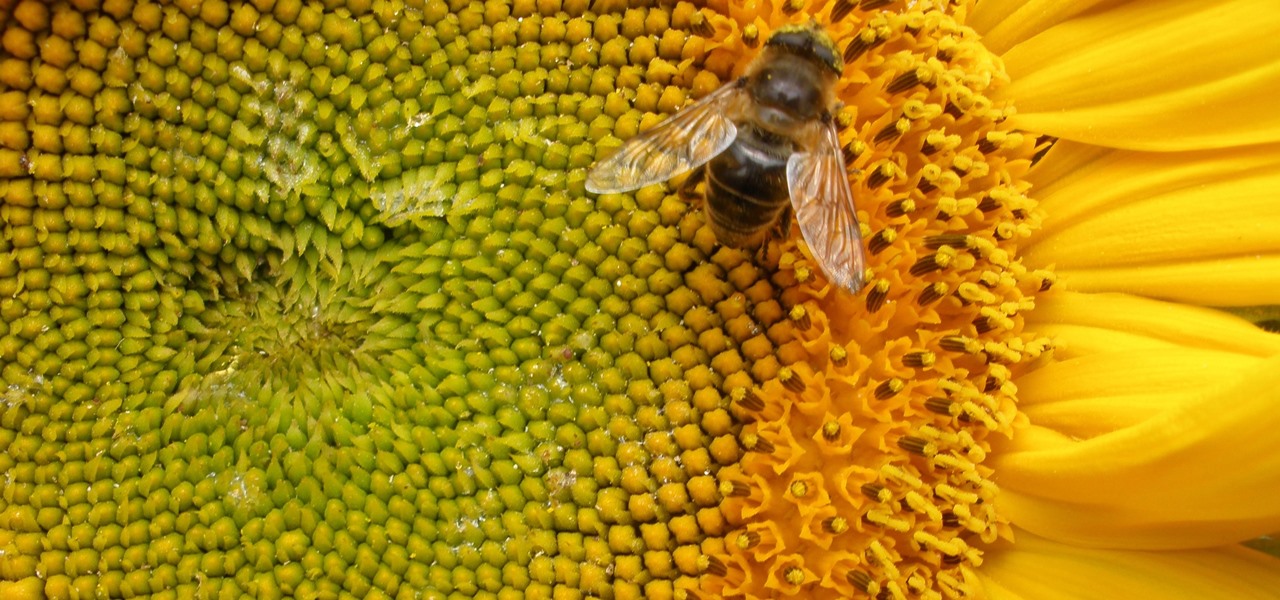

By connecting the dots between theory and real-life effect, two new studies offer more proof that neonicotinoid insecticides are causing extensive damage to honeybee colonies.
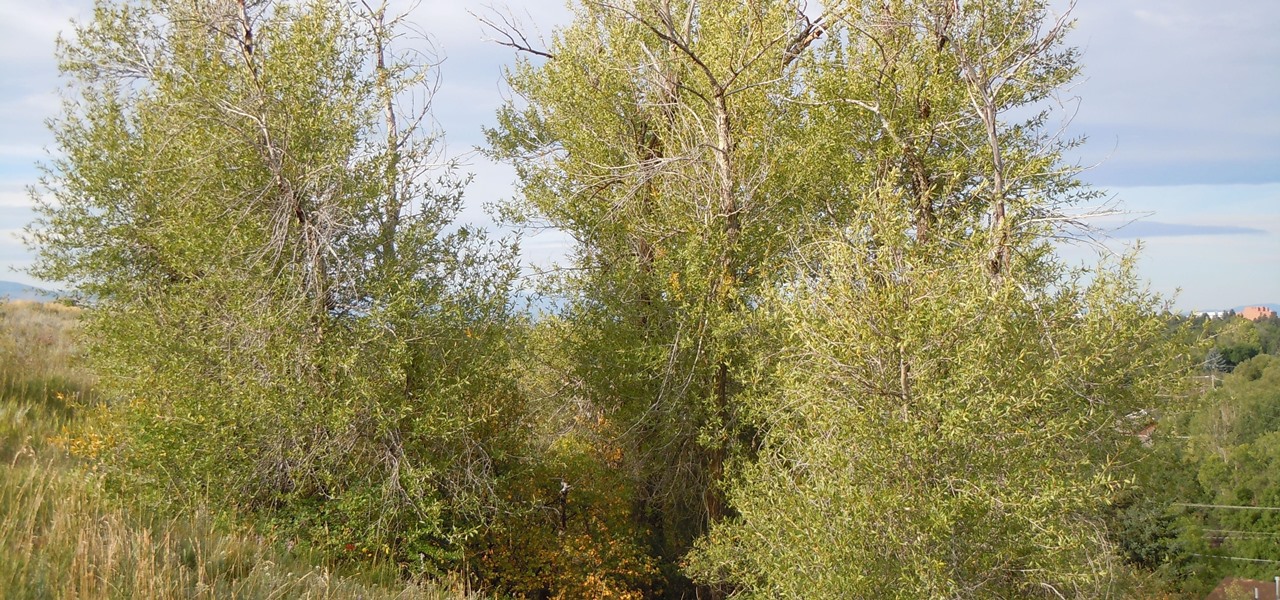

The future of forests looks dreary in the face of a warming climate, but scientists are exploring the relationship between soil microbes and the ability of trees to move to higher altitudes, a key component of their survival.
HIV-infected people who are treated long-term with antiviral drugs may have no detectable virus in their body, but scientists know there are pools of the virus hiding there, awaiting the chance to emerge and wreak havoc again. Since scientists discovered these latent pools, they have been trying to figure out if the remaining HIV is the cause of or caused by increased activation of the immune system.