Unless you've been living under a rock for the past few weeks, you're probably well aware that the Android world has been buzzing with excitement over the recently debuted Android L preview build that was released for the Nexus 5 and Nexus 7 at Google's I/O conference.

Downgrading your iPhone from iOS 8 beta back to iOS 7.1.1 is a really simple process, and a very necessary one if you're experiencing frozen screens and apps that either unexpectedly quit or don't even work at all.

Welcome back, my greenhorn hackers!
Currently in its alpha stage, Facebook has pushed forward a redesigned mobile app for Android users that provides a flat user interface and rearranged navigation tools.

While still extremely awesome, the Samsung Galaxy Gear smartwatch is limited as to what you can download on to it, especially apps. It also doesn't have its own internet access (only Bluetooth), so apps like Instagram, Facebook, and Vine have yet to make their way to the Gear Store.
With the release of iOS 7, the entire Internet was abuzz with what's the exact opposite of excitement as Apple's servers were overloaded, causing many download fails of the new operating system. Since then, many other bugs and issues have arisen that are fairly common with new Apple software updates, like iMessage fails and wallpaper complaints (to only name a few).

The transition from an iPhone to a Samsung Galaxy Note 2 or other Android device can be a tough one. A vastly different operating system and the ability to customize anything and everything might be too much for some people. Taking in all that new, while having to let go of the old, can be as daunting as climbing Mount Everest.

Hello! This post is not about craft, it's about cyber bullying. If you ever had such an experience, that an unknown hacker was bullying you for no reason at all, please follow my words. Thank you! Step 1: Let All the People You Know That Your Are Being Harassed.

Dyeing your hair is a great way to change your look. But if you don't do it right, the results can be pretty ghastly. If you seek a new do without the harsh chemicals, these steps will give you the locks you’ve been looking for.

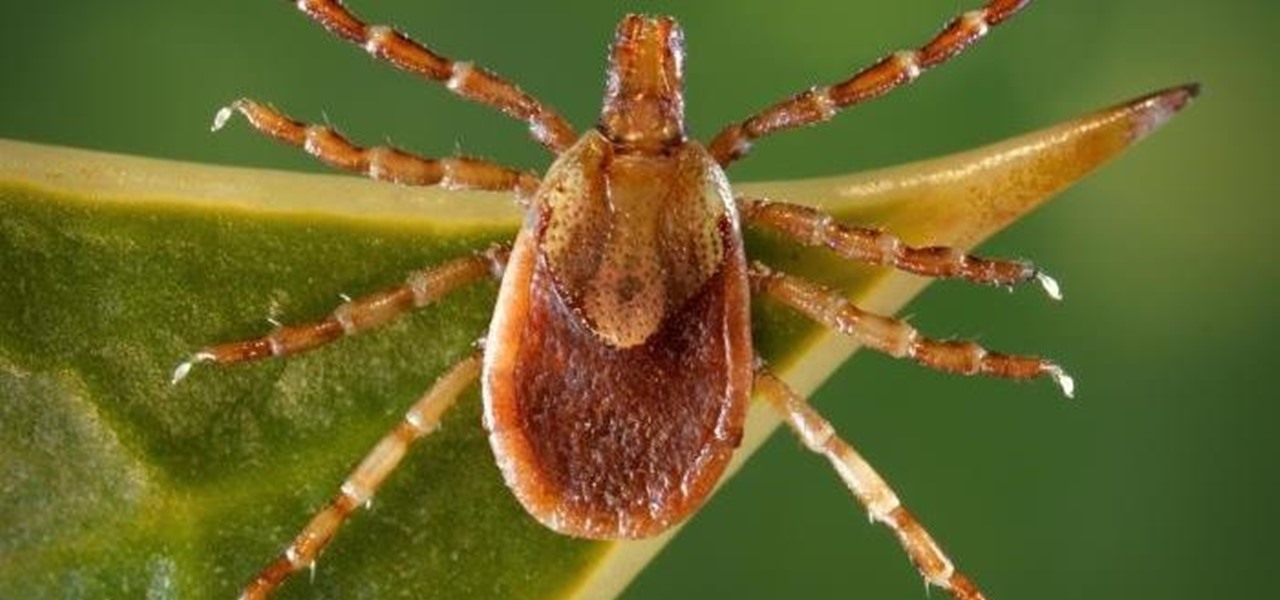
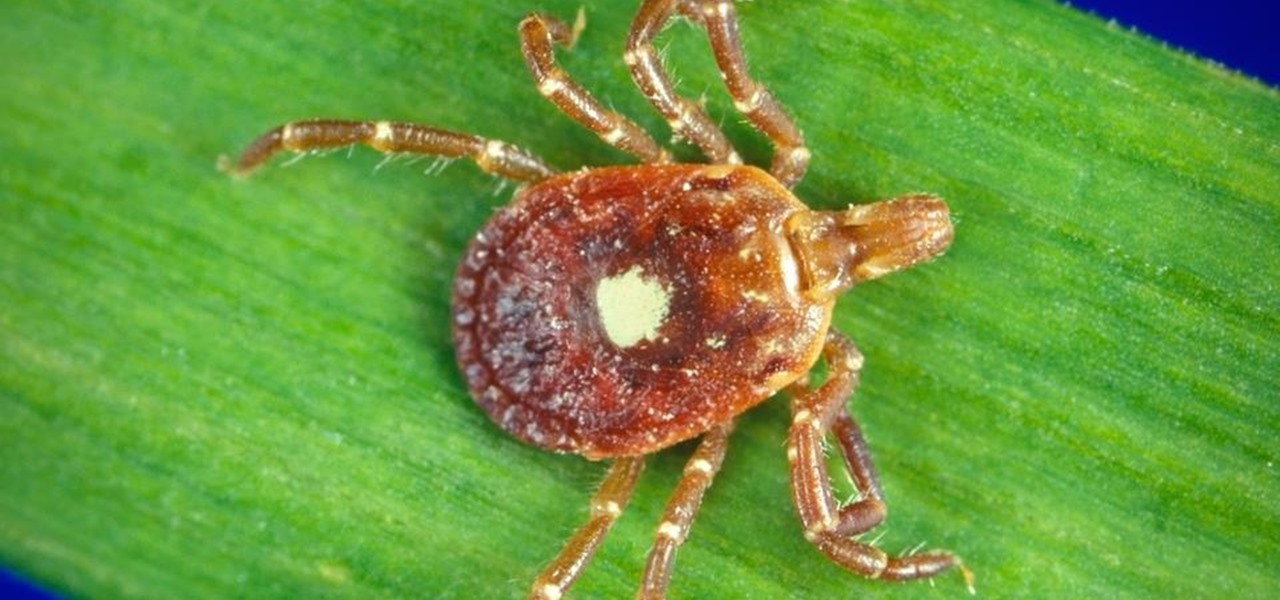
Tick bites should be treated immediately, the concern being transmission of Lyme disease. If you've received a tick bite, what you should do is to remove the tick promptly and carefully. Use tweezers to grasp the body of the tick near its head and pull out very gently to remove the tick whole without crushing it. Learn more about tick bites and how to treat them in this medical how-to video.

What is a cataract? A cataract is the clouding of that internal lens of the eye which is normally clear. That internal lens helps focus light as it comes through the pupil that when a lens starts becoming a little cloudy, patients sometimes complain that their vision seems a little foggy. There are certain risk behaviors that you can avoid to reduce the risk of getting cataracts. Get professional tips and advice on cataracts in this medical how-to video.

Afraid to wear black because of your dandruff problem? There are many ways to cure dandruff so don’t give up hope. Try the home remedies and if you need to there is always medicated shampoos for the problem.

Another name for jumper's knee is patellar tendinitis. Jumper's knee is an injury that affects the tendon connecting your kneecap (patella) to your shinbone. The patellar tendon plays a pivotal role in the way you use your legs. It helps your muscles extend your lower leg so that you can kick a ball, push the pedals on your bicycle, and jump up in the air. Learn about the different causes of, symptoms of, and treatments for jumper's knee in this video.

In mid-2021, TikTok rolled out three-minute videos, but it's not stopping there. The company is rolling out a feature that will let you record up to 10 minutes in a single TikTok video — only the update hasn't appeared for everyone yet.

The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic caused by the novel coronavirus has practically guaranteed that the virus, along with the phrases "social distancing" and "flattening the curve," will rank among the top search terms of 2020. USA Today combined the phrases in its latest augmented reality experience, which quizzes your knowledge in the best practices of social distancing.

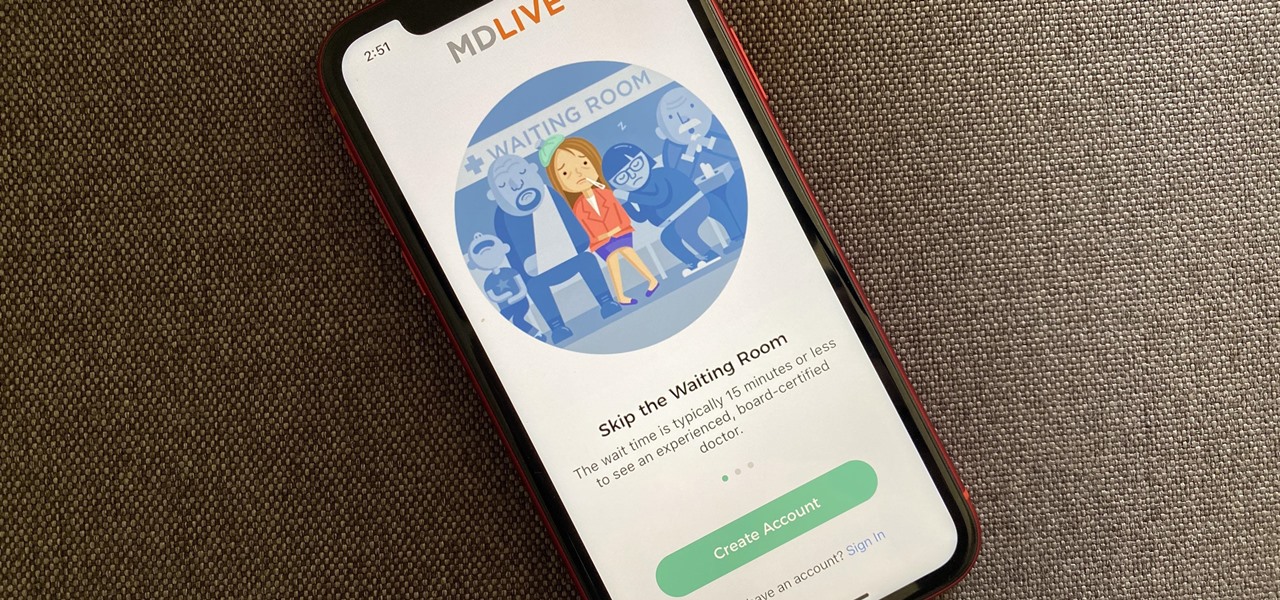
The World Health Organization has declared the new coronavirus a pandemic, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends video visits with a healthcare professional to reduce the risk of being exposed to the coronavirus that causes COVID-19. If you are experiencing mild flu-like symptoms, virtual doctor visits may also prevent you from endangering others.

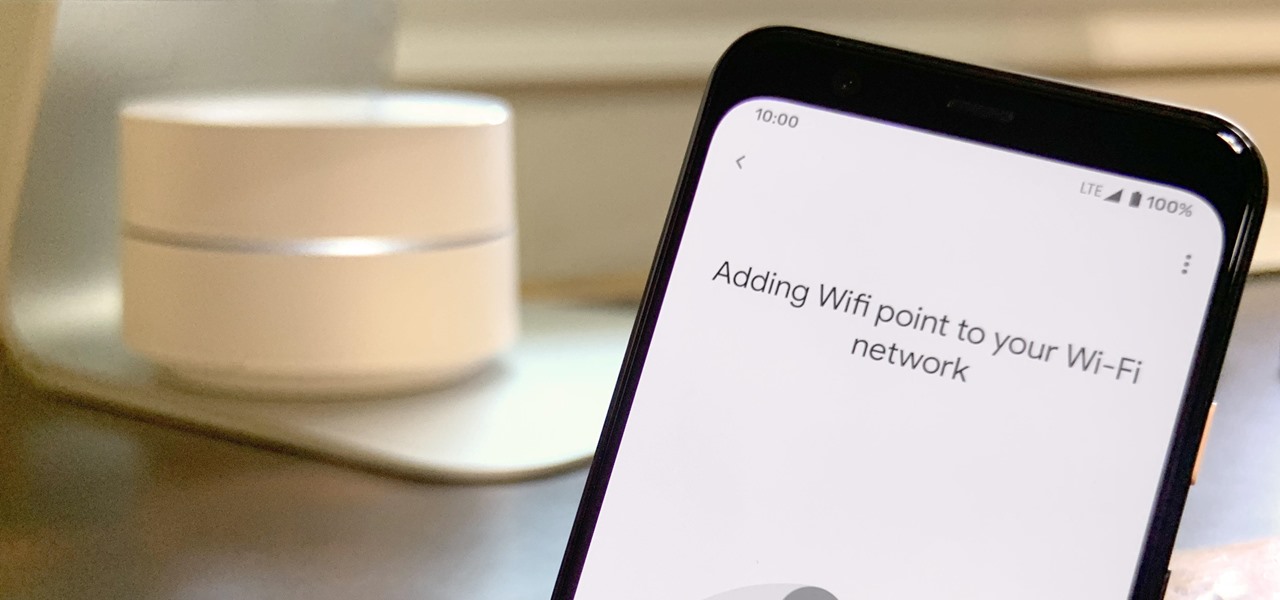
Google is known for merging older products into a new one's ecosystem for ease of use. The transition can take time, and that's the case with the old Google Wifi system now that Nest Wifi is out. Google is working on phasing out the dedicated Google Wifi app in favor of using the Google Home app for all your IoT needs.

Android 11 won't be available as a beta update for Pixel devices until May 2020. Until then, the only way to try the latest Android version is by manually installing it. Usually, this means carrier models are left out since their bootloaders are locked, but there's still a way to get it done.

Websites are often misconfigured in ways that allow an attacker to view directories that are not ordinarily meant to be seen. These directories can contain sensitive information such as private credentials or configuration files that can be used to devise an attack against the server. With a tool called Websploit, hackers can scan targets for these hidden directories without difficulty.

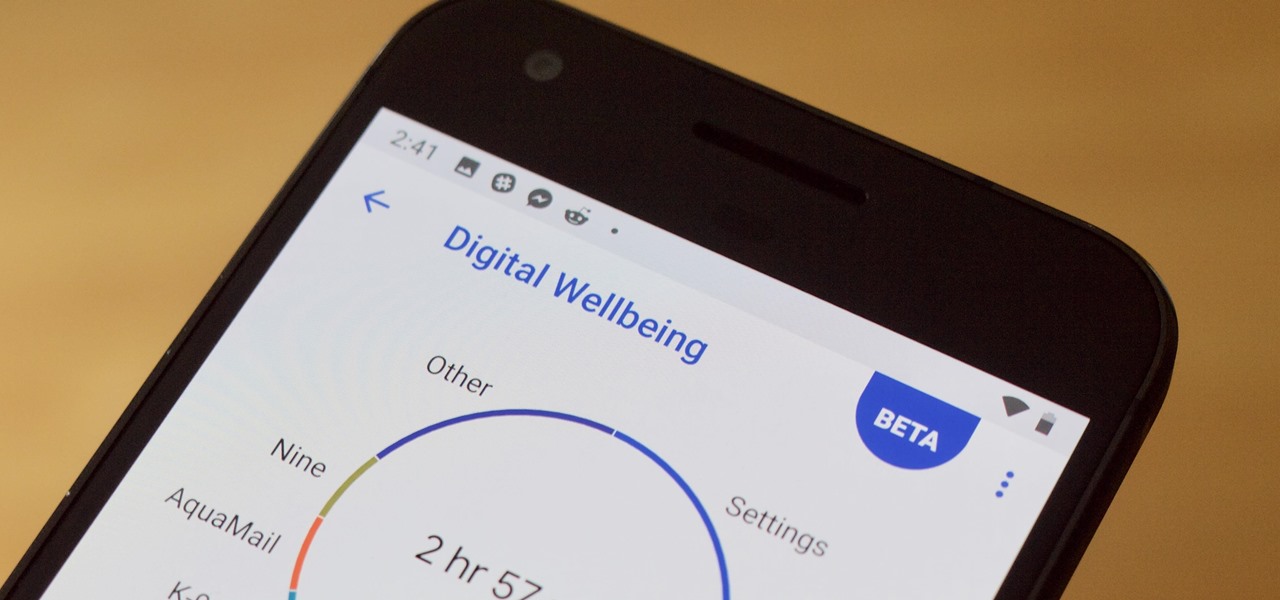
Is your smartphone taking over your life? Do you need help putting your Pixel down at night? Well, update to Android Pie! Android 9.0 comes with Digital Wellbeing, a new tool to both help you understand your smartphone habits and perhaps step away from the apps, games, and notifications every now and then.

As Magic Leap prepares to ship the Magic Leap One later this year, the company is putting its focus on mentoring developers and creators to build a content ecosystem for the spatial computing platform.

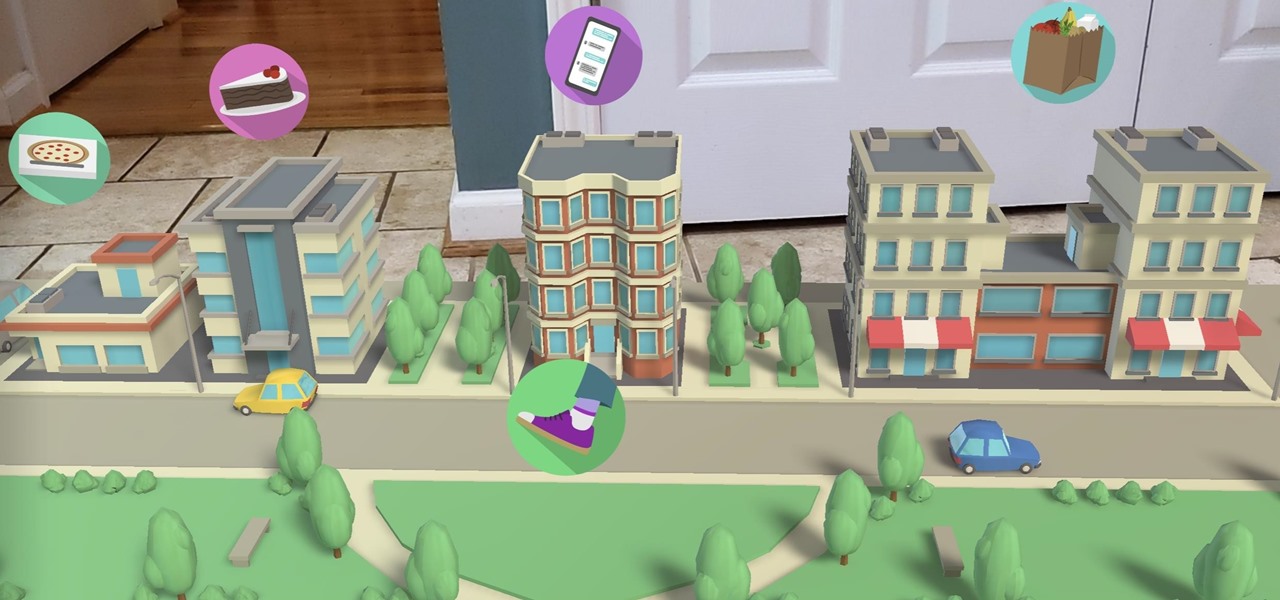
This week, we're beginning to see the wide ranging impacts of some of the early iterations of augmented reality hardware and software.

As expected, Apple began pushing out the final version of iOS 11.2.5 to all iPads, iPhone, and iPod touches today after 41 days of beta testing. Highlights include a fix for the ChaiOS vulnerability, a persistent Now Playing bar in Music, and some signs of AirPlay 2 just in time for the HomePod launch on Feb. 9.

A recent initiative by the Cherokee Nation American Indian Tribe delivers a success story for knocking out a silent killer — Hepatitis C.

A recent study offers information that might help combat a deadly virus that affects an estimated 300,000 people each year in West Africa.

Scientists know that bacteria create their own energy, get nutrients to run their cellular processes, and multiply. But, bacteria haven't been shown to respond to external mechanical stimulation or signals in a way that's similar to how our bodies respond to touch, until now.

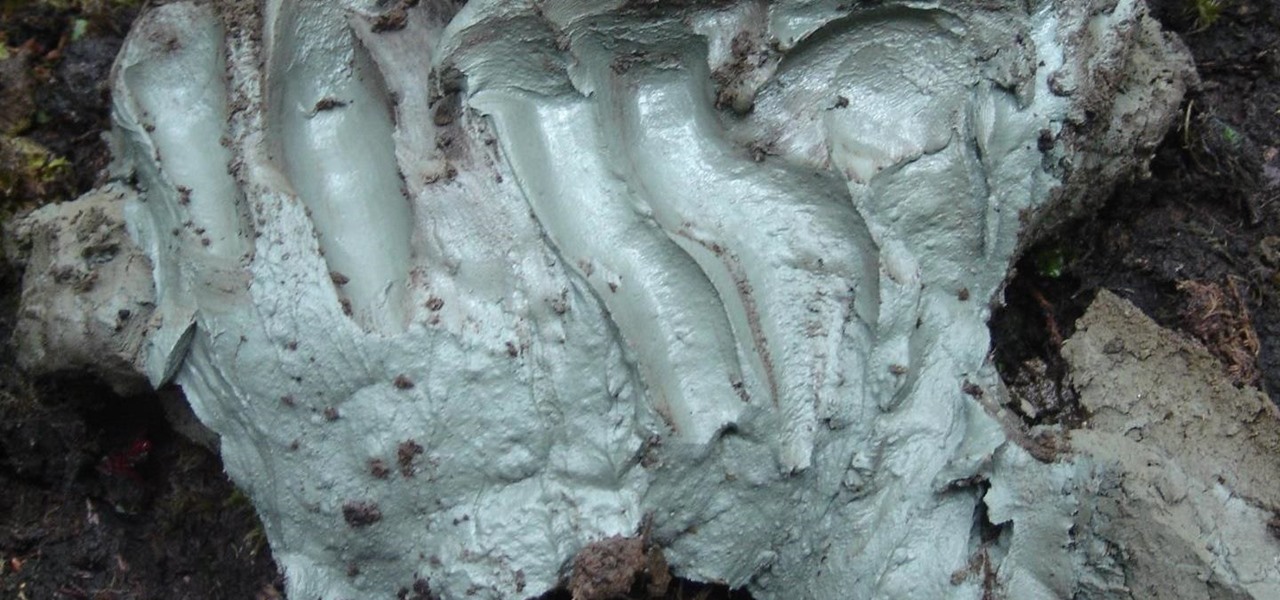
For as long as 14,000 years, the First Nations people of the Heitsuk Nation have made their home along the Central Coast of the Canadian province of British Columbia. Among the territory's inlets, islands, rivers, and valleys lie a clay deposit on the north side of Kisameet Bay, near King Island. For as long as most can remember, the tribe has used the clay as medicine. Now science says microbes that live in that clay may have important antibacterial properties.

Once we recover from the respiratory infection pneumonia, our lungs are better equipped to deal with the next infection — thanks to some special cells that take up residence there.

Cancer cells do a pretty good job of flying under the radar of our immune system. They don't raise the alarm bells signaling they are a foreign invader the way viruses do. That might be something scientists can change, though.

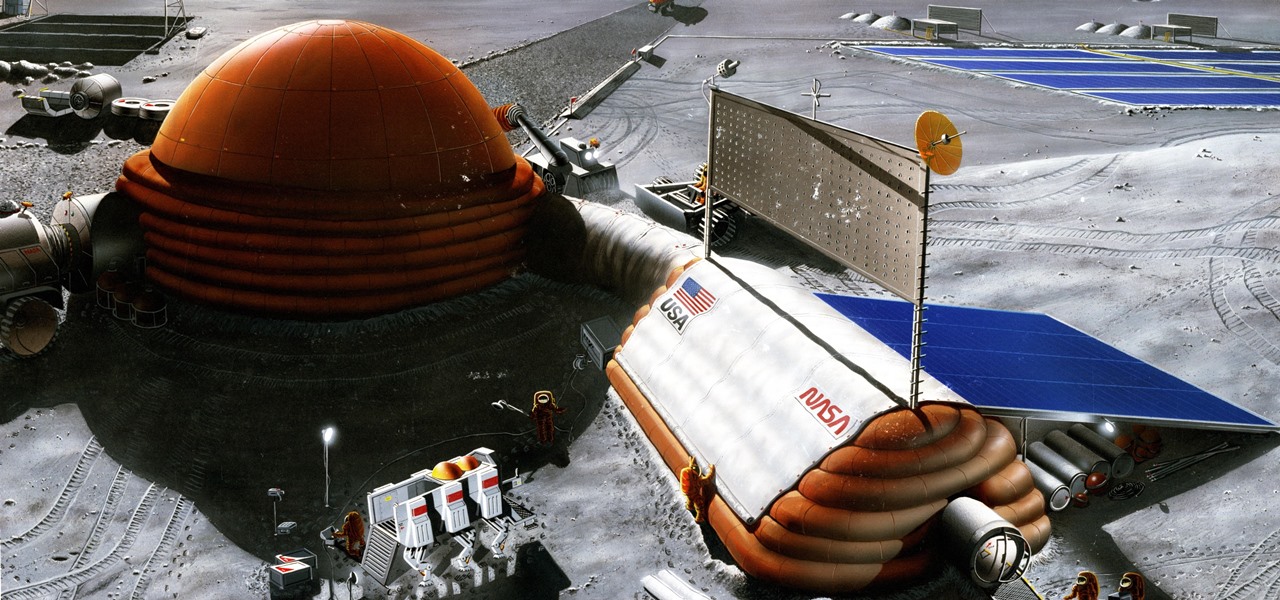
Wherever there are people, the party is sure to follow. Well, a party of microbes, at least. That is what scientists at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory have found after a 30-day microbial observation of the inflatable lunar/Mars analog habitat (IMAH).

A week into my internship, I experienced pretty serious back pain and slight difficulty breathing. I scheduled a doctor's appointment to make sure nothing was wrong, and I got a surprising diagnosis: bad posture.

It is not just a bad summer for ticks — it has been a bad decade for the spread of tick-borne infections. New surveillance from the CDC reports rapid expansion and increase in cases of babesiosis, a sometimes life-threatening disease, in Wisconsin.

Add breathing in your house as another possible danger to your health. If your home is sick, it's possible you could get sick too.

Maine reported their first measles case in 20 years yesterday, June 27, in a press release from the Maine CDC. Many other people may have been exposed and could show signs of infection soon, with the potential for outbreak brewing. The last measles case in Maine was in 1997.

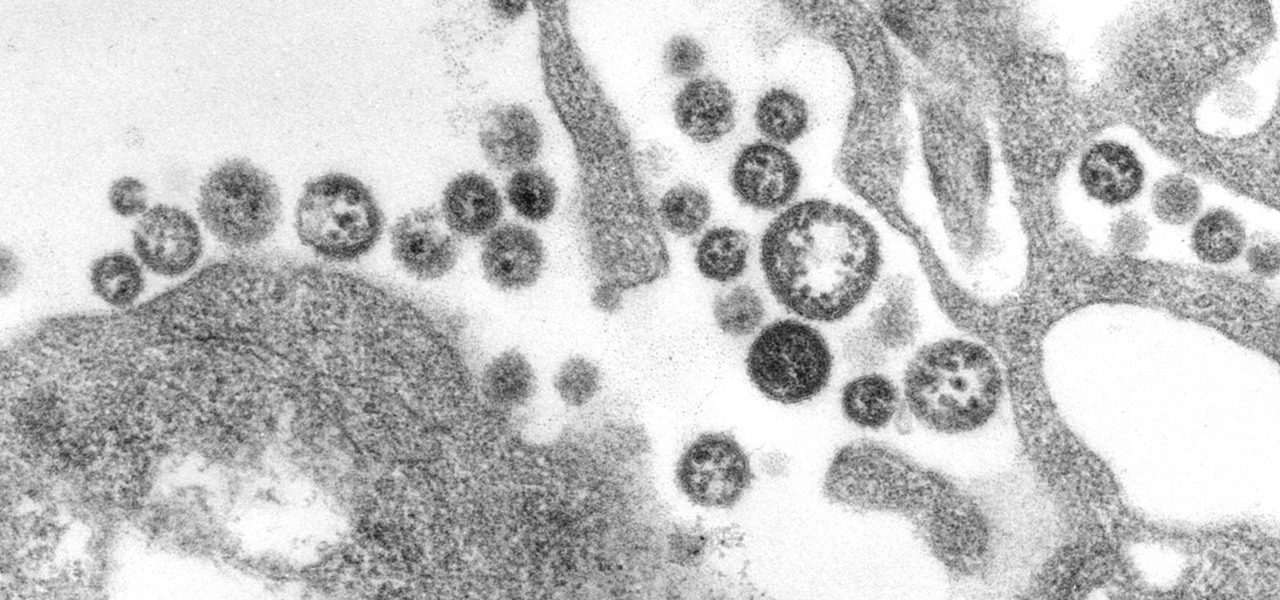
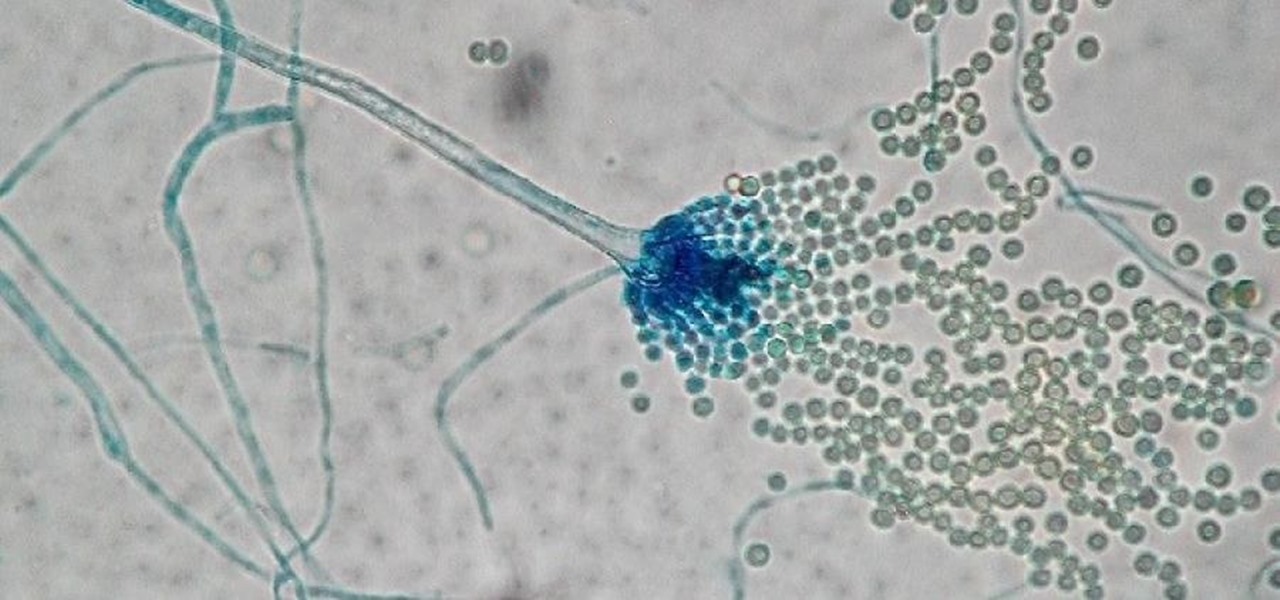
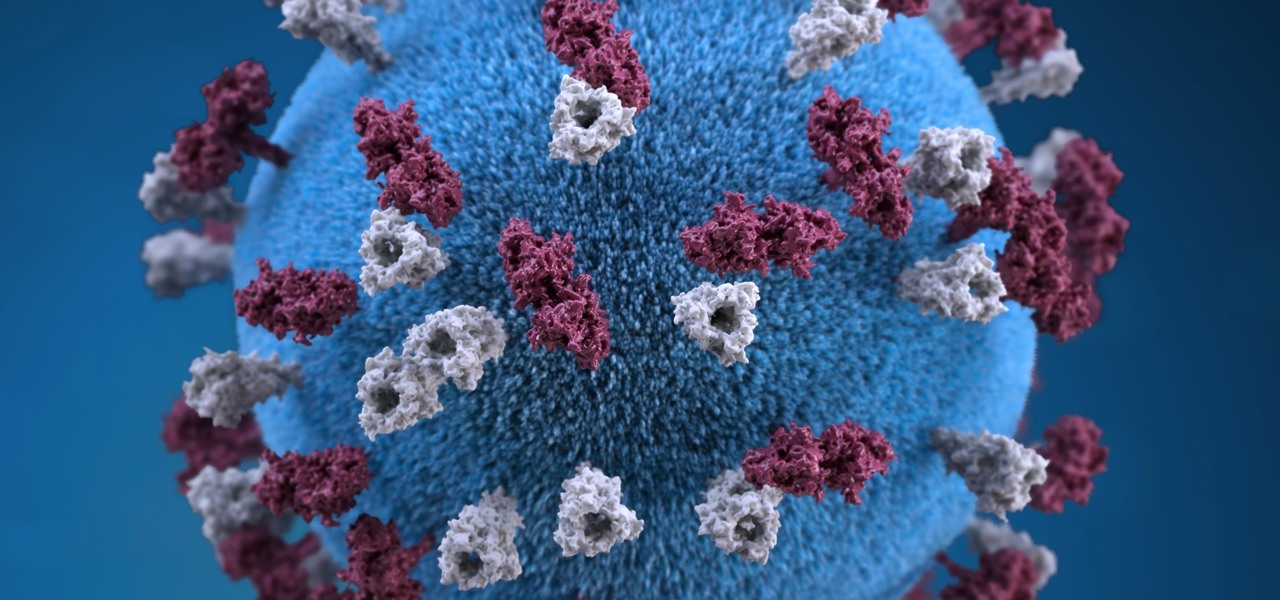
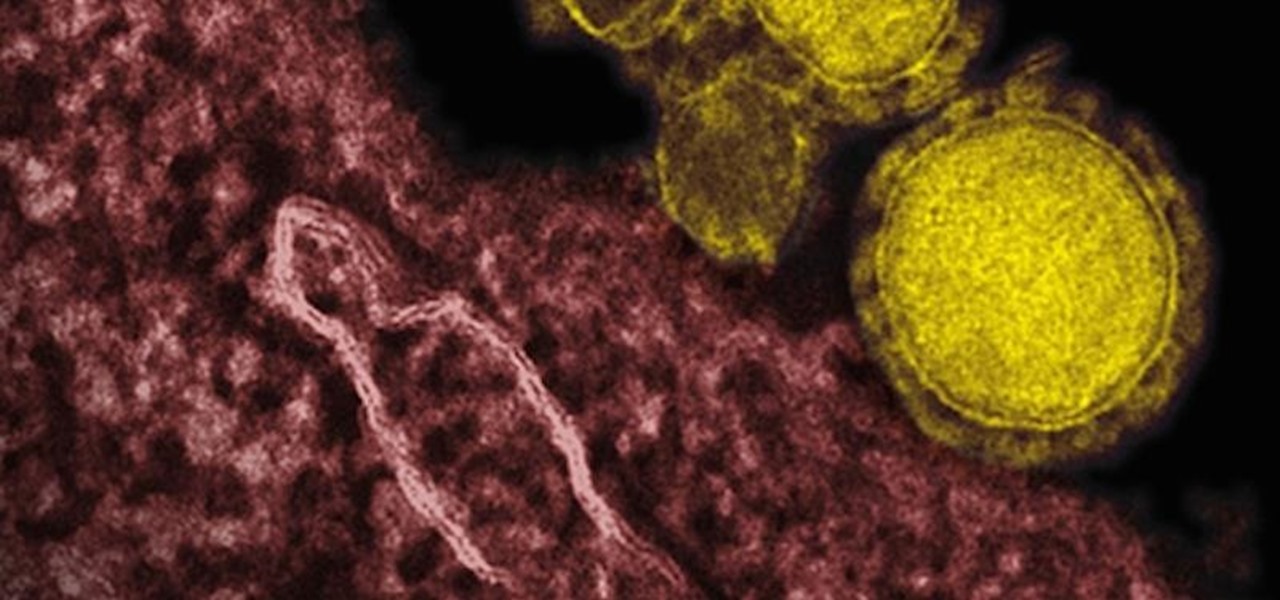
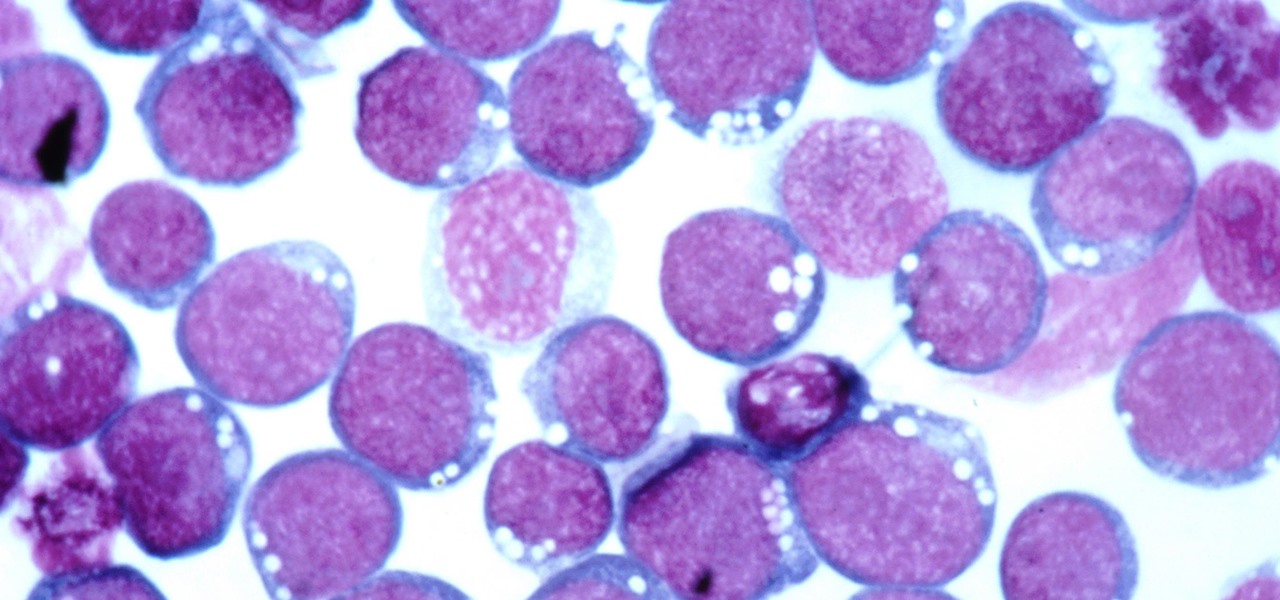
Coronaviruses are common viruses, and most of us catch one at some point — they cause about 30% of all common colds. A new accidental discovery could help fight these viruses, even the deadlier, emerging ones.

Dangerous to humans and dogs, Rocky Mountain Fever, along with several other tickborne infections, is on the rise.

The possibility of severe tickborne illness is increasing as an aggressive tick from the American southeast moves up the Atlantic Coast.

With summer just ahead, you, or your children, may be looking forward to some pool time or the water park. When planning water-based fun this year, keep a heads-up for microbes.

Most of us have already had an encounter with the Epstein-Barr virus, or EBV, for short. As part of the herpes family, it's one of the most common disease-causing viruses in humans. We get the disease with (or without) some nasty symptoms, then we recover. However, EBV stays in our body after the illness has ended, and it's one of the few viruses known to cause cancer.

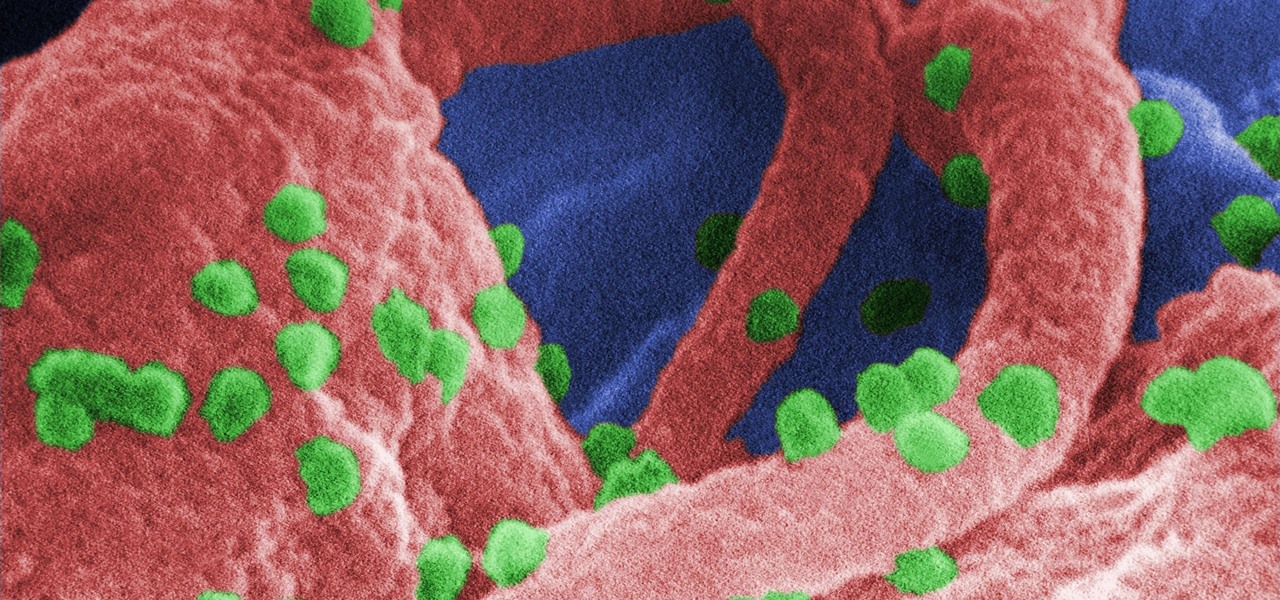
The problem with HIV is that it attacks and kills the very cells of the immune system that are supposed to protect us from infections — white blood cells. But a new technique, developed by scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) in La Jolla, California, offers a distinct HIV-killing advantage.