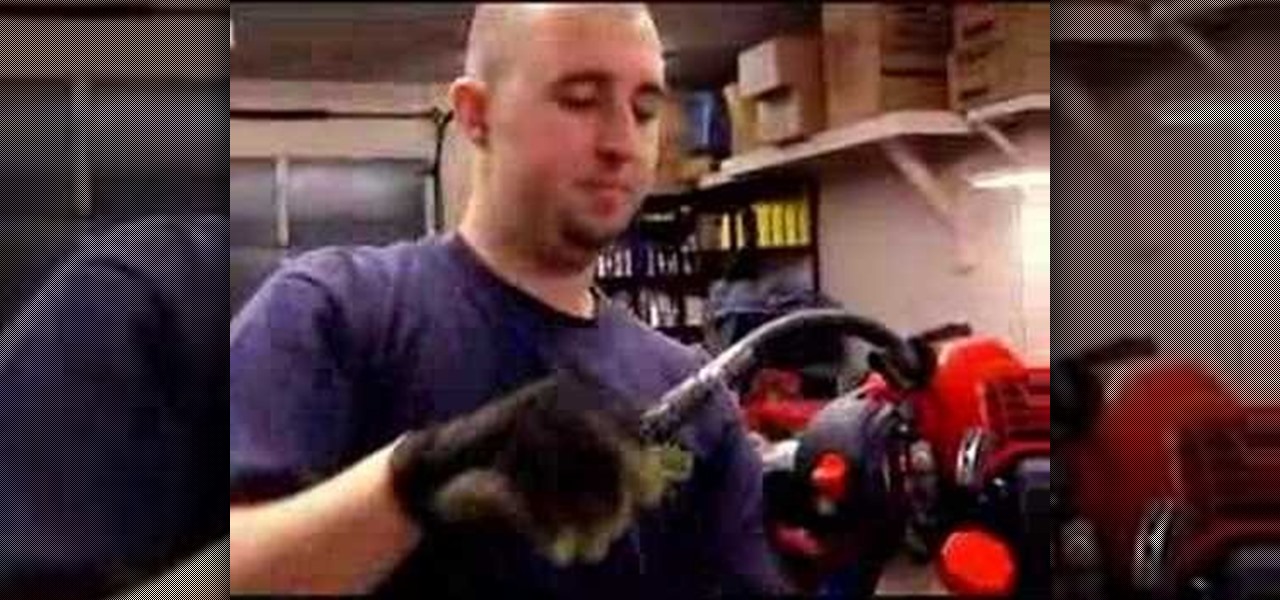

How To: Change the spark plug on a trimmer
This is a step by step DIY tutorial of how to change the spark plug on your trimmer or weed wacker.


This is a step by step DIY tutorial of how to change the spark plug on your trimmer or weed wacker.

This is a step by step DIY tutorial of how to change the air filter on your push mower.
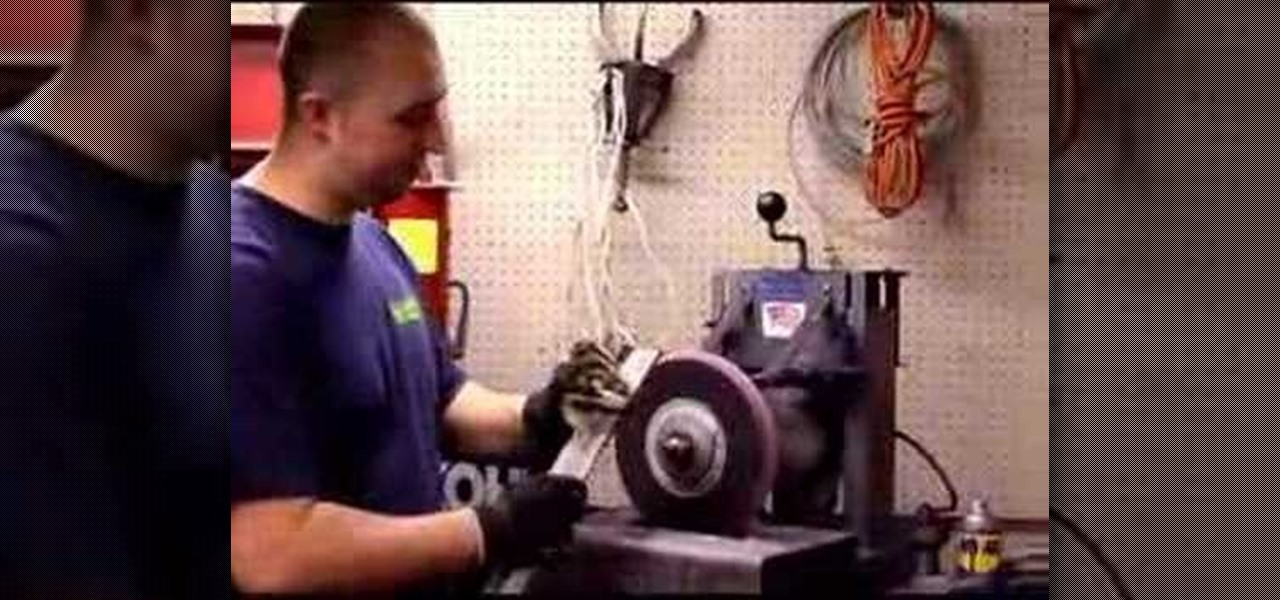

This is a step by step DIY tutorial of how to change and sharpen the blade on your push mower.
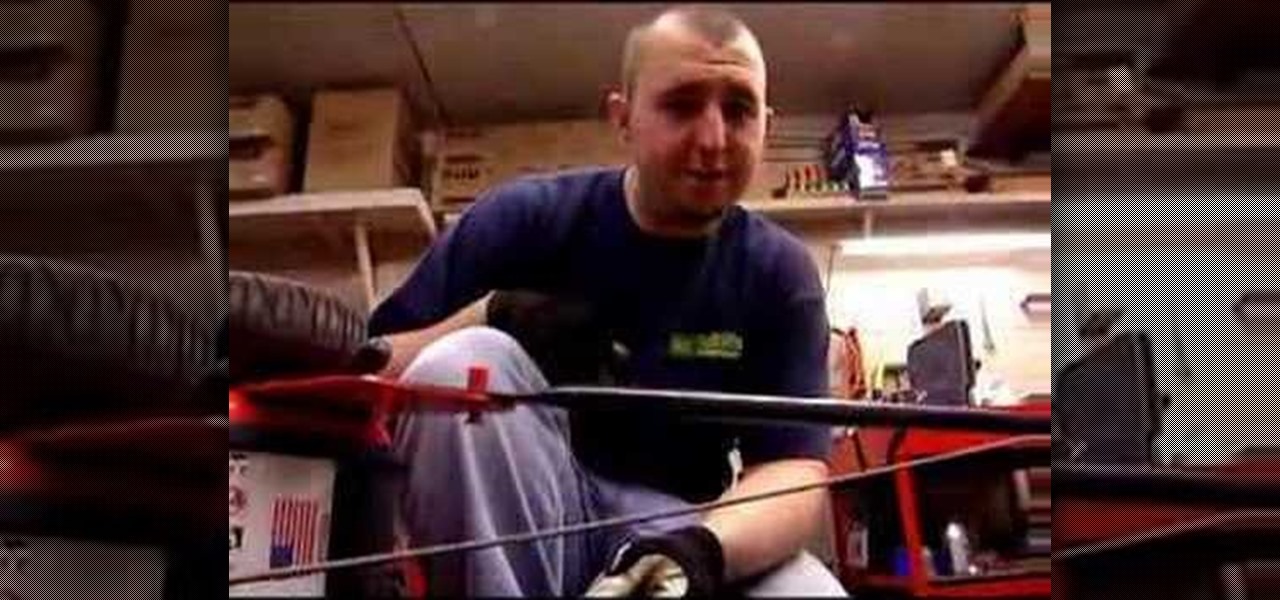

This is a step by step DIY tutorial of how to change the oil in your push mower.
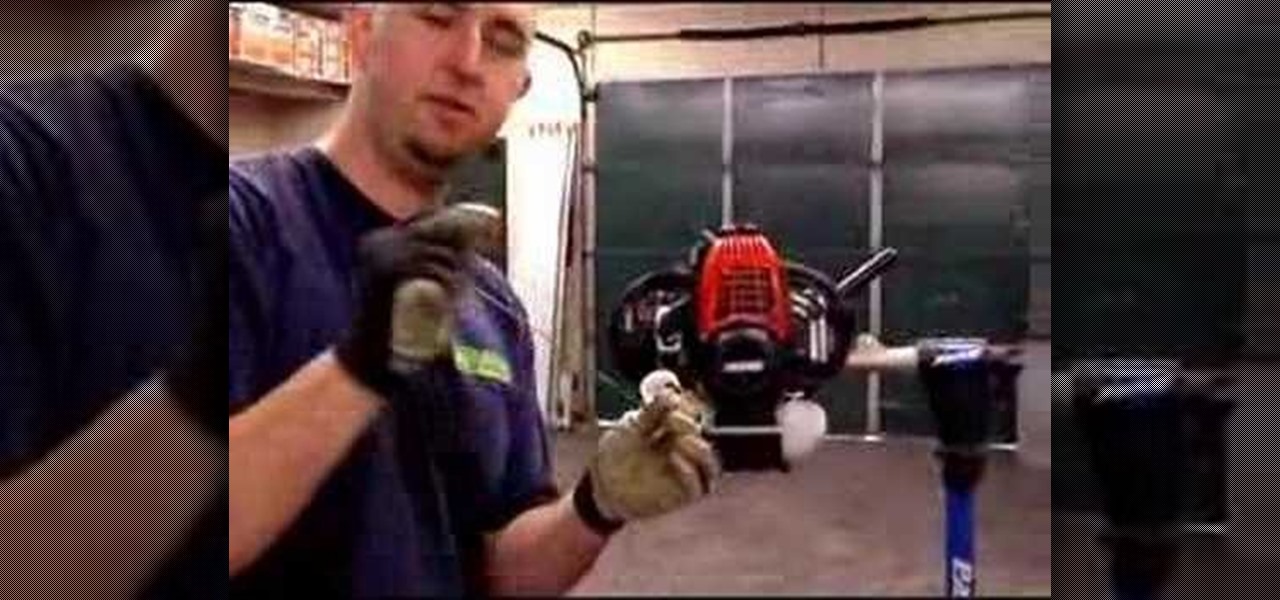

this is a step by step DIY tutorial of how to change the fuel filter on a garden trimmer or weed wacker.
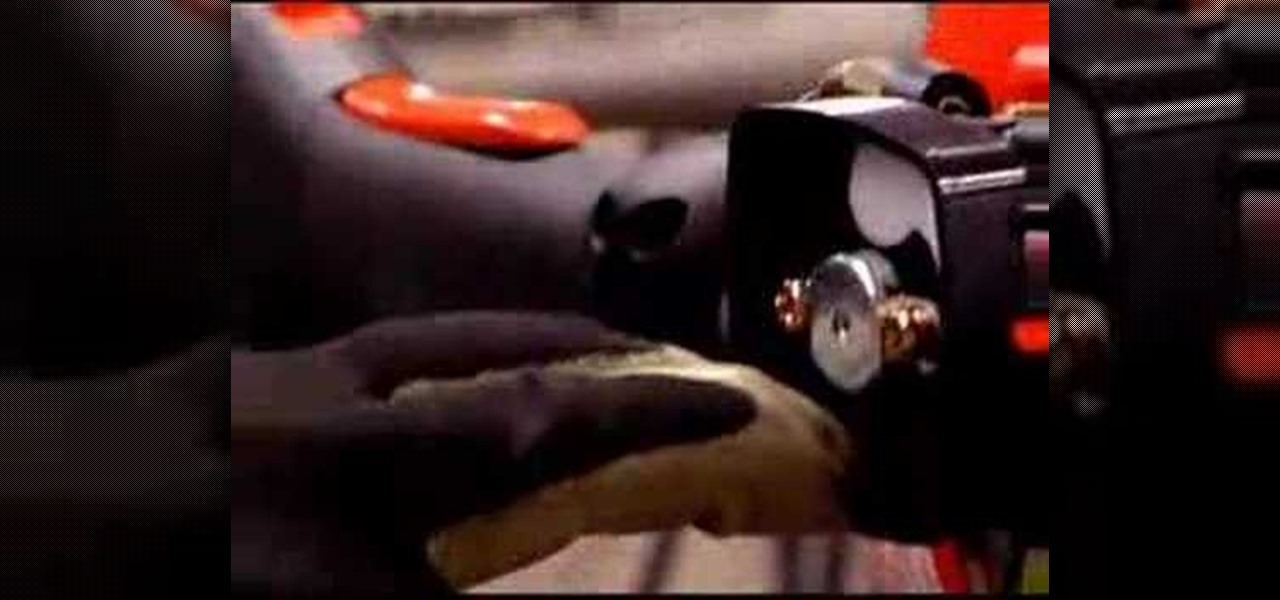

This is a step by step DIY tutorial of how to change the air filter on your trimmer or weed wacker.

This is a step by step DIY tutorial of how to change the air filter on your riding lawn mower.

This is a step by step DIY tutorial of how to restring a garden trimmer head.

This is a step by step DIY tutorial of how to change the fuel filter on your riding lawn mower.
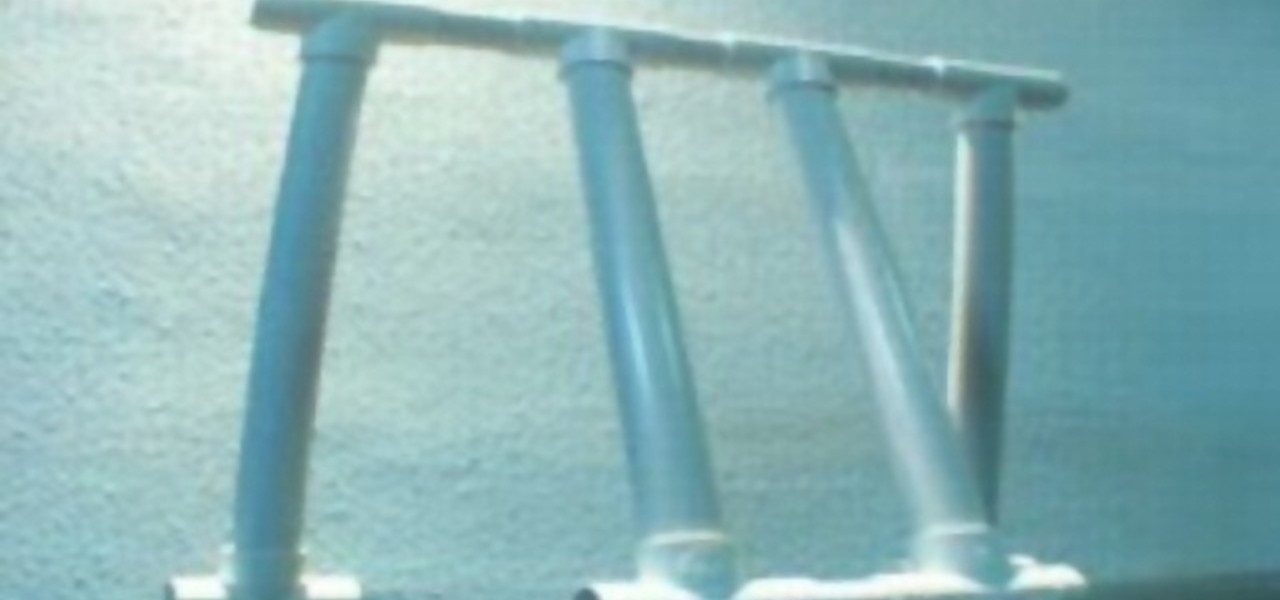

Make your own Passive Walker from this video instruction, no battery required, DIY from PVC tube, I show you how to build one for just 8 dollars, very easy and funny.

Make your own DIY Hydroponics System! This no-messing-around video is really helpful and instructive.
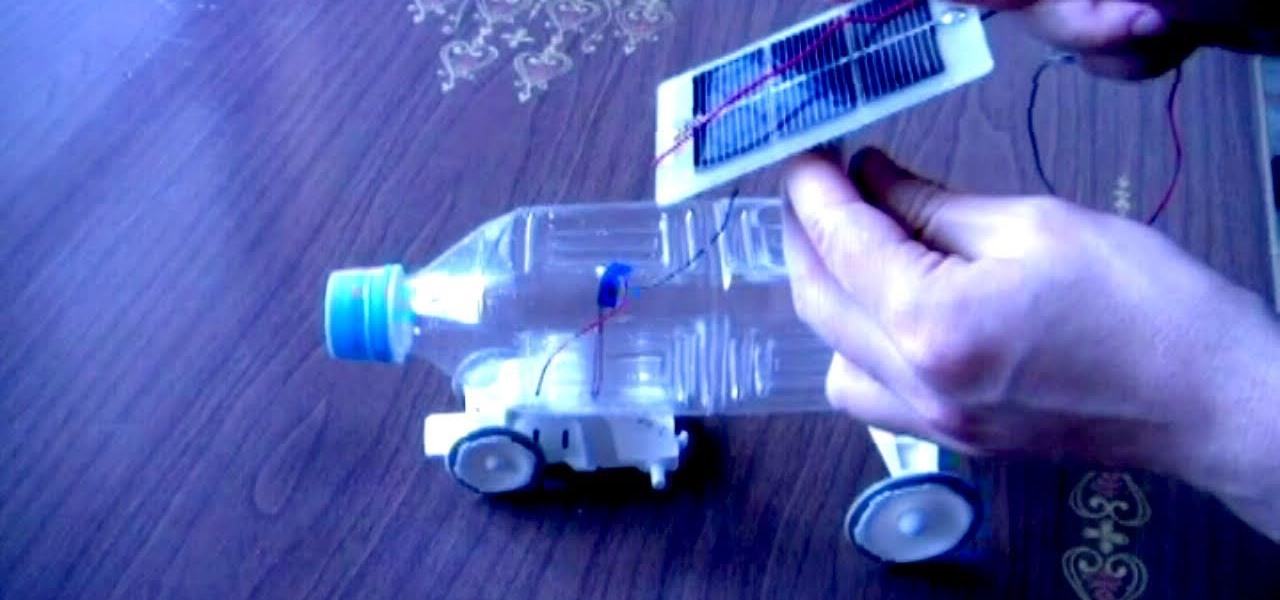

Watch and learn how to make this awesome DIY toy car that runs off solar power. This makeshift mini-vehicle is made from a plastic bottle, small motor, tires, supports and a solar panel. See if you can replicate this interesting solar toy, or see if you can come up with a better and cheaper design!

Ever wonder what goes on inside the engine of your car? Can you imagine at 5000 rpm there are 80+ explosions every second? Here's a DIY internal combustion engine that'll show what all that noise is about!
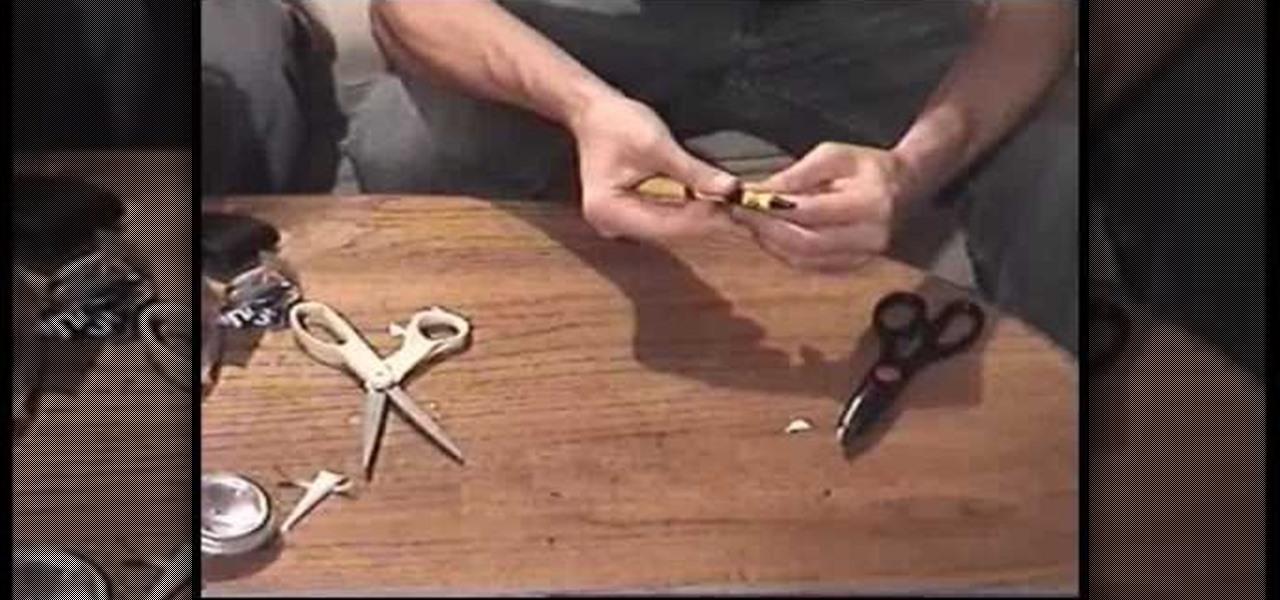

In this video we explain how to make and use Padlock Shims. Padlock Shims are used to unlock spring latch Padlocks.

This is a great DIY method of printmaking. using an old scanner found in the trash. Learn how to do monotype printing.
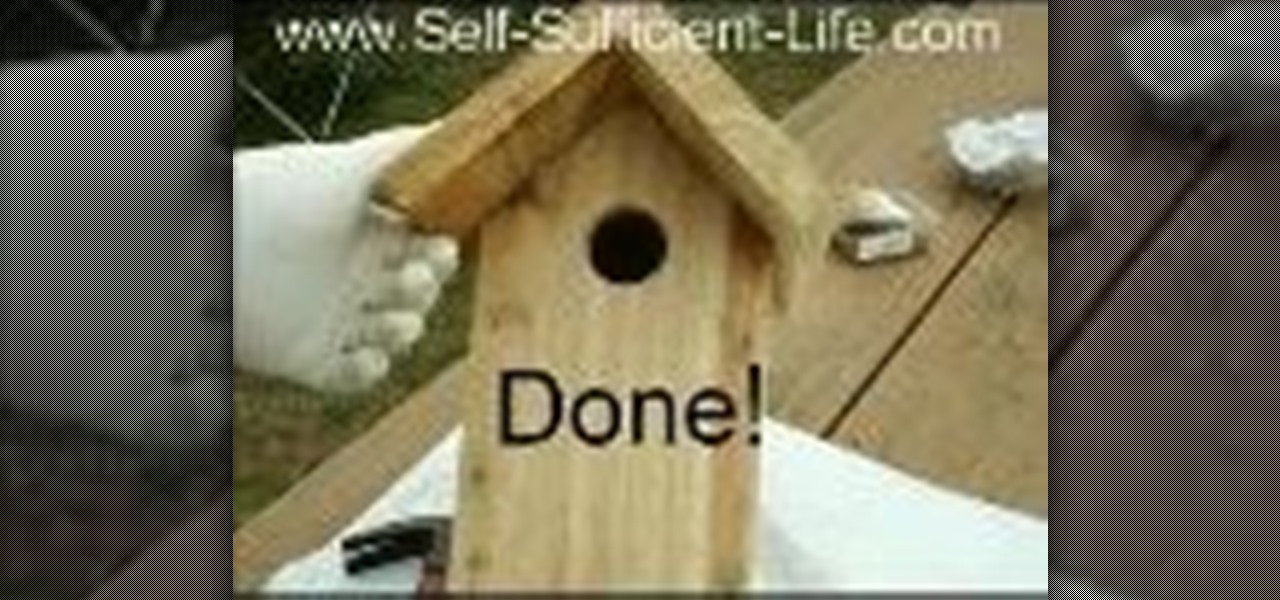

DIY Guide to building a birdhouse. This easy to make bird box can be built in 1 day out of one 6 foot long 1" by 6" plank of cedar. Attract more wild birds into your garden (or provide for those already there).

For all you whos resolution it was to start making your own clothes and DIY'in, this week were taking a look inside the mysteries of the sewing machine plus a look at our 2008 top DIY web picks.
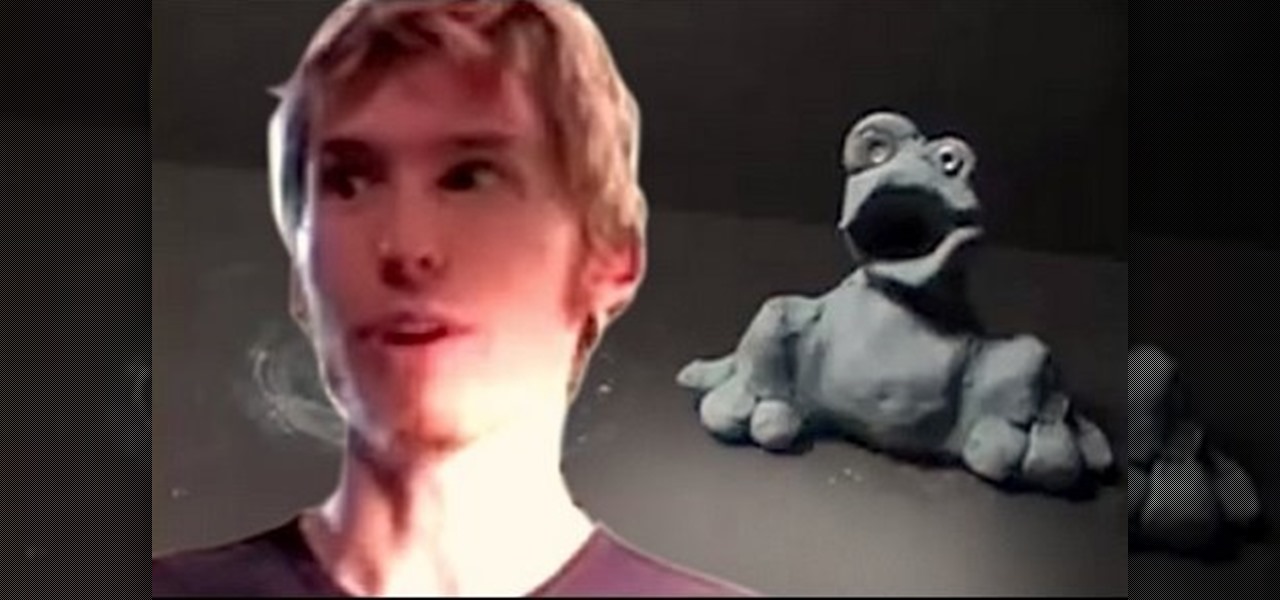

DIY Stop Motion Animator, Javan Ivey, shows us how to create stop motion movies with some great software and helpful hints.
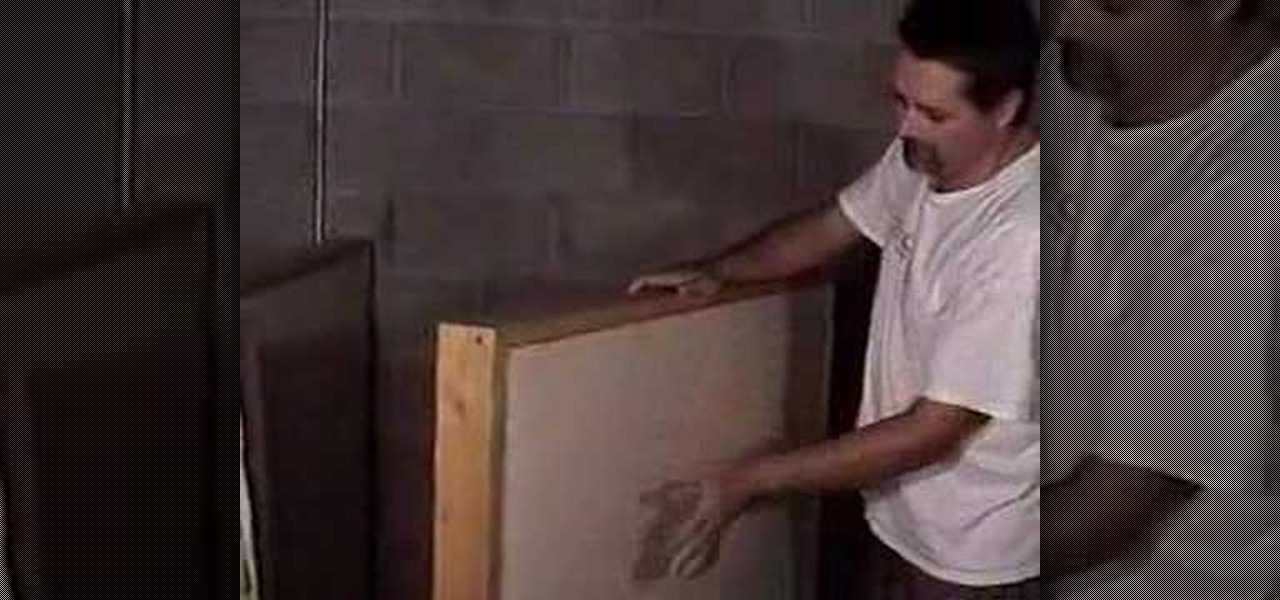

Build sound board for a studio at home, to insulate noise and sound. The subject of this DIY project was originally covered in a written article that is still required reading to finish the project as it gets into more detail regarding the actual construction of the boards.
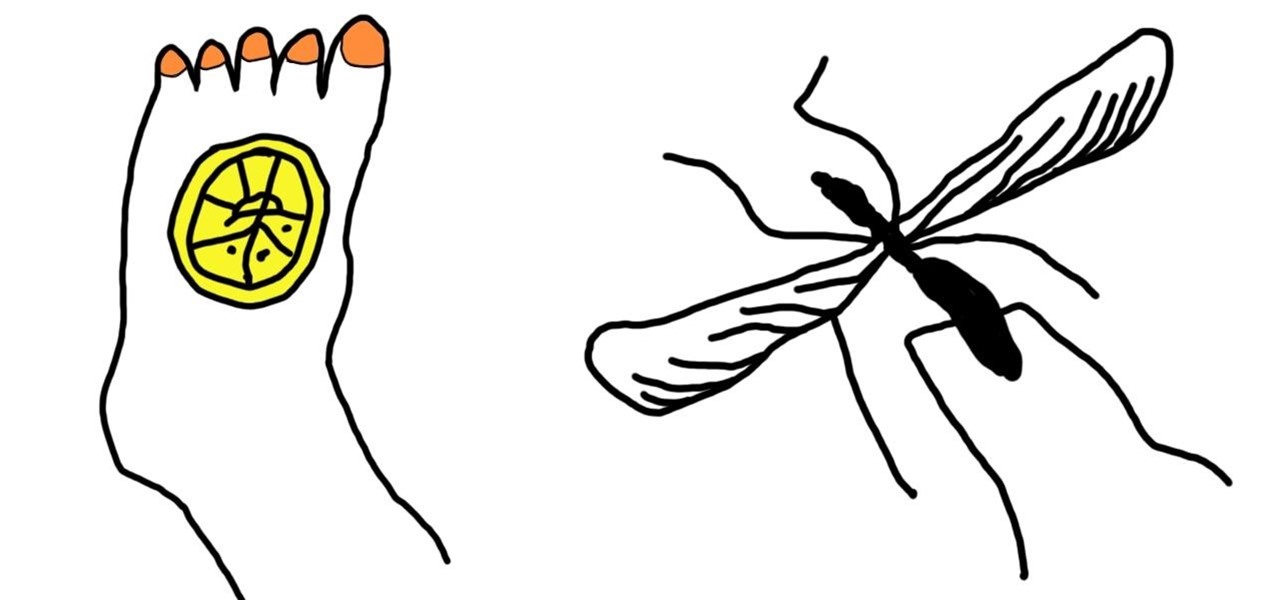
There are few things peskier in the summer than an unexpected mosquito bite swelling up on your arms and legs. Fortunately, there are many ways to heal your body of its annoying itch, ranging from fruit (lemon slices and banana peels) to common household items (baking soda and apple cider vinegar).
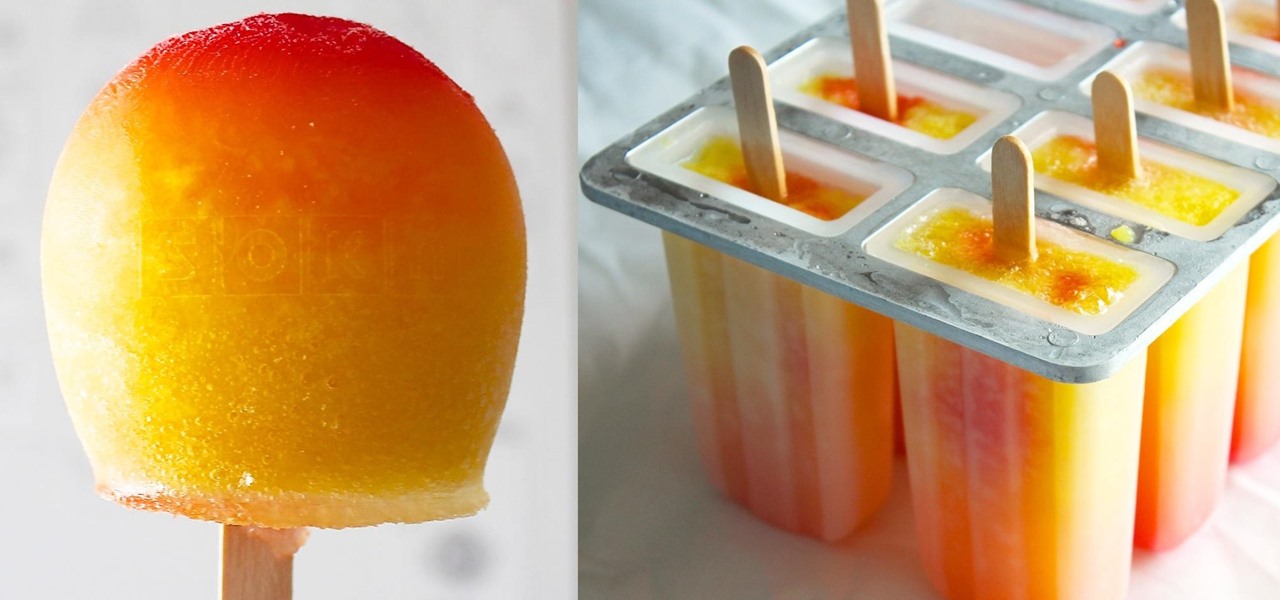

Sometimes just drinking your alcohol can feel a little dull and boring. Eating your alcohol, however, is always a party.
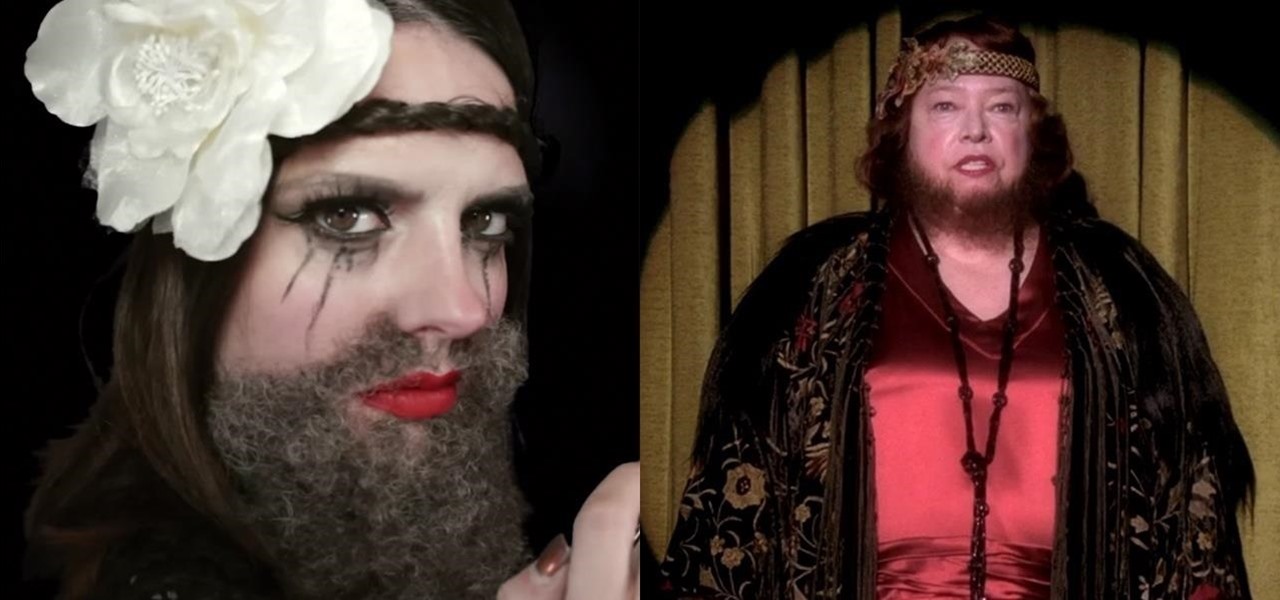

Bearded women are typically more freaky than scary—yet when it comes to American Horror Story, nothing is as it seems.
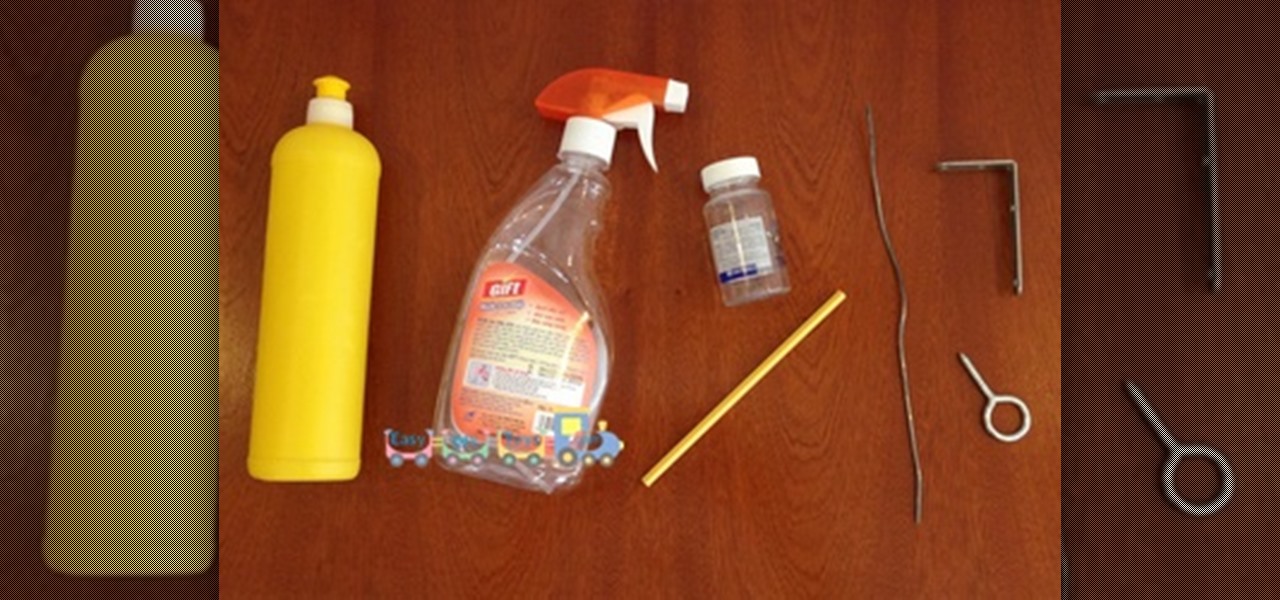

Do not point this gun to other! Kids SHOULD NOT use the darts in this tutorial as the ammunition, you should only use soft things like the cotton head of the ear-cleaner stick!
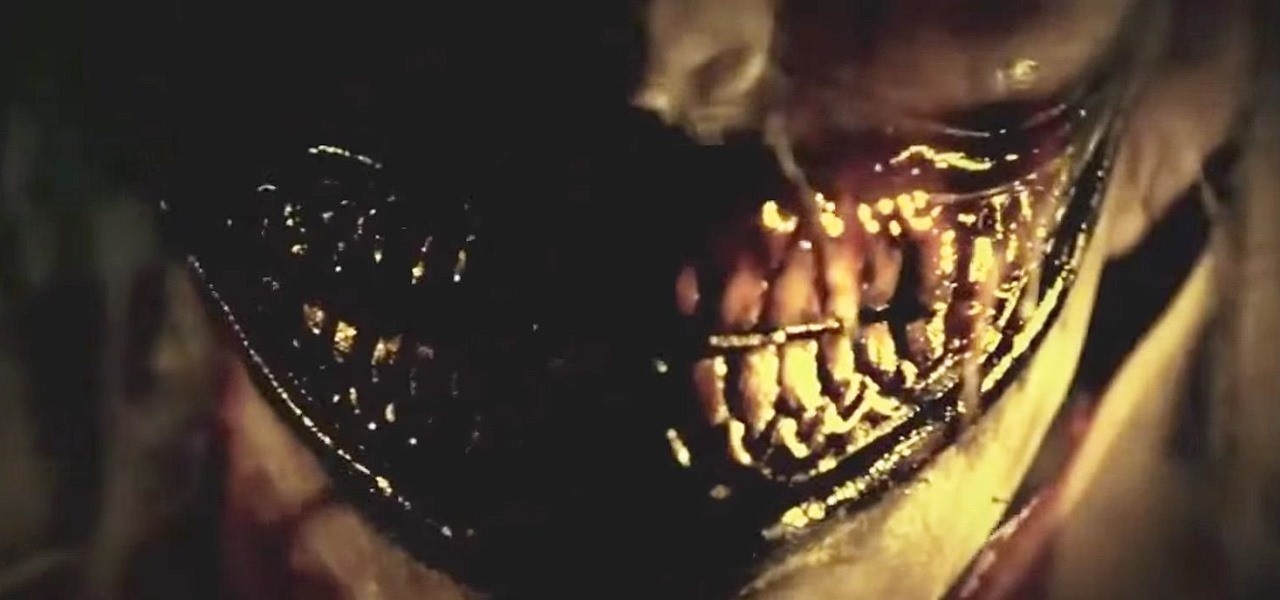

Every season of American Horror Story introduces characters who are truly terrifying. From the witches of Coven to the ghostly resident of the show's first season, each new chapter of the TV series offers a host of ghoulish and ghastly costume ideas perfect for scaring children on Halloween. Some grisly characters even span multiple series.
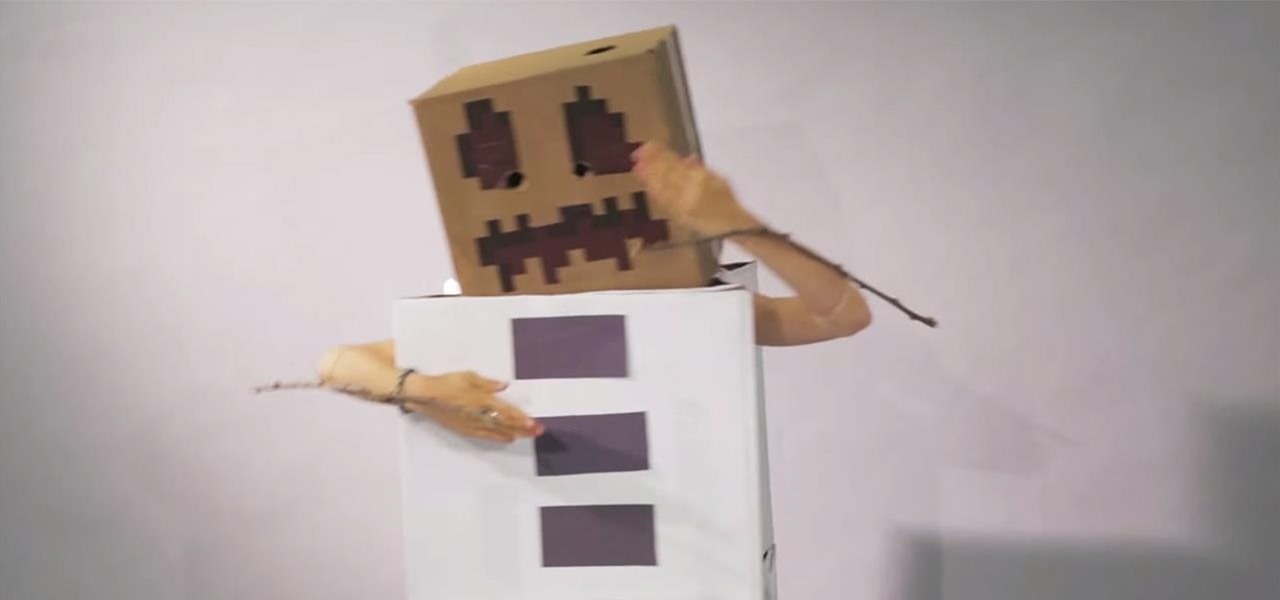

Minecraft is a simple game with a huge following, and is a great inspiration for easy, DIY Halloween costumes. We've already shown you guys how to make a Simple Steve costume and a Creeper costume—now it's time for a new Minecraft-inspired one.
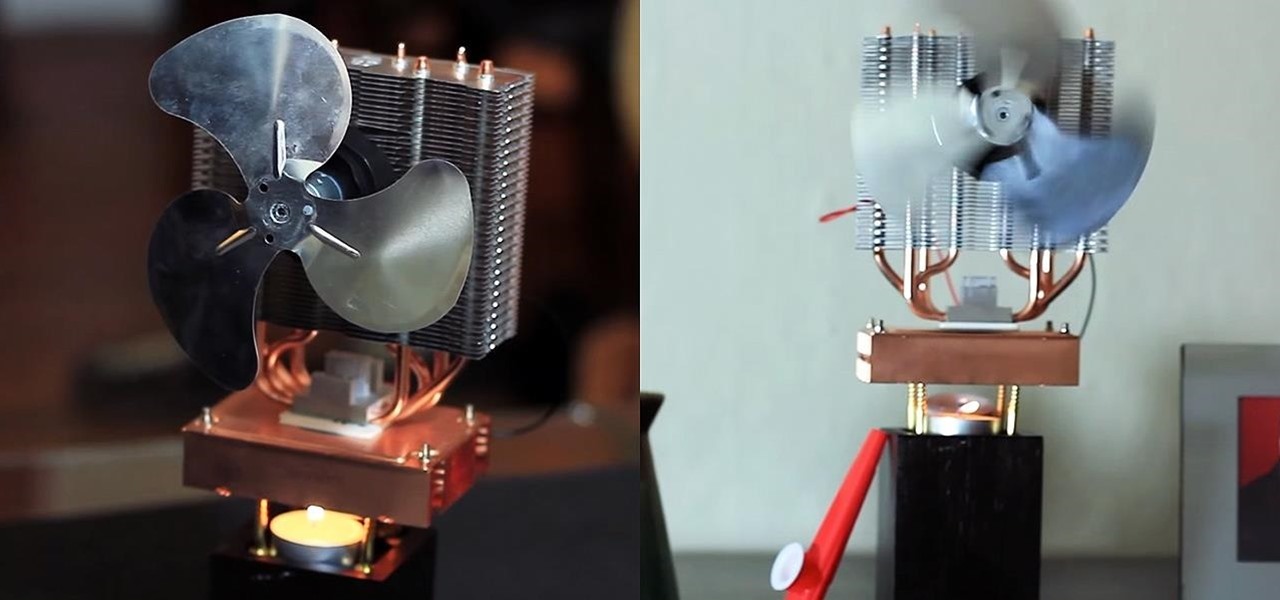
Staying cool in the summer heat sometimes feels like it takes all the energy in the world. But what about a fan using no-cost electrical energy? If you're looking to keep cool during a power outage, or if you don't want to break the bank by running your DIY air conditioner all day long, you can use candlelight to power a fan!
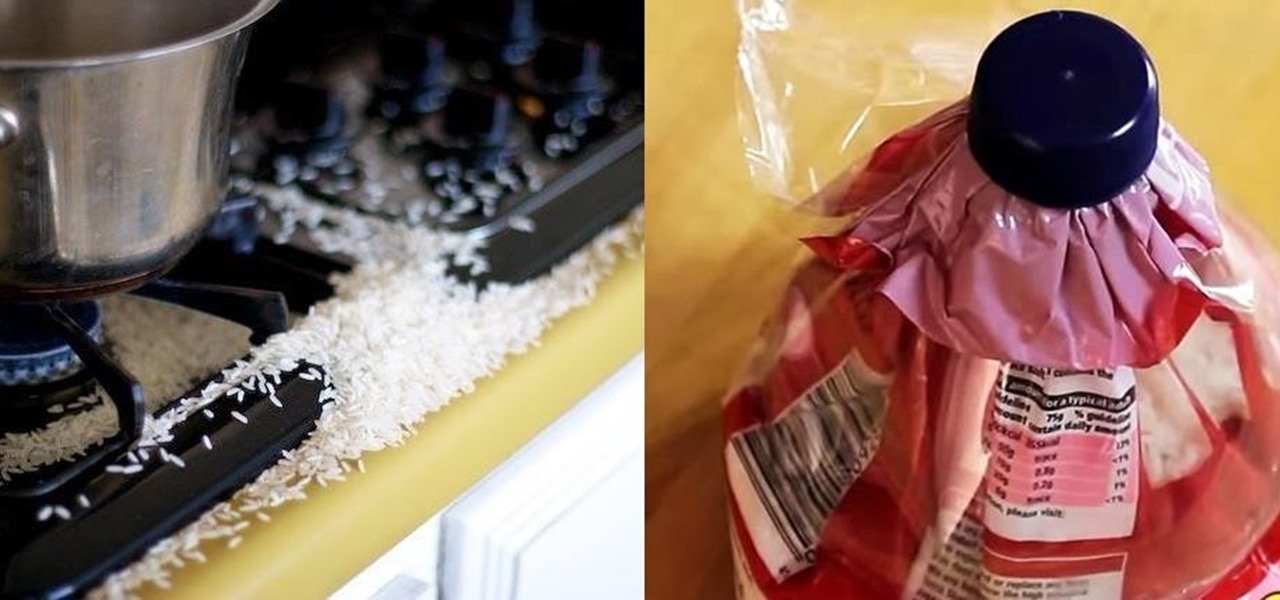

I love cheap, nutritious food: lentils, rice, toor dal, and other beans and grains. Even popcorn. The only problem is that they usually come in floppy plastic bags that make measuring ingredients more difficult. I usually open up one corner of the bag only to have everything come spilling out all at once whenever I try to pour out measured amounts.
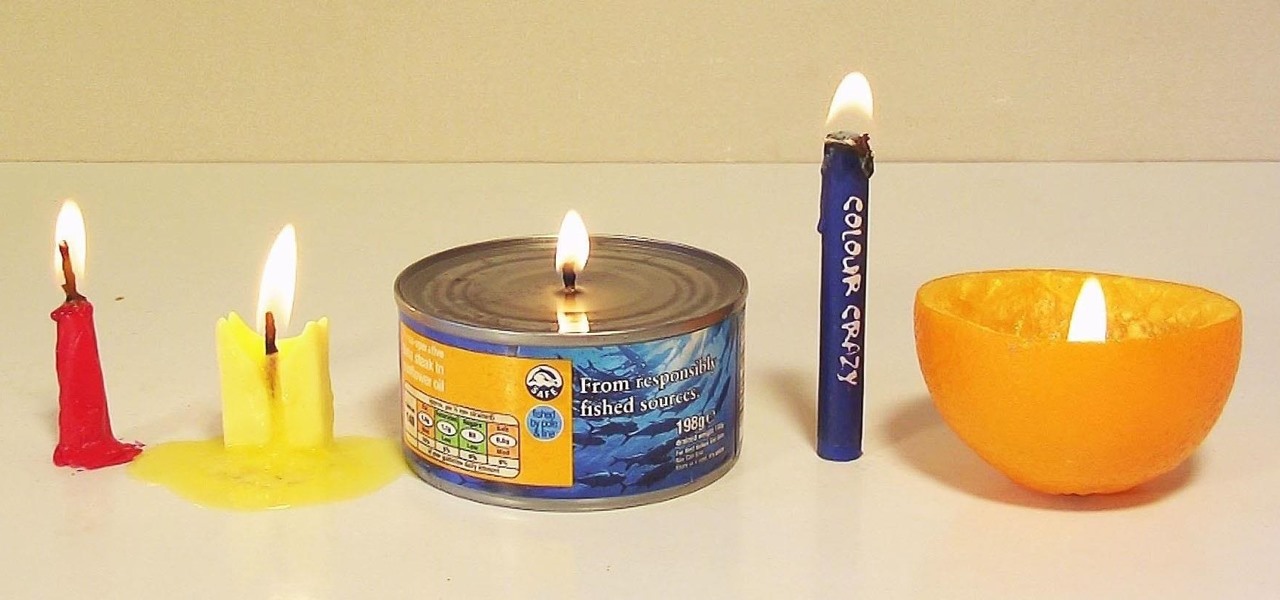

Candles can be pretty expensive, which is why most of you probably resort to flashlights during a power outage. But when your batteries run out, you're out of luck, unless you know one of these methods for making a DIY emergency candle out of household junk.
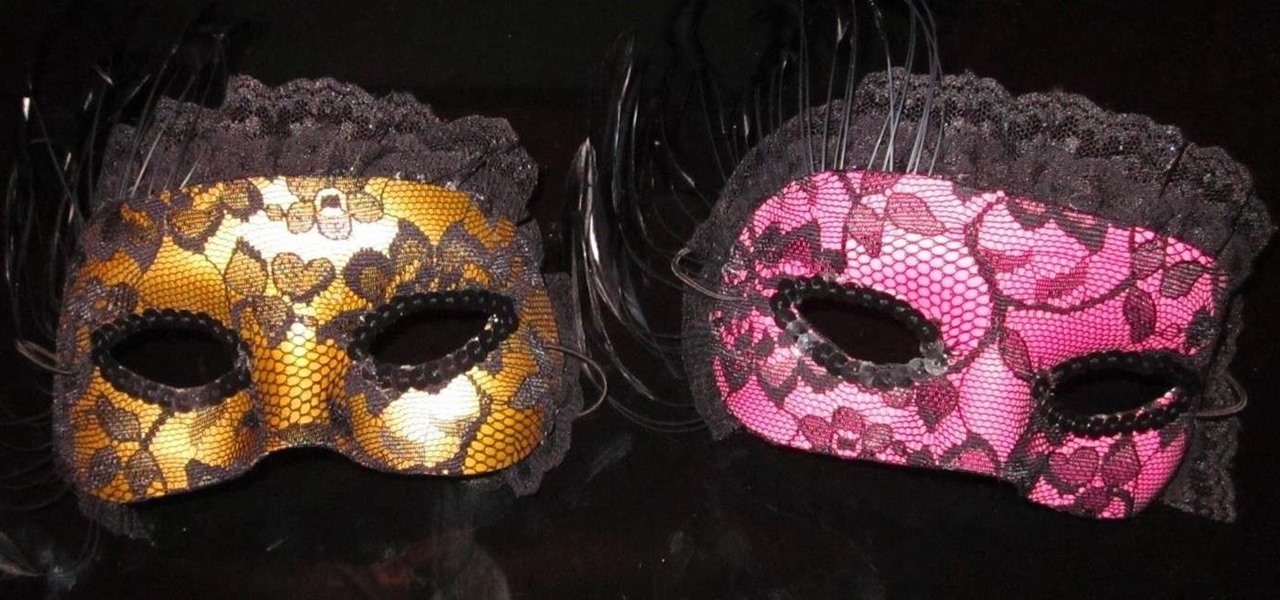

With only a day left until Halloween, a full and detailed costume is too much to throw together for most people. But you still have to dress up as something, right? No one will give you candy or let you into a Halloween party if you don't even put in some effort.
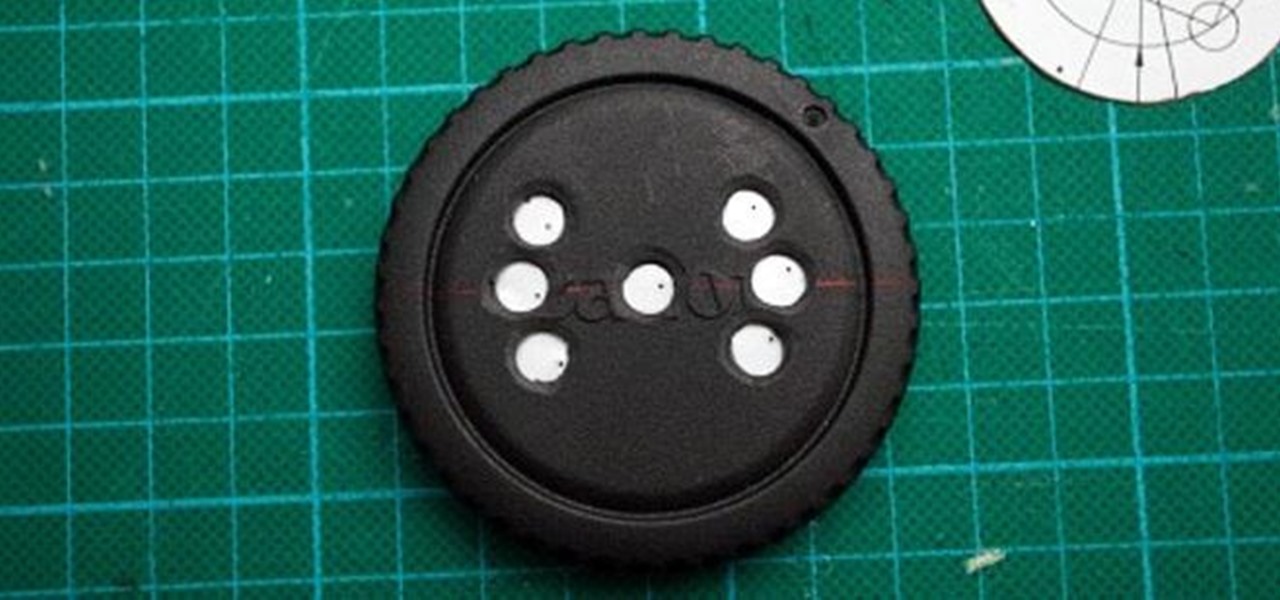

There are tons of ways to make your own pinhole camera out of everything from a juice box to a pine nut. If you have a DSLR, you can make a DIY pinhole lens for it for just a few bucks. David O'Sullivan over on DIY Photography made this one using a cheap body cap and an aluminum can. Here's how to make your own. David put up a template you can follow to make things easier, so start off by downloading it, then use a ruler to draw a line directly through the center of the body cap. Cut out the ...
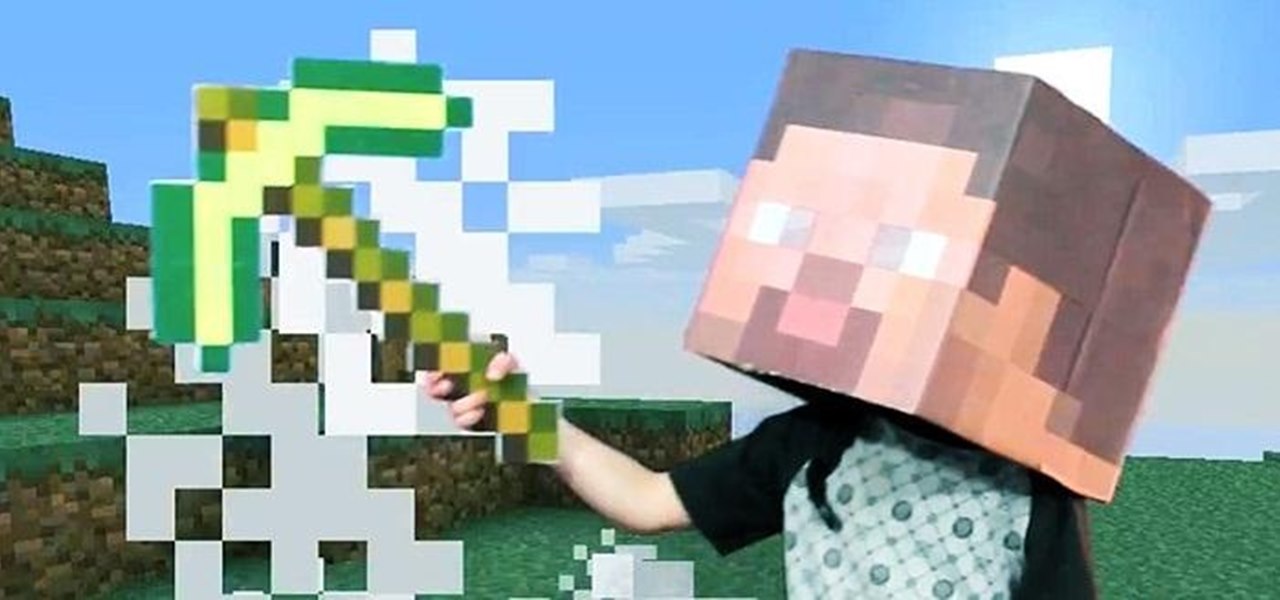

There's no doubt going to be a lot of Steves running around this Halloween, as Minecraft still has a huge community, but those posers are probably just buying their Minecraft costumes. Isn't the best part about Minecraft creating? So why let someone else create your costume?
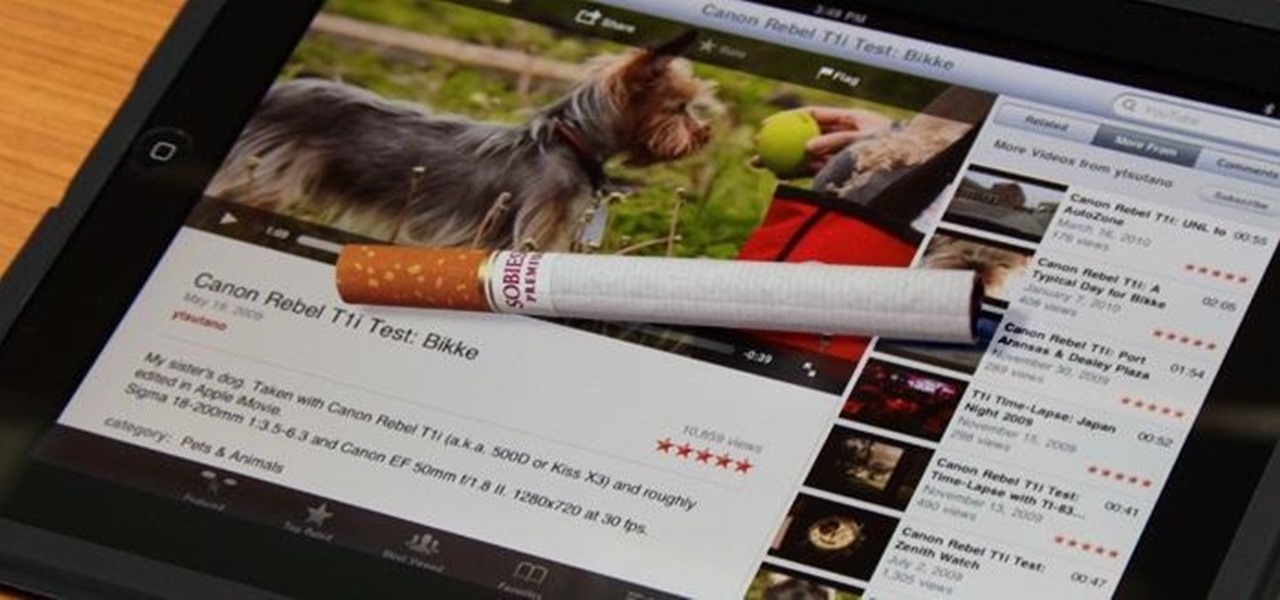
Fingers are very useful for many things in life—but fingers get dirty. With most smartphone and tablets using touchscreen technology, our fingers have become our greatest technological asset. But if you want to keep your phone or tablet from looking like this: Then you can try some of these awesome and easy DIY styluses.
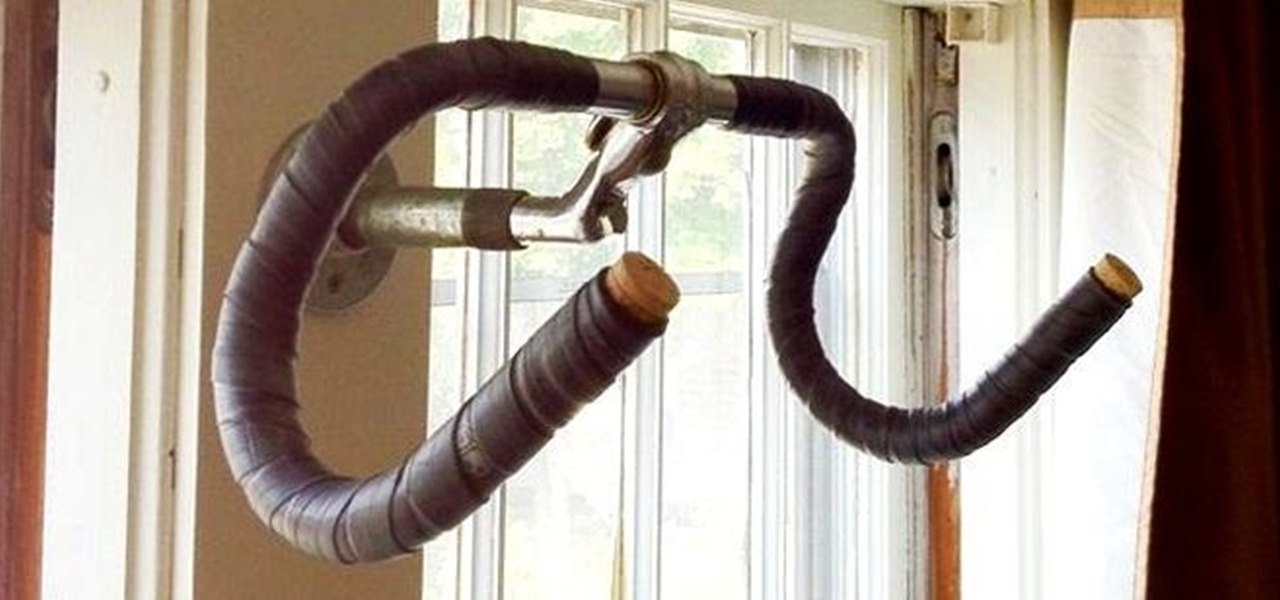

If you bike a lot and live in a small room or apartment, it can be tough to find the space to store your wheels. There are tons of bicycle racks and mounts you can buy, but where's the fun in that when they're so easy to DIY? Here are some of the best inexpensive solutions for your bike storage woes.
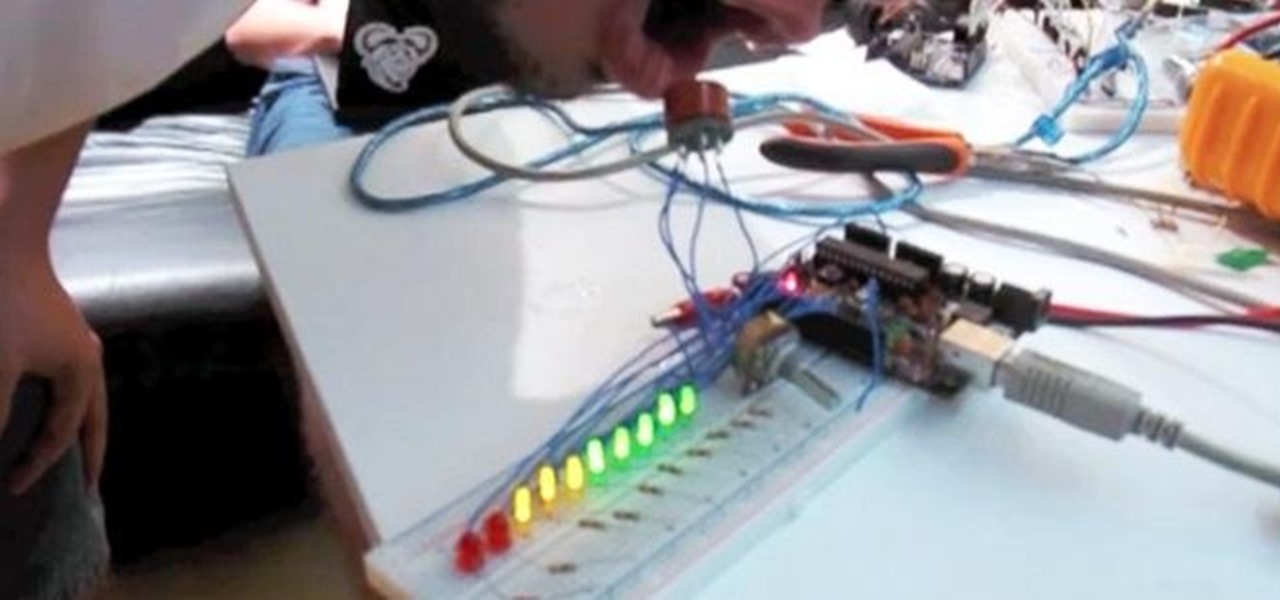

Whether you want to use it to keep your guests safe or just to see who's the most drunk, it's always fun to have your own breathalyzer at a party. We've seen DIY breathalyzers before, like this one by Craig Smith, but how about an Arduino breathalyzer?
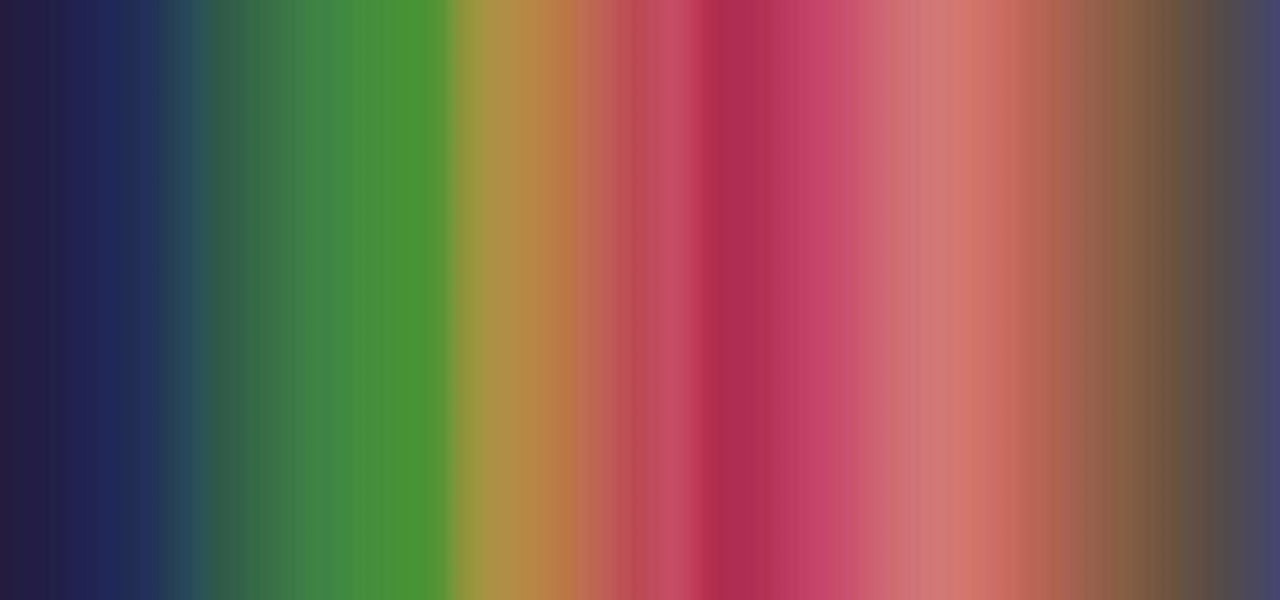

A spectrometer is a device that splits light into all of the different colors it's composed of that can't be seen with the naked eye. It does this by using a prism to refract or bend the light. Jeffrey Warren over at Public Labs created a tutorial showing how you can make your own video spectrometer and create spectra like the one pictured below. Any guesses as to what the subject is? Believe it or not, that's what whipped cream looks like when viewed through a spectrometer. You can do this w...
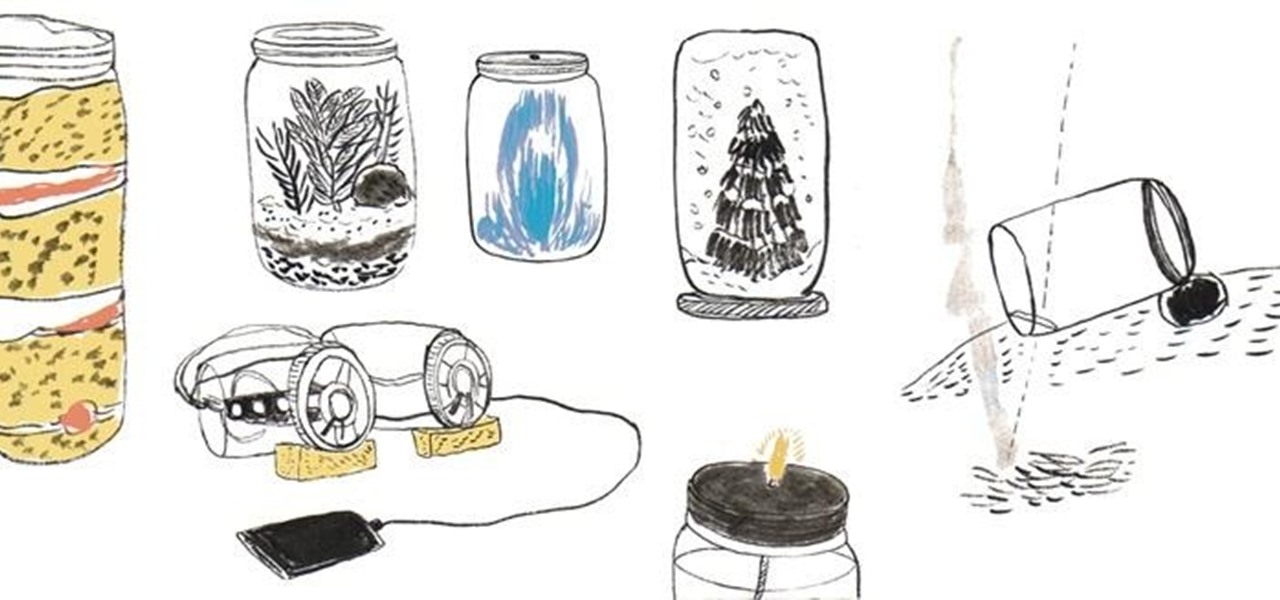

Invented by Philadelphia tinsmith John L. Manson in 1858 for canning and preserving perishables, mason jars are experiencing a major resurgence in the DIY community. In addition to being a handy storage device for both food and non-food items, its old-timey, quaintly antiquated look also makes for good drinking glasses, candle holders, flower vases and eye-pleasing decorations.

Shooting a photo or video in a car can be rather difficult without a proper mount, and if you want to secure your camera outside the car, it can be just plain expensive. Luckily, there are tons of DIY camera mounts for both inside and outside your vehicle, and most of them are pretty cheap to make. Here are some of the best.
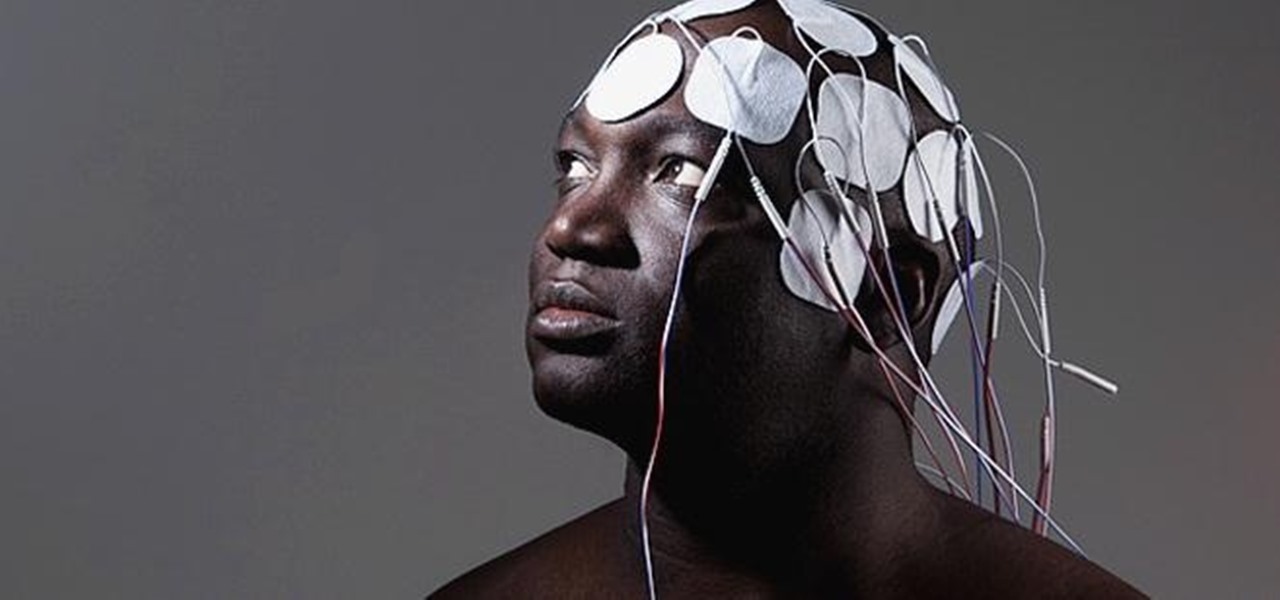

In 1958, Patrick Flanagan invented the Neurophone, a device patented in 1962 that allows radio signals to be picked up by the human nervous system. The skin is the organ that receives the signal, converting it into a modulated molecular vibration, which the brain interprets into sound. Basically, it gives one the ability to 'hear' through the skin, making it sound like the audio you're hearing is actually in your head. It's kind of like having headphones in your brain. The only problem was th...
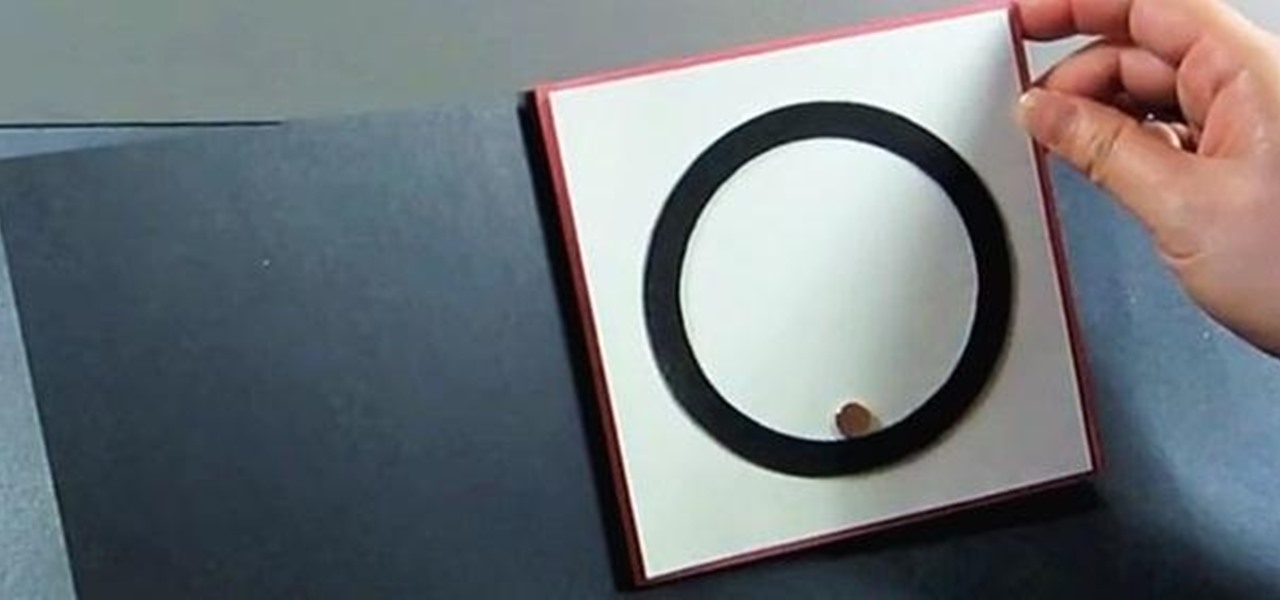

Magnetic ink is generally used by the banking industry to allow computers to read information off of a check, but that doesn't mean you can't have some fun with it. The guys over at openMaterials have figured out a great recipe for a DIY magnetic ink that you can use for an interesting art project—or just to mess around.
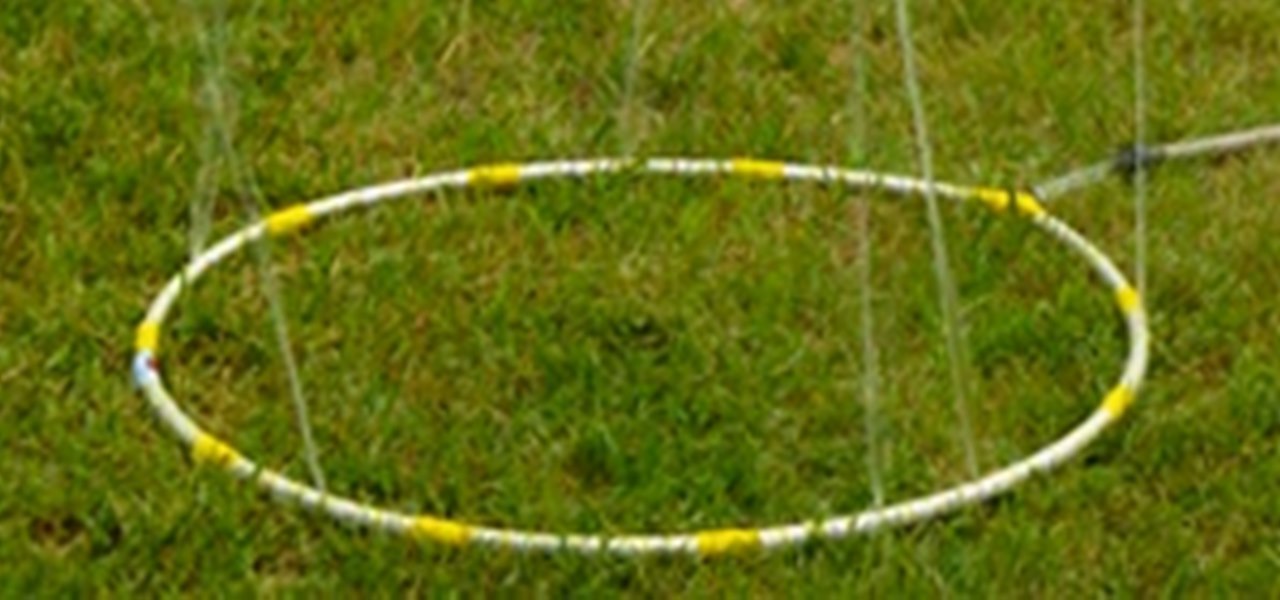

What’s better in the summer than playing around in the water? Lounging in the pool, water balloon fights, and playing in the sprinklers helps us forget how much it sucks to be outside in 100+ degree weather.