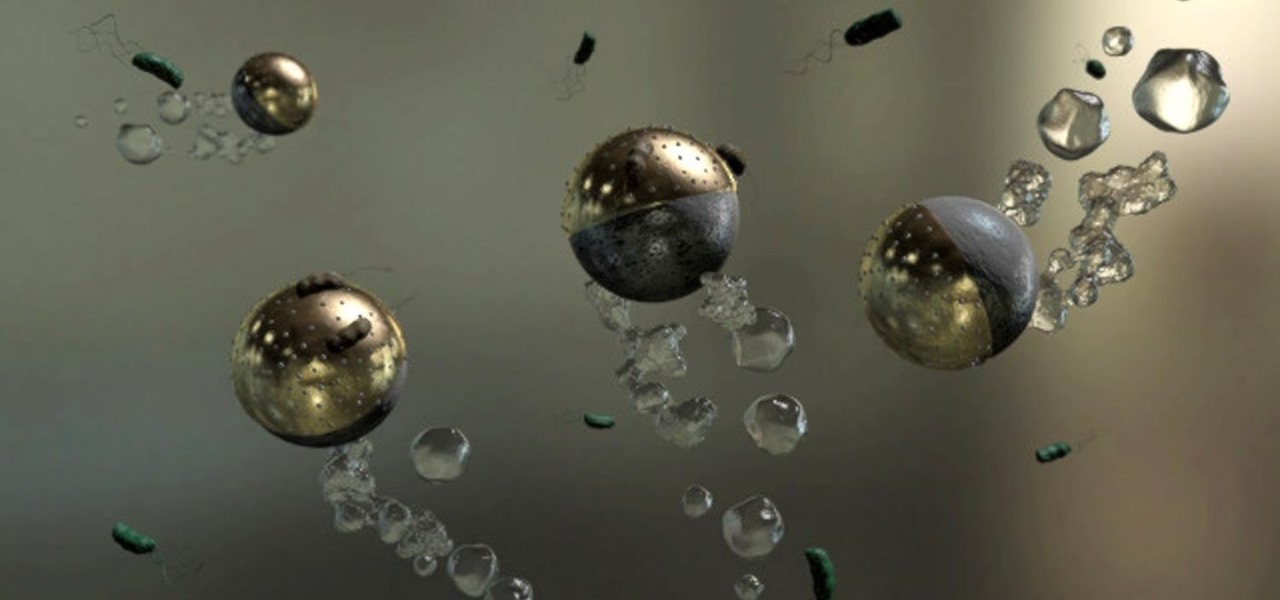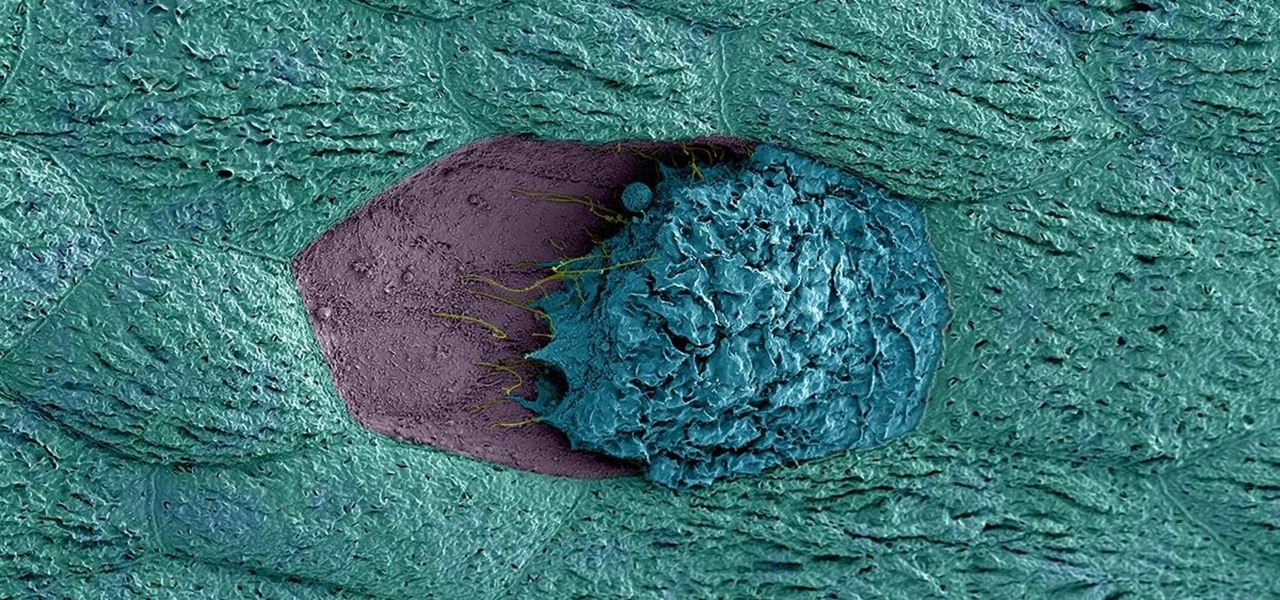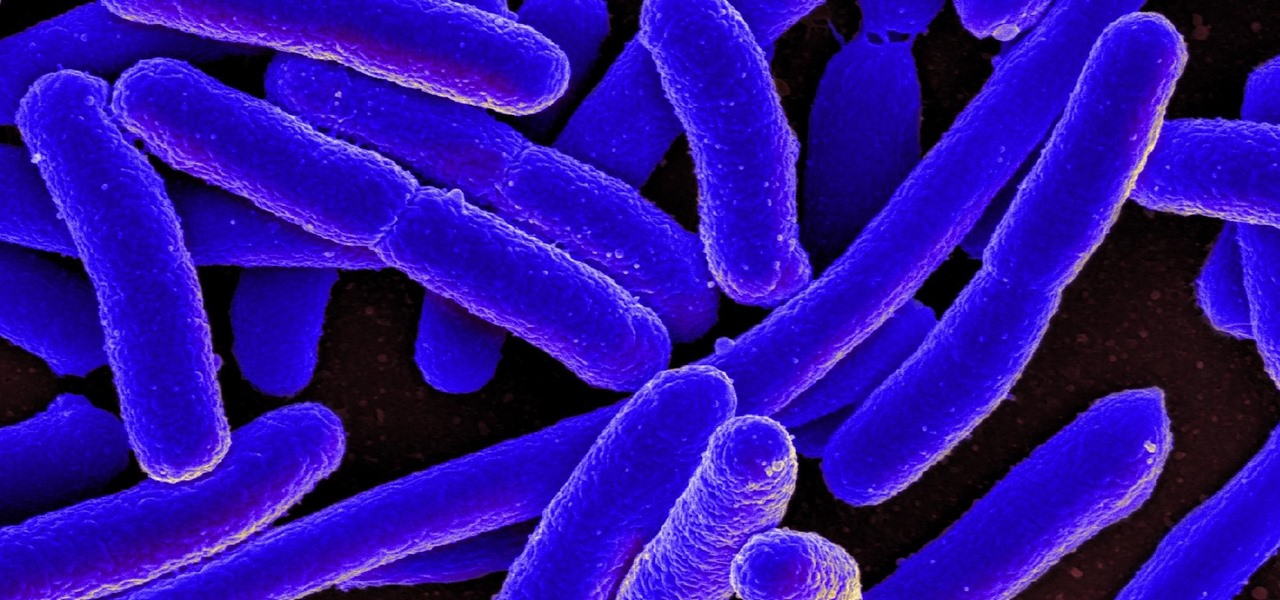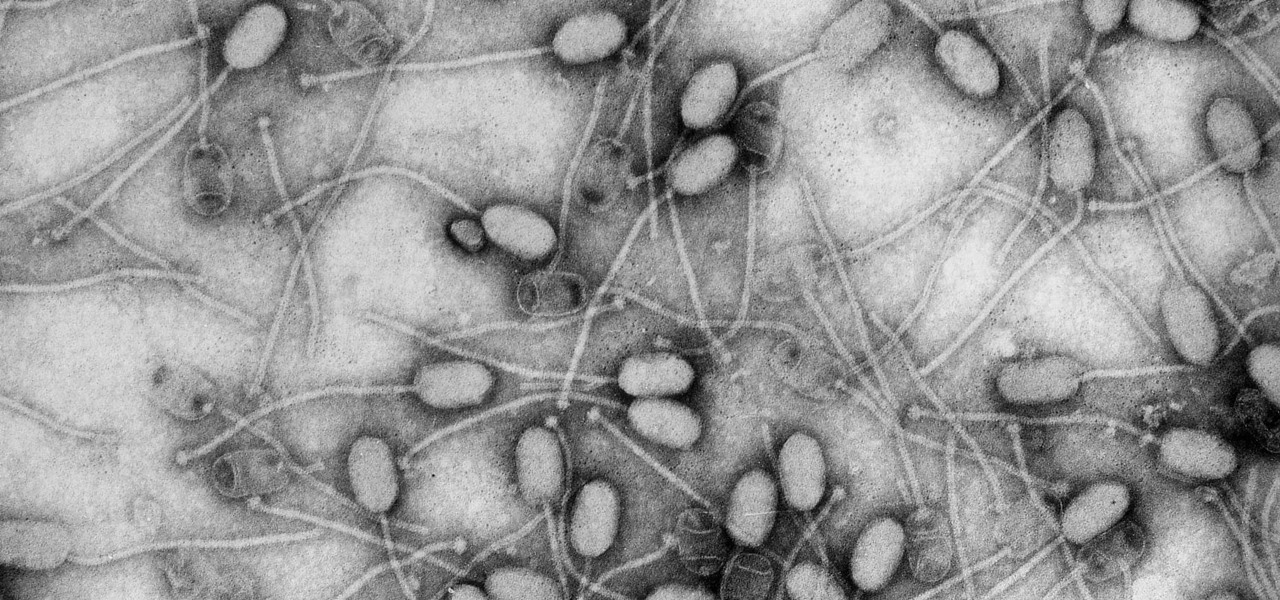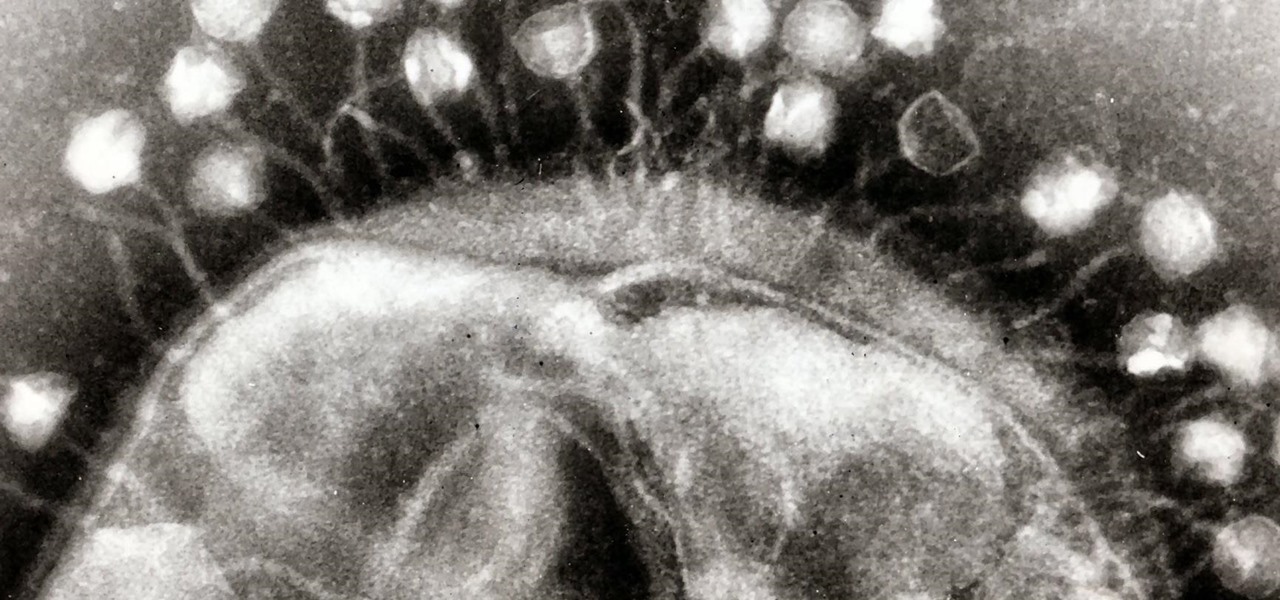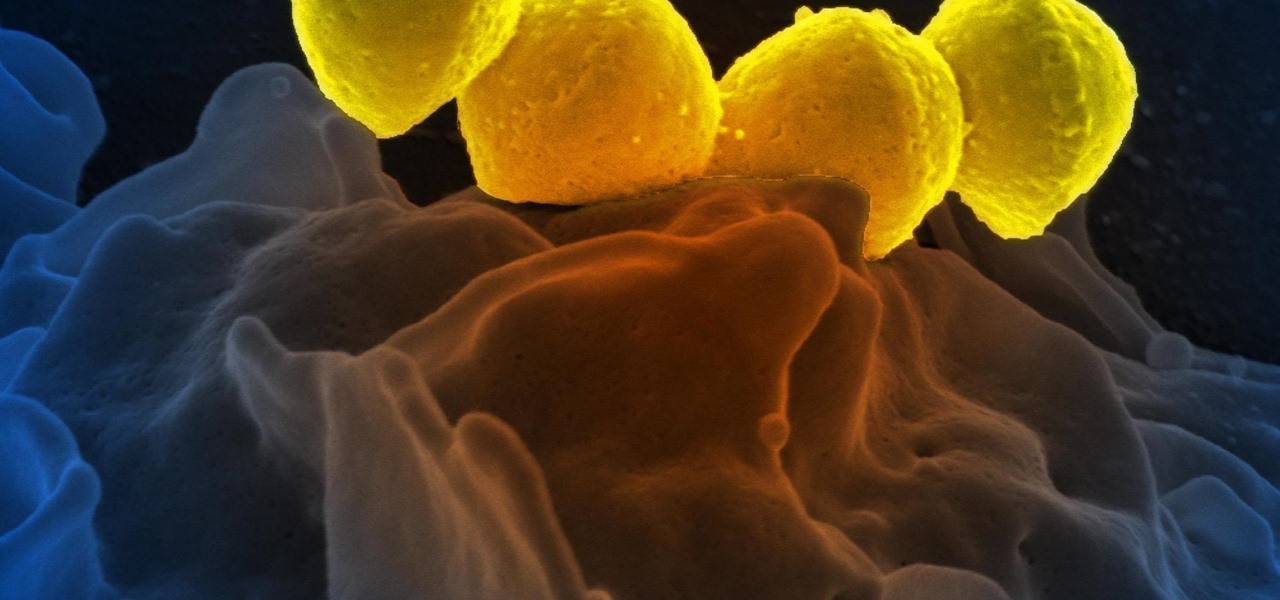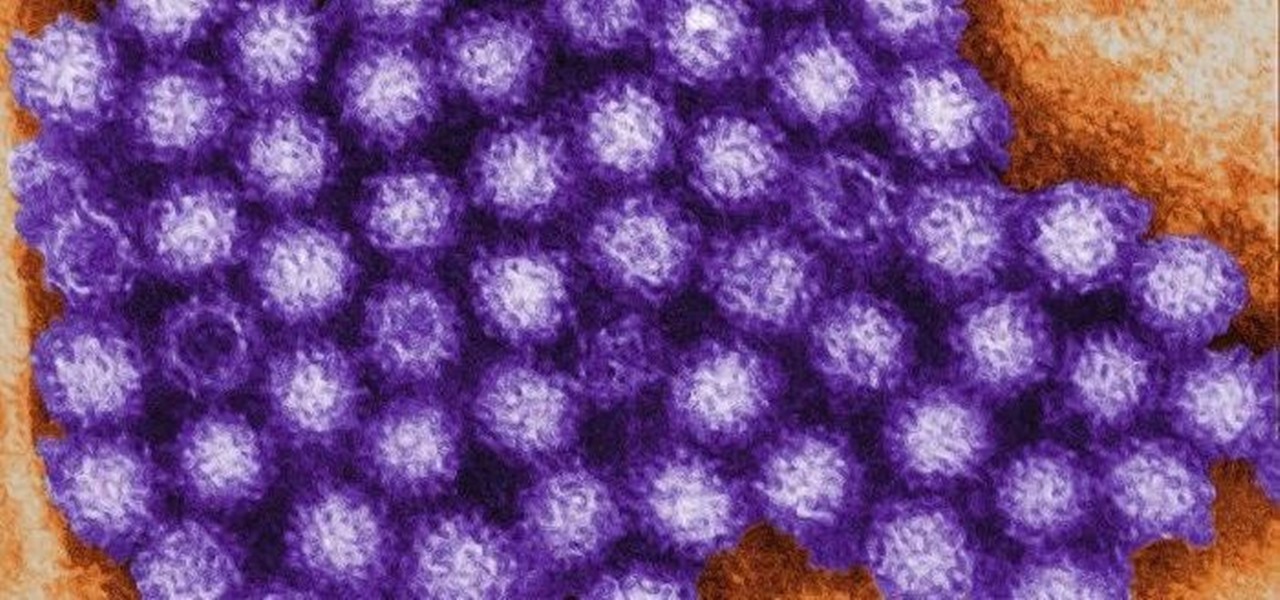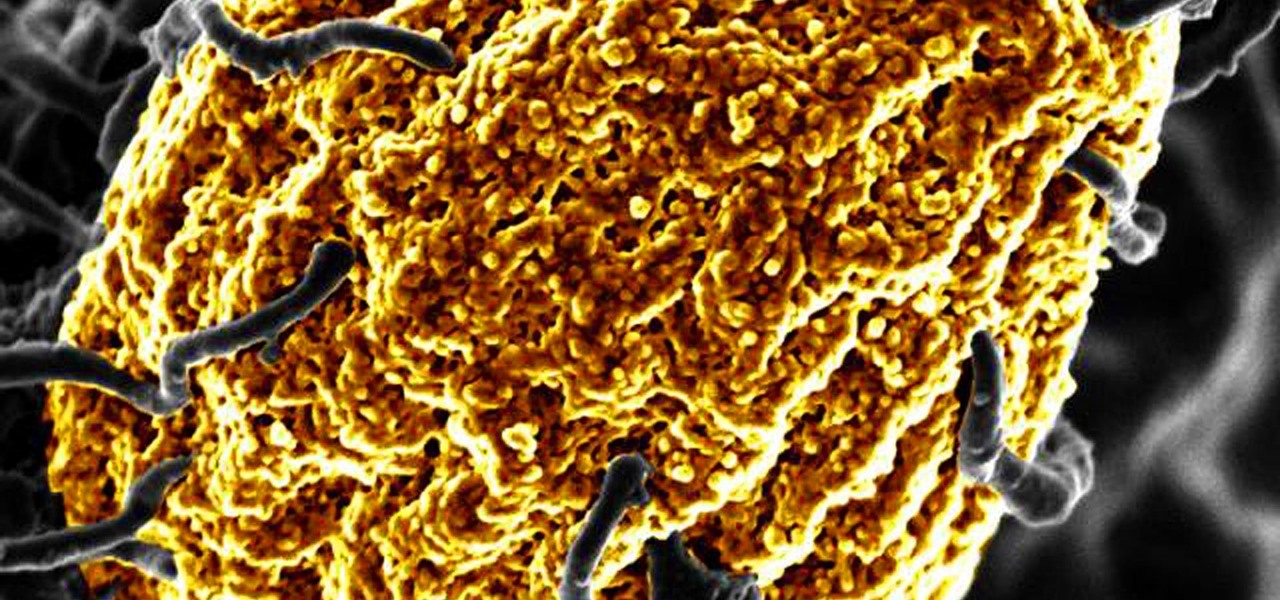
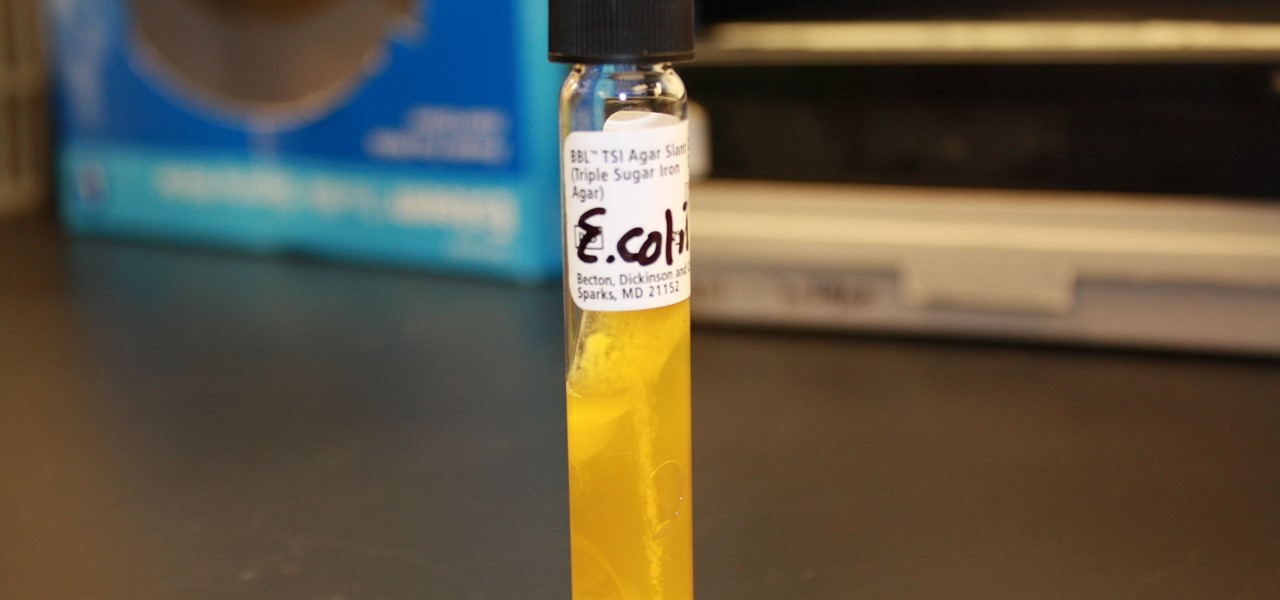
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) drive over eight million people to seek medical attention every year. Almost all — as many as 90% — of those infections are caused by Escherichia coli. Copper can kill bacteria, but E. coli has found a way to capture the copper, preventing its antibacterial action. Now, researchers have found that, in a cruel irony, the bacteria use the copper it grabs as a nutrient to feed its growth.

I.M. Healthy Original Creamy SoyNut Butter was recalled on March 4 after being linked to 16 Escherichia coli cases in nine states. Montessori of Alameda preschool in Portland is the latest victim in a multi-state E. coli outbreak caused by the nut-free butter.
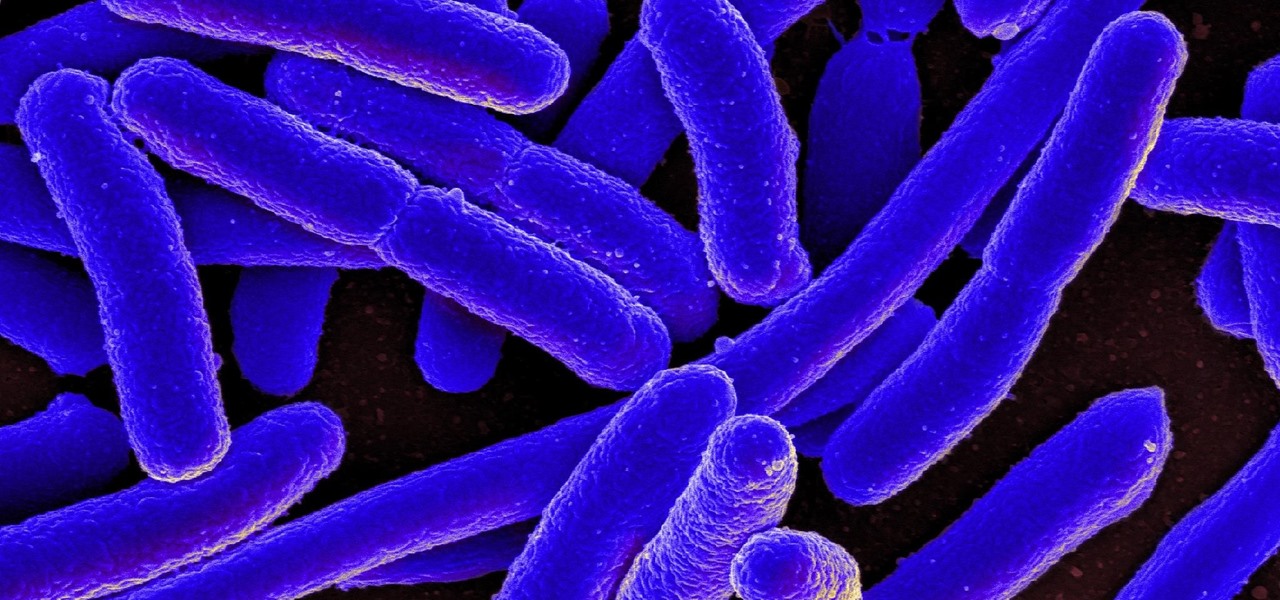
New research reveals how E. coli bacteria construct elaborate and effective tunnels to pump unwanted molecules like antibiotics and other toxins out of cells. The discovery could help us better understand how antibiotic resistance occurs and give us a leg-up to beat them at their own game.

There have been seven more people sickened from four states since the I.M. SoyNut Butter E. coli outbreak was announced earlier this month. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Washington Department of Health have confirmed the I.M. Healthy SoyNut Butter was the cause of the outbreak in an update today.
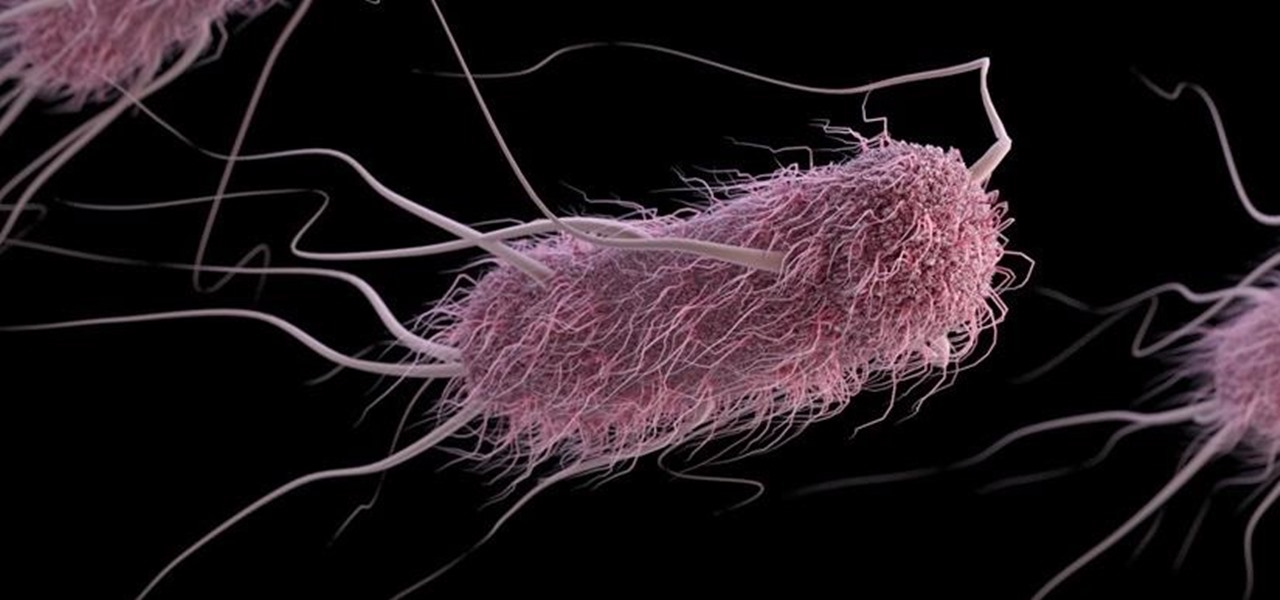
A gold-medal winning entry into the iGEM synthetic biology competition could change the way we look at Esherichia coli, the bacteria better known as E. coli.
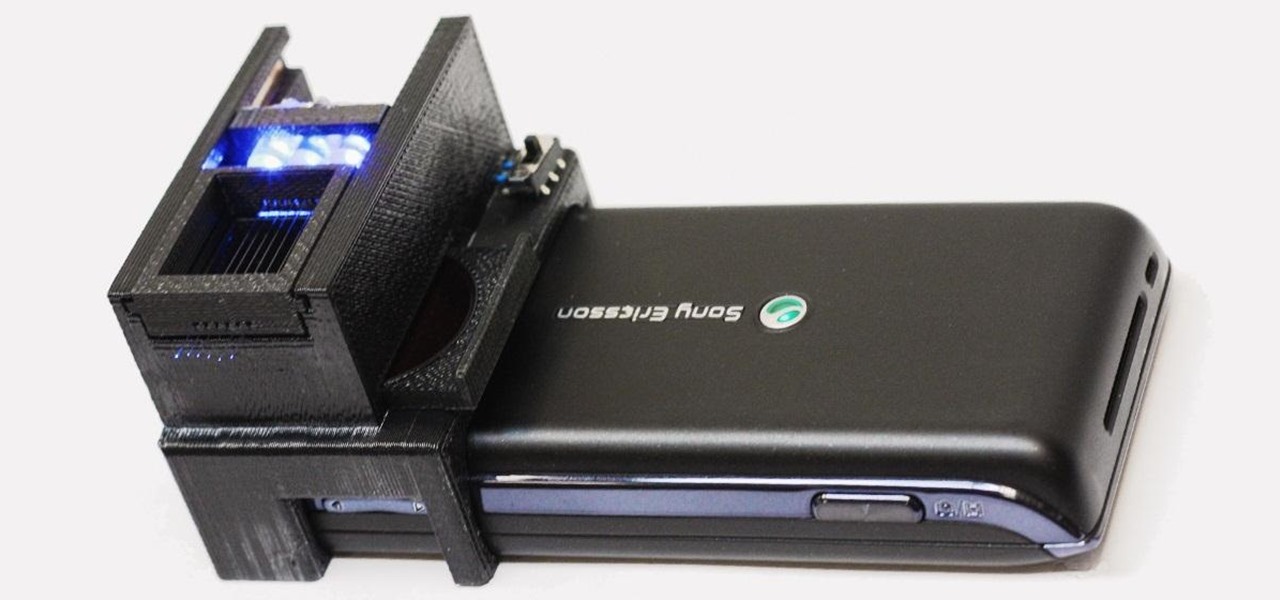

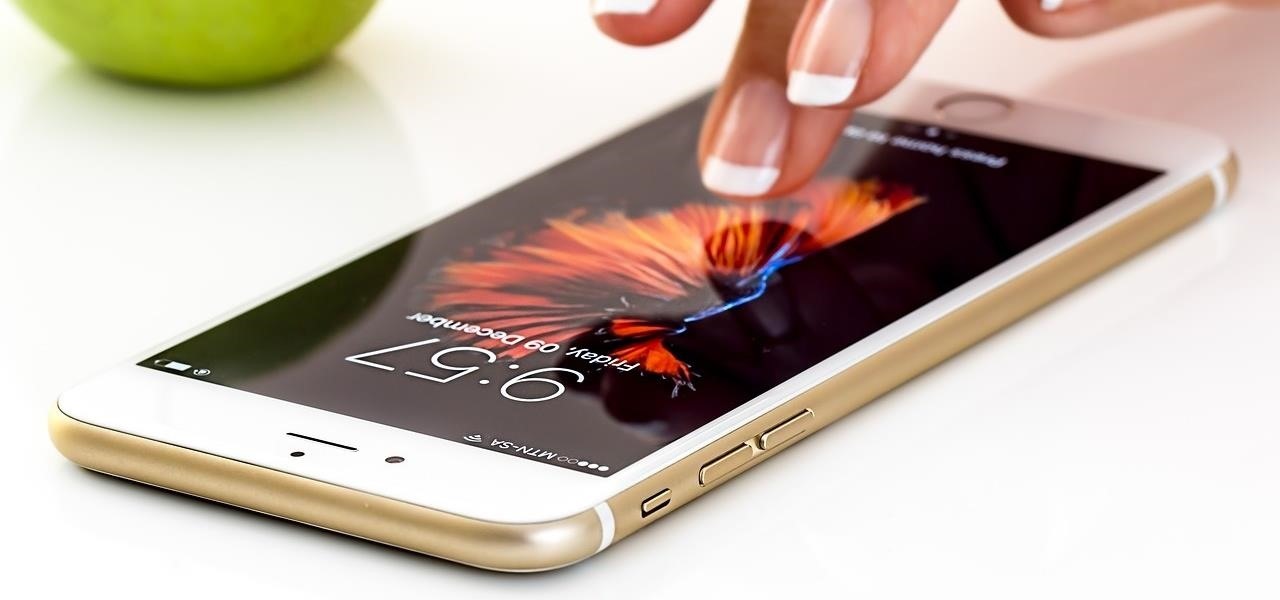
As deeply as smartphones are integrated into our daily lives, it's no surprise that people are finding ways to use them to stay healthy. From detecting cancer and radiation to diagnosing STDs, phones have come a long way, baby.

Some types of bacterial infections are notoriously tough to treat — and it's not all due to antibiotic resistance. The bacteria themselves are rugged and hard to penetrate with drugs.

Although their effectiveness is waning, antibiotics remain a front-line defense against many infections. However, new science reveals using the wrong antibiotic for an infection could makes things much worse.

Seagrass may help your favorite beach stay a little less toxic. A new study, led by Joleah Lamb, a postdoctoral researcher in the Harvell Lab at Cornell University, found that coastal seagrasses reduce levels of pathogens dangerous to humans and marine organisms in near-shore waters.

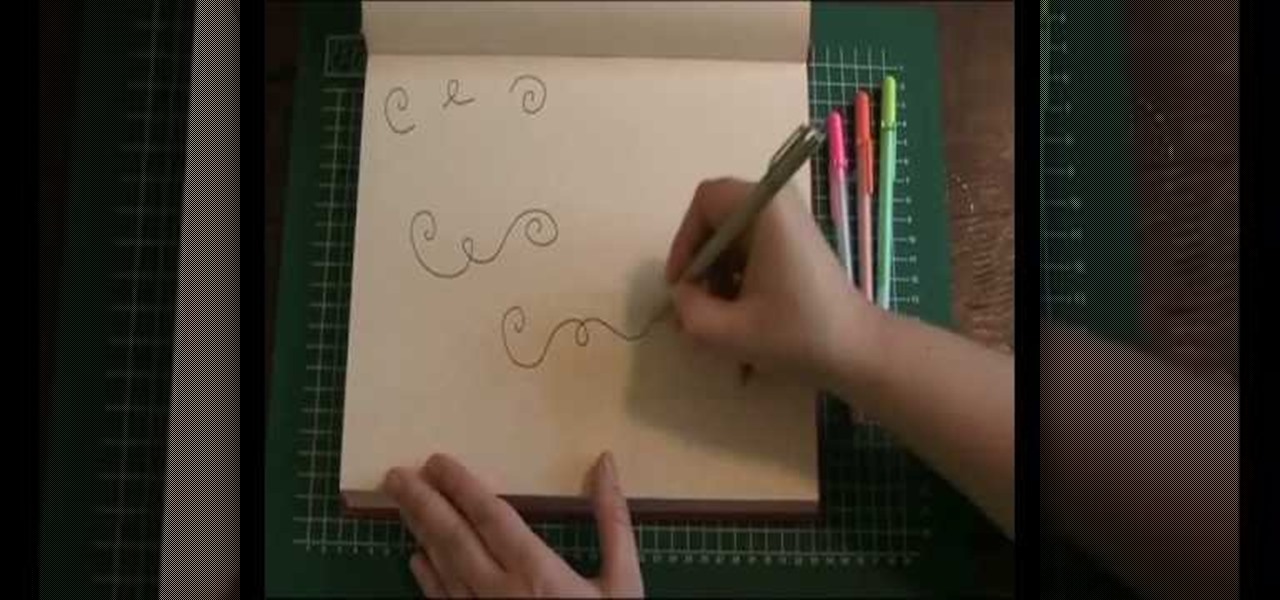
In this video, we learn how to draw a doodle with Marieke Blokland. Start off by writing the letter "e" in cursive, several times, making the letter larger as you go. Link the e's together, then when you get to the bottom of the paper it will be just a scribbled loop. Now, on the next page, draw more of these looped e's, dragging out the lines. On the next paper, draw spirals going from smaller to larger and going clockwise and counter-clockwise. Start to incorporate all of these shapes toget...

Most females have had at least one urinary tract infection in their lifetimes. Recurrent UTIs are particularly problematic in young, sexually active women, where about 80% of the infections are caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli, better known as E. coli.

Franklin Chef Becker shows you how to prepare a great chicken salad with off the shelf products. To make this salad, wash your lettuce, then add lemon juice, vinegar and olive oil. Mix peppers, cucumbers, scallions, salad, and chicken to complete this low carbohydrate dish for health watchers. Don't ingest any e-coli.

Cytochrome P450 (P450s) are proteins found in nearly all living organisms, which play roles that range from producing essential compounds and hormones to metabolizing drugs and toxins. We use some of the compounds synthesized by P450 in plants as medical treatments, but the slow growth and limited supply of these plants have put the drugs' availability in jeopardy and jacked up prices.

Look no further than Flint, Michigan, to discover the serious consequences of contaminated drinking water. Around the world, water polluted by pathogens and toxins sickens people or cuts them off from safe drinking water. Looking for a solution, researchers created tiny, swimming robots that pack a powerful punch against waterborne pathogens.

The number of households in the US that go hungry because they lack money for food hit a high of almost 15% in 2011. While that number continues to decline, nearly 13% of American households still go hungry.

As drug-resistant bacteria become more commonplace, researchers are looking for new antibacterial strategies to disrupt disease-causing microbes. Some scientists are working to create new drugs, while others are trying out drug combinations. Another group, however, are ditching pharmaceuticals altogether and experimenting with non-drug alternatives.

The U.S. Centers for Disease Control estimates that 73,000 people contract E. coli O157:H7 each year. The primary source of these illnesses is ground beef that has been improperly handled and cooked. Watch this video to learn how you can avoid the spread of this bacteria.

Scientists know that bacteria create their own energy, get nutrients to run their cellular processes, and multiply. But, bacteria haven't been shown to respond to external mechanical stimulation or signals in a way that's similar to how our bodies respond to touch, until now.

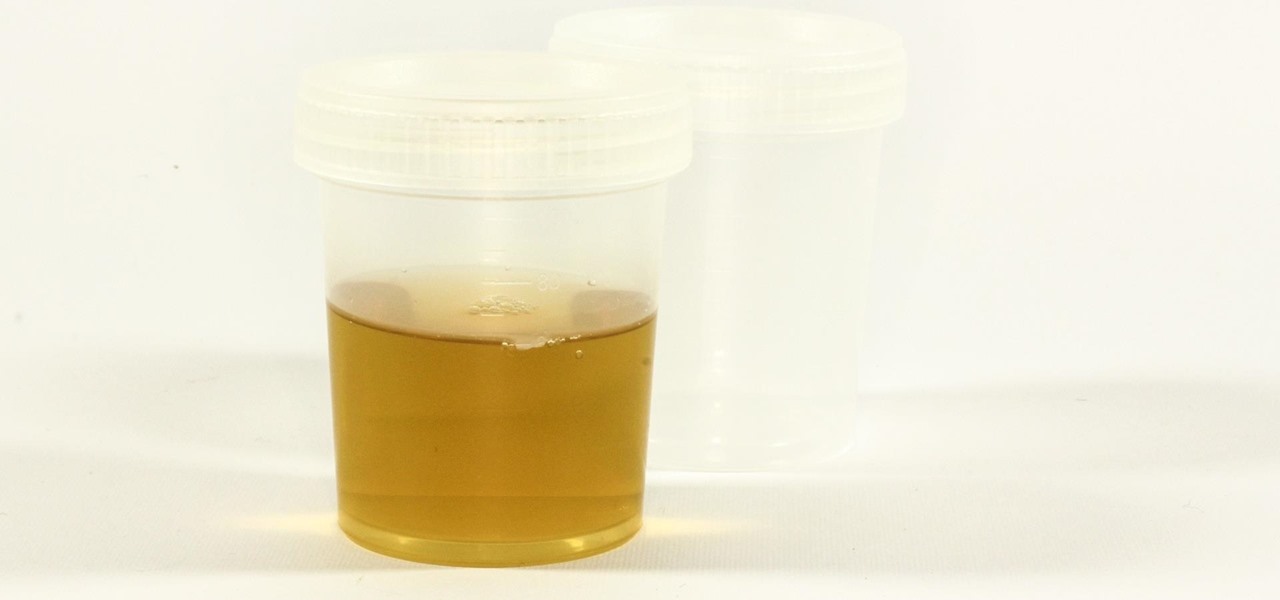
Have you ever had a burning sensation when you urinate? Low fever, back pain, and maybe cloudy urine? Male or female, it could have been a urinary tract infection. If it lasted long enough, the chances are good you went to the doctor for help. For about 20% of women, standard testing for a UTI does not reveal the presence of infection-causing bacteria, even though bacteria may be causing their symptoms. Well, a new test may provide better answers.

Food is both a necessity and a joy. Many people enjoy exploring, cooking, eating, and learning about foods from around the world. But the picture isn't always rosy. A new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), highlights the ways and whereabouts of food that make us sick.

Olla! In this lesson we will be learning how to tell the time in Spanish.

We know that healthcare-related facilities can be fertile ground for antibiotic-resistant bacteria, but recent research suggests your produce aisle might be too.

Fighting fire with fire, scientists are harnessing the adaptability of helpful microbes to challenge the adaptability of deadly microbes. What are we talking about? Hunting with phages — viruses that attack and kill bacteria.

The evolution of our infection-fighting systems may have something to teach modern scientists. That's what a group from the University of Granada in Spain found when they studied a protein that's been around for over four billion years. Their work, by senior author José Sánchez-Ruiz and colleagues in the Department of Physical Chemistry, was published in the journal Cell Reports.

In a recently released video, it was revealed that Formula-E's partner Roborace has developed a driverless race car that can complete laps at full racing speed.

Some Montana inhabitants have been making impassioned pleas to legalize raw milk this week. The debate took place during a hearing on House Bill 325, which was held by the Senate Agriculture, Livestock, and Irrigation Committee on Tuesday, March 21.

Even when no one is in your kitchen, it is crowded. The refrigerator, sink, and counters are all covered with microbes that are just hanging around. They are inadvertent remnants from the raw chicken you used in that recipe last night, brewing a bacterial cocktail in your Nespresso machine, or just growing their merry little colonies on your leftovers.

Significant strides have been in the race to find antibiotics to treat superbug infections — those caused by bacteria resistant to the antibiotics used to treat them. Now, an international team of scientists has discovered a new antibiotic produced by a microbe found in Italian soil.

Devastating and deadly, land mines are a persistent threat in many areas of the world. Funding to clear regions of land mines has been decreasing, but new research may offer a less dangerous method of locating hidden, underground explosives by using glowing bacteria.

Our quest to find new antibiotics has taken a turn — a turn down the road, that is. A team of scientists from the University of Oklahoma is scooping up roadkill and searching for bacteria on them that might yield the world's next antibiotic.

Have you ever had the stomach flu, aka the 24-hour flu? Well, chances are high that you never had influenza, but an intestinal infection called gastroenteritis.

New research suggests the bacteria that causes listeriosis may be a bigger threat in early pregnancy than previously thought. Usually considered a danger to late pregnancy, scientists suggest early undiagnosed miscarriages could be caused, in some cases, by infection with Listeria.

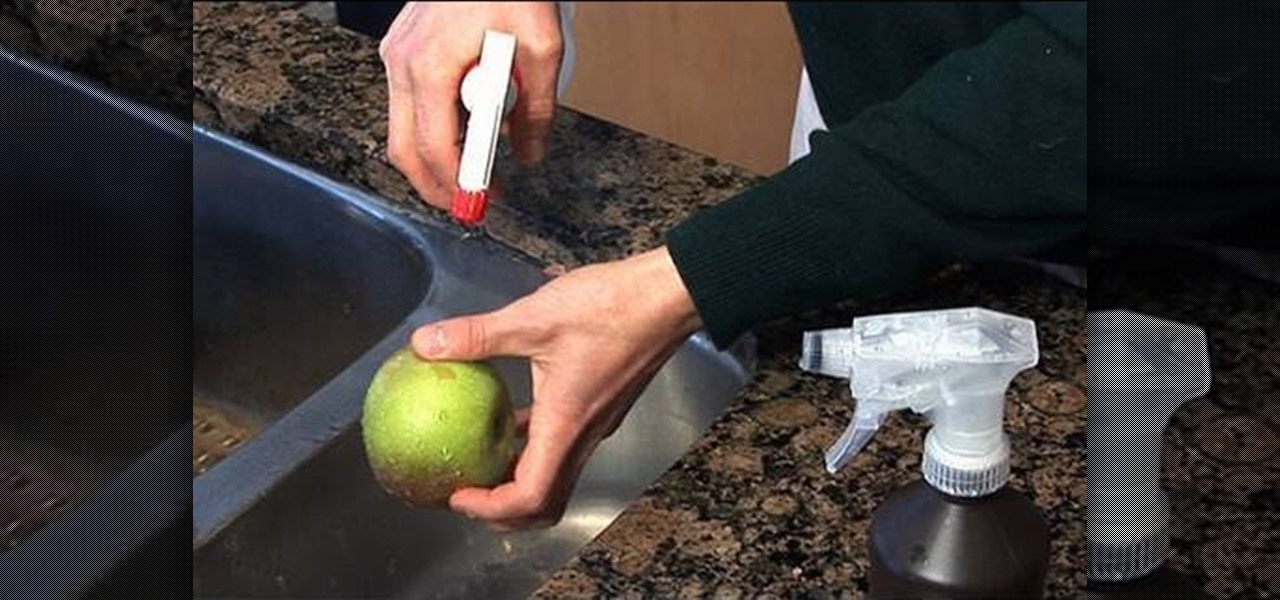
Keeping things clean is very important to prevent food born illnesses. Washing fruit is important. You can take care of many problems by just running them under water. You can use white vinegar and hydrogen peroxide to clean fruit. Start by spraying some white vinegar on the fruit and then a little hydrogen peroxide. After you spray the fruit with white vinegar and hydrogen peroxide rinse it in water and that will wash all the vinegar and peroxide off of the fruit. The vinegar and peroxide wi...

It won't come as a surprise to hear that your cell phone, tablet, and laptop are loaded with bacteria and other organic material. While most of these bacteria are harmless, there are good reasons to reduce the capability of your mobile devices to infect you—or other people.

What would it be like to have clothing that killed microbes? Or paper that repelled pathogens? A research team from Rutgers University has developed a prototype out of metalized paper to zap the bad guys without being super expensive. Sound good? Read on.

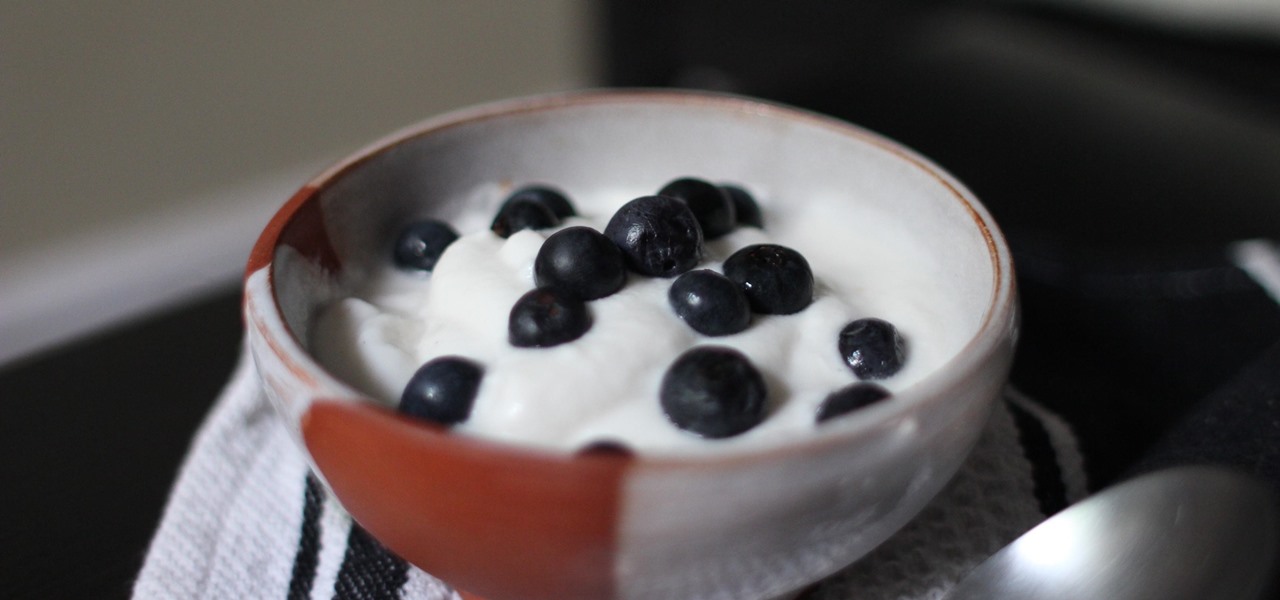
Yogurt is more than an excellent source of protein, calcium, and gut-healthy probiotic bacteria. A protein isolated from probiotic lactobacillus bacteria in yogurt is capable of inhibiting drug-resistant bacteria.

Wound infections don't usually enter the blood and become systemic, spreading the infection throughout our bodies, and there's a good reason for that: Our bodies actively work to prevent it, according to research that discovered a new use for a protein first discovered decades ago.

The body's usual response to a bacterial infection in the blood — called sepsis — takes time. It requires a carefully orchestrated sequence of events that gets the body's immune system ramped up to deal with the invading bacteria.

Antibiotic-resistant infections that usually occur only in hospital settings are spreading in communities, increasing hospital stays—and danger—for young children.

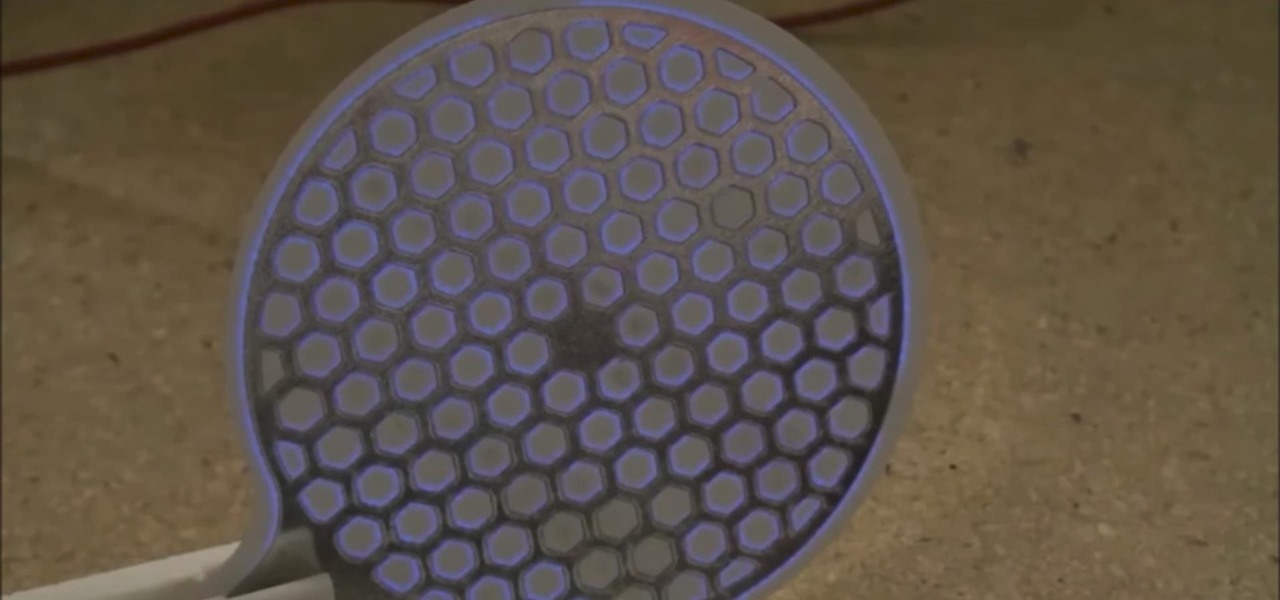
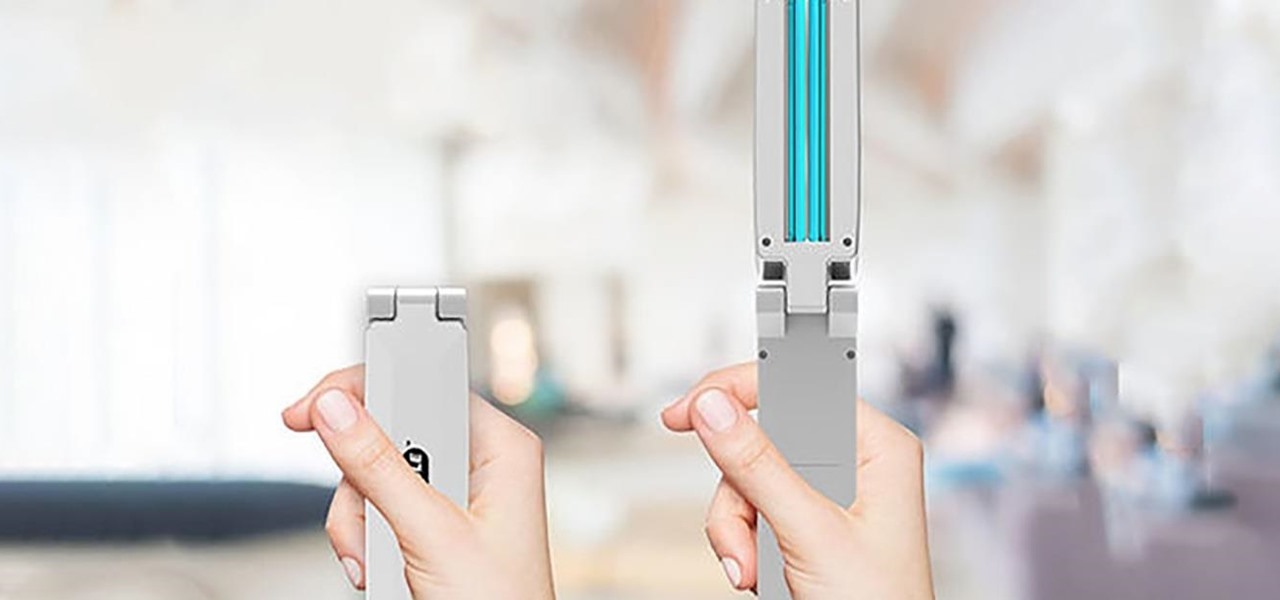
Maintaining a clean living space is important, but it shouldn't have to be a hassle. The KAPSULE™ UV Sanitizing Wand 2.0 is designed to keep surfaces pathogen-free. This powerful wand emits 254nm UV-C light and makes quick work of pathogens. In a laboratory test, KAPSULE even eliminated more than 99% of E-coli!