Network enumeration is one of the essential phases of an attack, but it can take a lot of time and effort depending on the size. We've all been spoiled by Nmap and similar tools, and while there is a learning curve involved, they are extremely useful. But there's also GoScan, a tool that builds upon Nmap, offering an automated way to enumerate networks and services quickly.

SMB (Server Message Block) is a protocol that allows resources on the same network to share files, browse the network, and print over the network. It was initially used on Windows, but Unix systems can use SMB through Samba. Today, we will be using a tool called Enum4linux to extract information from a target, as well as smbclient to connect to an SMB share and transfer files.

It's been said time and time again: reconnaissance is perhaps the most critical phase of an attack. It's especially important when preparing an attack against a database since one wrong move can destroy every last bit of data, which usually isn't the desired outcome. Metasploit contains a variety of modules that can be used to enumerate MySQL databases, making it easy to gather valuable information.

NetBIOS is a service that allows for communication over a network and is often used to join a domain and legacy applications. It is an older technology but still used in some environments today. Since it is an unsecured protocol, it can often be a good starting point when attacking a network. Scanning for NetBIOS shares with NBTScan and the Nmap Scripting Engine is a good way to begin.
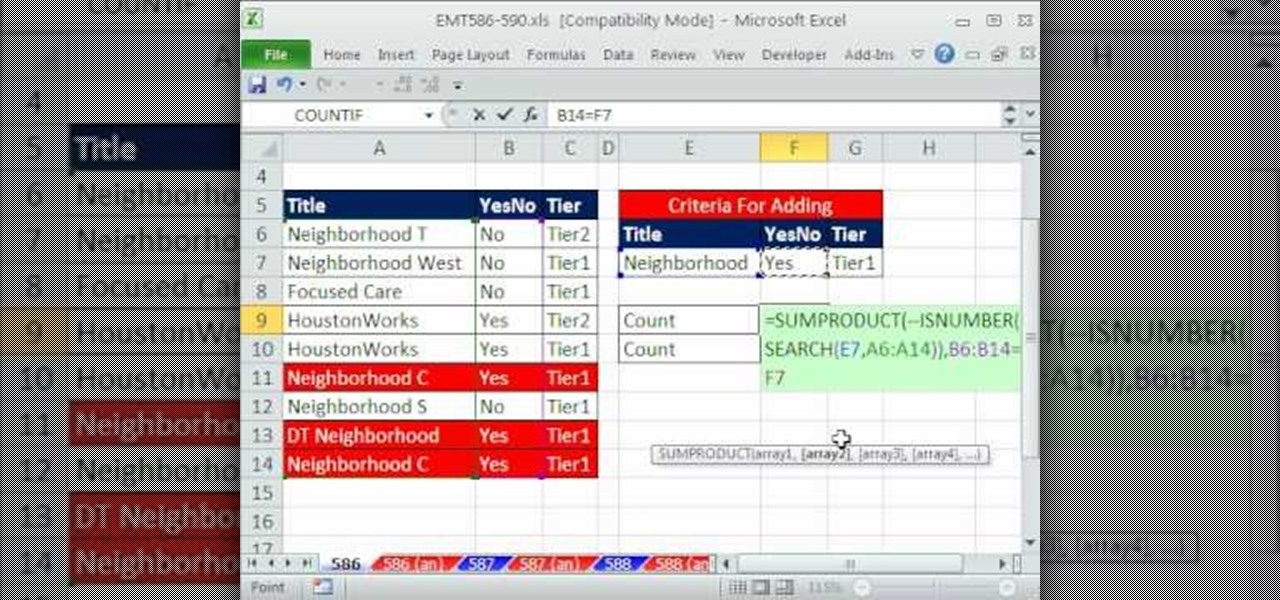
New to Microsoft Excel? Looking for a tip? How about a tip so mind-blowingly useful as to qualify as a magic trick? You're in luck. In this MS Excel tutorial from ExcelIsFun, the 586th installment in their series of digital spreadsheet magic tricks, you'll learn how to enumerate rows that meet 3 using the SEARCH function.
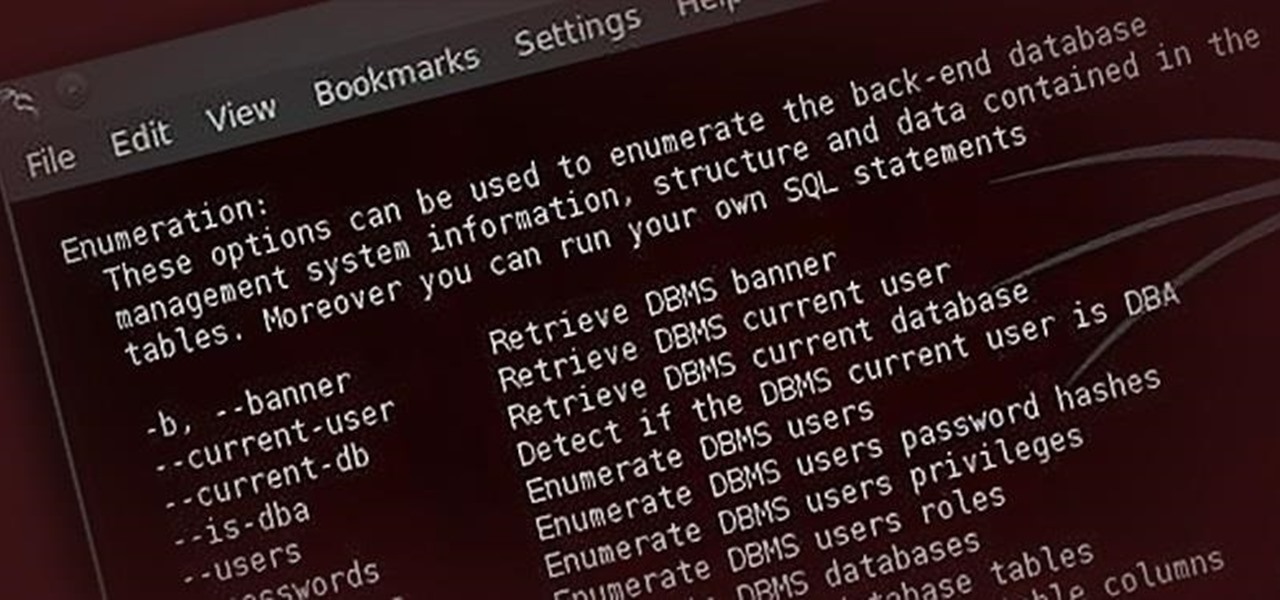
Welcome back, my greenhorn hackers! In a previous tutorial on hacking databases, I showed you how to find online databases and then how to enumerate the databases, tables, and columns. In this guide, we'll now exfiltrate, extract, remove—whatever term you prefer—the data from an online database.

Determining the antivirus and firewall software installed on a Windows computer is crucial to an attacker preparing to create a targeted stager or payload. With covert deep packet inspection, that information is easily identified.

One of the ultimate goals in hacking is the ability to obtain shells in order to run system commands and own a target or network. SQL injection is typically only associated with databases and their data, but it can actually be used as a vector to gain a command shell. As a lesson, we'll be exploiting a simple SQL injection flaw to execute commands and ultimately get a reverse shell on the server.

Deleted bank statements and private photos are still within an attacker's grasp, so don't think that emptying your recycling bin is enough to keep your files from coming back to life. It's possible for a hacker to recover compromising files and images from a backdoored computer completely without the victim's knowledge.

When approaching a target, having a precise and detailed plan of attack is absolutely necessary. One of the main goals is to increase the attack surface since the more opportunities there are for exploitation, the greater the chances of success. Subdomain enumeration is one method used to increase the attack surface, and we'll be using a tool called Subfinder to discover hidden subdomains.

Penetration-testing frameworks can be incredibly useful since they often streamline certain processes and save time by having a lot of tools available in one place. Of course, the most popular pentesting framework is undoubtedly Metasploit, but there are many others out there that cater to particular needs. For auditing web applications and servers, Tishna comes in handy.

Traditional subdomain enumeration techniques create a lot of noise on the target server and may alert intrusion detection systems to an attacker's intentions. For a stealthier approach, there's a tool with the capability of finding hundreds of subdomains related to the target website without alarming the server administrators.

Automation has been a buzz word for quite some time now, but the principles behind it are as strong as ever. For a hacker or pentester, Bash scripting is one form of automation that cannot be ignored. Virtually any command that can be run from the terminal can be scripted — and should be, in many cases — to save valuable time and effort. And a Bash script just happens to be great for recon.

With a tiny computer, hackers can see every website you visit, exploit services on the network, and break into your Wi-Fi router's gateway to manipulate sensitive settings. These attacks can be performed from anywhere once the attacker's computer has been connected to the router via a network implant.

Welcome back, my neophyte hackers! Have you ever had a neighbor that you're certain is up to no good? Maybe you've seen him moving packages in and out at all hours of the night? Maybe you've seen people go into his home and never come out? He seems like a creep and sometimes you hear strange sounds coming from his home? You know he's up to no good, but you aren't sure what it is exactly.

There are tons of tools out there that do all kinds of recon, but it can be hard to narrow down what to use. A great way to be more efficient is by taking advantage of scripting. This doesn't have to mean writing everything from scratch — it can simply mean integrating existing tools into a single, comprehensive script. Luckily, it's easy to create your own subdomain enumeration script for better recon.

No operating system is stricken with as many vulnerabilities as Windows, and it's often a race to release the latest patches to fix things. From an attacker's point of view, knowing which patches are present on a Windows machine can make or break successful exploitation. Today, we will be covering three methods of patch enumeration, using Metasploit, WMIC, and Windows Exploit Suggester.

Samba can be configured to allow any user with write access the ability to create a link to the root filesystem. Once an attacker has this level of access, it's only a matter of time before the system gets owned. Although this configuration isn't that common in the wild, it does happen, and Metasploit has a module to easily exploit this security flaw.

After exploiting a vulnerable target, scooping up a victim's credentials is a high priority for hackers, since most people reuse passwords. Those credentials can get hackers deeper into a network or other accounts, but digging through the system by hand to find them is difficult. A missed stored password could mean missing a big opportunity. But the process can largely be automated with LaZagne.

Welcome back, my greenhorn hackers! Throughout this series on Metasploit, and in most of my hacking tutorials here on Null Byte that use Metasploit (there are many; type "metasploit" into the search bar and you will find dozens), I have focused primarily on just two types of modules: exploits and payloads. Remember, Metasploit has six types of modules:

Without admin privileges, installing additional software, or modifying the Windows 10 firewall, an attacker can alter a router and perform a variety of exploits. It's accomplished by forwarding requests from Kali through a backdoored Windows computer to the router gateway with simple SSH tunnels.

Post-exploitation information gathering can be a long and drawn-out process, but it is an essential step when trying to pivot or establish advanced persistence. Every hacker should know how to enumerate a target manually, but sometimes it is worth it to automate the process. Metasploit contains post modules that can quickly gather valuable information about a target, saving both time and effort.

Reconnaissance is one of the most important and often the most time consuming, part of planning an attack against a target.

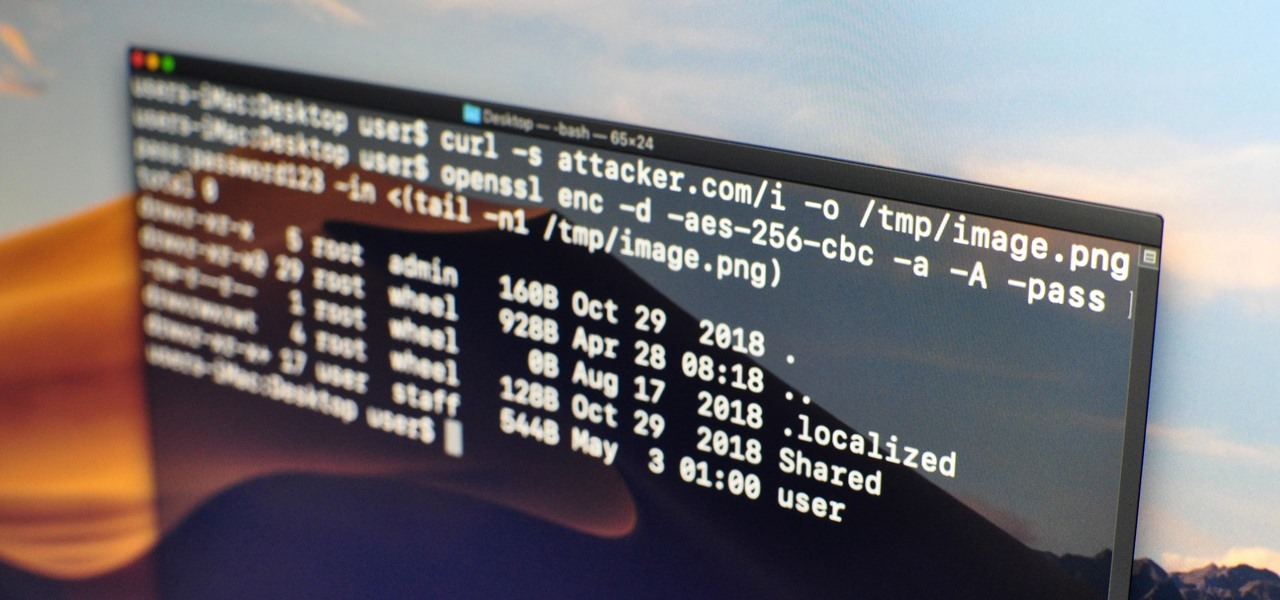
Firewall solutions for macOS aren't impervious to attacks. By taking advantage of web browser dependencies already whitelisted by the firewall, an attacker can exfiltrate data or remotely control a MacBook, iMac, Mac mini, or another computer running macOS (previously known as Mac OS X).

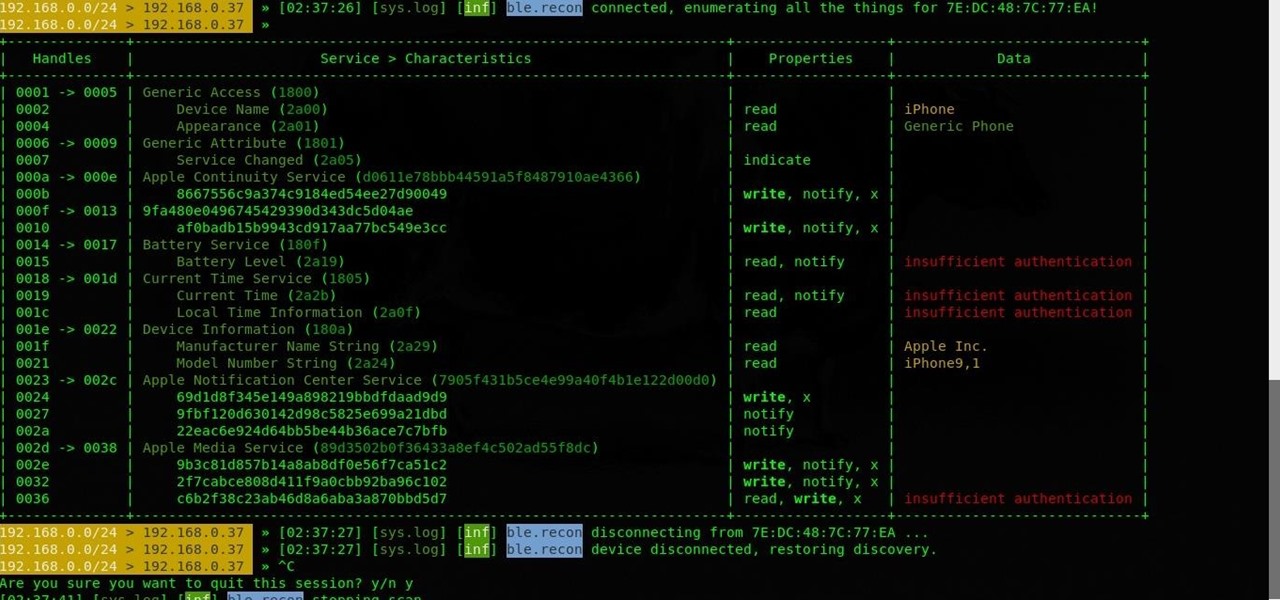
An incredible amount of devices use Bluetooth or Bluetooth Low Energy to communicate. These devices rarely have their radios switched off, and in some cases, are deliberately used as trackers for lost items. While Bluetooth devices support MAC address randomization, many manufacturers do not use it, allowing us to use tools like Bettercap to scan for and track Bluetooth devices.

With the number of web applications out there today, it comes as no surprise that there are just as many vulnerabilities waiting for hackers to discover. Finding those vulnerabilities can be a difficult task, but there are plenty of tools available to make the process easier. While it won't help find any zero-days, web scanners such as Uniscan will detect common vulnerabilities.

The ability to stay organized and be resourceful with data gathered from recon is one of the things that separates the true hackers from the script kiddies. Metasploit contains a built-in database that allows for efficient storage of information and the ability to utilize that information to better understand the target, which ultimately leads to more successful exploitation.

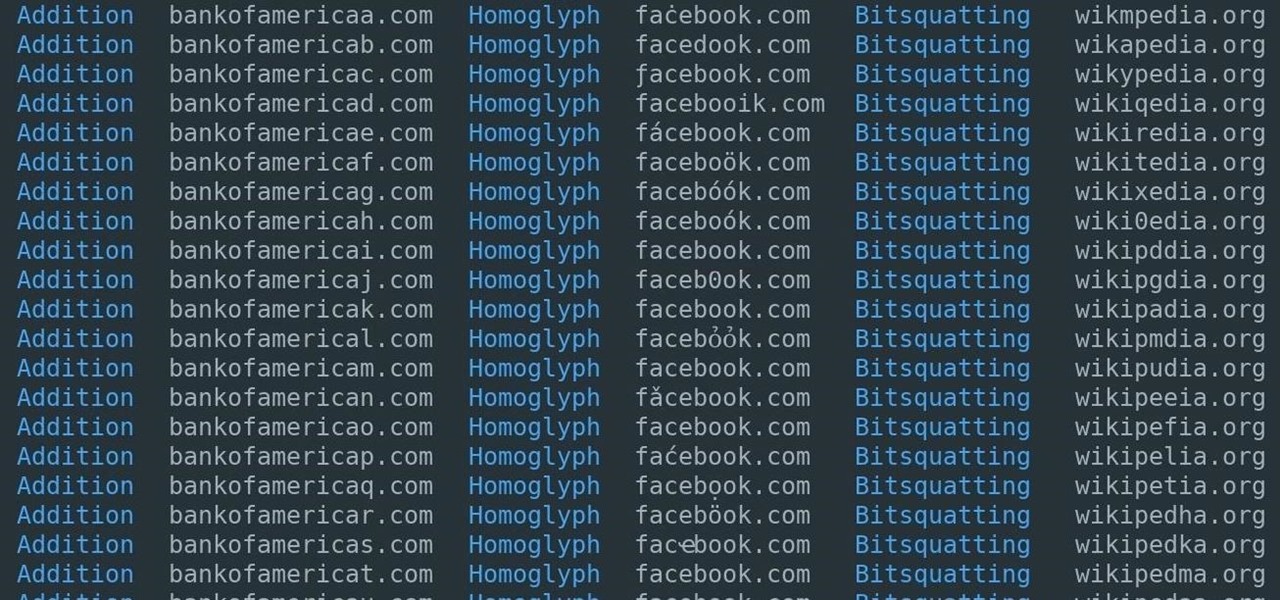
A convincing domain name is critical to the success of any phishing attack. With a single Python script, it's possible to find hundreds of available phishing domains and even identify phishing websites deployed by other hackers for purposes such as stealing user credentials.

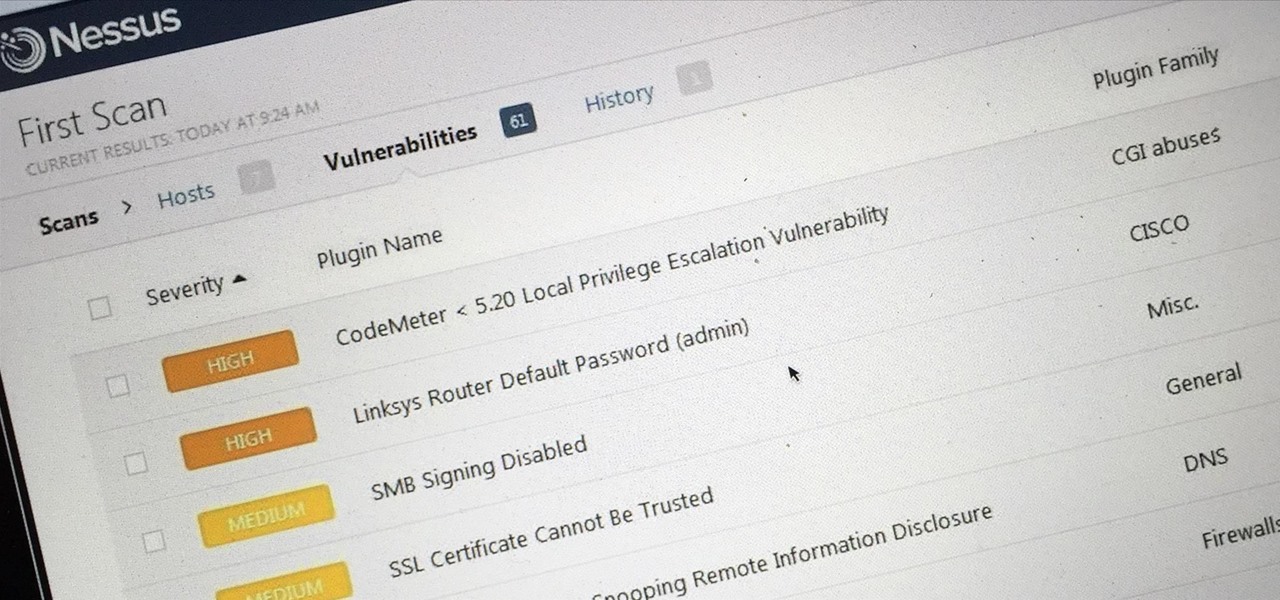
Welcome back, my tenderfoot hackers! Generally, you will want to perform a vulnerability scan before doing a penetration test. Vulnerability scanners contain a database of all known vulnerabilities and will scan your machine or network to see whether those vulnerabilities appear to exist. If they do, it is your job to test whether they are real and can be exploited.

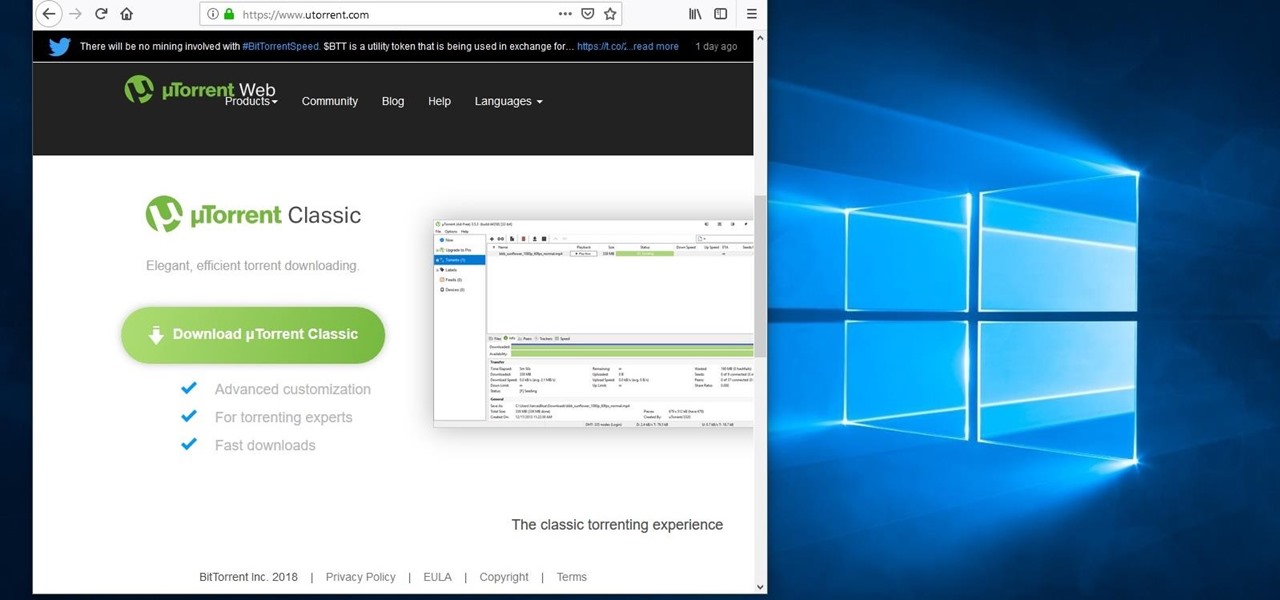
Compromised uTorrent clients can be abused to download a malicious torrent file. The malicious file is designed to embed a persistent backdoor and execute when Windows 10 reboots, granting the attacker remote access to the operating system at will.

Auditing websites and discovering vulnerabilities can be a challenge. With RapidScan and UserLAnd combined, anyone with an unrooted Android phone can start hacking websites with a few simple commands.

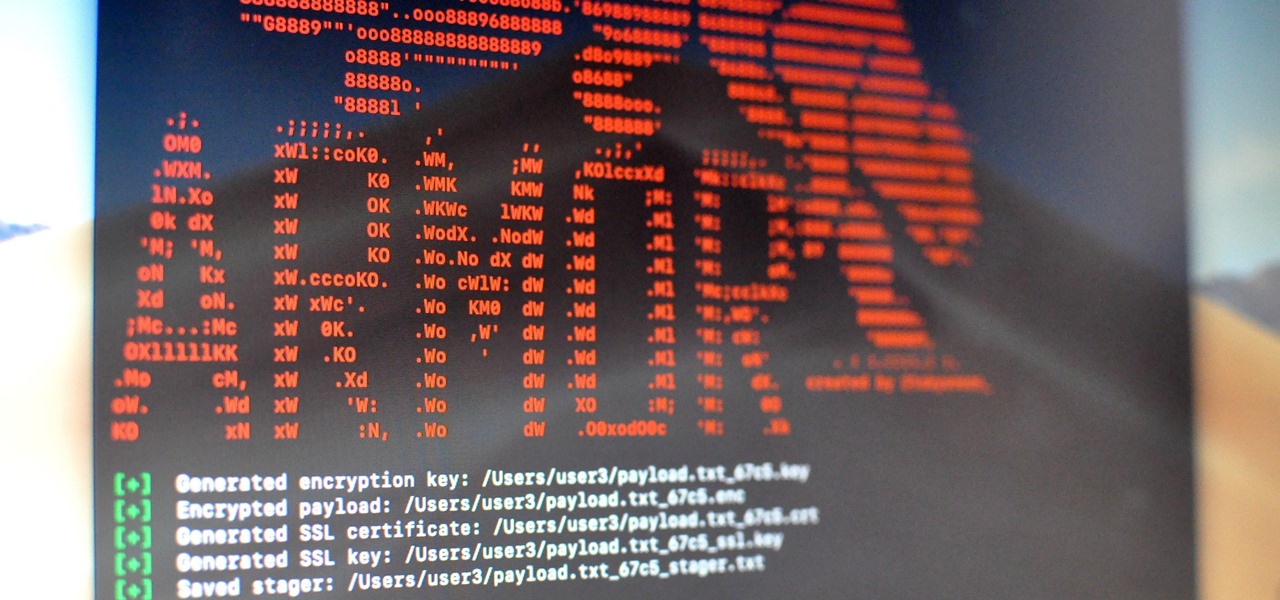
Encrypting payloads and encoding stagers are more effective against macOS than one might think. It's very easy to evade VirusTotal and macOS antivirus software using a few simple tricks.

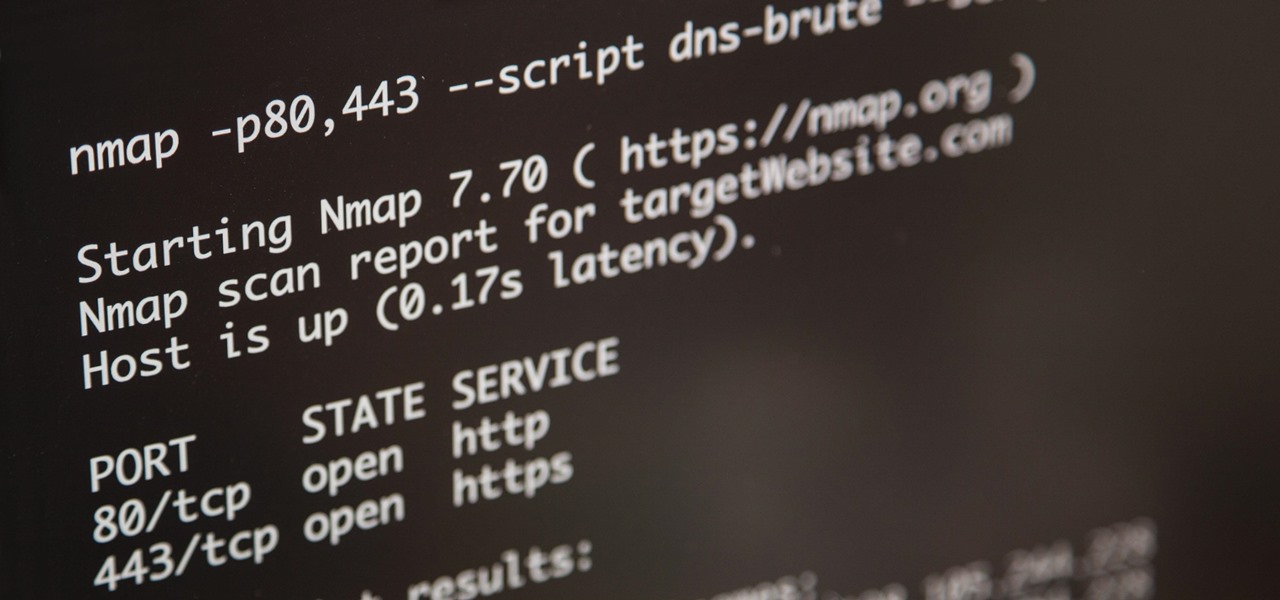
Nmap is more powerful than you know. With a few scripts, we can extend its functionality beyond a simple port scanner and start to identify details about target servers sysadmins don't want us to know.

Greetings my fellow hackers, In the previous article, I discussed briefly about ransomwares and their devastating capabilities. Devastating in a way that ransomwares are not only known to encrypt files but to also lockout some specific functions of the system and hold it up for a ransom.

It's been a while when the major web browsers first introduced HTTP Strict Transport Security, which made it more difficult to carry Man In The Middle (MITM) attacks (except IE, as always, which will support HSTS since Windows 10, surprised?).

Welcome back, my hacker apprentices! Metasploit framework is an incredible hacking and pentesting tool that every hacker worth their salt should be conversant and capable on.

With an ordinary birthday card, we can introduce a physical device which contains malicious files into someone's home and deceive them into inserting the device into a computer.

The moment arrives when you finally pop a shell on the web server you've been working on, only you find yourself in a strange environment with limited functionality. Restricted shells are often used as an additional line of defense and can be frustrating for an attacker to stumble upon. But with enough patience and persistence, it is possible to escape these restricted environments.

Data can be injected into images quickly without the use of metadata tools. Attackers may use this knowledge to exfiltrate sensitive information from a MacBook by sending the pictures to ordinary file-sharing websites.