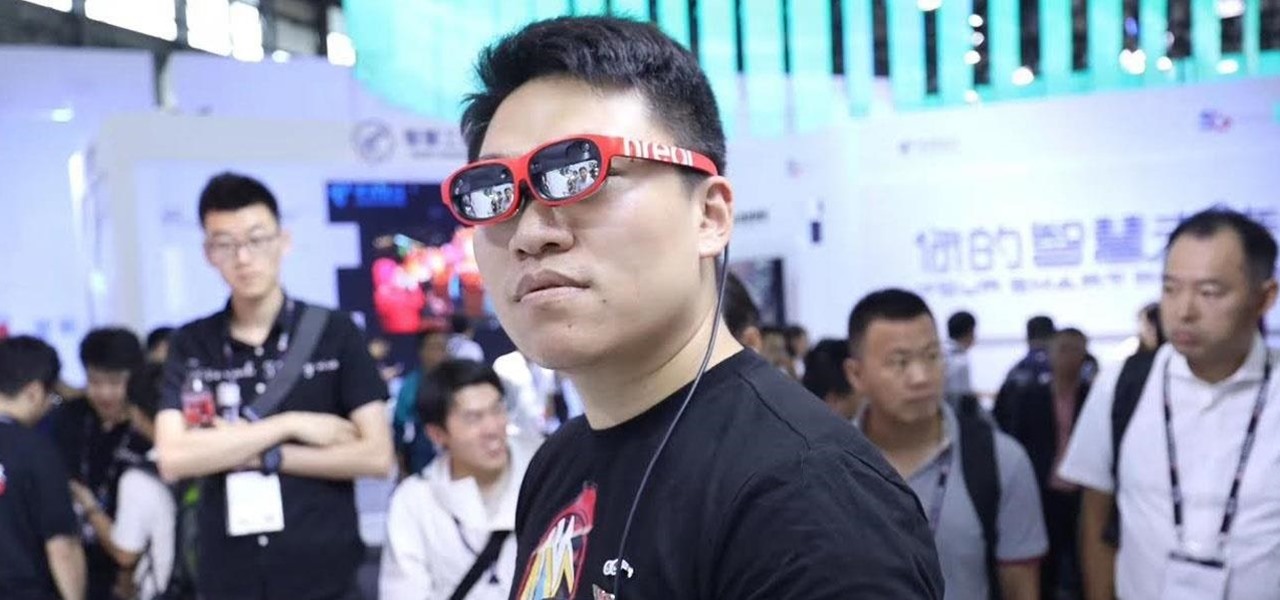
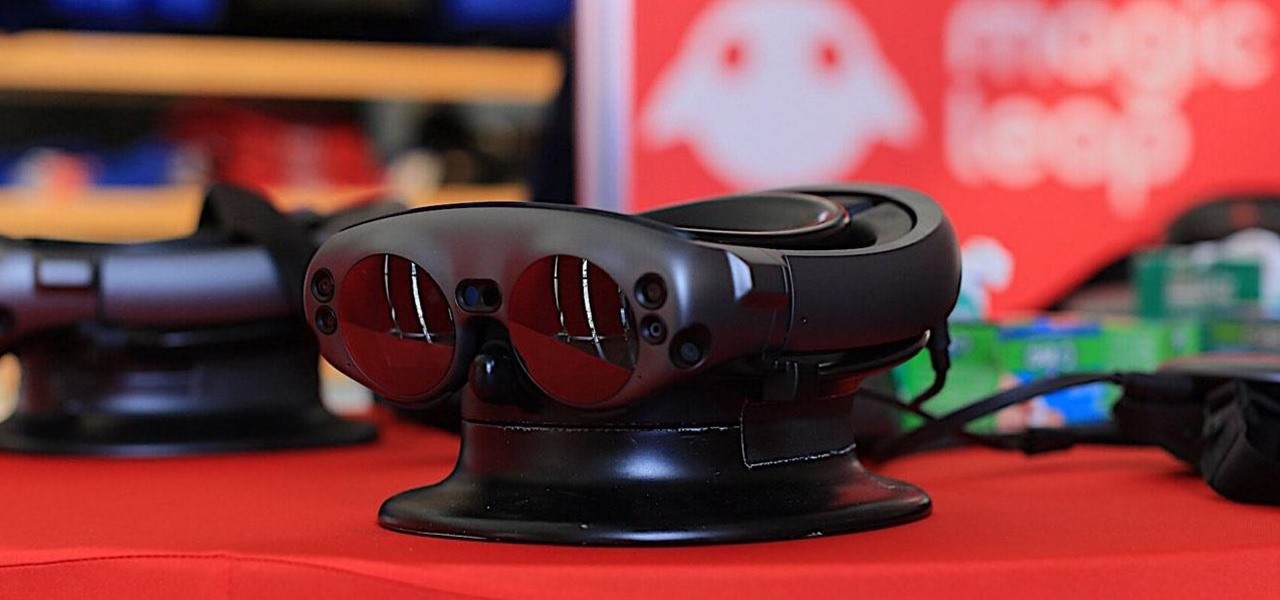
Noted poet T.S. Elliot once wrote that "April is the cruelest month." But Magic Leap might argue that March is the most miserable, as the Ides of March brought more legal woes to augmented reality startup. Elsewhere, its closely-held branding secrets have been spilled by way of the US Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO).
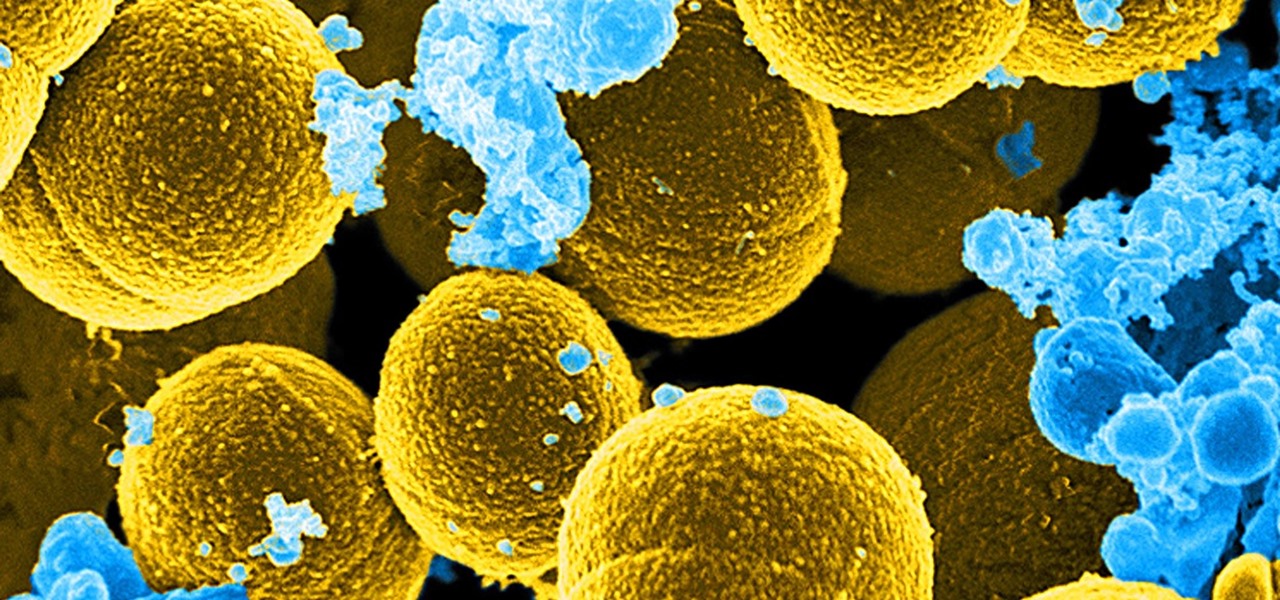
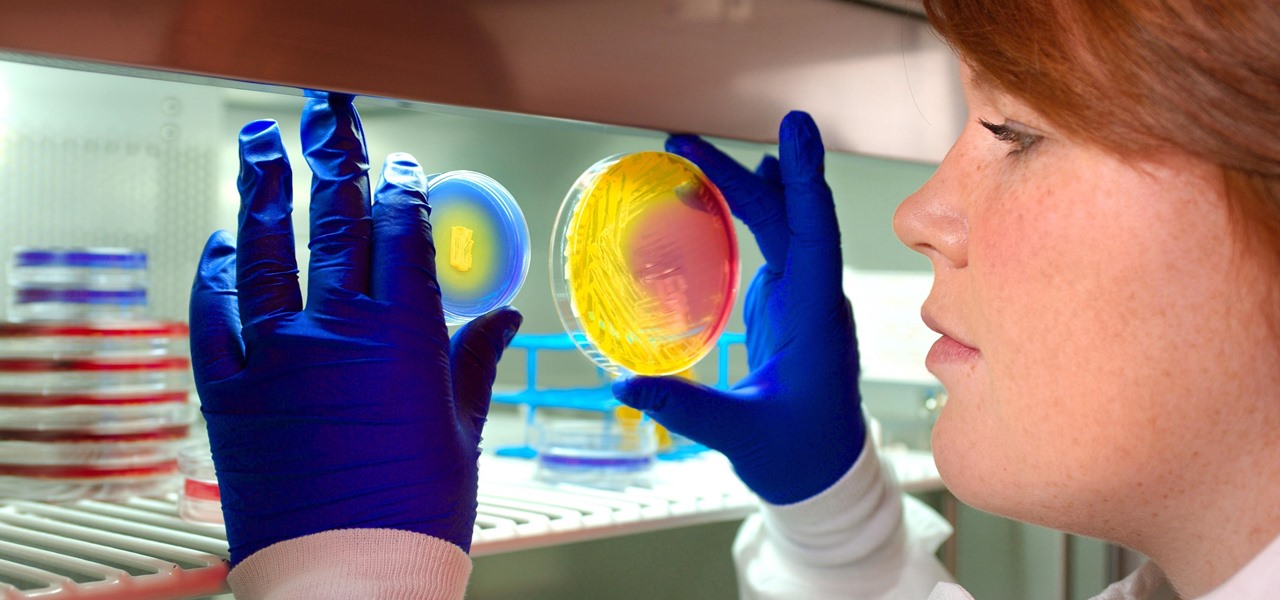
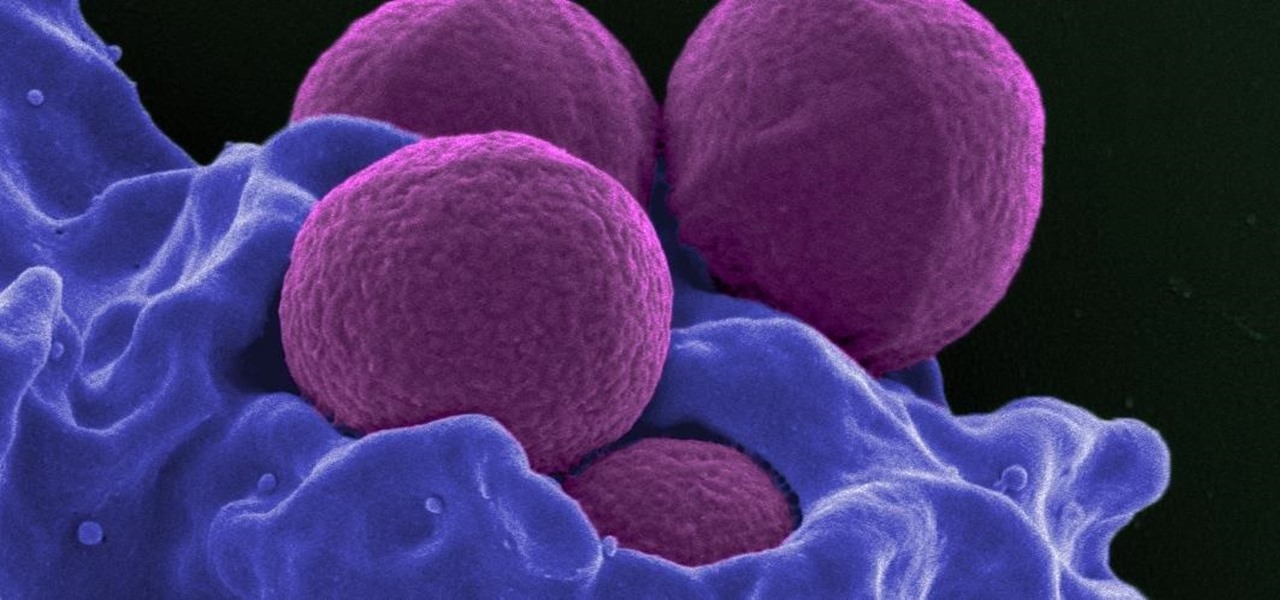
For once there is good news — surprising news, but good news — in the fight against antibiotic-resistant organisms. A recent study found that Staphylococcus aureus bacteria is becoming more sensitive to some key drugs used to treat it.

Cytochrome P450 (P450s) are proteins found in nearly all living organisms, which play roles that range from producing essential compounds and hormones to metabolizing drugs and toxins. We use some of the compounds synthesized by P450 in plants as medical treatments, but the slow growth and limited supply of these plants have put the drugs' availability in jeopardy and jacked up prices.
It looks like "going live" is another thing we all have to figure out how to do to remain relevant in this very Facebook-driven world. But why would you ever want to go live? That's really up to you.
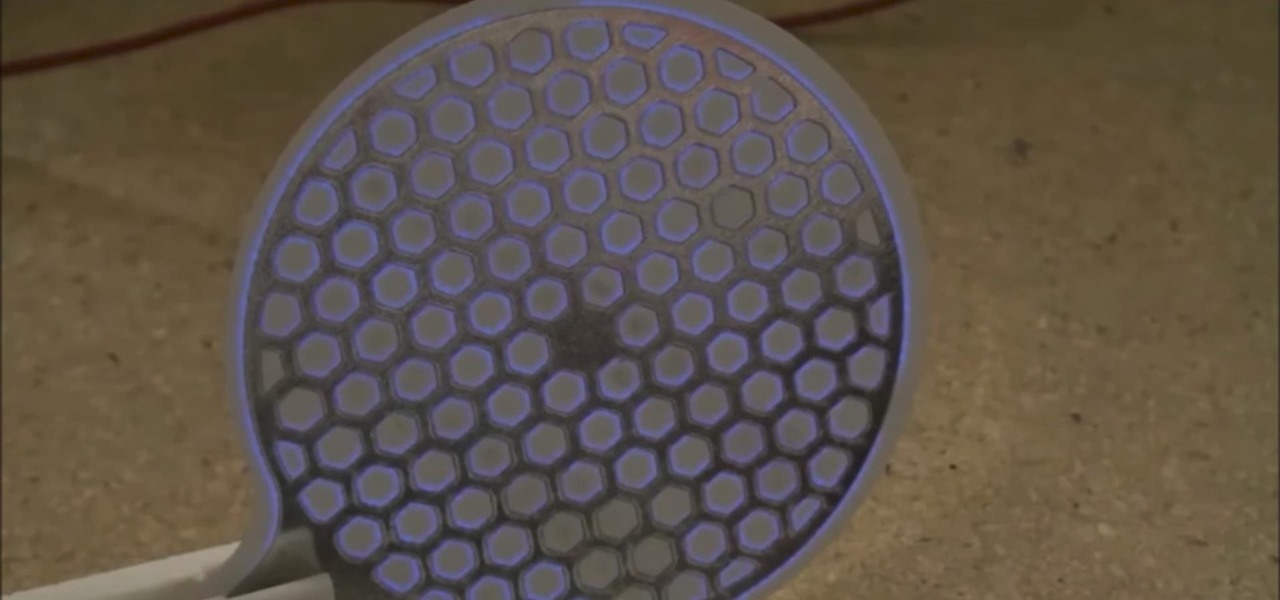

What would it be like to have clothing that killed microbes? Or paper that repelled pathogens? A research team from Rutgers University has developed a prototype out of metalized paper to zap the bad guys without being super expensive. Sound good? Read on.
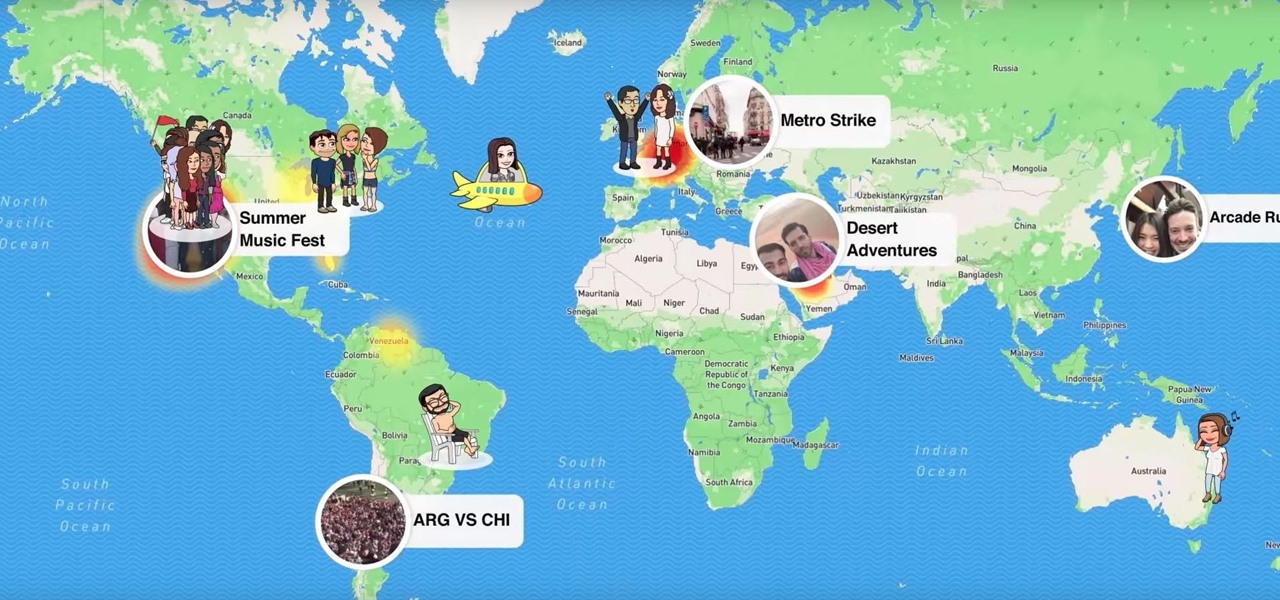
Snapchat's newest feature will allow you to see where your friends are posting from around the world. Called Snap Map, this easy-to-use update gives users the ability to view your friends' stories and locations on a map.

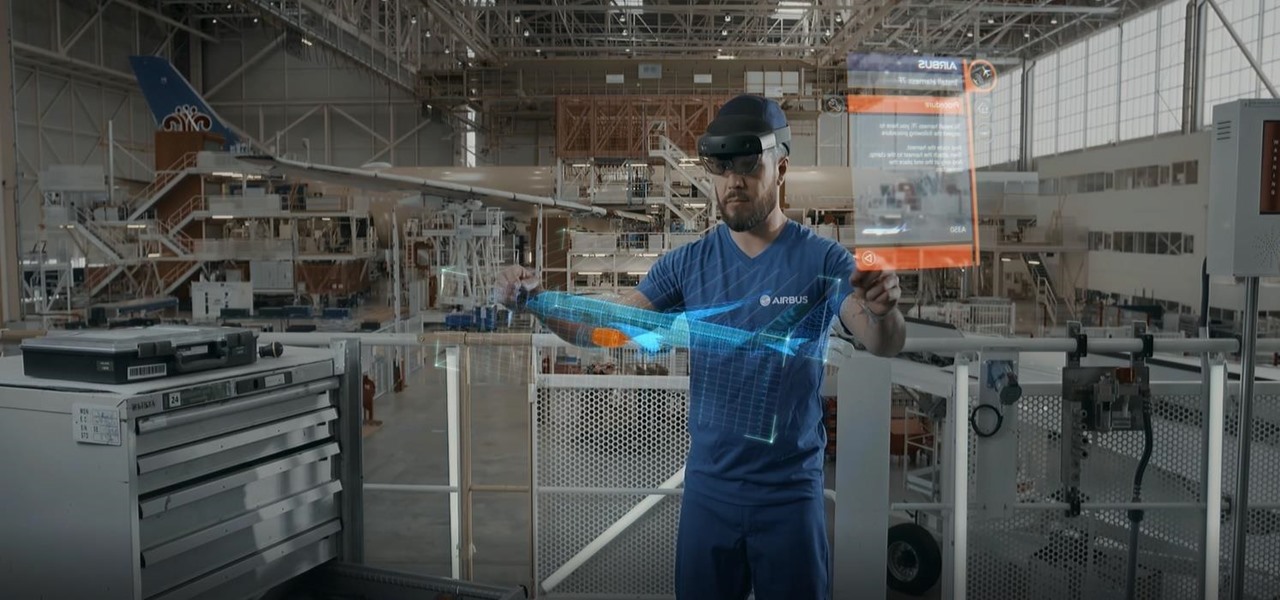
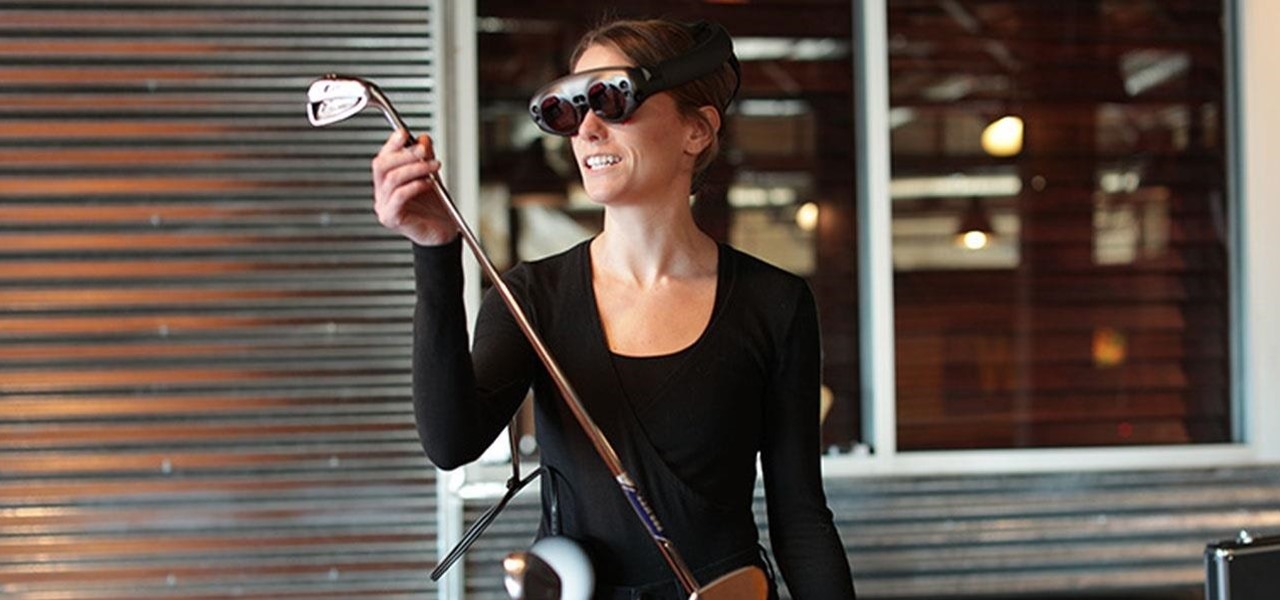
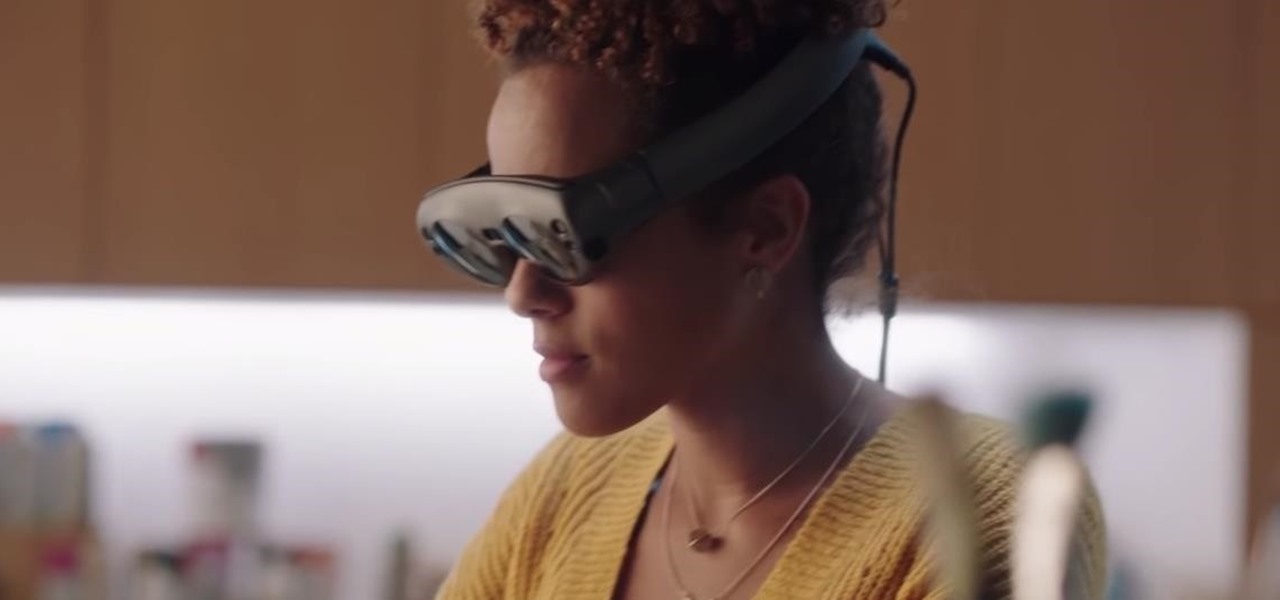
Magic Leap has always been intensely secretive about its work on its augmented reality headset, so it's interesting that they're now publicly recruiting developers to build software for the device before its launch.

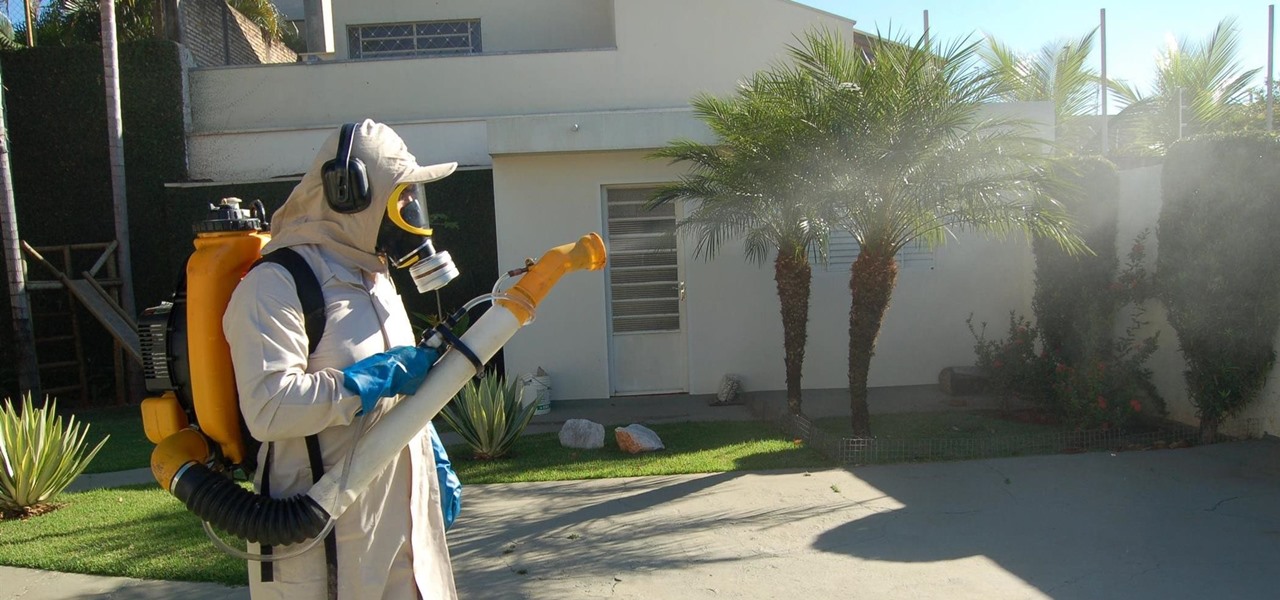
After a brief reprieve, Zika fear is back with a vengeance as the US mosquito population booms. And we're just now seeing the true impact of this devastating virus, as babies of mothers infected with the virus are being born.

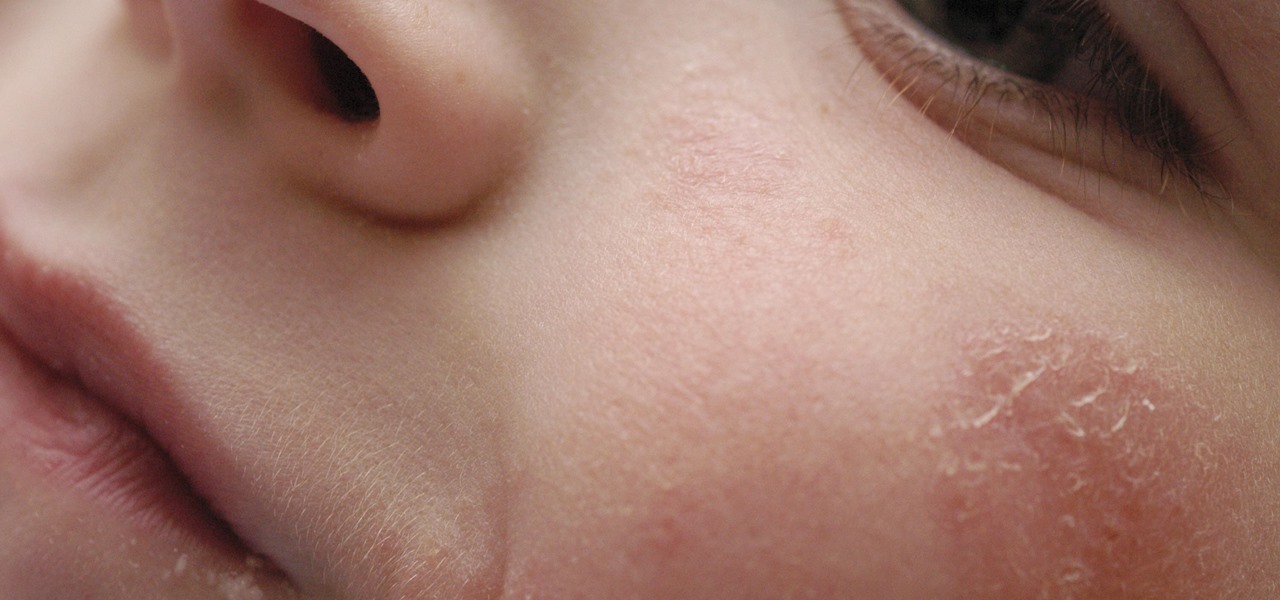
Most people know atopic dermatitis by its common name, eczema—that dry, flaky skin that itches incessantly. Along with the scratching comes frequent skin infections, often with Staphylococcus aureus.

There may be no other crustacean with as many names as the crawfish: crayfish, crawdad, crawdaddy, mudbug, Florida lobster, spiny lobster, rock lobster, and freshwater lobster (to name a few). But no matter what you call it, there's no denying that it's a popular delicacy in the South and beyond.

If there's one way to get a visceral response from someone, it's bringing up the DMV. Regardless of the reason, whether it's the long lines, disgruntled employees, or just general inefficiency, I have yet to meet a single person who doesn't mind the trip. Just look at all those happy faces.

Apple announced support for mobile driver's licenses and state identification cards in Apple Wallet back in 2021, and Arizona was the first state to jump on board in 2022. Fast forward to now, and only eight states let you add a driver's license or state ID to Apple Wallet on your iPhone and Apple Watch. It has been a slow rollout, but more states are coming or are at least showing interest.

In a stunning end-of-year twist to the Magic Leap versus Nreal legal saga, the China-based startup is now filing a motion against Magic Leap.

The week in AR business news started out with a bang with two bombshell reports that cast a shadow on the AR industry as a whole.

Is the augmented reality magic fading down in Plantation, Florida? That's the first question some may be asking following a casual revelation over the weekend that Magic Leap, the maker of the Magic Leap One, has assigned much of its patent portfolio over to JP Morgan Chase as collateral.

The enterprise sector is where the money is for augmented reality at the moment, and remote assistance apps are the go-to app for many enterprise customers. We took a look at the leading apps and platforms from this category, from the top contenders to the underdogs with unique features.

Now that Microsoft has squarely focused on the enterprise market with the HoloLens 2, it appears Lenovo is content to play follow-the-leader with its new augmented reality headset.

While Magic Leap turned heads at the Game Developers Conference with AR experiences at the Unity and Unreal Engine booths, news broke that the company was the winning bidder for ODG's patents.

The hype around augmented reality has risen to a fever pitch over the past two years, and if this week's selection of business news stories are any indication, the din is about to get down right deafening.

Unless you're one of the world's top golfers, there's a good chance you are not stepping onto the fairways of Pebble Beach Golf Links this weekend.

The augmented reality industry has a bright future built on innovation and growth, but that doesn't mean we can't look back at the close of the year to see what the industry has accomplished from a business perspective.

Magic Leap's recent flurry of patent applications prompted us to look around for any trademark movements from the company, and it turns out that the Florida-based company has been quite busy.

In what's becoming something of a regular occurrence, Magic Leap has yet another internal, unforced error on its hands. Thankfully, this time it's not about legal skirmishes or theft, but a rather unusual break from company protocol that has been quickly swept under the rug.

When you run an augmented reality company worth billions of dollars, backed by some of the biggest names in tech, and you haven't even released a product yet, even late night tweetstorms rank as worthy of dissection. Such is the case with Rony Abovitz, CEO of Magic Leap, who decided to spend a little time on Twitter on Wednesday to outline his vision of the future of immersive computing.

When the climate changes, so do all the things that rely on the climate, including people, plants, and pathogens. A European study recently took a broad look at what kind of microorganisms are most likely to be affected as climate change heats, cools, dries, and wets the world around us.

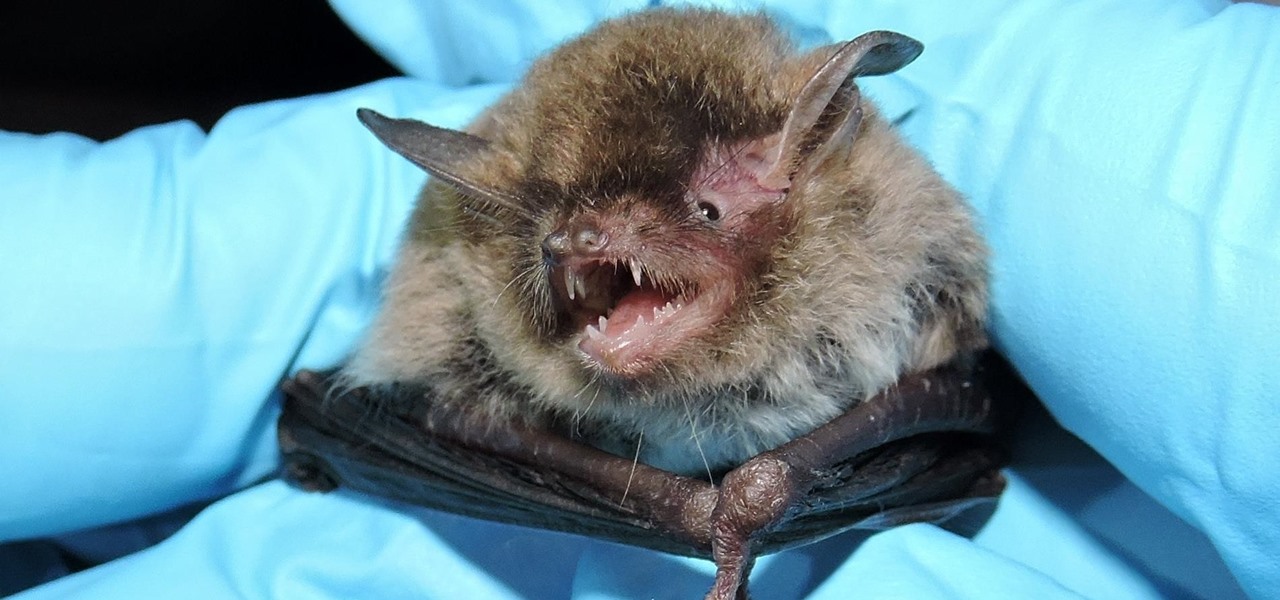
While not cuddly to most, bats are shy, skilled flyers that fill an important role in their environments. A new study reveals a deadly disease decimating North American bat populations has stepped up its attack on vulnerable bat populations in the summer months.

Staphylococcus aureus is a widespread bacteria — about a third of us have it on our body right now — usually in our nose or on our skin. And it probably isn't causing an infection. But, about 1% of people who have Staphylococcus aureus present have a type that is resistant to the antibiotic methicillin.

For a company more associated with debugging computer programs, Google's parent company, Alphabet, is making a name for itself by taking on the real thing — mosquitoes.

Despite longer live spans, almost half a million people die of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) each year, many of them preventable.

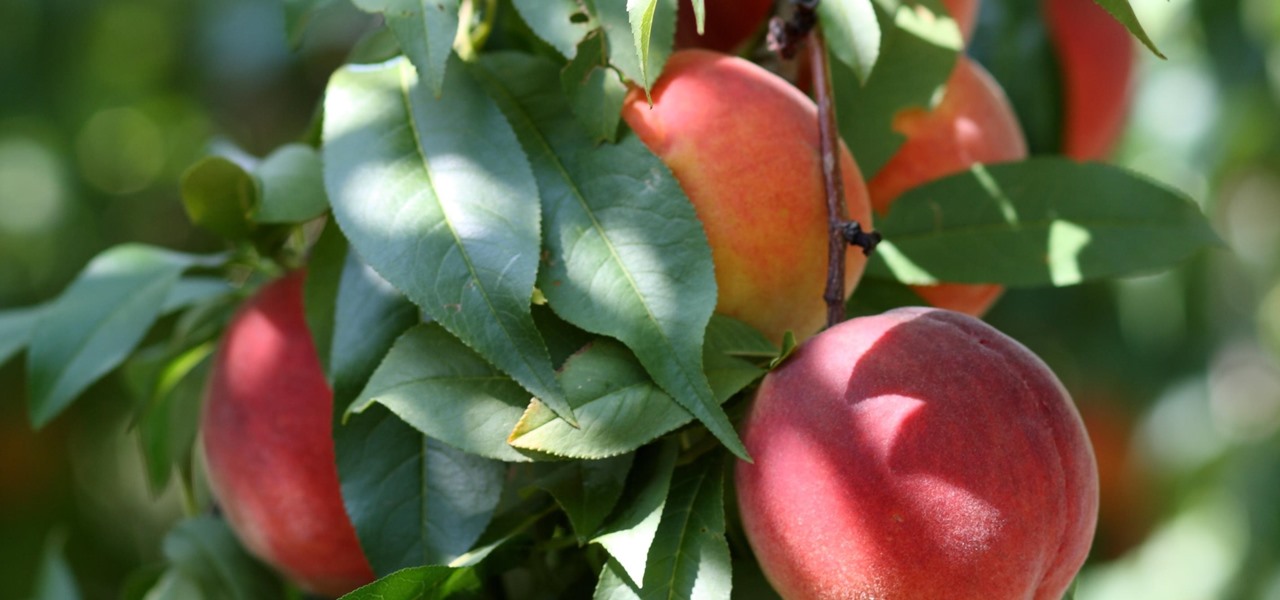
Peach trees and other related plants are susceptible to the devastation caused by fire blight, a contagious bacterial disease. Once contracted, infected trees have to be burned to contain the disease and prevent spread to nearby trees. Increasing resistance to antibiotic treatment has sent scientists in search of alternative ways to deal with the bacteria and prevent its catastrophic damage.

As researchers from Yale searched our environment for compounds to aid in the battle against drug-resistant bacteria, they got an unlikely assist from ticks.

The noses of kids who live in areas of intense pig farming may harbor antibiotic-resistant bacteria, presumably acquired from the animals, according to a new study by scientists at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, UNC Gillings School of Global Public Health, and Statens Serum Institut in Denmark, published in Environmental Health Perspectives.

It's about time people acknowledged that judging drug users would do nothing productive to help them. In the US this week, two new programs are launching that should help addicts be a little safer: Walgreens Healthcare Clinic will begin offering to test for HIV and hepatitis C next week, and Las Vegas is set to introduce clean syringe vending machines to stop infections from dirty needles.

Warning: If you are eating and for some reason still decided to click on this article, turn around now. Maui, Hawaii health officials have reported finding at least six cases of angiostrongyliasis, a parasitic lungworm that infects humans. Colloquially, it's known as rat lungworm disease. And if you think that name is awful, just wait until you hear what it does to the human body.

An advance in the race to stop birth defects caused by Zika-infected mothers has been made by a team of researchers from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, New York. They have identified the process Zika uses to gain entry into the placenta, and published their findings in the journal Biochemistry.

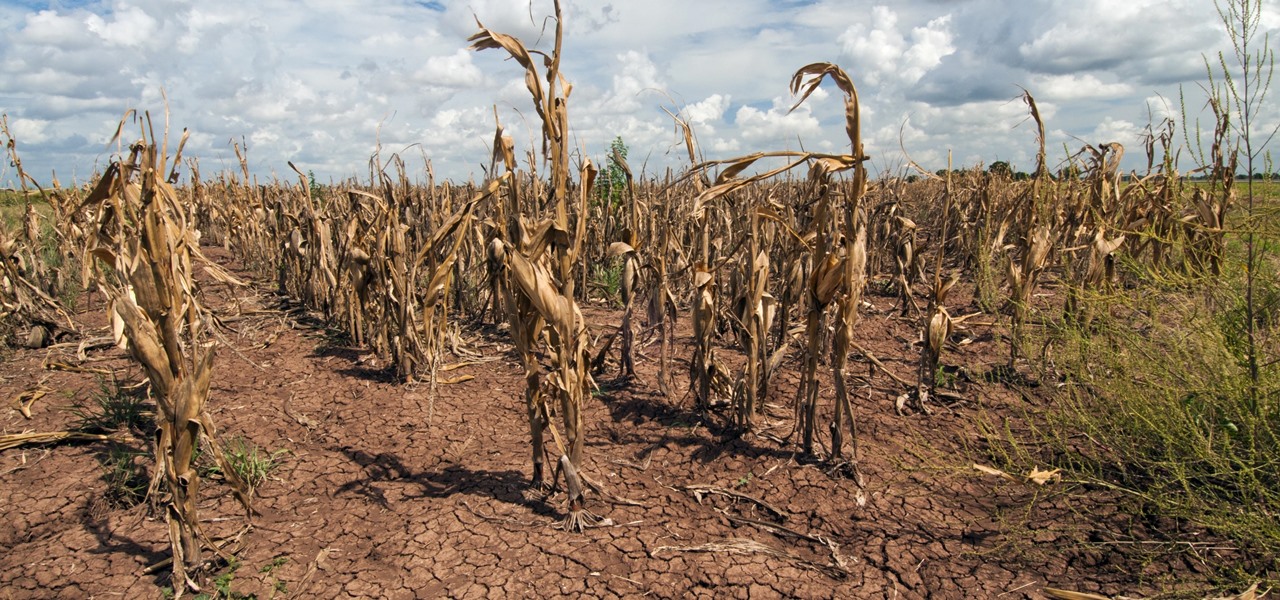
Growing populations and higher temperatures put pressure on world food supplies. Naturally occurring soil bacteria may save crops in drought-stressed areas, put more land into crop production, and produce more food.

Even as health authorities describe the symptoms of Zika infection in the general population as mild, a new surveillance study finds serious side effects are more common, and serious, than previously thought.

Hospitals are places we go to get well, and we don't expect to get sick or sicker there. But a study from researchers at the Cleveland Clinic, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, and Cleveland VA Medical Center in Ohio found that hospital floors in patient rooms were frequently contaminated with healthcare-associated pathogens—often dangerous multi-drug resistant bacteria.

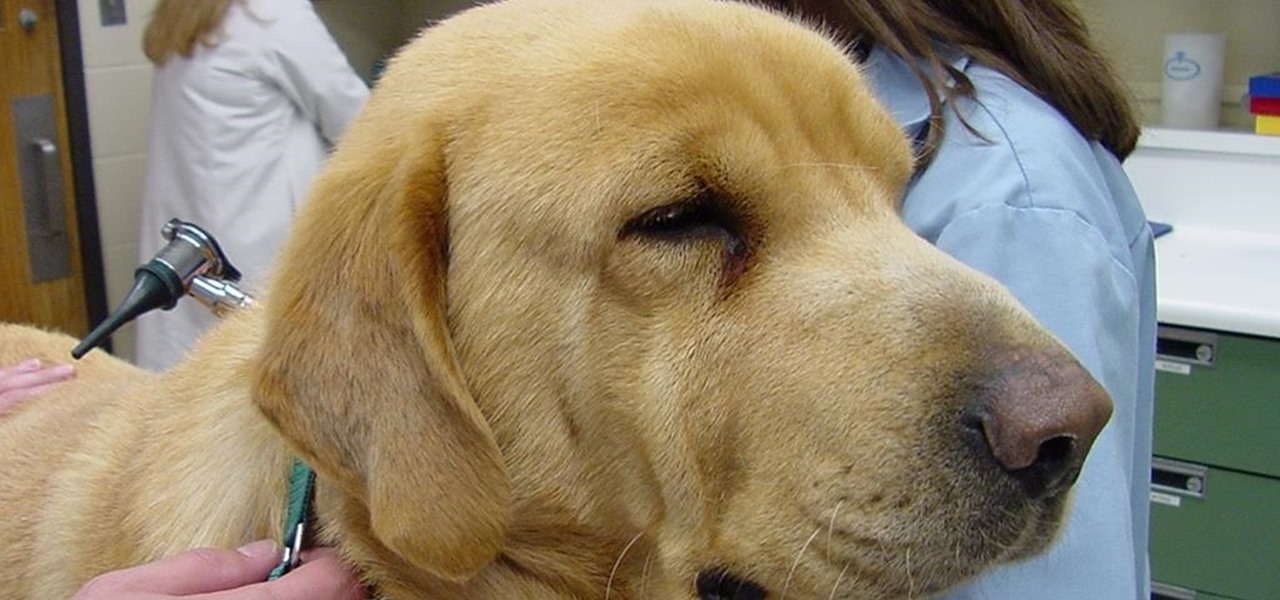
You know the signs—sneezing, fever, nagging cough, no energy, no appetite. It's the flu, but this time, it's your dog who's down and out. Yes, dogs get the flu, too. However, a team from the University of Rochester Medical Center and their collaborators have developed a new vaccine that may make the doggy flu a thing of the past.

Findings from a mouse study suggest that the Zika virus infection may have serious reproductive consequences for men.