One can easily get rid of acne scars without surgery by means of following steps. Identify the type of acne scars you have. See a dermatologist who can tell the difference between types of scars. For example, scars may be classified as ice pick, boxing, rolling or hypertrophy scars. Not every nonsurgical removal techniques will work with each type of scar. Get a chemical peel. A solution is applied to the skin which causes the top layer to peel off. This encourages new skin growth. Peels are ...

Dyeing your hair is a great way to change your look. But if you don't do it right, the results can be pretty ghastly. If you seek a new do without the harsh chemicals, these steps will give you the locks you’ve been looking for.

Tired of static cling? You can make your very own dryer balls that will prevent your clothes from having static clean and it only takes some yarn and pantyhose. You can even make scented dryer balls using this method.

Highlights add depth and interest to a hair color. Get that beachy, sun-kissed look and change up your style by adding some well placed highlights in your hair. You’ll save time and money by buying a kit and doing it yourself.

One of the hottest trends in gardening and nutrition is organically grown produce. Fruit and vegetables that are grown without the use of chemicals or stimulants are proven to be healthier for your body. In these videos our expert will teach you all the necessary steps to getting you own organic garden up and running. You will learn all about the different types of tools needed for organic gardening, as well as tips for choosing a garden site and planning your organic garden.

Sheryl is going to show you how to make homemade lye soap in this video series. Soap making is a chemical process. It is a lot of fun. However, it does require specific equipment and instructions and a reliable recipe. See what you'll need to do to get ready to start this project.

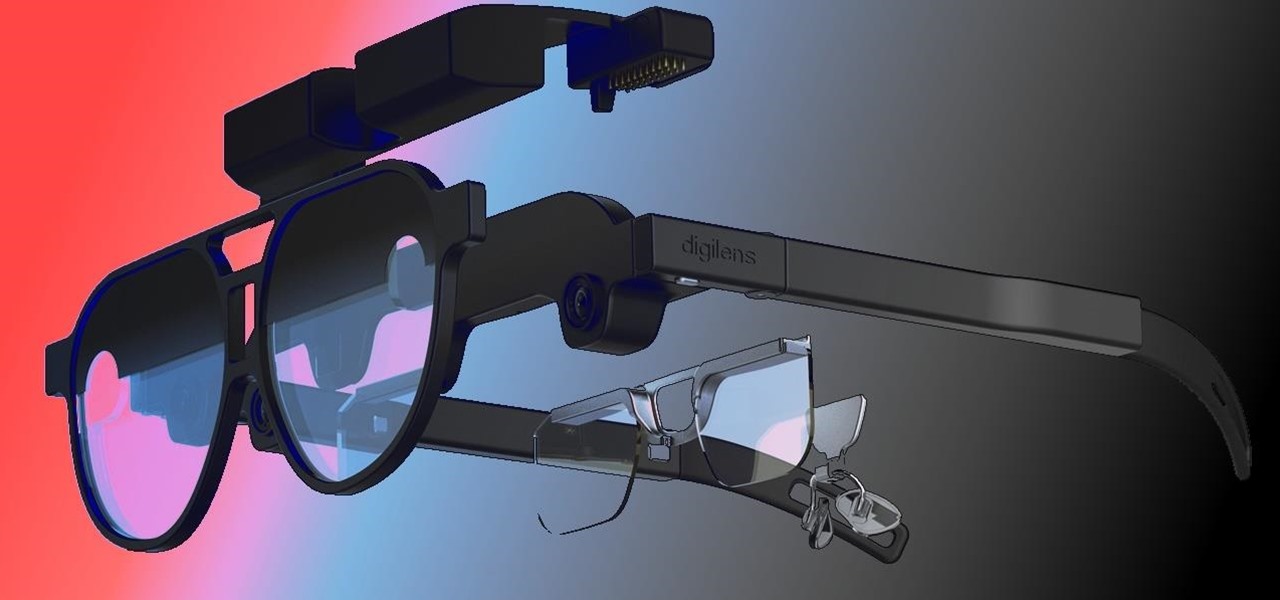
When it comes to the future of AR smartglasses, DigiLens has one word for you. Just one word. Are you listening? Plastics.

With so many competing outlets to reach people, accessing inboxes remains one of the most effective forms of communication. Yet newsletter creators run into a constant problem: bounced emails.

Although the Health app mostly focuses on fitness, Apple has slowly added features to help with other aspects of well-being, including hearing. In iOS 13, there's now a headphones volume tracker in Health that monitors audio levels and lets you know when your music, podcast, movie, or whatever else is too loud.

Android's settings menu is actually pretty daunting. There are options for nearly everything, so in the sea of various menus and submenus, it's easy to overlook important privacy and security settings. On Google's Pixel phones in particular, there are 20 such settings that you should double check.

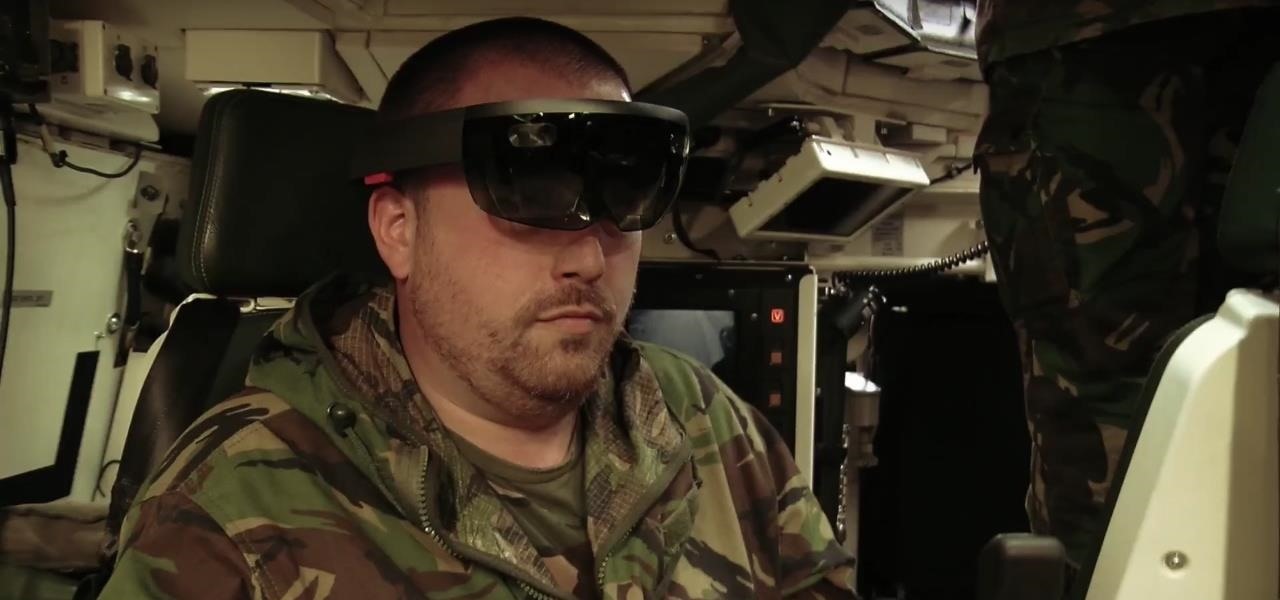
The recent announcement of a $480 million US Army contract awarded to Microsoft over Magic Leap for supplying 100,000 augmented reality headsets shows just a how lucrative the enterprise (and government) sector can be for AR.

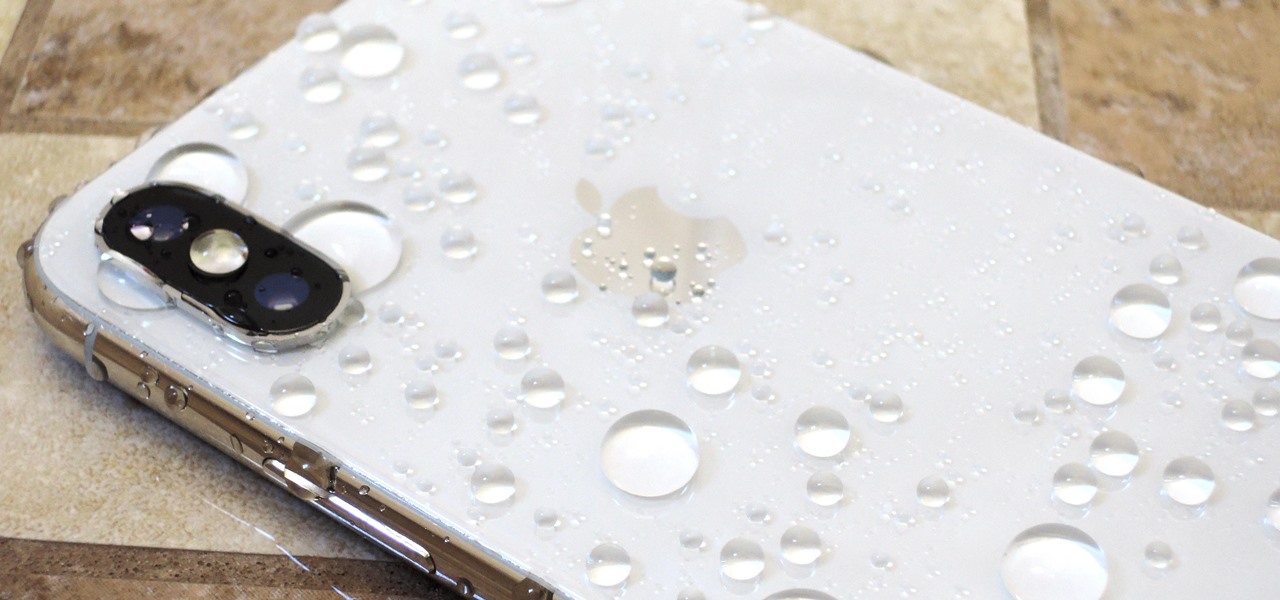
They're finally here. Apple announced three new iPhone models at their "Gather Round" event in Cupertino, and they're all absolutely gorgeous phones. With bezel-less screens and polished titanium edges, the iPhone XS, XS Max, and XR are truly marvels of engineering — but perhaps the most impressive design feat Apple pulled off is the fact that two of these models are rated IP68 under the IEC standard 60529.

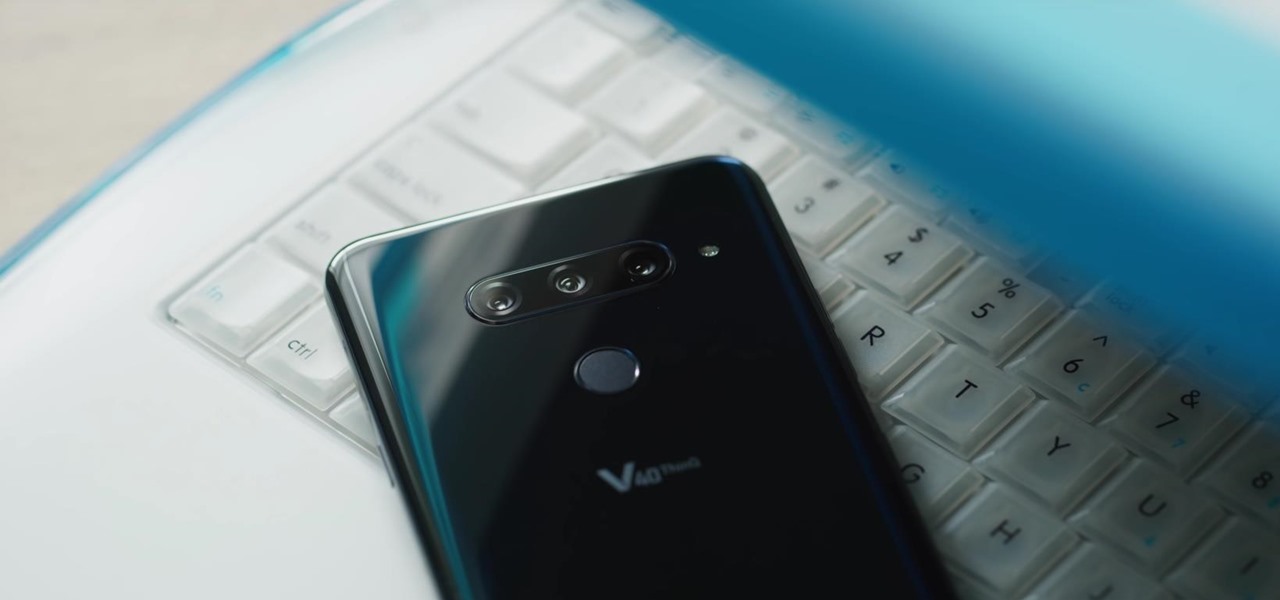
LG is really coming strong at the flagship smartphone market in 2018. They have already released three new flagship caliber smartphones this year: the V30S ThinQ, V35 ThinQ, and the G7 ThinQ. But LG isn't done with flagship phones yet — they've just announced the V40 ThinQ.

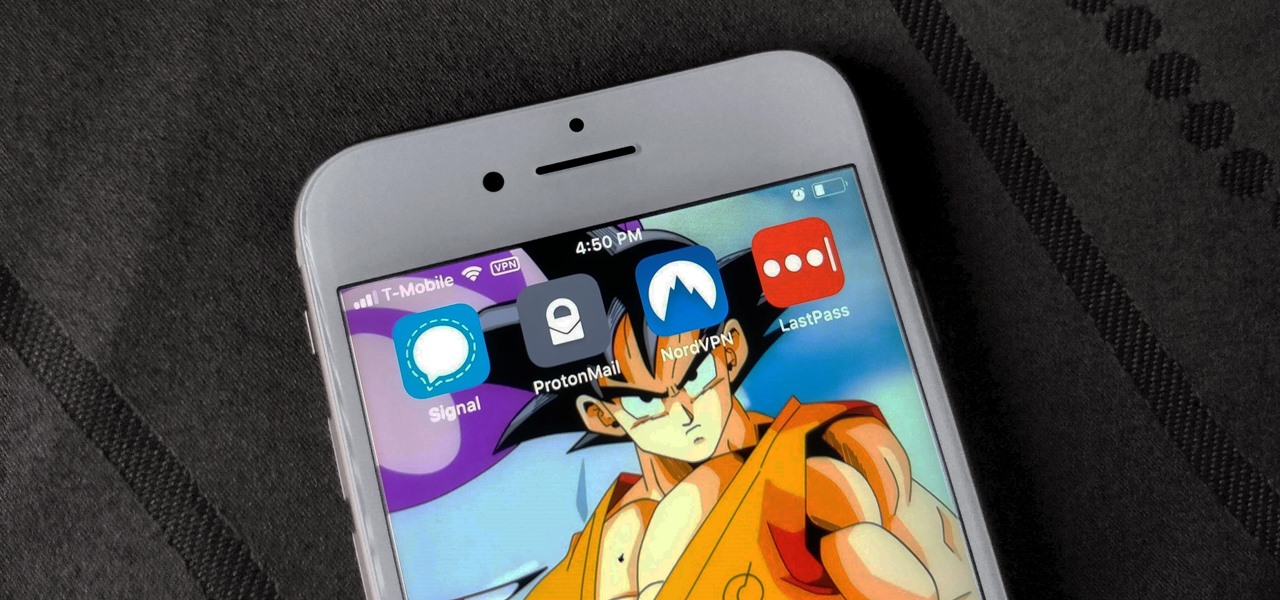
As the third-largest smartphone manufacturer in the world, Apple devices are a constant target for hackers everywhere. While iOS has seen fewer common vulnerabilities and exploits (CVEs) in recent years, iPhones still aren't hack-proof. Fortunately, you can strengthen your security with the help of a few apps.

Not to be outdone by Apple and it's new line of flagship phones, Google has followed suit and finally announced the followup to their highly regarded Pixel line of handsets — the aptly named Pixel 2. Thankfully, the tech giant has also joined in on the trend towards more durable devices, and has engineered both the Pixel 2 and Pixel 2 XL to have a rating of IP67 under the IEC standard 60529.

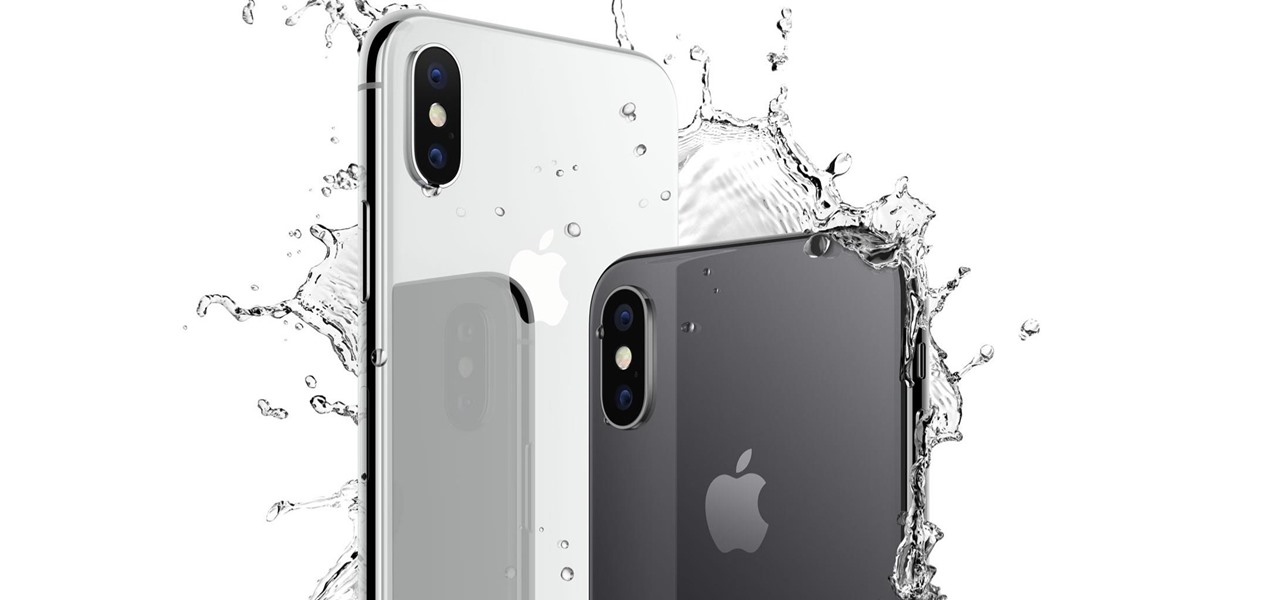
In case you didn't catch the big event in Cupertino, Apple just unveiled two of the most cutting-edge phones ever made — the iPhone 8 and the iPhone X. Out of the many glorious specs that were rattled off on stage, one stands out for being just a little confusing: Both models are rated IP67 under the IEC standard 60529.

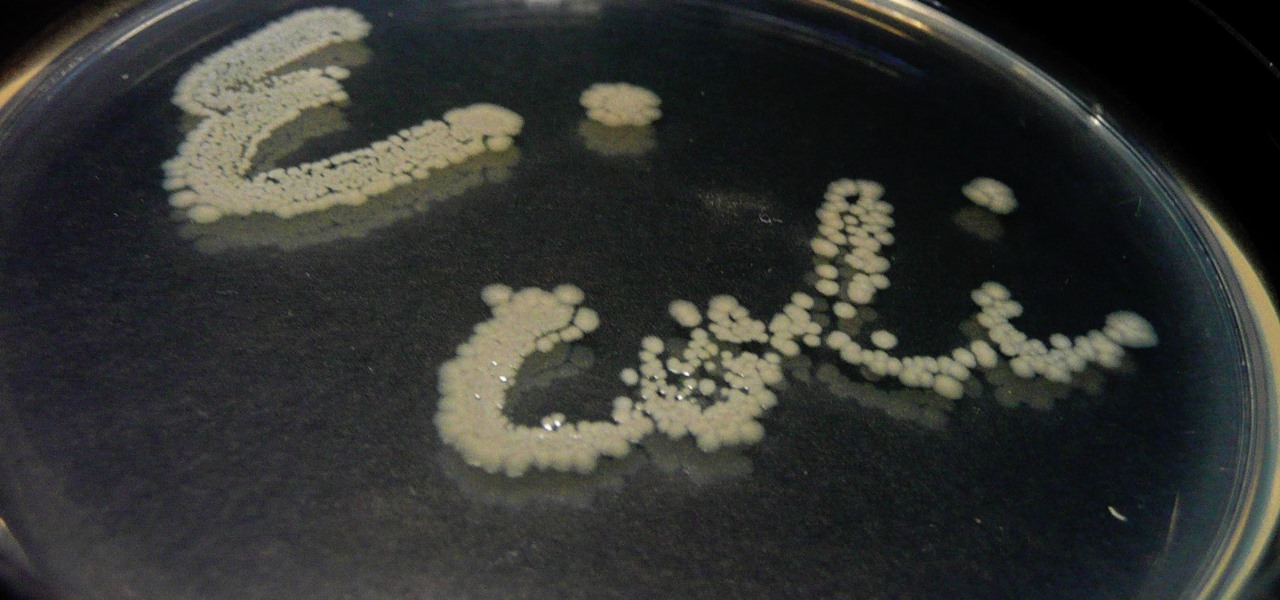
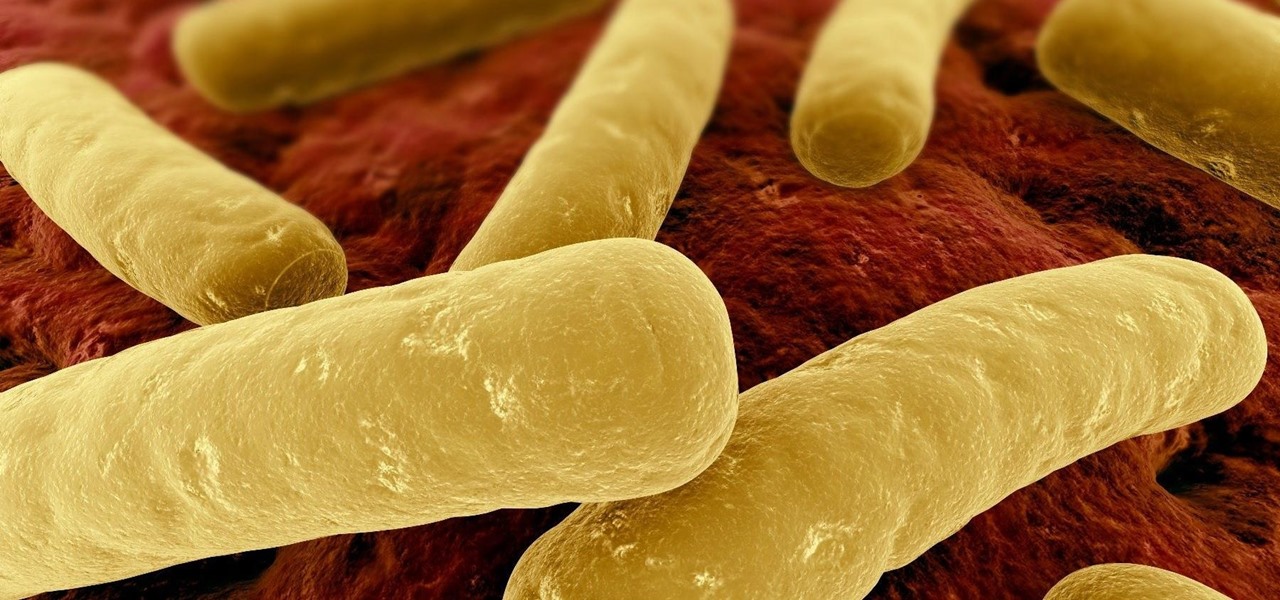
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) drive over eight million people to seek medical attention every year. Almost all — as many as 90% — of those infections are caused by Escherichia coli. Copper can kill bacteria, but E. coli has found a way to capture the copper, preventing its antibacterial action. Now, researchers have found that, in a cruel irony, the bacteria use the copper it grabs as a nutrient to feed its growth.

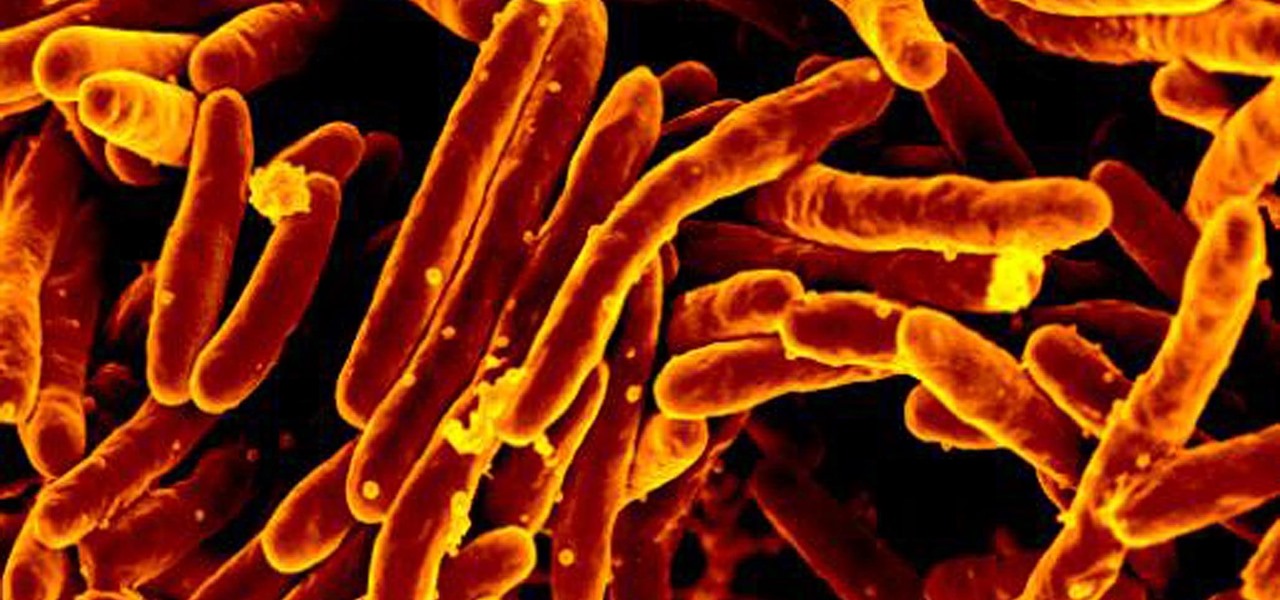
The incidence of tuberculosis (TB) is dropping in the US, but the World Health Organization (WHO) considers it to be epidemic in the rest of the world — there were over 10 million new cases in 2016.

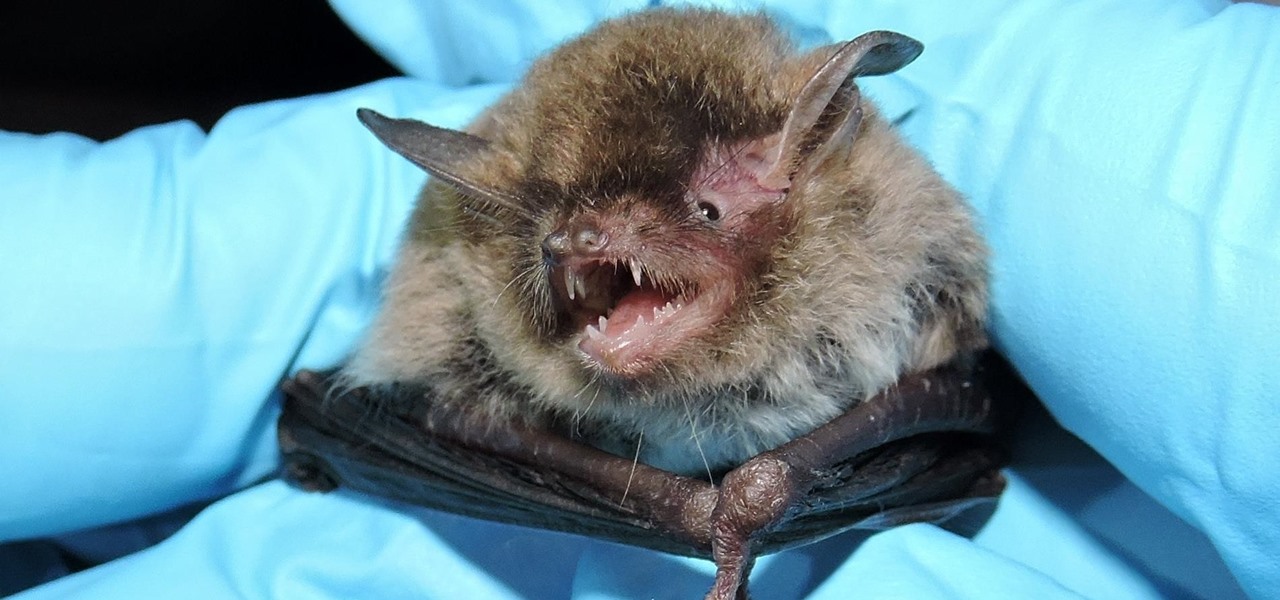
While not cuddly to most, bats are shy, skilled flyers that fill an important role in their environments. A new study reveals a deadly disease decimating North American bat populations has stepped up its attack on vulnerable bat populations in the summer months.

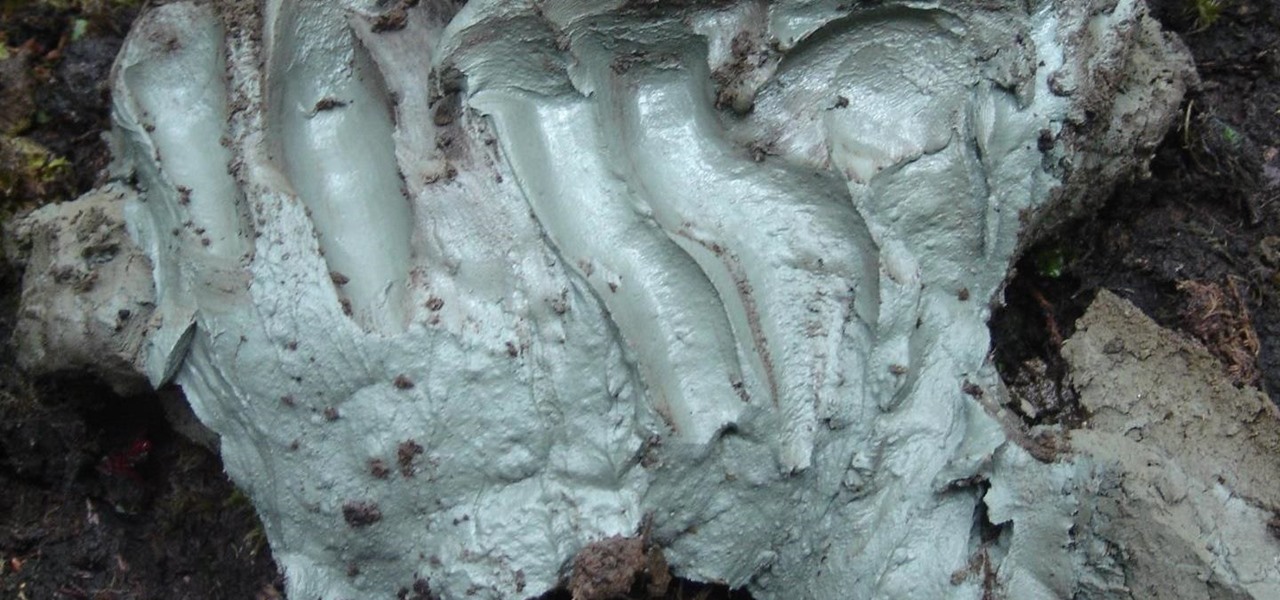
For as long as 14,000 years, the First Nations people of the Heitsuk Nation have made their home along the Central Coast of the Canadian province of British Columbia. Among the territory's inlets, islands, rivers, and valleys lie a clay deposit on the north side of Kisameet Bay, near King Island. For as long as most can remember, the tribe has used the clay as medicine. Now science says microbes that live in that clay may have important antibacterial properties.

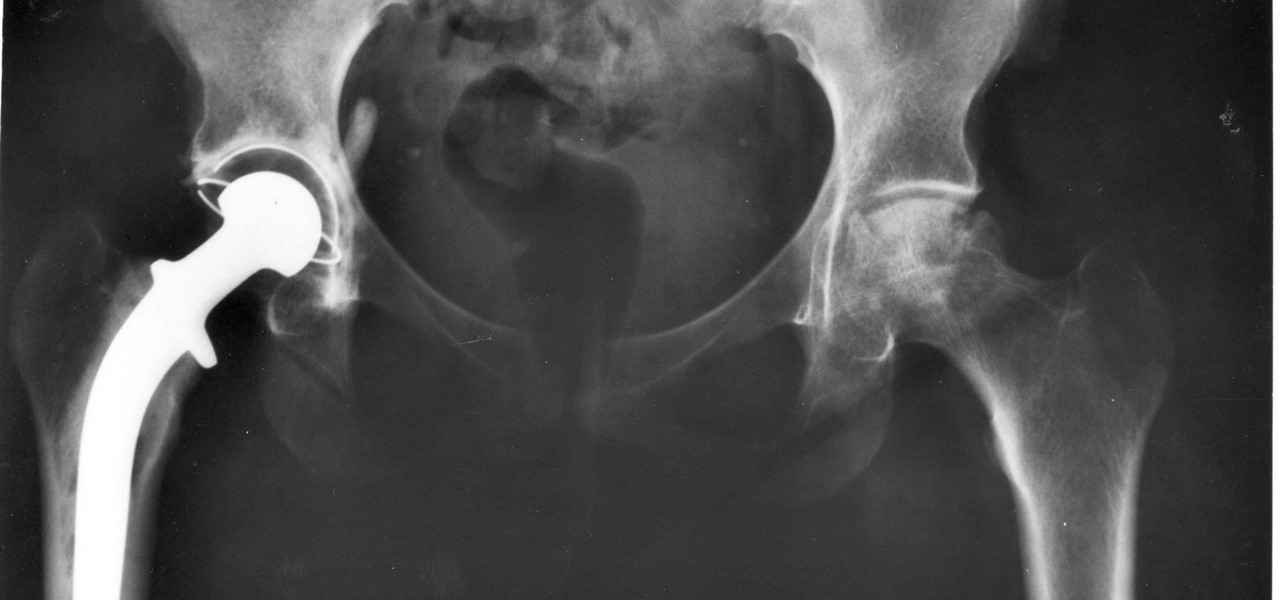
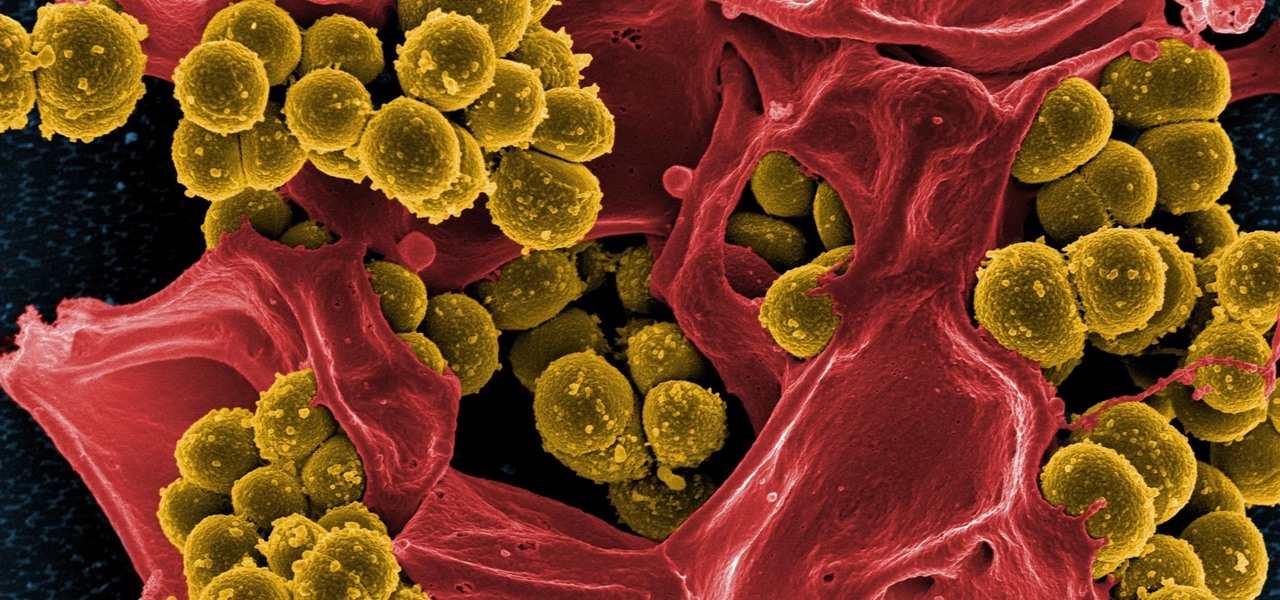
For about a million Americans each year, a joint replacement brings relief from pain and restored mobility. But, 5–10% of those people have to endure another surgery within seven years, and most of those are due to an infection in their new joint. If doctors could treat infections more effectively, patients could avoid a second surgery, more pain, and another rehabilitation.

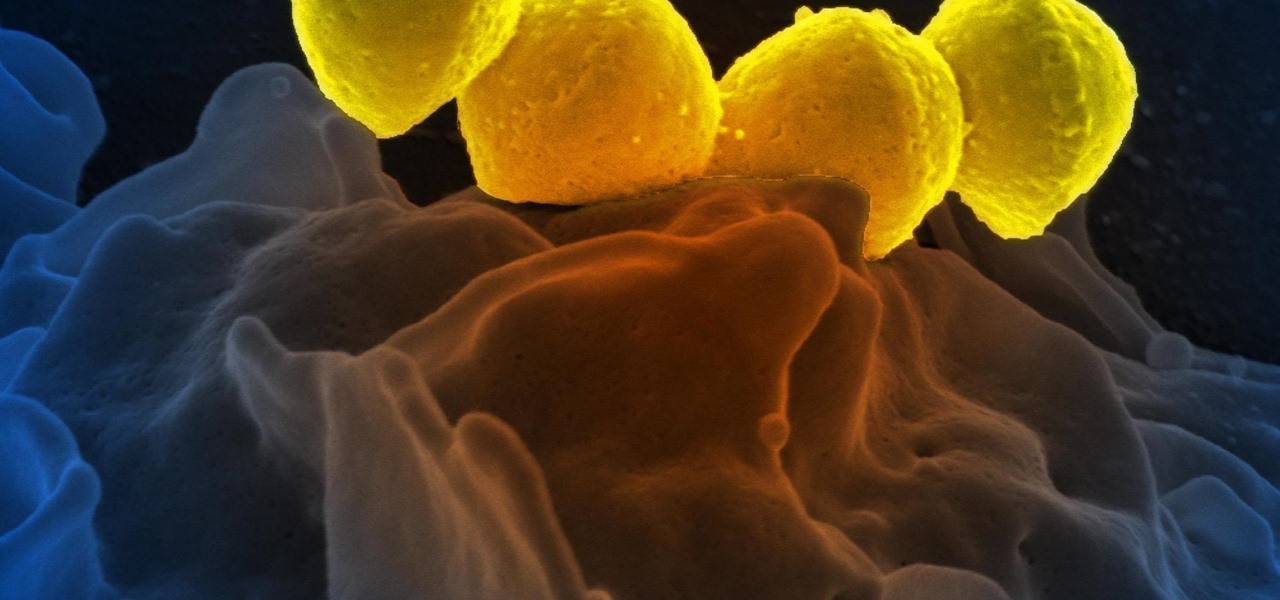
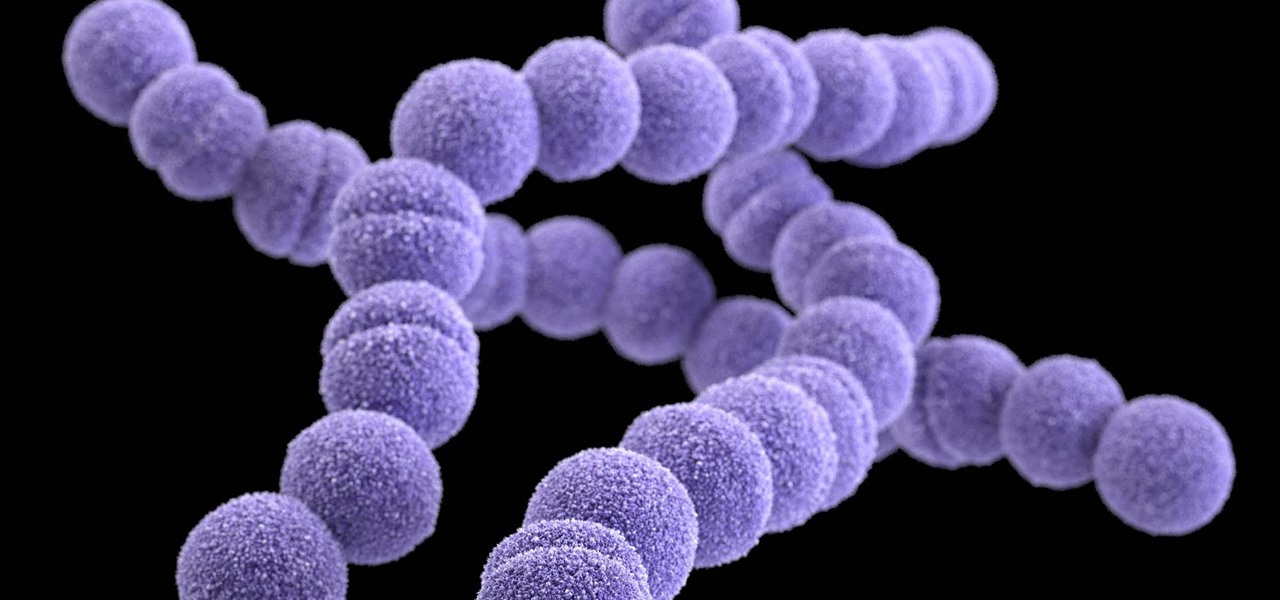
Unfortunately, the very places we go to receive health care put us at risk for becoming infected with superbugs, bacteria exposed to so many antibiotics that they have become immune to their effects. Clostridium difficile (C. diff) is one such bacteria. It causes inflammation of the colon and rampant diarrhea that can have life-threatening consequences. Part of its virulence lies in the tough spores formed by the bacteria. They are responsible for starting infections in the colon and for spre...

Our smartphones are full of personally-identifiable information. So much of what we do with these devices is tracked and recorded to make our experience more streamlined and personalized. For many users, that's a fair trade — but for privacy-minded folks, it's a raw deal.

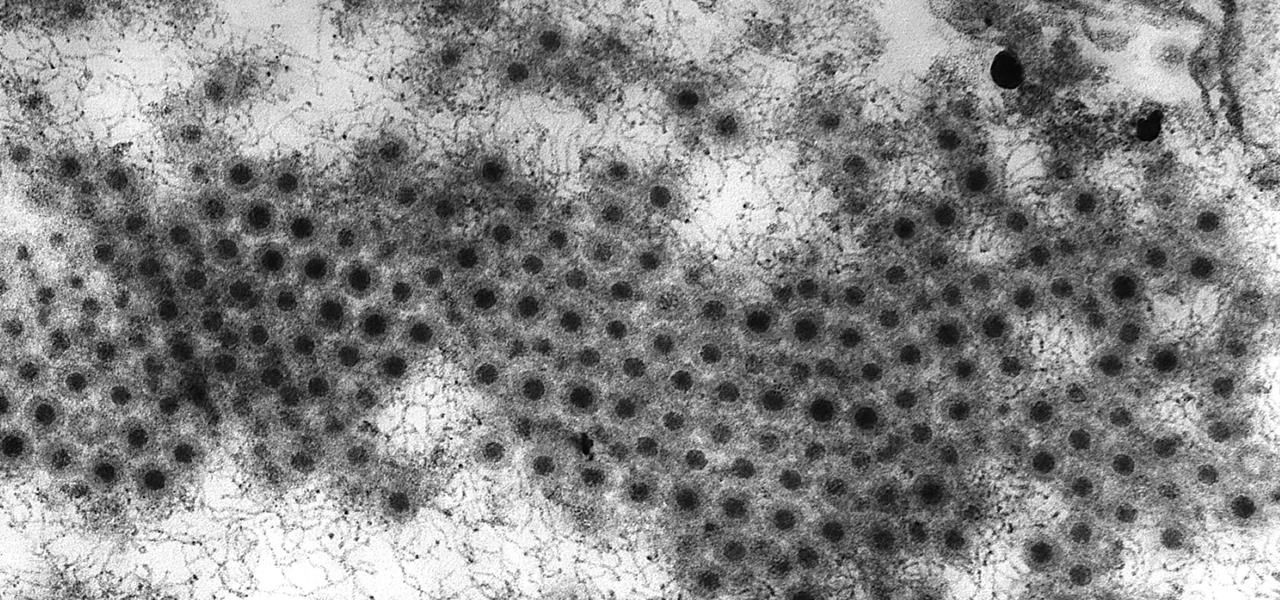
Even though HIV rates declined 18% between 2008 and 2014, 1.1 million people in the US are living with the infection. Part of that is because HIV is treatable, but not curable.

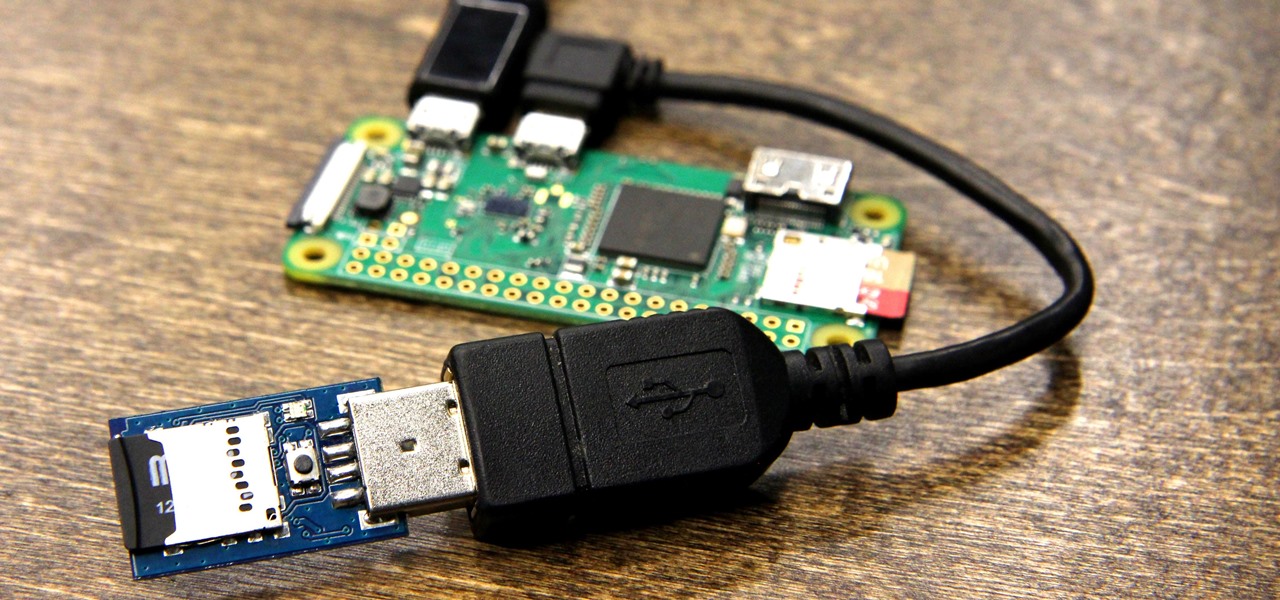
The USB Rubber Ducky comes with two software components, the payload script to be deployed and the firmware which controls how the Ducky behaves and what kind of device it pretends to be. This firmware can be reflashed to allow for custom Ducky behaviors, such as mounting USB mass storage to copy files from any system the Duck is plugged into.

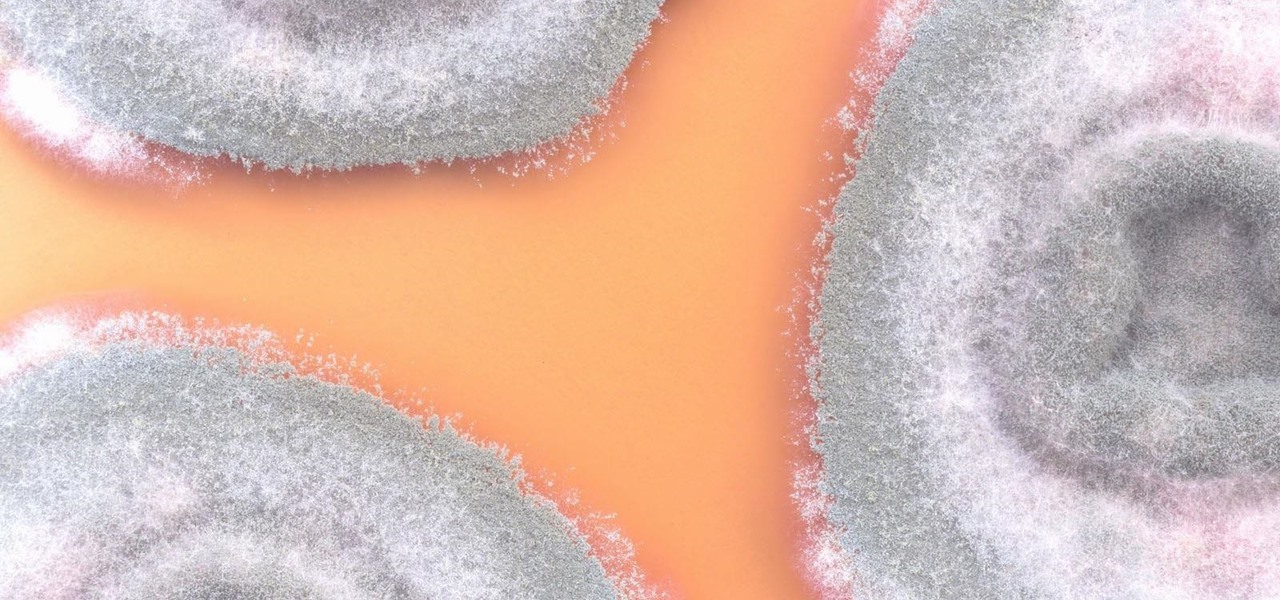
Significant strides have been in the race to find antibiotics to treat superbug infections — those caused by bacteria resistant to the antibiotics used to treat them. Now, an international team of scientists has discovered a new antibiotic produced by a microbe found in Italian soil.

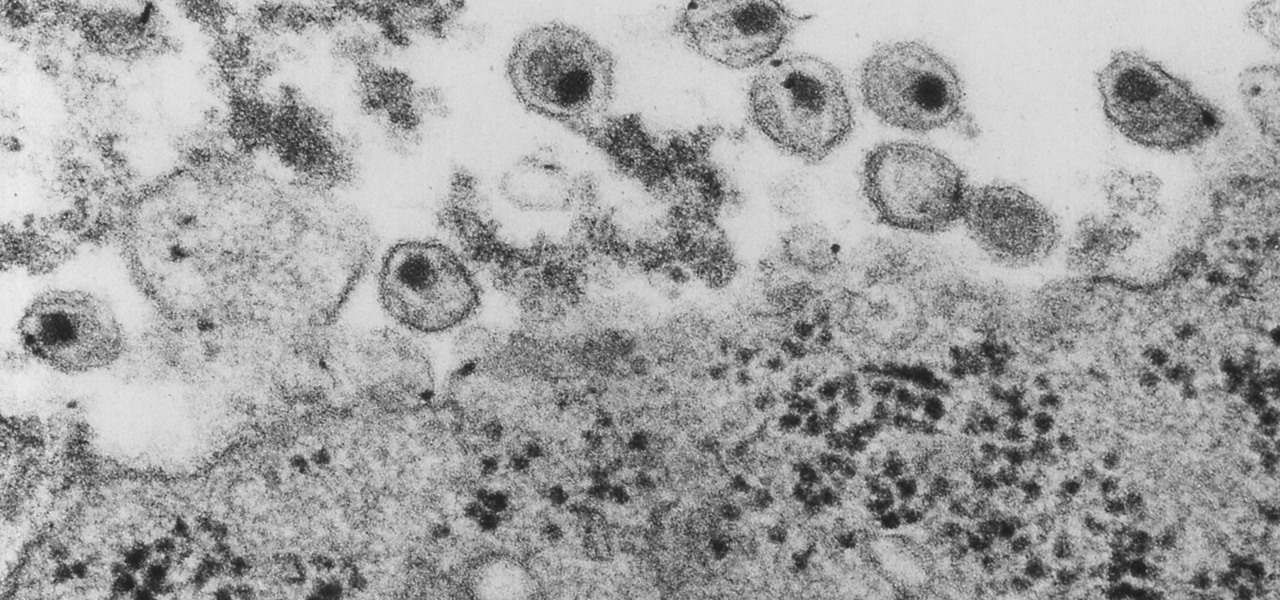
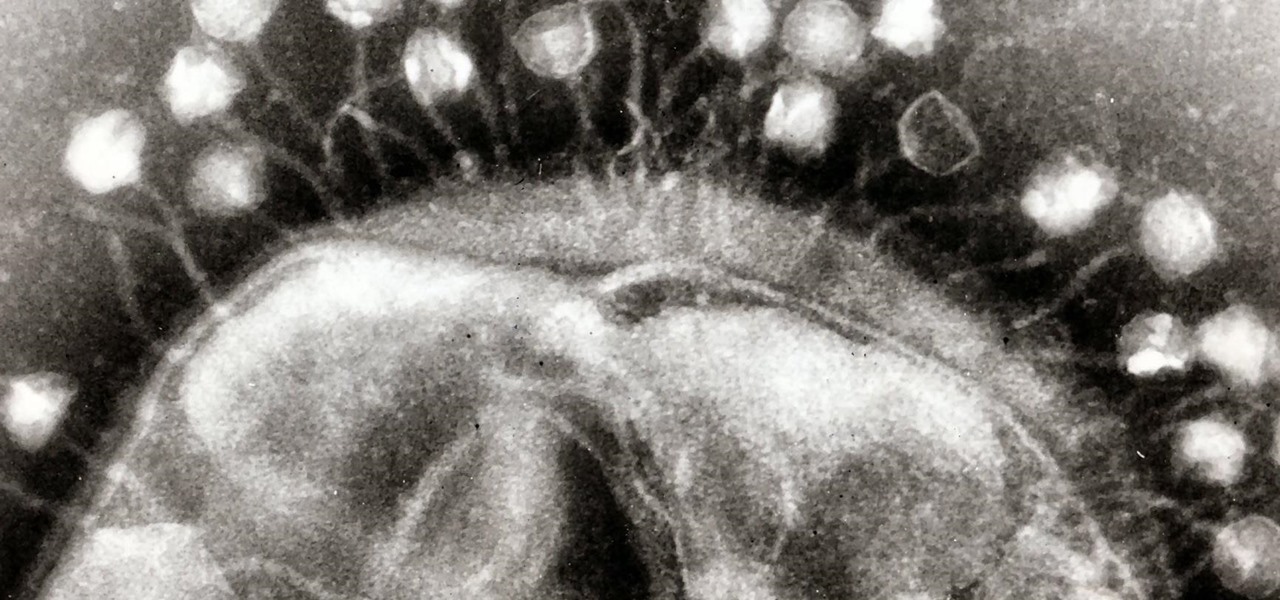
Most of us have already had an encounter with the Epstein-Barr virus, or EBV, for short. As part of the herpes family, it's one of the most common disease-causing viruses in humans. We get the disease with (or without) some nasty symptoms, then we recover. However, EBV stays in our body after the illness has ended, and it's one of the few viruses known to cause cancer.

Drug-resistant bacteria have made curing some infections challenging, if not nearly impossible. By 2050, it's estimated that 10 million people will be dying annually from infections with antibiotic-resistant organisms.

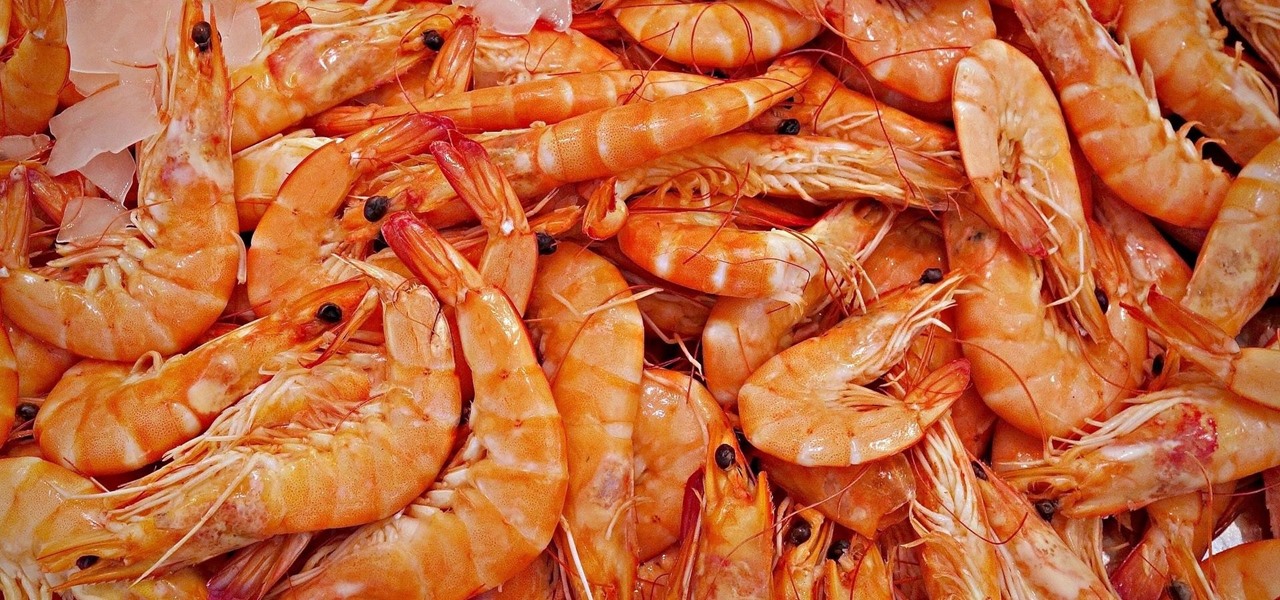
An innovative new wound dressing has been developed by a research team at Lodz University of Technology in Poland that uses crustacean shells to create a bandage that packs an antimicrobial punch — and even more potential to help solve a global problem.

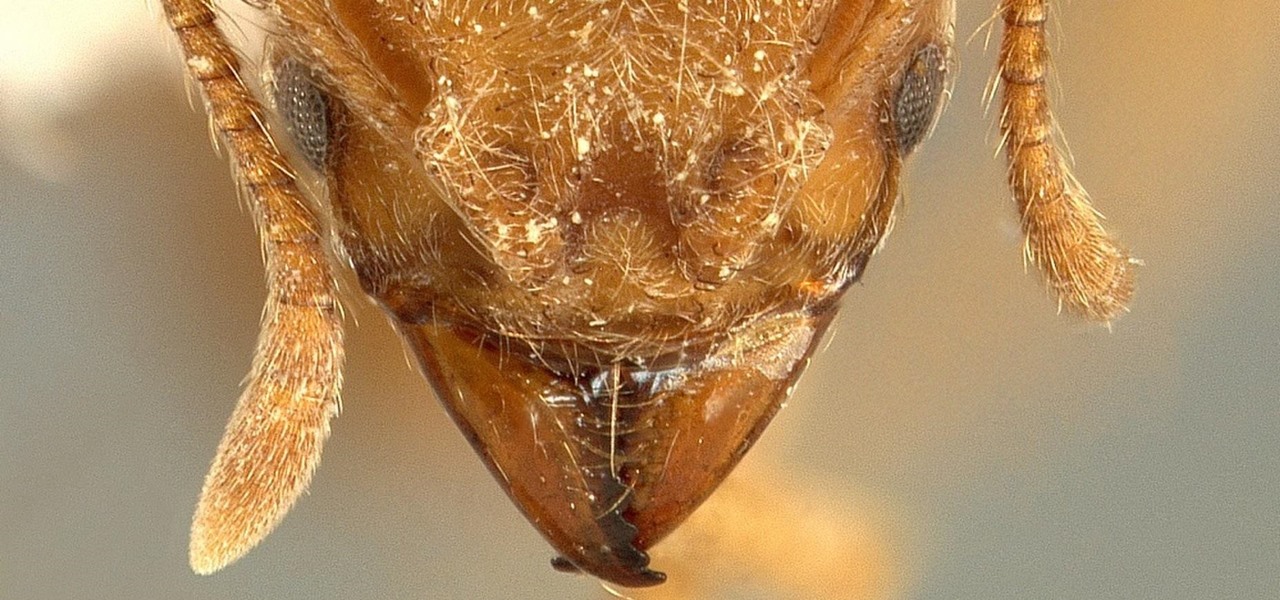
Long admired for their active and cooperative community behavior, some types of ants also wear a gardening hat. Nurturing underground fungus gardens, these ants have a win-win relationship that provides food for both ants and fungi. If we humans understand it better, it may just help us out, too.

We fight cancer in a variety of ways, but no matter whether drugs, biologics, or our immune cells are part of the battle, they can do a better job fighting back cancer if we can help them find the tumors.

The evolution of our infection-fighting systems may have something to teach modern scientists. That's what a group from the University of Granada in Spain found when they studied a protein that's been around for over four billion years. Their work, by senior author José Sánchez-Ruiz and colleagues in the Department of Physical Chemistry, was published in the journal Cell Reports.

On October 17, 1943, a story in the New York Herald Tribune read "Many laymen — husbands, wives, parents, brothers, sisters, friends — beg Dr. Keefer for penicillin," according to the American Chemical Society. Dr. Chester Keefer of Boston was responsible for rationing the new miracle drug, penicillin.

Viral infections have been the focus of attention in the development of autoimmune diseases—diseases where the body's immune system reacts to the body's own cells—because they trigger the immune system into action.

An advance in the race to stop birth defects caused by Zika-infected mothers has been made by a team of researchers from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, New York. They have identified the process Zika uses to gain entry into the placenta, and published their findings in the journal Biochemistry.

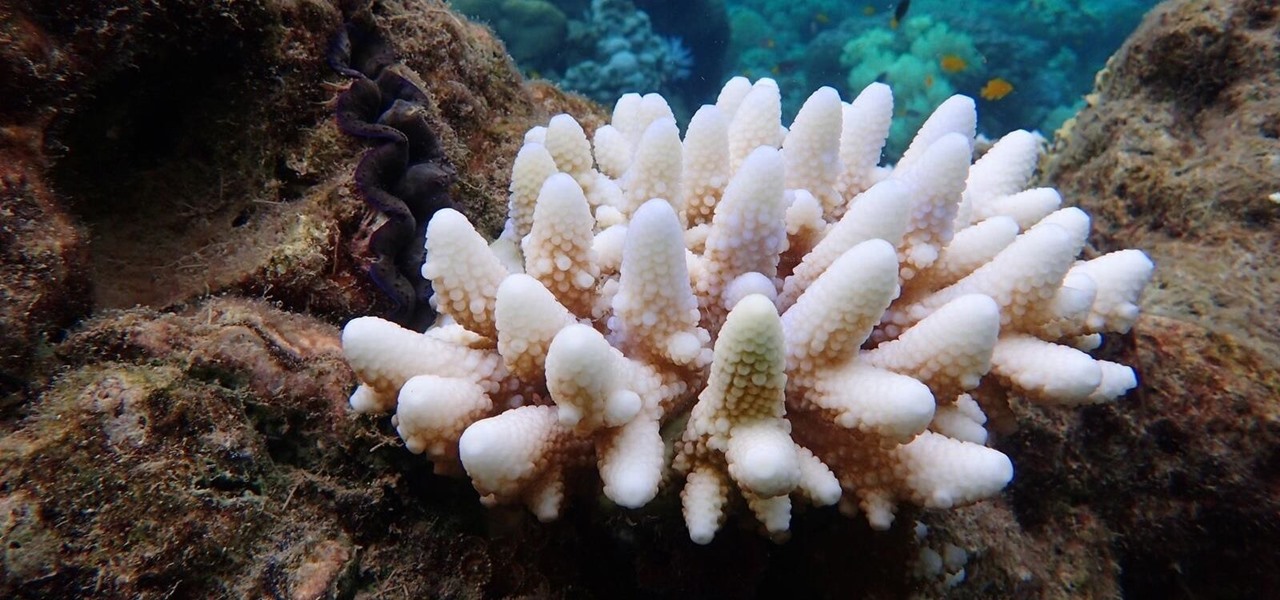
The Great Barrier Reef in Australia is the largest living system on the planet. Yet more than 90% of the reef is bleaching because of the loss of a tiny algae that lives within the coral.

In the past, infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) commonly led to dementia as the virus made its way to the brain. Even in effectively treated people, HIV can hide out and replicate in places like the brain, where it's tough to detect. That's why it's very concerning that half of all HIV-infected patients still report cognitive problems.

As drug-resistant bacteria become more commonplace, researchers are looking for new antibacterial strategies to disrupt disease-causing microbes. Some scientists are working to create new drugs, while others are trying out drug combinations. Another group, however, are ditching pharmaceuticals altogether and experimenting with non-drug alternatives.

Where in the world did it come from? All of a sudden, one day, someone had an infection with flesh-eating bacteria. It captured headlines and worldwide attention because it was such a severe, strange, uncontrollable, and really disgusting condition.

Starting in October, many Nexus 6P users have been experiencing a bug that causes their phone to completely shut down, even though there was 20% or more battery life remaining. At first, it was thought to be a direct result of the recent Android Nougat update, but a combination of factors indicate that this isn't necessarily the case—or, at least, it's not the only problem.