The Pixel 4 isn't for everyone, but it does have its appeal in several specific use cases. Thanks to Instagram, YouTube, and other social media platforms, the fitness industry and smartphone world are now intertwined like never before, and it appears Google's aware of this.
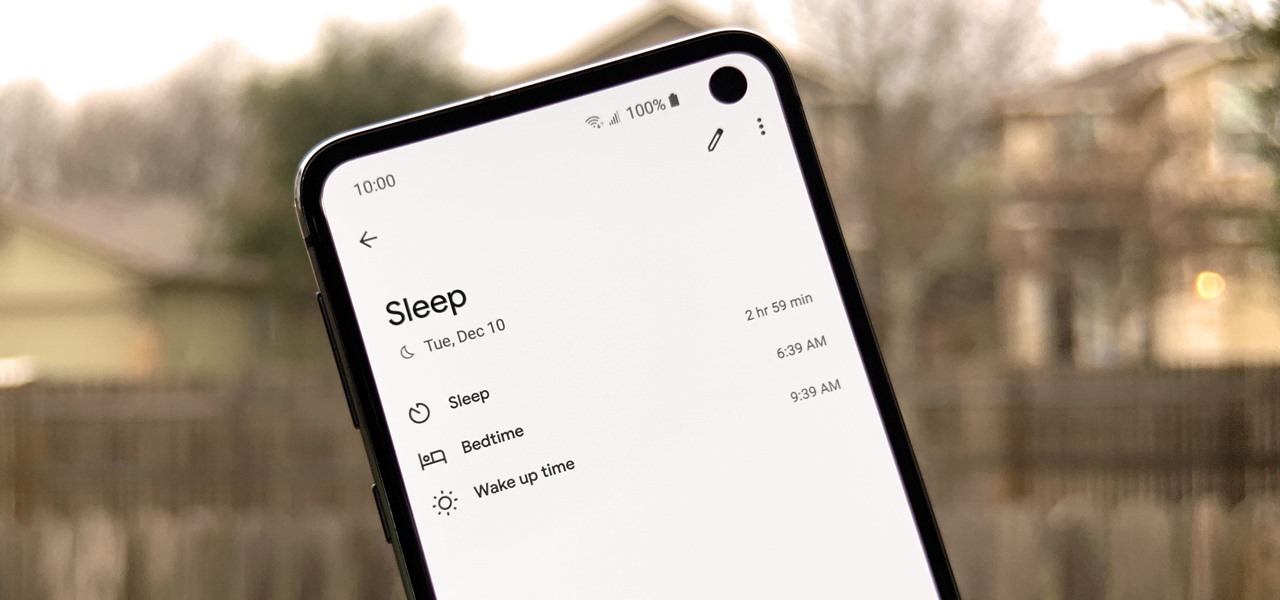
When trying to get fit, something that can easily be overlooked is your overall sleep quality. Your body needs sleep to recharge and it helps to maintain a healthy lifestyle, there's no denying it. Luckily, Google Fit can help you track your sleeping habits without having to jump through any hoops along the way.

New year, new me. You finally committed to working on the best physical you by going to the gym multiple days a week. Except about an hour in, you start getting really tired of it all. Before you run to the exit, pick up your phone.

A good smartphone can be the perfect workout companion. You have music for motivation, videos for pushing through boring cardio sessions, GPS to keep you on course, and even an array of sensors for gathering data about your workout. But not all phones are created equal when it comes to helping you stay fit.

In this era of smartphones, we all know very well how easily we can get addicted to our devices. Spending hours each day doing the endless scroll through Facebook and other social media sites just because we feel like we'll miss something if we don't. Both Google and Apple are aware of this and are trying to help control smartphone addition in their own way for Android and iOS.
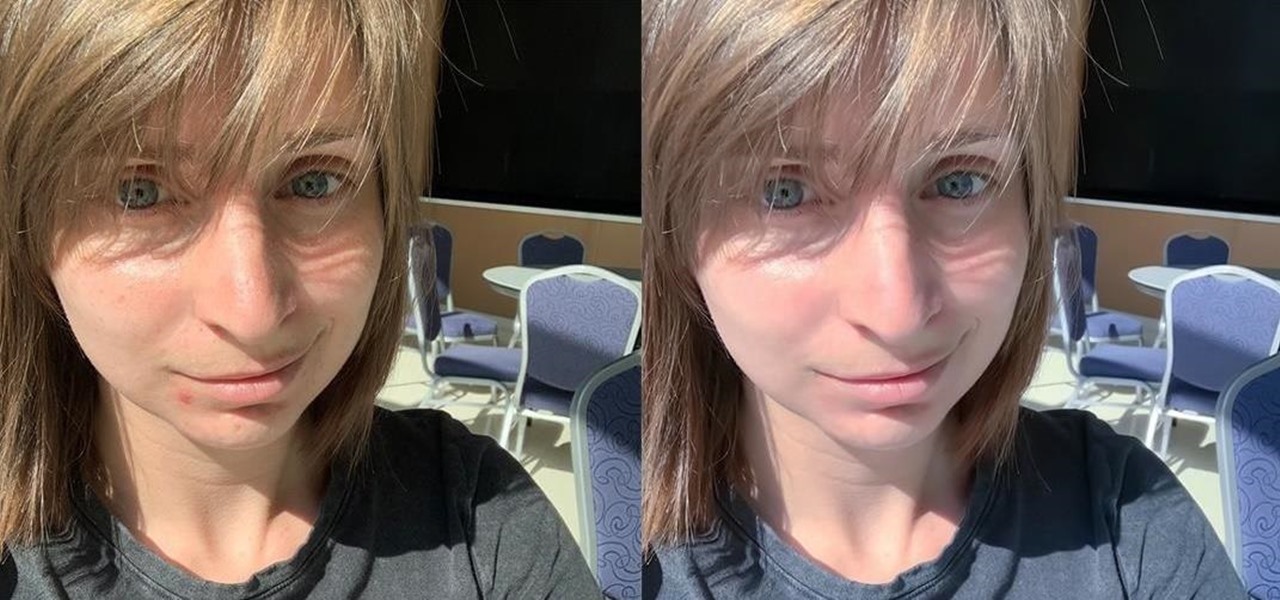

You finally did it! You've combined all your knowledge about photography and angle to take the perfect selfie. It looks stunning, and you cannot wait to post that bad boy to Instagram. But wait, what's this? Your skin looks so uneven and — is that a zit!? I guess the selfie gods were not in favor of your skin when you snapped it. Luckily, you can fix all of those minor flaws with the help of Photoshop Express.

Anyone who has been within a block of any wireless brick and mortar store or tech conference in the last couple of years has no doubt seen banners, posters, and videos promoting 5G high-speed wireless services on the way.

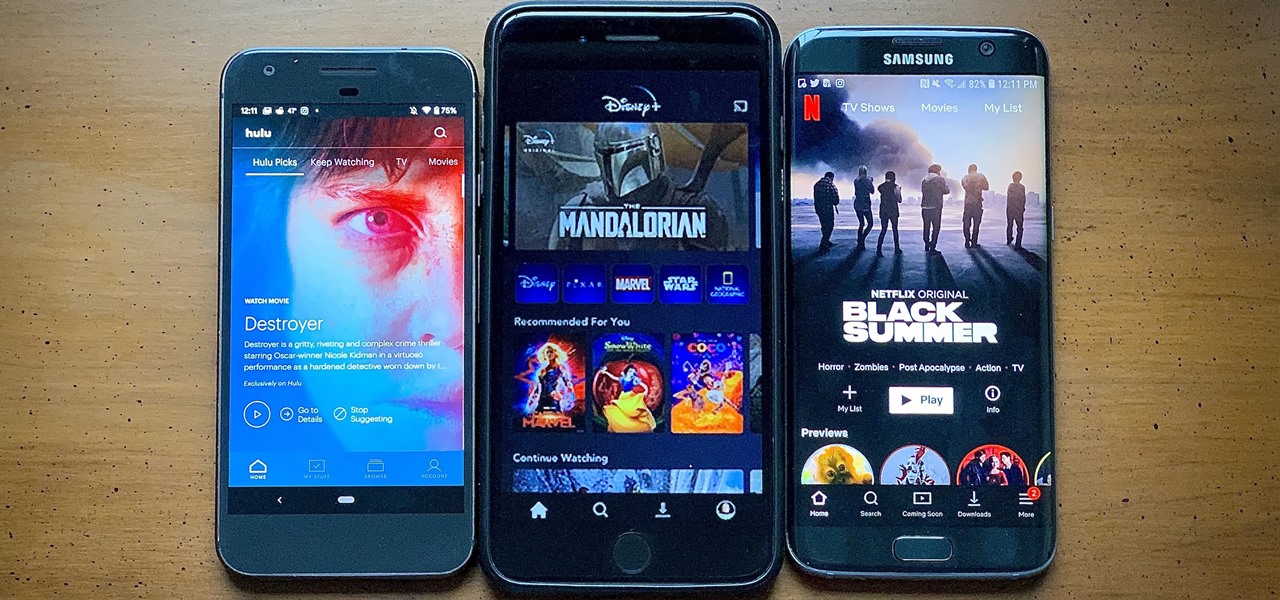
After much anticipation, Disney finally revealed its plans for its exclusive streaming service. Disney+ launches Nov. 12, and with it, all of the Disney content you know and love. But do you really need another streaming app in your life? We asked the same thing, so we broke down what we know about Disney+ and compared it to the current competition.

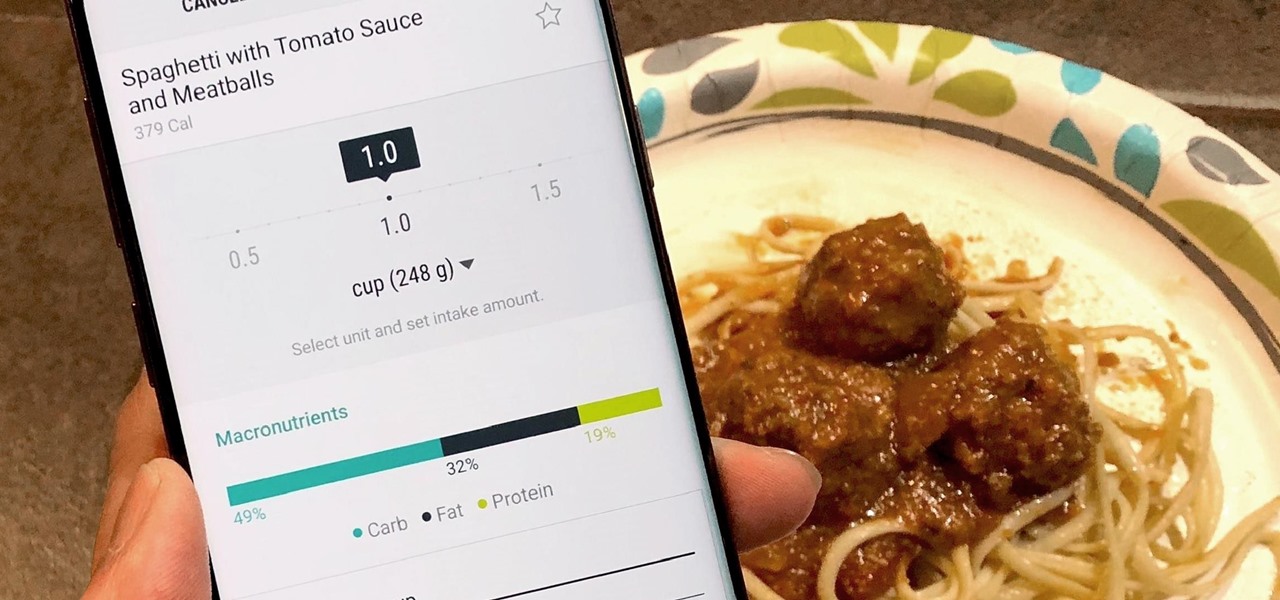
The most essential part of a healthy lifestyle is managing your diet — after all, what would be the point of a daily workout regimen if you were eating junk food? Thankfully, Samsung Health makes it easy to record your calorie and nutrient intake to get a clear picture of your dietary habits and how you can make them better.

Facebook added a new feature that lets you post 3D versions of your portrait mode photos for all your family and friends to see on their smartphones, computers, and virtual reality goggles. These new 3D photos add a whole new dimension to your images with movement and more depth.

After months of beta testing, Siri Shortcuts has finally arrived on all iPhones that support iOS 12. Anyone familiar with Workflow will understand how useful it is to set custom Siri commands for your favorite apps. Of course, your favorite apps need to be compatible with Shortcuts in order to take advantage of the new feature.

As Magic Leap prepares to ship the Magic Leap One later this year, the company is putting its focus on mentoring developers and creators to build a content ecosystem for the spatial computing platform.

BlackBerry has formally unveiled its latest flagship, the KEY2, during an exclusive event in New York. The Android-powered KEY2 retains its distinctive BlackBerry aesthetics with a physical QWERTY keyboard. Here's all the juicy details regarding Blackberry's followup to the venerable KEYone.

Samsung's big reveal of the Galaxy S9 and S9+ at Mobile World Congress revolved around its "reimagined" camera and augmented reality capabilities.

As the first Animal Crossing game on mobile devices, it's clear that Nintendo had a more social experience in mind for Pocket Camp, and I'm not talking about all the animal friends you can make. You can add other players to your list of human friends, and they're incredibly useful for a wide array of tasks.

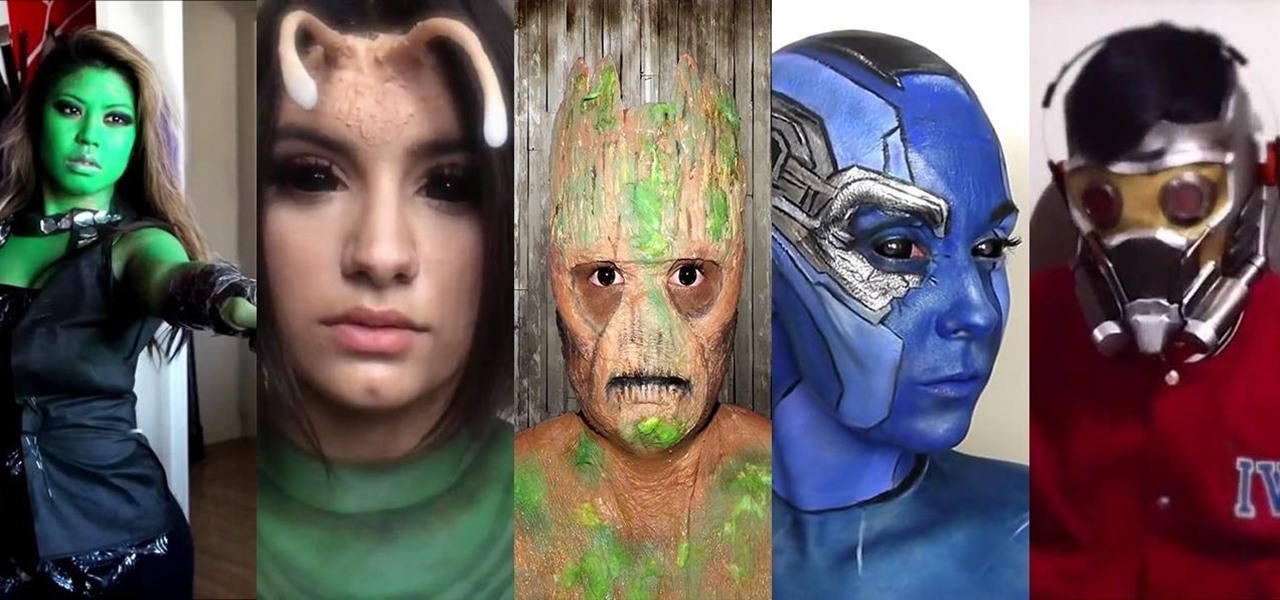
The Guardians of the Galaxy have to be the most fun superhero team to have at a Halloween party. They dance, they break the rules, and they definitely have the grooviest music. So the Guardians are a great bunch to pick from for your Halloween costume — or even for a themed group costume. Just imagine the badass vibe when you all walk into a venue together with Star-Lord blasting "Cherry Bomb" from a portable speaker. Here's a roundup of some of the best Guardians of the Galaxy costume guides...

This is a tale about microbes, a man who became a hermit, and the parchment that carries both of their stories.

A virus easily spread among trout and salmon could make it harder to keep your favorite fish on the menu.

Alright, let's dig into this and get the simple stuff out of the way. We have a journey ahead of us. A rather long journey at that. We will learn topics ranging from creating object filtering systems to help us tell when a new object has come into a scene to building and texturing objects from code.

A recent initiative by the Cherokee Nation American Indian Tribe delivers a success story for knocking out a silent killer — Hepatitis C.

While IKEA is collaborating with Apple for its ARKit furniture app, Marxent is ready to help the rest of the interior decorating and home improvement crowd with their apps.

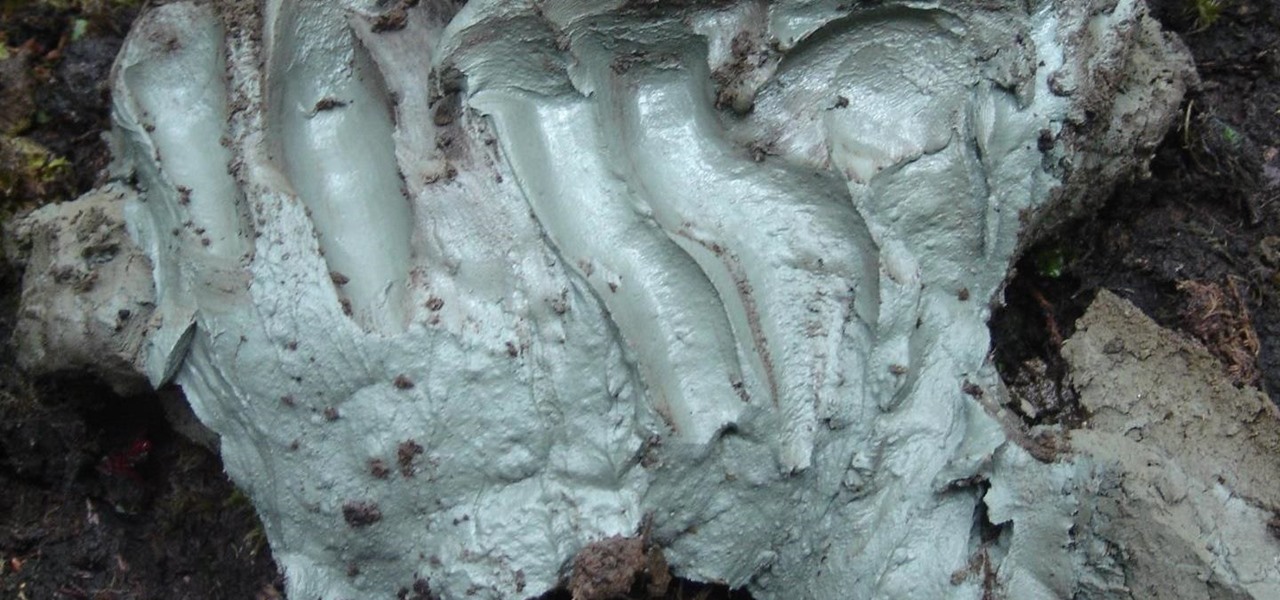
For as long as 14,000 years, the First Nations people of the Heitsuk Nation have made their home along the Central Coast of the Canadian province of British Columbia. Among the territory's inlets, islands, rivers, and valleys lie a clay deposit on the north side of Kisameet Bay, near King Island. For as long as most can remember, the tribe has used the clay as medicine. Now science says microbes that live in that clay may have important antibacterial properties.

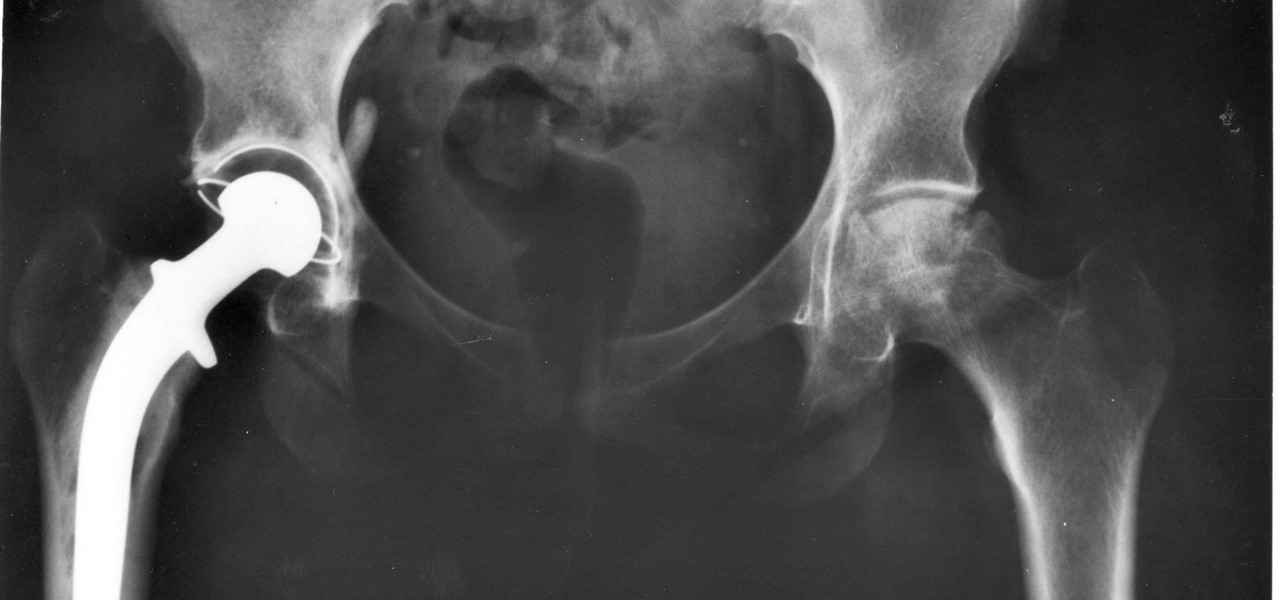
For about a million Americans each year, a joint replacement brings relief from pain and restored mobility. But, 5–10% of those people have to endure another surgery within seven years, and most of those are due to an infection in their new joint. If doctors could treat infections more effectively, patients could avoid a second surgery, more pain, and another rehabilitation.

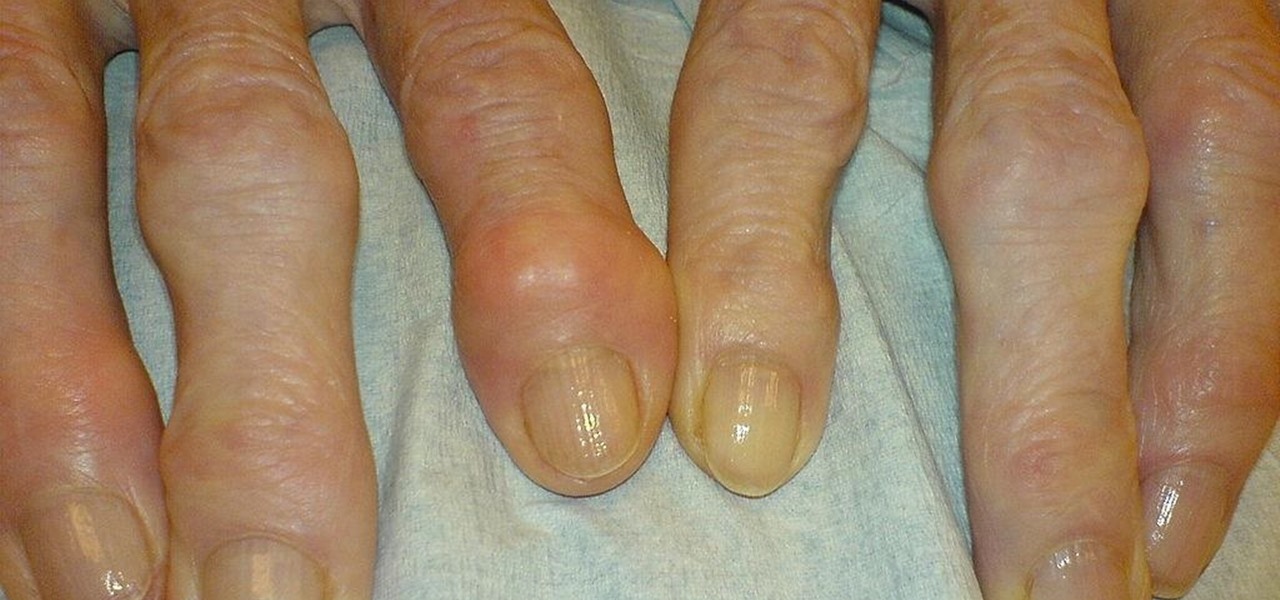
As if the swollen, painful joints of rheumatoid arthritis weren't enough, the disease is the result of our immune system turning against cells of our own body. Ever since this realization, scientists have worked to find the trigger that sets the immune system off. Scientists believe that gut bacteria may have a role in initiating the abnormal immune response. Now, a team of researchers from Boston has figured out how that might occur.

After years of telling patients to finish any prescribed course of antibiotics completely, a group of researchers in the UK say it is no longer necessary, and could even be harmful if we want to preserve the antibiotics we can still use.

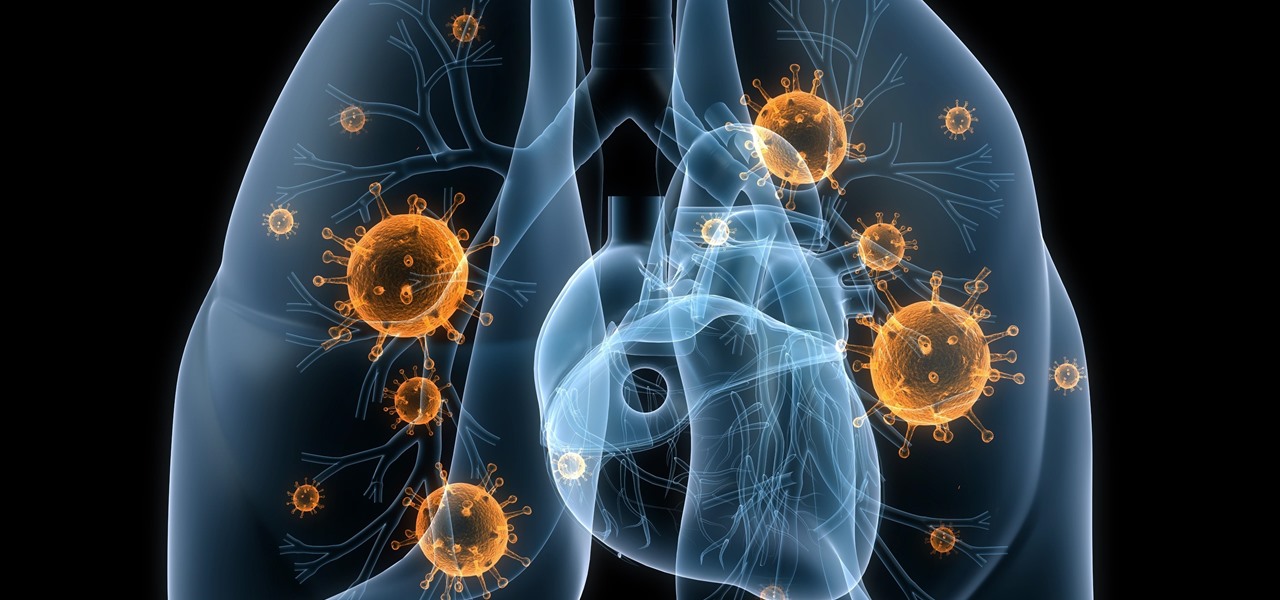
Once we recover from the respiratory infection pneumonia, our lungs are better equipped to deal with the next infection — thanks to some special cells that take up residence there.

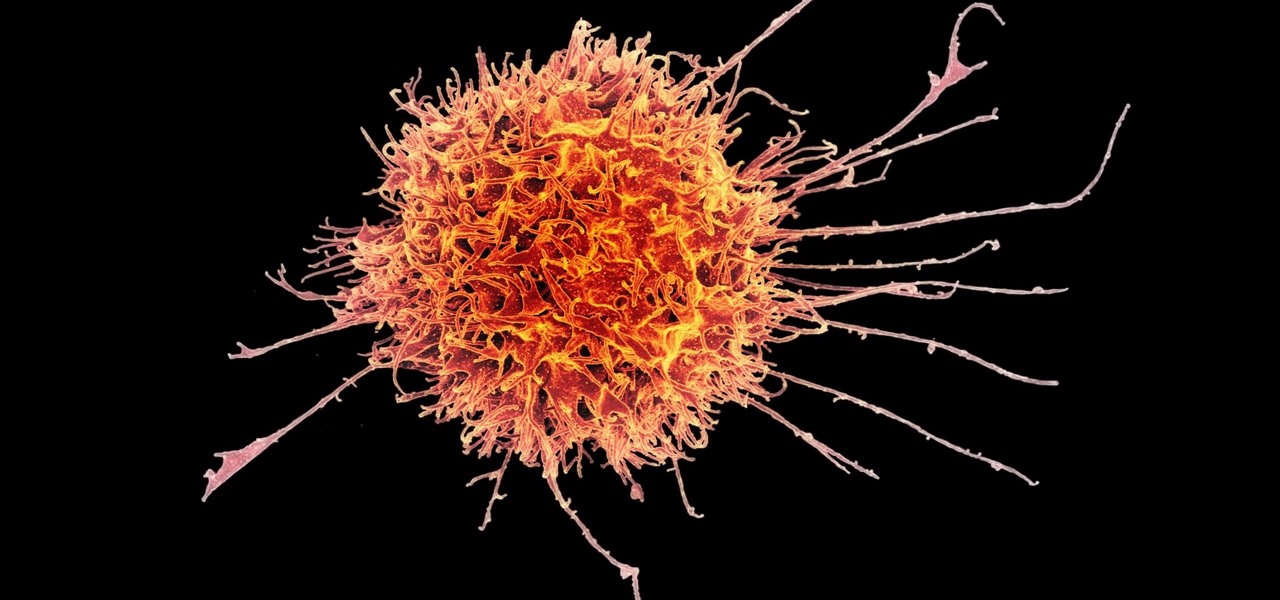
Cancer cells do a pretty good job of flying under the radar of our immune system. They don't raise the alarm bells signaling they are a foreign invader the way viruses do. That might be something scientists can change, though.

Not all bacteria in the eyes cause infection. A group of researchers from the National Eye Institue has shown that not only is there a population of bacteria on the eyes that reside there but they perform an important function. They help activate the immune system to get rid of bad, potentially infection-causing — pathogenic — bacteria there.

New research explores how the bacteria on the penis can leave men more susceptible to infection with HIV.

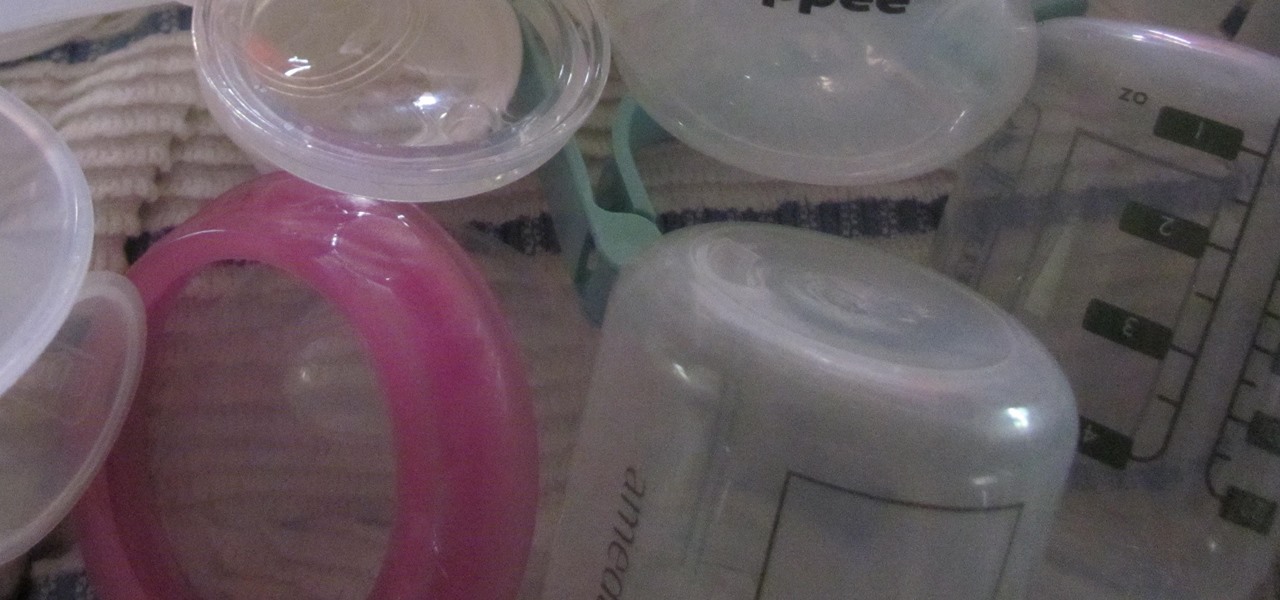
Foodborne infections often occur through the contamination of equipment, food-prep tools, and unsanitary surfaces. A recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reminds us that breast pump parts are part of the food-delivery chain — and they can become contaminated too.

It seems almost every carrier now has an unlimited data plan, and free Wi-Fi is now available in more places than ever before. If you want to be connected, it has never been easier — but that still doesn't mean that everyone can stream as much as they please.

The herpes simplex virus (HSV) can cause devastating complications for infected newborns whose mothers have genital herpes. Understanding risk and research can help you, and your baby, when the time comes.

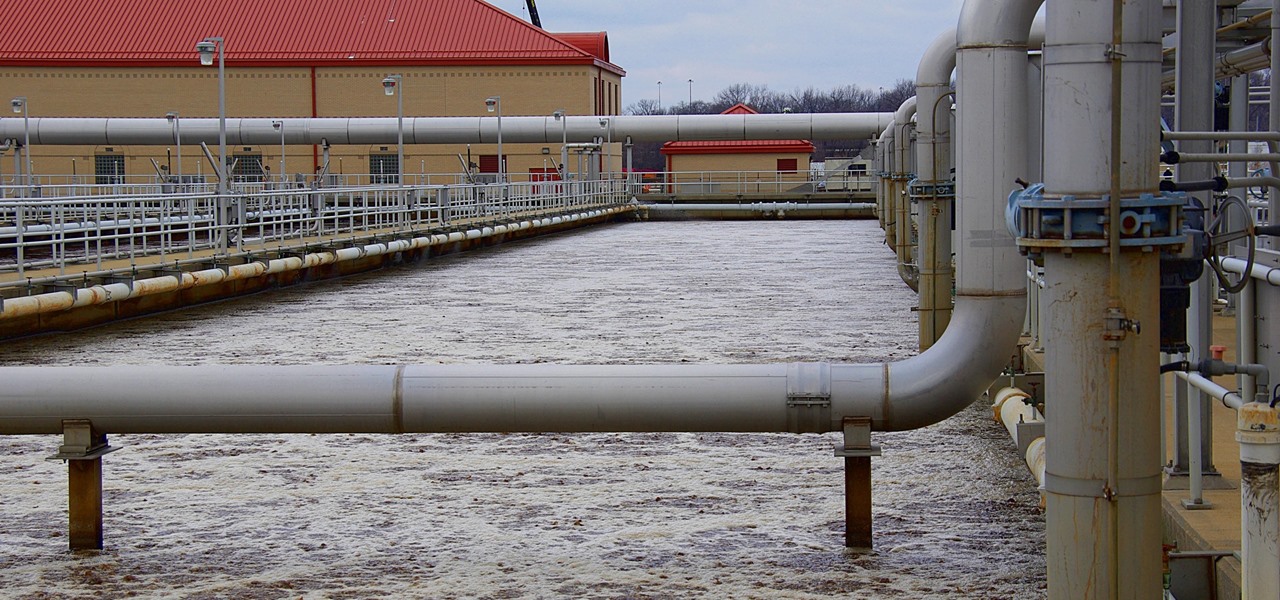
Everything from disposed of drugs to hormones and disease-causing bacteria — anything that is rinsed or flushed down the drain — can contaminate wastewater.

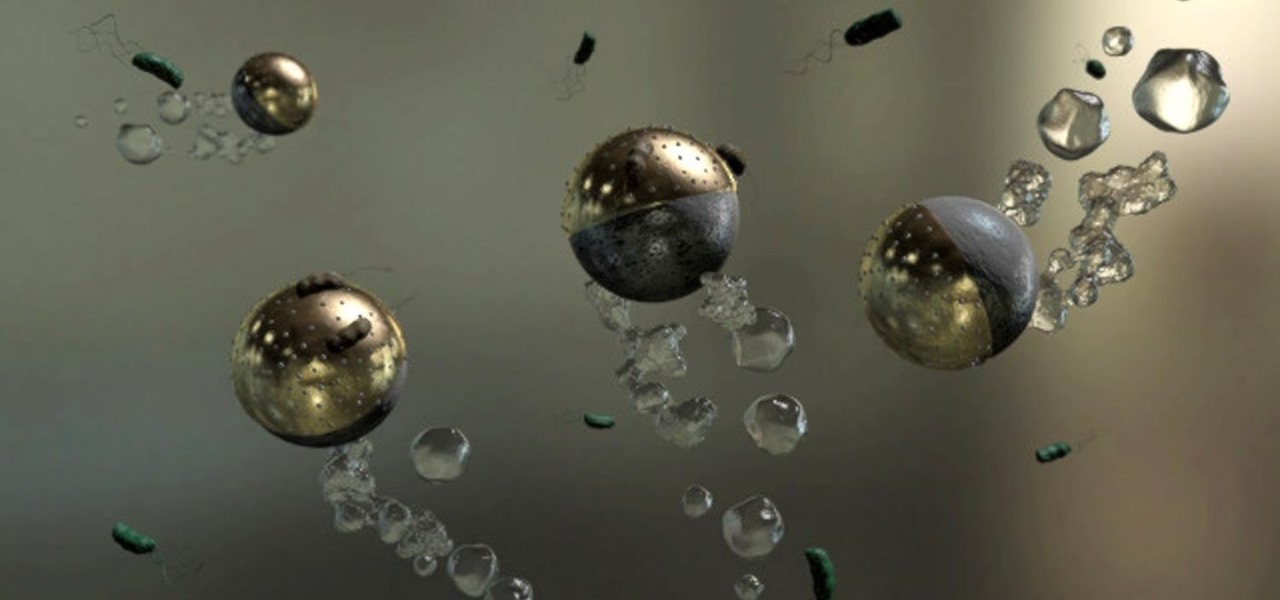
Look no further than Flint, Michigan, to discover the serious consequences of contaminated drinking water. Around the world, water polluted by pathogens and toxins sickens people or cuts them off from safe drinking water. Looking for a solution, researchers created tiny, swimming robots that pack a powerful punch against waterborne pathogens.

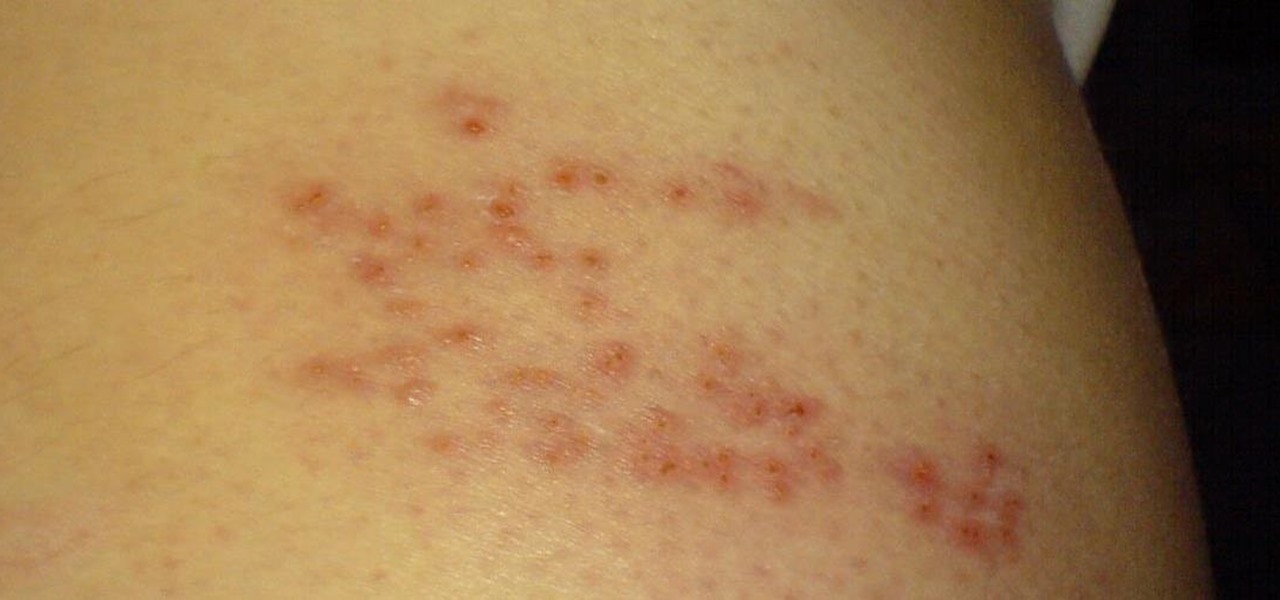
People who have heart disease get shingles more often than others, and the reason has eluded scientists since they first discovered the link. A new study has found a connection, and it lies in a defective white cell with a sweet tooth.

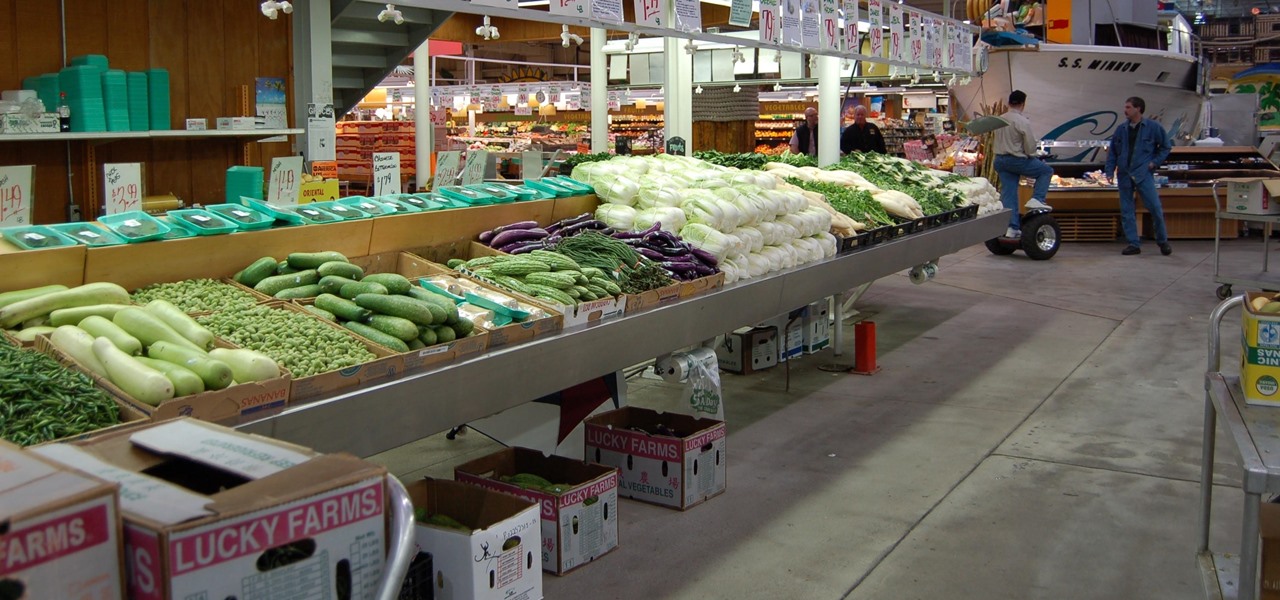
We know that healthcare-related facilities can be fertile ground for antibiotic-resistant bacteria, but recent research suggests your produce aisle might be too.

Intense exercise can cause problems with our digestive tract. It even has a name — "Exercise-induced Gastrointestinal Syndrome." Simply put, strenuous exercise can damage the gut and let the bacteria that reside there potentially pass into the bloodstream.

With summer just ahead, you, or your children, may be looking forward to some pool time or the water park. When planning water-based fun this year, keep a heads-up for microbes.

Most of us have already had an encounter with the Epstein-Barr virus, or EBV, for short. As part of the herpes family, it's one of the most common disease-causing viruses in humans. We get the disease with (or without) some nasty symptoms, then we recover. However, EBV stays in our body after the illness has ended, and it's one of the few viruses known to cause cancer.

The problem with HIV is that it attacks and kills the very cells of the immune system that are supposed to protect us from infections — white blood cells. But a new technique, developed by scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) in La Jolla, California, offers a distinct HIV-killing advantage.