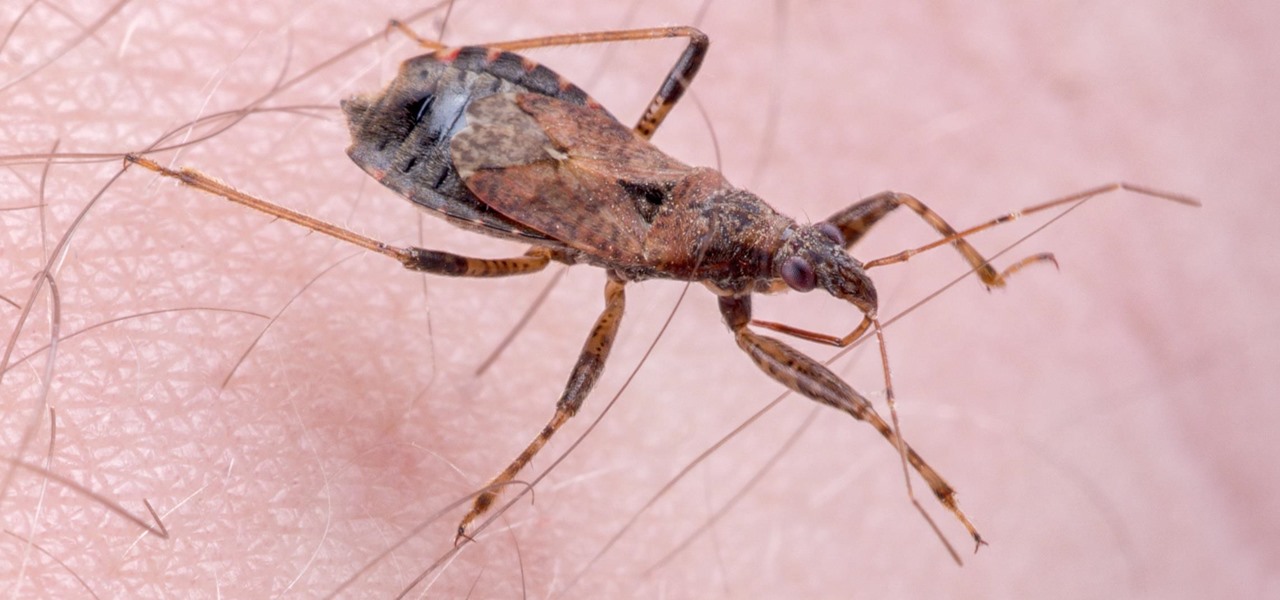
If you live with pets, you know where their tongue has been, yet you let them kiss and lick you all they want without even thinking twice about it. I've heard people say that a dog's mouth is very clean, and that their saliva, delivered by licking, can help heal wounds, but is that really true?

On June 11, 2016, an Arizona woman died from what appeared to be several infections, including pneumonia. She likely caught at least one of these from her dog.

The culprit probably wasn't what doctors were expecting when a 57-year-old man in Hong Kong came to the hospital. The patient was admitted to the intensive care unit in critical condition. A clue to the cause of the infection would lie in the man's profession—he was a butcher.

After California college student Luis Ortiz blacked out and was taken to the hospital in 2015, doctors were startled to discover the reason his brain was swelling—a one-centimeter long, wriggling tapeworm living within a ventricle in the middle of his brain.
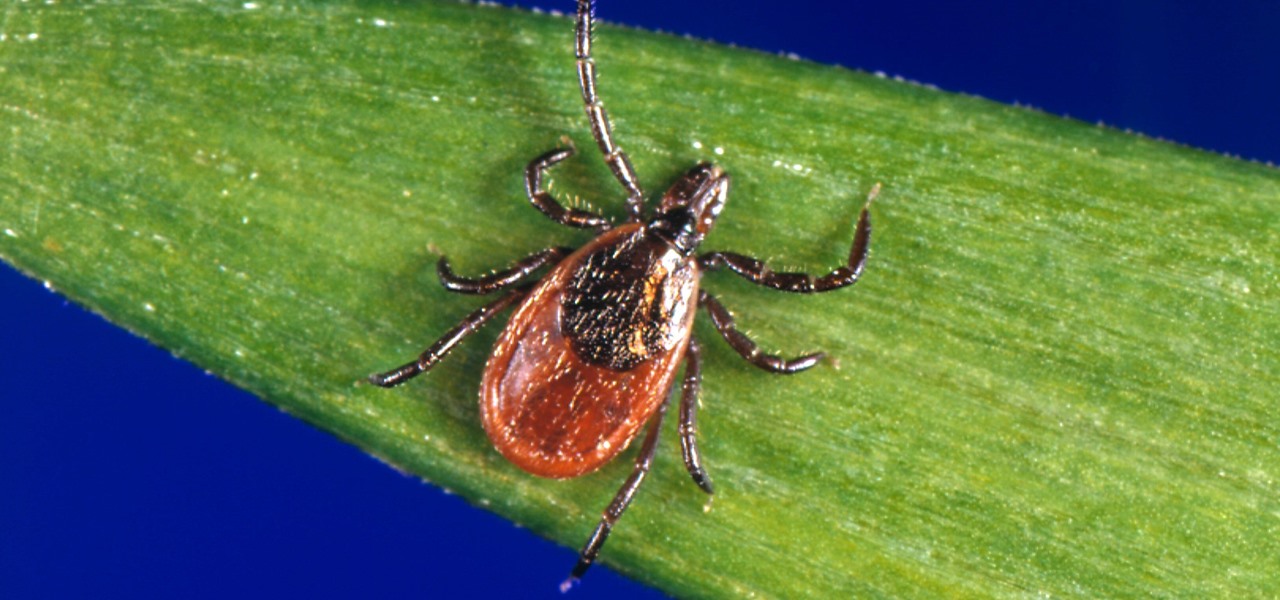

In the US, ticks can spread several pathogens in one bite. A new test offers physicians the ability to identify what infections ticks are carrying and can detect if one of the pathogens could be the spreading Powassan virus.
We might think of Zika as a mosquito-borne virus that effects developing fetuses, but, it also can be passed through sex by either a man or a woman, just like herpes and other STD viruses. New research has shown that vaginal bacteria can inhibit sexually transmitted Zika virus and Herpes Simplex Virus-2 in women.

Wound infections don't usually enter the blood and become systemic, spreading the infection throughout our bodies, and there's a good reason for that: Our bodies actively work to prevent it, according to research that discovered a new use for a protein first discovered decades ago.

Our canine best friends could spread our bacterial worst nightmare, according to a recent study. The problem with drug-resistant bacteria is well known. Overused, poorly used, and naturally adaptive bacteria clearly have us outnumbered. As science drives hard to find alternative drugs, therapies, and options to treat increasingly resistant infections, humans are treading water, hoping our drugs of last resort work until we figure out better strategies.

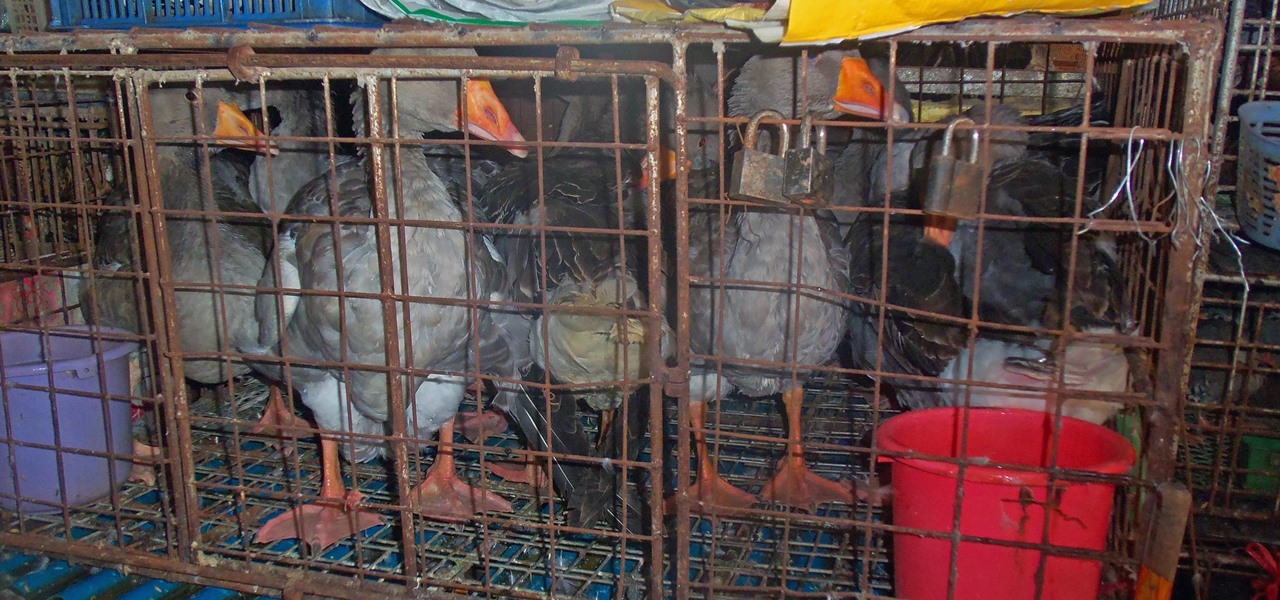
Antibiotics used to prevent diseases in livestock are creating a world of hurt for humans and the soil we depend on for food. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a global health issue. The overuse, underuse, and poor use of these life-saving drugs is rapidly removing them as a treatment option for serious infections in humans—plus bacteria are naturally adaptive.

Every year, 100-200 people in the US contract leptospirosis, but usually 50% of the cases occur in Hawaii where outdoor adventurers are exposed to Leptospira bacteria found in freshwater ponds, waterfalls, streams, and mud. That's why it's so alarming that two people in the Bronx have been diagnosed with the disease and a 30-year-old man has died from it.

Cats give us so much—companionship, loyalty, love... and now the bird flu. Several weeks ago, a veterinarian from the Animal Care Centers of New York City's Manhattan shelter caught H7N2 from a sick cat. According to a press release from the NYC Health Department on December 22, "The illness was mild, short-lived, and has resolved." This isn't the first time cats have passed infections on to humans, but it is the first time they passed on the bird flu—avian flu H7N2, to be exact.

Coronaviruses are common viruses, and most of us catch one at some point — they cause about 30% of all common colds. A new accidental discovery could help fight these viruses, even the deadlier, emerging ones.

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimated that there were 212 million cases of malaria across the world in 2015, and 429,000 of those people died — mostly children living in Africa. Preventing and treating those infections has been a challenging world priority. That makes a new malaria drug discovery — published in Science Translational Medicine — incredibly important.

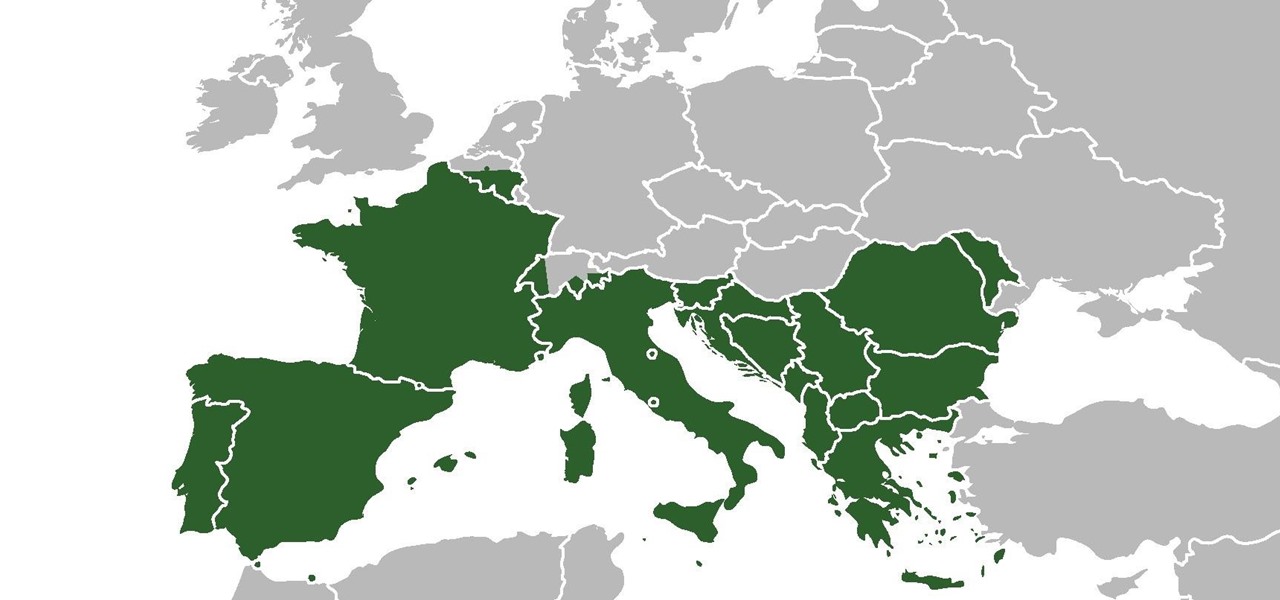
The beauty of southern Europe won't protect it from invasions of disease-carrying ticks and mosquitoes—in fact, the Mediterranean climate and landscape may be part of the reason the bloodsuckers are expanding there, bringing unique and terrifying diseases in their wake.

Avian flu is making the news again with new human cases in China reported in January. What does "avian flu" mean to you—and how dangerous is it?

When the climate changes, so do all the things that rely on the climate, including people, plants, and pathogens. A European study recently took a broad look at what kind of microorganisms are most likely to be affected as climate change heats, cools, dries, and wets the world around us.

The growing list of dangerous antibiotic resistant organisms has just acquired three new members. Researchers have discovered three new species of Klebsiella bacteria, all of which can cause life-threatening infections and have genes that make them resistant to commonly used antibiotics.

Like humans, cats can suffer infections caused by ticks, and too often, the disease is fatal. Learn about tickborne diseases that affect cats and what you can do to protect Fluffy from an untimely demise.

Lyme is a growing threat as we move into warmer weather in the US. Researchers have said this year could be one of the worst for this tick-borne disease, as a skyrocketing mouse population and warmer temperatures increase the risk.

It's not the bacteria itself that takes lives and limbs during invasive flesh-eating bacteria infections. It's the toxins secreted by the group A Streptococcus bacteria invading the body that causes the most damage.

When the mosquito that carries the malaria parasite (Plasmodium falciparum) bites someone, the parasite must travel to the liver where it undergoes part of its lifecycle before infecting red blood cells and spreading to its next host. Until now, the first step of how the parasite gets to the liver hasn't been clear.

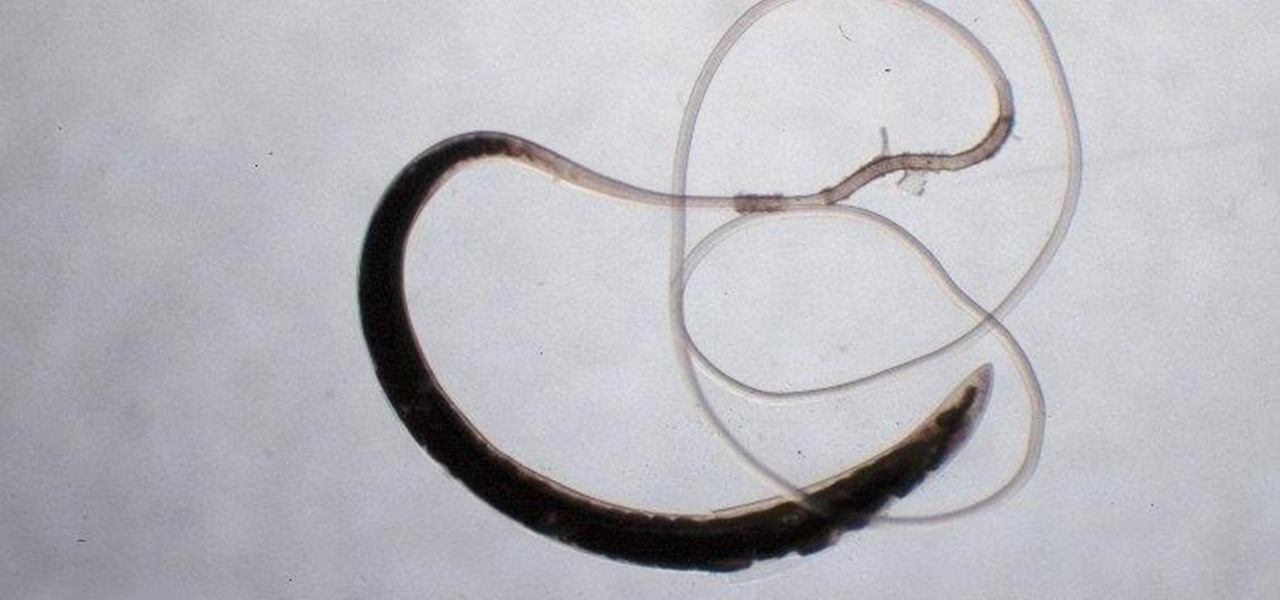
Somewhere around 600–800 million people in the world are infected with whipworm (Trichuris trichiura), an infection they got from ingesting soil or water contaminated with feces of infected animals or people containing the parasite's eggs.

A rose by any other name may smell as sweet, but one annoying invasive weed may hold the answer to treating the superbug MRSA. Researchers from Emory University have found that the red berries of the Brazilian peppertree contain a compound that turns off a gene vital to the drug-resistance process.

We usually associate Salmonella bacteria with a dangerous type of food poisoning, but they actually are pretty good at seeking out tumors. That trait made the bacteria a great candidate to deliver a protein that would help knock tumors out.

Joe McKenna died when he was 30 years old. A young married man with his future ahead of him, he was cleaning up the station where he worked as a fireman. Struck by a piece of equipment fallen from a shelf, Joe complained of a sore shoulder. Over the next week, Joe worsened and ended up in the hospital. Chilled, feverish, and delirious, his organs shut down from an infection we'd now call septic shock.

New weapons are needed to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Instead of drugs, scientists have discovered in an animal study that they may be able to harness vampire bacteria to vanquish pneumonia.

A promising new antibiotic has been discovered in, of all things, another bacteria. Burkholderia bacteria live in diverse habitats, including soil, plants, and humans where they thrive by knocking out other microbes that compete with them for resources or threaten their existence. Scientists have discovered they accomplish this by producing a very effective antibiotic.

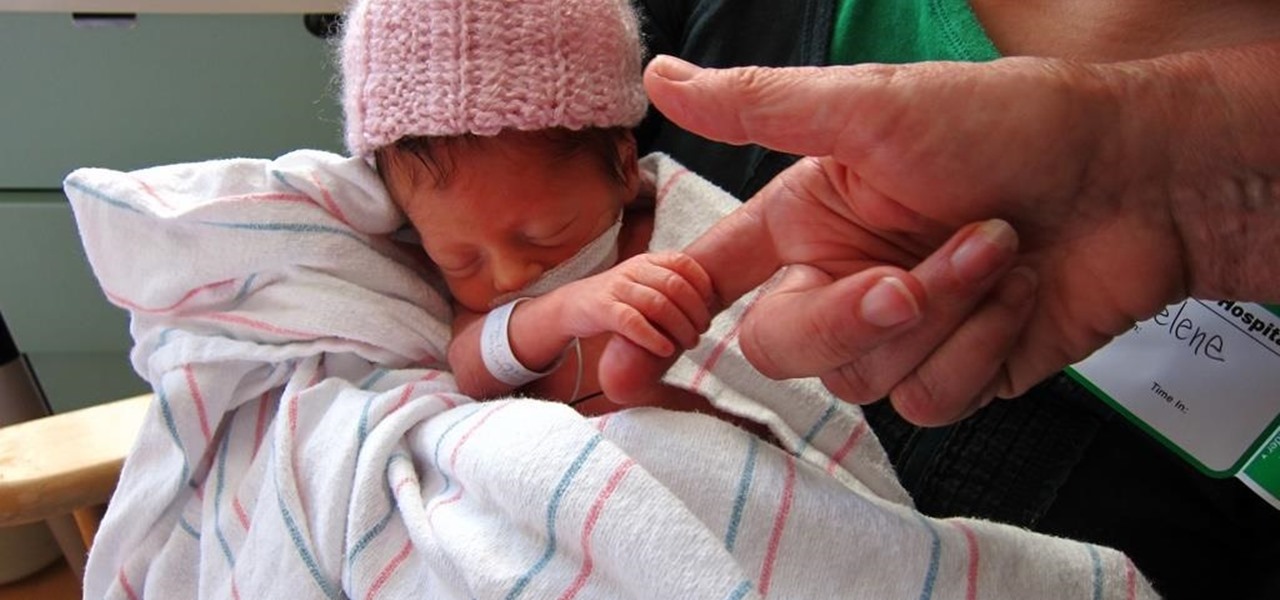
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is the most commonly occurring lower respiratory tract viral infection in young children and usually isn't serious, but in premature infants and babies under six months old, the infection can be severe, and even fatal.

Streptococcus and staphylococcus bacteria produce toxins that can cause toxic shock syndrome.

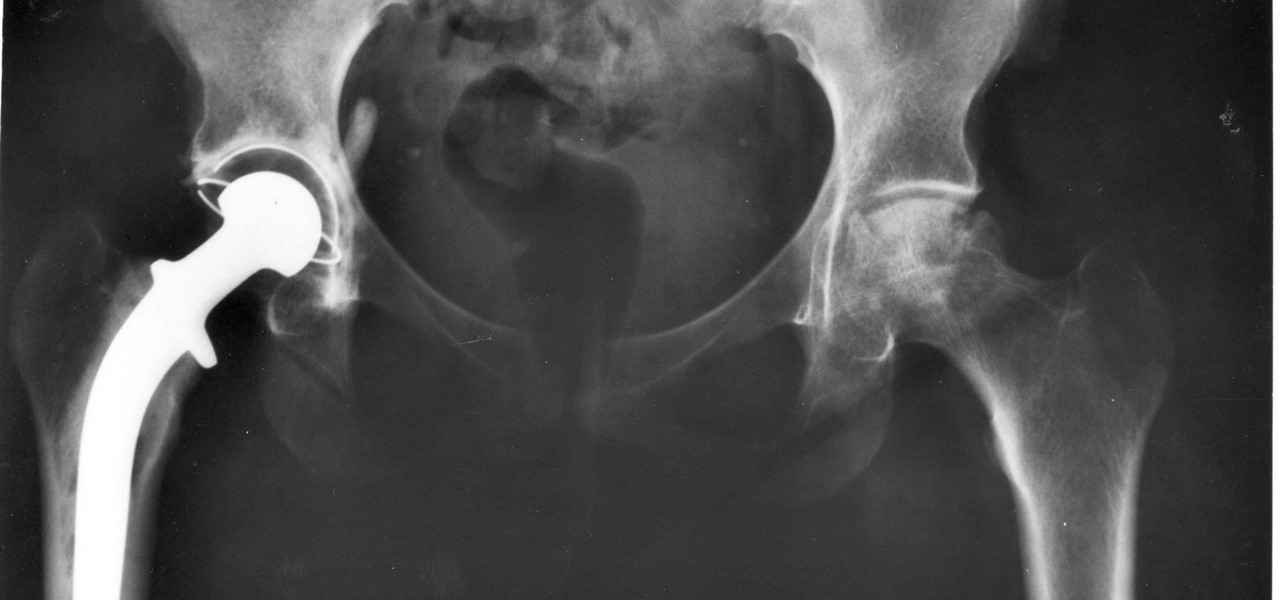
For about a million Americans each year, a joint replacement brings relief from pain and restored mobility. But, 5–10% of those people have to endure another surgery within seven years, and most of those are due to an infection in their new joint. If doctors could treat infections more effectively, patients could avoid a second surgery, more pain, and another rehabilitation.

Gonorrhea infections reached a peak in 1975, then decreased until 2009, when infection rate started rising and has increased each year since. With the rise of antibiotic resistance, those numbers are only going to get worse — unless we find new treatments against the bacteria.

Transmitted by a sandfly one-third the size of a mosquito, parasitic Leishmania protozoa are responsible for a flesh-destroying disease that kills an estimated 20,000 people per year. Two new studies offer understanding of how the parasite provides immunity through persistence and why some people suffer more virulent forms of the disease.

Rising on the world stage, dengue fever is transmitted by mosquitoes — and apparently air travel too.

If you know that ticks spread Lyme disease, you may already know you might also catch a bunch of other infections from them. One of the lesser-known diseases spread by ticks is infection with the bacterium Anaplasma phagocytophilium, called anaplasmosis.

Dangerous to humans and dogs, Rocky Mountain Fever, along with several other tickborne infections, is on the rise.

You may not have heard of visceral leishmaniasis, onchocerciasis, or lymphatic filariasis, and there is a reason for that. These diseases, part of a group of infections called neglected tropical diseases (NTDs), impact more than a billion people on the planet in countries other than ours. Despite the consolation that these often grotesque illnesses are "out of sight, out of mind," some of these infections are quietly taking their toll in some southern communities of the US.

China just confirmed a sixth avian flu outbreak since October. On Tuesday, the Ministry of Agriculture stated that there had been another instance of bird flu in the Hubei province, of the H5N6 influenza virus. The outbreak occurred in the city of Daye, which is home to some 900,000 people, but hasn't been linked to human infections yet.

Antibiotic-resistant infections that usually occur only in hospital settings are spreading in communities, increasing hospital stays—and danger—for young children.

Lighthouses and signal fires may have been the first social media. Without the ability to share language, a distant light meant "humans here." A new study from the University of California, San Diego, finds that bacteria can also send out a universal sign to attract the attention of their own, and other bacterial species.

Findings from a mouse study suggest that the Zika virus infection may have serious reproductive consequences for men.