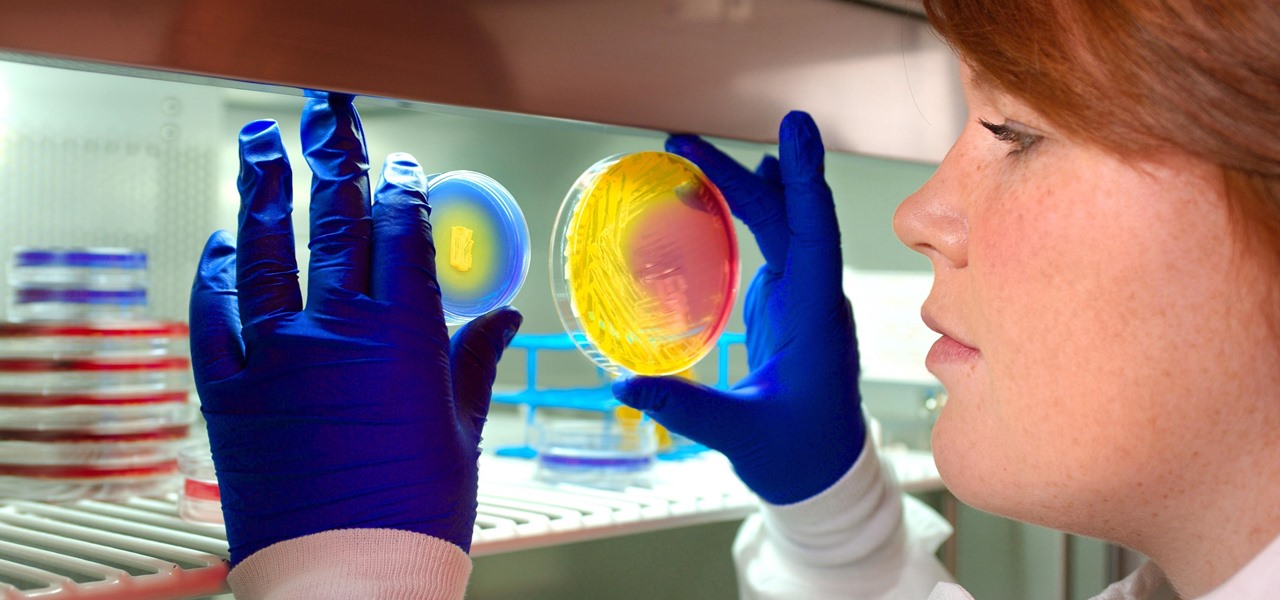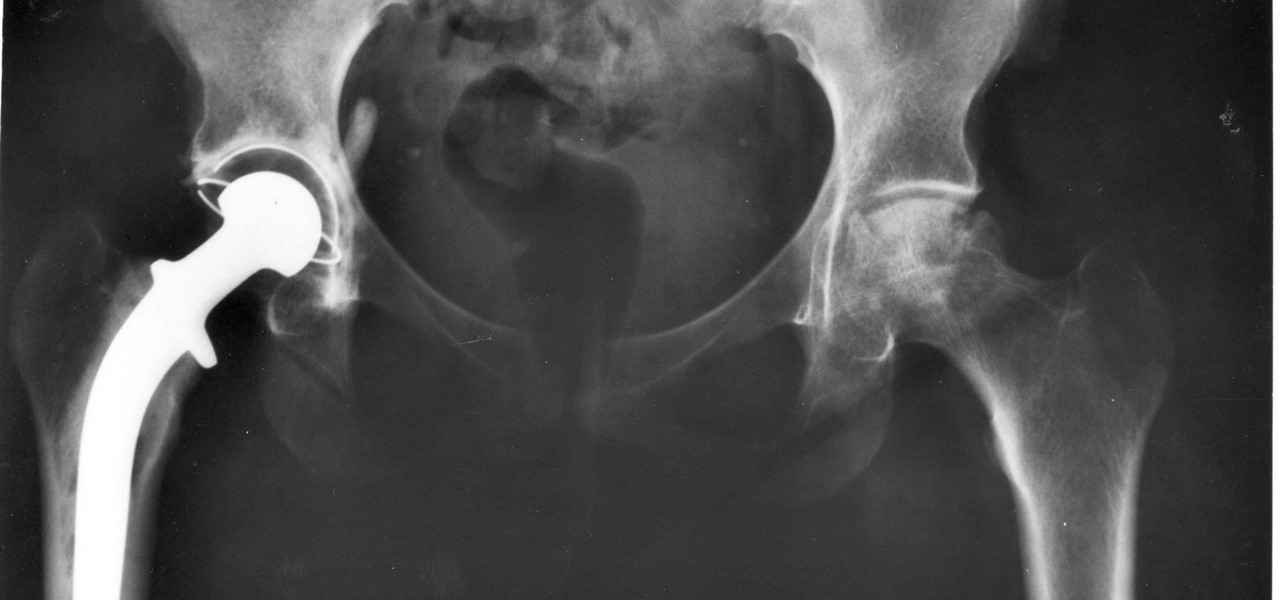
For about a million Americans each year, a joint replacement brings relief from pain and restored mobility. But, 5–10% of those people have to endure another surgery within seven years, and most of those are due to an infection in their new joint. If doctors could treat infections more effectively, patients could avoid a second surgery, more pain, and another rehabilitation.
Cancer cells do a pretty good job of flying under the radar of our immune system. They don't raise the alarm bells signaling they are a foreign invader the way viruses do. That might be something scientists can change, though.

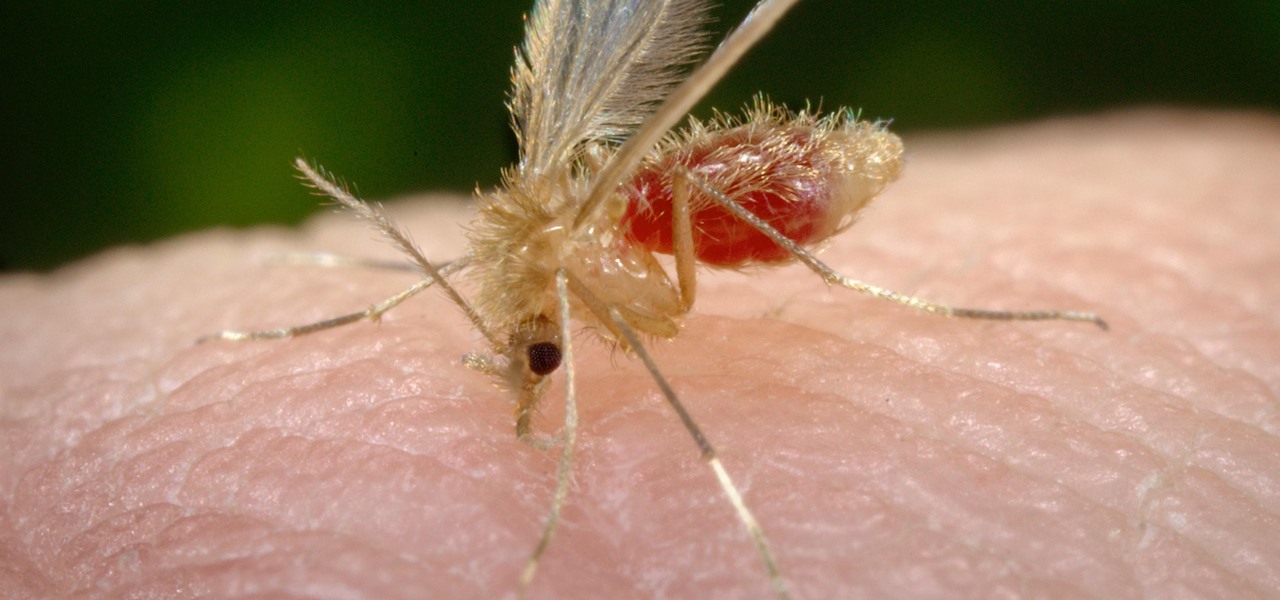
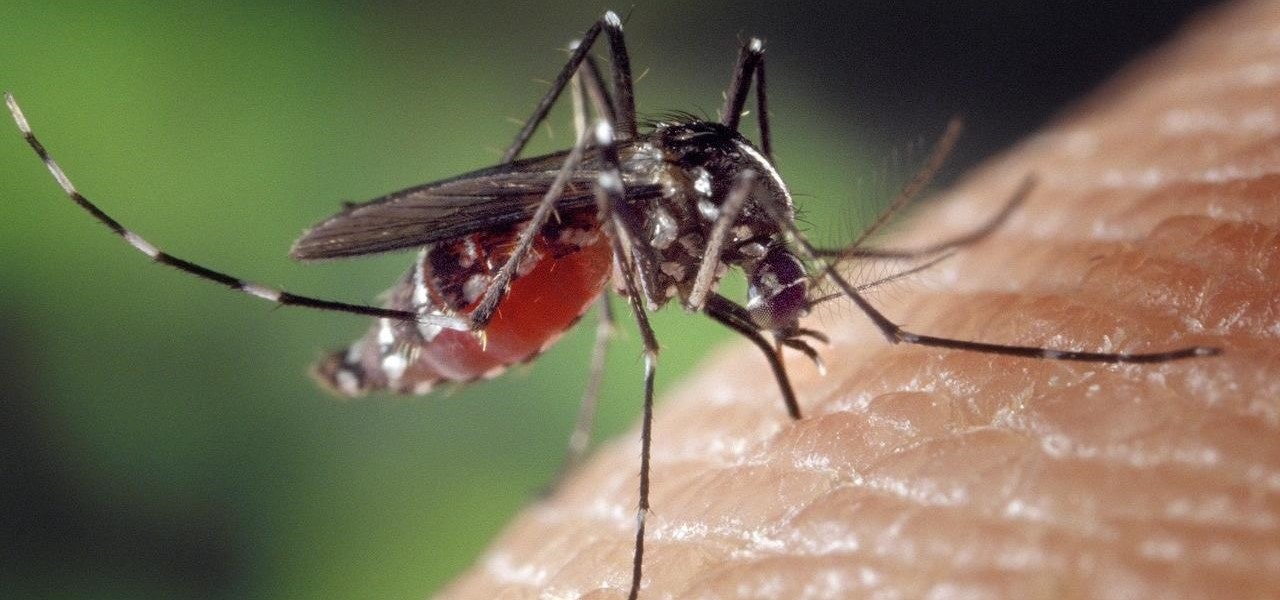
For a company more associated with debugging computer programs, Google's parent company, Alphabet, is making a name for itself by taking on the real thing — mosquitoes.
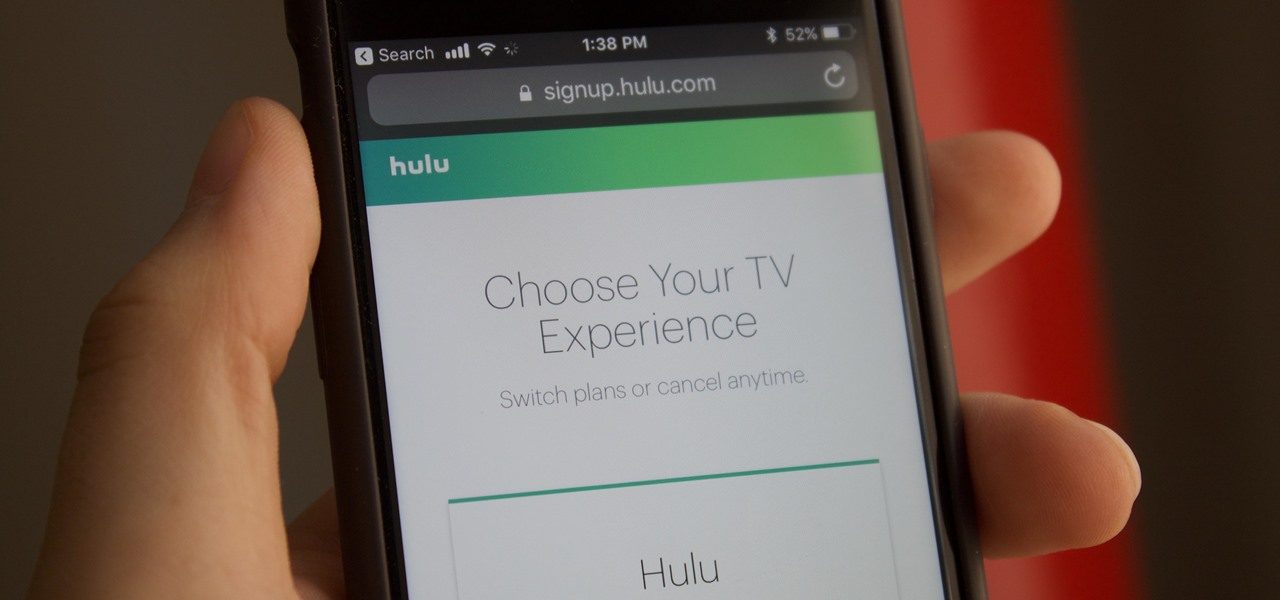
Hulu used to be simple — just a site with all the latest clips and episodes from your favorite shows. Watch some ads, watch some free TV. Easy, right? Not so much anymore. Hulu is no longer free, and on top of that, offers different pricing plans and add-ons.

Nvidia has emerged as the indisputable leader in chips for Level 3 and even more advanced driverless applications, catching some of the world's largest semiconductor makers and automotive suppliers by surprise.

Forget Waymo, Uber, Tesla, and other other heavily mediatized driverless contenders — German premium carmaker Audi AG has become the first OEM to introduce a Level 3 car sold in retail channels.

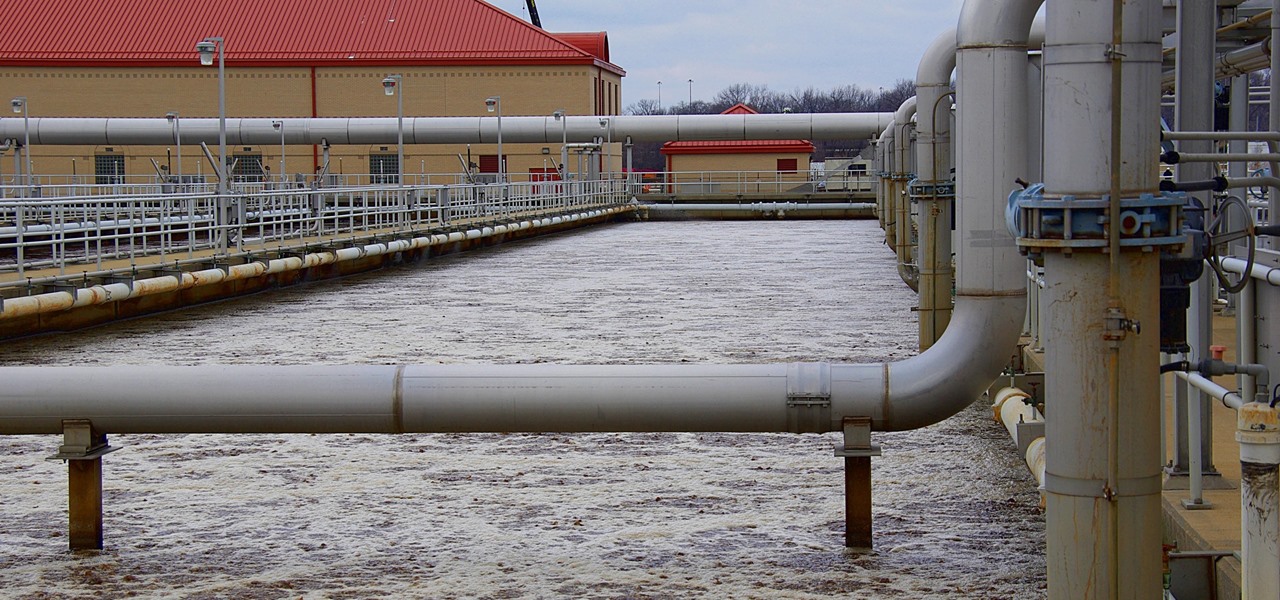
Everything from disposed of drugs to hormones and disease-causing bacteria — anything that is rinsed or flushed down the drain — can contaminate wastewater.

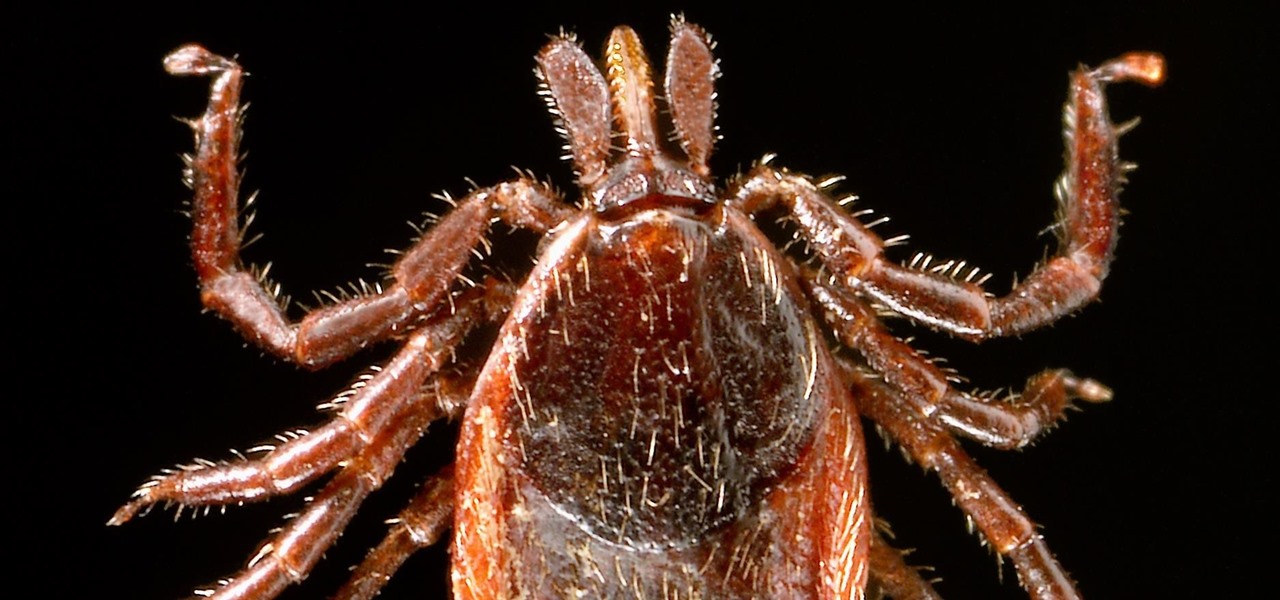
If you know that ticks spread Lyme disease, you may already know you might also catch a bunch of other infections from them. One of the lesser-known diseases spread by ticks is infection with the bacterium Anaplasma phagocytophilium, called anaplasmosis.

Alzheimer's disease — an irreversible, progressive brain disorder — is the sixth leading cause of death in the US and more than afflicts 5 million Americans. As if those numbers aren't scary enough, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention expect that number to nearly triple by 2050.

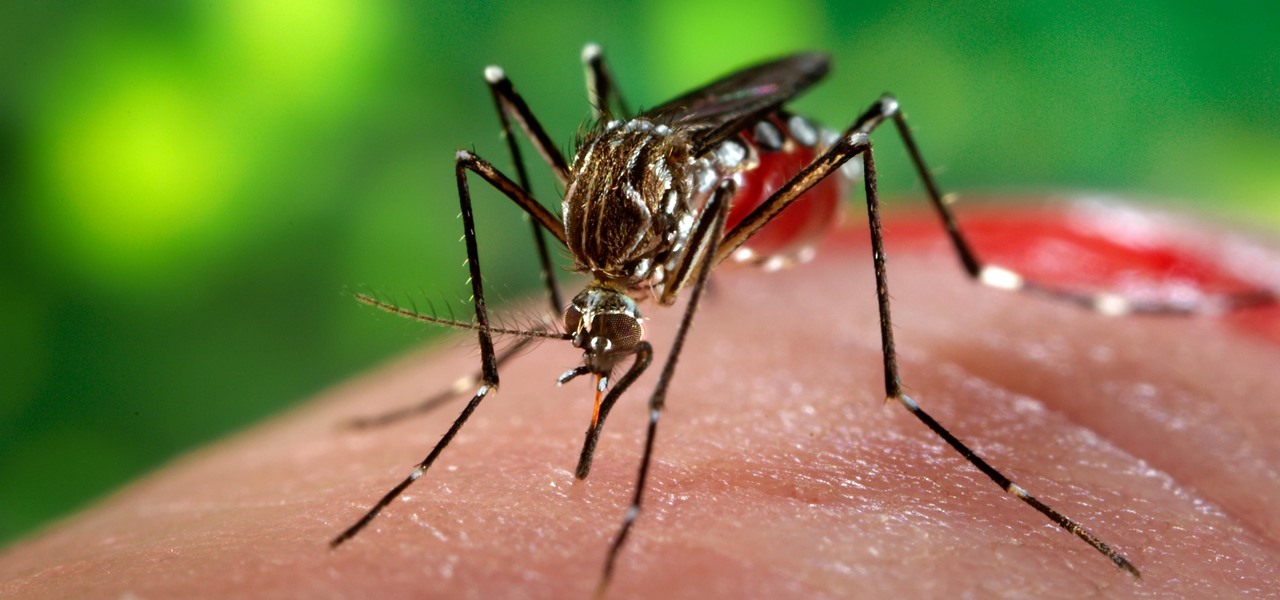
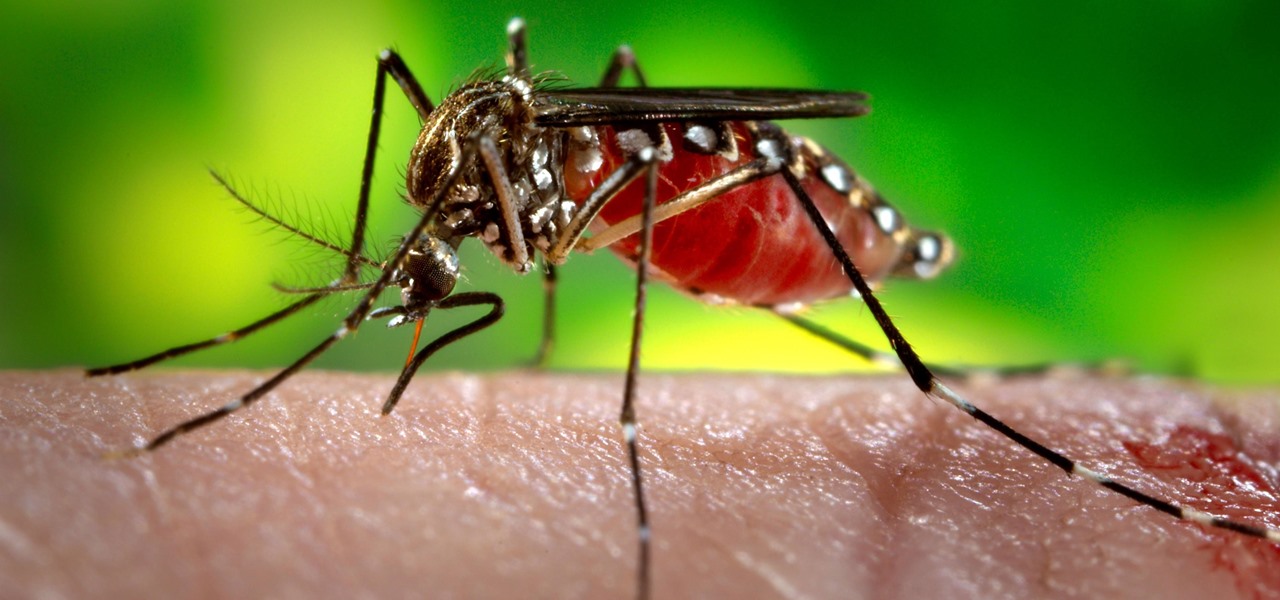
Mosquitoes are a big problem, and citronella candles are not the solution. There are a lot of mosquito species. The American Mosquito Control Association reports there are more than 3000 mosquito species in the world, and about 200 of those occur in the US. The most common are the Aedes, Anopheles, and Culex species. These are also the three mosquito species most likely to transmit serious illness, and all of them live in the US.

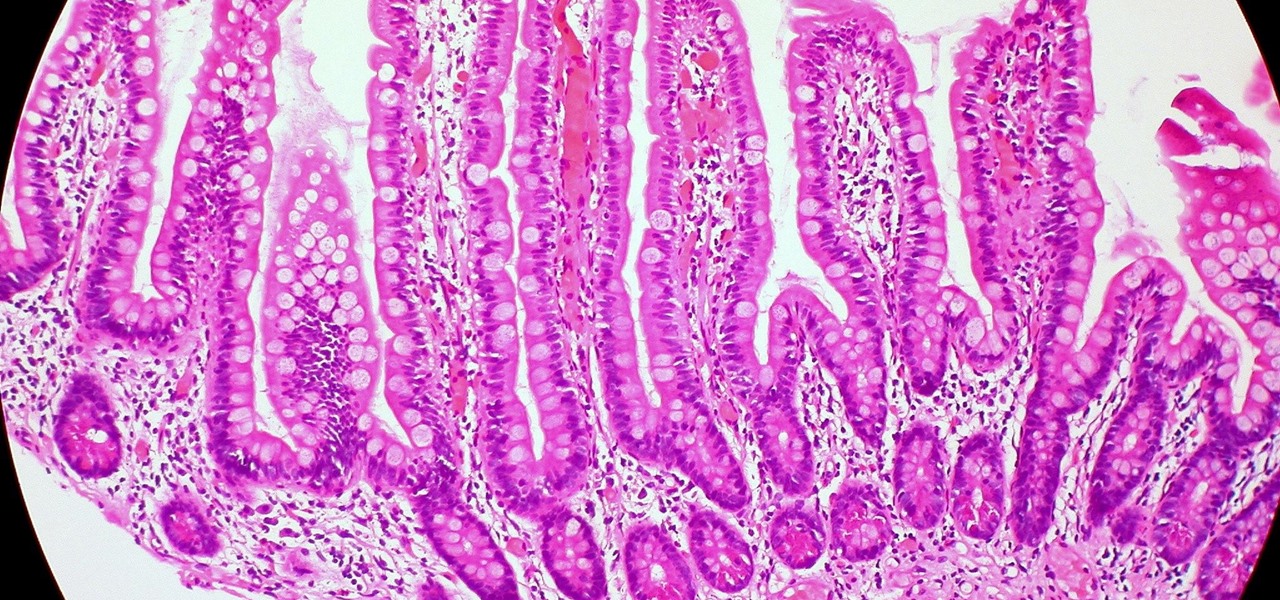
Several recent research studies have pointed to the importance of the microbes that live in our gut to many aspects of our health. A recent finding shows how bacteria that penetrate the mucus lining of the colon could play a significant role in diabetes.

As researchers from Yale searched our environment for compounds to aid in the battle against drug-resistant bacteria, they got an unlikely assist from ticks.

Even though the Ebola virus was discovered as recently as 1976, over 30,000 people have been infected since, and half have died a horrible death. Since there's no way to cure the infection, the world desperately needs a way to prevent it — and the five similar viruses in its family, the ebolaviruses.

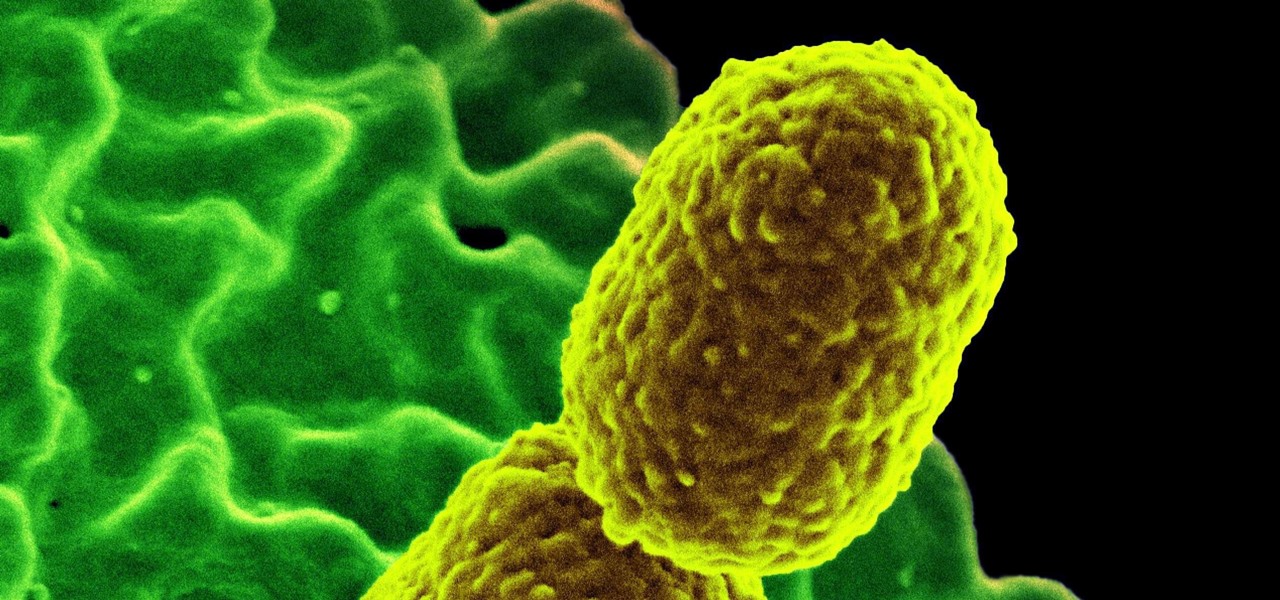
The bacteria Klebsiella pneumoniae is a bad actor known for being antibiotic-resistant and causing a variety of serious infections in hospitals, including pneumonia, surgical site wounds, and meningitis. K. pneumoniae is something you do not want to encounter if you have a compromised immune system.

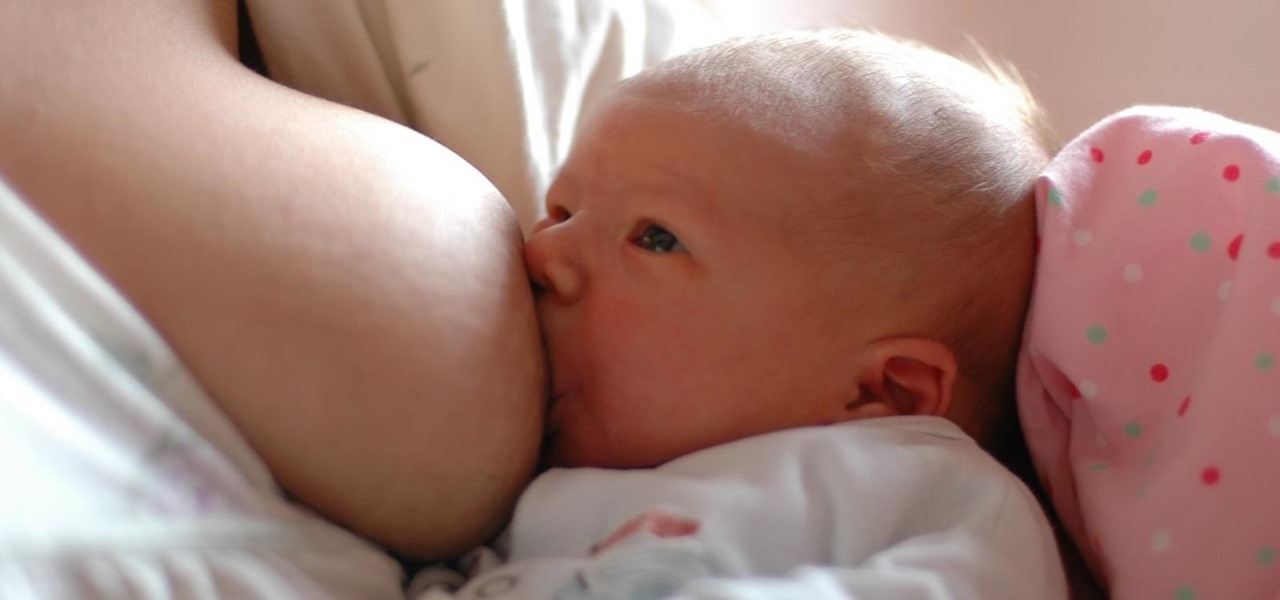
Breastfeeding is the ultimate in farm-to-table dining. It is sustenance prepared just for the baby and delivered with a very personal touch. Along with bonding, breastfeeding provides powerful protection to infants and young children in the form of beneficial bacteria, hormones, vitamins, protein, sugar, and antibodies manufactured on site to support infant health.

The evolution of our infection-fighting systems may have something to teach modern scientists. That's what a group from the University of Granada in Spain found when they studied a protein that's been around for over four billion years. Their work, by senior author José Sánchez-Ruiz and colleagues in the Department of Physical Chemistry, was published in the journal Cell Reports.

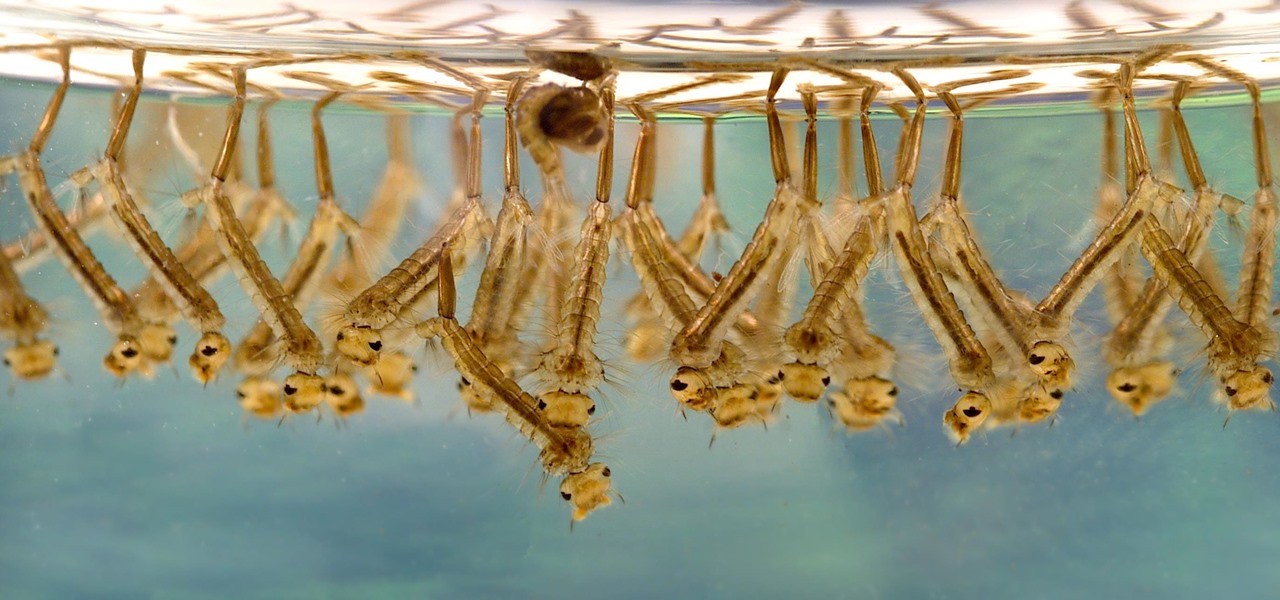
When just floating peacefully in the water with their brood mates, the Culex mosquito larvae in the image above does not look very frightening. But in their adult form, they are the prime vector for spreading West Nile virus — a sometimes mild, sometimes fatal disease.

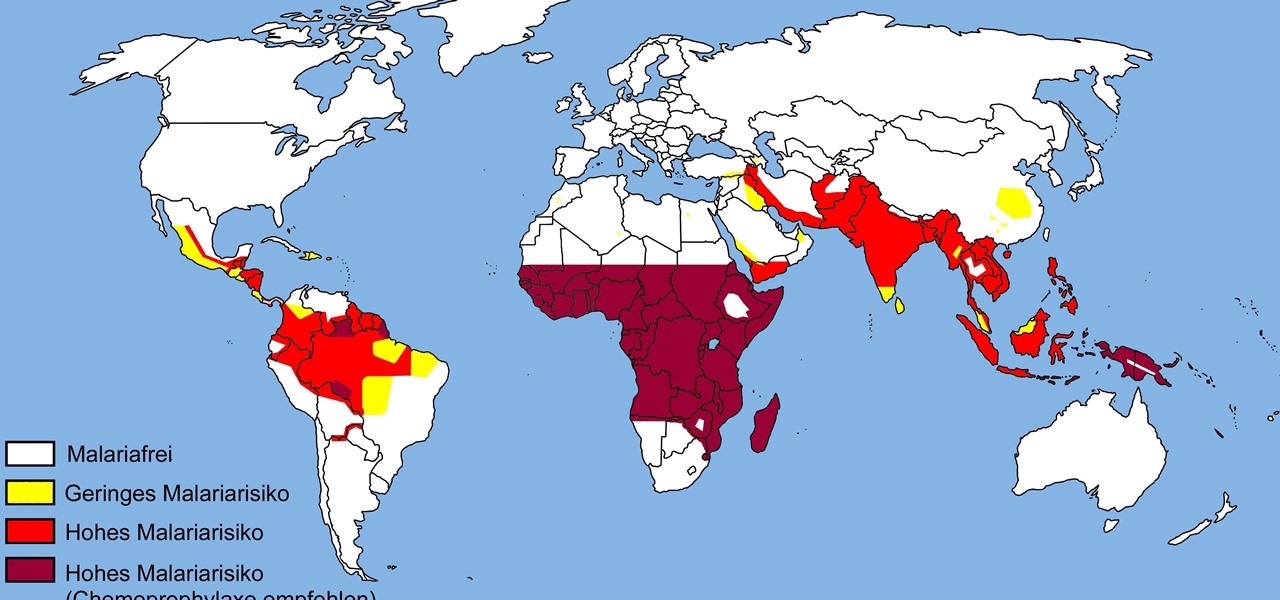
The theme for 2017's World Malaria Day, which is today, April 25, is "End Malaria for Good." For many Americans, this might seem like an odd plea. Especially since Malaria is seemingly an obsolete problem here. However, on World Malaria Day, it's important to remember the danger of malaria is still very much present in the US. And around the world, the disease is at the epicenter of a global crisis.

Our quest to find new antibiotics has taken a turn — a turn down the road, that is. A team of scientists from the University of Oklahoma is scooping up roadkill and searching for bacteria on them that might yield the world's next antibiotic.

In the ongoing search to find better ways to use antibiotics, an extract made from maple syrup has some surprisingly important medical benefits.

Growing populations and higher temperatures put pressure on world food supplies. Naturally occurring soil bacteria may save crops in drought-stressed areas, put more land into crop production, and produce more food.

There could be a fresh outbreak of the Zika virus in the Americas as the weather heats up and the mosquito population blooms.

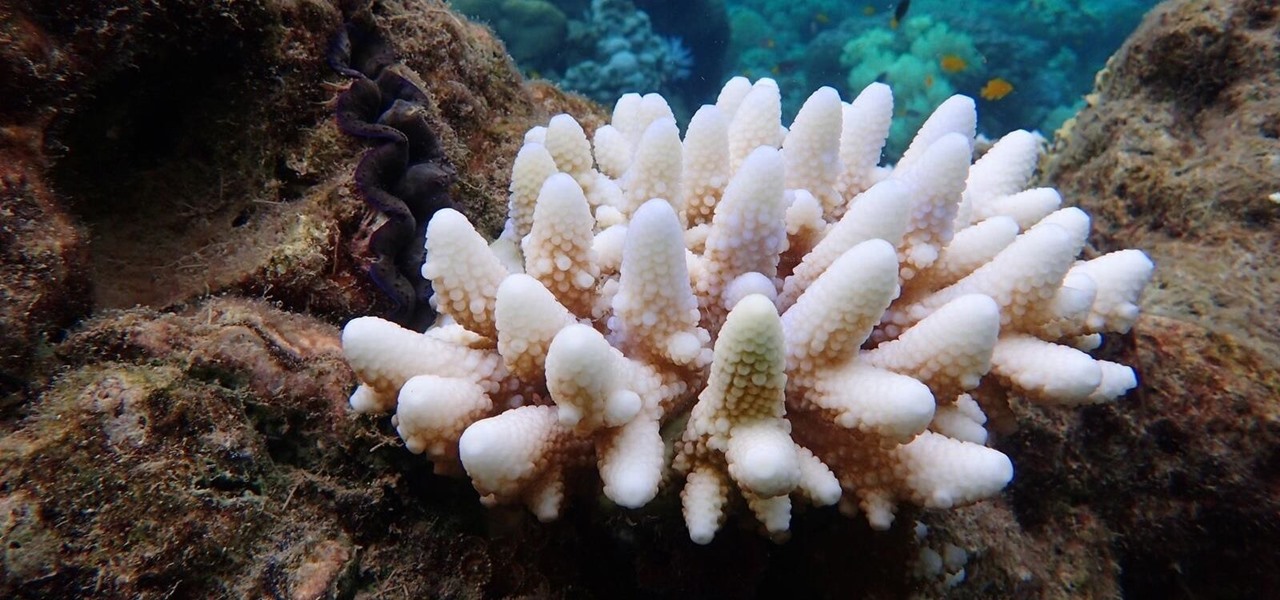
The Great Barrier Reef in Australia is the largest living system on the planet. Yet more than 90% of the reef is bleaching because of the loss of a tiny algae that lives within the coral.

An outbreak of anthrax from contaminated meat in Tanzania sickened dozens of people and moves the danger of this deadly bacteria back into focus.

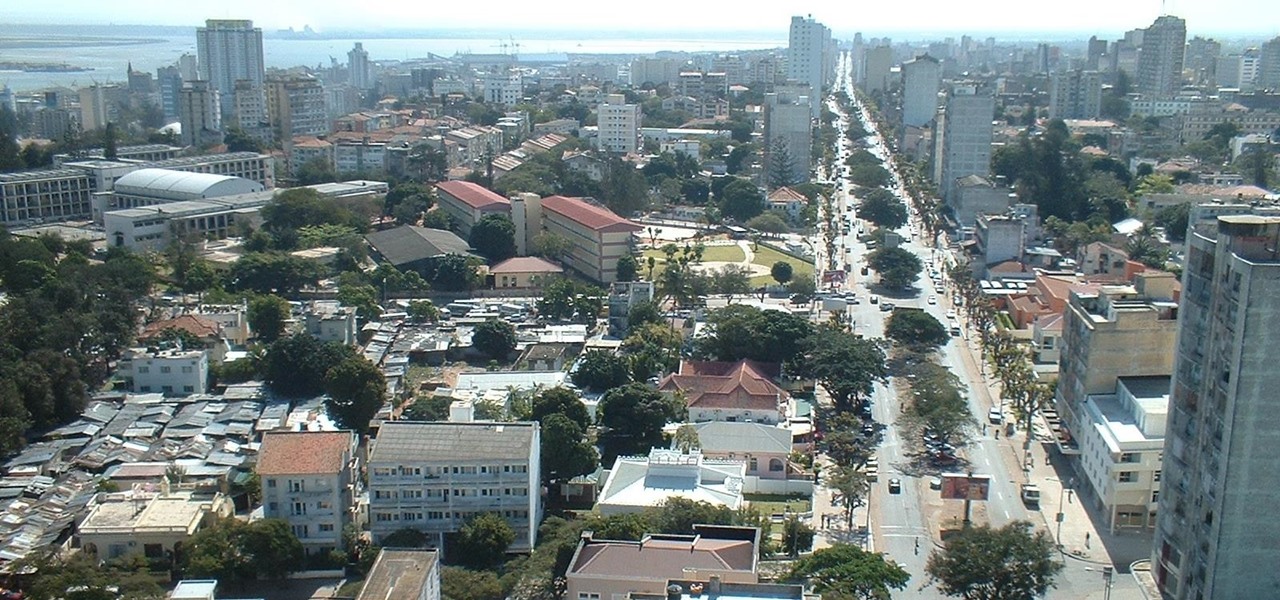
Cholera is rapidly spreading in Mozambique, with over 1,200 people infected. Since the outset of 2017, cholera has spread from the capital city of Maputo (pictured above) to three of its ten provinces. Health officials report other areas in the country are seeing case counts rise, and two deaths have been logged so far.

In a world increasingly regulated by computers, bugs are like real-life cheat codes. They give you the power to break the rules and do good or bad without ever leaving your seat. And government agencies around the world are discovering and stockpiling unreported bugs as cyberweapons to use against anybody they see fit.

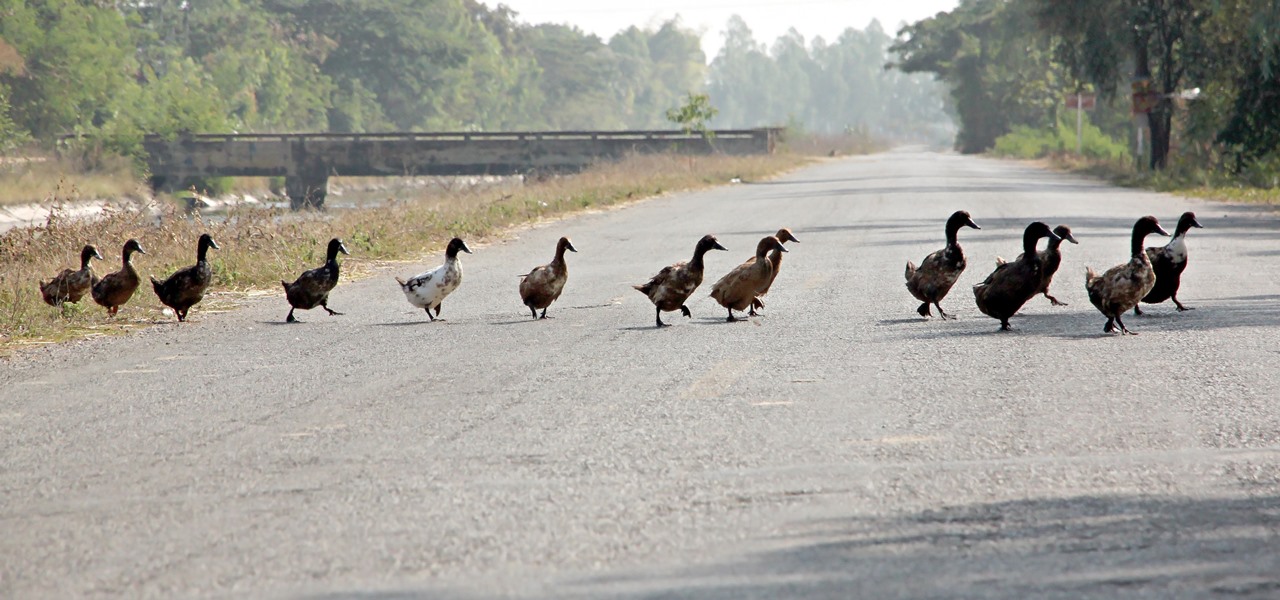
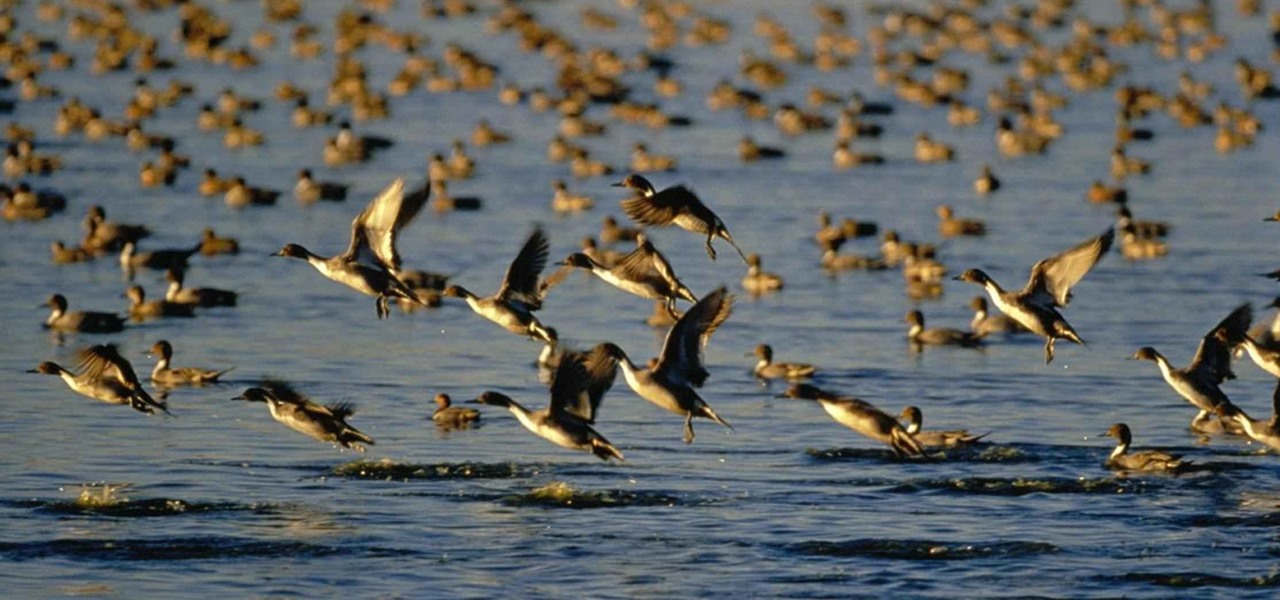
Over 6,500 waterfowl—mostly ducks—have died in Canyon County, Idaho, stricken by avian cholera. The outbreak started in February, and before it's over, it may not only be Idaho's largest outbreak, but one of the largest in the country.

Arsenic occurs naturally in the environment, but it is also one of the most commonly found heavy metals in wastewater, deposited there by inappropriate disposal and arsenical pesticides, for example.

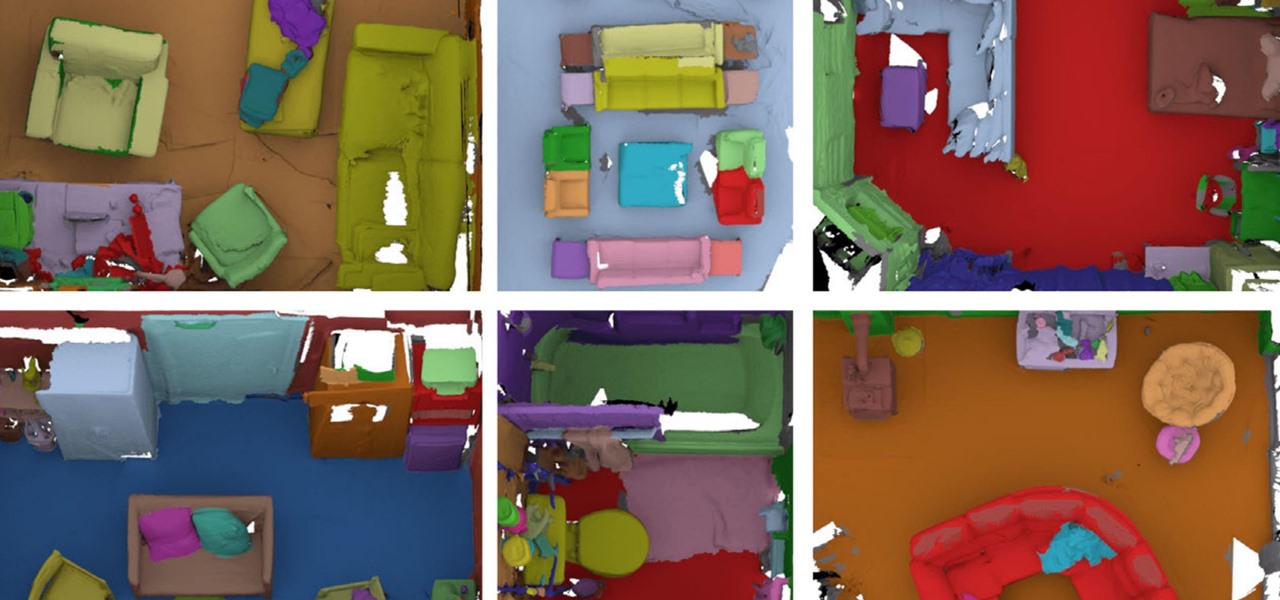
A group of researchers from Stanford University and Princeton University has put together the largest RGB-D video dataset to date with over 1,500 scans of over 700 different locations across the world, for a total of 2.5 million views.

As drug-resistant bacteria become more commonplace, researchers are looking for new antibacterial strategies to disrupt disease-causing microbes. Some scientists are working to create new drugs, while others are trying out drug combinations. Another group, however, are ditching pharmaceuticals altogether and experimenting with non-drug alternatives.

Even if your cat drives you a little nuts, don't worry, because a new study says that cats pose no risk to your mental health.

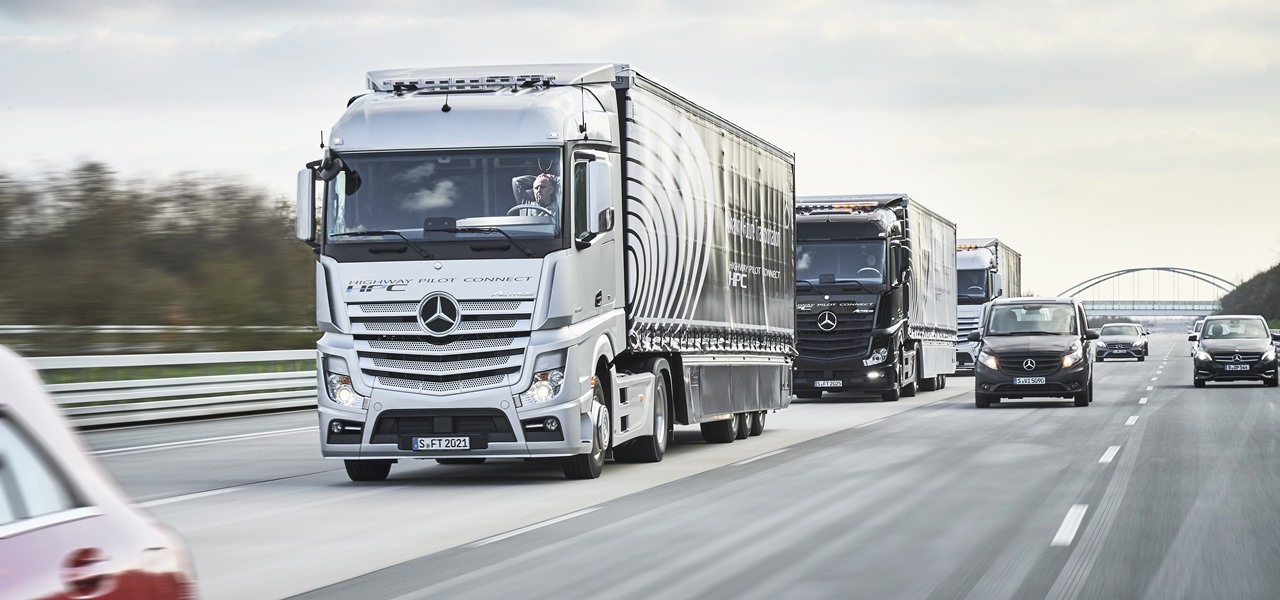
Japan is in the process of curbing its aging population and mature workforce. According to The Diplomat, the country's population has been declining at a steady rate. To meet future productivity demands in commercial and industrial sectors, local officials are turning to self-driving technology, including truck platooning, where three or five vehicles travel autonomously in a string formation. This practice, according to a study by MIT, can reduce fuel consumption by up to 20% (more about thi...

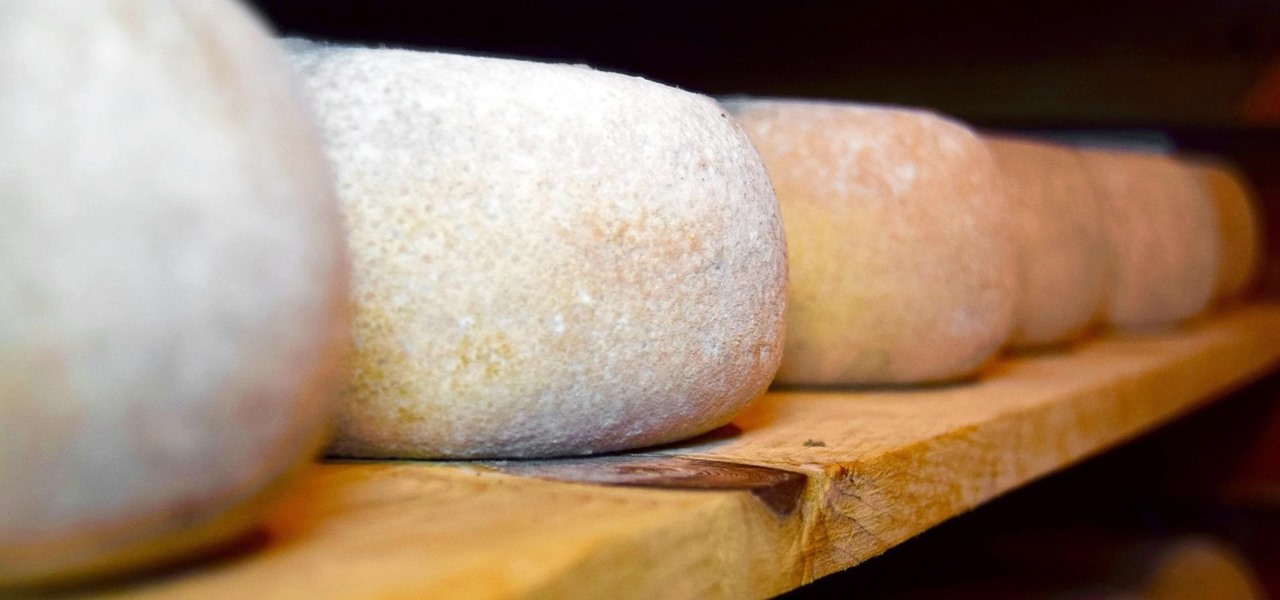
If you want to appreciate the value of microbes, look no further than a chunk of cheese. Because cheese roughly traces back to the Neolithic Era, we might say the earliest cheesemakers were the first humans to manipulate microbes—without even knowing it. Now, thanks to microbiologists and the long tradition of cheesemaking, we know a lot more about the microbes that make our favorite types of cheese possible.

Transmitted by a sandfly one-third the size of a mosquito, parasitic Leishmania protozoa are responsible for a flesh-destroying disease that kills an estimated 20,000 people per year. Two new studies offer understanding of how the parasite provides immunity through persistence and why some people suffer more virulent forms of the disease.

Where in the world did it come from? All of a sudden, one day, someone had an infection with flesh-eating bacteria. It captured headlines and worldwide attention because it was such a severe, strange, uncontrollable, and really disgusting condition.

The largest and arguably most widely known event of its type, especially in the US, the Sundance Film Festival is an annual celebration of independent film—ones made outside the Hollywood system. This year, a new type of experience appeared at the Sundance Film Festival in an installation called "The Journey to the Center of the Natural Machine." This mixed reality presentation offered the user the newest type of storytelling in a long and important line—continuation of the species kind of im...

Using extreme time-lapse microscopy, scientists watched a virus take over a bacteria to create a cell that looked and functioned more like a plant or animal cell. True story.

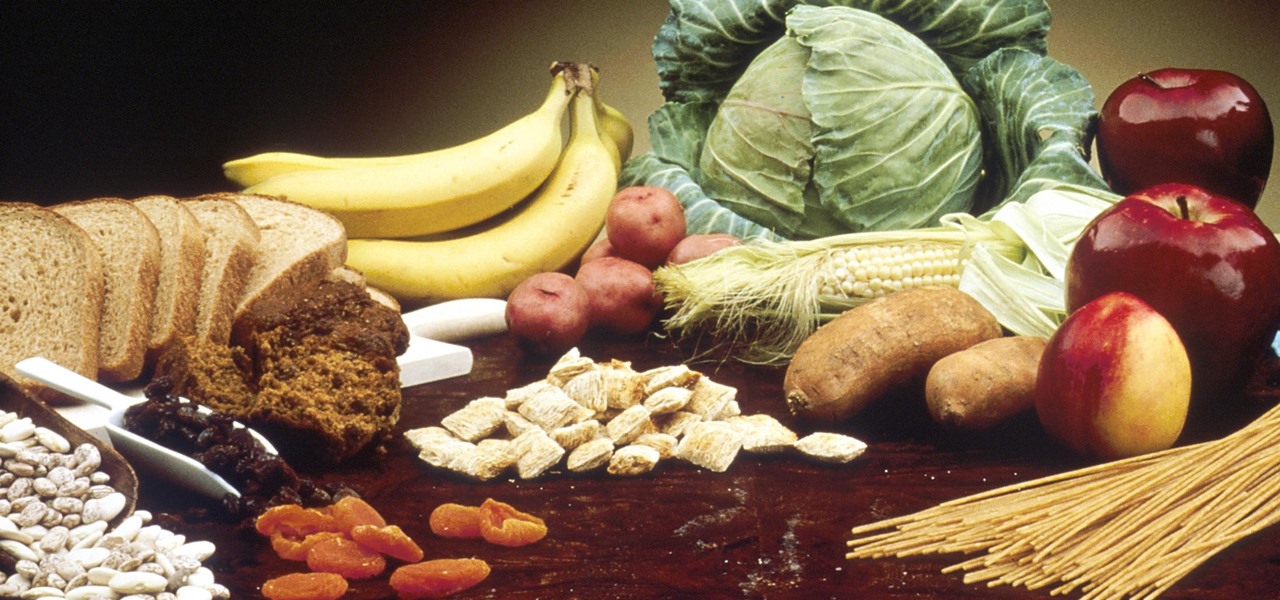
We all know you are what you eat—or so the expression goes—but it's good to remember that what you are (at least intestinally) is mainly bacteria. A new study has shown that what you eat, and how your gut microbiome reacts to that food, might be a key player in your risk of developing a certain type of colon cancer—and changing your diet can help decrease your risk.

Using mathematical modeling, researchers suggest weather and warming created the "perfect storm" that drove the Zika outbreak in 2016.

When the time comes to replace your car, you most likely have a checklist of criteria that you would like on the new one. Your car is possibly the most expensive possession you have—or the second-most expensive, after your home—so you want to make sure that you are not only getting what you want, but that you are getting the best deal possible.