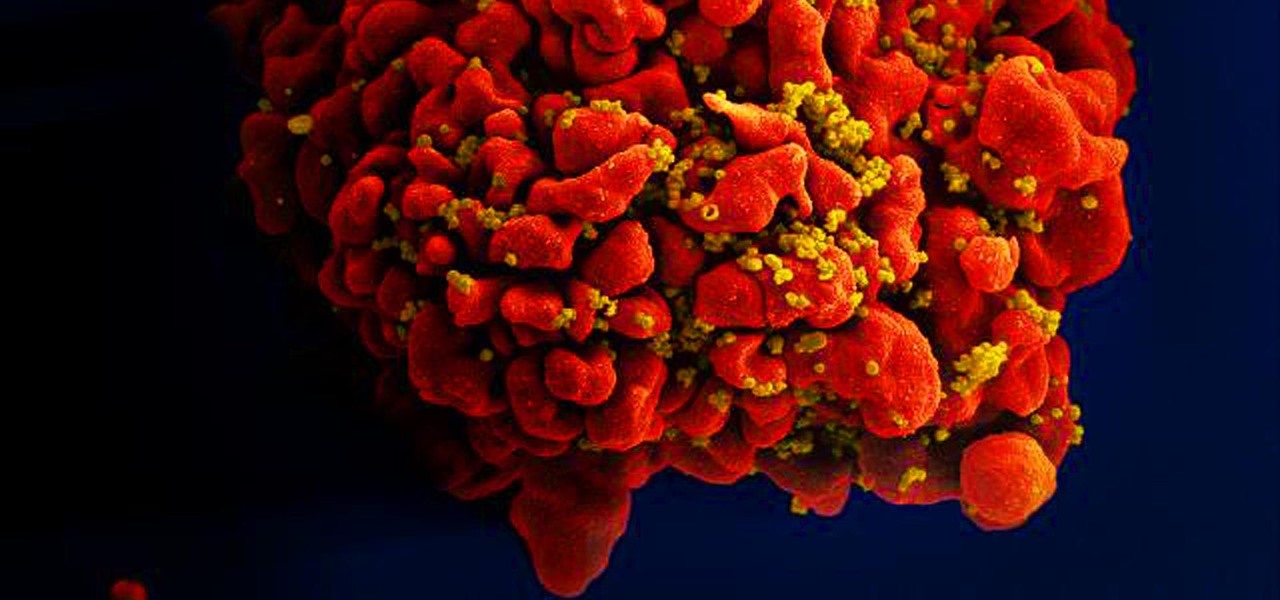
News: Researchers May Be Closing in on a Vaccine Against HIV
Results of an early-stage clinical trial of an HIV vaccine could mean a hoped-for breakthrough in the battle against AIDS.


Results of an early-stage clinical trial of an HIV vaccine could mean a hoped-for breakthrough in the battle against AIDS.
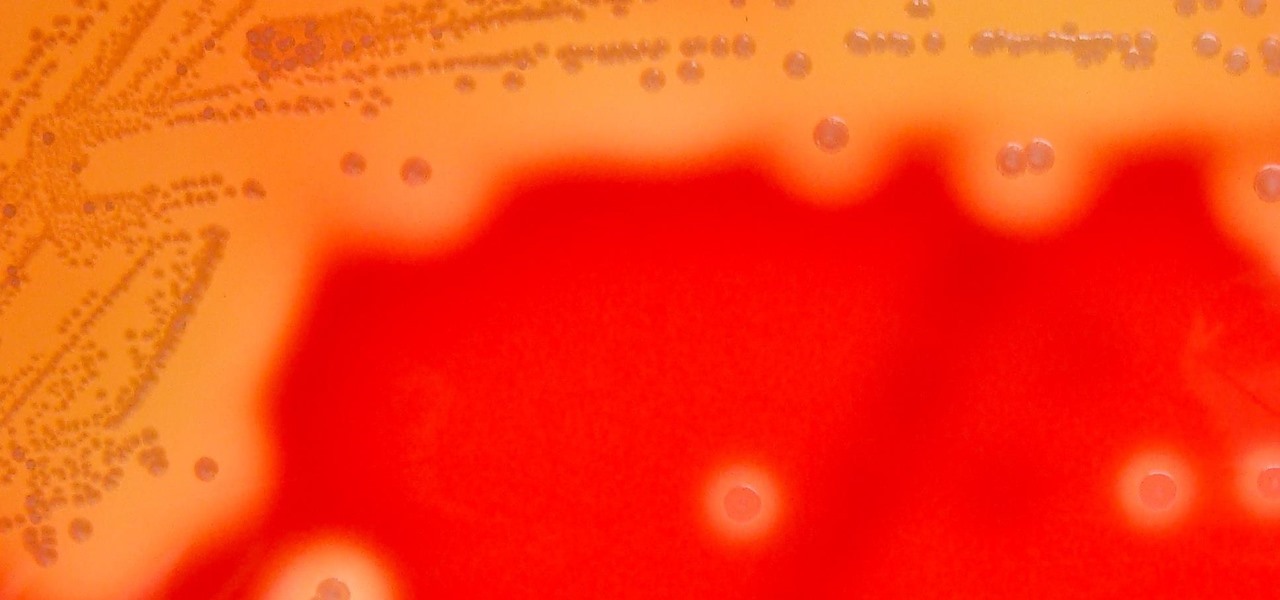
Streptococcus and staphylococcus bacteria produce toxins that can cause toxic shock syndrome.
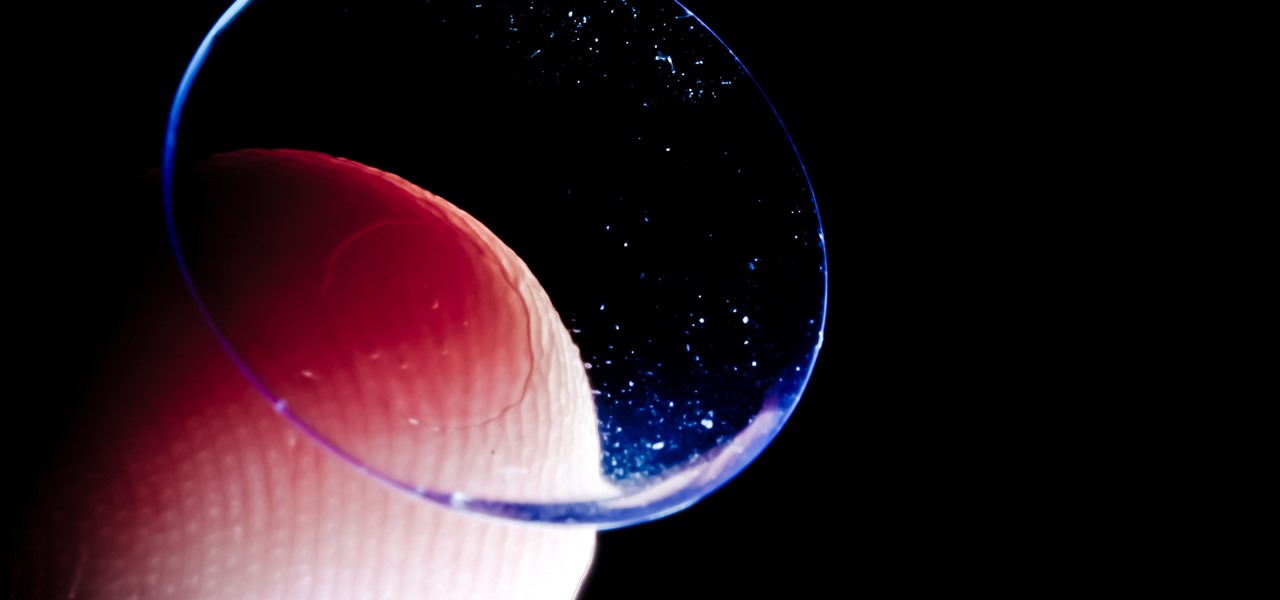
Acanthamoeba keratitis (AK), a rare eye infection caused by the Acanthamoeba ameba found in tap water, affects a few dozen people in the US every year. In some cases, it can have devastating effects, like what Irenie Ekkeshis has experienced; She was blinded by AK in her right eye due to a contaminated contact lens.
Obstetric tetanus in an unvaccinated Amish woman after a home birth has emphasized the need for preventative healthcare.
There have been mumps outbreaks in three different US colleges so far this year as instances of the illness are on the rise, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).

A state of emergency has been declared in Malaysia's northeastern Kelantan state after an outbreak of avian influenza virus H5N1.

Antibiotic-resistant infections that usually occur only in hospital settings are spreading in communities, increasing hospital stays—and danger—for young children.

Most of us equate feeling cold with catching a virus—but we've also heard plenty of debunkers proselytizing that being cold isn't what gives you the flu.
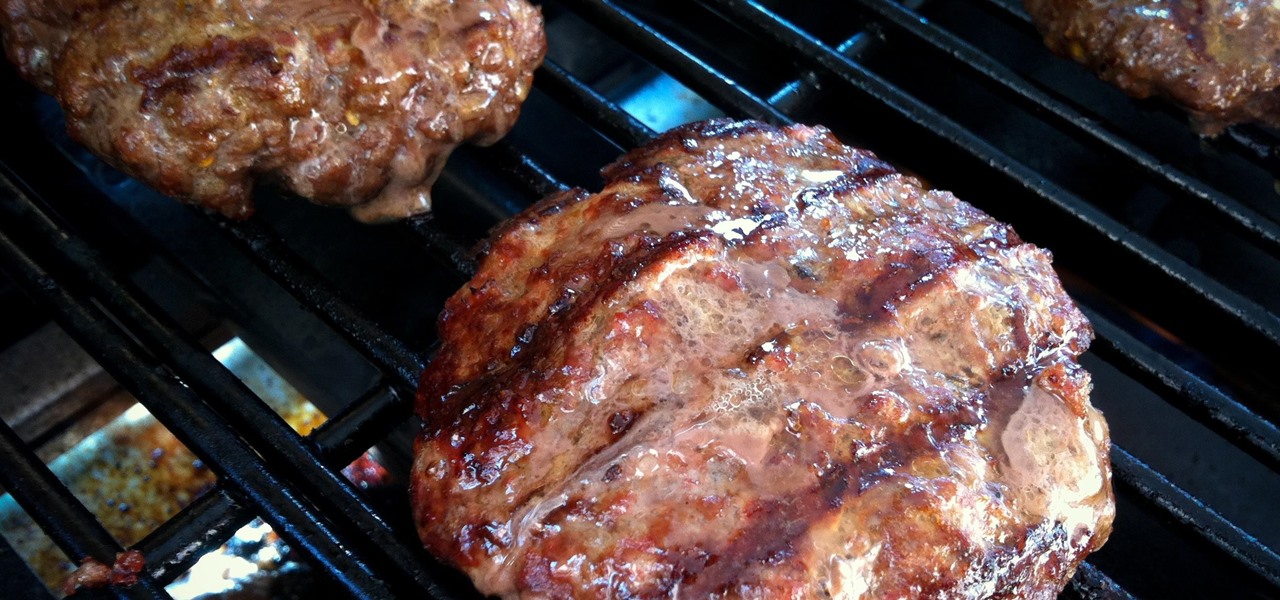

Beef aficionados love a medium-rare burger, but many people are wary of meat that's on the pink or red side since it might contain bacteria. Is it possible to enjoy a burger that's perfectly juicy and yet also cooked thoroughly enough to destroy all traces of salmonella, E. coli, and other microbes that cause foodborne illness? Absolutely! You just need to know a trick (or three).

Every year the fine folks at Row Three do a post-TIFF mega-wrap up, collecting the micro-blurbs of a bunch of attendees into a giant meta-analysis of what everyone liked, loved, hated, etc. etc.. We'll link to that post when it goes up on the weekend, but in the mean time, here's my contribution:

Hello! This tutorial is made for all who like to sunbath, but also do not want to get those tiny first wrinkles too soon. Or even skin cancer.

This is a tale about microbes, a man who became a hermit, and the parchment that carries both of their stories.

A recent initiative by the Cherokee Nation American Indian Tribe delivers a success story for knocking out a silent killer — Hepatitis C.
Once we recover from the respiratory infection pneumonia, our lungs are better equipped to deal with the next infection — thanks to some special cells that take up residence there.
It is not just a bad summer for ticks — it has been a bad decade for the spread of tick-borne infections. New surveillance from the CDC reports rapid expansion and increase in cases of babesiosis, a sometimes life-threatening disease, in Wisconsin.
Add breathing in your house as another possible danger to your health. If your home is sick, it's possible you could get sick too.
A new medical development is going to change the way many of us look at getting the flu vaccine. A painless flu vaccine skin patch is making needles and vials a thing of the past. Researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University have shown that a flu vaccine can be administered safely and comfortably with this new patch, which delivers the vaccine through a matrix of tiny dissolving microneedles.
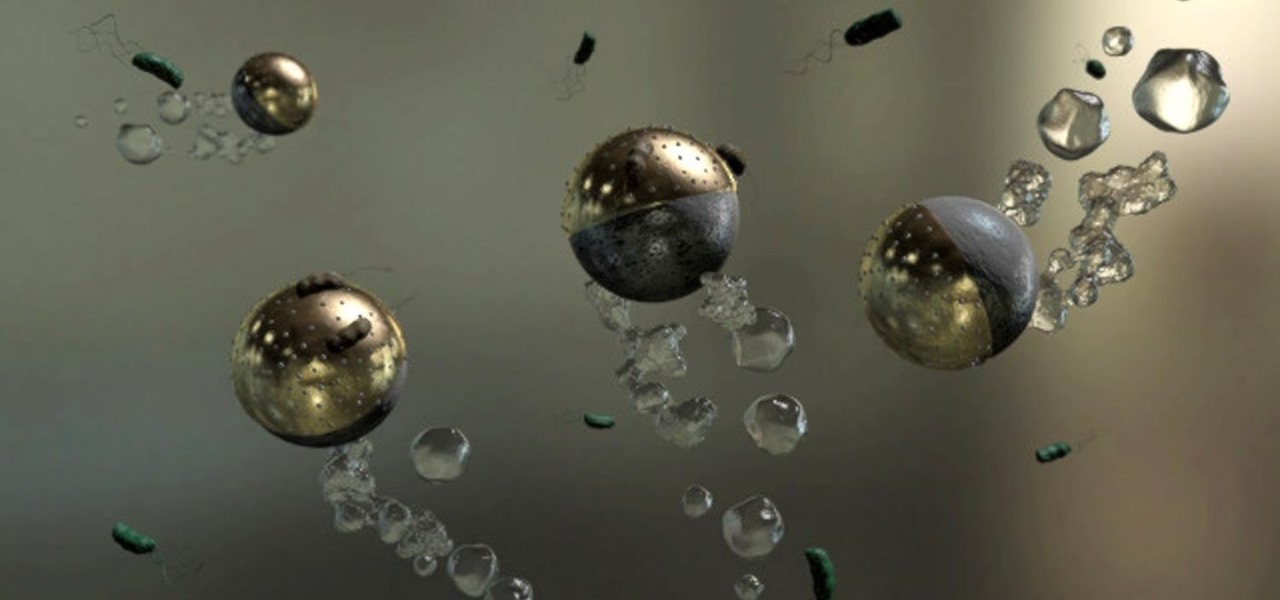

Look no further than Flint, Michigan, to discover the serious consequences of contaminated drinking water. Around the world, water polluted by pathogens and toxins sickens people or cuts them off from safe drinking water. Looking for a solution, researchers created tiny, swimming robots that pack a powerful punch against waterborne pathogens.

Despite the threat of superbugs, physicians continue to prescribe antibiotics when they might not be needed, and patients are suffering.
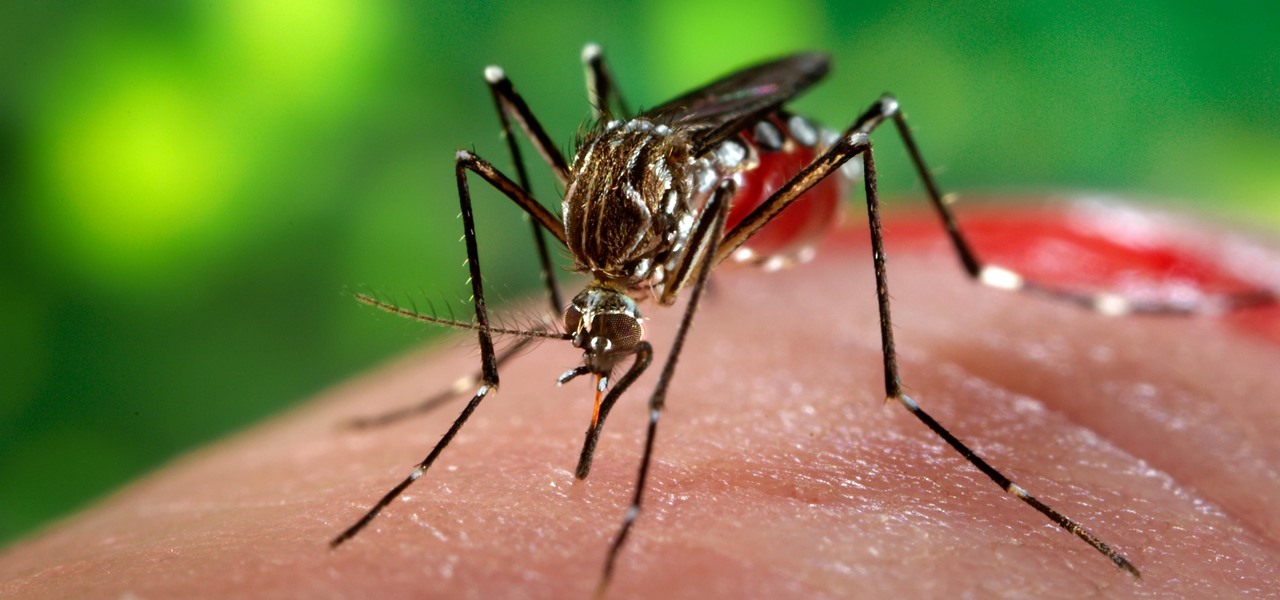

Mosquitoes are a big problem, and citronella candles are not the solution. There are a lot of mosquito species. The American Mosquito Control Association reports there are more than 3000 mosquito species in the world, and about 200 of those occur in the US. The most common are the Aedes, Anopheles, and Culex species. These are also the three mosquito species most likely to transmit serious illness, and all of them live in the US.

Listeria monocytogenes bacteria don't play fair. Healthy people can usually handle the food-borne infection, but the bacterial infection hits pregnant women, fetuses and cancer patients very hard. Interestingly, a new study found that other bacteria may help prevent Listeria infections in those people.
Most of us have already had an encounter with the Epstein-Barr virus, or EBV, for short. As part of the herpes family, it's one of the most common disease-causing viruses in humans. We get the disease with (or without) some nasty symptoms, then we recover. However, EBV stays in our body after the illness has ended, and it's one of the few viruses known to cause cancer.
Could your fever, body aches, cough, and sore throat be the flu? Soon, finding out may not involve a trip to the doctor.
In the worst measles outbreak in the state since 1990, the Minneapolis Department of Heath races to contain the spread of an infection believed to have originated from an infected traveler. Mistaken attitudes and unvaccinated travelers are creating a world of hurt and disease for Americans. A recent study found that more than half of eligible travelers from the US are electing to skip their pre-trip measles vaccine.
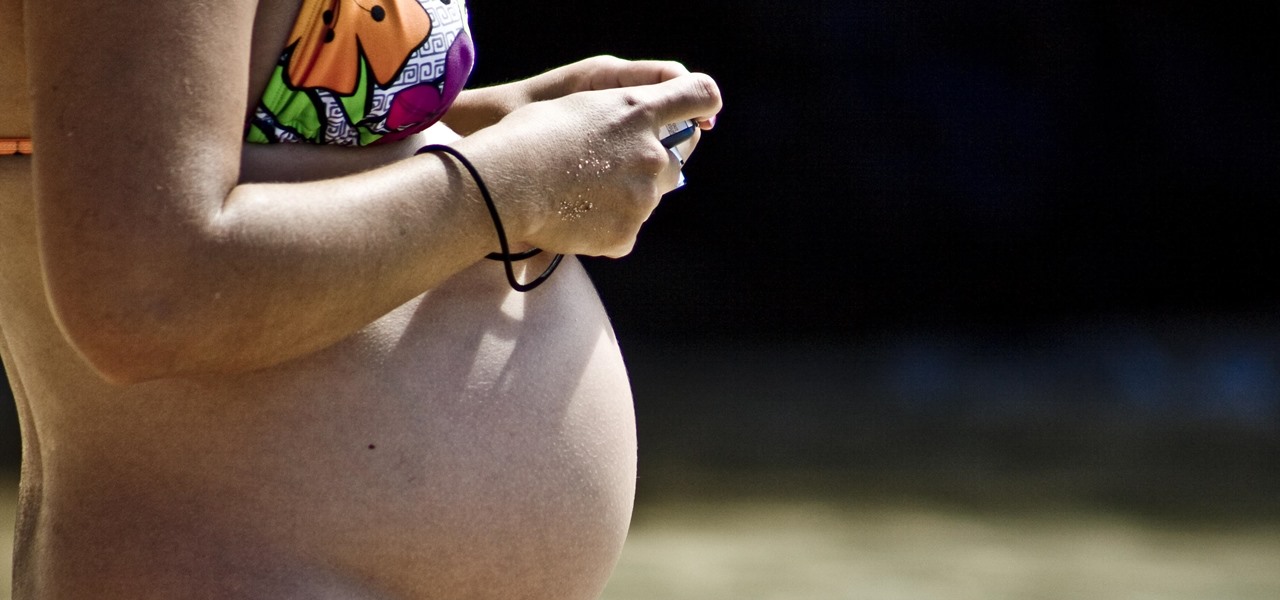

As if being pregnant did not come with enough worry, a new study found that certain antibiotics are linked to an increased risk of spontaneous abortion, or miscarriage — a terrifying finding for any expectant mother.
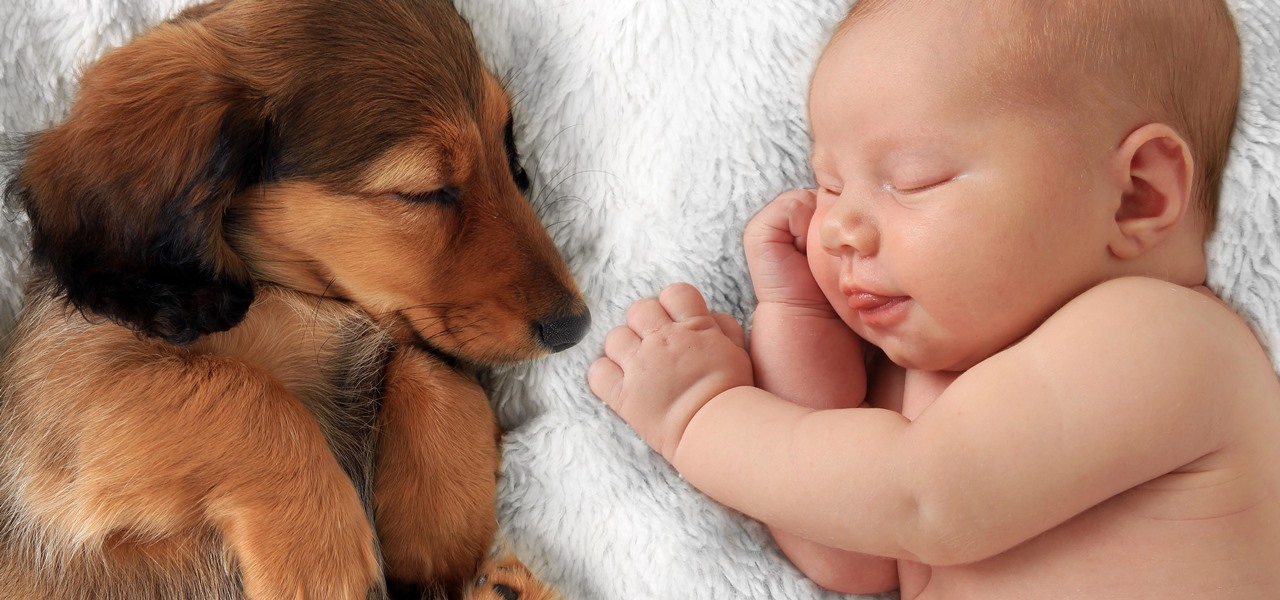

For many of us, pets are important family members. They give us loyalty, companionship, and comfort. Now, researchers have given us another reason to welcome them into the family: Babies from families with furry pets — the majority of which were dogs — had higher levels of two types of beneficial gut bacteria.
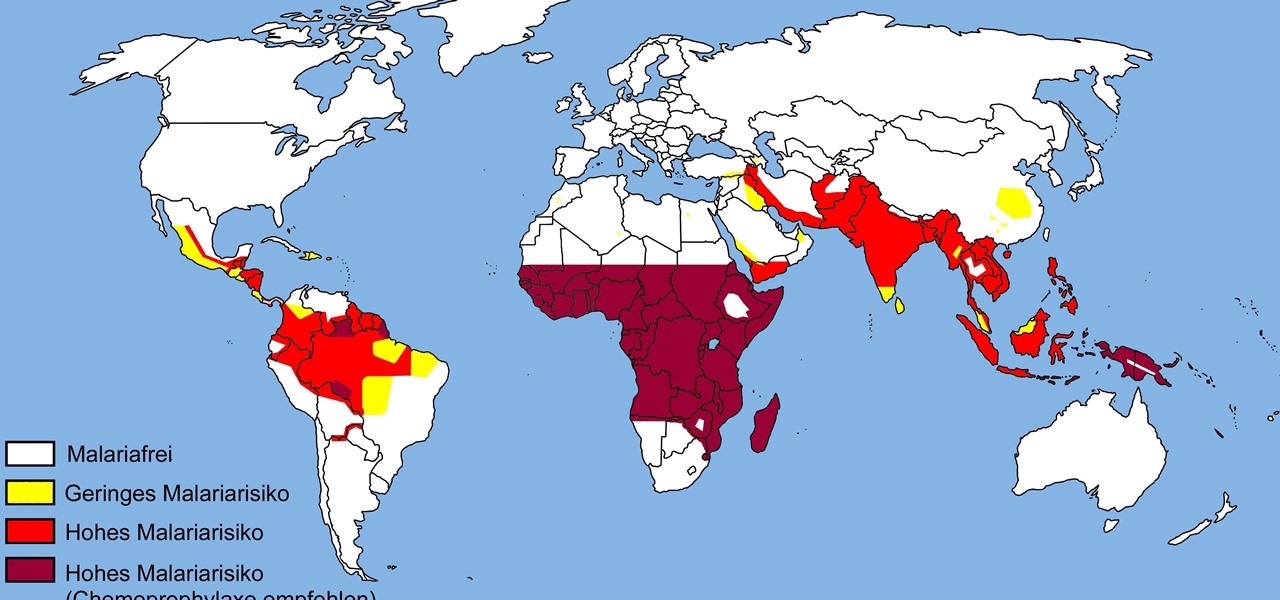
The theme for 2017's World Malaria Day, which is today, April 25, is "End Malaria for Good." For many Americans, this might seem like an odd plea. Especially since Malaria is seemingly an obsolete problem here. However, on World Malaria Day, it's important to remember the danger of malaria is still very much present in the US. And around the world, the disease is at the epicenter of a global crisis.
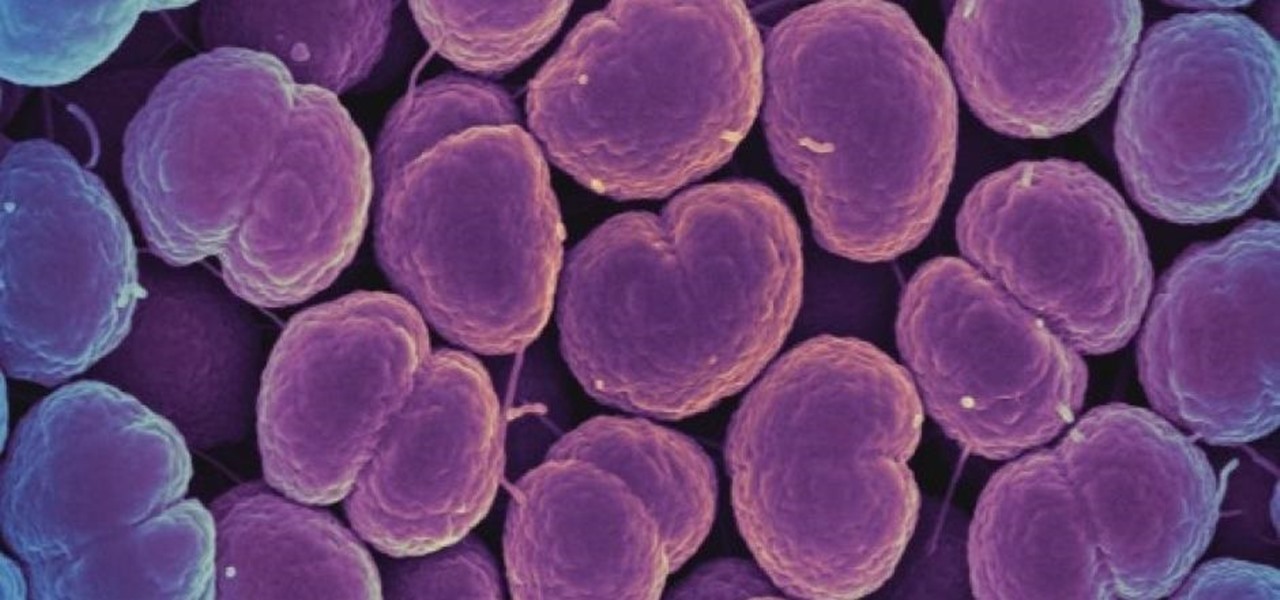
The ability of one microbe to adapt is giving it a whole new career as a sexually transmitted disease. Usually content with the back of the throat and nose of those who carry it, the dangerous pathogen Neisseria meningitidis has adapted to cause an illness that looks a lot like gonorrhea.
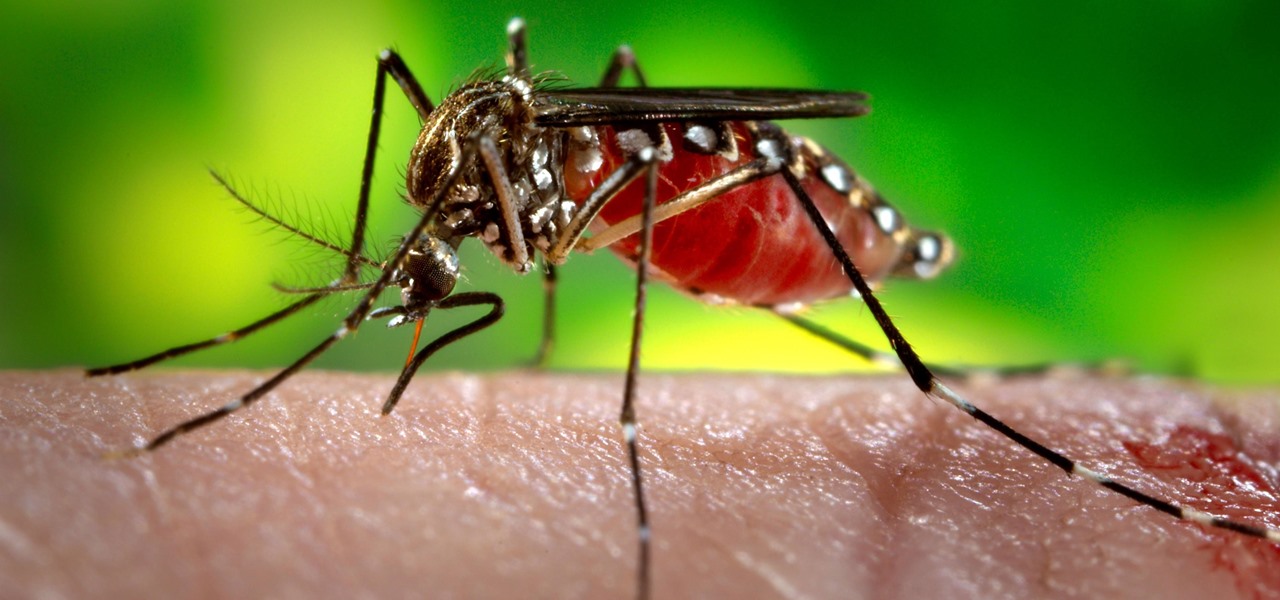

There could be a fresh outbreak of the Zika virus in the Americas as the weather heats up and the mosquito population blooms.
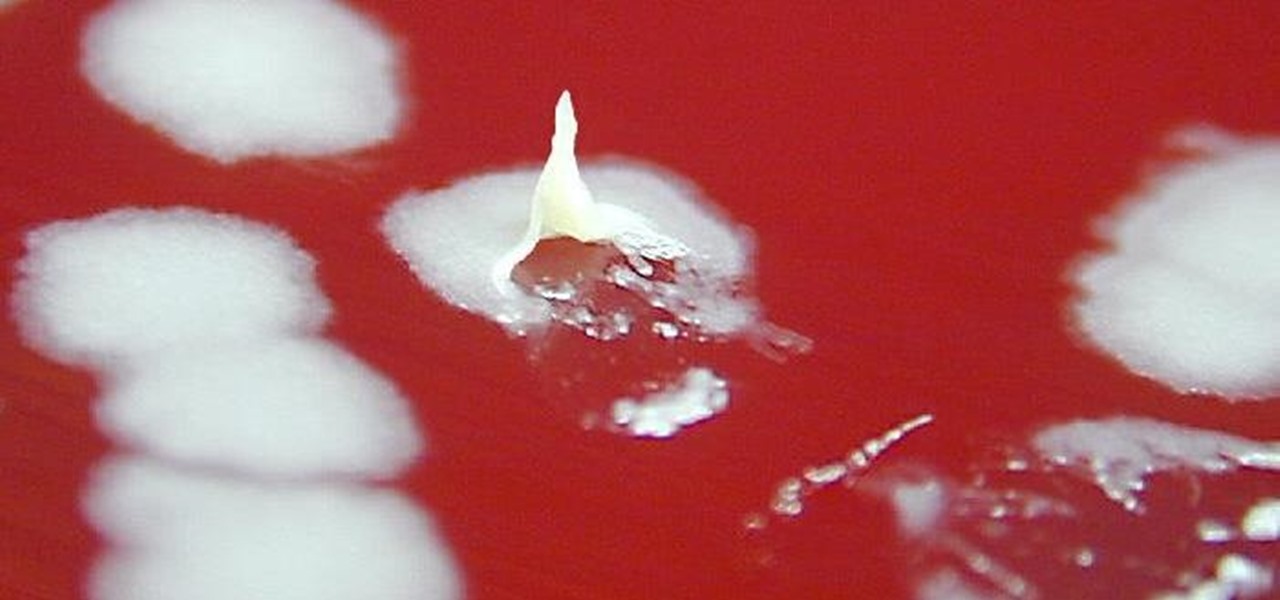
An outbreak of anthrax from contaminated meat in Tanzania sickened dozens of people and moves the danger of this deadly bacteria back into focus.
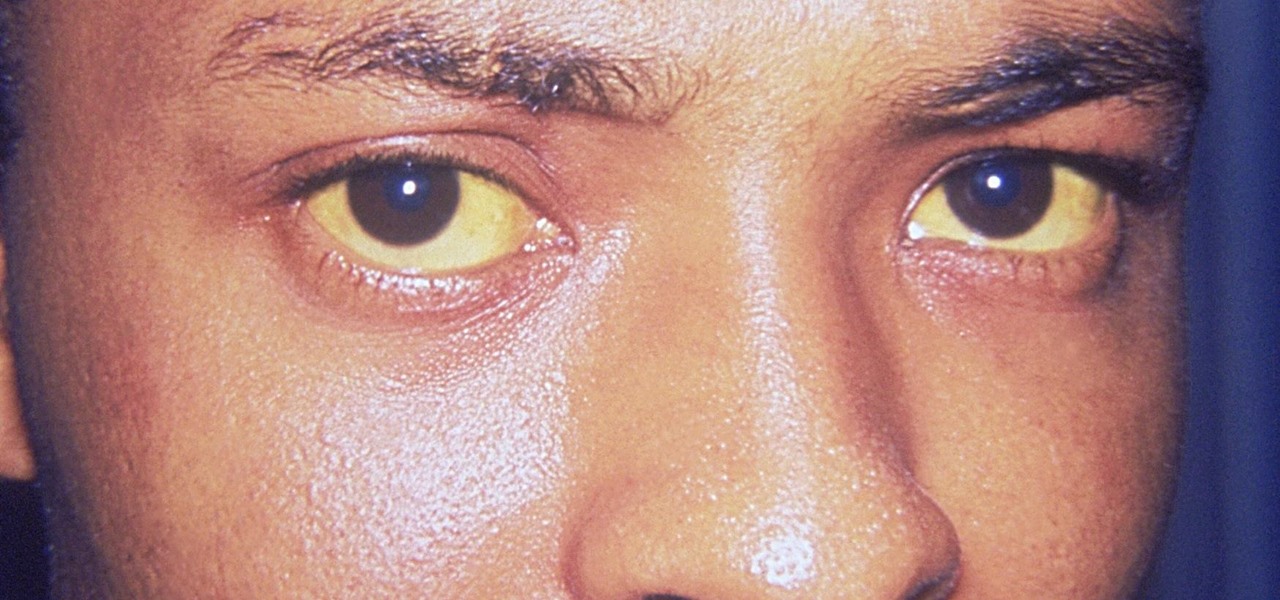
Yellow fever has emerged again in Brazil, causing death and disease to people unprepared for this mosquito-borne illness.
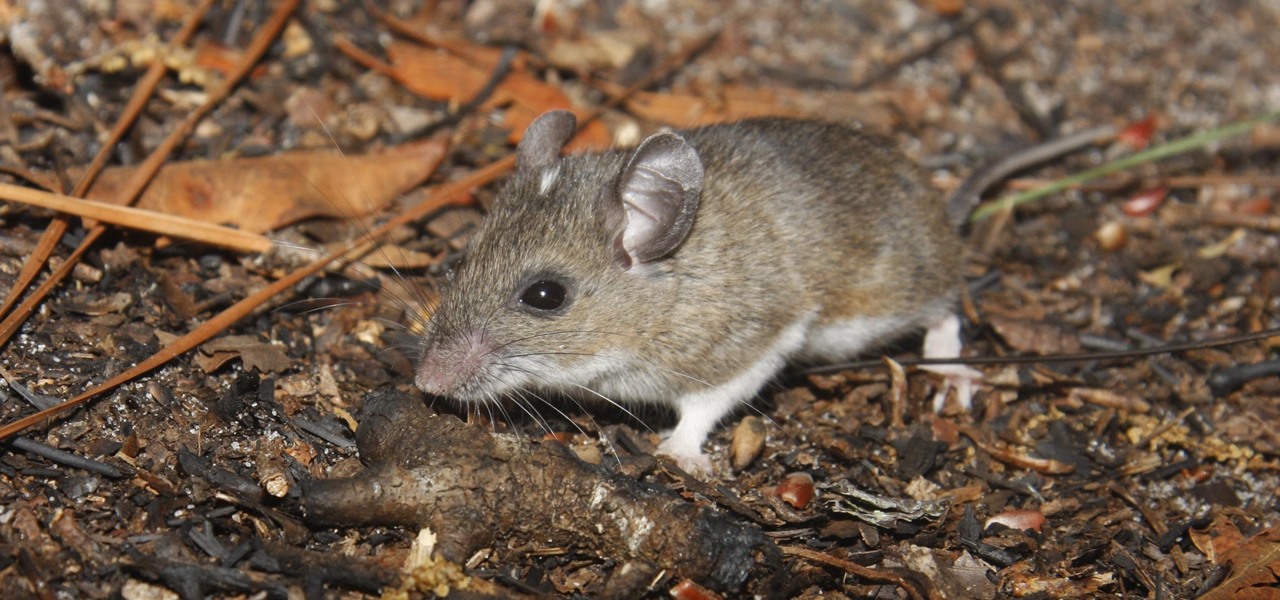

For regions that experienced a boom in mouse populations last year, scientists say 2017 could see a surge in cases of Lyme disease.
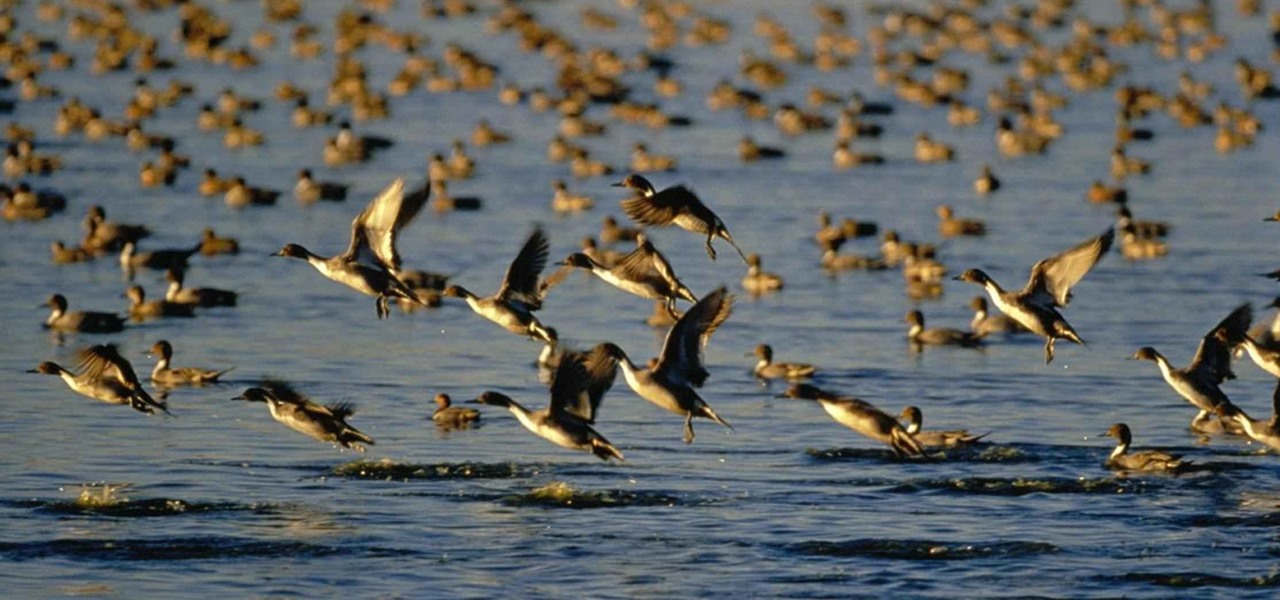

Over 6,500 waterfowl—mostly ducks—have died in Canyon County, Idaho, stricken by avian cholera. The outbreak started in February, and before it's over, it may not only be Idaho's largest outbreak, but one of the largest in the country.
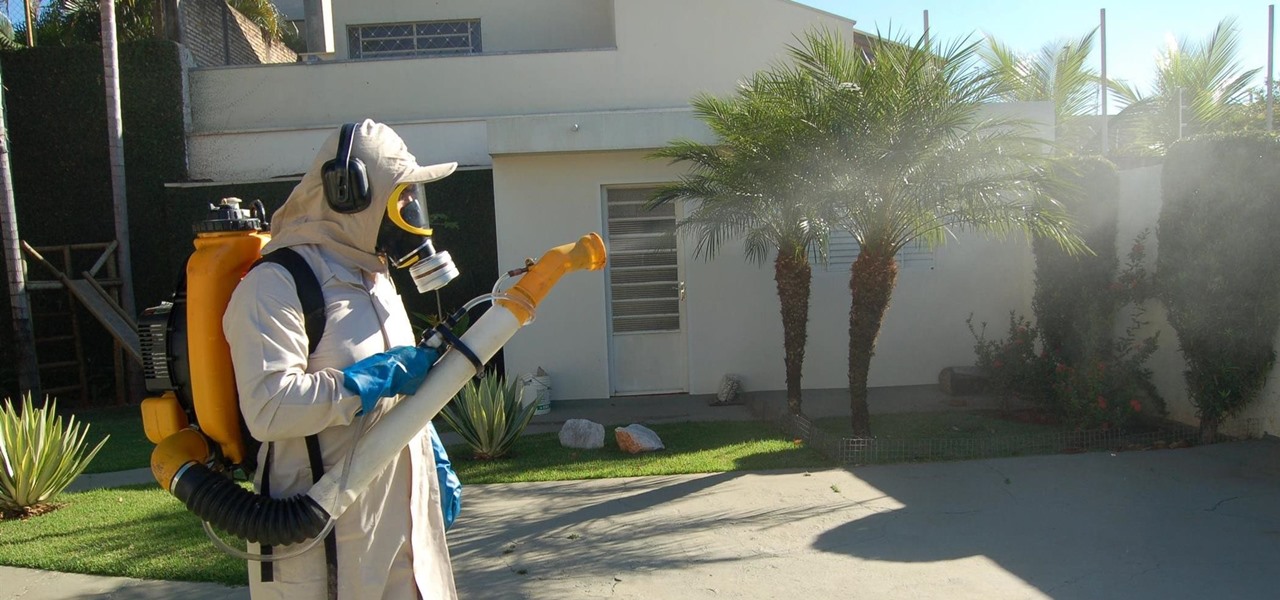

Even as health authorities describe the symptoms of Zika infection in the general population as mild, a new surveillance study finds serious side effects are more common, and serious, than previously thought.
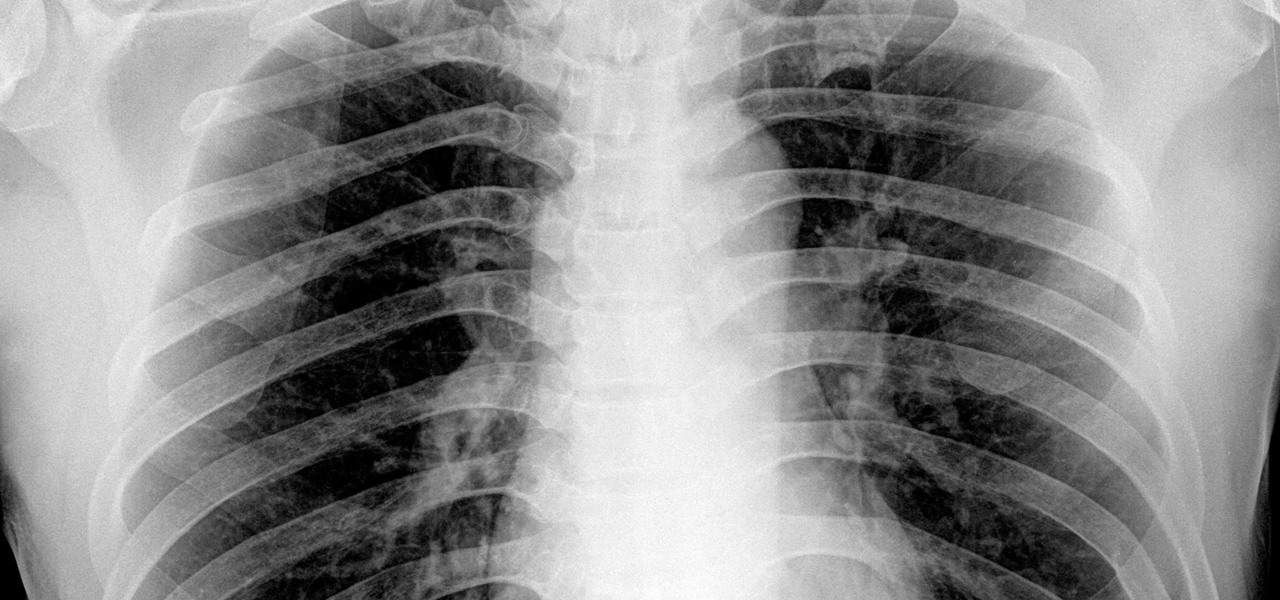
By looking for the mechanism that allows influenza A to invade lung cells, scientists also discovered a treatment that might block the virus from taking hold there.

Even if your cat drives you a little nuts, don't worry, because a new study says that cats pose no risk to your mental health.

New research suggests the bacteria that causes listeriosis may be a bigger threat in early pregnancy than previously thought. Usually considered a danger to late pregnancy, scientists suggest early undiagnosed miscarriages could be caused, in some cases, by infection with Listeria.

Every year, 100-200 people in the US contract leptospirosis, but usually 50% of the cases occur in Hawaii where outdoor adventurers are exposed to Leptospira bacteria found in freshwater ponds, waterfalls, streams, and mud. That's why it's so alarming that two people in the Bronx have been diagnosed with the disease and a 30-year-old man has died from it.

The pathogen referred to as a "nightmare bacteria" is quietly adapting and spreading faster than anticipated.

Despite the availability of a vaccine against it, almost 50% of men aged 18-59 in the US are infected with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Why?