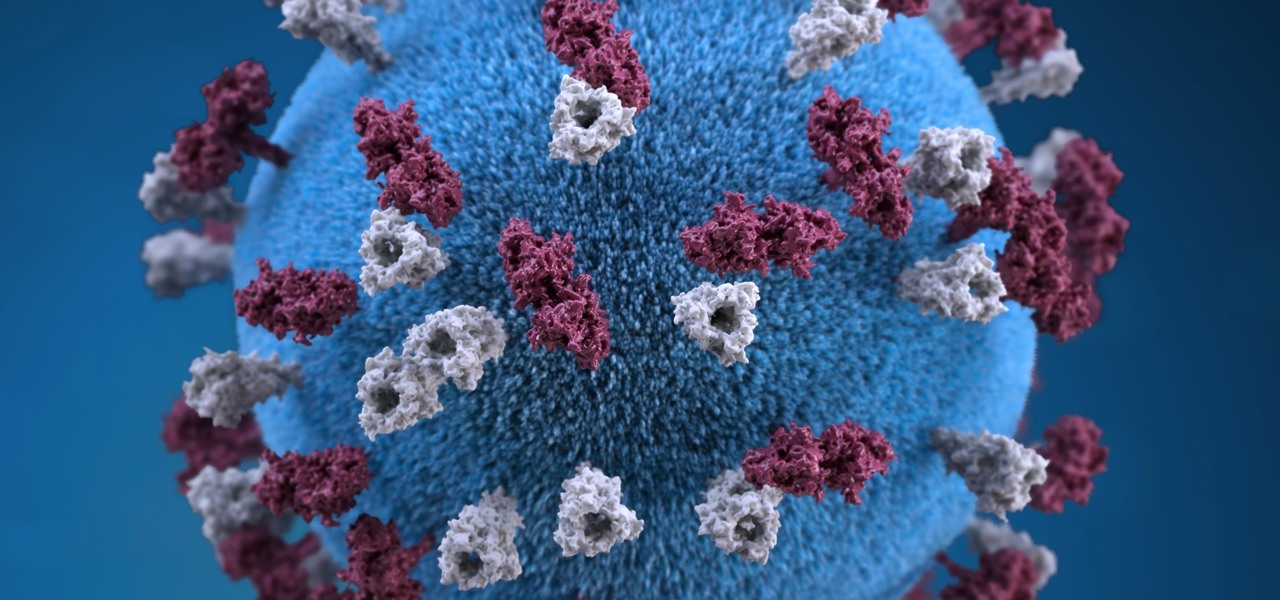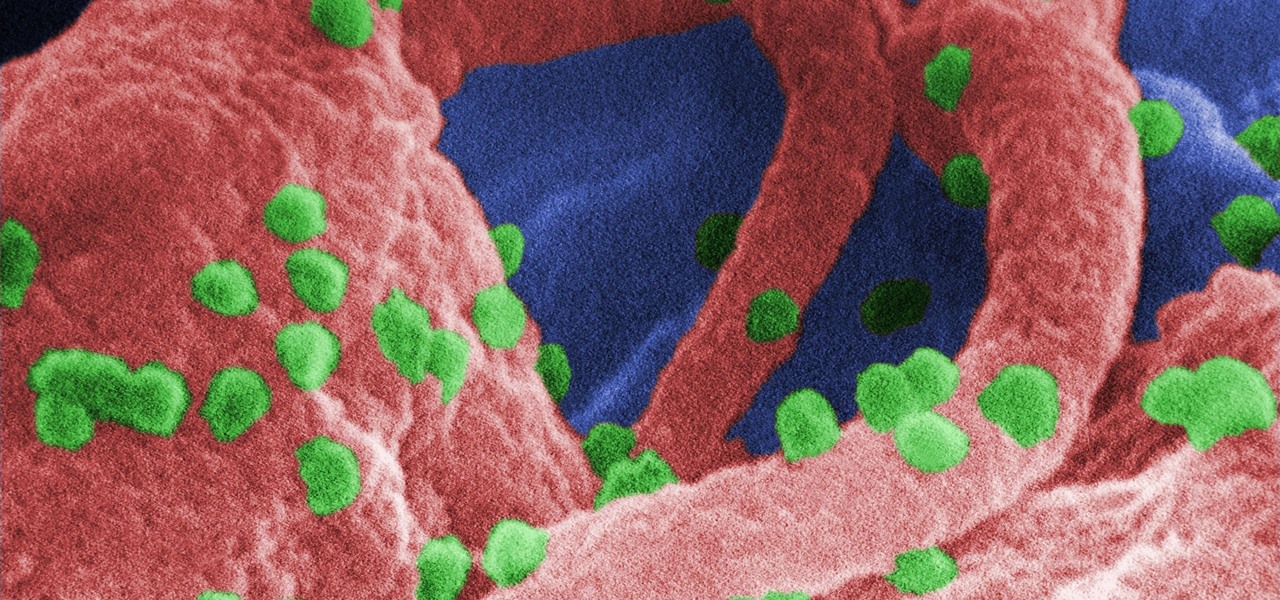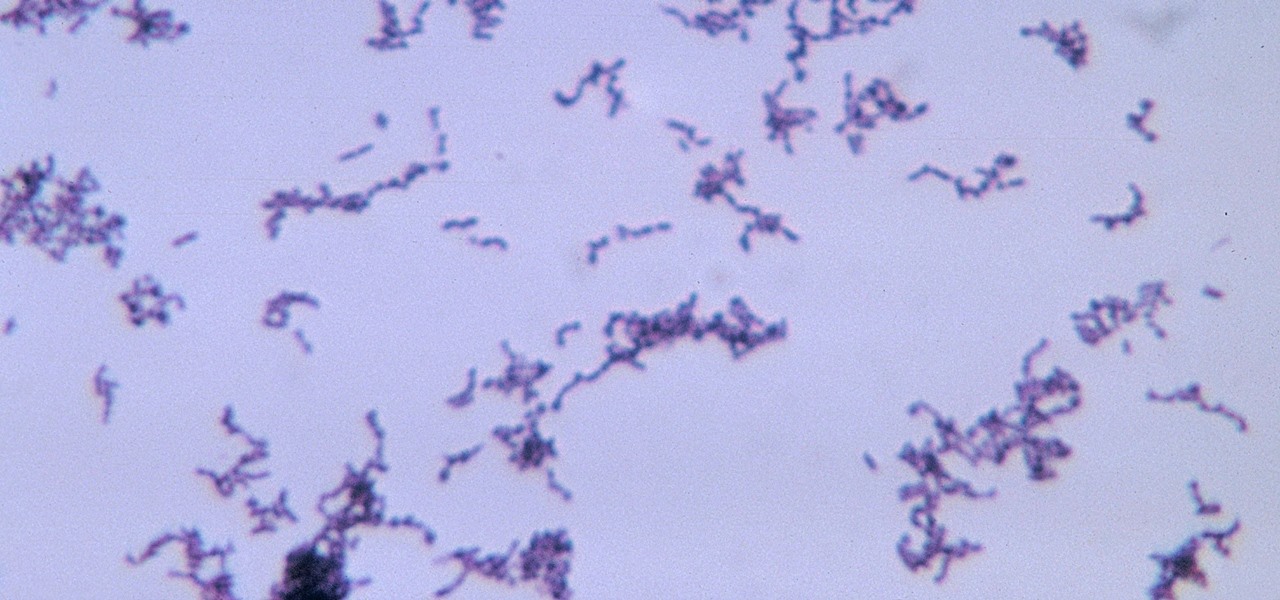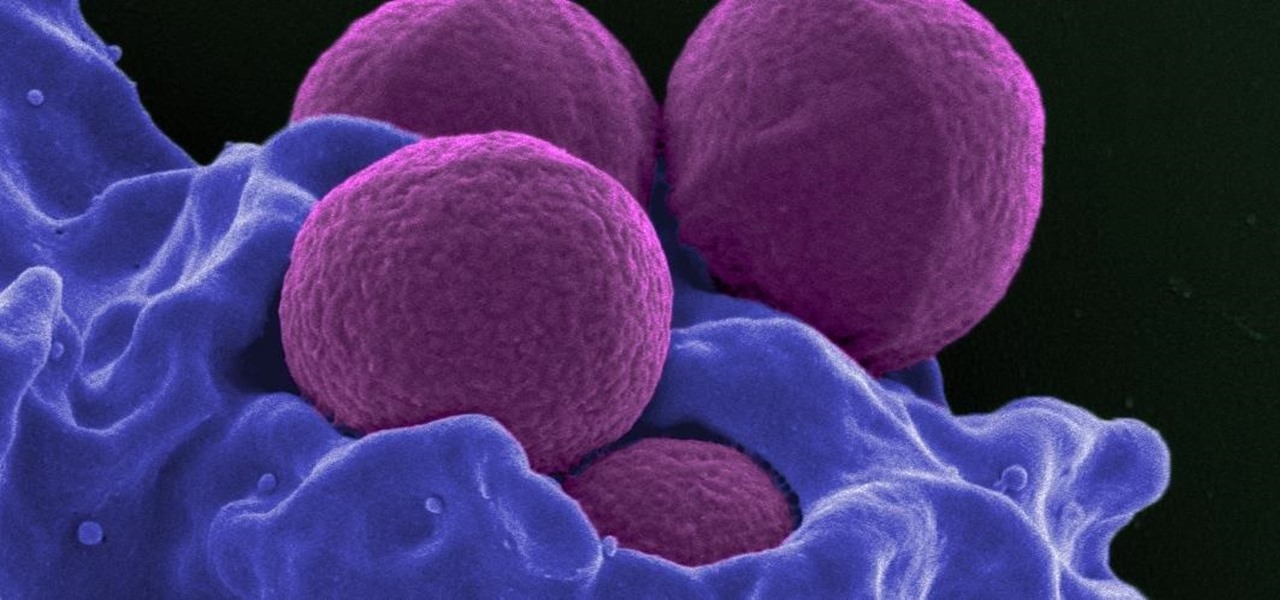
Staphylococcus aureus is a widespread bacteria — about a third of us have it on our body right now — usually in our nose or on our skin. And it probably isn't causing an infection. But, about 1% of people who have Staphylococcus aureus present have a type that is resistant to the antibiotic methicillin.

Colorectal cancer — cancer of the colon or rectum — is the third most commonly diagnosed cancer in the US. To reduce the chances of a diagnosis we are all urged to stop smoking, keep our weight down, decrease our intake of alcohol and red meat, keep active, and get screened for colon cancer. But, new research has found something that participates in the development of colorectal cancer that might not be as easy to control: A strep bacteria that promotes tumor growth.

Sex makes the world go 'round, and when it does, so does gonorrhea. Finally some good news on the growing menace of drug-resistant gonorrhea — a large, long-term study shows a vaccine may work in reducing the incidence of an increasingly dangerous infection.

Montezuma's revenge, the runs, the trots, or just diarrhea — everyone gets it sooner or later. What exactly is diarrhea good for, if anything?

Everything from disposed of drugs to hormones and disease-causing bacteria — anything that is rinsed or flushed down the drain — can contaminate wastewater.
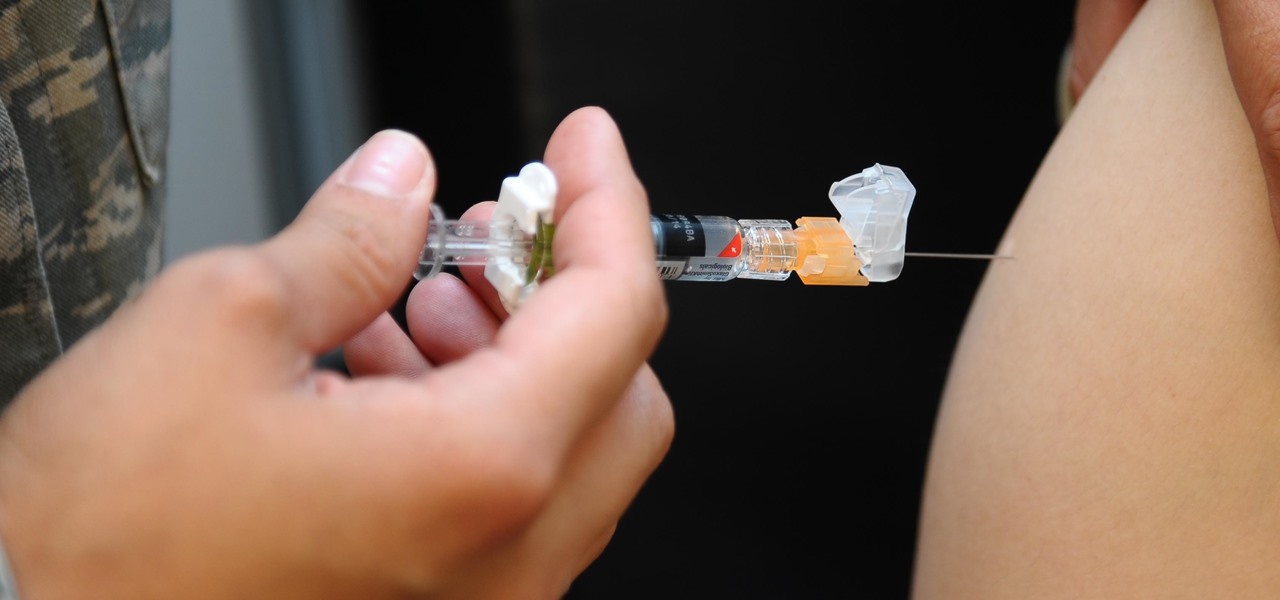
A new medical development is going to change the way many of us look at getting the flu vaccine. A painless flu vaccine skin patch is making needles and vials a thing of the past. Researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University have shown that a flu vaccine can be administered safely and comfortably with this new patch, which delivers the vaccine through a matrix of tiny dissolving microneedles.

Maine reported their first measles case in 20 years yesterday, June 27, in a press release from the Maine CDC. Many other people may have been exposed and could show signs of infection soon, with the potential for outbreak brewing. The last measles case in Maine was in 1997.

I have nightmares about trying to reply to hundreds of strangers on social media. To prevent the overwhelming feeling of having to small talk with people I don't know, I'm now aiming for more control over the ways that people can contact me. One way is to stop users from hitting me up on Instagram Stories.

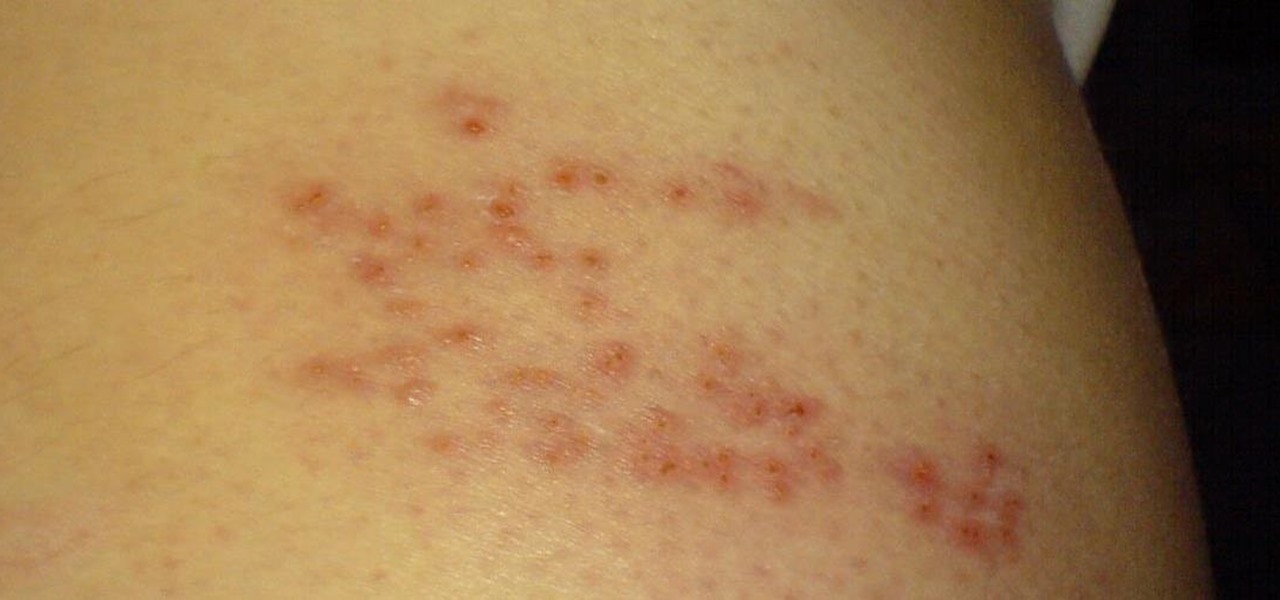
People who have heart disease get shingles more often than others, and the reason has eluded scientists since they first discovered the link. A new study has found a connection, and it lies in a defective white cell with a sweet tooth.

Bone loss and belly fat may no longer be certain fates of menopause, thanks to new research from an international team of scientists.

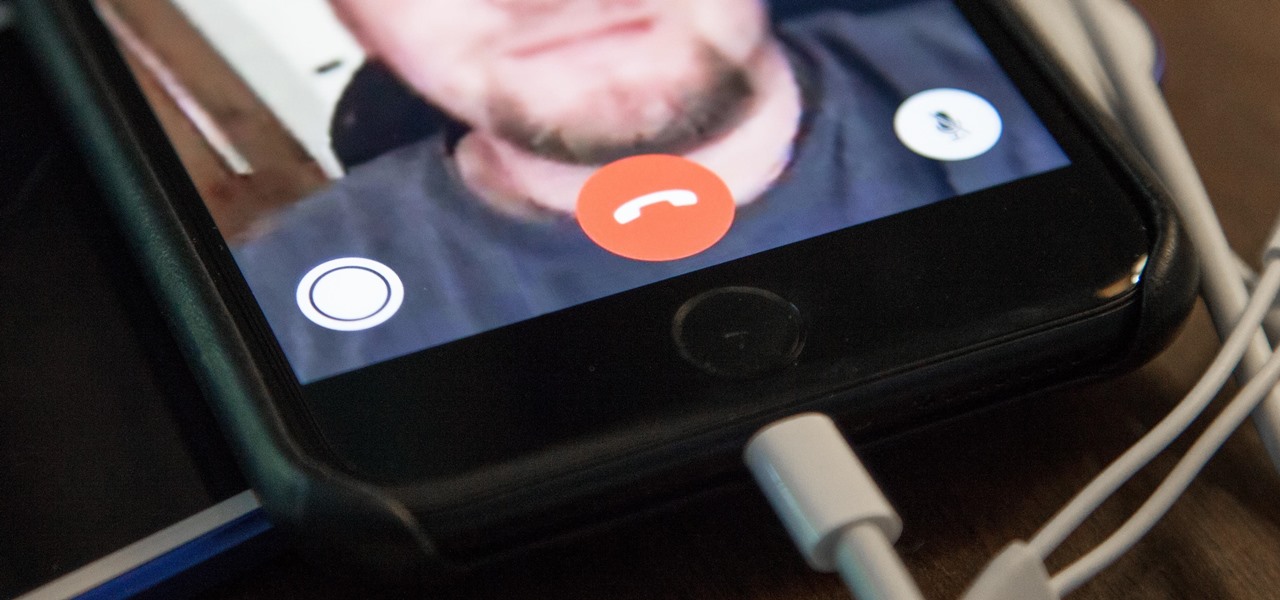
When you're taking a video in the Camera app on your iPhone, there's a little white shutter button in the corner that lets you take a still image while you're filming. Apple brought that same concept over to the FaceTime app in iOS 11, iOS 12, and higher, so you can take Live Photos of your friends during video chats.

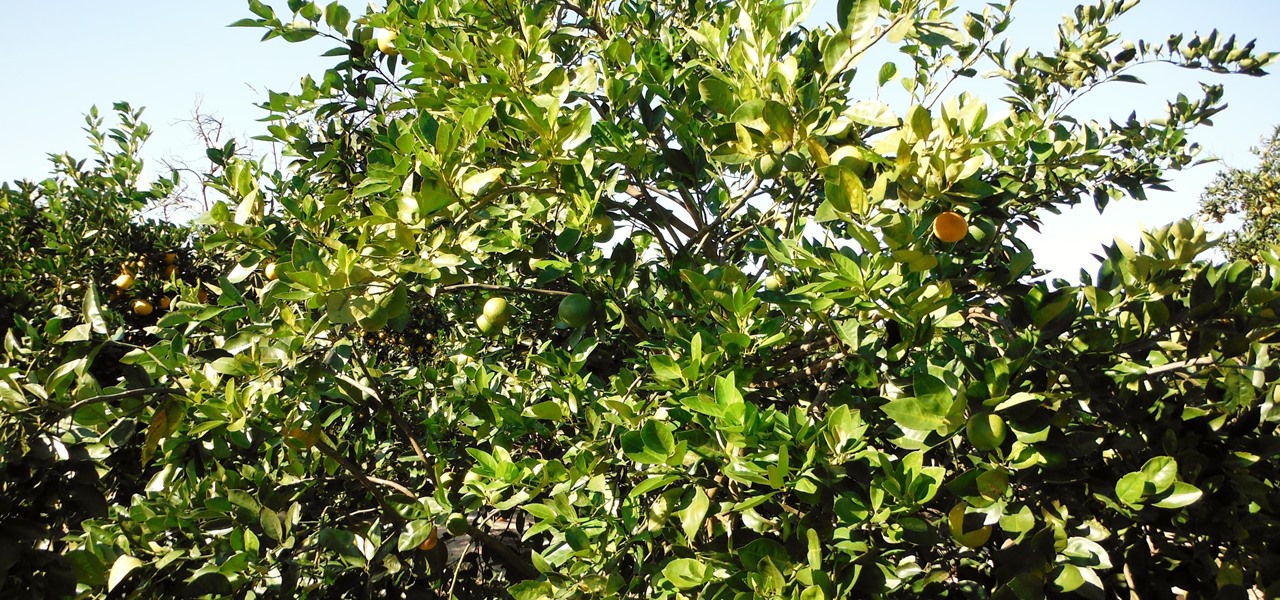
Citrus greening disease — caused by a bacteria spread by psyllid insects — is threatening to wipe out Florida's citrus crop. Researchers have identified a small protein found in a second bacteria living in the insects that helps bacteria causing citrus greening disease survive and spread. They believe the discovery could result in a spray that could potentially help save the trees from the bacterial invasion.

Because of Android's new SafetyNet system, certain apps can now block rooted users or prevent you from accessing them altogether — but at least for now, there are still ways around these restrictions.

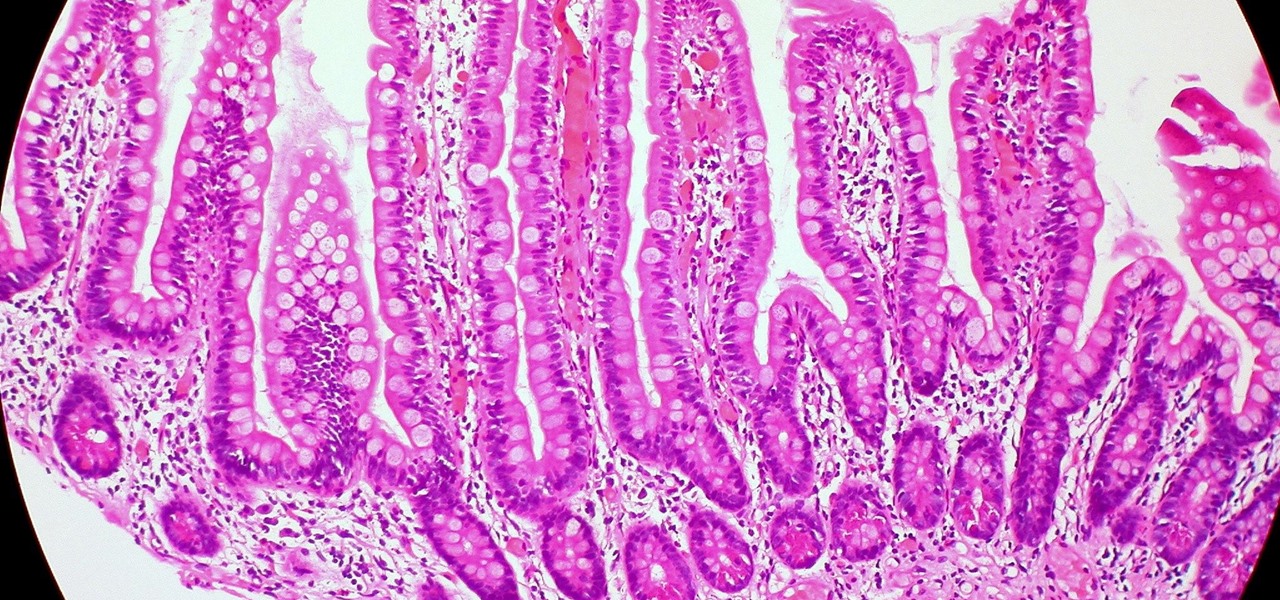
Several recent research studies have pointed to the importance of the microbes that live in our gut to many aspects of our health. A recent finding shows how bacteria that penetrate the mucus lining of the colon could play a significant role in diabetes.

Stakeholders in the driverless industry are anxiously awaiting changes the US Department of Transportation (DOT) is making to self-driving vehicle guidelines.

The Galaxy S8's AMOLED display is prone to screen burn-in, particularly with the navigation and status bars. But hiding these bars would make it hard to navigate your phone — that's where Pie Controls come into play.

Dengue fever is a danger to anyone living or visiting tropical or subtropical regions. It can be hard to detect the infection in its earliest and most treatable phase, especially in children. Luckily, new research highlights better techniques for triaging the disease in infected children with more severe symptoms, potentially saving lives.

The problem with HIV is that it attacks and kills the very cells of the immune system that are supposed to protect us from infections — white blood cells. But a new technique, developed by scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) in La Jolla, California, offers a distinct HIV-killing advantage.

As if being pregnant did not come with enough worry, a new study found that certain antibiotics are linked to an increased risk of spontaneous abortion, or miscarriage — a terrifying finding for any expectant mother.

The noses of kids who live in areas of intense pig farming may harbor antibiotic-resistant bacteria, presumably acquired from the animals, according to a new study by scientists at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, UNC Gillings School of Global Public Health, and Statens Serum Institut in Denmark, published in Environmental Health Perspectives.

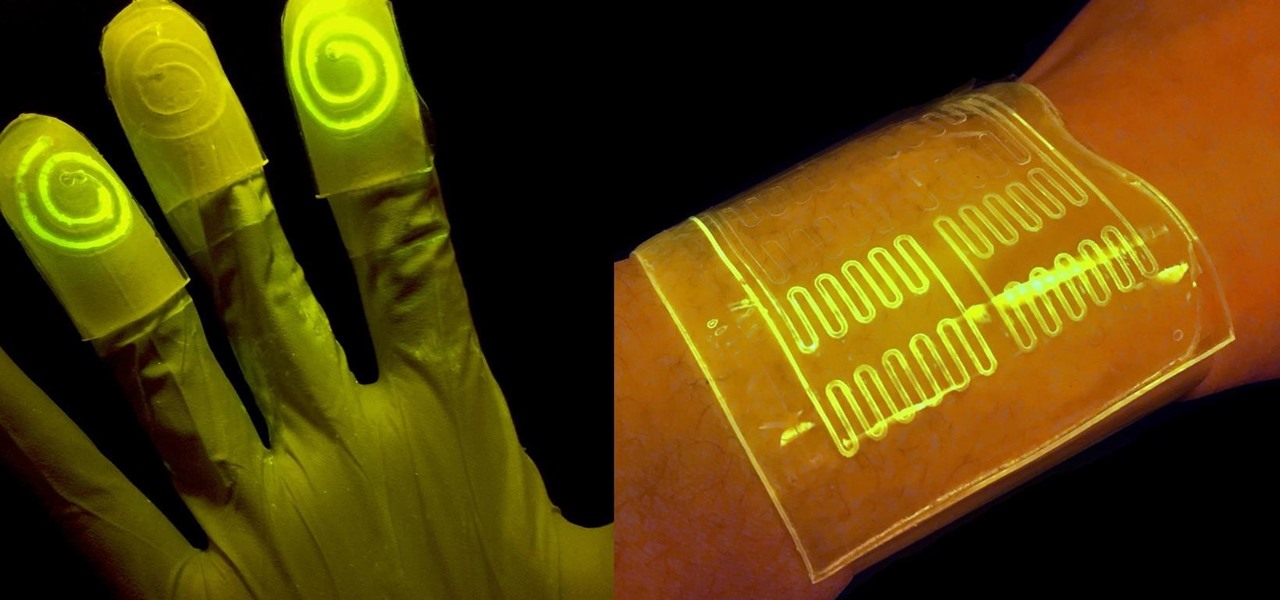
While at work, you notice your gloves changing color, and you know immediately that you've come in contact with dangerous chemicals. Bandages on a patient signal the presence of unseen, drug-resistant microbes. These are ideas that might have once seemed futuristic but are becoming a reality as researchers move forward with technology to use living bacteria in cloth to detect pathogens, pollutants, and particulates that endanger our lives.

You may not have heard of visceral leishmaniasis, onchocerciasis, or lymphatic filariasis, and there is a reason for that. These diseases, part of a group of infections called neglected tropical diseases (NTDs), impact more than a billion people on the planet in countries other than ours. Despite the consolation that these often grotesque illnesses are "out of sight, out of mind," some of these infections are quietly taking their toll in some southern communities of the US.

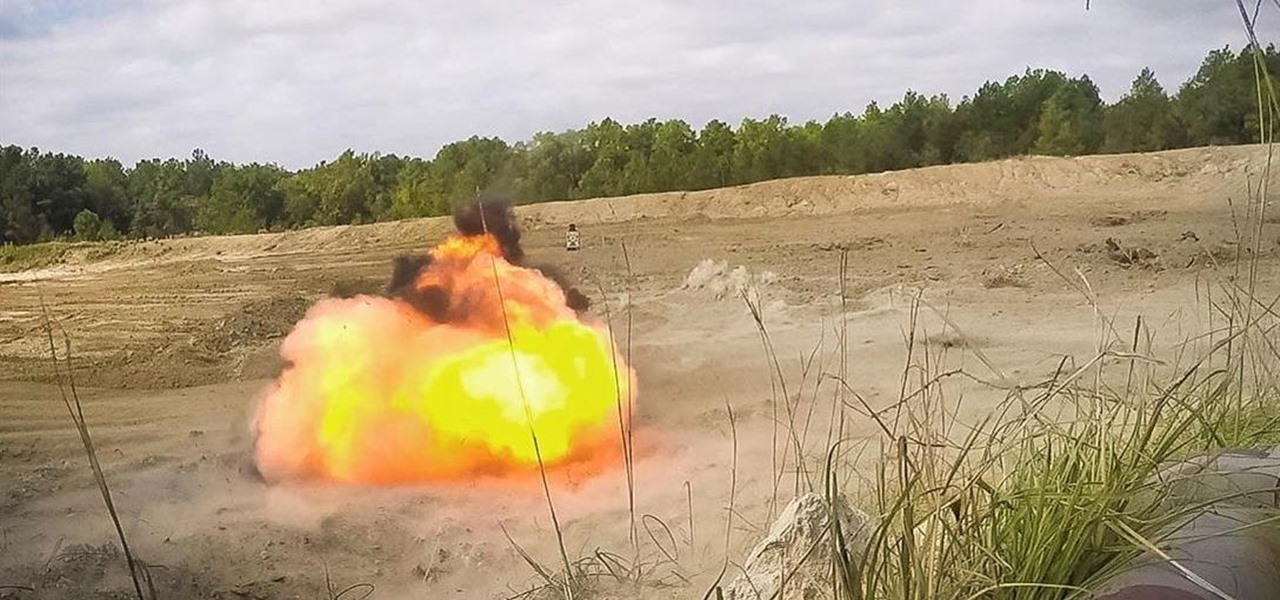
Devastating and deadly, land mines are a persistent threat in many areas of the world. Funding to clear regions of land mines has been decreasing, but new research may offer a less dangerous method of locating hidden, underground explosives by using glowing bacteria.

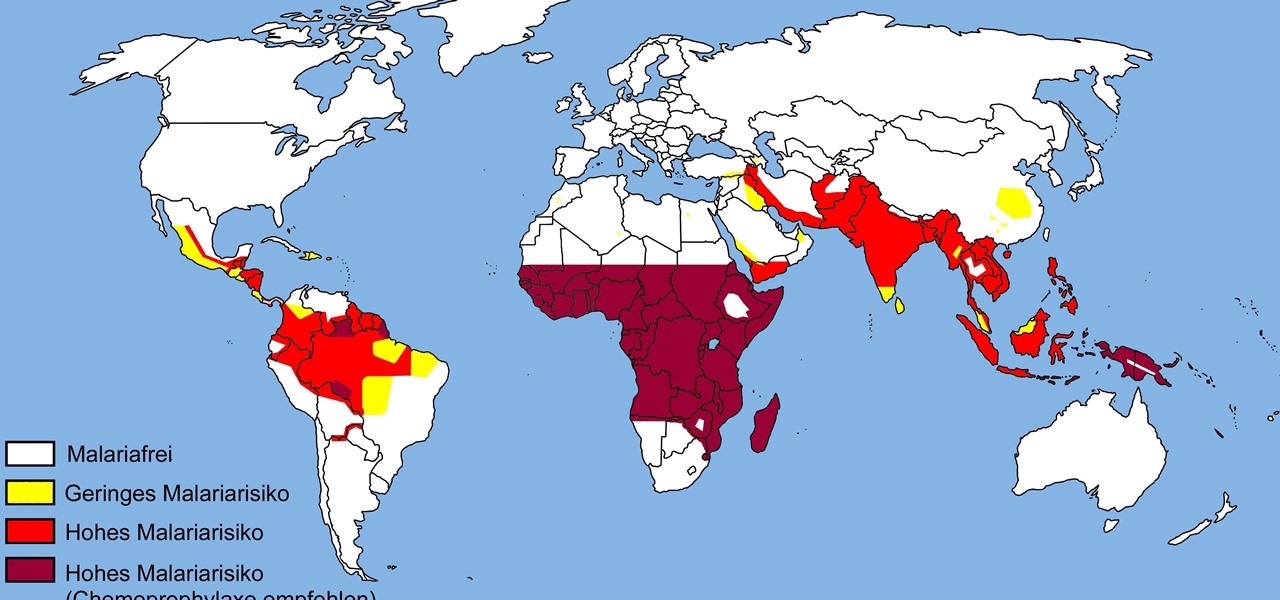
The theme for 2017's World Malaria Day, which is today, April 25, is "End Malaria for Good." For many Americans, this might seem like an odd plea. Especially since Malaria is seemingly an obsolete problem here. However, on World Malaria Day, it's important to remember the danger of malaria is still very much present in the US. And around the world, the disease is at the epicenter of a global crisis.

It's about time people acknowledged that judging drug users would do nothing productive to help them. In the US this week, two new programs are launching that should help addicts be a little safer: Walgreens Healthcare Clinic will begin offering to test for HIV and hepatitis C next week, and Las Vegas is set to introduce clean syringe vending machines to stop infections from dirty needles.

Our quest to find novel compounds in nature that we can use against human diseases —a process called bioprospecting — has led a research team to a small frog found in India. From the skin slime of the colorful Hydrophylax bahuvistara, researchers reported finding a peptide — a small piece of protein — that can destroy many strains of human flu and can even protect mice against the flu.

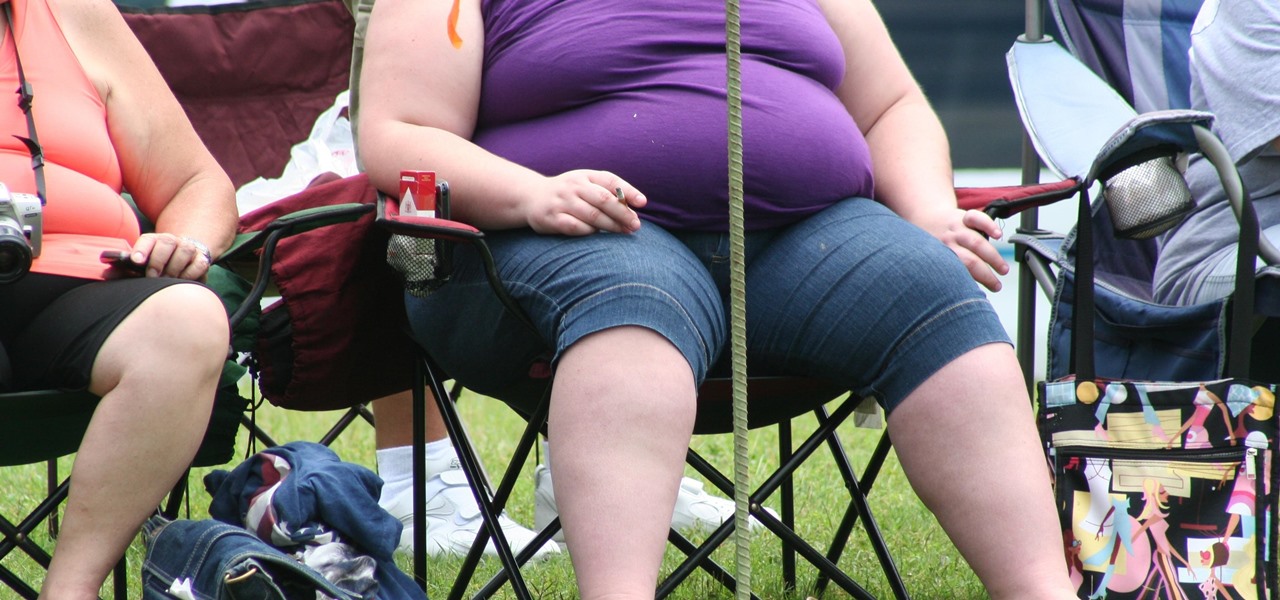
Potbellies don't have to happen as we age, according to two studies done on twins published online in the International Journal of Obesity.

Viral infections have been the focus of attention in the development of autoimmune diseases—diseases where the body's immune system reacts to the body's own cells—because they trigger the immune system into action.

The squiggly guys in this article's cover image are Propionibacterium acnes. These bacteria live in low-oxygen conditions at the base of hair follicles all over your body. They mind their own business, eating cellular debris and sebum, the oily stuff secreted by sebaceous glands that help keep things moisturized. Everybody has P. acnes bacteria—which are commonly blamed for causing acne—but researchers took a bigger view and discovered P. acnes may also play a part in keeping your skin clear.

Apple has removed support for older 32-bit applications in the new iOS 11, which was to be expected after the 10.3 update added the ability to detect apps that are still running 32-bit processes on your iPad, iPhone, or iPod touch. Apple even excluded restore images for 32-bit devices such as the iPhone 5 and iPad (4th gen) in the iOS 10.3.2 beta 1 update for developers, so this shouldn't be a surprise.

The photo-centric Instagram app is a great way to share "evergreen" pictures and videos when compared to Snapchat and Facebook's new Messenger Day feature. But like all social media, keeping the account secure is an essential aspect, as it restricts unwanted viewers from seeing your content and can prevent unauthorized users from accessing your account. Instagram has several methods for locking down the account including a new two-factor authentication (2FA) mechanism.

Tremendous strides have been made in the treatment and outlook for patients infected with HIV, the human immunodeficiency virus. Treatment with a combination of antiretroviral drugs can keep patients with HIV alive for decades, without symptoms of the infection. The trouble is, if HIV-infected people stop taking their medications, the virus takes over in full force again—because the virus hides out quietly in cells of the immune system, kept in check, but not killed by the treatment.

Making a NANDroid backup can save you from all sorts of flashing-related mishaps and accidents. Bootloops, SystemUI crashes, accidental wipes, bad ZIPs, or a dozen other possibilities—there's almost no condition in which a NANDroid is unable to correct problems with your device. However, recent changes to Android have created an almost paradoxical situation where restoring a NANDroid can actually lock you out of your phone.

Over 6,500 waterfowl—mostly ducks—have died in Canyon County, Idaho, stricken by avian cholera. The outbreak started in February, and before it's over, it may not only be Idaho's largest outbreak, but one of the largest in the country.

A robust appetite for imported foods is leading to increased disease outbreak in the US. Despite the locovore and slow food movements, America's demand for foreign foods is picking up. According to a study published in the journal of Emerging Infectious Diseases, demand for imported fresh fruits, vegetables, and seafoods has jumped in recent years.

By looking for the mechanism that allows influenza A to invade lung cells, scientists also discovered a treatment that might block the virus from taking hold there.

Every year, 100-200 people in the US contract leptospirosis, but usually 50% of the cases occur in Hawaii where outdoor adventurers are exposed to Leptospira bacteria found in freshwater ponds, waterfalls, streams, and mud. That's why it's so alarming that two people in the Bronx have been diagnosed with the disease and a 30-year-old man has died from it.

SSH local forwarding is a must for covering your tracks and getting out there to do your work. Also called SSH tunneling, this process will put one or more steps between your machine and the machine you're working on, for security and other purposes. It can be a bit daunting for newbies to get down, and that's where Punchabunch comes in.

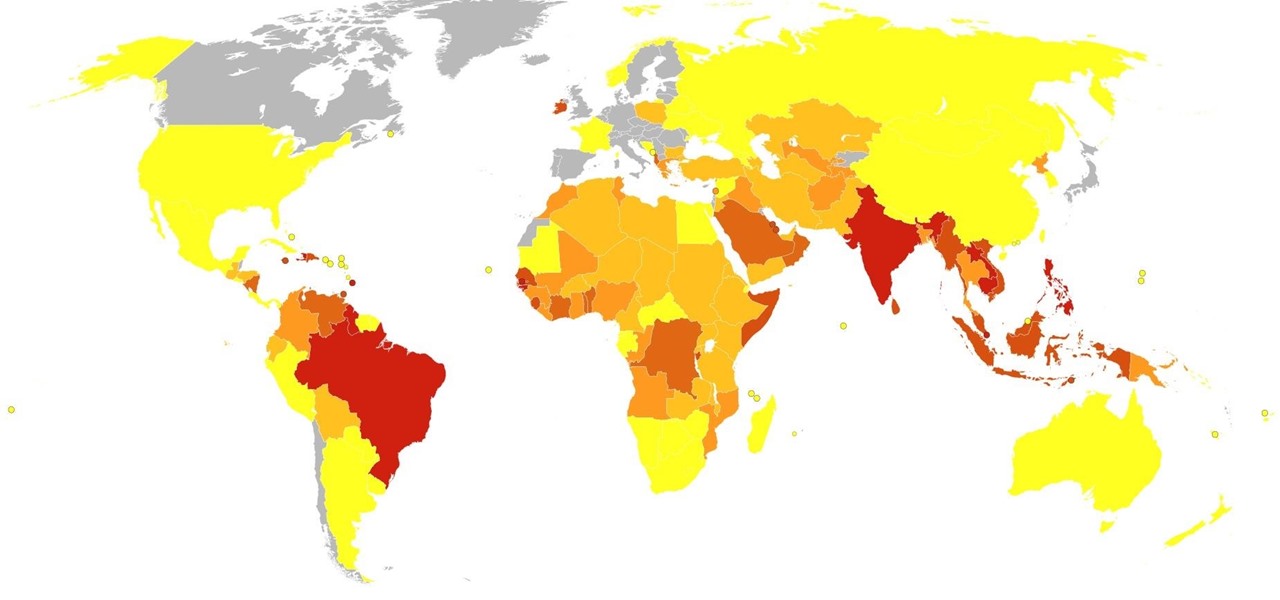
The pathogen referred to as a "nightmare bacteria" is quietly adapting and spreading faster than anticipated.

It hasn't even been eight years since Candida auris was discovered—cultured and identified from the ear canal of a patient in Japan—and now it's drug-resistant, setting up residence in hospitals, killing patients, and wreaking havoc across the globe.