Most Android launchers limit you to three choices: Icons, widgets, and folders. It's better than nothing, but it's still pretty hard to find the best look without overcrowding your home screen. You could fill everything up with icons, but then you'd have an iPhone. You could toss everything into folders, but that would always require an extra tap. You could mix in some widgets, but that would take up valuable space. So what do you do? Action Launcher has the answer.
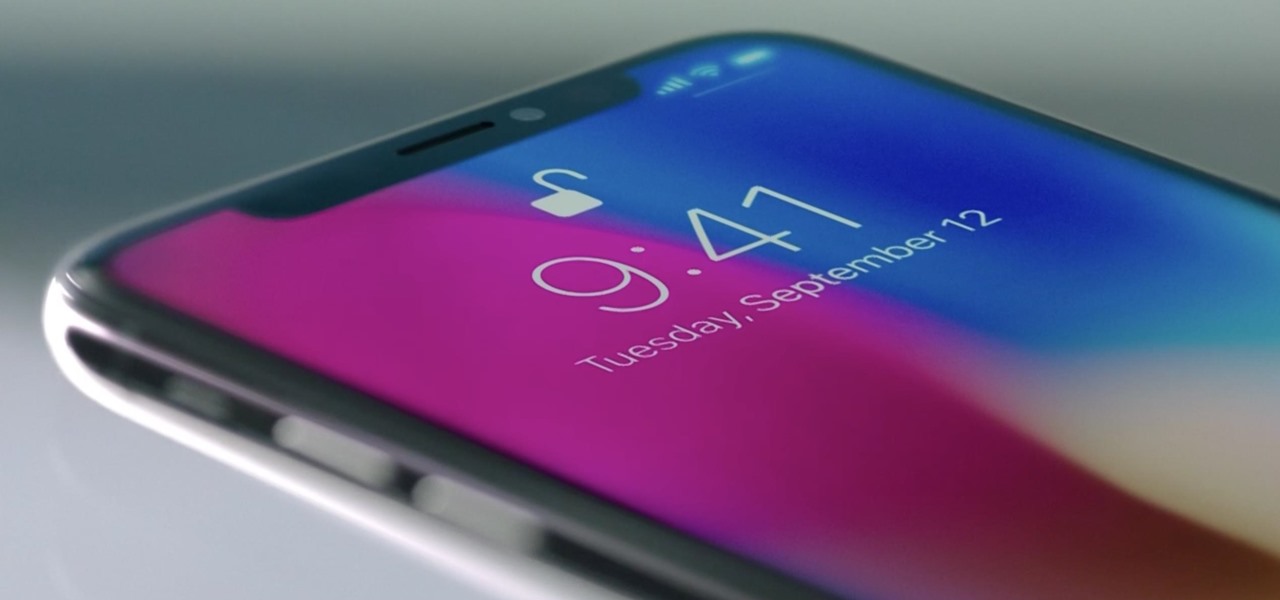

The new iPhone X will be released on Friday, Nov. 3, in Apple Stores located in over 55 countries and territories. For those of you who would rather skip the in-stores lines that will start building well before the 8 a.m. local time openings, you can preorder the iPhone X on Friday, Oct. 27, starting at 12:01 a.m. PDT.
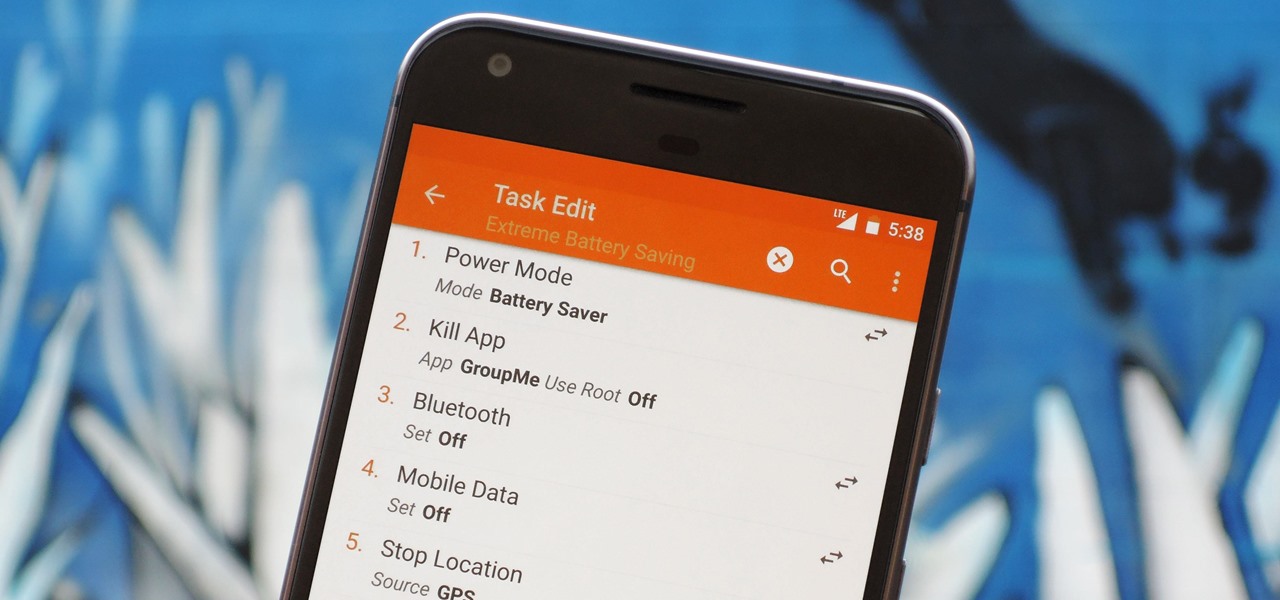
There are two core components to any Tasker automation: A profile and a task. Profiles are basically a set of conditions that must be met before Tasker will do anything. Tasks, on the other hand, are the actions Tasker will perform when your profile's conditions have been met. Think of them like triggers and actions, respectively. Or a cause and an effect.
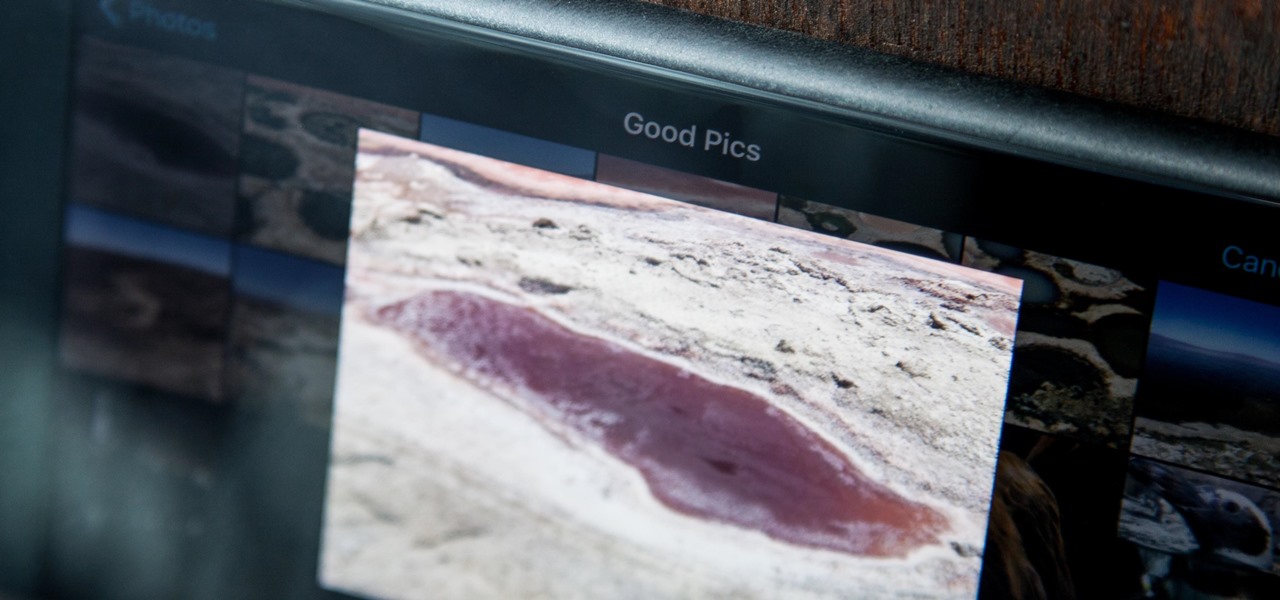

In most cases, when you create a movie project in iMovie for iPhone, you're starting with just a few media clips. There's no reason to select every photo or video at once, and that's likely a hard task anyway. Adding additional media footage to your movie project couldn't be any easier, especially when it comes to photos.
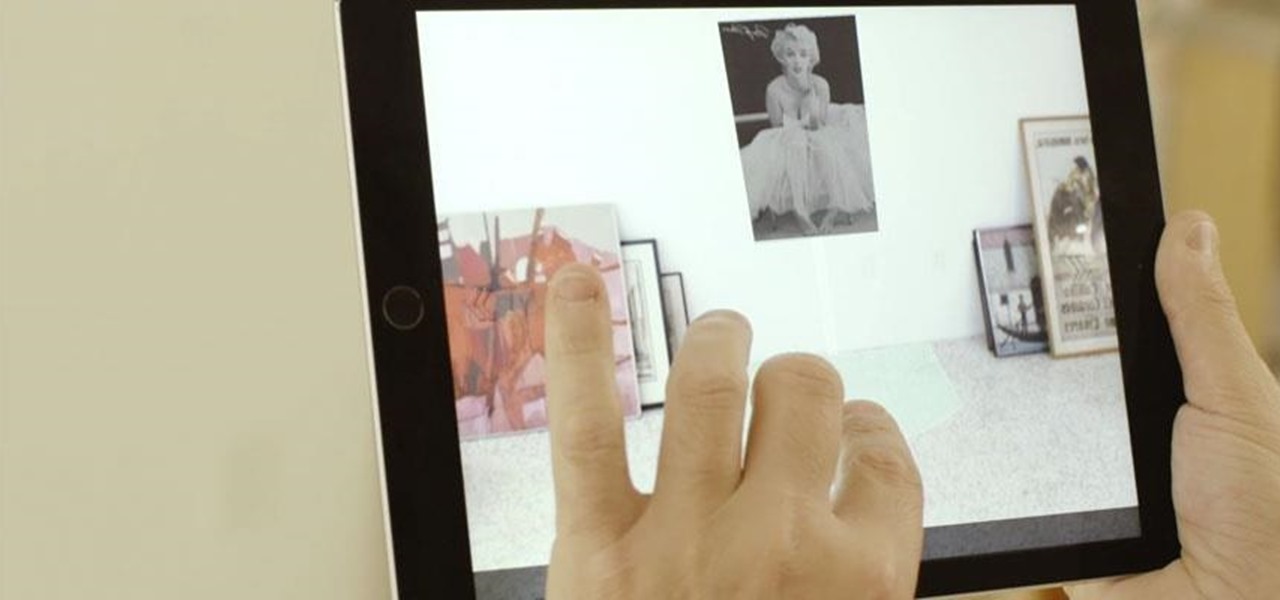

While IKEA is collaborating with Apple for its ARKit furniture app, Marxent is ready to help the rest of the interior decorating and home improvement crowd with their apps.

Bacteria, viruses and other germs sometimes set off the immune system to overreact, producing a severe condition called sepsis. Sepsis is so dangerous that it is the leading cause of death of children across the world, killing a million kids every year, mostly in developing countries. Probiotic bacteria might be able to prevent sepsis and infections, but no large research studies have been done to find out whether that actually works. Until now.

Scientists know that bacteria create their own energy, get nutrients to run their cellular processes, and multiply. But, bacteria haven't been shown to respond to external mechanical stimulation or signals in a way that's similar to how our bodies respond to touch, until now.

The world around us keeps getting smarter. Not only do we have advanced AI services like the Google Assistant, but now we've got the Internet of Things connecting physical objects to the digital world. It's amazing when you think about it, but the real sci-fi stuff starts to happen when these two technologies intersect.

The growing list of dangerous antibiotic resistant organisms has just acquired three new members. Researchers have discovered three new species of Klebsiella bacteria, all of which can cause life-threatening infections and have genes that make them resistant to commonly used antibiotics.

Rising on the world stage, dengue fever is transmitted by mosquitoes — and apparently air travel too.

Once we recover from the respiratory infection pneumonia, our lungs are better equipped to deal with the next infection — thanks to some special cells that take up residence there.

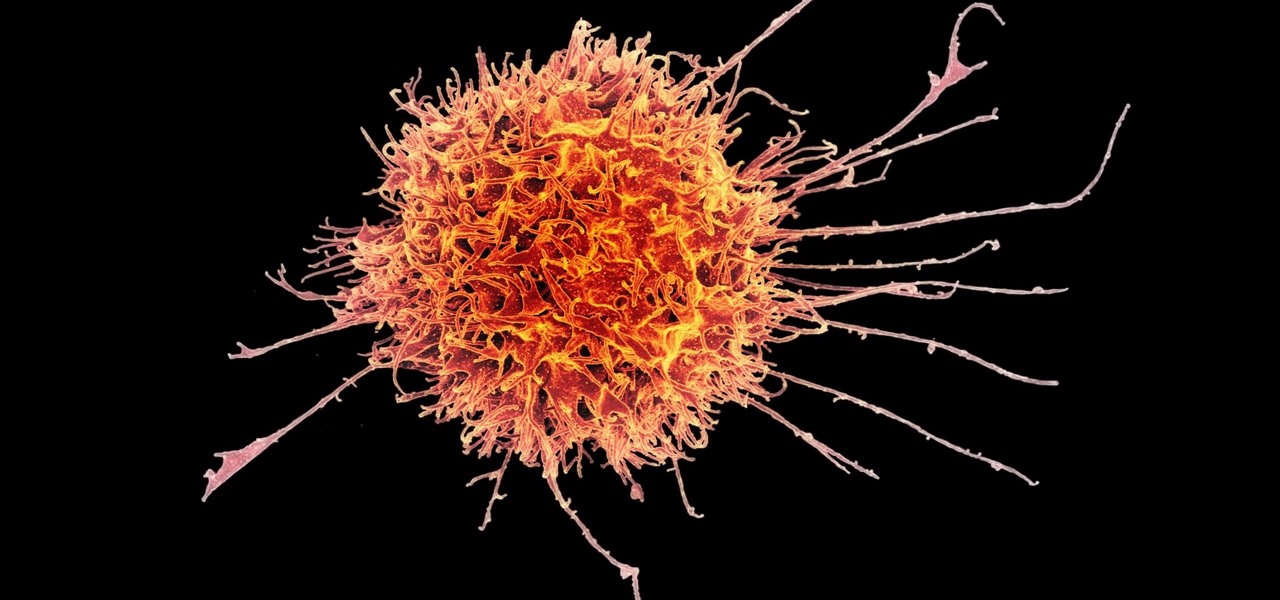
Cancer cells do a pretty good job of flying under the radar of our immune system. They don't raise the alarm bells signaling they are a foreign invader the way viruses do. That might be something scientists can change, though.

Long before Nvidia figured out how to embed neural networks in its graphics processor units (GPUs) for driverless vehicles, it and other chipmakers were already making the same kinds of devices for 3D games and other apps.

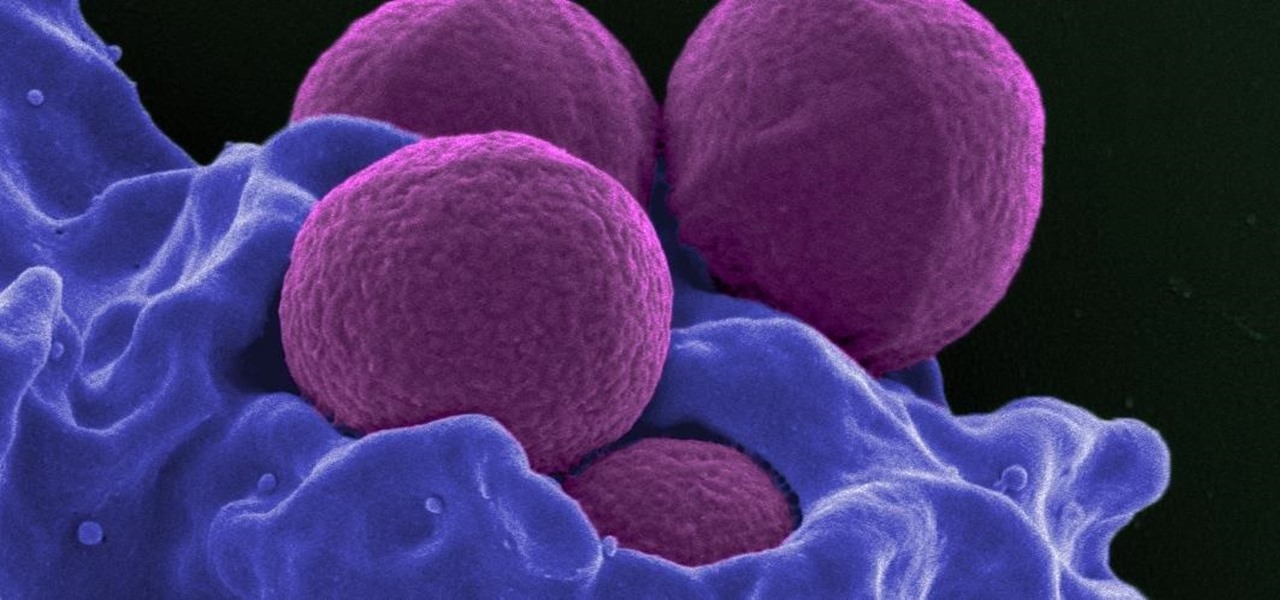
Staphylococcus aureus is a widespread bacteria — about a third of us have it on our body right now — usually in our nose or on our skin. And it probably isn't causing an infection. But, about 1% of people who have Staphylococcus aureus present have a type that is resistant to the antibiotic methicillin.

For a company more associated with debugging computer programs, Google's parent company, Alphabet, is making a name for itself by taking on the real thing — mosquitoes.

Casey Hudson, the one-time project director for games like Star Wars: The Knights of the Old Republic and the original Mass Effect trilogy, has announced his return to his former home, Bioware as the General Manager. Of course, that also means he is leaving his role at Microsoft Studios as Creative Director, where he was reportedly working on both Xbox One and HoloLens projects.

Nvidia has emerged as the indisputable leader in chips for Level 3 and even more advanced driverless applications, catching some of the world's largest semiconductor makers and automotive suppliers by surprise.

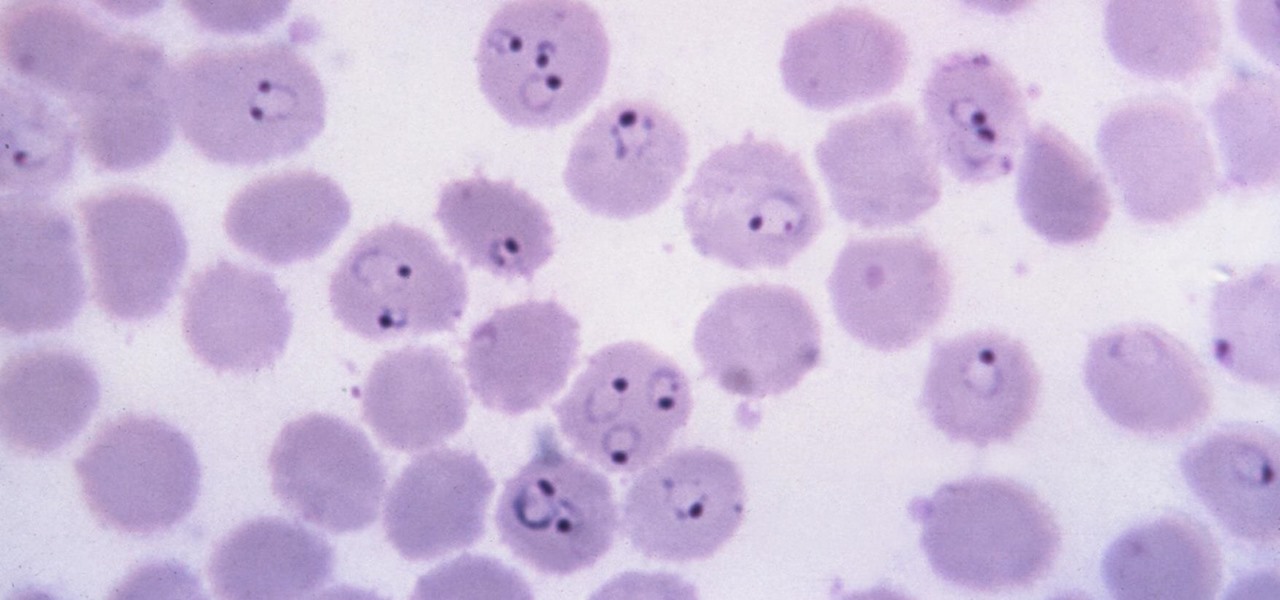
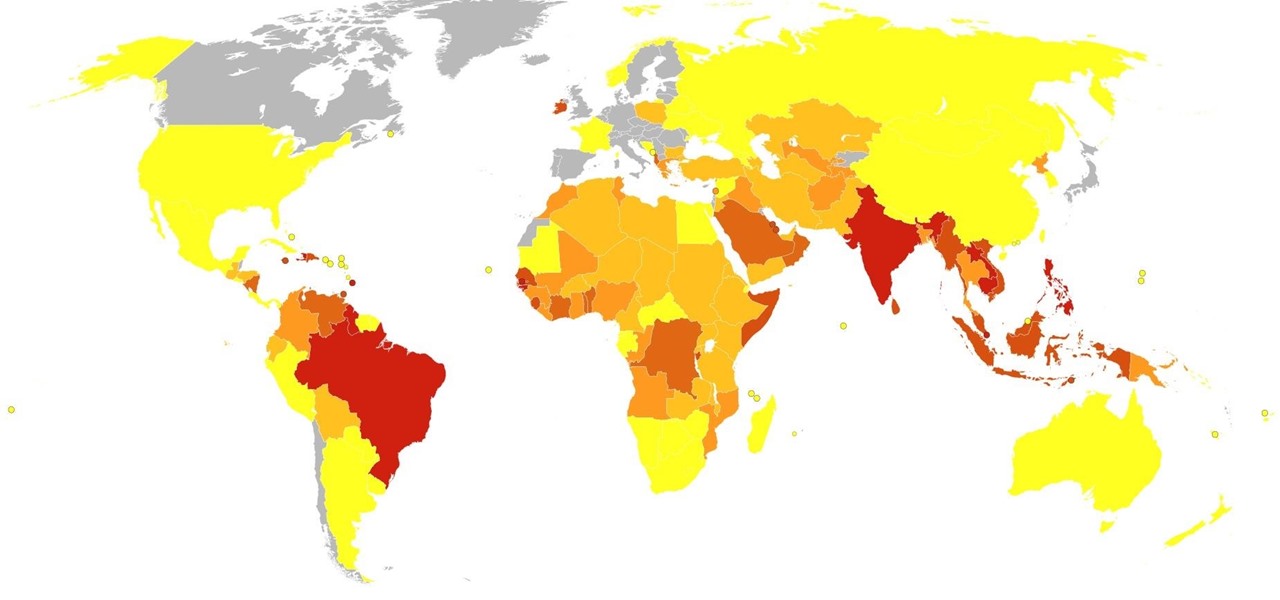
Malaria is a massive worldwide health problem. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate that 212 million cases of malaria occurred worldwide in 2015 and 429,000 of the infected people died.

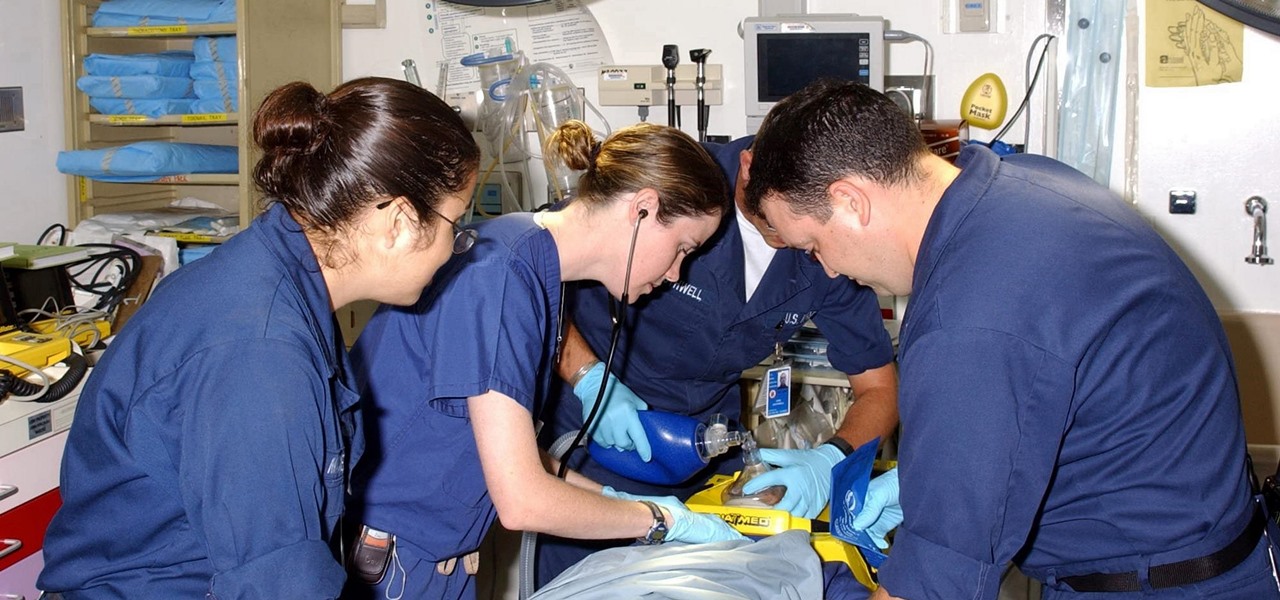
With a death rate of one in five, sepsis is a fast-moving medical nightmare. New testing methods might improve your odds of survival if this infection ever hits you.

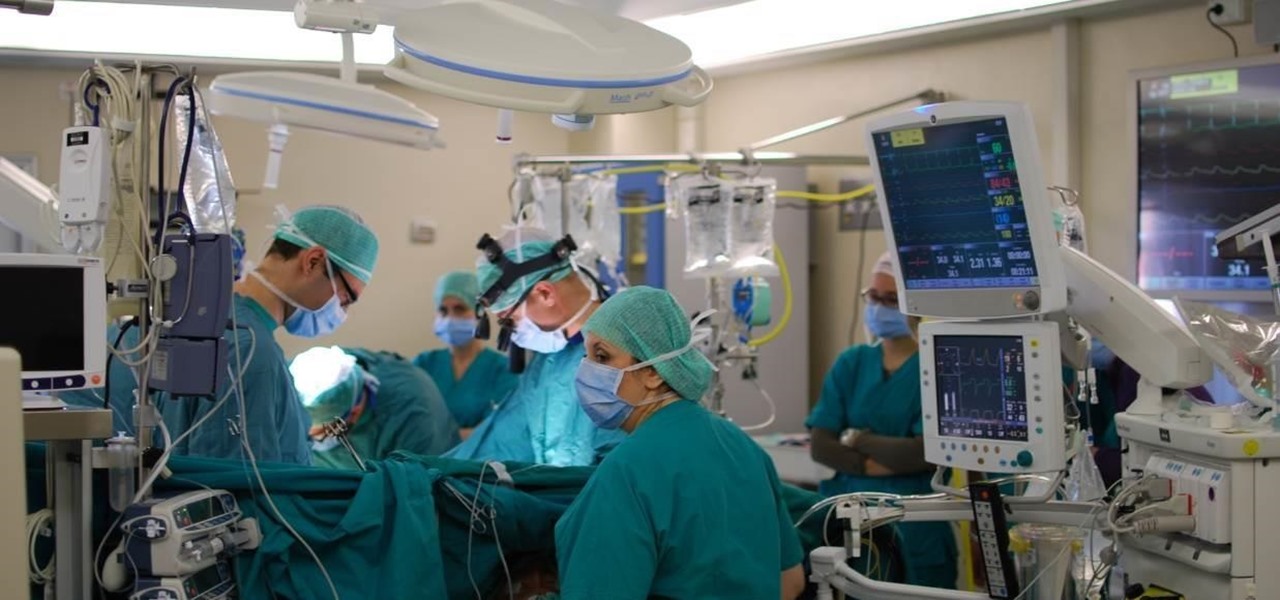
More bad news for patients who have undergone heart surgery in the past five years. A new study suggests about one-third of heater-cooler units used in cardiac procedures remain contaminated with a slow-growing, potentially fatal bacteria.

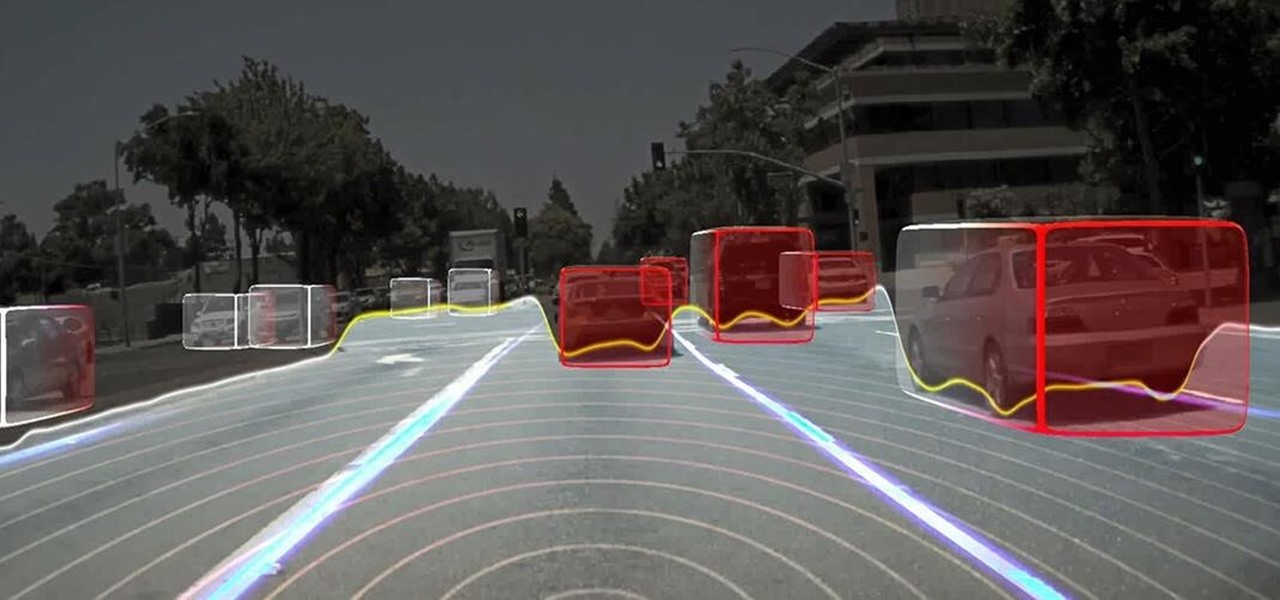
A vulnerability in the design of LiDAR components in driverless cars is far worse than anything we've seen yet outside of the CAN bus sphere — with a potentially deadly consequence if exploited.

The search is on to find antibiotics that will work against superbugs — bacteria that are rapidly becoming resistant to many drugs in our antibiotic arsenal.

I spent just about my entire weekend trying to break the 800, 900, and 1,000 levels of Instagram — because it's a game, y'all — by playing around with my follower count. I shamelessly manipulated my IG account in such a way that was extremely time consuming and left many of my friends pretty pissed off at me as I spent most of my time glued to my phone. (Sorry, friends. I know I'm obsessed.)

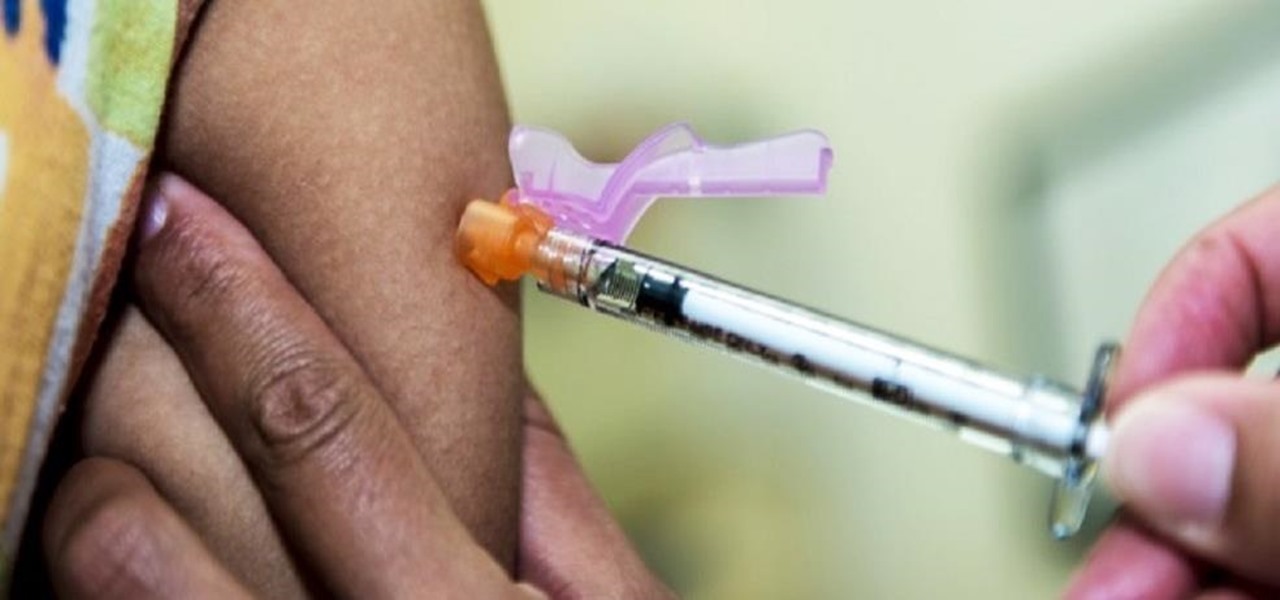
It's not always easy to get to the root of an infection outbreak. Epidemiologists study infected people, contacts, and carefully examine where the infections happened and when. In the case of a 2012 outbreak of pertussis — whooping cough — in Oregon, scientists just published an analysis of how vaccination status affected when a child became infected during the outbreak.

Alzheimer's disease — an irreversible, progressive brain disorder — is the sixth leading cause of death in the US and more than afflicts 5 million Americans. As if those numbers aren't scary enough, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention expect that number to nearly triple by 2050.

While restaurants and classrooms have enacted policies banning cell phones, one father has had enough of his kids' obsessive phone habits. Dr. Tim Farnum is now seeking to ban the sale of smartphones to children under 13.

Seeing that wonderful blue verified badge on Twitter really adds something to your public persona, doesn't it? That's why, when I found out that the average person could get verified on Twitter with the right tools, I jumped on the chance to add that little blue check to my own personal account.

Even before we are born, our immune system is hard at work. New research shows how the developing fetal immune system takes advantage of the time and opportunity of gestation — in the presence of mom's cells and tissues — to develop a sense of self.

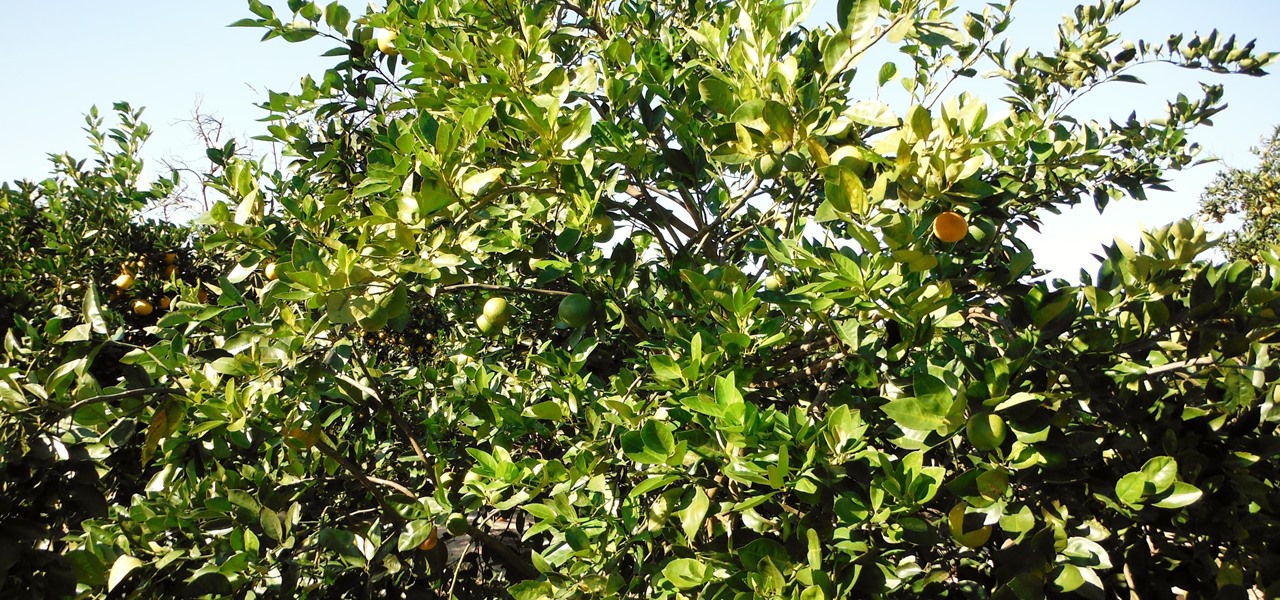
Citrus greening disease — caused by a bacteria spread by psyllid insects — is threatening to wipe out Florida's citrus crop. Researchers have identified a small protein found in a second bacteria living in the insects that helps bacteria causing citrus greening disease survive and spread. They believe the discovery could result in a spray that could potentially help save the trees from the bacterial invasion.

Intense exercise can cause problems with our digestive tract. It even has a name — "Exercise-induced Gastrointestinal Syndrome." Simply put, strenuous exercise can damage the gut and let the bacteria that reside there potentially pass into the bloodstream.

The Massachusetts Department of Public Health (DPH) issued a health alert for a Boston mumps outbreak, on Monday, June 5th, to healthcare providers and local boards of health. There have been 12 reported cases of mumps during the recent outbreak. The affected residents' symptoms occurred between March 24th and May 31st, and 10 of the 12 had symptoms after May 9th. There have been 35 confirmed cases of mumps in 2017 in Massachusetts, and "nearly 300" suspected cases in the continuing outbreak.

A groundbreaking new Android feature called seamless updates was announced at Google I/O 2016. No longer would we have to wait for updates to download and install — instead, they'd be applied silently in the background, and the new Android version would be waiting on us the next time we restarted our phones.

If imitation truly is the sincerest form of flattery, then Snapchat must be blushing profusely as Instagram continues to shamelessly copy its features and dig into its wallet. Instagram has also managed to copy some of the security aspects — or lack thereof — of one of Snapchat's hottest characteristics.

Dengue fever is a danger to anyone living or visiting tropical or subtropical regions. It can be hard to detect the infection in its earliest and most treatable phase, especially in children. Luckily, new research highlights better techniques for triaging the disease in infected children with more severe symptoms, potentially saving lives.

Activating the body's own immune system to fight cancer is the goal of immunotherapy. It's less toxic than chemotherapy and works with our body's natural defenses. The trouble is, it doesn't work for most patients — only about 40% of cancer patients get a good response from immunotherapy. But coupling it with another type of cancer therapy just might deliver the punch that's needed to knock out cancer.

Even though the Ebola virus was discovered as recently as 1976, over 30,000 people have been infected since, and half have died a horrible death. Since there's no way to cure the infection, the world desperately needs a way to prevent it — and the five similar viruses in its family, the ebolaviruses.

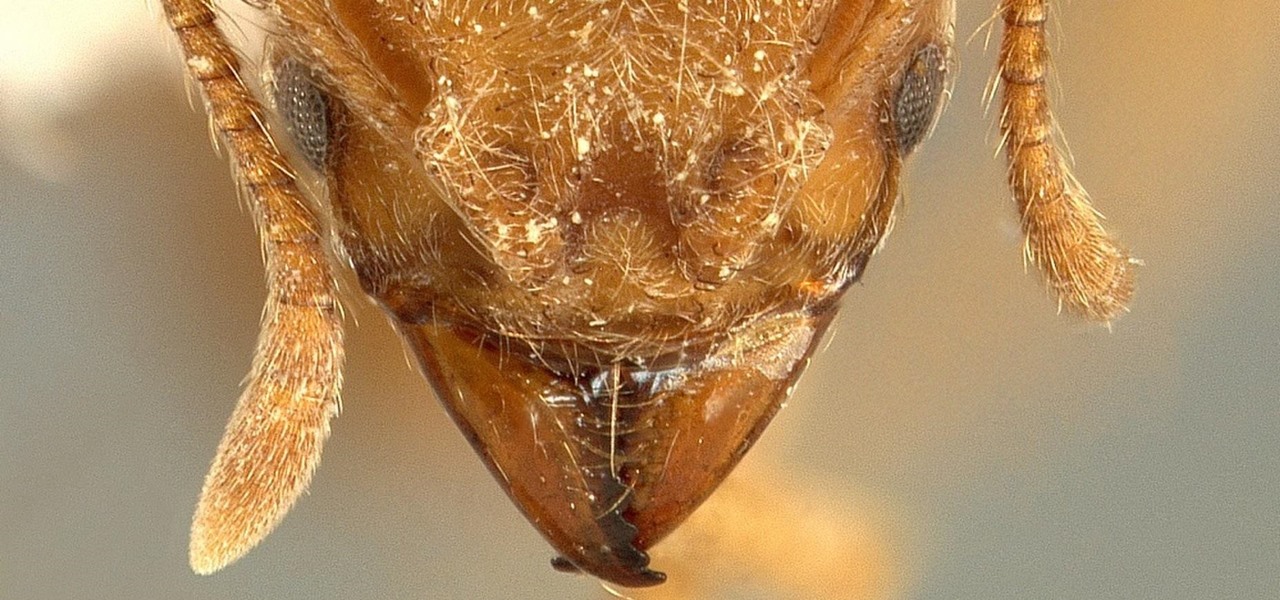
Long admired for their active and cooperative community behavior, some types of ants also wear a gardening hat. Nurturing underground fungus gardens, these ants have a win-win relationship that provides food for both ants and fungi. If we humans understand it better, it may just help us out, too.

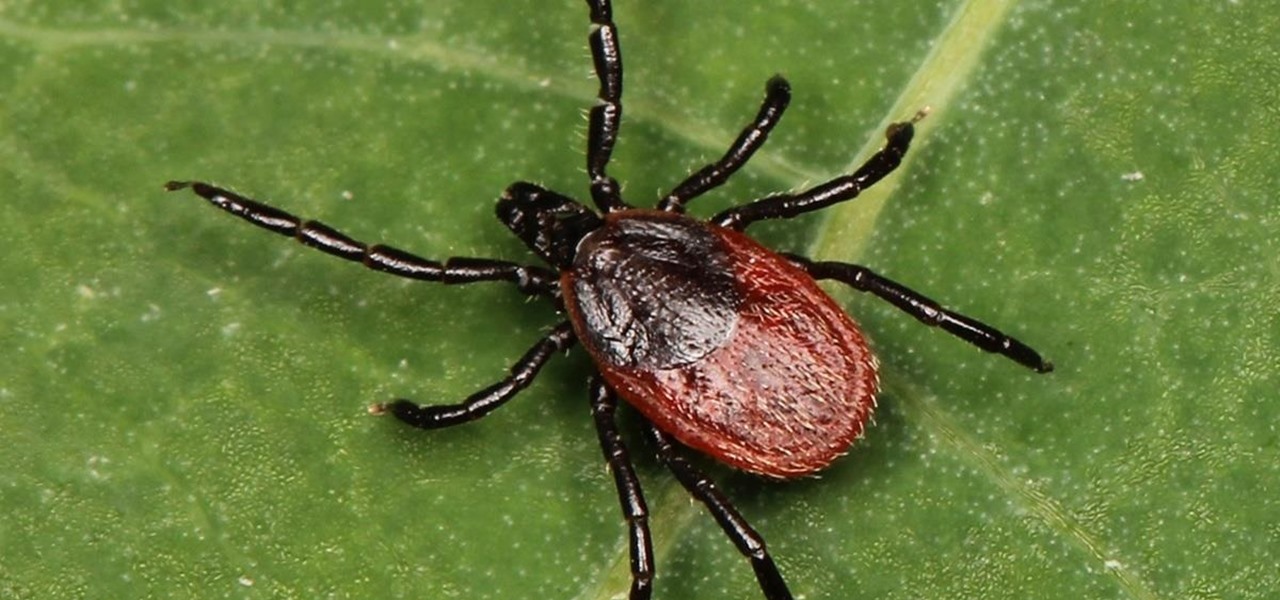
Lyme is a growing threat as we move into warmer weather in the US. Researchers have said this year could be one of the worst for this tick-borne disease, as a skyrocketing mouse population and warmer temperatures increase the risk.

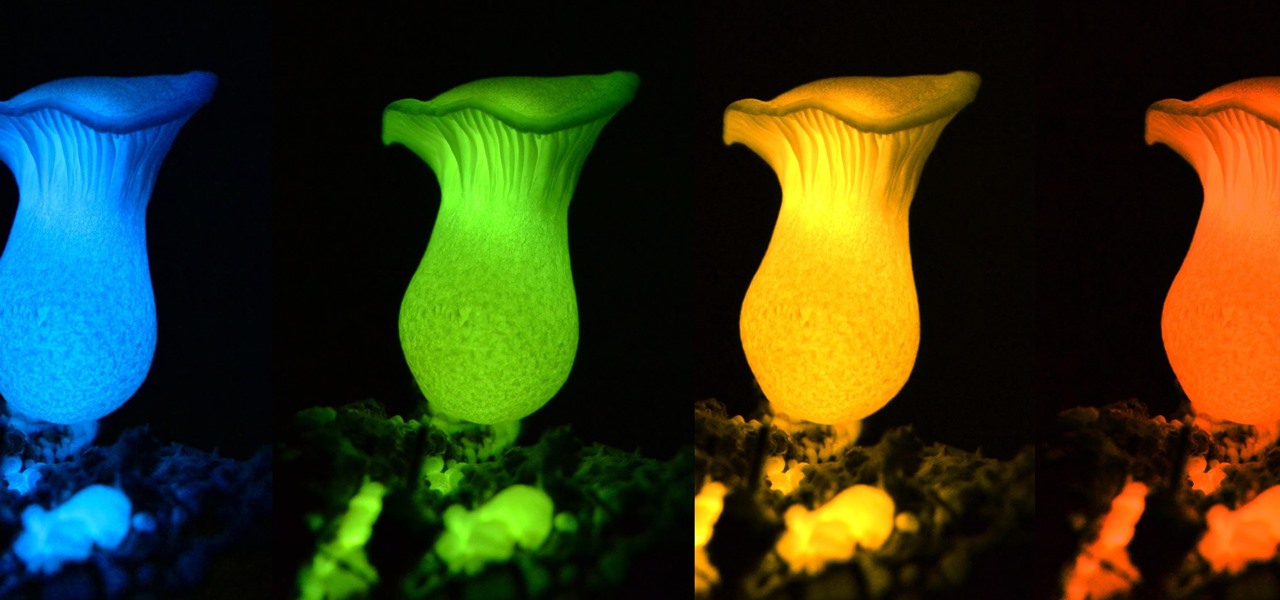
Bioluminescence — the ability of an organism to produce and emit light — is nature's light show. Plants, insects, fish, and bacteria do it, and scientists understand how. Until now, though, we didn't know how fungi glow.

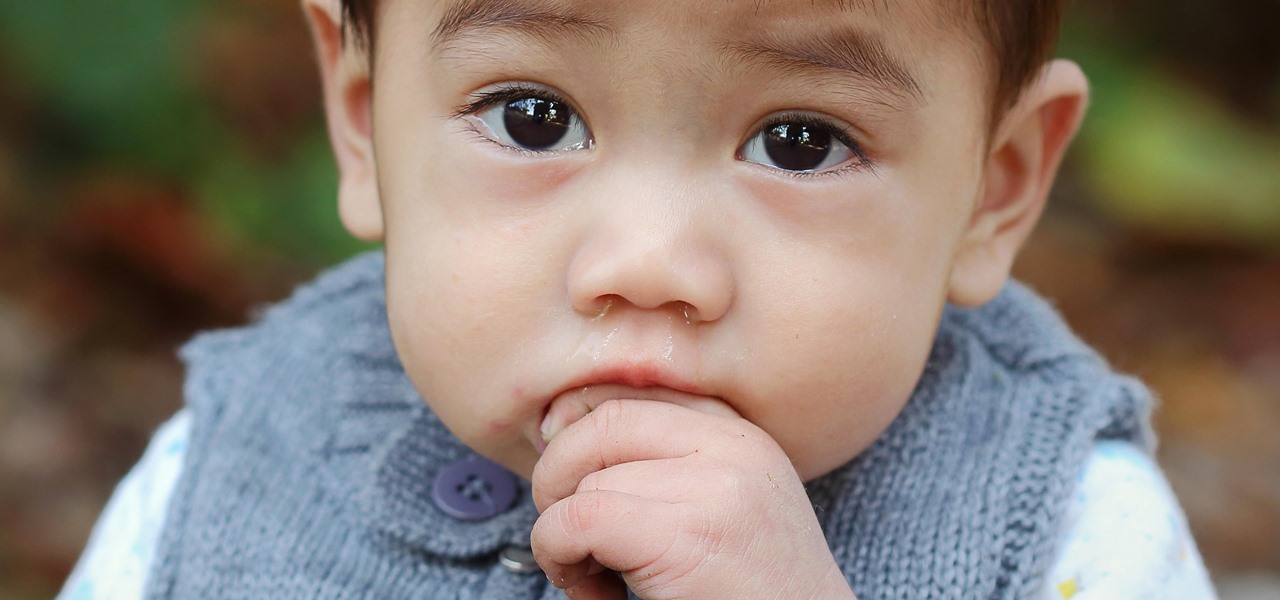
The noses of kids who live in areas of intense pig farming may harbor antibiotic-resistant bacteria, presumably acquired from the animals, according to a new study by scientists at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, UNC Gillings School of Global Public Health, and Statens Serum Institut in Denmark, published in Environmental Health Perspectives.