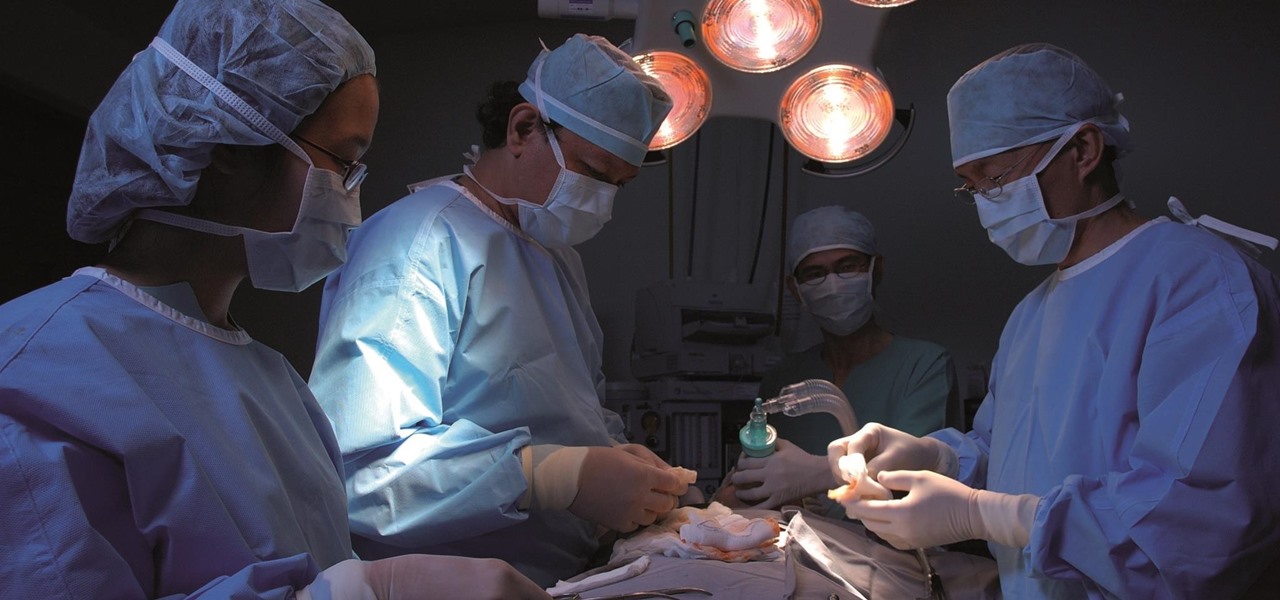
Dramatic new research may change the fate of the hundreds of people who wait for a kidney transplant every year. The study hinged on the ability to cure hepatitis C infections, a possibility that became a reality in 2014.
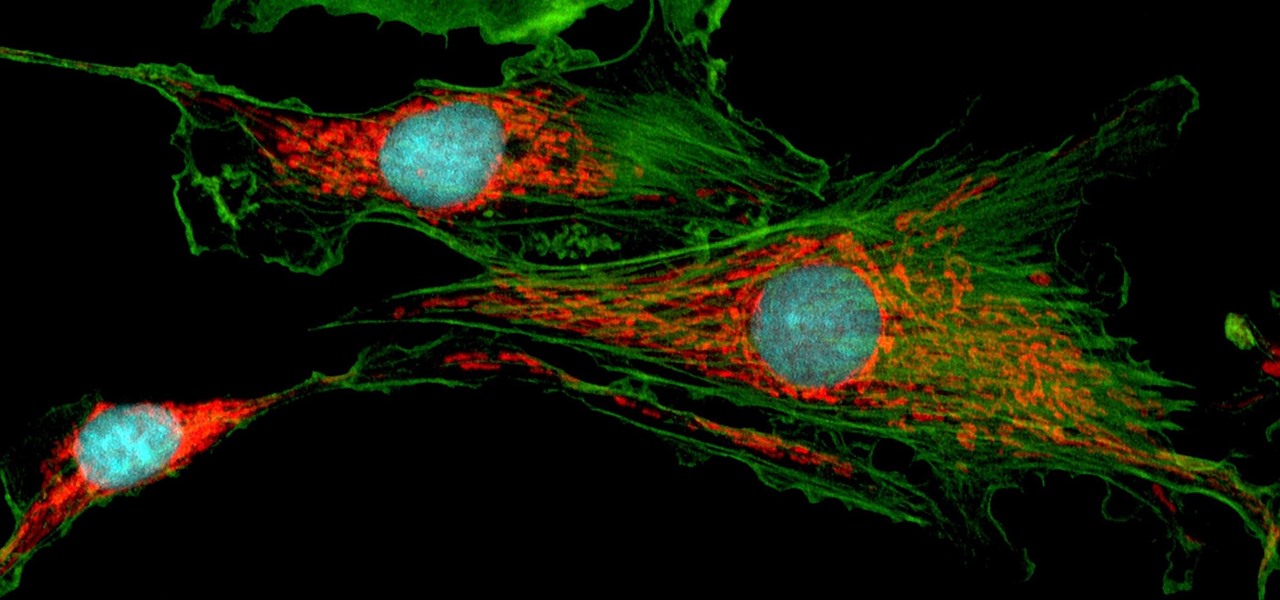
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of our cells because they generate energy to power them. But they also play a key role in the death of cells when they're damaged, infected, stressed, no longer needed, or at the end of their life.
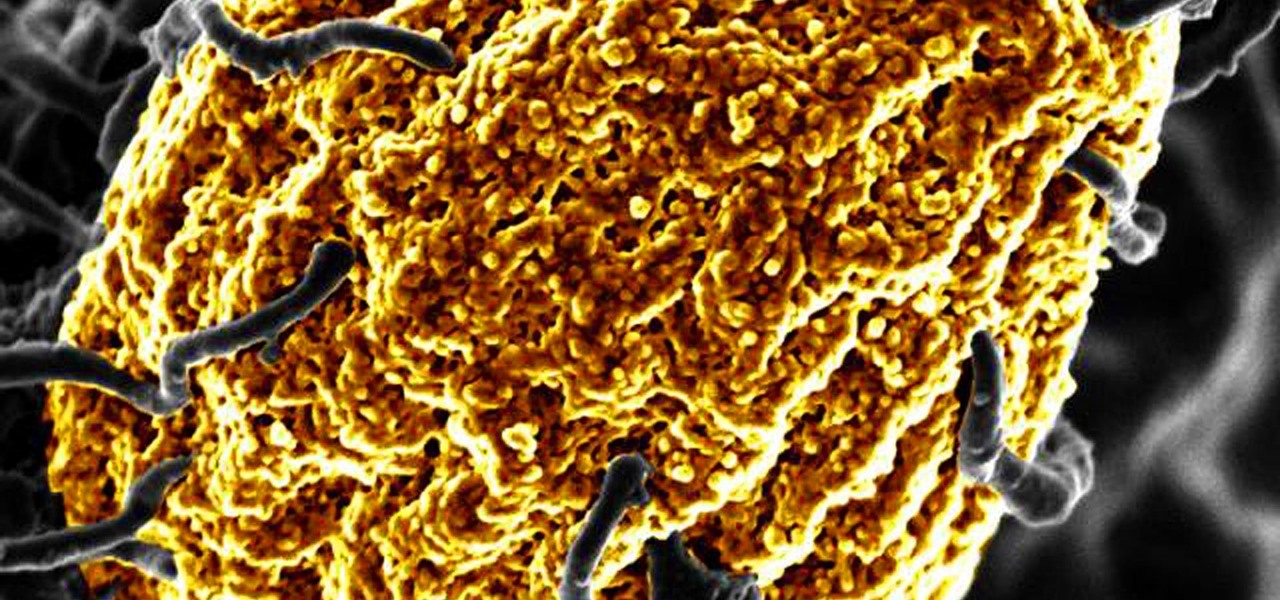
Wound infections don't usually enter the blood and become systemic, spreading the infection throughout our bodies, and there's a good reason for that: Our bodies actively work to prevent it, according to research that discovered a new use for a protein first discovered decades ago.
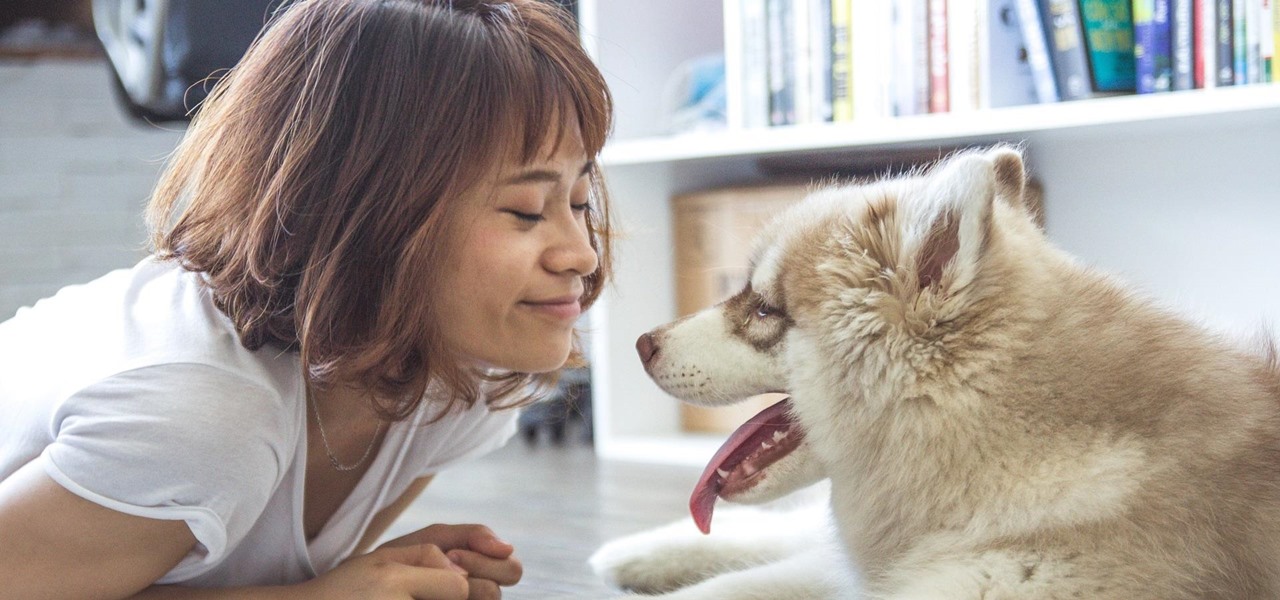

Our canine best friends could spread our bacterial worst nightmare, according to a recent study. The problem with drug-resistant bacteria is well known. Overused, poorly used, and naturally adaptive bacteria clearly have us outnumbered. As science drives hard to find alternative drugs, therapies, and options to treat increasingly resistant infections, humans are treading water, hoping our drugs of last resort work until we figure out better strategies.
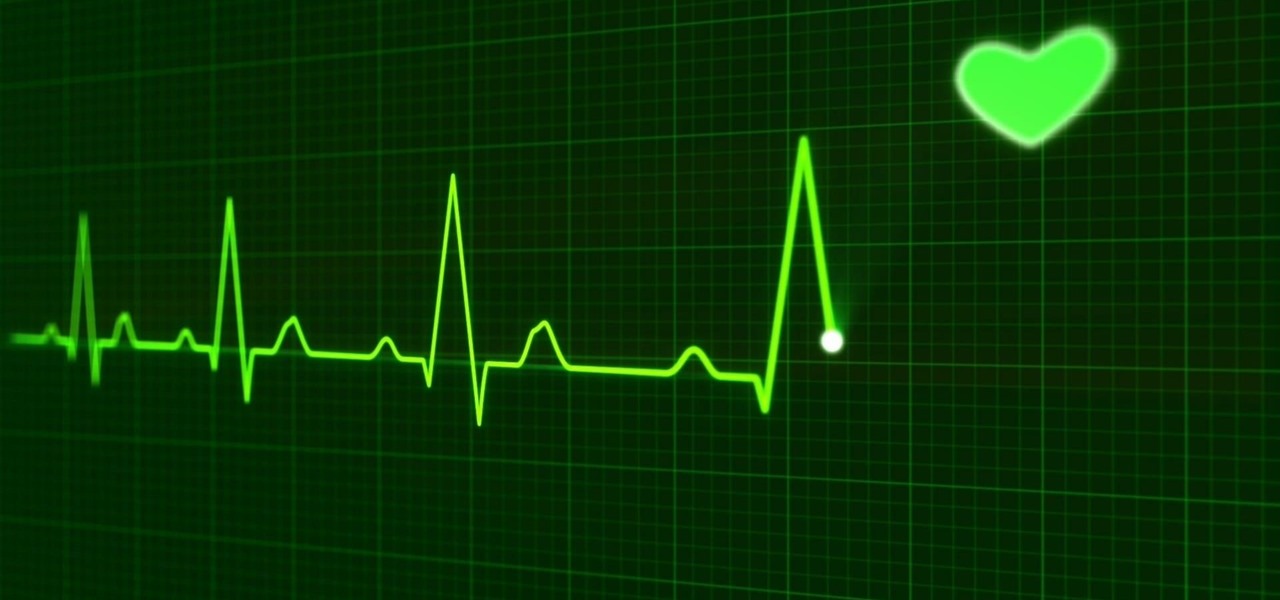

Electrical impulses course through our heart and keep it beating. That's why a jolt from an automated external defibrillator can boost it back into action if the beating stops. But new research says there may be more to keeping a heart beating than just electrical impulses.
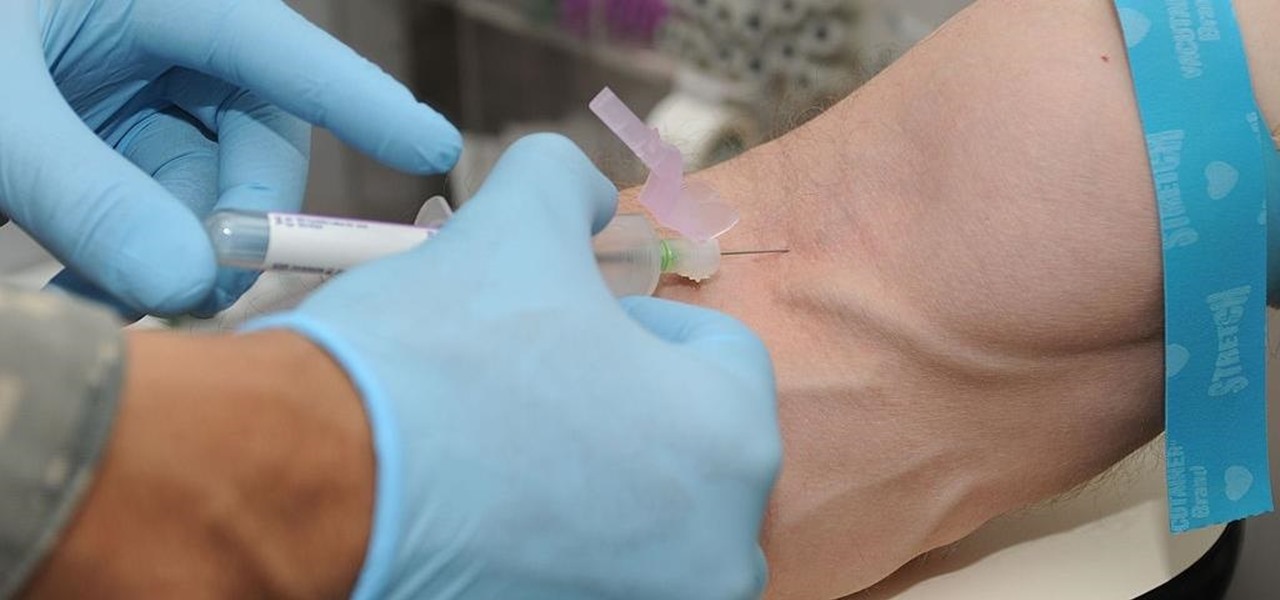
US blood banks have assured the American public that they have the tools to prevent a Zika contamination, despite the rapid spread of the disease.

How can bacteria that lives in the throat of 10%–35% of people—without causing an infection—cause life-threatening meningitis and sepsis in others?

When the mosquito that carries the malaria parasite (Plasmodium falciparum) bites someone, the parasite must travel to the liver where it undergoes part of its lifecycle before infecting red blood cells and spreading to its next host. Until now, the first step of how the parasite gets to the liver hasn't been clear.

There's now more reasons to make sick workers stay home—a new game theory study suggests adequate hand washing and other illness-aversion tactics aren't as useful as we thought to keep you from getting infected when a virus or bacteria is circulating.

Nokia, the Finnish telecommunications company, is about to shake things up a bit after its networks sales in the final quarter of last year declined 14% compared to sales in 2015.

Overweight kids often become overweight adults. New research suggests a couple reasons why and suggested that there may be ways to intercept that fate.

Antibiotic-resistant infections that usually occur only in hospital settings are spreading in communities, increasing hospital stays—and danger—for young children.

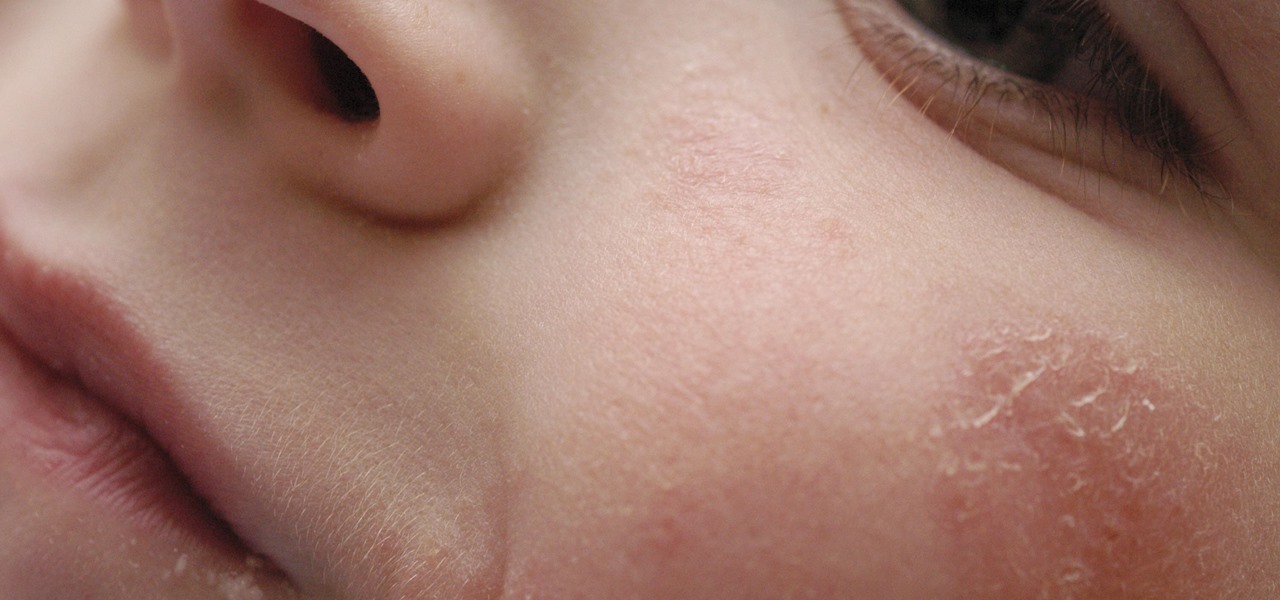
Most people know atopic dermatitis by its common name, eczema—that dry, flaky skin that itches incessantly. Along with the scratching comes frequent skin infections, often with Staphylococcus aureus.

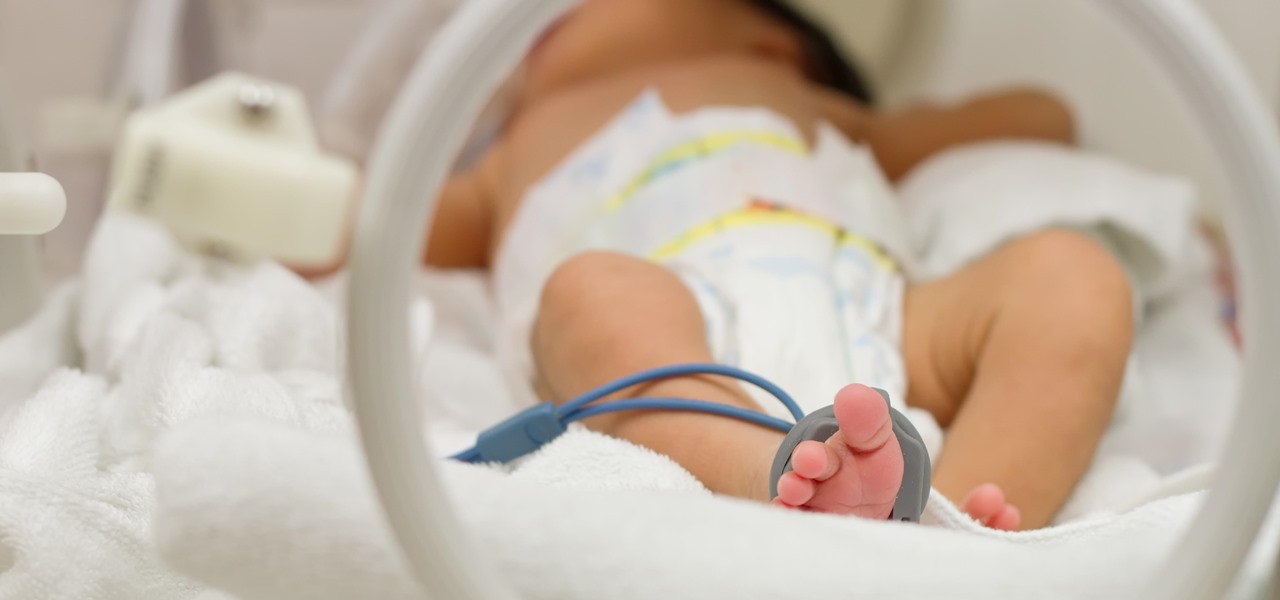
The rate of preterm birth has been increasing in the United States for unknown reasons, causing increased health risks for infants born too soon. But researchers may have found a signal that could help doctors plan ahead for, or even prevent, early birth with a simple swab of the vagina and cervix during pregnancy.

Some bacteria can already do it—generate electric current, that is—and those microbes are called "electrogenic." Now, thanks to the work of a research group from the University of California, Santa Barbara, we know how to easily turn non-electrogenic bacteria into electricity producers.

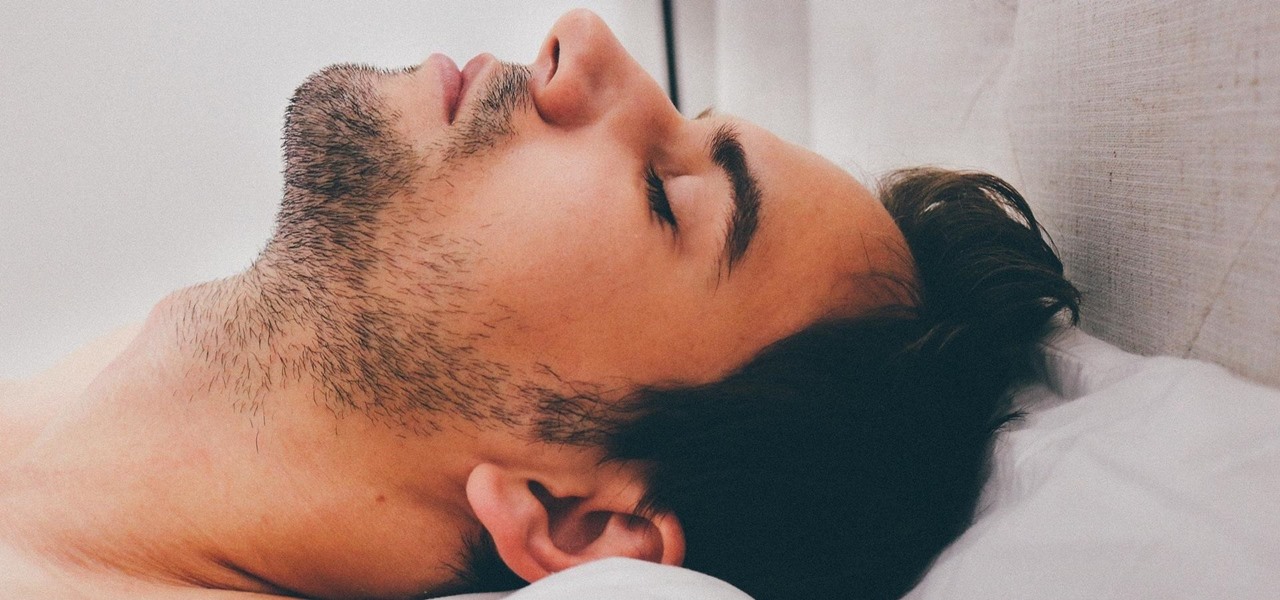
Sleep lets our body processes rest and restores us for the next day, so a bad night's sleep can ruin the following twenty-four hours and even make us feel sick. Now, new research published in the journal Sleep cements the idea that loss of sleep actually leaves us vulnerable to sickness.

Most of us equate feeling cold with catching a virus—but we've also heard plenty of debunkers proselytizing that being cold isn't what gives you the flu.

Editor's Note: The research described in the article below has been criticized and any conclusions based off this research should be examined with a skeptical eye. The article has been edited to reflect these issues.

The book that started it all (published in 1967). When Virginia Harvey wrote this book, she remarked that macramé was almost a lost art...

According to WitsView, 8-inch displays will rule the tablet scene this year at 11.9% market share, compared to yesteryear's 2.6% market share. By year's end, it'll be almost 18%.

If you want to quickly pick up a new skill over the holidays, learning to build your own Apple apps is one of the most impressive ones you can work on. This complete course bundle on SwiftUI and iOS 14 will have you submitting your own iOS apps to the App Store in just two weeks. Right now, The iOS 14 & SwiftUI Bootcamp Bundle is on sale at 95% off, for just $24.99 (regular price $600).

When trying to get fit, something that can easily be overlooked is your overall sleep quality. Your body needs sleep to recharge and it helps to maintain a healthy lifestyle, there's no denying it. Luckily, Google Fit can help you track your sleeping habits without having to jump through any hoops along the way.

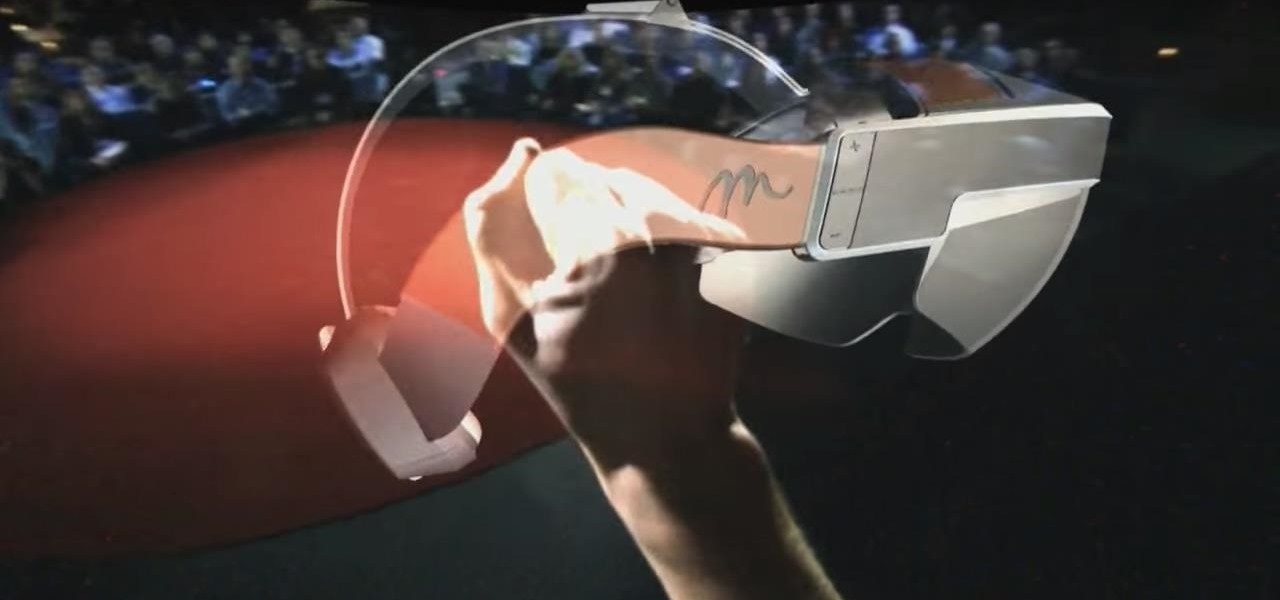
Despite its status as a hot commodity amongst emerging technologies, the augmented reality industry is not immune to the ebbs and flows that occur in every industry.

The augmented reality industry has a bright future built on innovation and growth, but that doesn't mean we can't look back at the close of the year to see what the industry has accomplished from a business perspective.

Investors continue to bet on augmented reality, both for short-term returns and long-term plays. This week, Niantic reportedly picked up another round of funding from Samsung and others, based on the success of PokémonGO and the prospects for future revenue. Likewise, investors see value in WaveOptics, whose waveguide displays could make consumer smaller AR smartglasses possible within the next year.

US customers might soon get access to their first Xiaomi smartphone. The fourth largest OEM has been eyeing a US launch for years, with rumors indicating a debut by Q1 2019. Now, it looks like the Mi 8 Anniversary Edition will be the first device.

This is a tale about microbes, a man who became a hermit, and the parchment that carries both of their stories.

A vaccine against HIV might prevent the disease that we can't seem to cure. Some HIV patients make antibodies that can take down the virus, much the way a vaccine might. But, scientists haven't been able to provoke that type of response in other people. However, in a process that might work in humans, a group of researchers has successfully generated antibodies in cows that neutralize multiple strains of HIV.

When the climate changes, so do all the things that rely on the climate, including people, plants, and pathogens. A European study recently took a broad look at what kind of microorganisms are most likely to be affected as climate change heats, cools, dries, and wets the world around us.

A recent study offers information that might help combat a deadly virus that affects an estimated 300,000 people each year in West Africa.

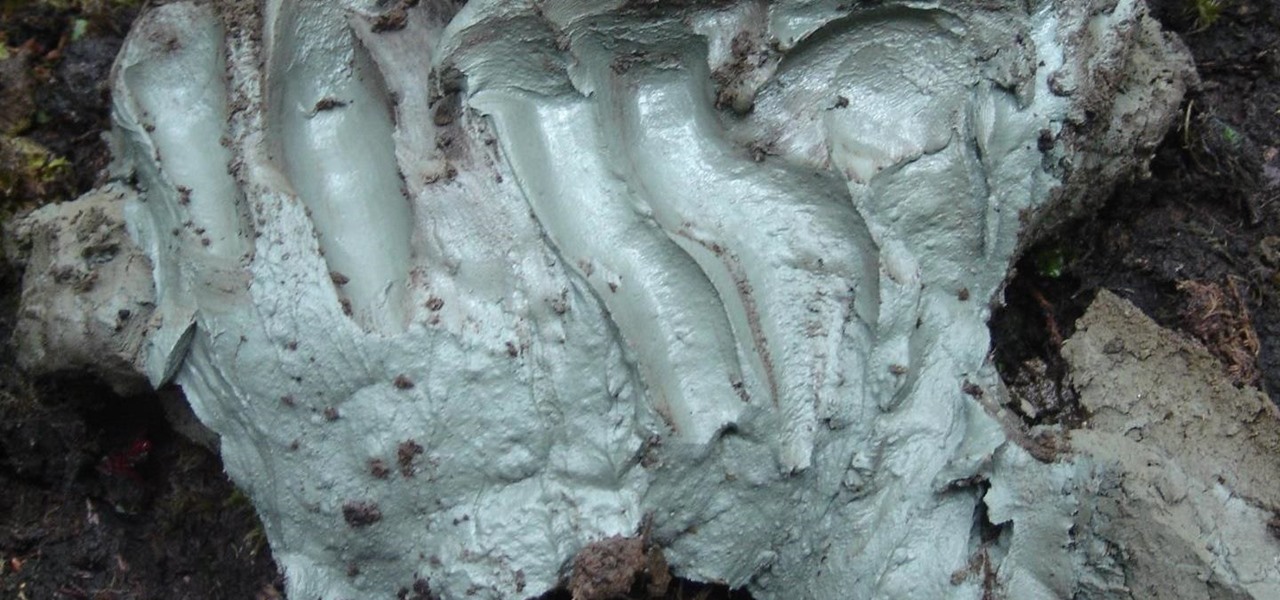
For as long as 14,000 years, the First Nations people of the Heitsuk Nation have made their home along the Central Coast of the Canadian province of British Columbia. Among the territory's inlets, islands, rivers, and valleys lie a clay deposit on the north side of Kisameet Bay, near King Island. For as long as most can remember, the tribe has used the clay as medicine. Now science says microbes that live in that clay may have important antibacterial properties.

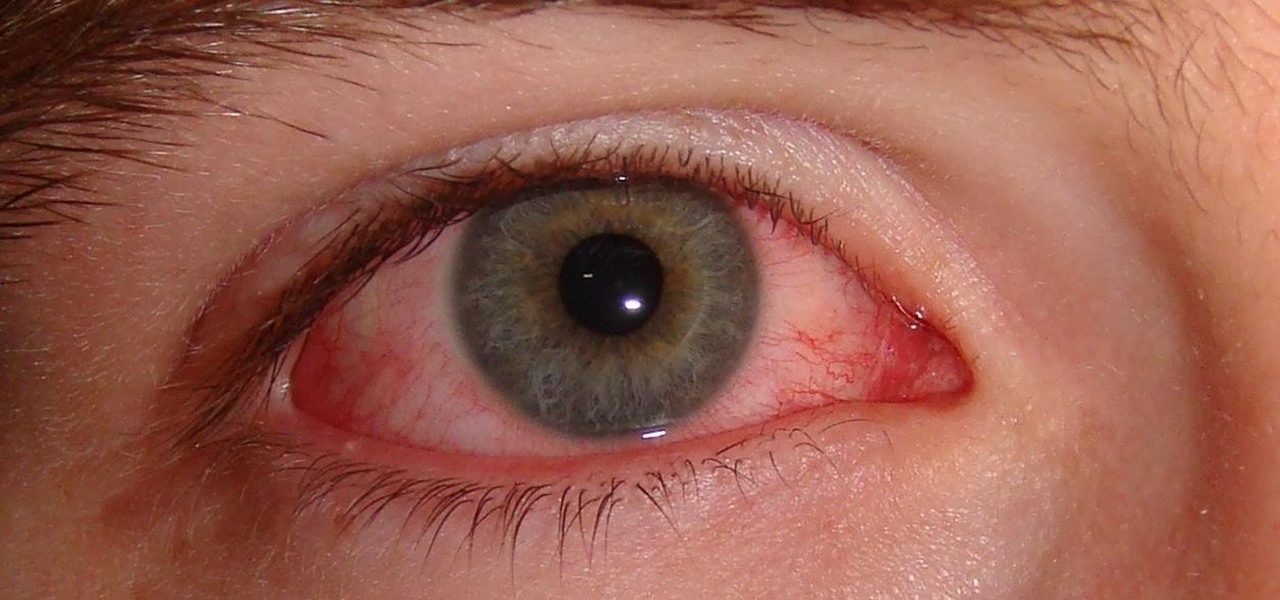
Crusty, itchy, red eyes? There is a decent chance you could have conjunctivitis, or pink eye, an infection of the thin lining around the eye and the eyelid, caused by bacteria, an allergen, virus, or even your contact lenses. Whatever the cause — you call up your doctor to get a prescription to clear it up, right? Not really.

Unfortunately, the very places we go to receive health care put us at risk for becoming infected with superbugs, bacteria exposed to so many antibiotics that they have become immune to their effects. Clostridium difficile (C. diff) is one such bacteria. It causes inflammation of the colon and rampant diarrhea that can have life-threatening consequences. Part of its virulence lies in the tough spores formed by the bacteria. They are responsible for starting infections in the colon and for spre...

Love is the spice of life — it is also the microbes that couples share through sickness and in health, through the bathroom and in a hallway.

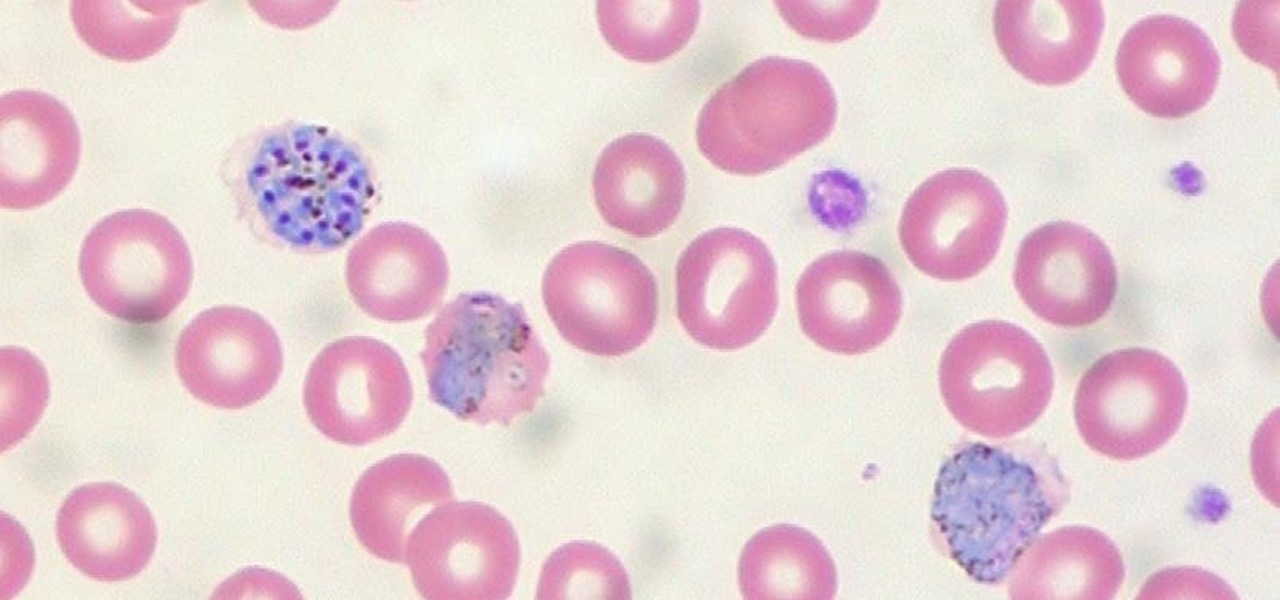
The growing list of dangerous antibiotic resistant organisms has just acquired three new members. Researchers have discovered three new species of Klebsiella bacteria, all of which can cause life-threatening infections and have genes that make them resistant to commonly used antibiotics.

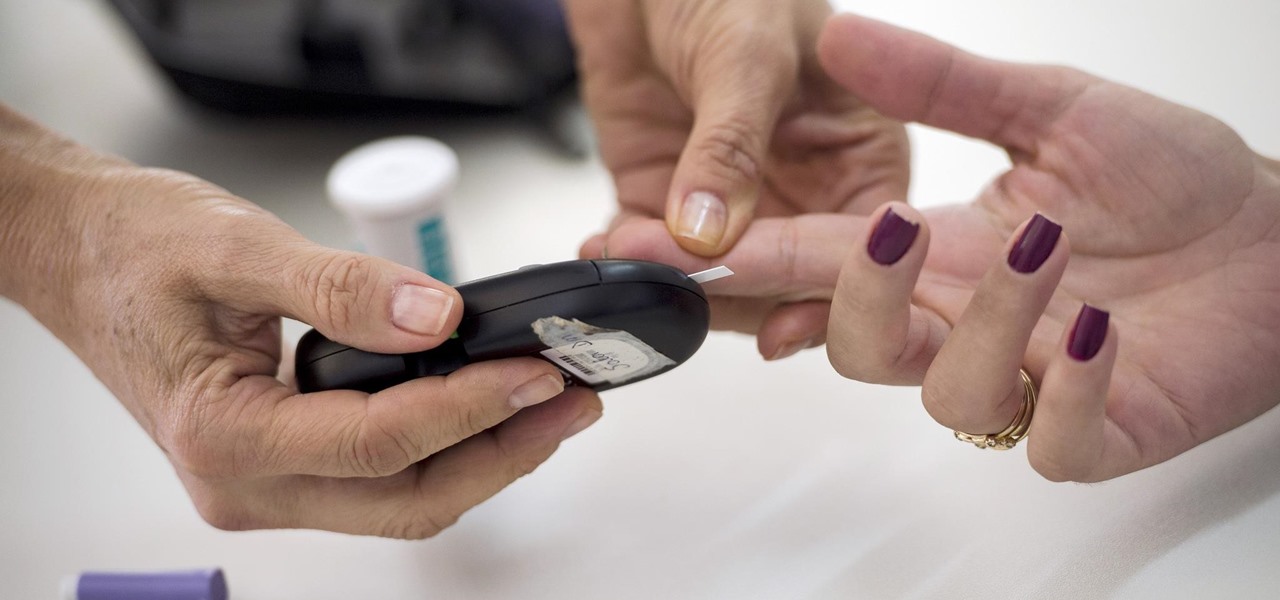
More than one in ten people in the US have type 2 diabetes — that's over 29 million people. It's characterized by excessive sugar (glucose) in the blood due to the development of resistance to insulin, the hormone that normally metabolizes glucose.

An older man dies of Zika. A younger man who cares for him catches Zika — but doctors cannot pinpoint how the disease was transmitted. While proximity to the patient is sufficient explanation for the rest of us, for microbe hunters, it is a medical mystery. Why? Zika is not known to transmit from person-to-person casually.

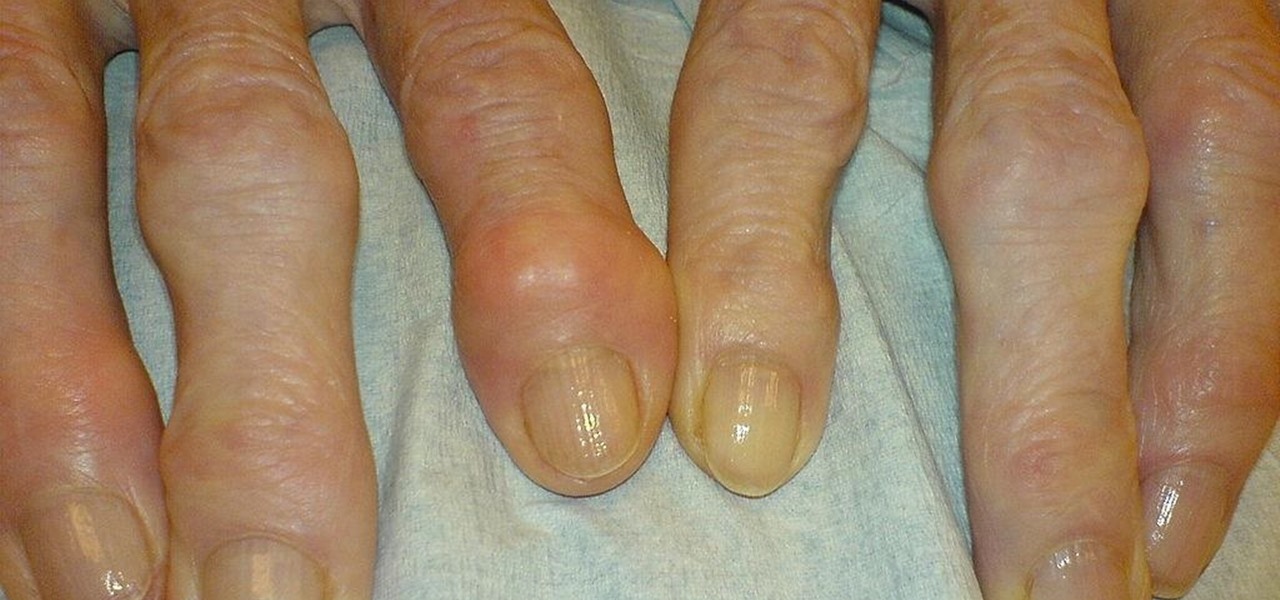
As if the swollen, painful joints of rheumatoid arthritis weren't enough, the disease is the result of our immune system turning against cells of our own body. Ever since this realization, scientists have worked to find the trigger that sets the immune system off. Scientists believe that gut bacteria may have a role in initiating the abnormal immune response. Now, a team of researchers from Boston has figured out how that might occur.

After years of telling patients to finish any prescribed course of antibiotics completely, a group of researchers in the UK say it is no longer necessary, and could even be harmful if we want to preserve the antibiotics we can still use.

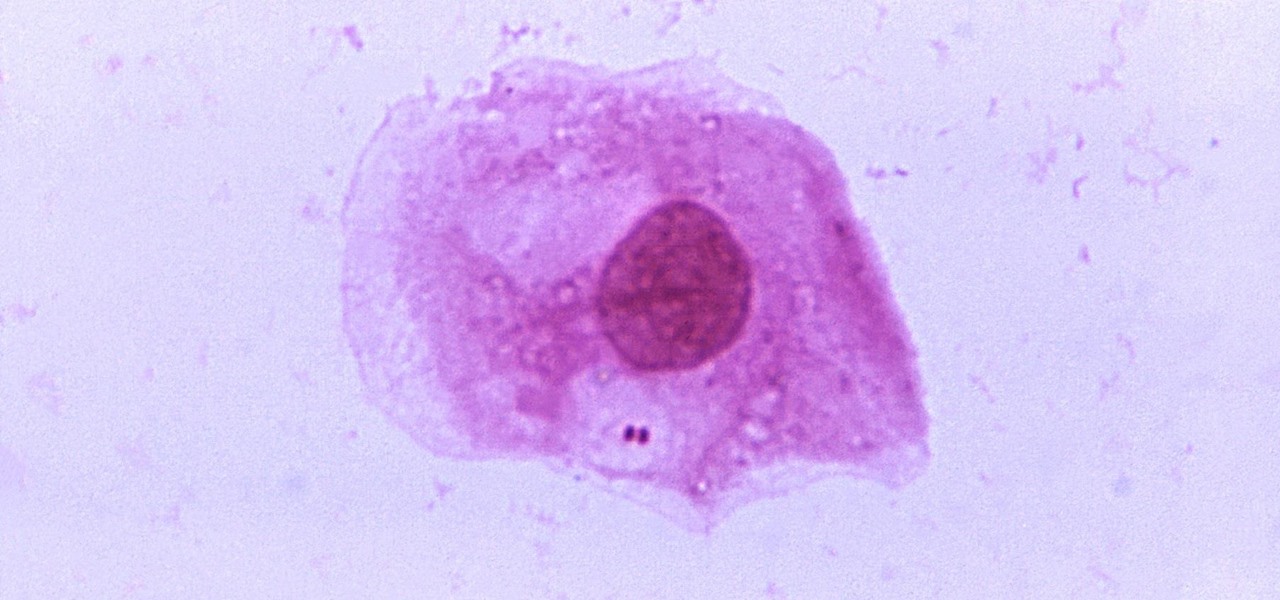
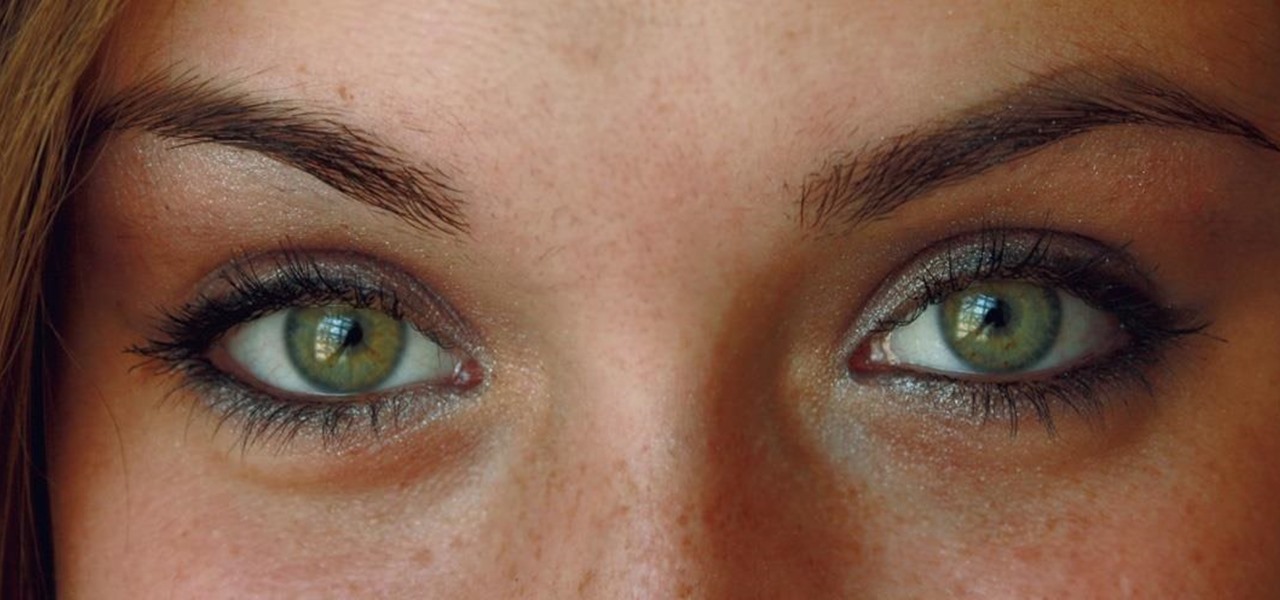
Not all bacteria in the eyes cause infection. A group of researchers from the National Eye Institue has shown that not only is there a population of bacteria on the eyes that reside there but they perform an important function. They help activate the immune system to get rid of bad, potentially infection-causing — pathogenic — bacteria there.