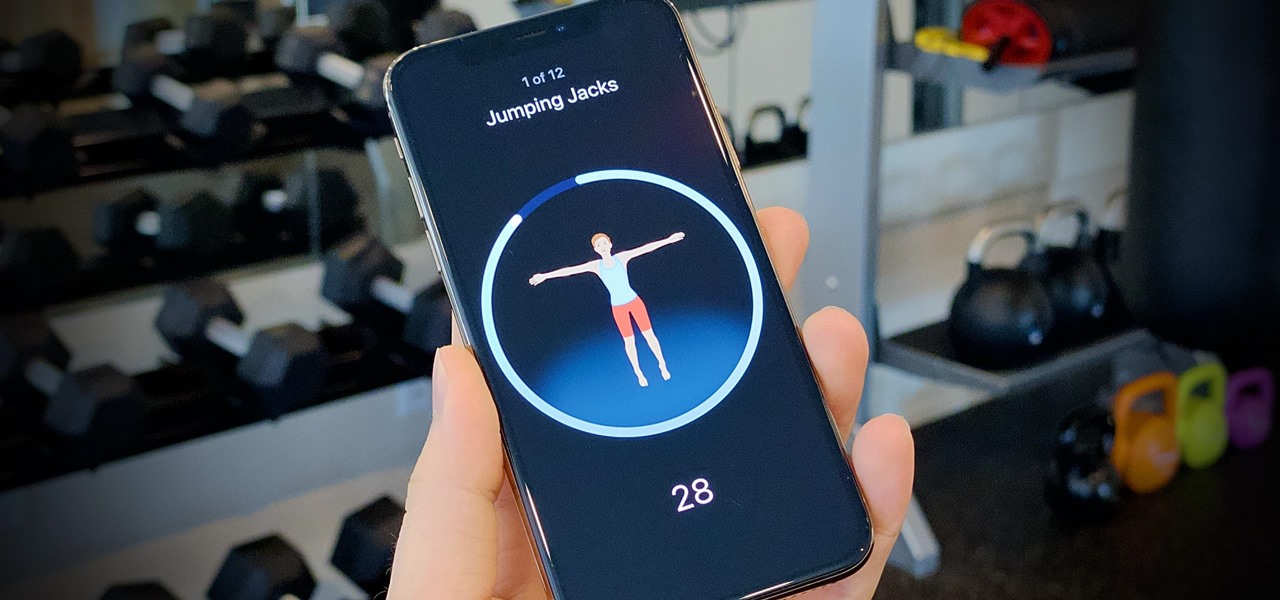
We all want to be healthy, but in practice, it can be tricky, especially from the fitness angle. Our lives seem busier and busier, which makes hitting the gym quite the challenge. What if we told you there was a real way to work on your fitness in the comfort of your own home — in just seven minutes a day? All you need is a chair, a wall, and a 7-minute workout app.
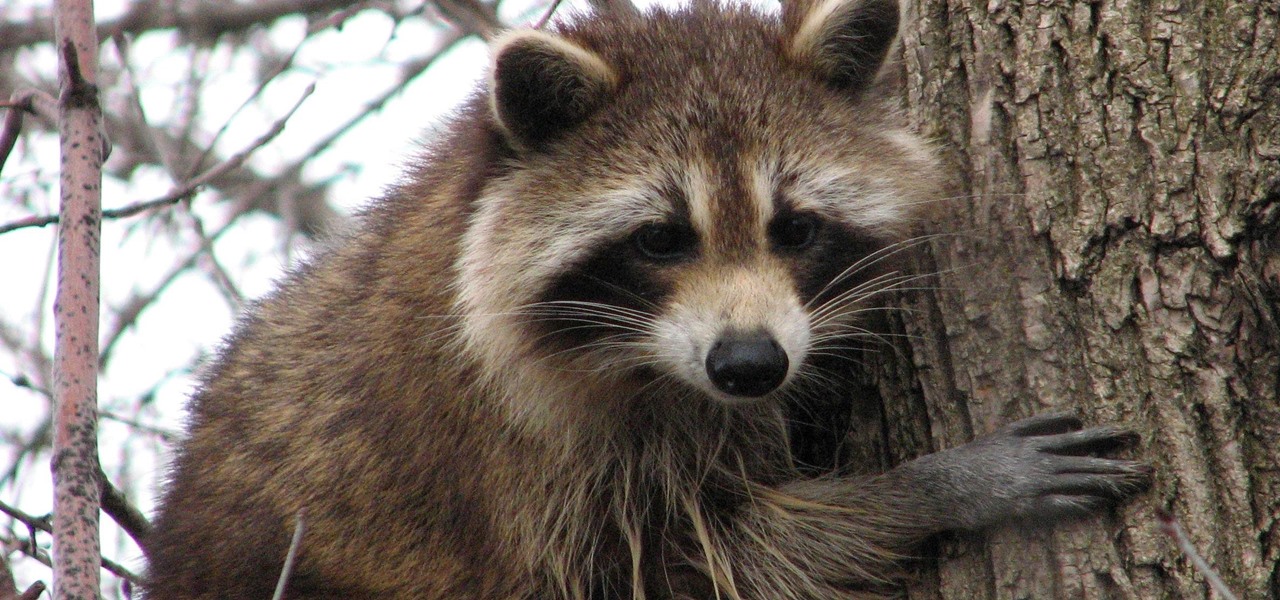

So cute, so furry, and so chock full of parasites. While raccoons are fun to watch, they are neither friendly nor clean — and they can make you sick in more ways than one.

Food is both a necessity and a joy. Many people enjoy exploring, cooking, eating, and learning about foods from around the world. But the picture isn't always rosy. A new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), highlights the ways and whereabouts of food that make us sick.
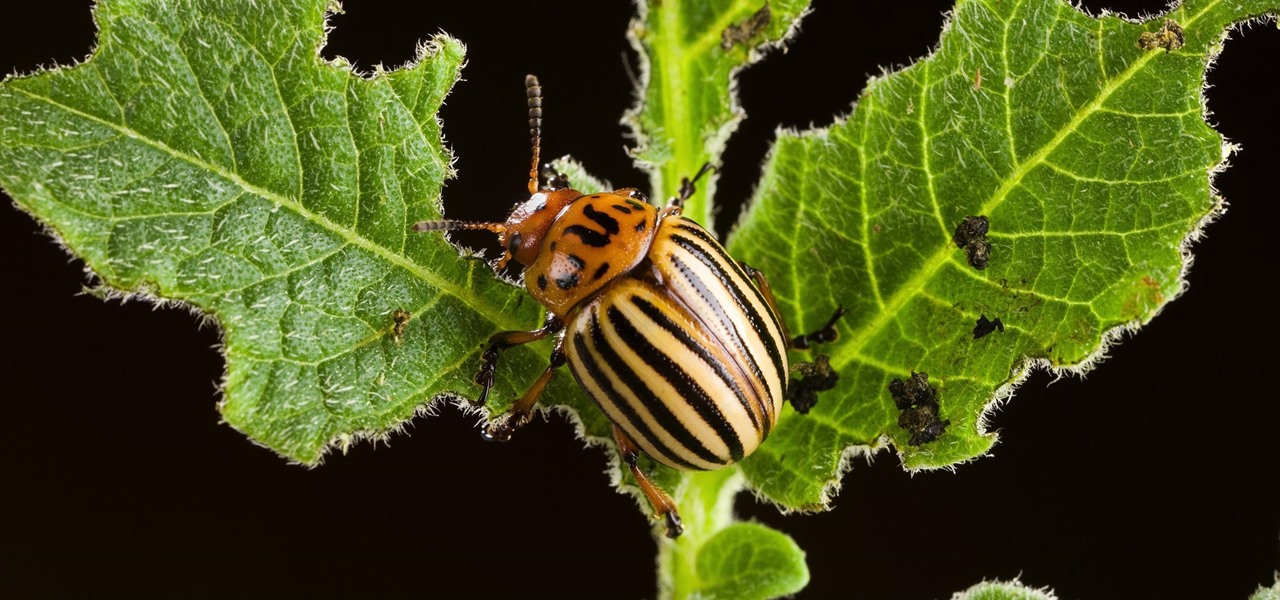

Before you bite into that beautiful tomato in your garden, the tomato fruitworm, or the Colorado potato beetle, might have beat you to it.

There are all kinds of theories—many supported by science—about what causes Alzheimer's disease. Tangles of protein called ß-amyloid (pronounced beta amyloid) plaques are prominently on the list of possible causes or, at least, contributors. An emerging theory of the disease suggests that those plaques aren't the problem, but are actually our brains' defenders. They show up to help fight an infection, and decades later, they become the problem.

When Kaci Hickox, a Doctors Without Borders nurse, returned to New Jersey from working with Ebola patients in West Africa in 2014, she was surprised by her reception. Instead of a quiet return to her home in Maine after four weeks on the front line of Ebola treatment, she was quarantined by the State of New Jersey in Newark. She later filed a lawsuit in U.S. District Court for violation of her civil rights, false imprisonment, and invasion of privacy.

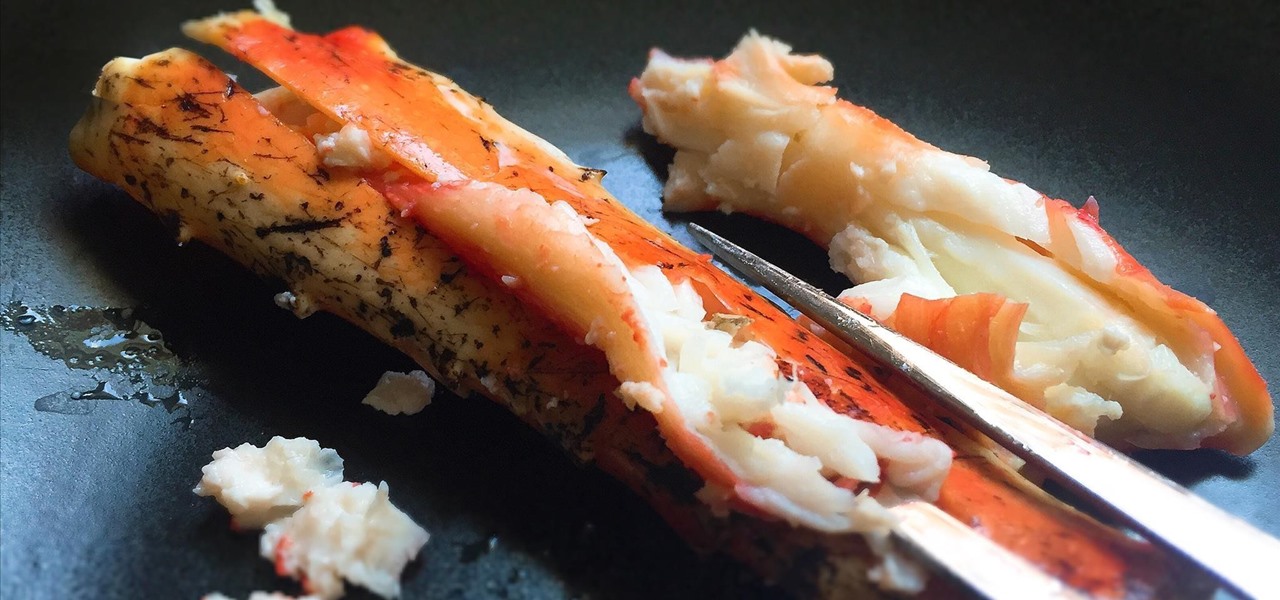
For many of you, the carving fork only comes out at Thanksgiving as an essential turkey-slicing aid. Perhaps you pull it out of the knife block to slice up the occasional roast. But the carving fork (also known as kitchen fork) can be used for many more tasks around the kitchen, and some of the more unusual involve your favorite shellfish.

Minor mishaps occur all the time in the kitchen, whether you cut your finger while dicing an onion, scorched your hand in a grease fire, or burned the roof of your mouth because you were to eager to taste-test your killer pasta sauce.

There are a variety of ways to speed up your body’s ability to heal. Things like keeping the incision clean, resting, nutritious foods and physical therapy will get you feeling strong quickly. Avoid negativity, as it may actually slow down your recovery. No one likes to be laid up in bed after surgery. Follow the advice on your “get well soon” card and be back to your old self in no time.

Learn what to expect when receiving acupuncture therapy, its methods, procedures & techniques, and information on the ancient medical practice of acupuncture from a Chinese medicine expert in these free video clips.

Weight loss is a very important factor in society today and everyone is looking for new ways to make it easier to lose weight. Learn what to expect when receiving acupuncture therapy and how it can help with hormone balance from a Chinese medicine expert in these free video clips.

Weight loss is a very important factor in society today and everyone is looking for new ways to make it easier to lose weight. Learn what to expect when receiving acupuncture therapy and how it can help with weight loss from a Chinese medicine expert in these free video clips.

In this health video series, our experts are going to give you some techniques to use for pain relief that come from a branch of Chinese medicine called “acupressure.” Like acupuncture without needles, acupressure is a traditional therapy where one applies local pressure on the body at various strategic points.

Your iPhone's Health app has a new medications hub that can be a one-stop destination for all the medicine, vitamins, and supplements you're taking. Adding new entries is easy and well worth the effort to get reminders to take your meds, learn about drug interactions, easily share your routine, and track your history to see what is and isn't working for you.

Who's ready to let future Facebook augmented reality smartglasses read their brain? Well, ready or not, the tech giant is making progress in the area of brain control interfaces (BCI) by funding research.

Reading the augmented reality news lately has felt a bit like reading a John Grisham novel, as the business side of things has dripped with legal drama.

More than one in ten people in the US have type 2 diabetes — that's over 29 million people. It's characterized by excessive sugar (glucose) in the blood due to the development of resistance to insulin, the hormone that normally metabolizes glucose.

Once we recover from the respiratory infection pneumonia, our lungs are better equipped to deal with the next infection — thanks to some special cells that take up residence there.

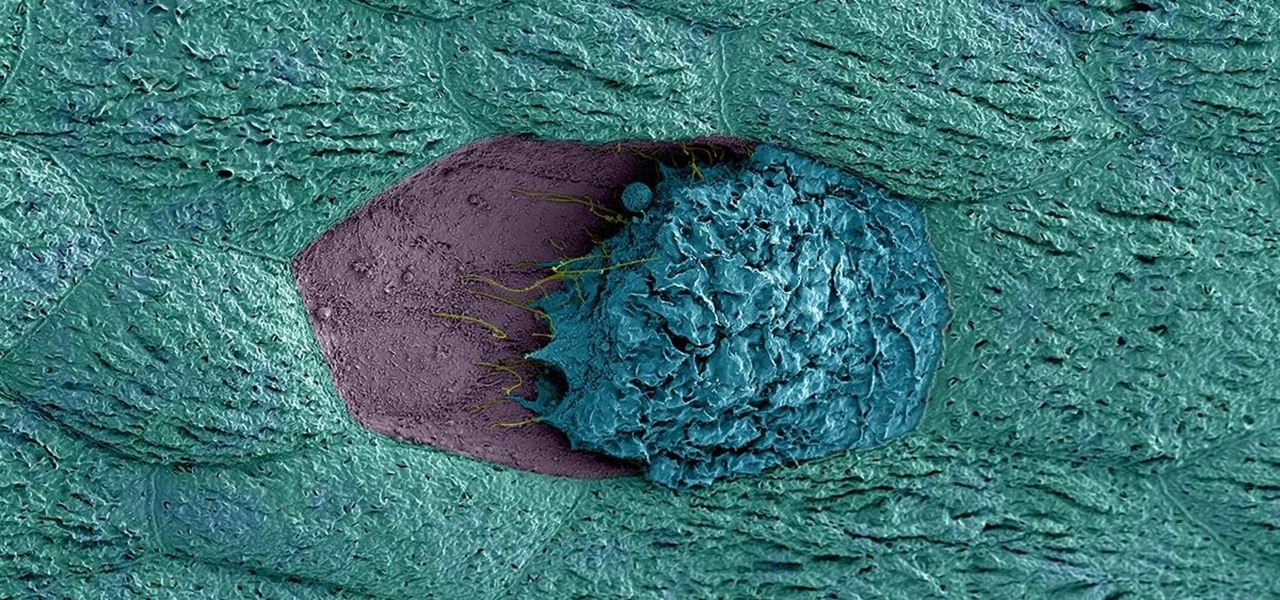
Staphylococcus aureus is a widespread bacteria — about a third of us have it on our body right now — usually in our nose or on our skin. And it probably isn't causing an infection. But, about 1% of people who have Staphylococcus aureus present have a type that is resistant to the antibiotic methicillin.

When you think about preparing for an internship, I'm sure your first thought is to go shopping for professional outfits or to brush up on technical skills. While that's all important, there's so much more for you to think about.

The herpes simplex virus (HSV) can cause devastating complications for infected newborns whose mothers have genital herpes. Understanding risk and research can help you, and your baby, when the time comes.

More bad news for patients who have undergone heart surgery in the past five years. A new study suggests about one-third of heater-cooler units used in cardiac procedures remain contaminated with a slow-growing, potentially fatal bacteria.

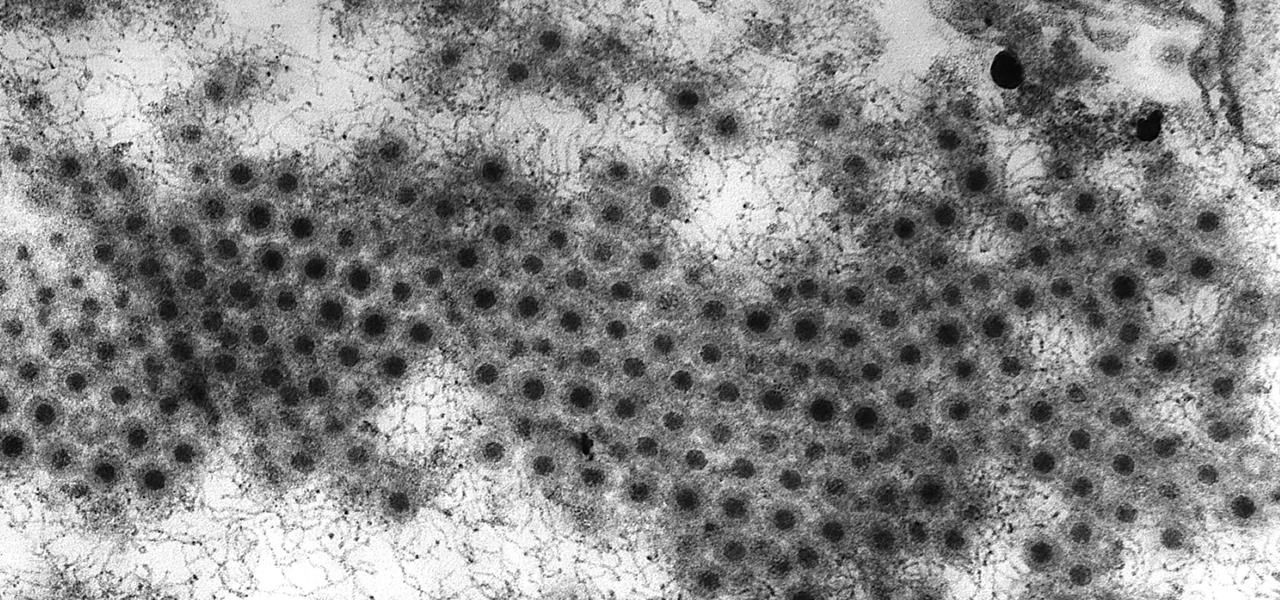
Coronaviruses are common viruses, and most of us catch one at some point — they cause about 30% of all common colds. A new accidental discovery could help fight these viruses, even the deadlier, emerging ones.

Bone loss and belly fat may no longer be certain fates of menopause, thanks to new research from an international team of scientists.

Despite the threat of superbugs, physicians continue to prescribe antibiotics when they might not be needed, and patients are suffering.

HIV infections persist despite treatment that successfully decreases viral blood levels to the point where doctors can't detect the virus. But that doesn't mean the person is cured. The virus hides in the body, not replicating, just waiting for a chance to jump out of the shadows and reemerge.

Move over whole wheat — white bread may be back in style after a new study shows that it may be your gut microbes that decide what kind of bread is best for you.

Listeria monocytogenes bacteria don't play fair. Healthy people can usually handle the food-borne infection, but the bacterial infection hits pregnant women, fetuses and cancer patients very hard. Interestingly, a new study found that other bacteria may help prevent Listeria infections in those people.

Most of us have already had an encounter with the Epstein-Barr virus, or EBV, for short. As part of the herpes family, it's one of the most common disease-causing viruses in humans. We get the disease with (or without) some nasty symptoms, then we recover. However, EBV stays in our body after the illness has ended, and it's one of the few viruses known to cause cancer.

As researchers from Yale searched our environment for compounds to aid in the battle against drug-resistant bacteria, they got an unlikely assist from ticks.

In the worst measles outbreak in the state since 1990, the Minneapolis Department of Heath races to contain the spread of an infection believed to have originated from an infected traveler. Mistaken attitudes and unvaccinated travelers are creating a world of hurt and disease for Americans. A recent study found that more than half of eligible travelers from the US are electing to skip their pre-trip measles vaccine.

Being infected with HIV means a lifetime of antiviral therapy. We can control the infection with those drugs, but we haven't been able to cure people by ridding the body completely of the virus. But thanks to a new study published in Molecular Therapy by scientists at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine (LKSOM) at Temple University and the University of Pittsburgh, all that may change.

Colorado State University scientists have developed new tech that quickly identifies the presence of Zika virus in mosquito populations — and in human body fluid.

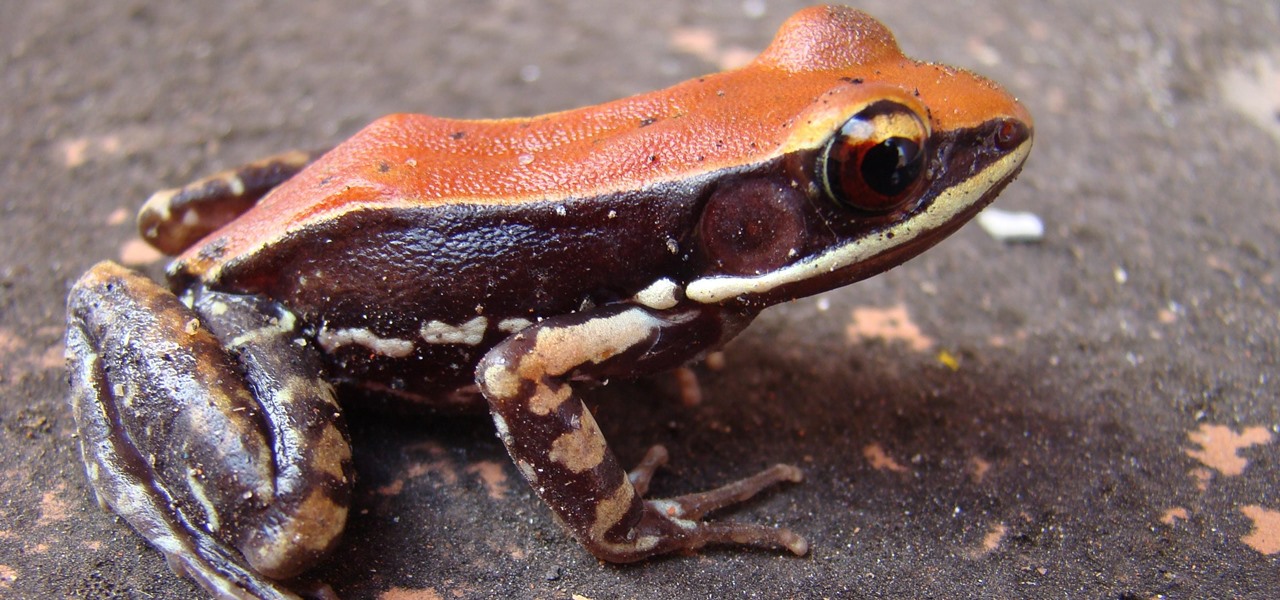
Our quest to find novel compounds in nature that we can use against human diseases —a process called bioprospecting — has led a research team to a small frog found in India. From the skin slime of the colorful Hydrophylax bahuvistara, researchers reported finding a peptide — a small piece of protein — that can destroy many strains of human flu and can even protect mice against the flu.

Viral infections have been the focus of attention in the development of autoimmune diseases—diseases where the body's immune system reacts to the body's own cells—because they trigger the immune system into action.

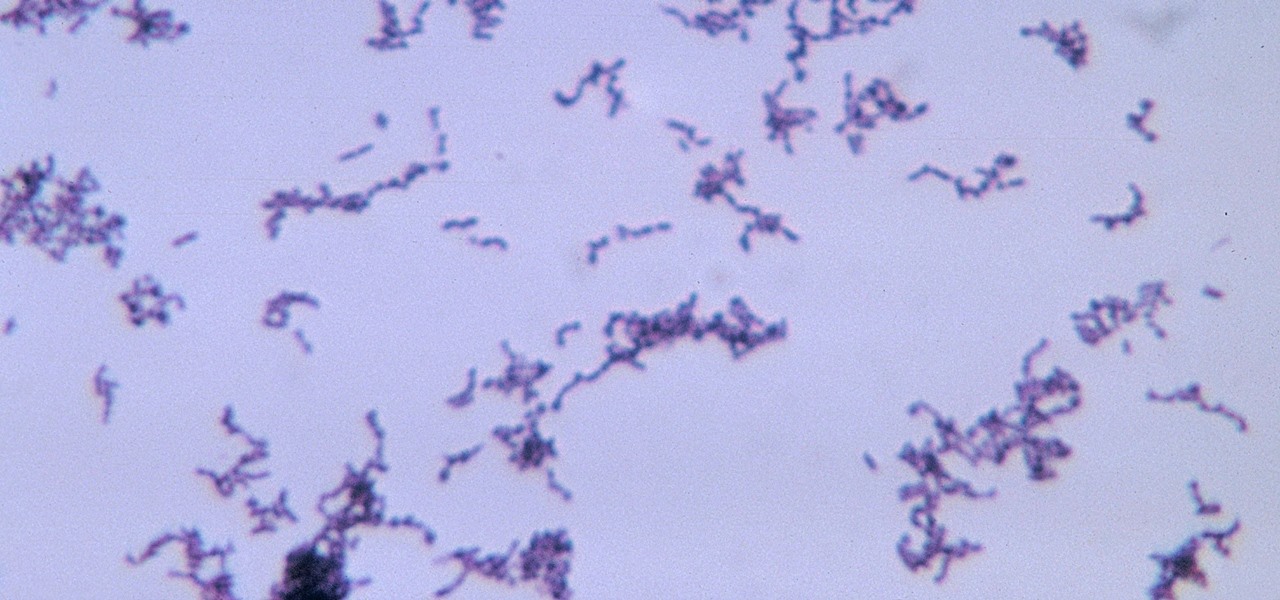
The squiggly guys in this article's cover image are Propionibacterium acnes. These bacteria live in low-oxygen conditions at the base of hair follicles all over your body. They mind their own business, eating cellular debris and sebum, the oily stuff secreted by sebaceous glands that help keep things moisturized. Everybody has P. acnes bacteria—which are commonly blamed for causing acne—but researchers took a bigger view and discovered P. acnes may also play a part in keeping your skin clear.

To keep fungal pathogens at bay in their crowded homes, wood ants mix potions to create powerful protection for their nest and their young.

Most females have had at least one urinary tract infection in their lifetimes. Recurrent UTIs are particularly problematic in young, sexually active women, where about 80% of the infections are caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli, better known as E. coli.

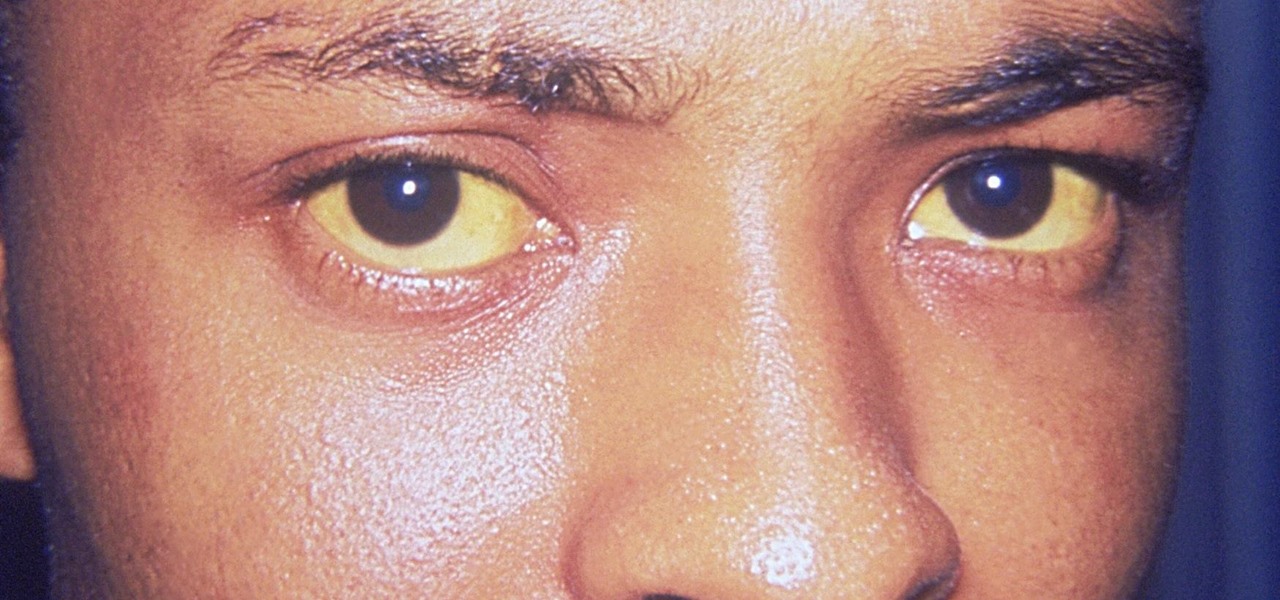
Yellow fever has emerged again in Brazil, causing death and disease to people unprepared for this mosquito-borne illness.

In the past, infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) commonly led to dementia as the virus made its way to the brain. Even in effectively treated people, HIV can hide out and replicate in places like the brain, where it's tough to detect. That's why it's very concerning that half of all HIV-infected patients still report cognitive problems.