Containers are isolated software instances representing applications, servers, and even operating systems—complete with all of their dependencies, libraries configuration files, etc.—and they're taking over the corporate world. The ephemeral, portable nature of containers help them stay current and speedy, and they can work on pretty much any computer, virtual machine, and cloud.

Welcome back, my budding hackers! This is the initial post of a new series on how to hack Facebook. It's important to note here that each hack I'll be covering is very specific. I have said it before, but I feel I need to repeat it again: there is NO SILVER BULLET that works under all circumstances. Obviously, the good folks at Facebook have taken precautions to make certain that their app is not hacked, but if we are creative, persistent, and ingenious, we can still get in.

If you want to carry a variety of network adapters without looking suspicious, a perfect solution is accessing them through Airserv-ng. Tucked away in the Aircrack-ng suite, this tool allows a hacker to plug any number of network adapters into a Raspberry Pi and access them over a Wi-Fi or Ethernet connection.

In 2019, the Raspberry Pi 4 was released with specs including either 1 GB, 2 GB, or 4 GB of memory, a Broadcom BCM2711B0 quad-core A72 SoC, a USB Type-C power supply, and dual Micro-HDMI outputs. Performance and hardware changes aside, the Pi 4 Model B runs Kali Linux just as well, if not better, than its predecessors. It also includes support for Wi-Fi hacking on its internal wireless card.
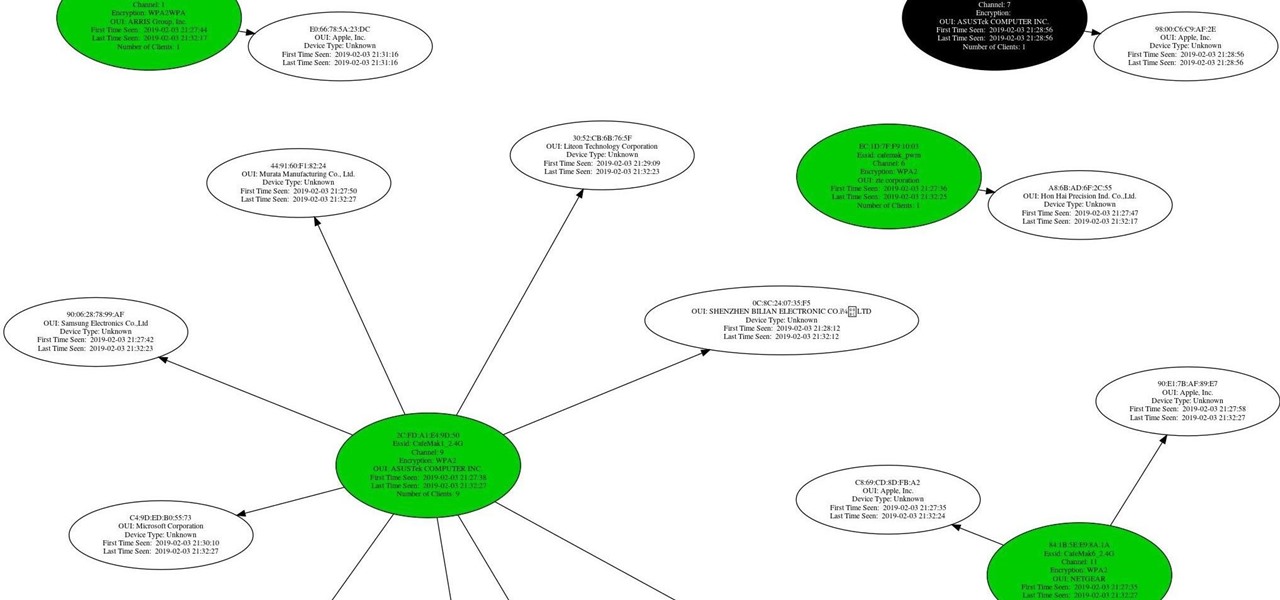
What if you could easily visualize which access point every Wi-Fi device nearby is connected to in a matter of seconds? While programs like Airodump-ng can intercept this wireless information, making it easy for hackers to use and understand is another challenge. Fortunately, a tool called Airgraph-ng can visualize the relationships between Wi-Fi devices from only a few seconds of wireless observation.

Greetings my fellow hackers.

Welcome back, my neophyte hackers! I have already done a few tutorials on password cracking, including ones for Linux and Windows, WEP and WPA2, and even online passwords using THC Hydra. Now, I thought it might be worthwhile to begin a series on password cracking in general. Password cracking is both an art and a science, and I hope to show you the many ways and subtleties involved.

Many of my aspiring hackers have written to me asking the same thing. "What skills do I need to be a good hacker?"

Welcome back, my hacker trainees! A score of my readers have been begging for tutorials on how to hack Wi-Fi, so with this article, I'm initiating a new series dedicated to Wi-Fi hacks. This will probably be around 6-9 articles, starting with the basics of the technologies. I can hear you all groan, but you need to know the basics before you get into more advanced hacking. Then hopefully, developing your own hacks.

Wi-Fi tools keep getting more and more accessible to beginners, and the LAZY script is a framework of serious penetration tools that can be explored easily from within it. This powerful and simple tool can be used for everything from installing new add-ons to grabbing a WPA handshake in a matter of seconds. Plus, it's easy to install, set up, and utilize.

Hacking Wi-Fi is a lot easier than most people think, but the ways of doing so are clustered around a few common techniques most hackers use. With a few simple actions, the average user can go a long way toward defending against the five most common methods of Wi-Fi hacking, which include password cracking, social engineering, WPS attacks, remote access, and rogue access points.

If you want to follow Null Byte tutorials and try out Kali Linux, the Raspberry Pi is a perfect way to start. In 2018, the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ was released featuring a better CPU, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Ethernet built in. Our recommended Kali Pi kit for beginners learning ethical hacking on a budget runs the "Re4son" Kali kernel and includes a compatible wireless network adapter and a USB Rubber Ducky.

As was mentioned by the great OTW last week, TOR, aka The Onion Router, has had its integrity attacked by the NSA. In an attempt to reduce the anonymity granted by the service, the NSA has opened a great many nodes of their own. The purpose is presumably to trace the origin of a communication by compromising some entrance and exit nodes. Once both are compromised, it is much easier to correlate traffic with a particular individual.

Despite the security concerns that have plagued Facebook for years, most people are sticking around and new members keep on joining. This has led Facebook to break records numbers with over 1.94 billion monthly active users, as of March 2017 — and around 1.28 billion daily active users.

The $35 Raspberry Pi is an amazingly useful single-board computer (SBC) with a good balance of price, performance, and connectivity options. But for some projects, it just isn't enough. Whether you need more computing power, a smaller size, or better machine-learning capabilities, there are other options available.

Apple's macOS operating system is just as vulnerable to attacks as any Windows 10 computer or Android smartphone. Hacker's can embed backdoors, evade antivirus with simple commands, and utilize USB flash drives to completely compromise a MacBook. In this always-updated guide, we'll outline dozens of macOS-specific attacks penetration testers should know about.

Smartphones and laptops are constantly sending Wi-Fi radio signals, and many of these signals can be used to track us. In this guide, we'll program a cheap IoT device in Arduino to create hundreds of fake networks with common names; This will cause nearby devices to reveal their real trackable MAC address, and it can even let an attacker take over the phone's data connection with no warning.

Identifying security software installed on a MacBook or other Apple computer is important to hackers and penetration testers needing to compromise a device on the network. With man-in-the-middle attacks, packets leaving the Mac will tell us a lot about what kind of antivirus and firewall software is installed.

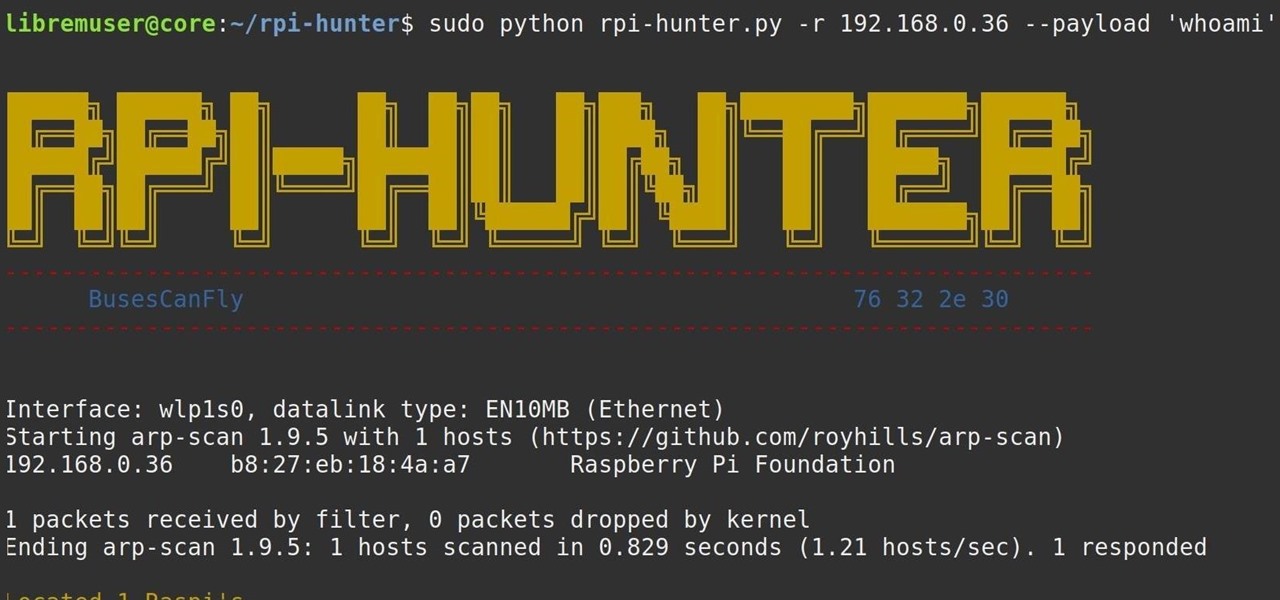
When setting up a Raspberry Pi, it's easy to overlook changing the default password. Like many IoT devices, the Raspberry Pi's default Raspbian operating system installs with a widely-known default password, leaving the device vulnerable to remote access. Using a tool called rpi-hunter, hackers can discover, access, and drop custom payloads on any weak Pi connected to the same network.

SSL stands for Secure Socket Layer. It's an encryption standard used on most sites' login pages to avoid their users' passwords being packet sniffed in simple plain-text format. This keeps the users safe by having all of that traffic encrypted over an "https" connection. So, whenever you see "https://" in front of the URL in your browser, you know you're safe... or are you?

OpenVPN is the open-source VPN (Virtual Private Network) client, used over the PPTP (Point to Point Tunneling Protocol). It allows you to connect to a remote network over a secure, encrypted connection and mask your IP addresses over all ports. Since there is only one "hop," the network speeds are barely effected and are far more secure.

Hey Everyone! Welcome to my post. We have seen a numerous GUI Tool in kali linux. Armitage, wireshark, Burpsuite etc,. Lets see an another GUI tool.

When your computer first connects to a nework, it sends out a request on the network to lease an IP from the router. The router then leases your computer an unused IP address, which is used as a unique routing address for sending traffic that is meant for you, to you. As everything tends to, this method has its flaws.

I have had a lot of people ask me, "How does my neighbor keep getting into my wireless?!". Chances are, these people are all using WEP, a deprecated wireless encryption protocol. Either that, or you are using one weak WPA passphrase.