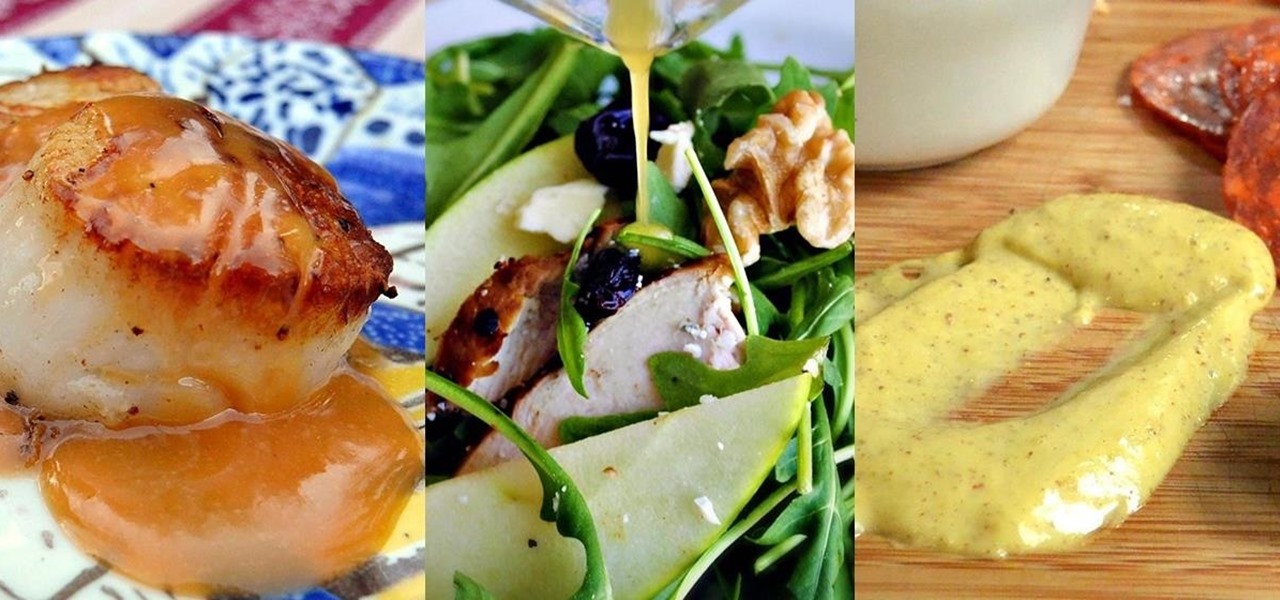
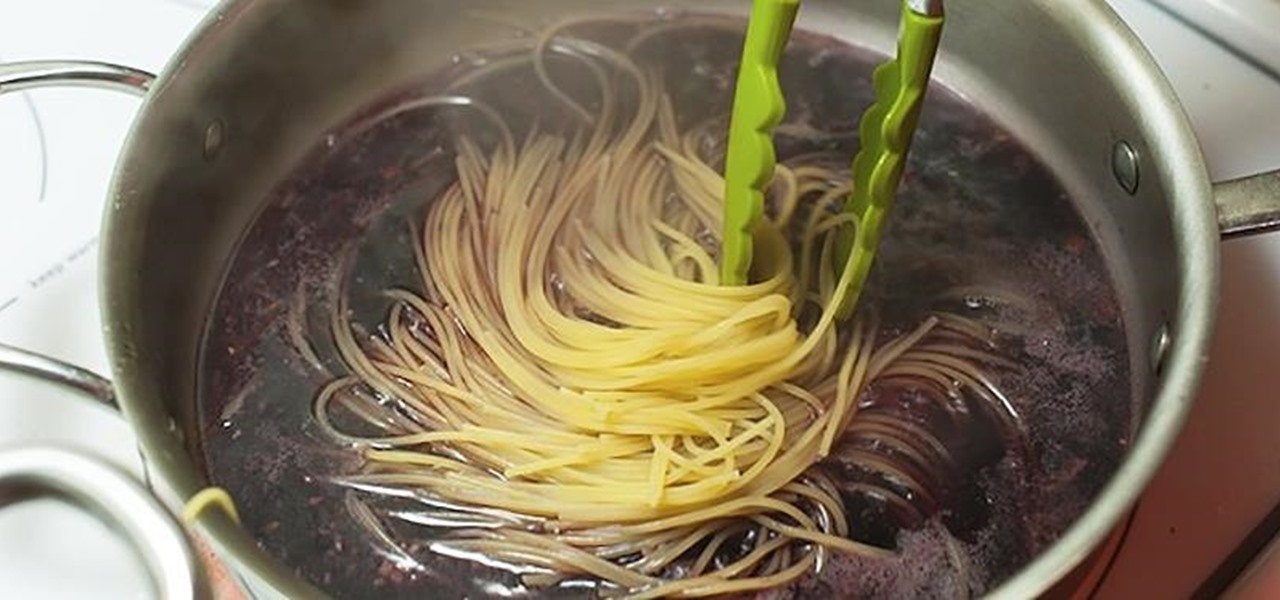
The way in which cooking can be used to both illustrate science and create a beautiful bite of food is fascinating to me. And emulsions, the results of combining liquid fat and water, are a fantastic example of science in harmony with great cooking.
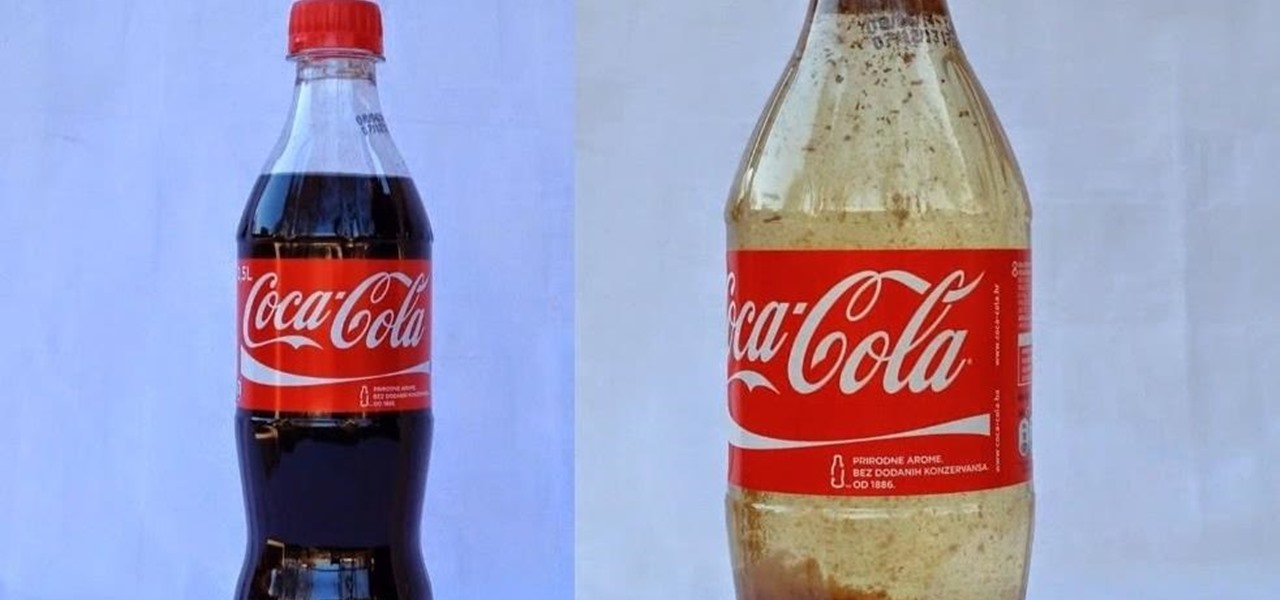

Interesting reaction coke and milk The reaction of phosphoric acid (V) to proteins in the milk - they are cut and causes a precipitate

Chances are that you've been using your microwave just to nuke leftovers, but they can do so much more than heat up last night's dinner—microwaves can help you peel garlic more quickly, get more juice out of lemons, disinfect your kitchen, dry out herbs, give beauty products new life, cause exciting explosions, and even arc weld.

The oven is arguably our most essential kitchen appliance (right alongside the fridge, freezer, and yes, even the microwave). But even though we've been using them for a few millennia, many of us know so little about our ovens that our cooking or baking can feel like a roll of the dice sometimes.
Fresh herbs can be delicate, and it's not always easy to figure out how to cut, crush, or muddle them to make the most of their flavors. Get too rough, and you have a bunch of bruised and muddy-tasting herbs, which is due to too much chlorophyll being released. Don't do enough prep, and the herbs don't release the essential oils and volatile molecules that are the foundation of their flavor.

Video: . Dent Repair - Using a Stud Welder Gun

You probably already know that cooking involves a ton of chemistry. Bread rises because of the reaction between the flour and leavener, and the delicious crust on your steak is formed by the Maillard reaction. Understanding the chemistry going on behind the scenes is one of the best ways to improve the quality of your food—it's much easier to fix a problem when you know what's causing it.

Learn how to separate two glasses that are stuck together with this Howcast video tutorial. You nested two glasses when you put them away — and now they're stuck! Gently pry them apart with this system.

New research reveals how E. coli bacteria construct elaborate and effective tunnels to pump unwanted molecules like antibiotics and other toxins out of cells. The discovery could help us better understand how antibiotic resistance occurs and give us a leg-up to beat them at their own game.

Some types of bacterial infections are notoriously tough to treat — and it's not all due to antibiotic resistance. The bacteria themselves are rugged and hard to penetrate with drugs.

The body's usual response to a bacterial infection in the blood — called sepsis — takes time. It requires a carefully orchestrated sequence of events that gets the body's immune system ramped up to deal with the invading bacteria.

Microsoft Build 2017, the first of Microsoft's big developer conferences for the year, is just a few weeks away. This very popular conference, which has been going on since 2011, is known to sell out fast. In 2015, it sold out in under an hour, and in 2016, in less than 5 minutes. This year was no different, according to VentureBeat; While not quite as fast as last year with so many rumors of HoloLens on the horizon at the time, this year's Build was sold out in 8 hours. And for this year's B...

Imagine you have mastered the perfect cherry pie for your annual work picnic but, upon taking it out of its airtight pie carrier, your heart sinks as you realize the crust has turned to mush thanks to the moisture from the filling. Sound familiar?

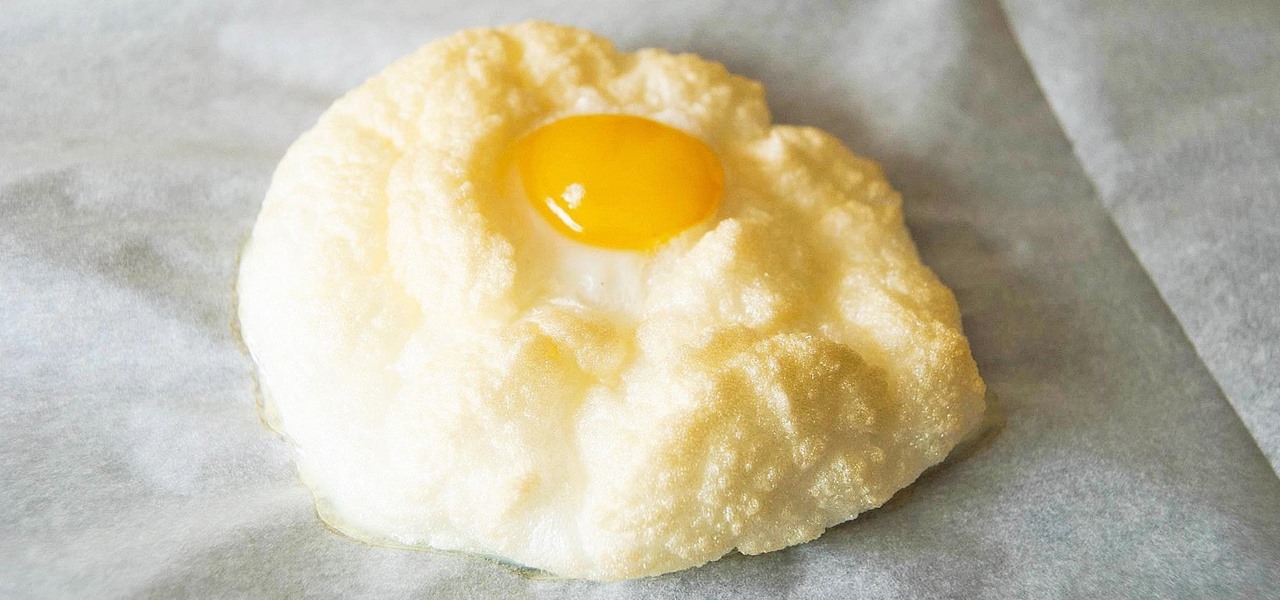
Scrambled, sunny side up, hard-boiled, soft-boiled, over easy, and poached: there are only so many ways to cook an egg before you get bored and look for inspiration somewhere else.

Living on a budget often means compromising what you want for what you need—or at least, for what's affordable. But that doesn't necessarily mean you have to compromise on flavor, especially if you know the right tips and tricks to make something spectacular out of the ordinary.

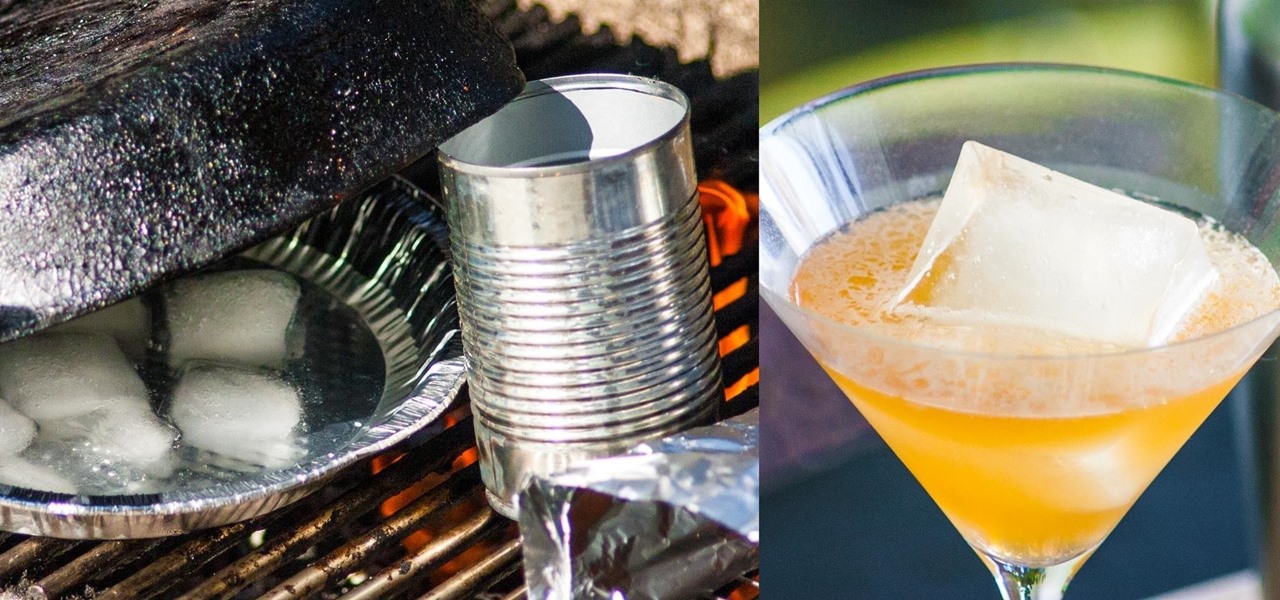
A long time ago I was reading an issue of Saveur and saw an article about a trendsetting bar in Portland. The bartender at the joint had started making enormous blocks of smoked ice for his cocktails. When a patron ordered a drink that called for the smoked ice, the bartender would chip off a large chunk and place it in a glass with the booze. Then, as the ice slowly melted, the drink would take on more and more smoky notes, and the flavor profile of the beverage would change with every passi...

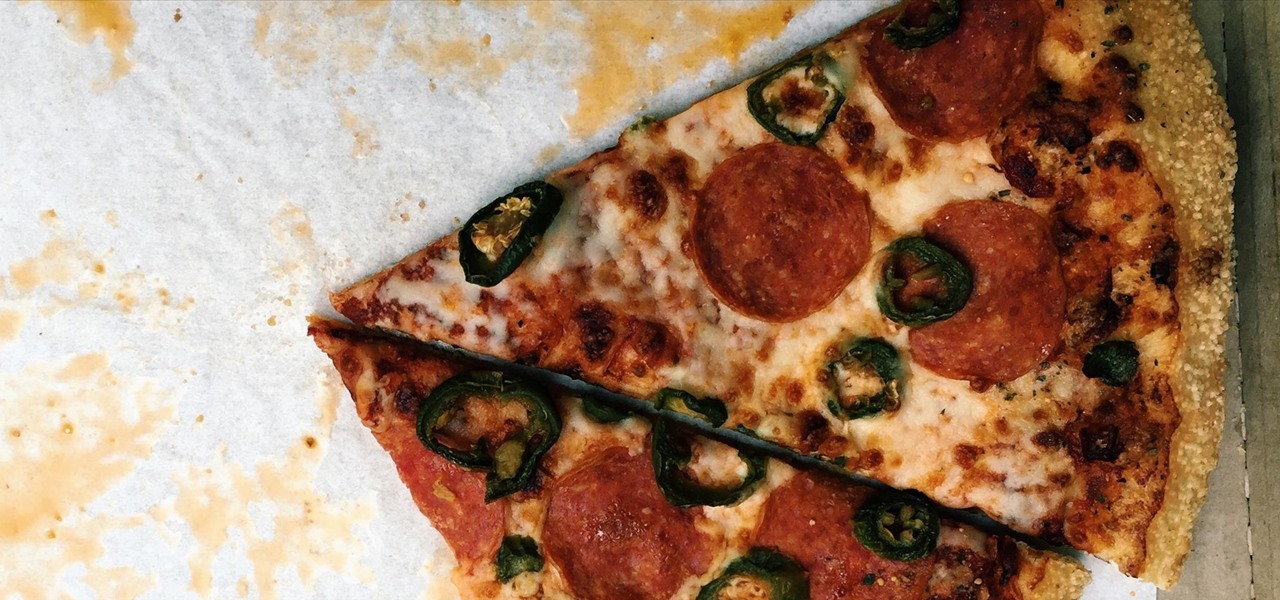
Cold pizza is the holy grail of leftovers. That's a statement that elicits a slew of impassioned feelings. Either you love the idea of biting into soft crust and cold, fatty cheese, or scowl at the idea of pizza that isn't hot, crisp, and melty. Yet if we were to stand by the former sentiment, how would we argue on its behalf? Food Science Explains Why Cold Pizza Rules

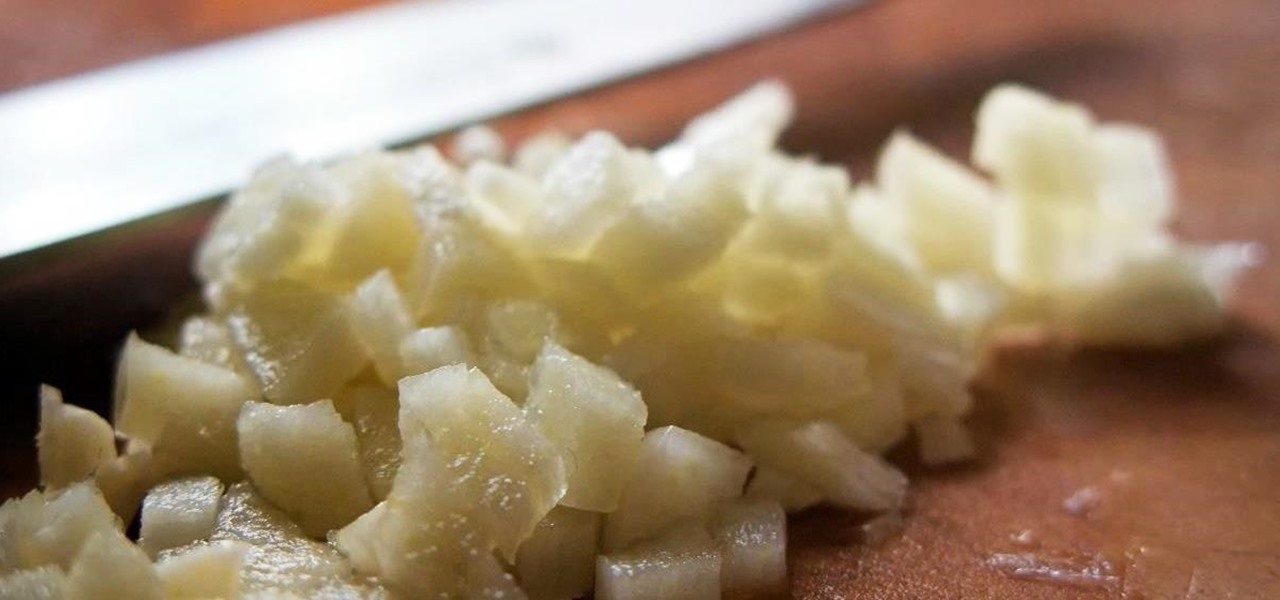
It's a shame that one of the world's tastiest foods can be such a pain to prep. Most cooks are familiar with this conundrum: chopping or crushing garlic releases a pungent liquid that causes bits of garlic to stick your knife and hands, creating a messy affair. So what is going on here? The common assumption is that the garlic is releasing some kind of oil, but the truth is that this liquid rinses away easily in water. Yet one of the basic precepts of chemistry is that oil and water don't mix.

One booze hack that's been making the rounds for years is that inserting a spoon by the handle in a champagne bottle's neck will preserve its carbonation. This is one of those tips that I wish were true. Champagne is a great thing to have around on a special occasion, and it seems a shame to pour any leftovers down the drain once its lost its fizz. While there's lots of anecdotal evidence surrounding this trick, Harold McGee and Stanford University chemist Richard Zare debunked this myth as d...

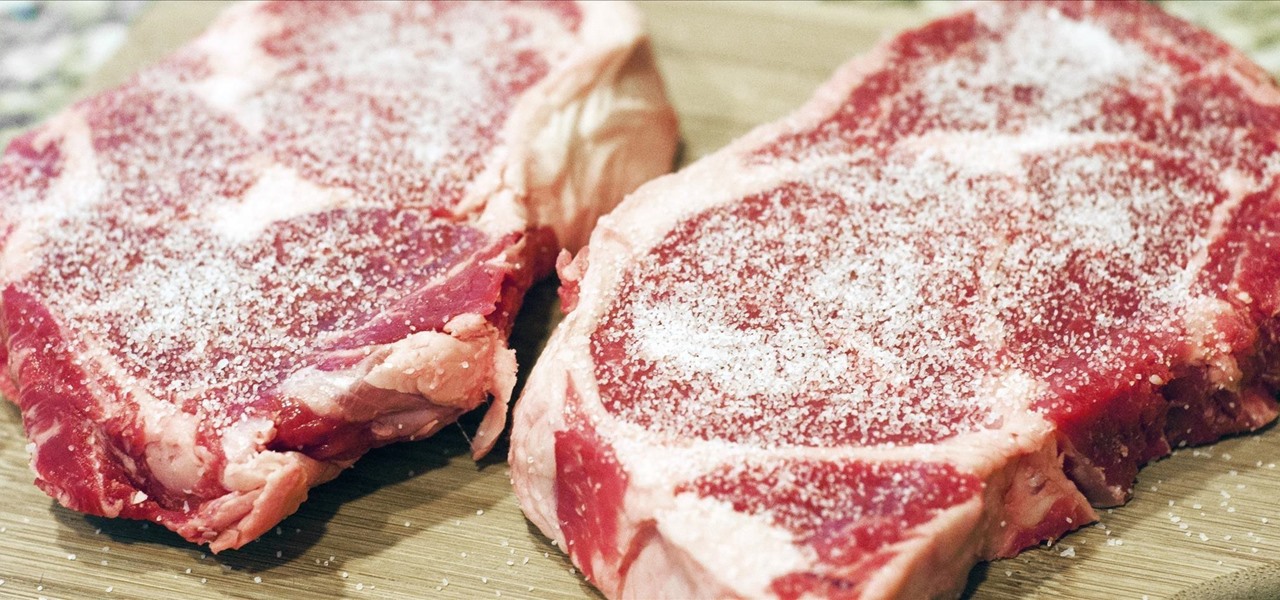
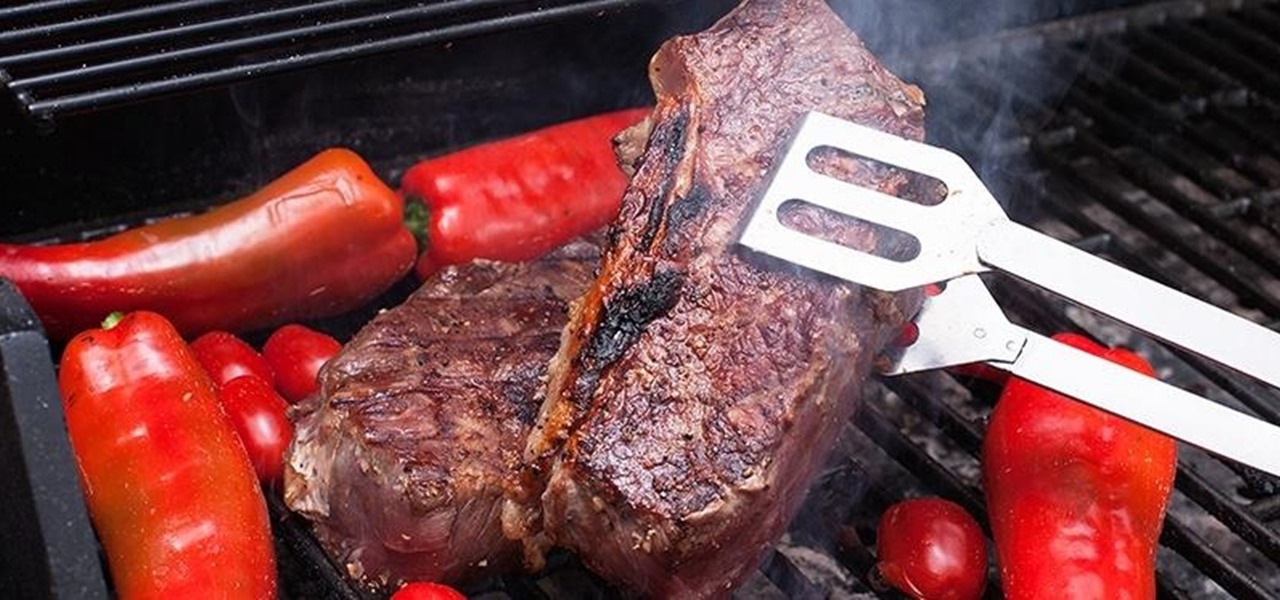
To flip, or not to flip, that is the real question. When you're nervously standing over the stove or grill, what do you do with that steak before you?

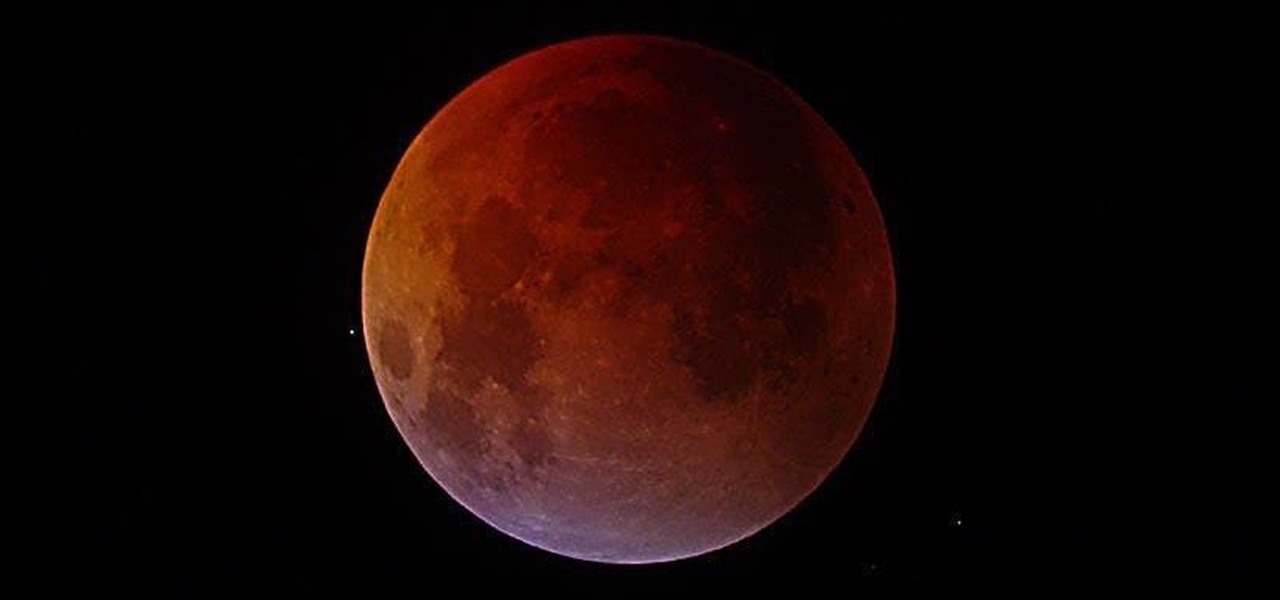
Get ready to look up in the night sky very soon, because you're in for a real treat. There will be a total lunar eclipse on the night of Monday, April 14th, and folks living in the United States, Canada, and parts of Central and South America will be able to see the moon turn a dark blood-red shade for a little over an hour. This will be the first in a series of four total eclipses that are to happen over the next two years. What Is a Blood Moon?

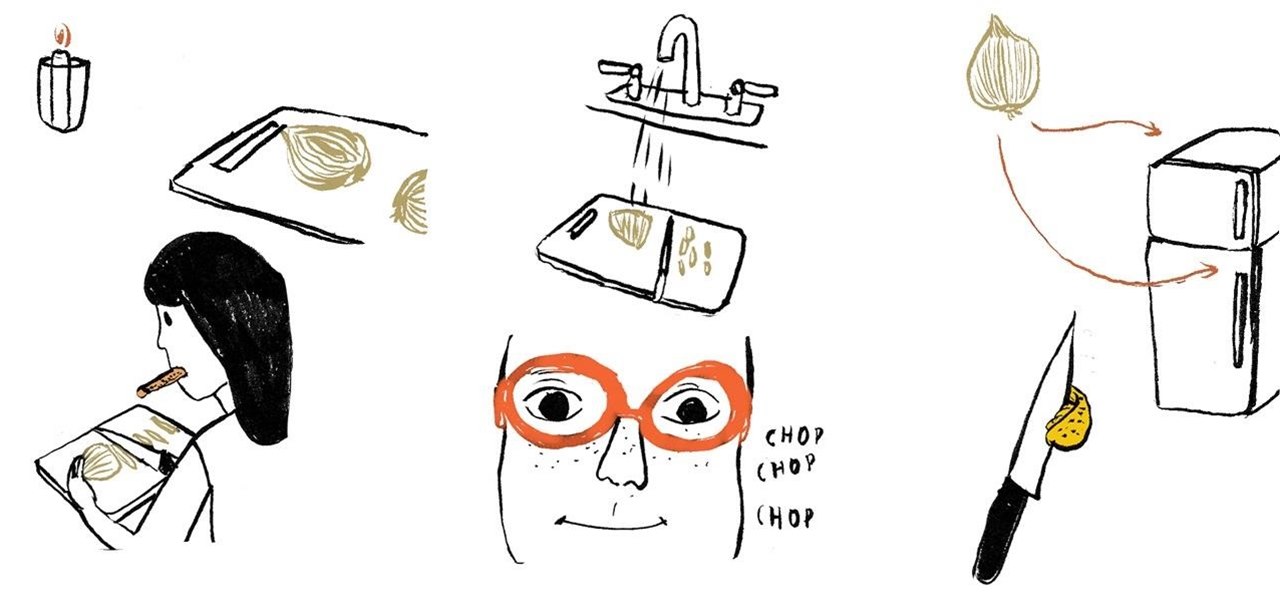
Is it possible to cut or chop onions in the kitchen without stinging eyes and looking as if you just watched the saddest movie ever? Before we get to that answer, it's important to know why we tear up when cutting raw onions in the first place. What is this irritant? Are you reacting to the odor? The answer to the latter question is "no," and the irritant responsible is amino acid sulfoxides.

Scientists know that bacteria create their own energy, get nutrients to run their cellular processes, and multiply. But, bacteria haven't been shown to respond to external mechanical stimulation or signals in a way that's similar to how our bodies respond to touch, until now.

For as long as 14,000 years, the First Nations people of the Heitsuk Nation have made their home along the Central Coast of the Canadian province of British Columbia. Among the territory's inlets, islands, rivers, and valleys lie a clay deposit on the north side of Kisameet Bay, near King Island. For as long as most can remember, the tribe has used the clay as medicine. Now science says microbes that live in that clay may have important antibacterial properties.

Montezuma's revenge, the runs, the trots, or just diarrhea — everyone gets it sooner or later. What exactly is diarrhea good for, if anything?

An innovative new wound dressing has been developed by a research team at Lodz University of Technology in Poland that uses crustacean shells to create a bandage that packs an antimicrobial punch — and even more potential to help solve a global problem.

Being infected with HIV means a lifetime of antiviral therapy. We can control the infection with those drugs, but we haven't been able to cure people by ridding the body completely of the virus. But thanks to a new study published in Molecular Therapy by scientists at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine (LKSOM) at Temple University and the University of Pittsburgh, all that may change.

Our quest to find new antibiotics has taken a turn — a turn down the road, that is. A team of scientists from the University of Oklahoma is scooping up roadkill and searching for bacteria on them that might yield the world's next antibiotic.

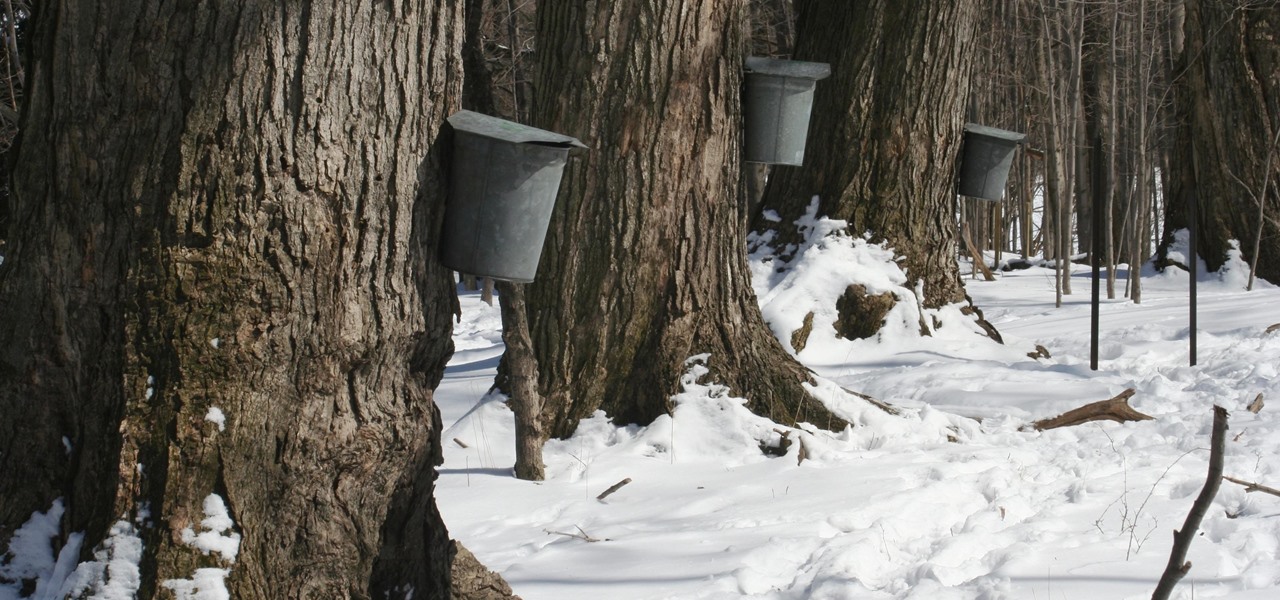
In the ongoing search to find better ways to use antibiotics, an extract made from maple syrup has some surprisingly important medical benefits.

An advance in the race to stop birth defects caused by Zika-infected mothers has been made by a team of researchers from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, New York. They have identified the process Zika uses to gain entry into the placenta, and published their findings in the journal Biochemistry.

By looking for the mechanism that allows influenza A to invade lung cells, scientists also discovered a treatment that might block the virus from taking hold there.

As fun as it is to see Fido's face light up when you feed him table scraps, American dogs are getting fat. The good news is that research is homing in on nutritional strategies to boost canine capabilities to maintain a healthy weight.

Ah, wine. The bouquet fills your nose. The rich finish fills your mouth with soft flavors of oak and raspberries. The wine warms your belly and soothes your mind. Yeast and their biochemical factory help create this feast for your senses. Thanks to a research group from France, we now have a little more information on how that process works and a little more appreciation for yeast's contribution.

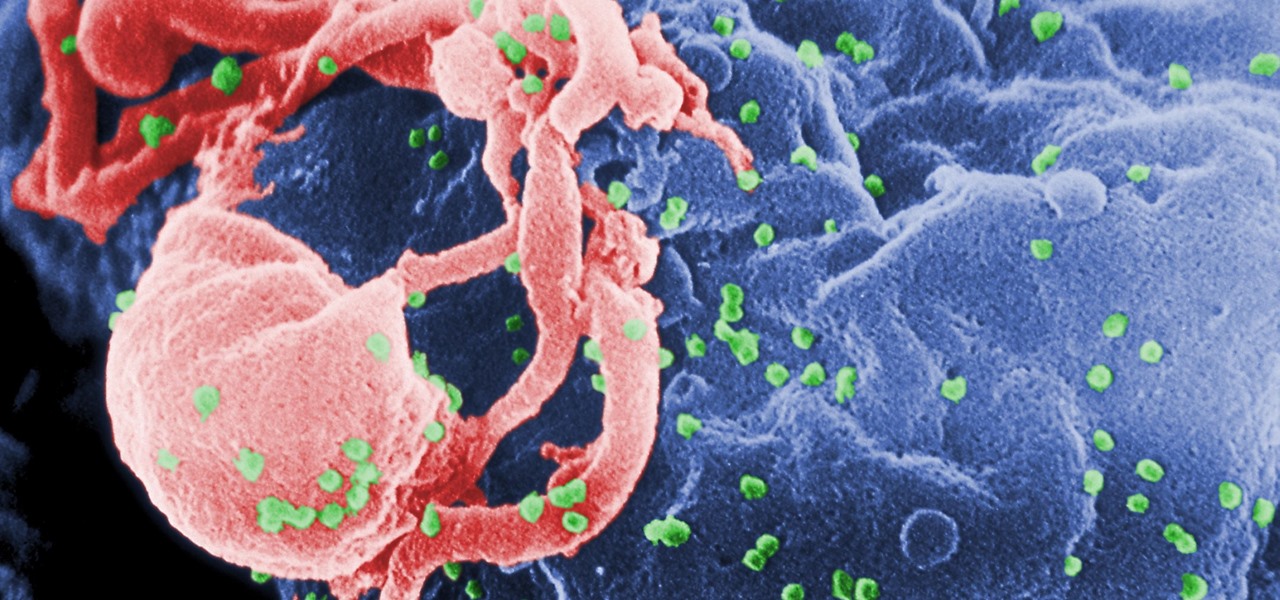
Over 1.2 million people in the US are infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)—and one out of eight of them don't know it. Even after decades of intense research into the virus, there's still no cure for it. One of the big problems is that the virus hides out in certain cells of the body, resisting treatments that kill it.

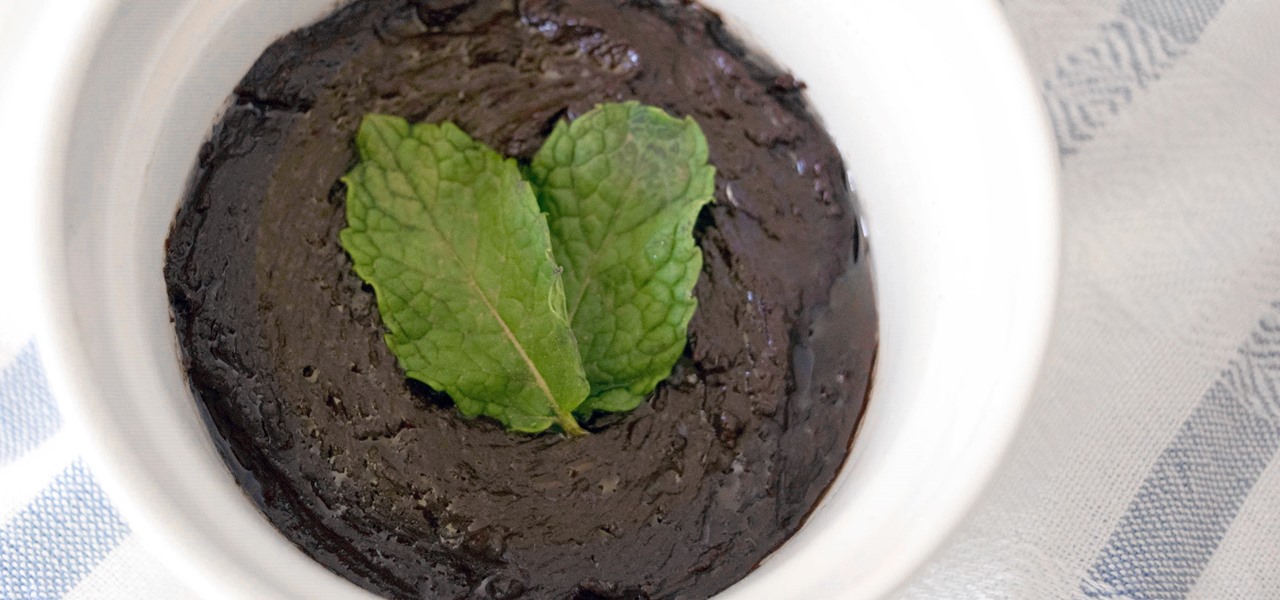
As a self-proclaimed chocoholic, any day with chocolate mousse in it is a good day in my book. And thanks to prominent chemist Hervé This, one of the founding fathers of molecular gastronomy, chocolate mousse is not only easy to make every single day—but only requires two ingredients.

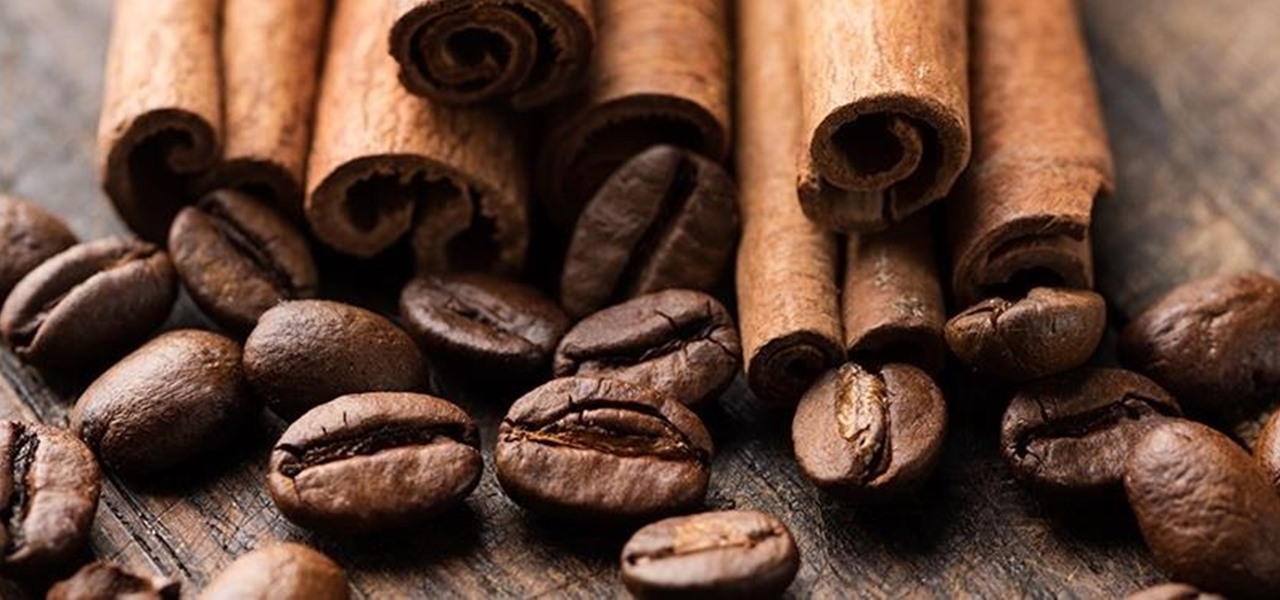
Creamer, milk (whole or skim), sugar, or even butter—you've probably added at least one of these to your coffee to improve its taste at some point. If you're looking for something different, though, try a new twist with a dash of cinnamon. This sweet, sharp spice can do so much more than improve coffee's taste, and I've got 10 examples for you to consider.

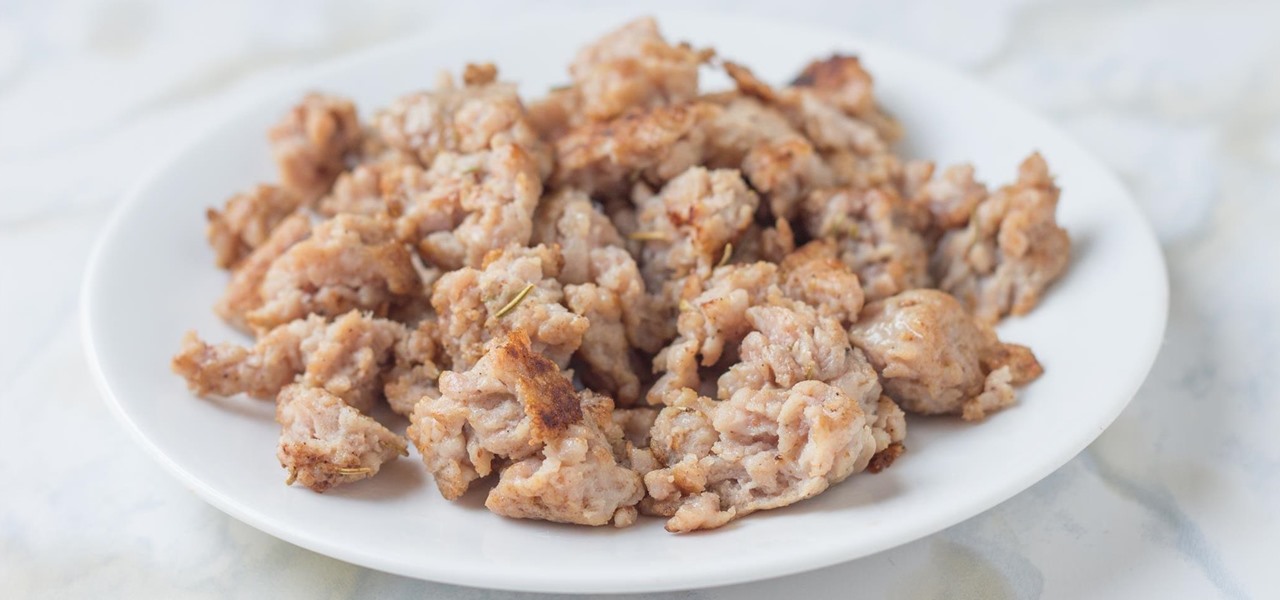
I hate wasting money. To be fair: I doubt there are many people out there who relish the idea, but I especially hate it. And I also dislike spending in excess of what I need. This happens all too often, I feel, when it comes to recipes that involve using sausage.

Just what are probiotics and why are they so good for you? Probiotics are "viable microorganisms" that can confer lots and lots of health benefits if they reach your intestine while they're alive. You may have heard them described as "friendly bacteria."

Who doesn't enjoy sitting down to a nice dinner with a cocktail in hand? After a long day, a drink is a great way to unwind. Yet your favorite spirits can do more than just help you relax after work. By utilizing alcohol in the kitchen, you can enhance everything from how food tastes to your health.

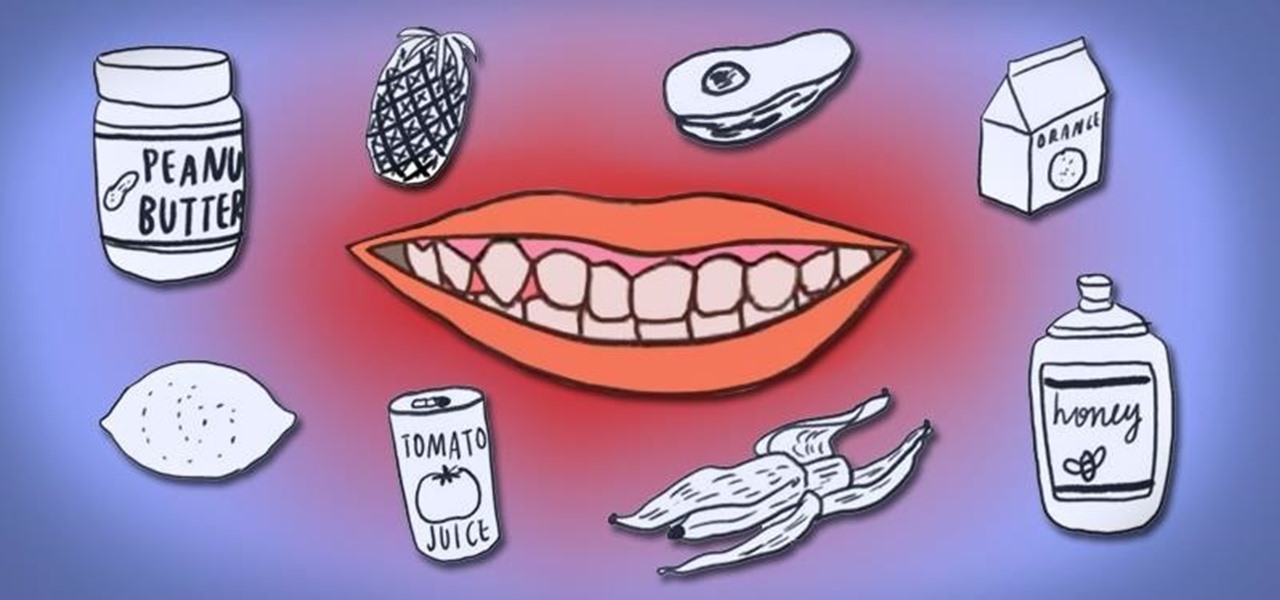
Mouth burning with pain from eating too much hot sauce or some seriously "spicy" food? Well, ignore your first instinct and steer clear of that cup of cold water — it won't help. Instead, reach for a glass of milk, a lemon slice, a spoonful of sugar, or some starchy bread to dilute the painful heat on your tongue.