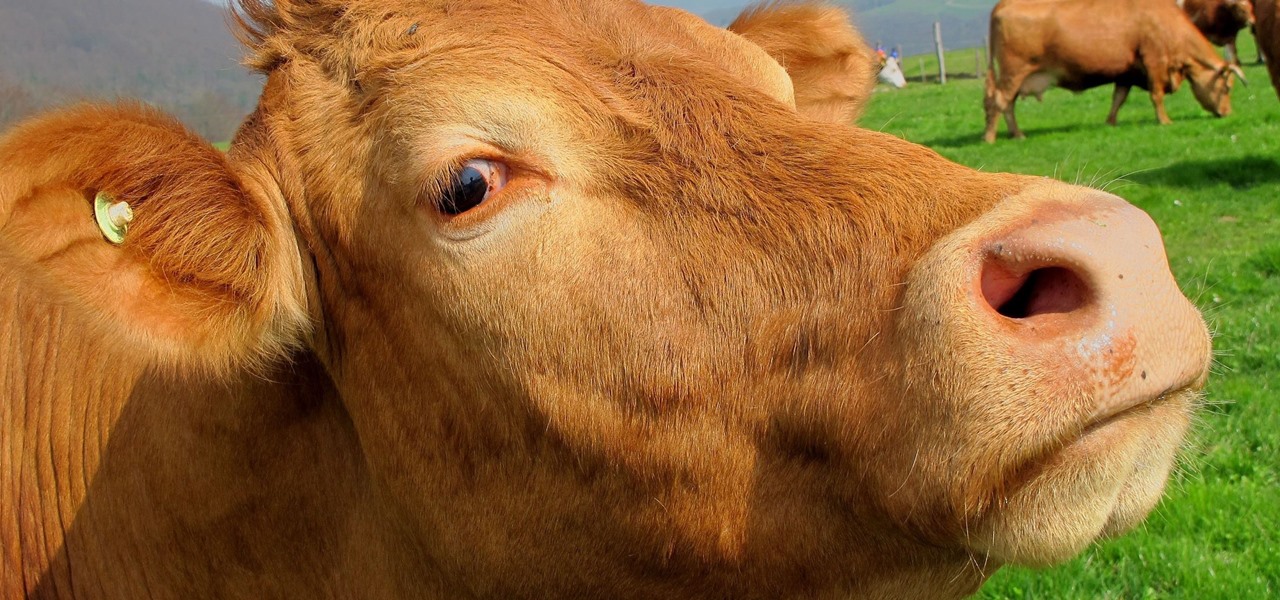
A vaccine against HIV might prevent the disease that we can't seem to cure. Some HIV patients make antibodies that can take down the virus, much the way a vaccine might. But, scientists haven't been able to provoke that type of response in other people. However, in a process that might work in humans, a group of researchers has successfully generated antibodies in cows that neutralize multiple strains of HIV.

When the climate changes, so do all the things that rely on the climate, including people, plants, and pathogens. A European study recently took a broad look at what kind of microorganisms are most likely to be affected as climate change heats, cools, dries, and wets the world around us.
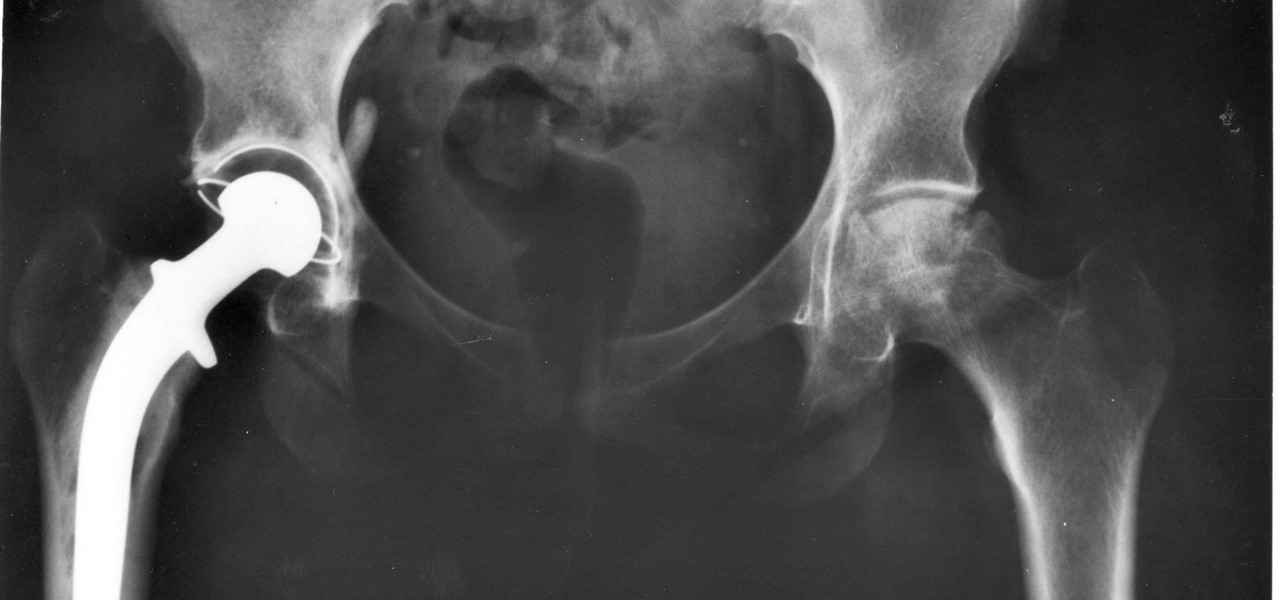
For about a million Americans each year, a joint replacement brings relief from pain and restored mobility. But, 5–10% of those people have to endure another surgery within seven years, and most of those are due to an infection in their new joint. If doctors could treat infections more effectively, patients could avoid a second surgery, more pain, and another rehabilitation.
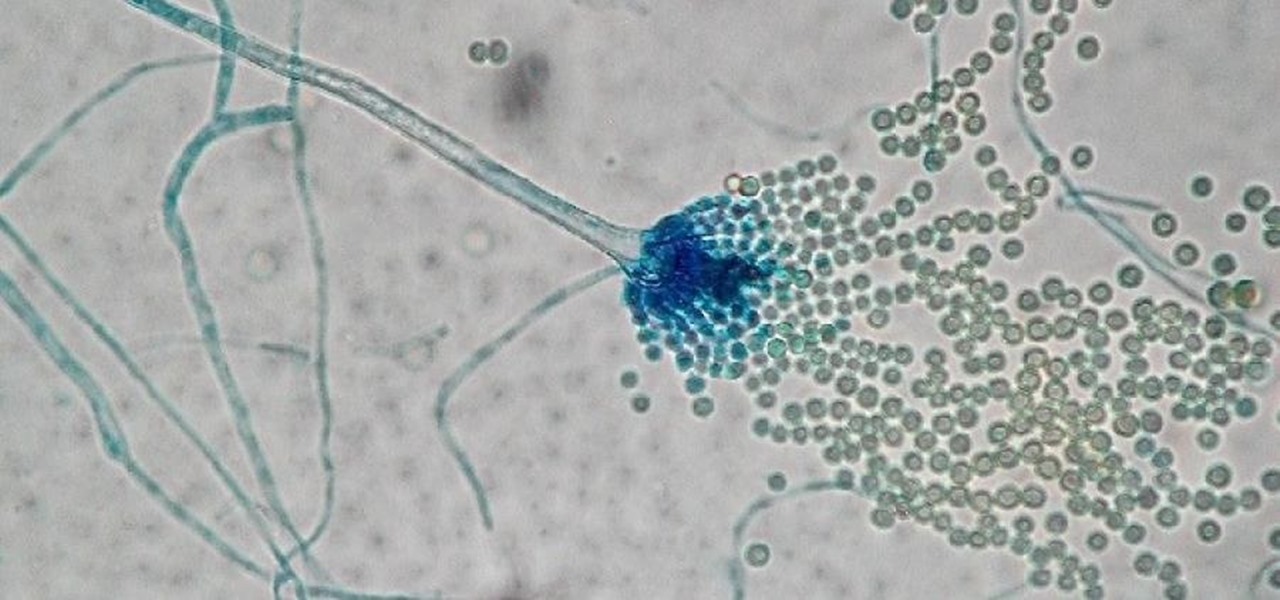
The growing list of dangerous antibiotic resistant organisms has just acquired three new members. Researchers have discovered three new species of Klebsiella bacteria, all of which can cause life-threatening infections and have genes that make them resistant to commonly used antibiotics.

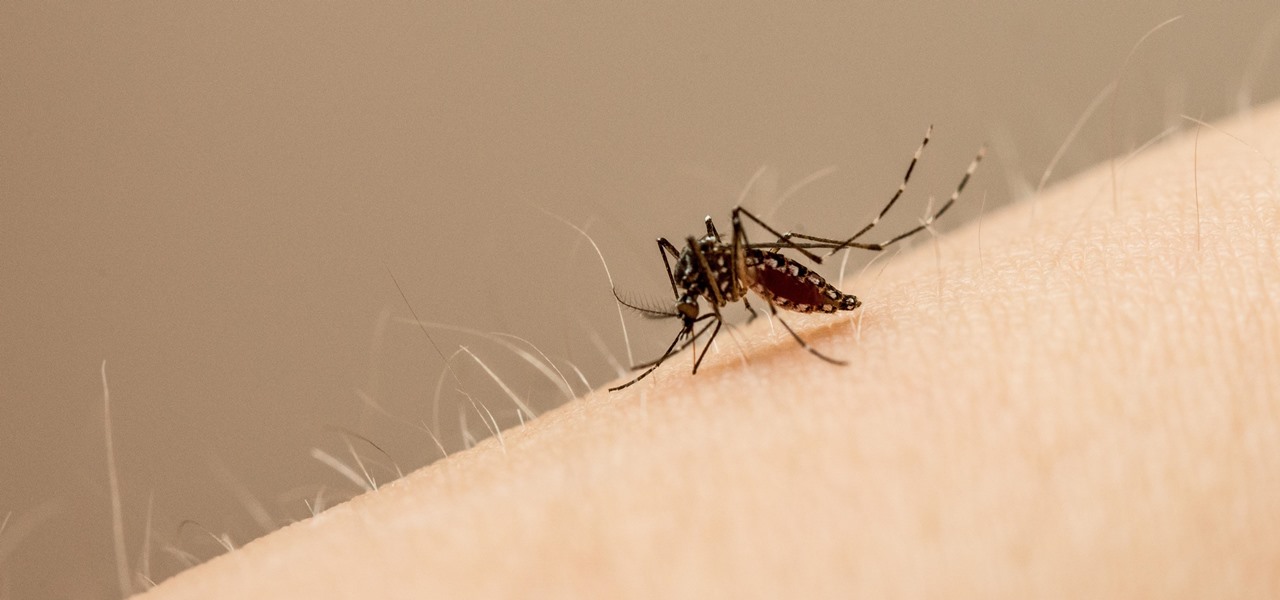
Rising on the world stage, dengue fever is transmitted by mosquitoes — and apparently air travel too.
Cancer cells do a pretty good job of flying under the radar of our immune system. They don't raise the alarm bells signaling they are a foreign invader the way viruses do. That might be something scientists can change, though.

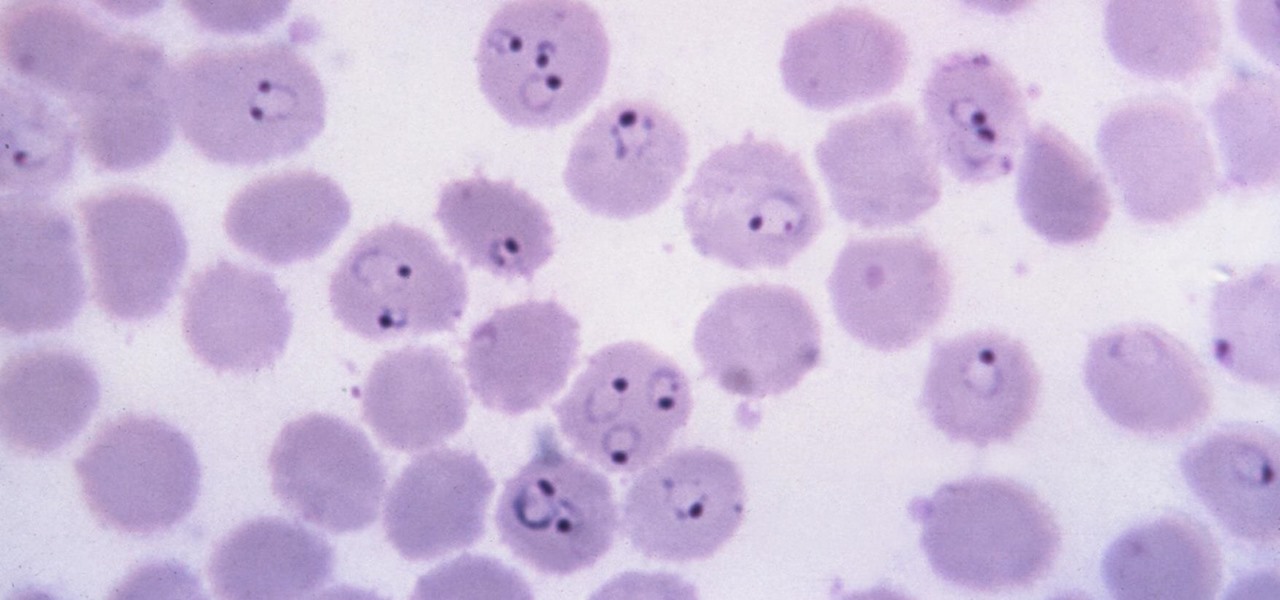
Malaria is a massive worldwide health problem. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate that 212 million cases of malaria occurred worldwide in 2015 and 429,000 of the infected people died.

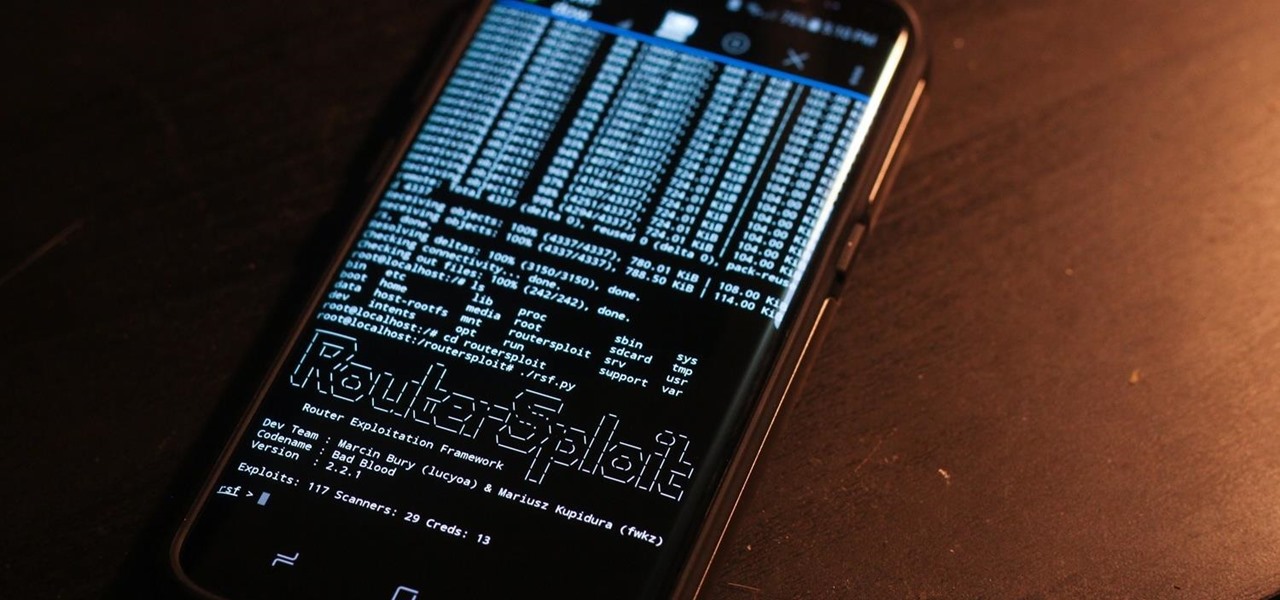
RouterSploit is a powerful exploit framework similar to Metasploit, working to quickly identify and exploit common vulnerabilities in routers. And guess what. It can be run on most Android devices.

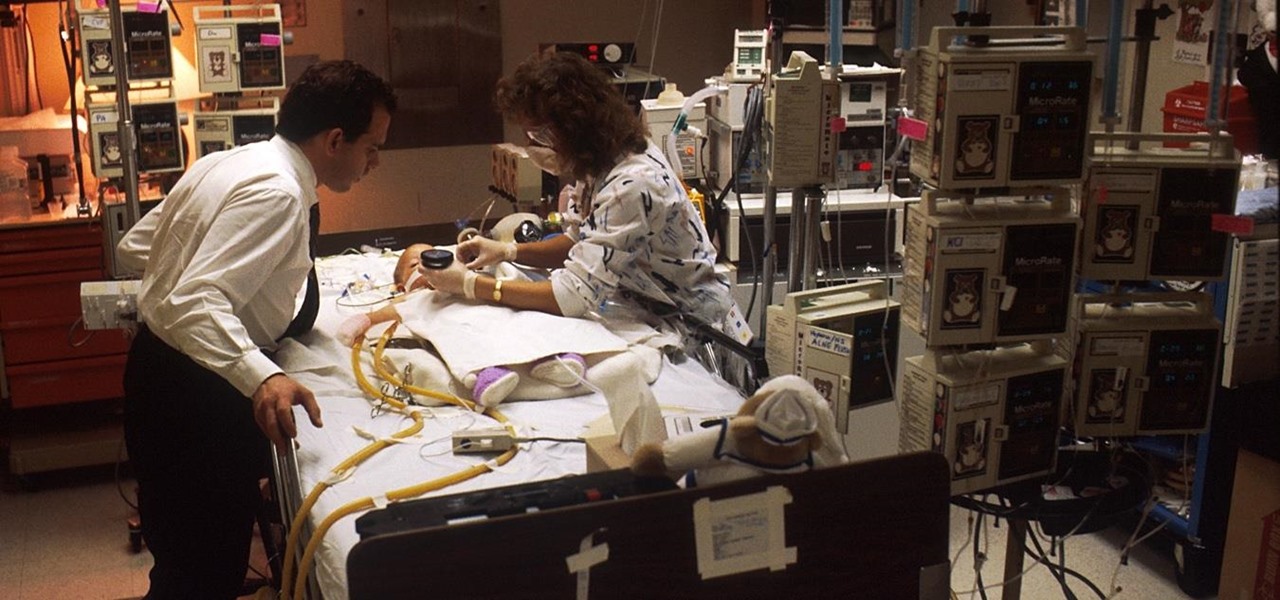
Twelve-year old Rory Staunton took a dive for a basketball during gym class and came up with a cut on his arm. The school nurse applied a couple of band-aids, without cleaning the cut, and off he went. In approximately three days, hospital physicians told his parents there was nothing else that they could do for their son; he was dead.

For younger children, a day at the playground is not complete without some sandbox time. Long a favorite of children and parents, sandboxes could also be sheltering dangerous pathogens.

Peach trees and other related plants are susceptible to the devastation caused by fire blight, a contagious bacterial disease. Once contracted, infected trees have to be burned to contain the disease and prevent spread to nearby trees. Increasing resistance to antibiotic treatment has sent scientists in search of alternative ways to deal with the bacteria and prevent its catastrophic damage.

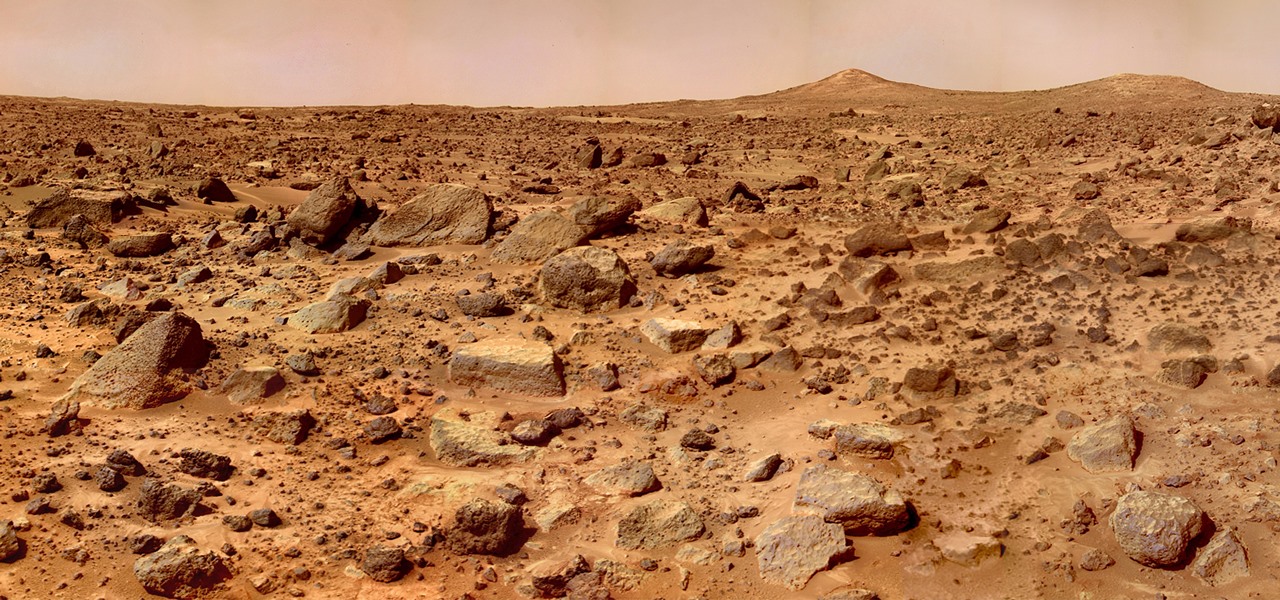
A new study casts real suspicion on the possibility of life on Mars. Why? It seems the surface of the planet may be downright uninhabitable for microbial life as we know it.

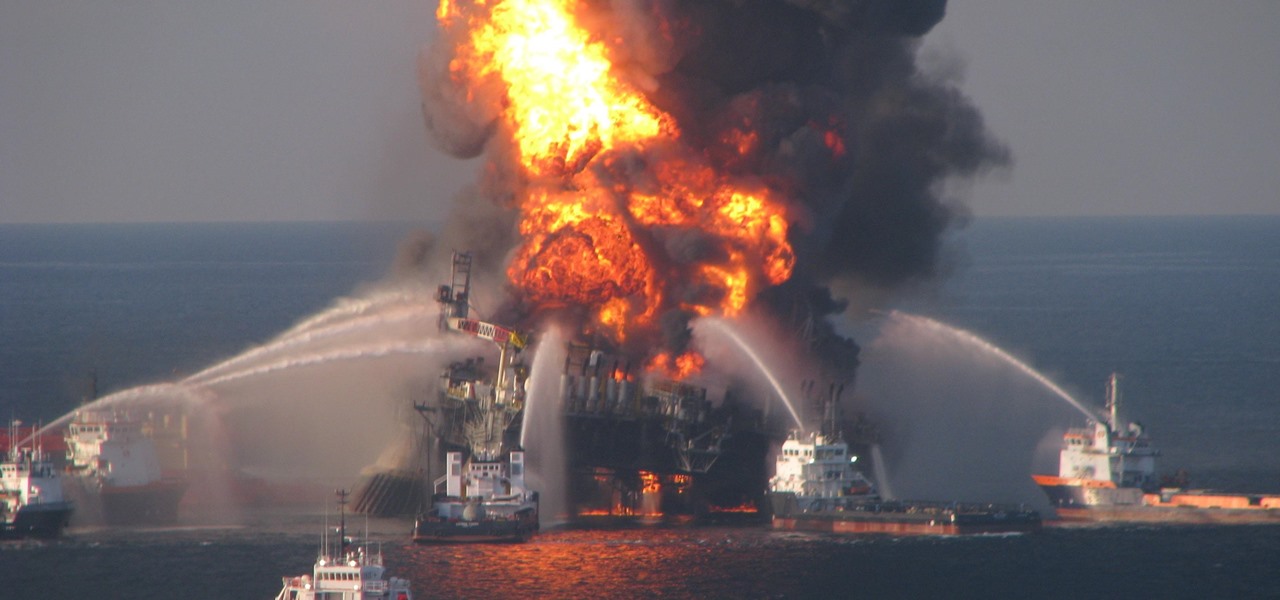
The Deepwater Horizon oil spill that began on April 20, 2010, was the largest maritime oil spill in history. Killing 11 people and discharging 4.1 million barrels of oil and natural gas into the Gulf of Mexico, the event was an unparalleled personal, environmental, and business disaster. It was also the first major oil spill to take place in the deep ocean.

Add breathing in your house as another possible danger to your health. If your home is sick, it's possible you could get sick too.

A new medical development is going to change the way many of us look at getting the flu vaccine. A painless flu vaccine skin patch is making needles and vials a thing of the past. Researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University have shown that a flu vaccine can be administered safely and comfortably with this new patch, which delivers the vaccine through a matrix of tiny dissolving microneedles.

Coronaviruses are common viruses, and most of us catch one at some point — they cause about 30% of all common colds. A new accidental discovery could help fight these viruses, even the deadlier, emerging ones.

HIV infections persist despite treatment that successfully decreases viral blood levels to the point where doctors can't detect the virus. But that doesn't mean the person is cured. The virus hides in the body, not replicating, just waiting for a chance to jump out of the shadows and reemerge.

Legionnaires' disease is named after 1976 outbreak in Philadelphia that sickened 221 people and killed 34. More often striking adults over the age of 50, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently reported two cases where newborns contracted the often fatal disease — at their moment of birth.

It's no secret that devices leak data, but sometimes they do so in ways you may not expect. Your phone, laptop, printer, and IOT devices leak Wi-Fi information that can (and is) used to track you.

Dengue fever is a danger to anyone living or visiting tropical or subtropical regions. It can be hard to detect the infection in its earliest and most treatable phase, especially in children. Luckily, new research highlights better techniques for triaging the disease in infected children with more severe symptoms, potentially saving lives.

We've worked hard to reduce the flow of toxic chemicals into our waterways, which means no more DDT and other bad actors to pollute or destroy wildlife and our health. But one observation has been plaguing scientists for decades: Why are large quantities of one toxic chemical still found in the world's oceans?

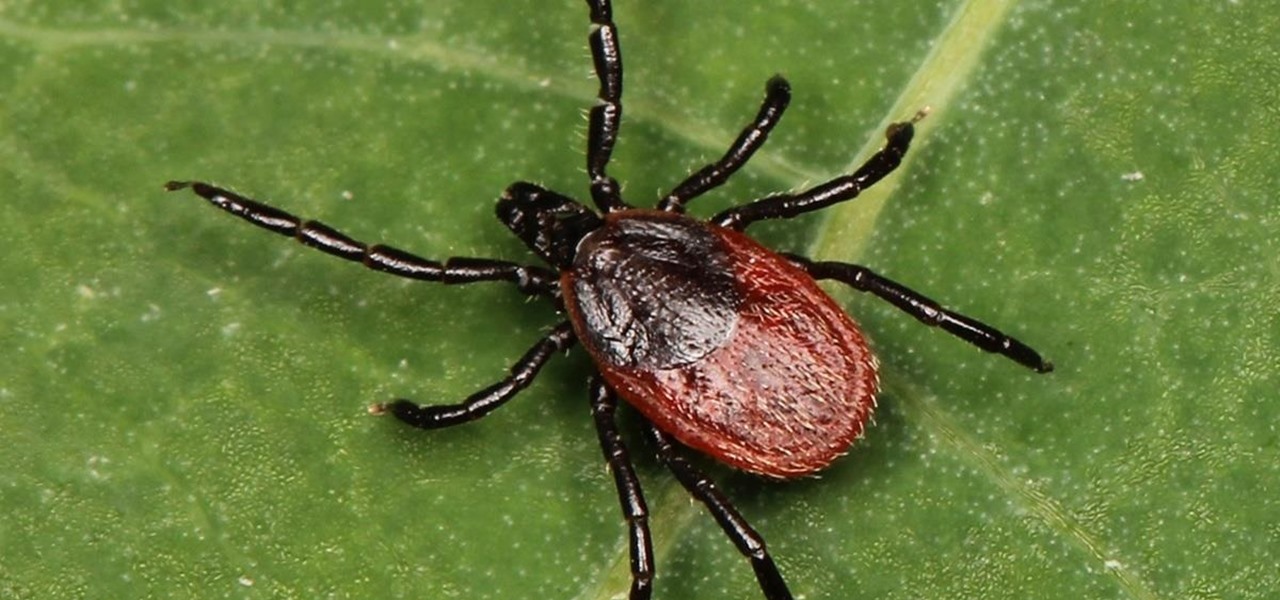
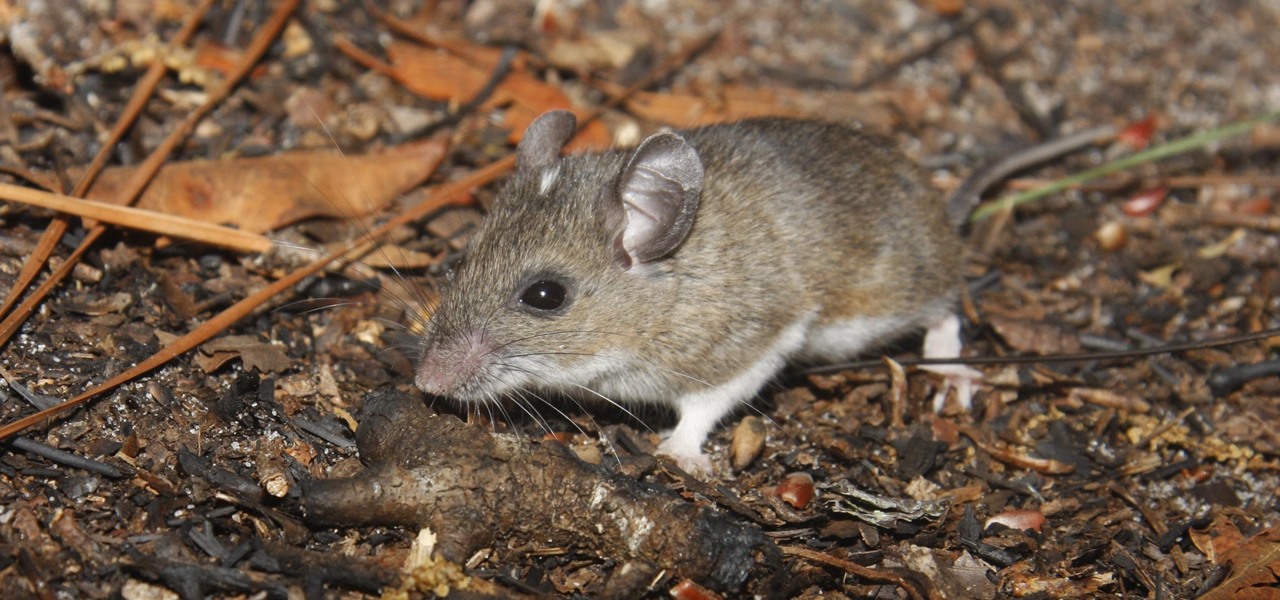
Lyme is a growing threat as we move into warmer weather in the US. Researchers have said this year could be one of the worst for this tick-borne disease, as a skyrocketing mouse population and warmer temperatures increase the risk.

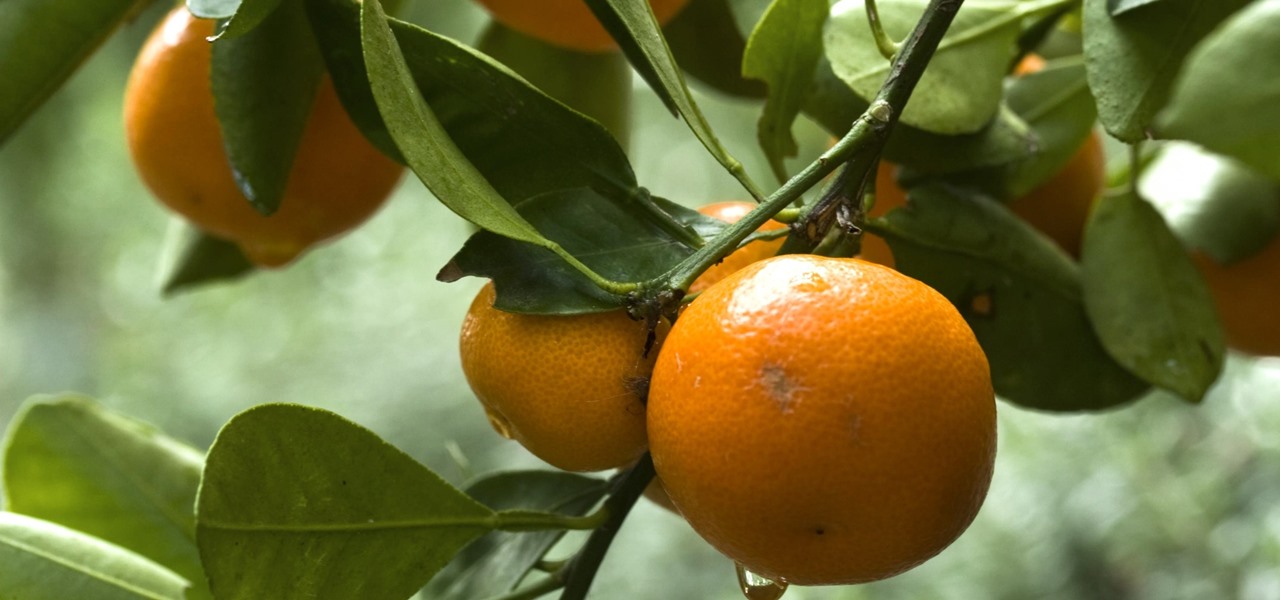
A disease called "citrus greening" has devastated and permanently altered citrus production in the United States, but a vaccine that could protect orange trees may be part of a winning strategy to beat the bacteria that is killing the trees.

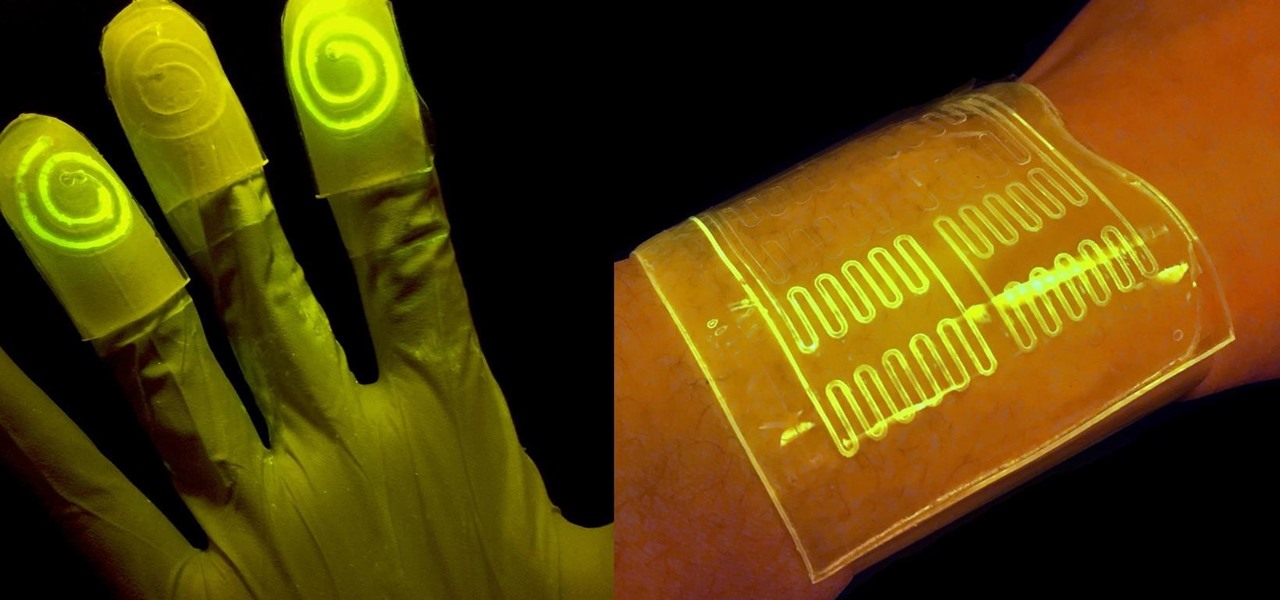
While at work, you notice your gloves changing color, and you know immediately that you've come in contact with dangerous chemicals. Bandages on a patient signal the presence of unseen, drug-resistant microbes. These are ideas that might have once seemed futuristic but are becoming a reality as researchers move forward with technology to use living bacteria in cloth to detect pathogens, pollutants, and particulates that endanger our lives.

Up until now, enabling full-time Immersive Mode on an Android device has been a tedious task which required you to run individual ADB commands each time you wanted to toggle it on or off. This was a shame, too, since Immersive Mode helps reclaim lots of screen real estate by auto-hiding your navigation and status bars.

Colorado State University scientists have developed new tech that quickly identifies the presence of Zika virus in mosquito populations — and in human body fluid.

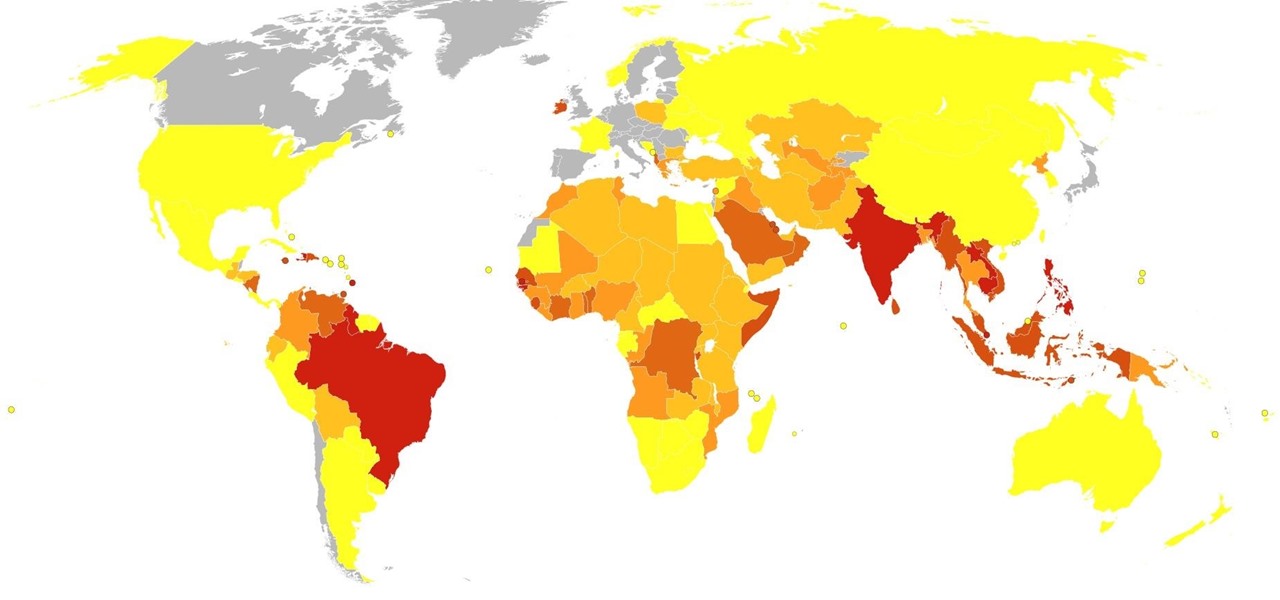
You may not have heard of visceral leishmaniasis, onchocerciasis, or lymphatic filariasis, and there is a reason for that. These diseases, part of a group of infections called neglected tropical diseases (NTDs), impact more than a billion people on the planet in countries other than ours. Despite the consolation that these often grotesque illnesses are "out of sight, out of mind," some of these infections are quietly taking their toll in some southern communities of the US.

Devastating and deadly, land mines are a persistent threat in many areas of the world. Funding to clear regions of land mines has been decreasing, but new research may offer a less dangerous method of locating hidden, underground explosives by using glowing bacteria.

The ability of one microbe to adapt is giving it a whole new career as a sexually transmitted disease. Usually content with the back of the throat and nose of those who carry it, the dangerous pathogen Neisseria meningitidis has adapted to cause an illness that looks a lot like gonorrhea.

Our quest to find new antibiotics has taken a turn — a turn down the road, that is. A team of scientists from the University of Oklahoma is scooping up roadkill and searching for bacteria on them that might yield the world's next antibiotic.

Warning: If you are eating and for some reason still decided to click on this article, turn around now. Maui, Hawaii health officials have reported finding at least six cases of angiostrongyliasis, a parasitic lungworm that infects humans. Colloquially, it's known as rat lungworm disease. And if you think that name is awful, just wait until you hear what it does to the human body.

An advance in the race to stop birth defects caused by Zika-infected mothers has been made by a team of researchers from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, New York. They have identified the process Zika uses to gain entry into the placenta, and published their findings in the journal Biochemistry.

At the moment, it would be safe to say that demand for devices running Tango, Google's augmented reality smartphone platform, is relatively low among consumers. Kaon Interactive, a B2B software company who has built more than 5,000 interactive applications for use at trade shows, remote sales demonstrations, and other customer engagements, is betting that there is a market for the devices in sales and marketing.

The search for a cancer treatment that selectively finds and kills only the cancerous cells has just made a giant leap forward.

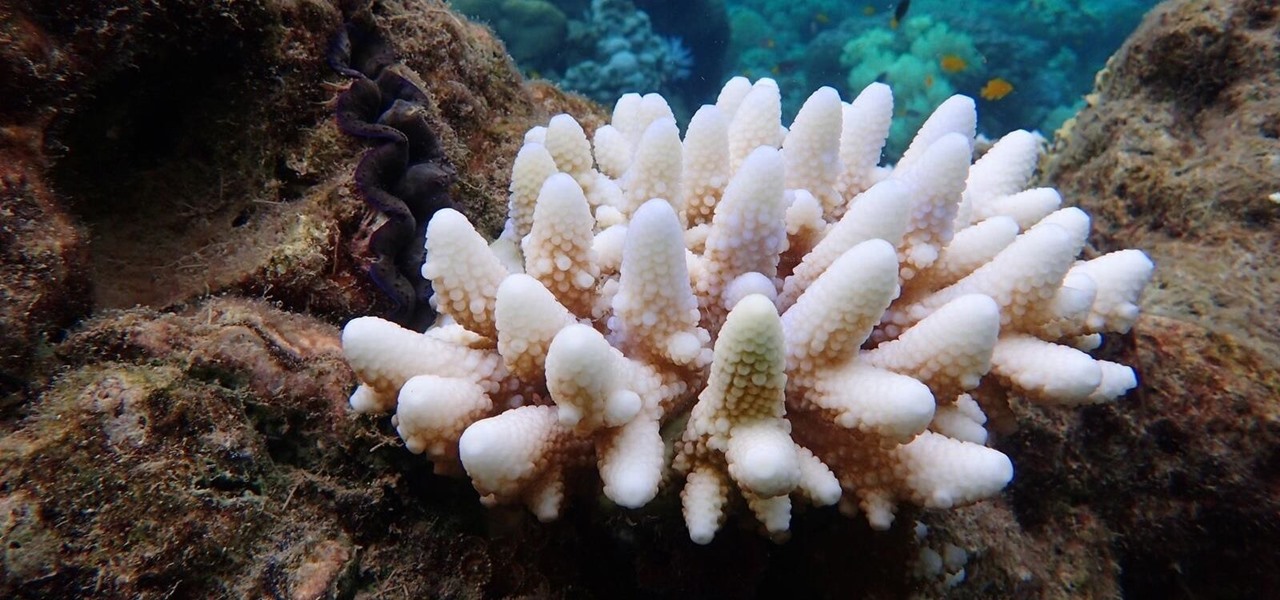
The Great Barrier Reef in Australia is the largest living system on the planet. Yet more than 90% of the reef is bleaching because of the loss of a tiny algae that lives within the coral.

An outbreak of anthrax from contaminated meat in Tanzania sickened dozens of people and moves the danger of this deadly bacteria back into focus.

For regions that experienced a boom in mouse populations last year, scientists say 2017 could see a surge in cases of Lyme disease.

Hospitals are places we go to get well, and we don't expect to get sick or sicker there. But a study from researchers at the Cleveland Clinic, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, and Cleveland VA Medical Center in Ohio found that hospital floors in patient rooms were frequently contaminated with healthcare-associated pathogens—often dangerous multi-drug resistant bacteria.

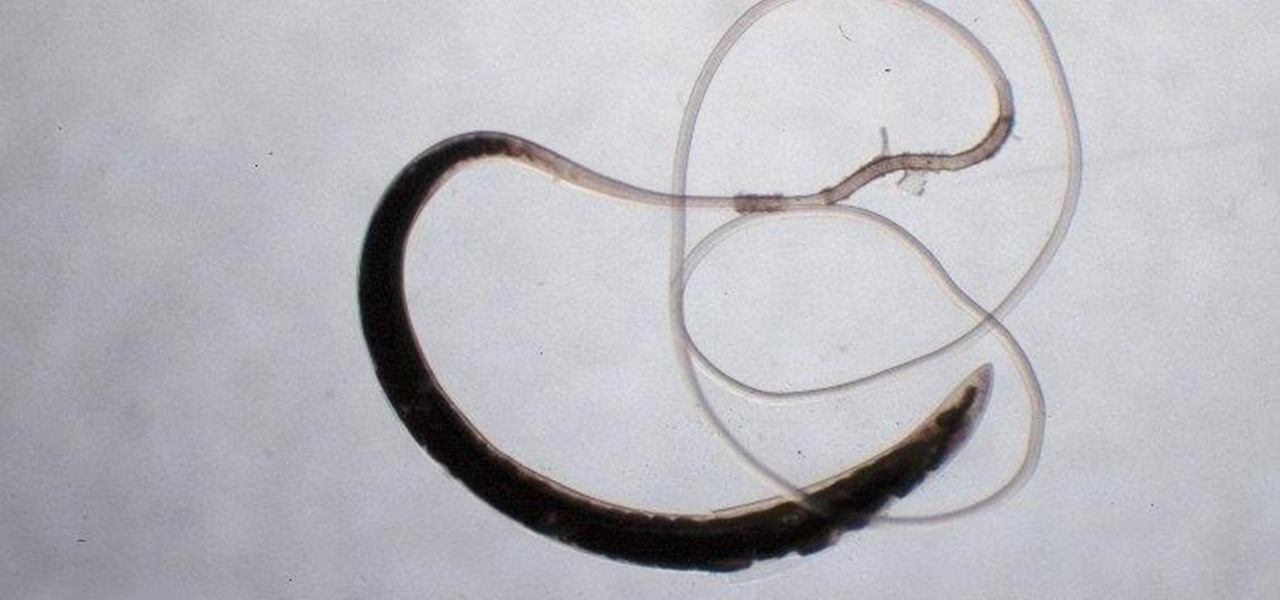
Somewhere around 600–800 million people in the world are infected with whipworm (Trichuris trichiura), an infection they got from ingesting soil or water contaminated with feces of infected animals or people containing the parasite's eggs.

Marijuana is legal to use for medical purposes in 28 states and the District of Columbia, but the quick development of this new industry could have left some regulation issues in the lurch.