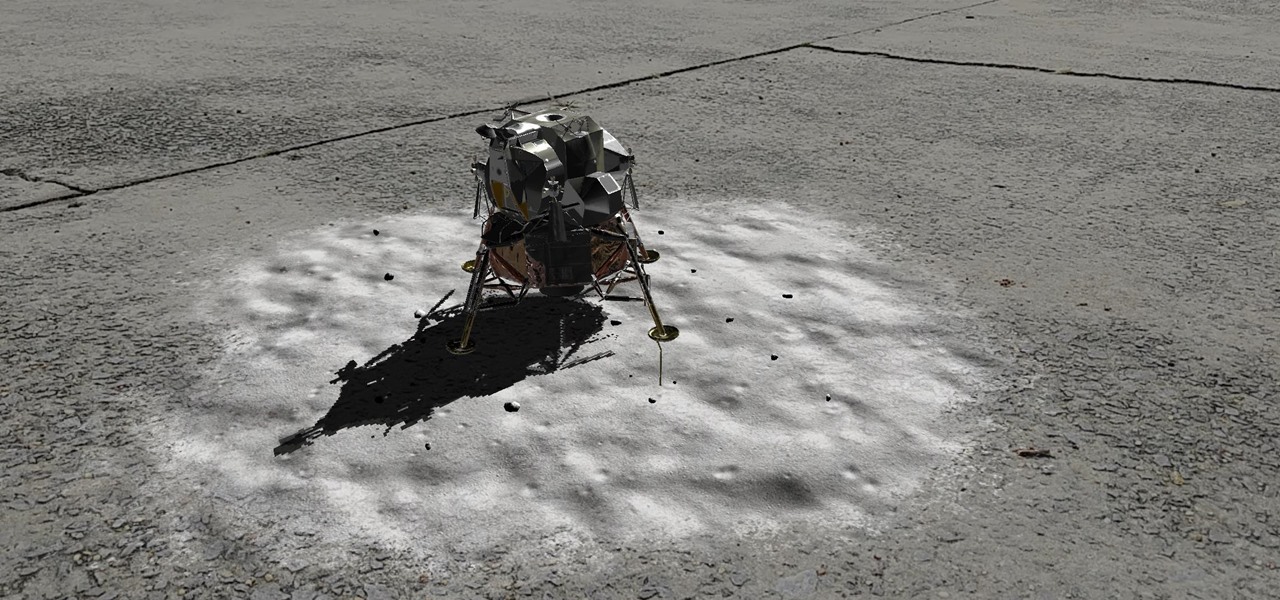
Unless you've been hiding under a (moon) rock for the past month, you already know that Saturday, July 20 is the 50th anniversary of NASA's Apollo 11 lunar landing.

For the first time, you can officially use a computer mouse with your iPhone, thanks to Apple's new Accessibility settings in iOS 13. It works for all types of Bluetooth mice, so if you have one, it'll already work. Plus, those with wireless receivers and even wired mice are supported by using a USB to Lightning adapter.
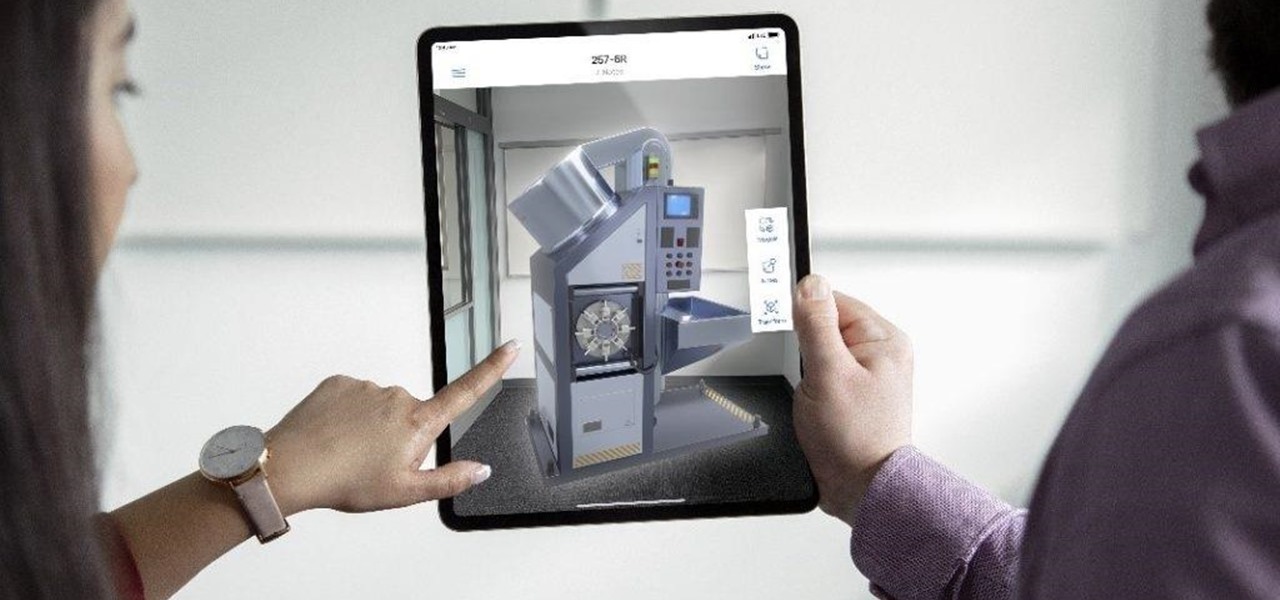

The augmented reality industry had enough twists this week to surprise even M. Night Shyamalan.
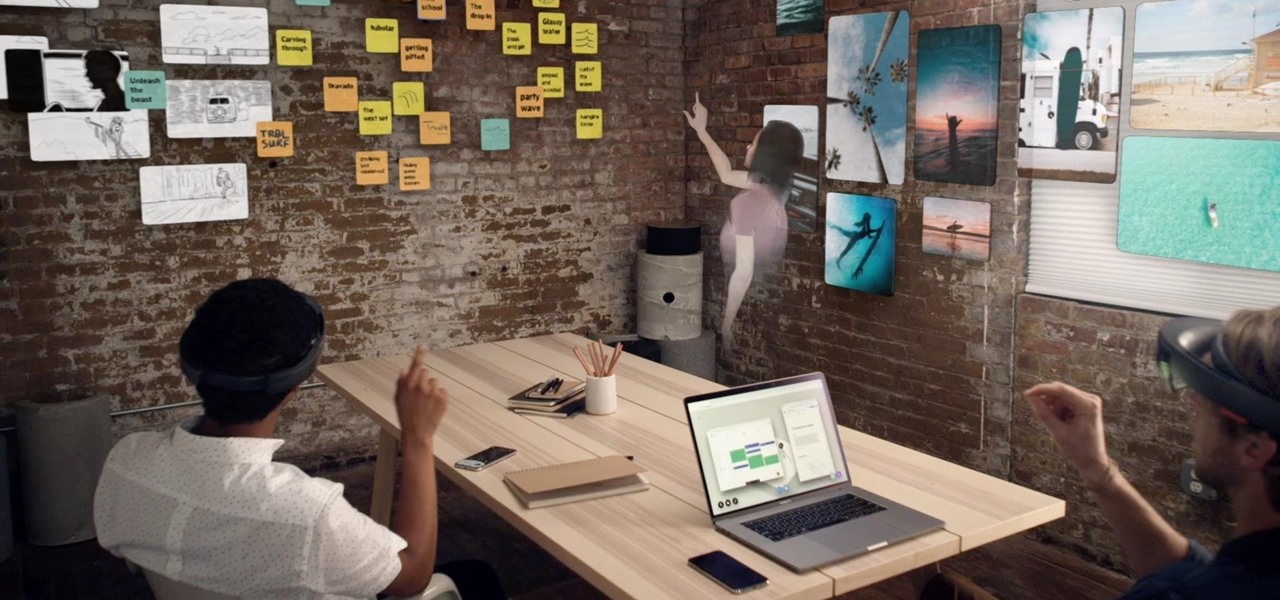

Last week, Twilio showed off how avatar-based chat communications will work on the Magic Leap One, and now a new startup has unveiled yet another way that augmented reality telepresence and remote collaboration can take place on the device.

By now, you already know that the Magic Leap One ships with an array of apps to immediately get you accustomed to operating in your new spatial computing reality. The first one we're going to focus on is Screens, an app we told you about previously, but only now have managed to try for ourselves.
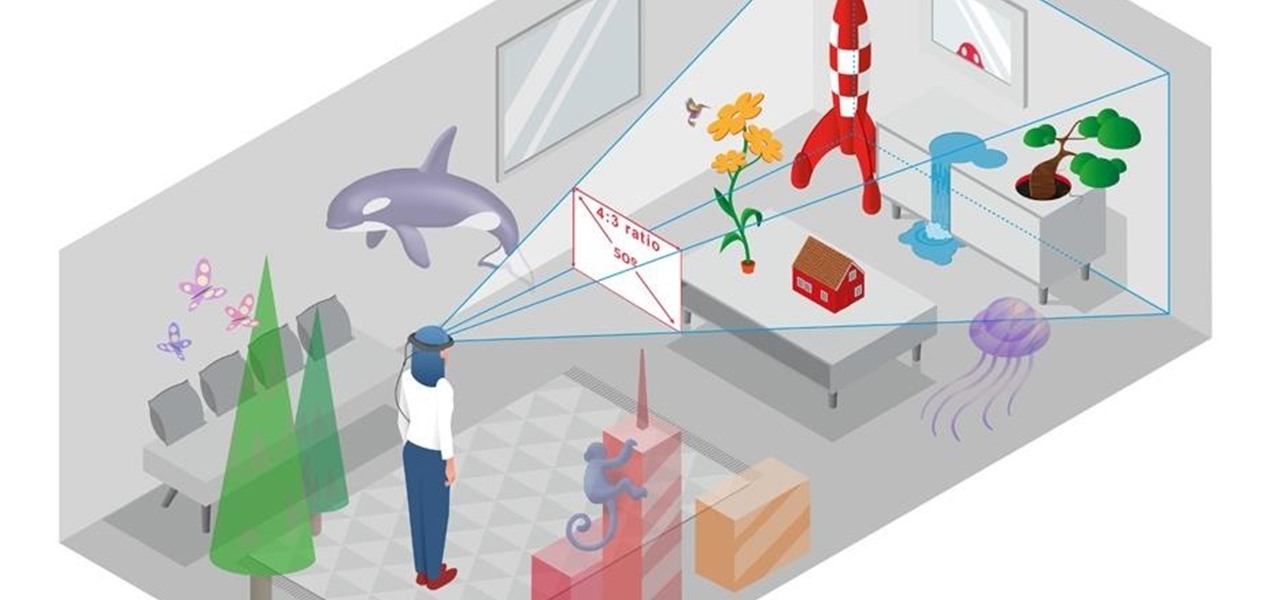
In the lead up to the Magic Leap One launch, Magic Leap has been coy about what the actual field of view (FoV) is for its first commercial product.

While there is a lot to be excited about when it comes to iOS 12 in general, iPhone X users will not just get the same new features and tweaks that all other iPhones will get — they'll get a few unique ones that will make the device even more desirable to those who don't have one yet. Also, iPhone XS, XS Max, and XR users will also see these benefits out of the box.

During E3, many major game developers announced plans to bring console and PC franchises to mobile. These titles are designed for more serious gamers with competition in mind. All of this points to a shift in mobile hardware priorities — soon, gamers will need gaming phones just like PC players need a gaming rig.

Google collects an enormous amount of personal data. While some of this data is used for targeted ads, others tidbits of info such as our location are used to improve our mobile experience. While it is natural for us to distrust Google's intentions, by allowing their data collection, we can add new functionality to our favorite apps.

One of the biggest improvements with the Galaxy S9 and S9+ is the redesigned camera, with the latter scoring an impressive 99 overall on DxOMark. But with an abundance of features and enhancements, tweaking the camera's settings for optimal performance can be a little confusing.

Mobile World Congress 2018 is here, and with it, Samsung has officially announced the highly anticipated Galaxy S9 and S9+. While we already knew much about the new phones, Samsung's presentation officially filled us in on what to expect from the S9's cameras, including dual aperture, two cameras, and super slo-mo.

The Pixel 2 has finally arrived. Google unveiled their newest flagship phones on October 4th, and there's quite a few changes in store. For one thing, most of Google's official renders have already showed us something new: The Pixel 2 and Pixel 2 XL will have a Google Search bar at the bottom of their home screens.

A virus easily spread among trout and salmon could make it harder to keep your favorite fish on the menu.

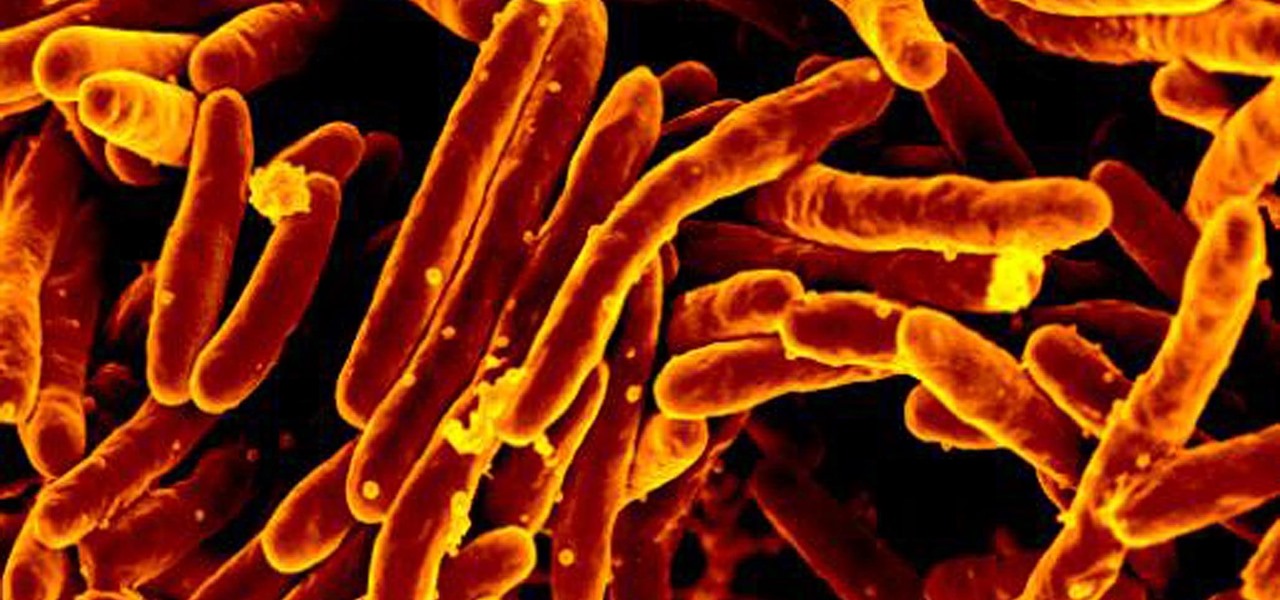
The incidence of tuberculosis (TB) is dropping in the US, but the World Health Organization (WHO) considers it to be epidemic in the rest of the world — there were over 10 million new cases in 2016.

After years of telling patients to finish any prescribed course of antibiotics completely, a group of researchers in the UK say it is no longer necessary, and could even be harmful if we want to preserve the antibiotics we can still use.

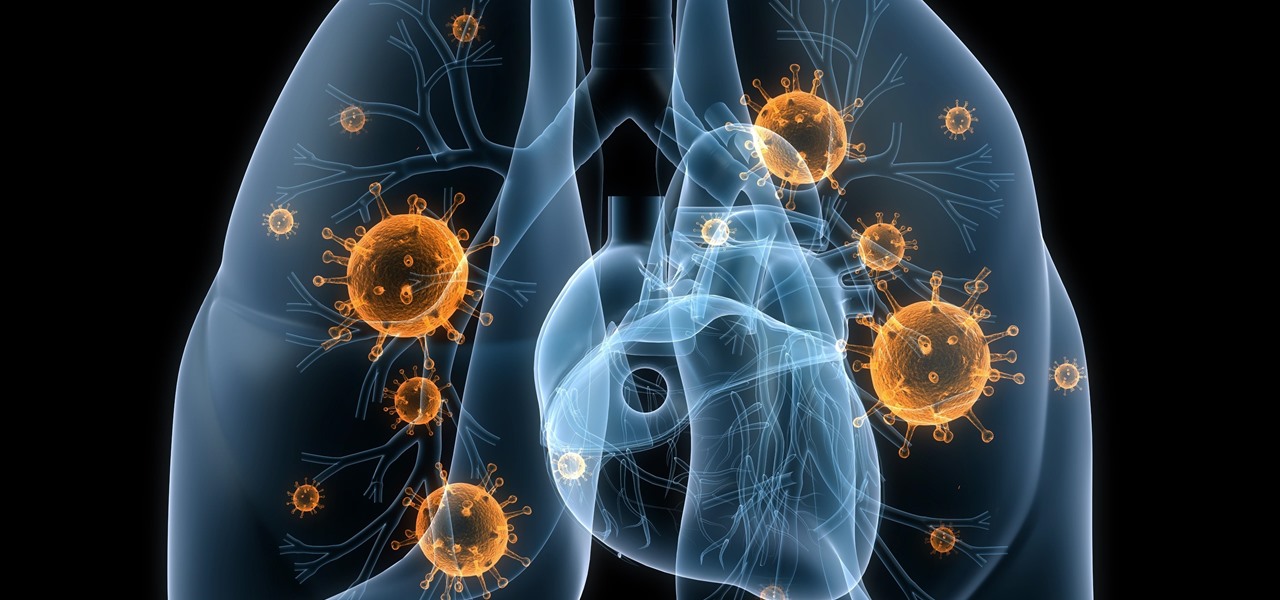
Once we recover from the respiratory infection pneumonia, our lungs are better equipped to deal with the next infection — thanks to some special cells that take up residence there.

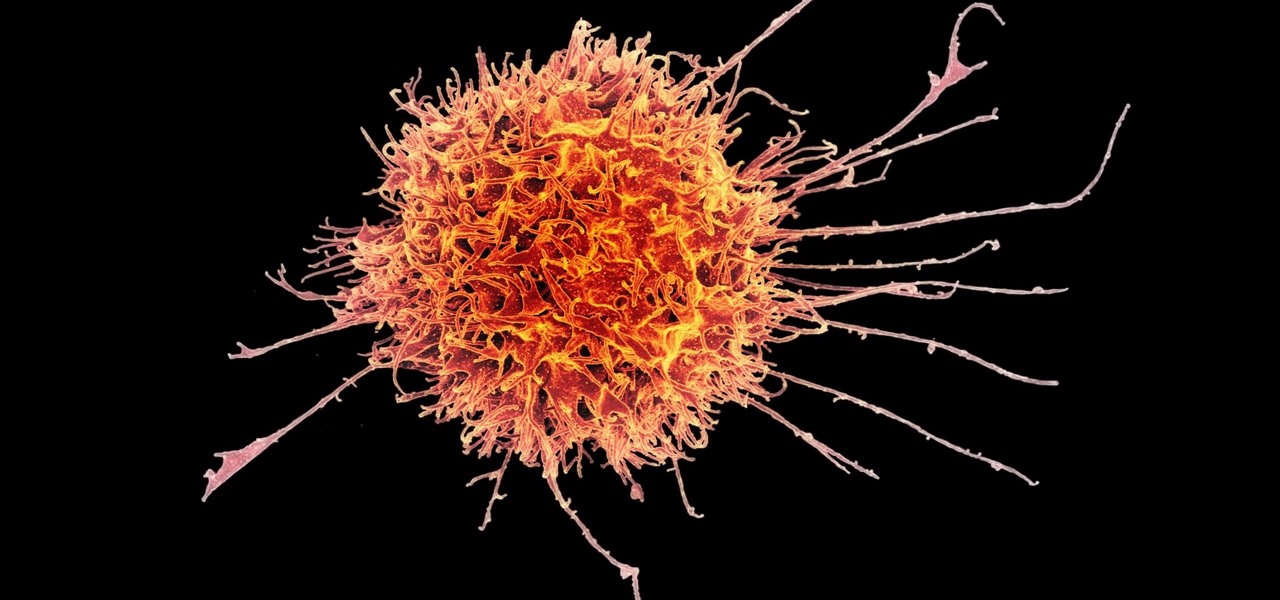
Cancer cells do a pretty good job of flying under the radar of our immune system. They don't raise the alarm bells signaling they are a foreign invader the way viruses do. That might be something scientists can change, though.

New research explores how the bacteria on the penis can leave men more susceptible to infection with HIV.

A week into my internship, I experienced pretty serious back pain and slight difficulty breathing. I scheduled a doctor's appointment to make sure nothing was wrong, and I got a surprising diagnosis: bad posture.

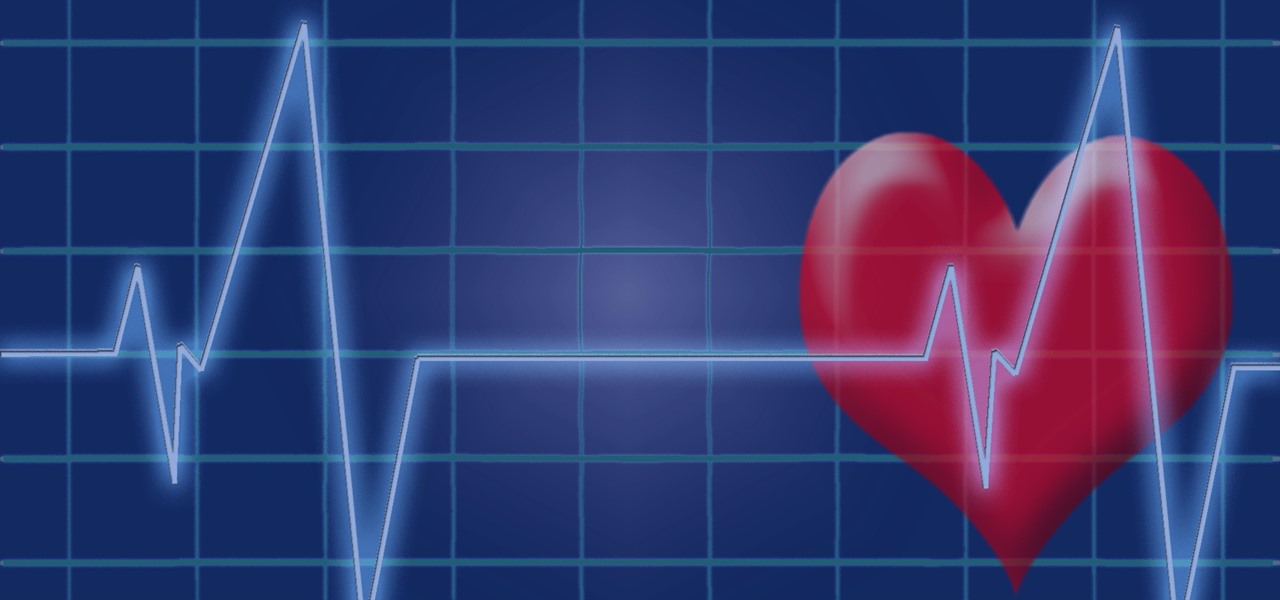
Heart disease is the leading cause of death of men and women in the US. Over half a million Americans die from it annually. Atherosclerosis — a build up of plaque in the arteries — is a common feature of heart disease and can be caused by smoking, fats and cholesterol in the blood, diabetes, and high blood pressure.

Despite longer live spans, almost half a million people die of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) each year, many of them preventable.

Peach trees and other related plants are susceptible to the devastation caused by fire blight, a contagious bacterial disease. Once contracted, infected trees have to be burned to contain the disease and prevent spread to nearby trees. Increasing resistance to antibiotic treatment has sent scientists in search of alternative ways to deal with the bacteria and prevent its catastrophic damage.

Montezuma's revenge, the runs, the trots, or just diarrhea — everyone gets it sooner or later. What exactly is diarrhea good for, if anything?

Add breathing in your house as another possible danger to your health. If your home is sick, it's possible you could get sick too.

Deadly rat lungworm parasites have found their way into Florida. The parasitic worm relies on snails and rats to complete its life cycle, but don't let this nematode's name fool you. This worm can cause meningitis and death in humans who inadvertently consume snails, frogs, or crustaceans harboring the infective parasite.

Tesla hopes high-level personnel changes will help it gain an edge in neural network knowhow for its models' self-drive features, following the replacement of its Autopilot chief and the appointment of a recent Stanford grad to head its AI and Autopilot vision research.

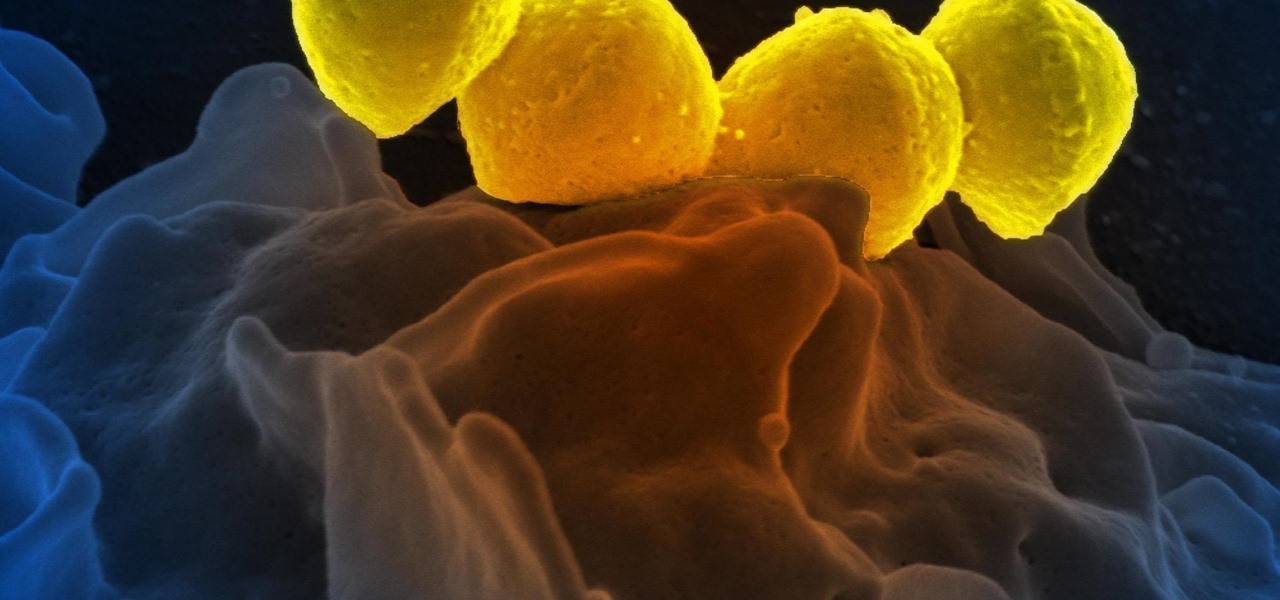
Significant strides have been in the race to find antibiotics to treat superbug infections — those caused by bacteria resistant to the antibiotics used to treat them. Now, an international team of scientists has discovered a new antibiotic produced by a microbe found in Italian soil.

Legionnaires' disease is named after 1976 outbreak in Philadelphia that sickened 221 people and killed 34. More often striking adults over the age of 50, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently reported two cases where newborns contracted the often fatal disease — at their moment of birth.

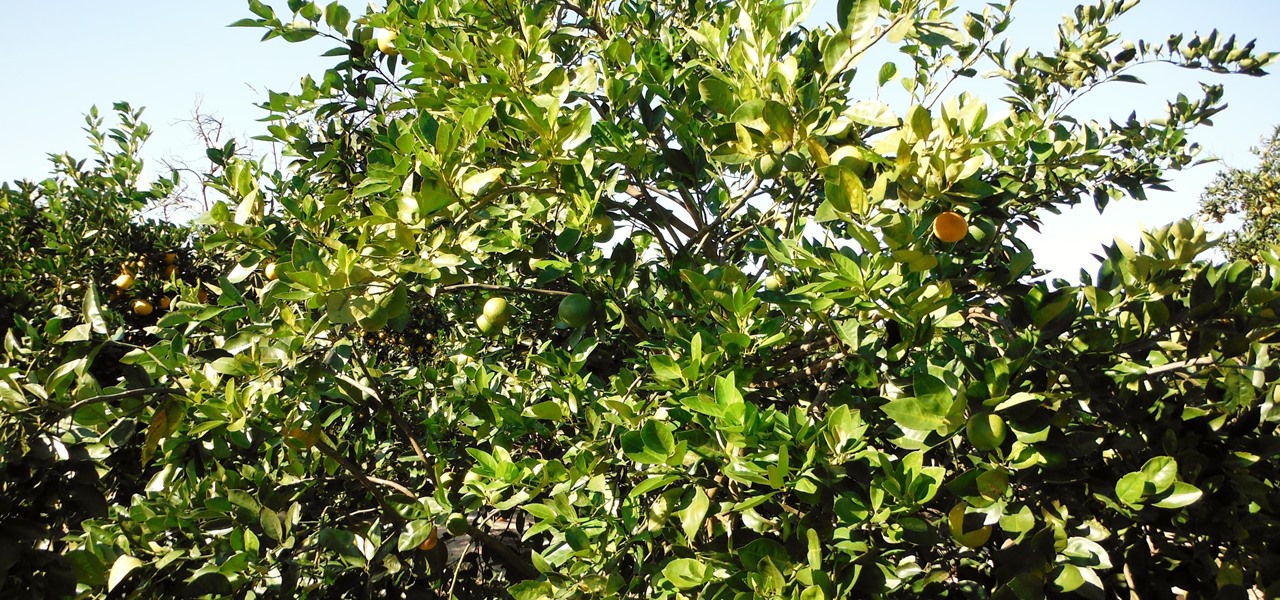
Citrus greening disease — caused by a bacteria spread by psyllid insects — is threatening to wipe out Florida's citrus crop. Researchers have identified a small protein found in a second bacteria living in the insects that helps bacteria causing citrus greening disease survive and spread. They believe the discovery could result in a spray that could potentially help save the trees from the bacterial invasion.

Zika is a threat to unborn babies — the virus can cause neurological damage if it infects a mother during pregnancy. But as with many things, our solutions to the problem aren't always all that much better than the problem itself.

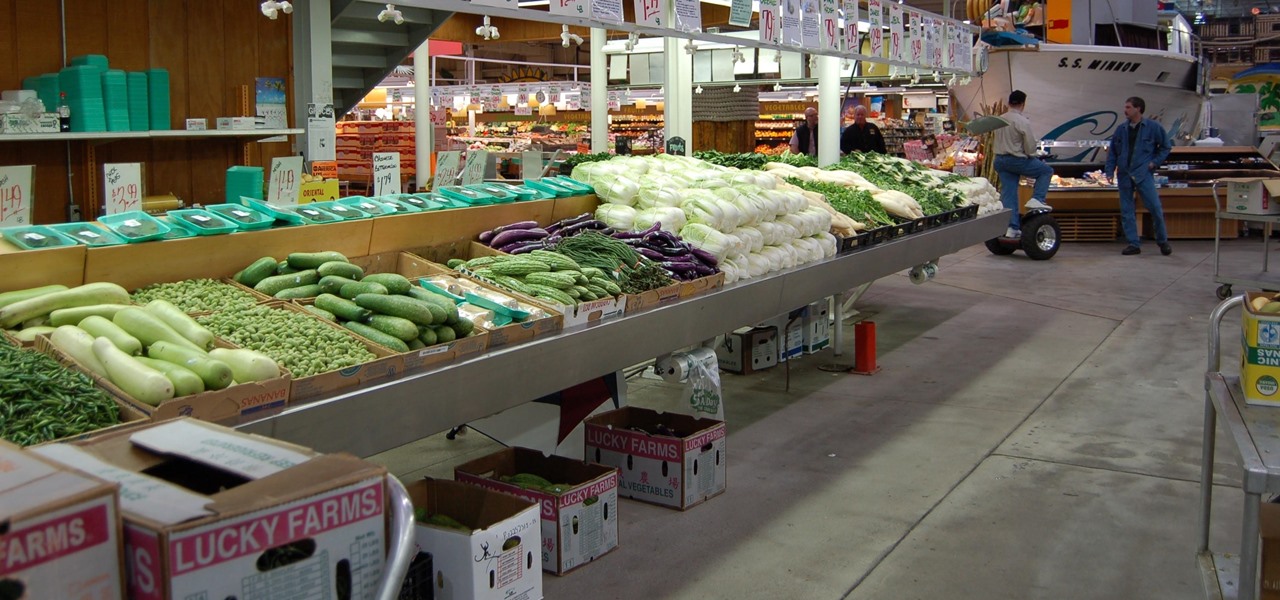
We know that healthcare-related facilities can be fertile ground for antibiotic-resistant bacteria, but recent research suggests your produce aisle might be too.

As researchers from Yale searched our environment for compounds to aid in the battle against drug-resistant bacteria, they got an unlikely assist from ticks.

Activating the body's own immune system to fight cancer is the goal of immunotherapy. It's less toxic than chemotherapy and works with our body's natural defenses. The trouble is, it doesn't work for most patients — only about 40% of cancer patients get a good response from immunotherapy. But coupling it with another type of cancer therapy just might deliver the punch that's needed to knock out cancer.

As headlines focus on melting glaciers and rising water levels caused by global warming, climate change is quietly taking its toll on the nearly invisible occupants of this planet, the microbes.

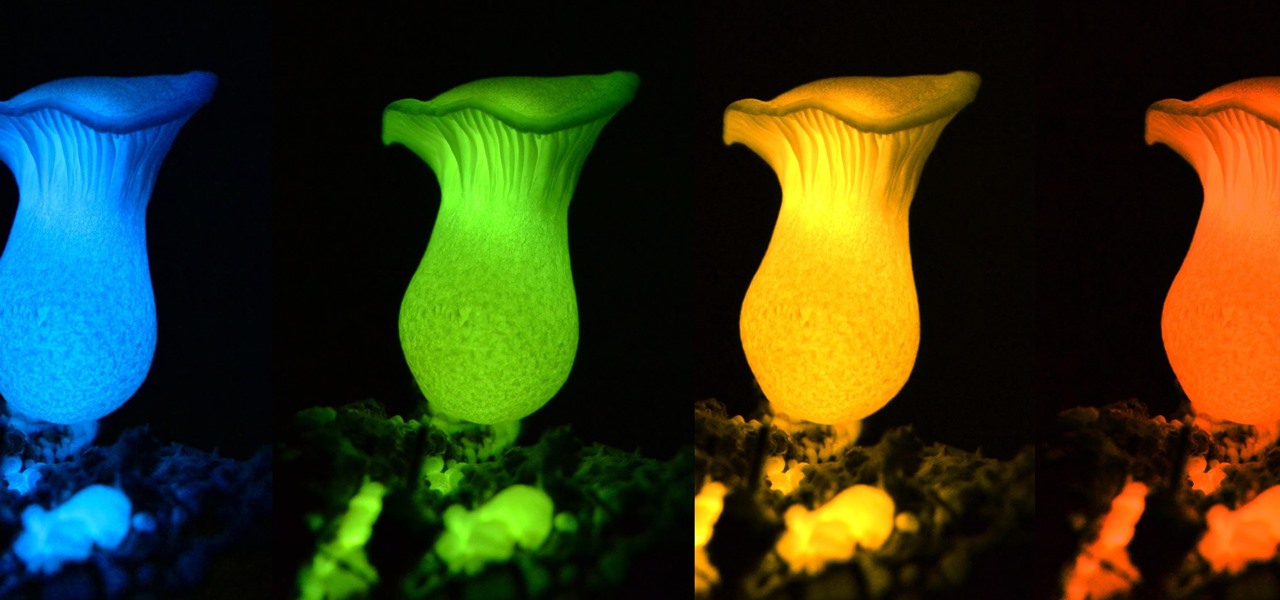
Bioluminescence — the ability of an organism to produce and emit light — is nature's light show. Plants, insects, fish, and bacteria do it, and scientists understand how. Until now, though, we didn't know how fungi glow.

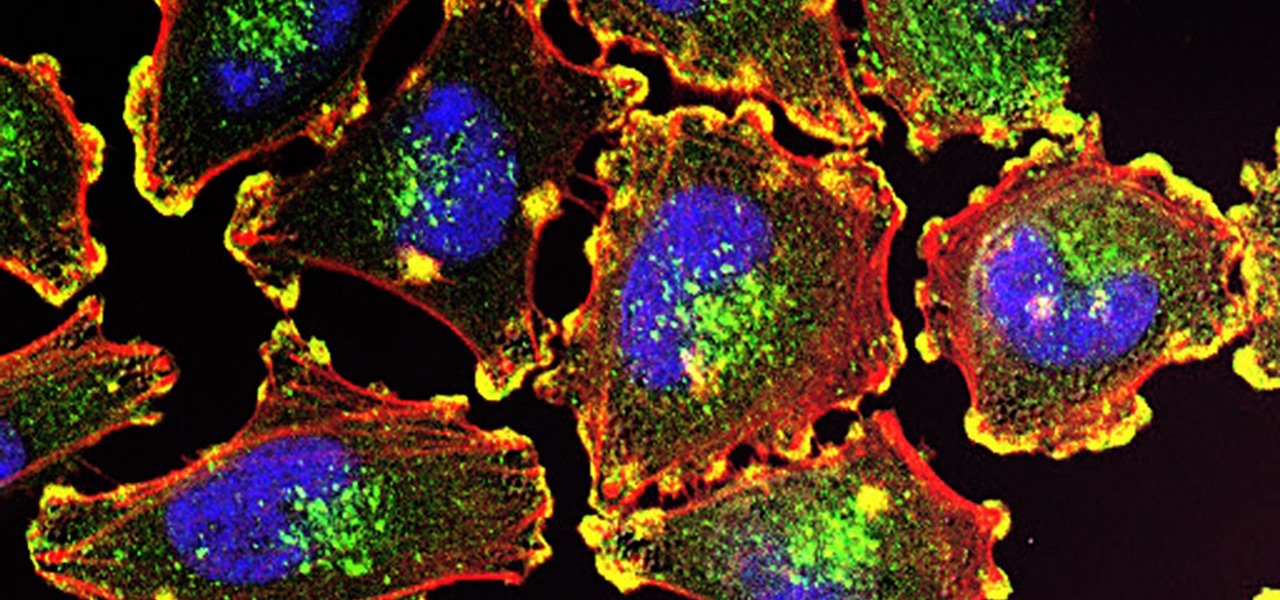
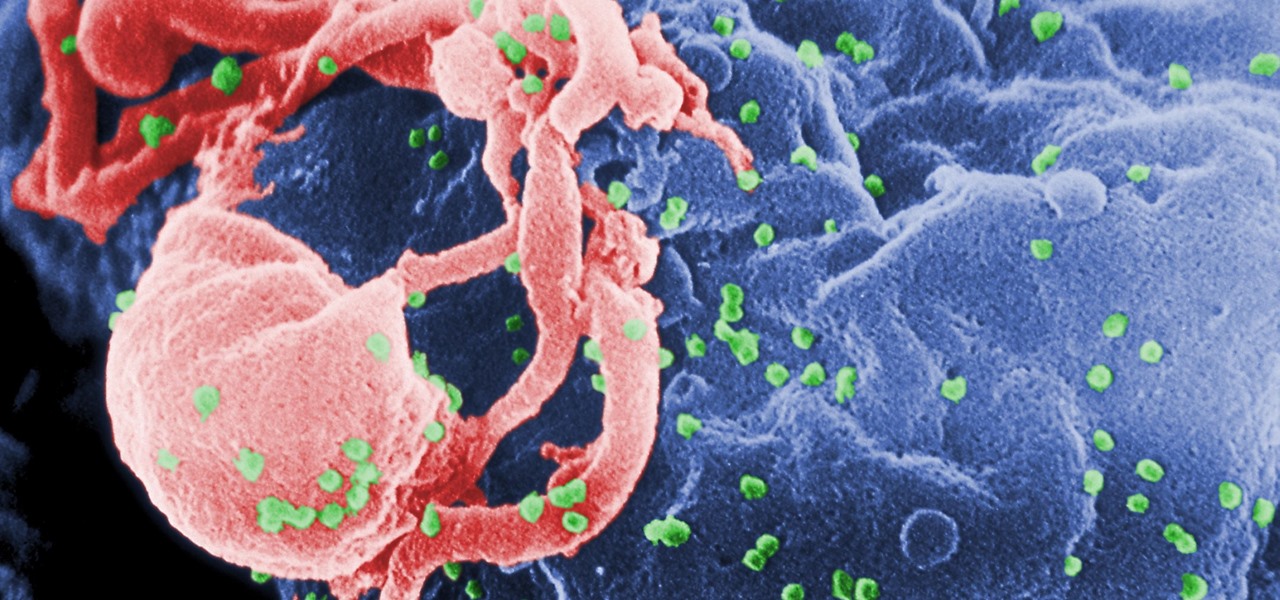
Being infected with HIV means a lifetime of antiviral therapy. We can control the infection with those drugs, but we haven't been able to cure people by ridding the body completely of the virus. But thanks to a new study published in Molecular Therapy by scientists at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine (LKSOM) at Temple University and the University of Pittsburgh, all that may change.

Our quest to find novel compounds in nature that we can use against human diseases —a process called bioprospecting — has led a research team to a small frog found in India. From the skin slime of the colorful Hydrophylax bahuvistara, researchers reported finding a peptide — a small piece of protein — that can destroy many strains of human flu and can even protect mice against the flu.

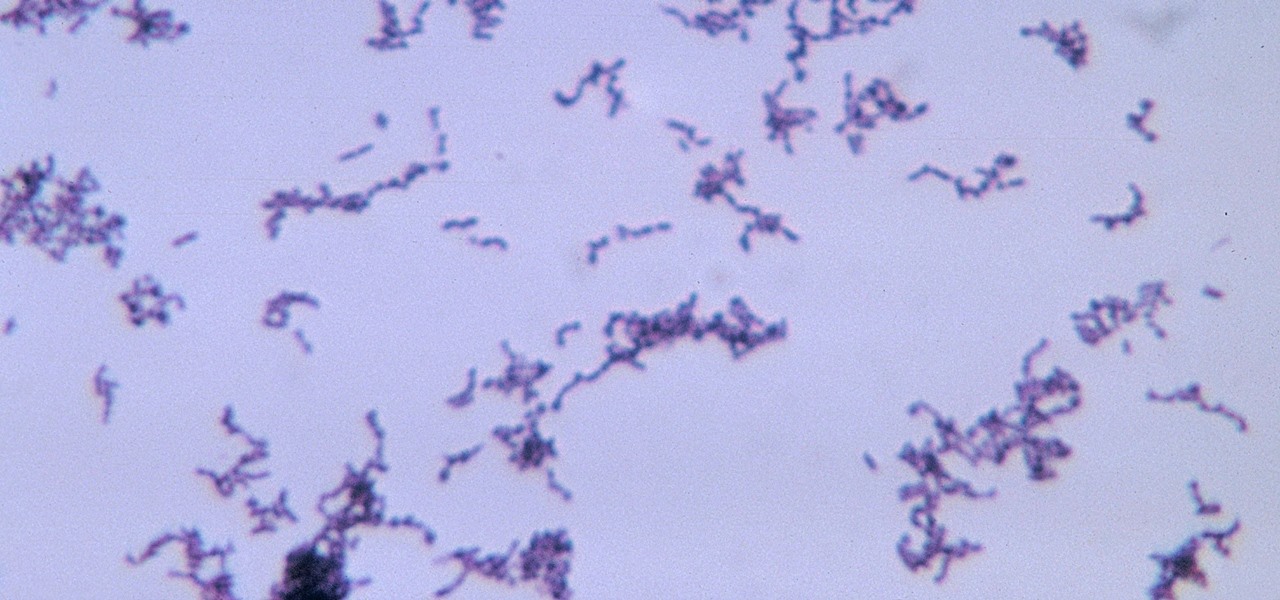
The squiggly guys in this article's cover image are Propionibacterium acnes. These bacteria live in low-oxygen conditions at the base of hair follicles all over your body. They mind their own business, eating cellular debris and sebum, the oily stuff secreted by sebaceous glands that help keep things moisturized. Everybody has P. acnes bacteria—which are commonly blamed for causing acne—but researchers took a bigger view and discovered P. acnes may also play a part in keeping your skin clear.

Growing populations and higher temperatures put pressure on world food supplies. Naturally occurring soil bacteria may save crops in drought-stressed areas, put more land into crop production, and produce more food.

To keep fungal pathogens at bay in their crowded homes, wood ants mix potions to create powerful protection for their nest and their young.