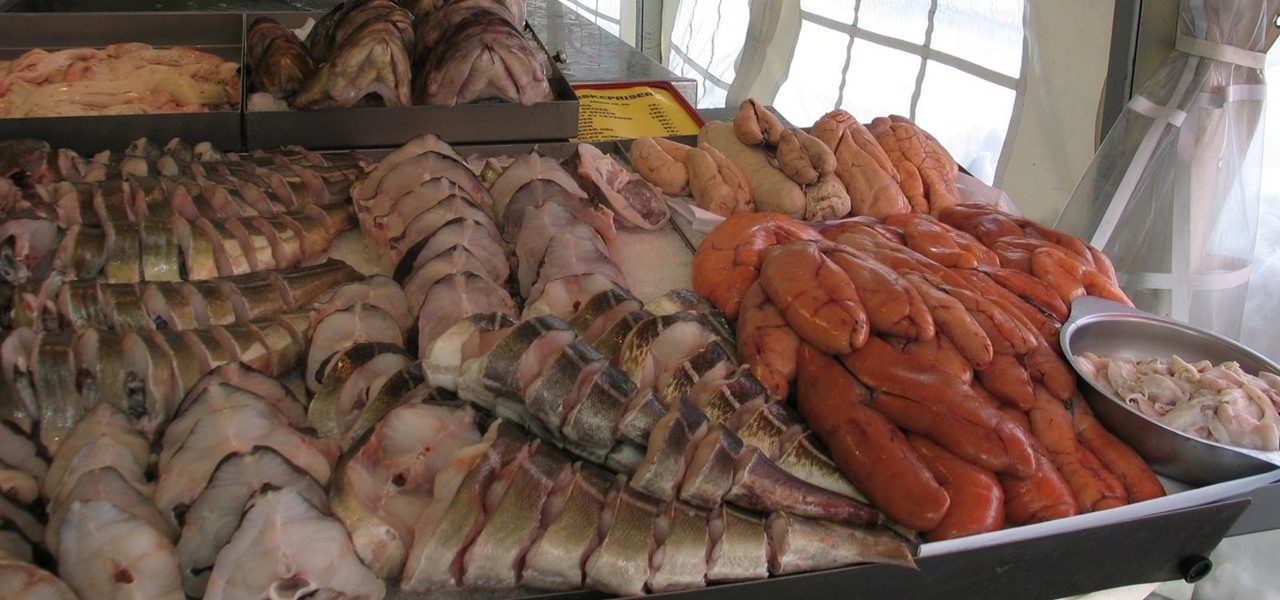
Food is both a necessity and a joy. Many people enjoy exploring, cooking, eating, and learning about foods from around the world. But the picture isn't always rosy. A new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), highlights the ways and whereabouts of food that make us sick.
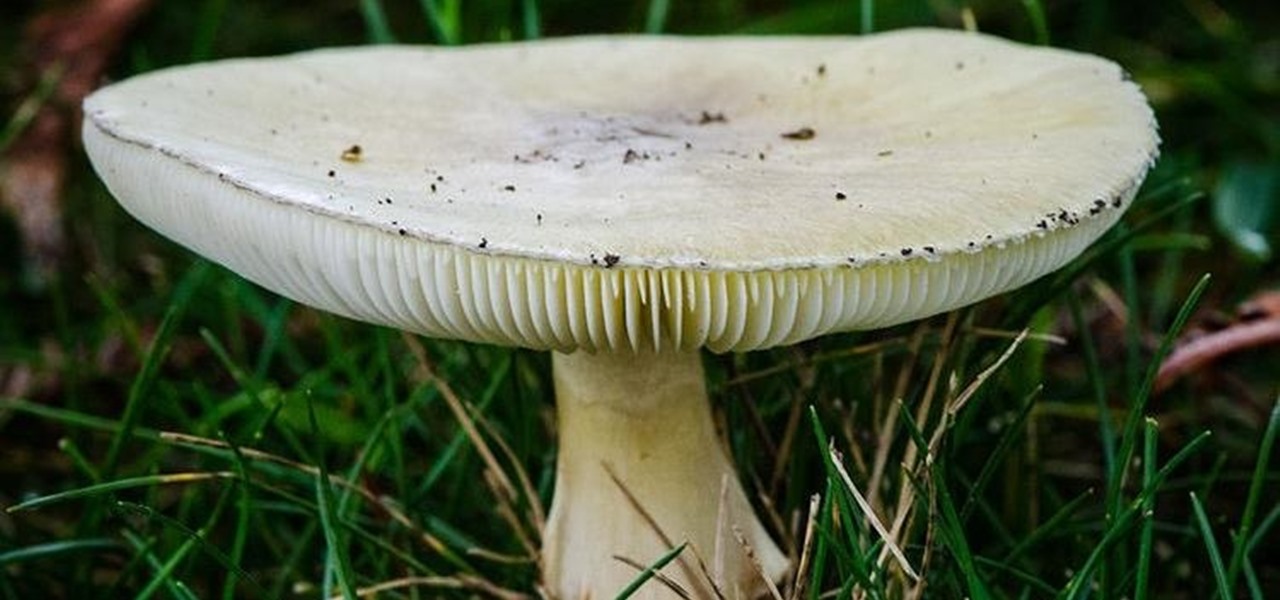

There is a reason the Amanita phalloides mushroom is called the "Death Cap." It can kill you. Mushrooms are a type of fungi, an organism that produces thread-like mycelia that often produce spores. Spores allow the fungi to reproduce. Molds, lichens, and yeast are all fungi, but the most visible fungi are mushrooms. Some fungi are delicious, but others can cause disease or, and still others, like Penicillium, can cure it.
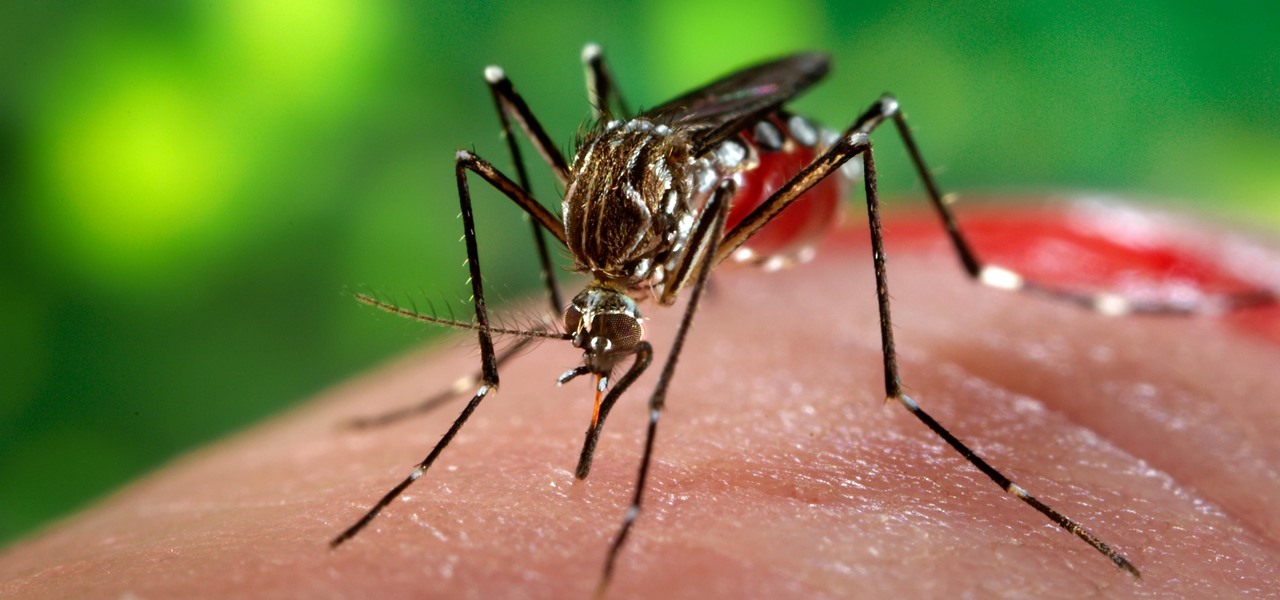

Mosquitoes are a big problem, and citronella candles are not the solution. There are a lot of mosquito species. The American Mosquito Control Association reports there are more than 3000 mosquito species in the world, and about 200 of those occur in the US. The most common are the Aedes, Anopheles, and Culex species. These are also the three mosquito species most likely to transmit serious illness, and all of them live in the US.
The Massachusetts Department of Public Health (DPH) issued a health alert for a Boston mumps outbreak, on Monday, June 5th, to healthcare providers and local boards of health. There have been 12 reported cases of mumps during the recent outbreak. The affected residents' symptoms occurred between March 24th and May 31st, and 10 of the 12 had symptoms after May 9th. There have been 35 confirmed cases of mumps in 2017 in Massachusetts, and "nearly 300" suspected cases in the continuing outbreak.
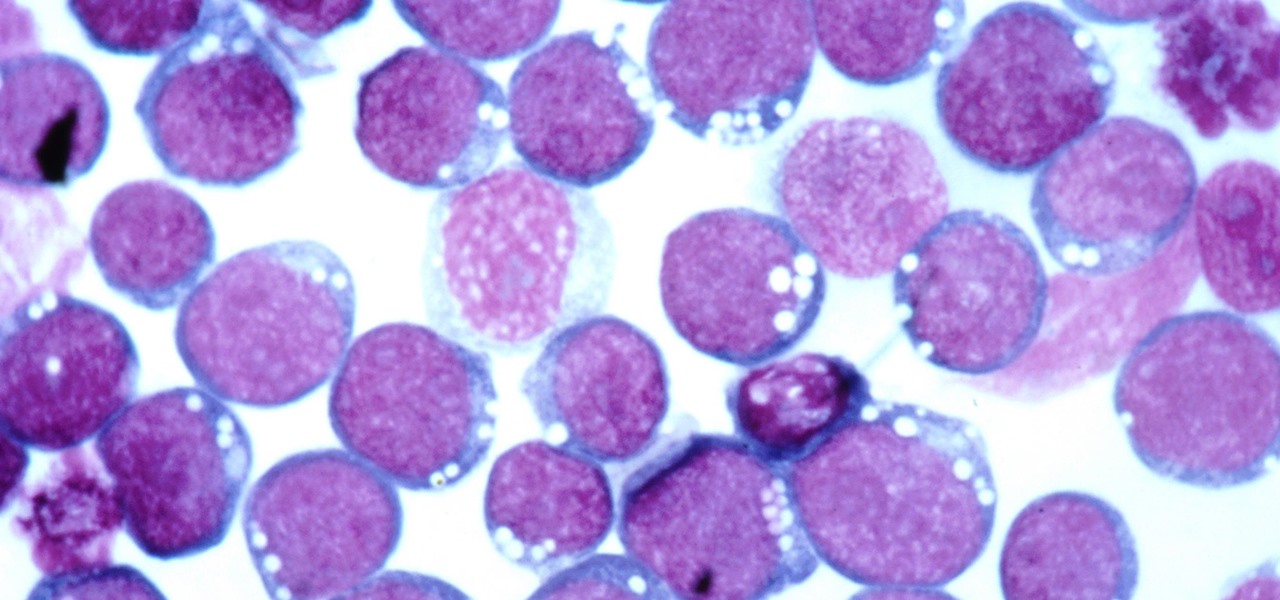
Most of us have already had an encounter with the Epstein-Barr virus, or EBV, for short. As part of the herpes family, it's one of the most common disease-causing viruses in humans. We get the disease with (or without) some nasty symptoms, then we recover. However, EBV stays in our body after the illness has ended, and it's one of the few viruses known to cause cancer.
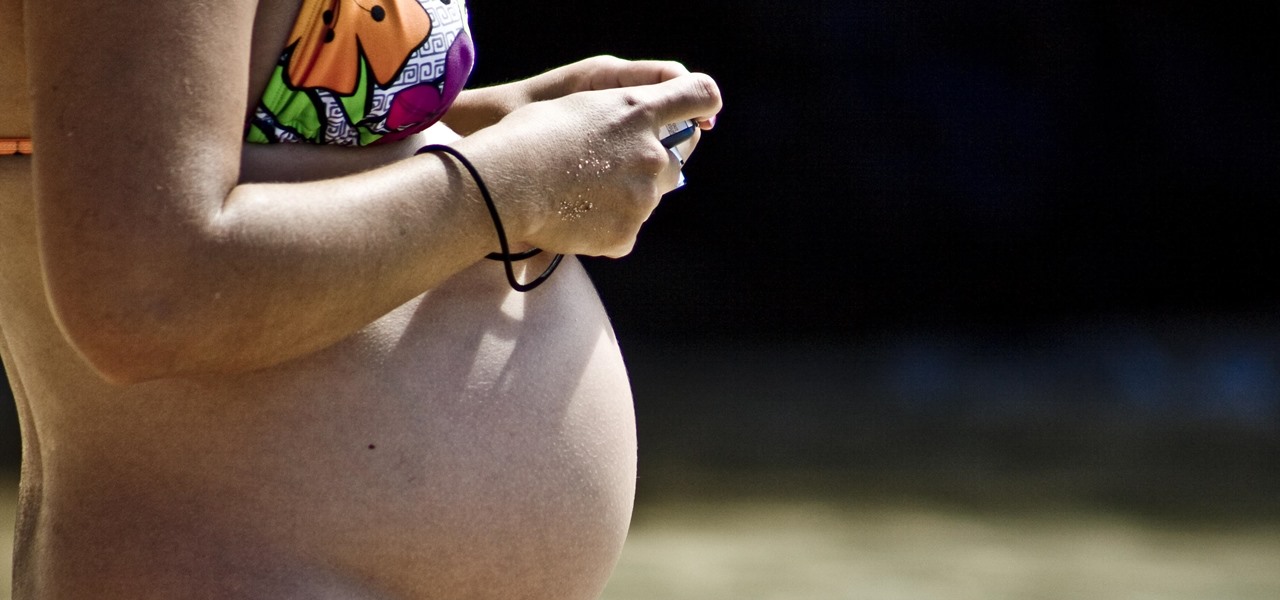

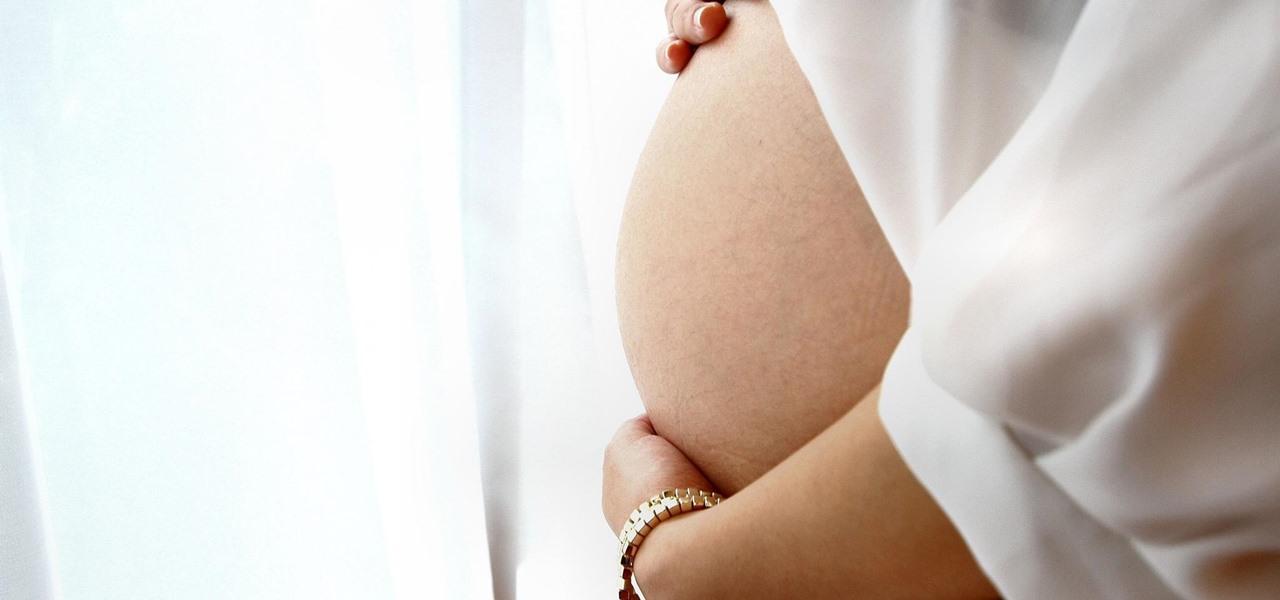
As if being pregnant did not come with enough worry, a new study found that certain antibiotics are linked to an increased risk of spontaneous abortion, or miscarriage — a terrifying finding for any expectant mother.

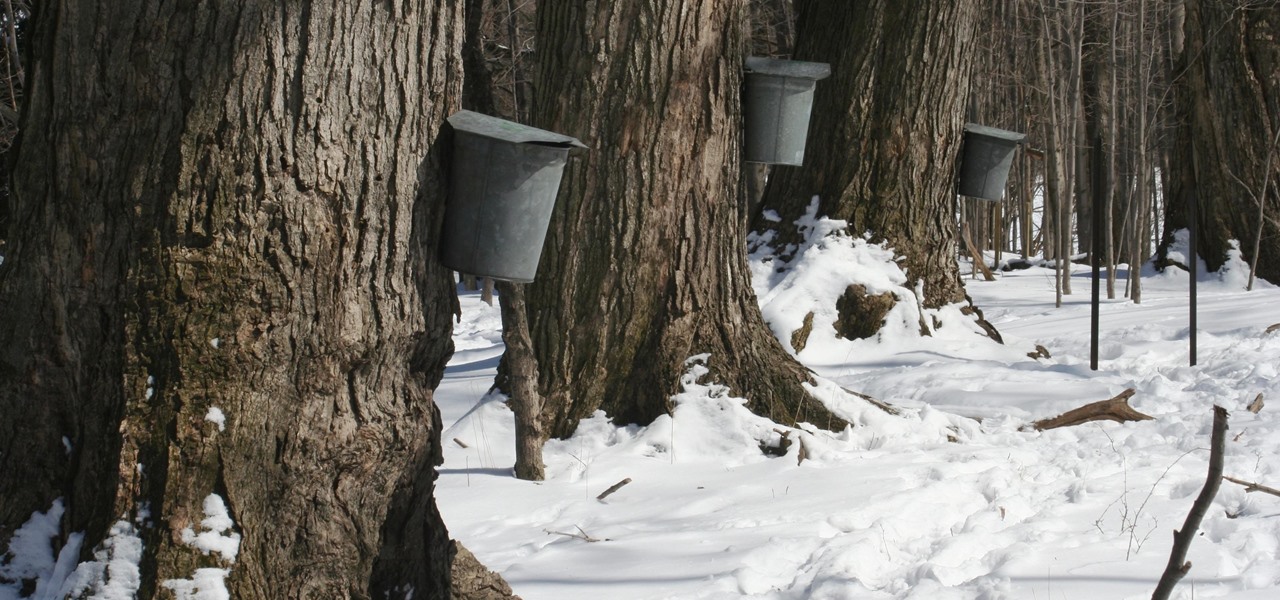
In the ongoing search to find better ways to use antibiotics, an extract made from maple syrup has some surprisingly important medical benefits.

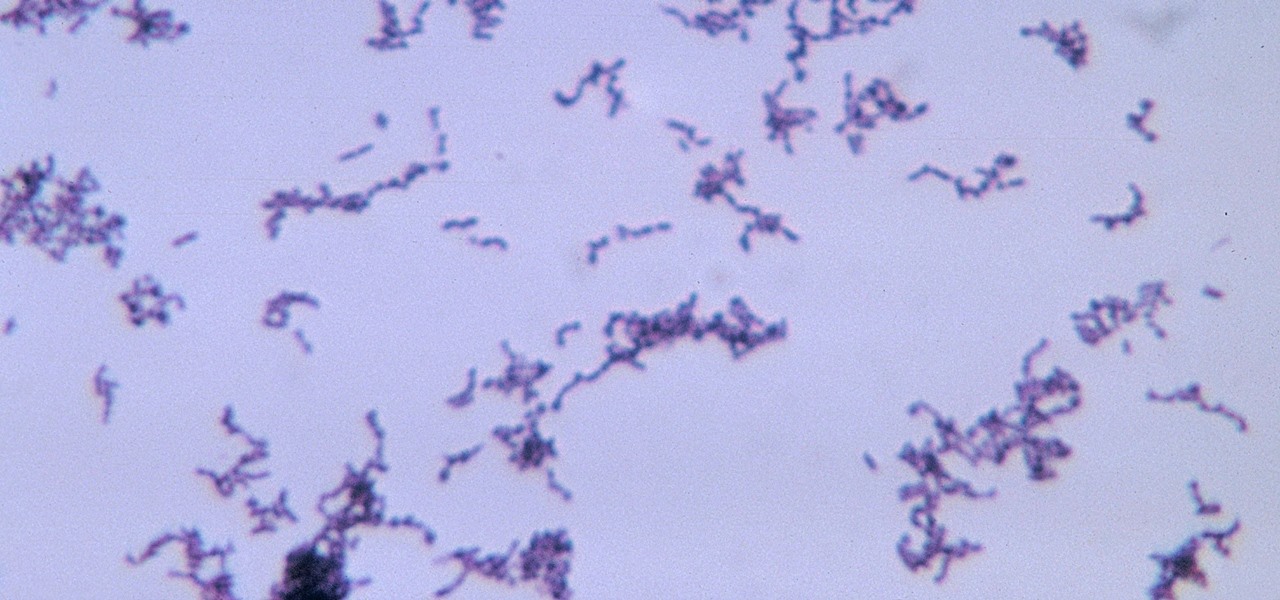
The squiggly guys in this article's cover image are Propionibacterium acnes. These bacteria live in low-oxygen conditions at the base of hair follicles all over your body. They mind their own business, eating cellular debris and sebum, the oily stuff secreted by sebaceous glands that help keep things moisturized. Everybody has P. acnes bacteria—which are commonly blamed for causing acne—but researchers took a bigger view and discovered P. acnes may also play a part in keeping your skin clear.

An advance in the race to stop birth defects caused by Zika-infected mothers has been made by a team of researchers from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, New York. They have identified the process Zika uses to gain entry into the placenta, and published their findings in the journal Biochemistry.

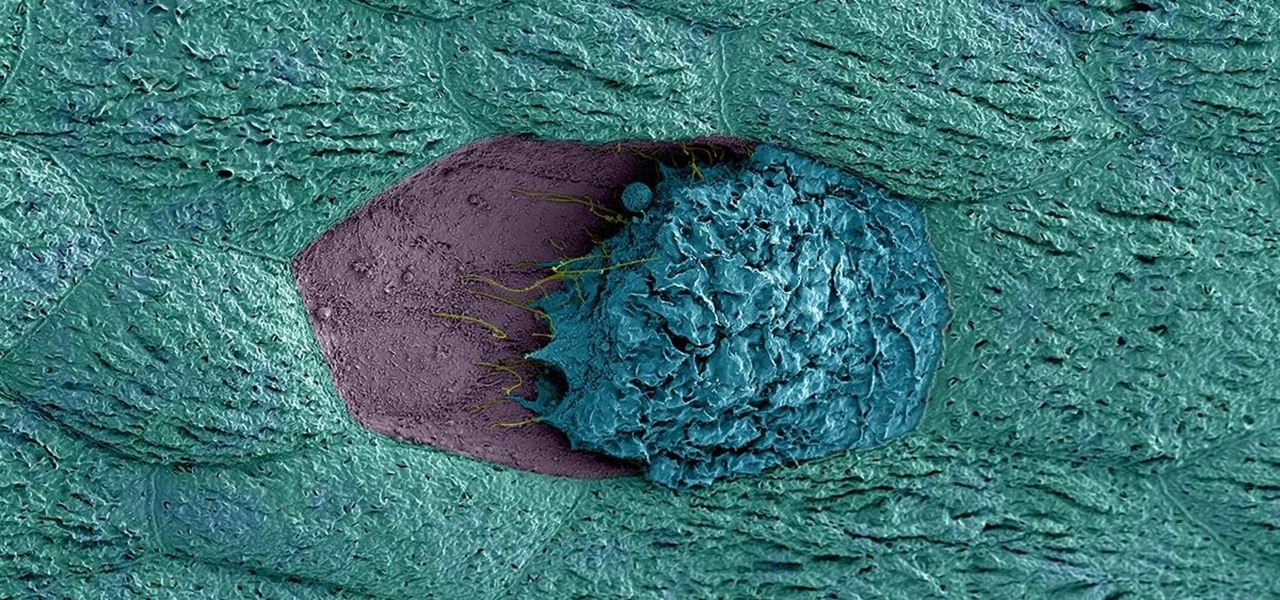
Most females have had at least one urinary tract infection in their lifetimes. Recurrent UTIs are particularly problematic in young, sexually active women, where about 80% of the infections are caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli, better known as E. coli.

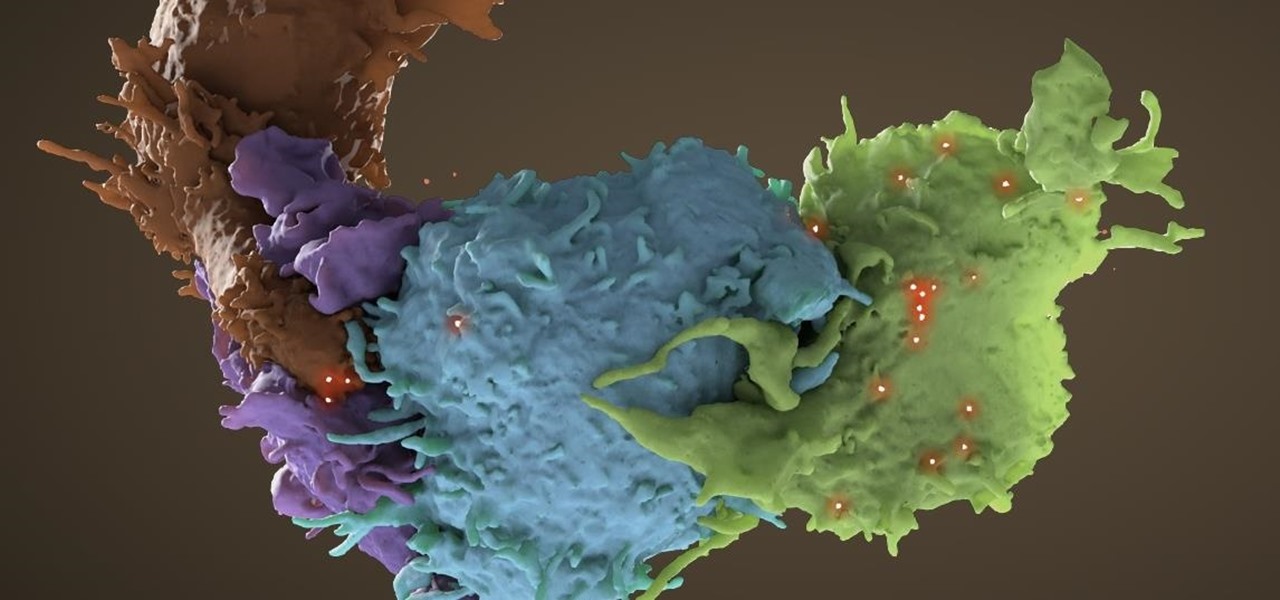
The search for a cancer treatment that selectively finds and kills only the cancerous cells has just made a giant leap forward.

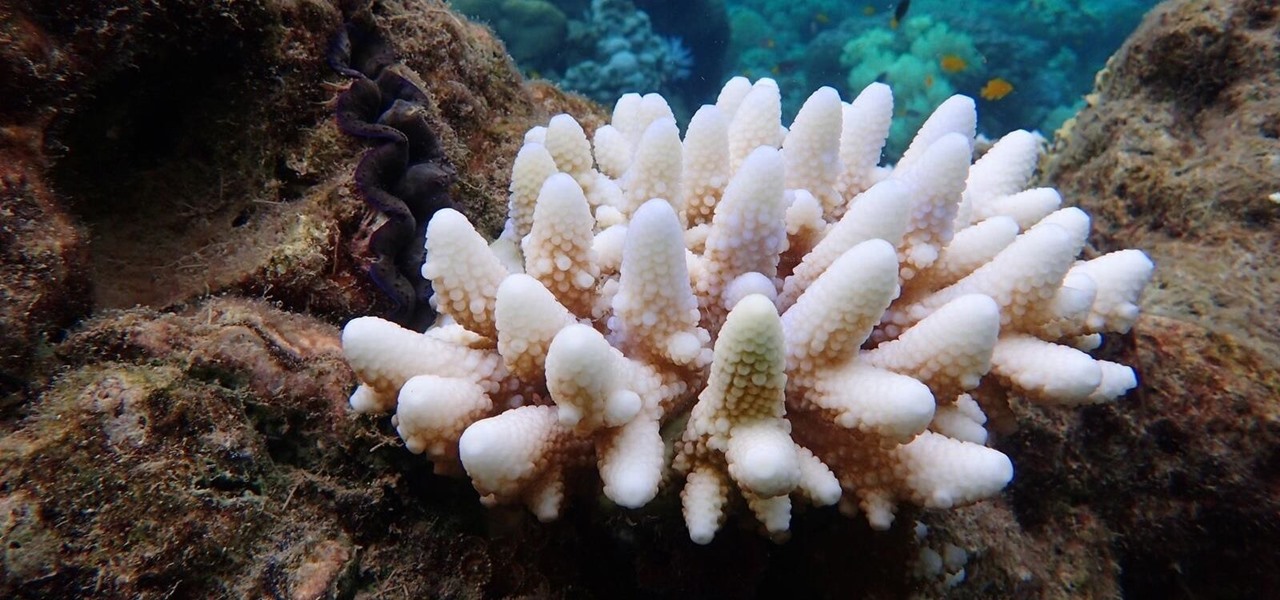
The Great Barrier Reef in Australia is the largest living system on the planet. Yet more than 90% of the reef is bleaching because of the loss of a tiny algae that lives within the coral.

Tremendous strides have been made in the treatment and outlook for patients infected with HIV, the human immunodeficiency virus. Treatment with a combination of antiretroviral drugs can keep patients with HIV alive for decades, without symptoms of the infection. The trouble is, if HIV-infected people stop taking their medications, the virus takes over in full force again—because the virus hides out quietly in cells of the immune system, kept in check, but not killed by the treatment.

An outbreak of anthrax from contaminated meat in Tanzania sickened dozens of people and moves the danger of this deadly bacteria back into focus.

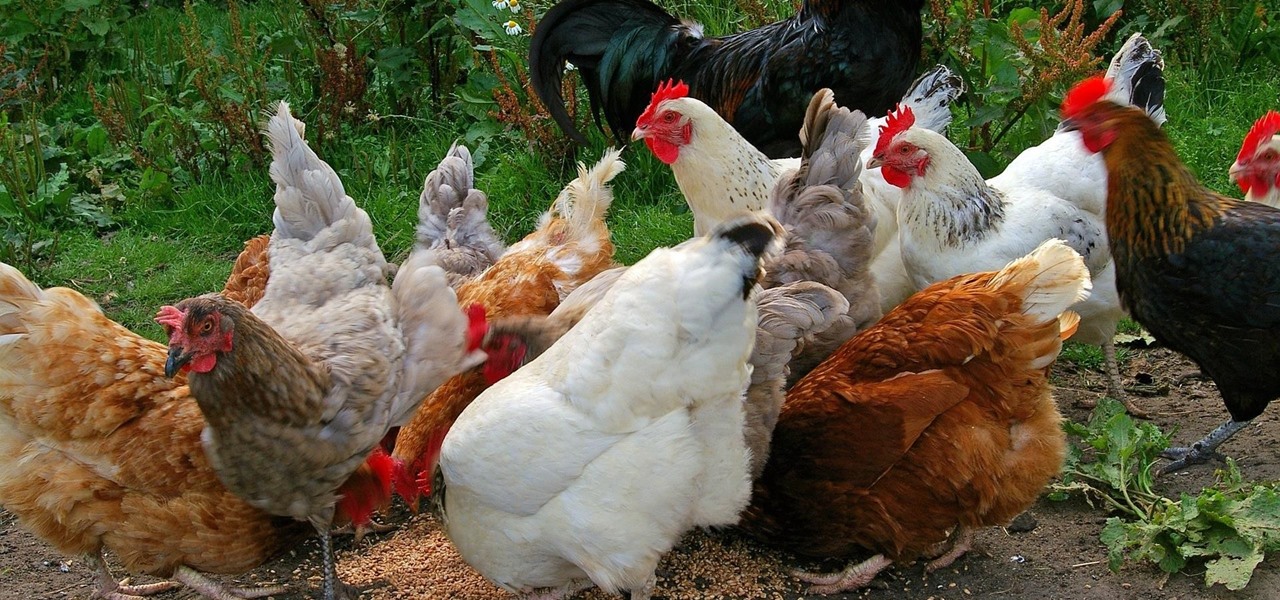
You can get eggs and high-quality compost from backyard chickens—but you can also get Salmonella.

In the past, infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) commonly led to dementia as the virus made its way to the brain. Even in effectively treated people, HIV can hide out and replicate in places like the brain, where it's tough to detect. That's why it's very concerning that half of all HIV-infected patients still report cognitive problems.

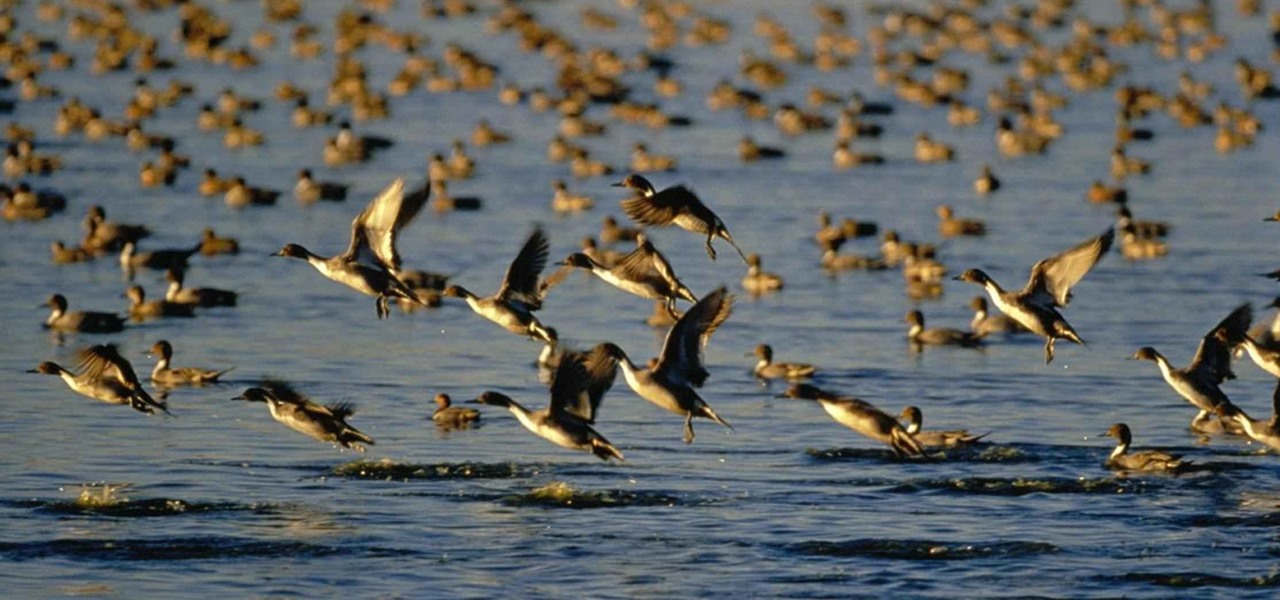
Over 6,500 waterfowl—mostly ducks—have died in Canyon County, Idaho, stricken by avian cholera. The outbreak started in February, and before it's over, it may not only be Idaho's largest outbreak, but one of the largest in the country.

By looking for the mechanism that allows influenza A to invade lung cells, scientists also discovered a treatment that might block the virus from taking hold there.

With new diet and health claims coming at you everyday, it's sometimes hard to know what to believe. Well, here's a bright spot: A pair of studies confirm that whole grains are healthy for you, and for the diversity of microbes living in your gut.

Maternal infection with genital herpes, or other pathogens, during early pregnancy could increase risk of autism, or other neurodevelopmental disorders, says a new study.

Avian flu is making the news again with new human cases in China reported in January. What does "avian flu" mean to you—and how dangerous is it?

The pathogen referred to as a "nightmare bacteria" is quietly adapting and spreading faster than anticipated.

Although their effectiveness is waning, antibiotics remain a front-line defense against many infections. However, new science reveals using the wrong antibiotic for an infection could makes things much worse.

Lighthouses and signal fires may have been the first social media. Without the ability to share language, a distant light meant "humans here." A new study from the University of California, San Diego, finds that bacteria can also send out a universal sign to attract the attention of their own, and other bacterial species.

Humanity is standing on an infection precipice. As antibacterial resistant grows, we're running out of options, and a recent scary case of total antibiotic resistance is a frighting view of our potential future. In the end, it was septic shock that took the life of a 70-year old woman with an incurable infection. One of few such cases in the US, her death could nonetheless be the shape of things to come.

After California college student Luis Ortiz blacked out and was taken to the hospital in 2015, doctors were startled to discover the reason his brain was swelling—a one-centimeter long, wriggling tapeworm living within a ventricle in the middle of his brain.

Cats give us so much—companionship, loyalty, love... and now the bird flu. Several weeks ago, a veterinarian from the Animal Care Centers of New York City's Manhattan shelter caught H7N2 from a sick cat. According to a press release from the NYC Health Department on December 22, "The illness was mild, short-lived, and has resolved." This isn't the first time cats have passed infections on to humans, but it is the first time they passed on the bird flu—avian flu H7N2, to be exact.

Findings from a mouse study suggest that the Zika virus infection may have serious reproductive consequences for men.

With the height of the flu season ahead, there are some good reasons to keep a flu vaccination in mind.

Using a technology we like to call "Hive Computing," several Android apps allow you to contribute idle processing power to help further scientific research. This basically means that when you're not using your phone or tablet, it can join forces with other idle devices to form a supercomputer that scientists can use to potentially make a world-changing breakthrough.

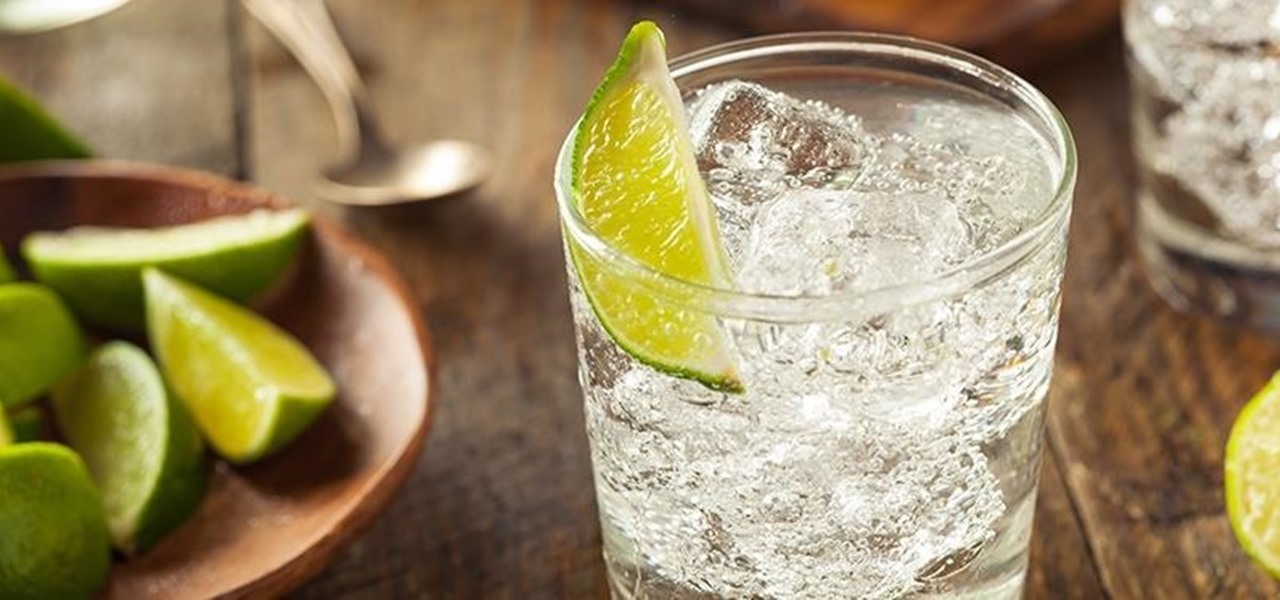
Alcohol isn't exactly considered a healthy lifestyle choice; more often than not, it's associated with empty calories and bad decisions. But that doesn't mean there aren't a few benefits to drinking in moderation. In fact, gin is a liquor with a wealth of potential benefits to offer. So read on, and discover ten ways in which gin might actually be a good drink for you.

Though many students spend four years of high school learning a foreign language, most of us probably retained very little. Chalk it up to the carelessness of youth, but chances are you've since been in situations or places that left you wishing you paid more attention in class or had continued practicing long after you graduated.

One of the vital fashion accessories is sunglasses. Sunglasses assist in creating a sort of unique identity for you. Your age, the shape of your face and of course your personal taste influences the precise style you decide on. There are some basic factors that must be put into consideration when you are thinking of buying your pair of sunglasses. It is important to be educated about what makes a quality pair of sunglasses. So when you want to choose your next pair of sunglasses, keep the fol...

Lose weight while sitting on the bus, train, or in your car with these stealthy moves. You Will Need

There's an epidemic on the Internet, and the disease—Facebook. It's an addiction comparable to a hot cup of coffee in the morning or a soothing cigarette throughout the day—in worse case scenarios, a hit from the crack pipe. If you're on Facebook, you know what I'm talking about. You're addicted to finding out what's going on with your friends and addicted to telling those friends everything you're doing. You can't stop, even when you're at work.

In a previous post, I wrote about how controversy changed SCRABBLE, about how the SCRABBLE Dictionary evolved thanks to Judith Grad and her crusade to rid the world of derogatory and racist words. She won, at least in some manner, but the fact still remains, racist or not—words are words, and they're here to stay.

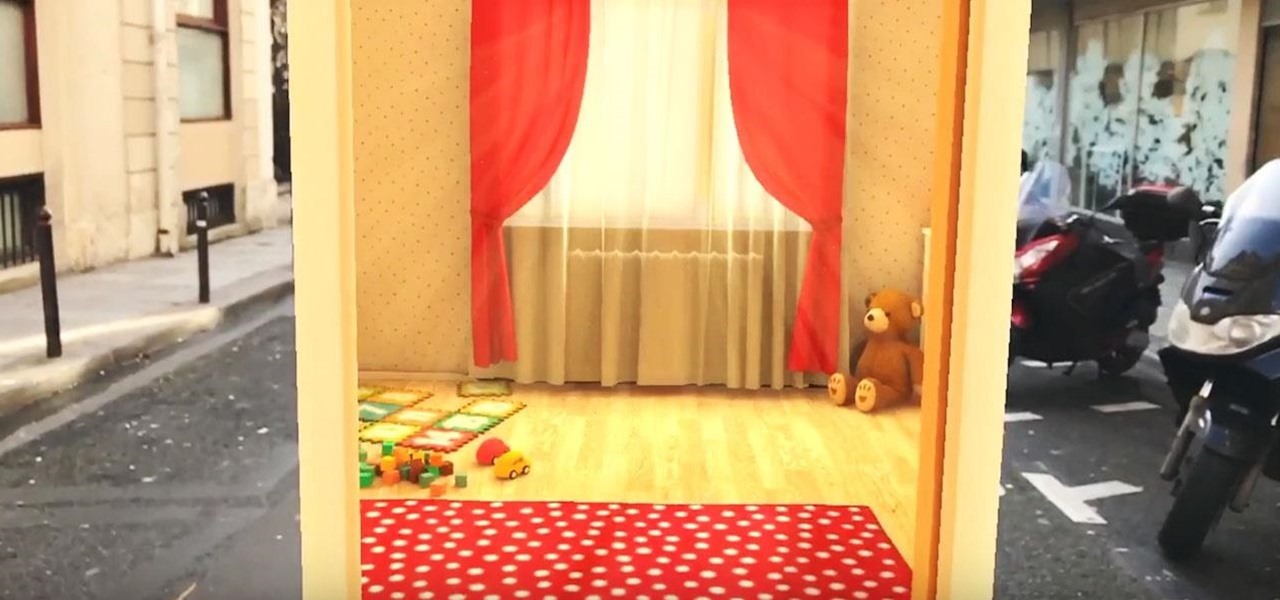
Next to things like natural disasters and disease, the specter of war is one of the only things that threatens to derail the 21st century's long stretch of technological innovation. Now a new app is using augmented reality to remind us of that by focusing on those most impacted by war — children.

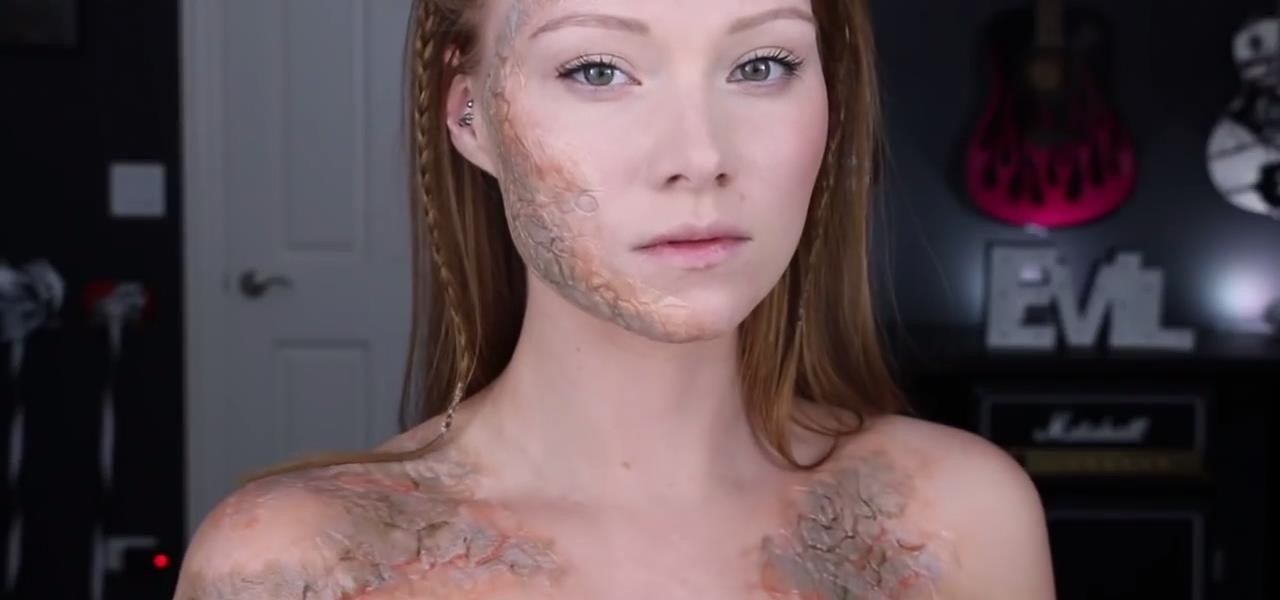
There aren't many people who will believe that a prosthetic zipper face or gunshot wound to the eye (disgusting as they are) are real, but greyscale from Game of Thrones? That'll really unsettle people for awhile because it totally looks like an actual, honest-to-God infection that someone in 2017 could conceivably have. Which makes it very effective come Halloween, whether it's for a full-on Princess Shireen, Jorah Mormont, or Stone Man costume, or to just infect a completely different chara...

Despite mounting scientific evidence that viruses can cause changes in learning and memory, the reasons have remained elusive.

With significant advancements in the treatment and prevention of HIV, you'd think the stigma surrounding the deadly virus and AIDS, the syndrome the infection causes in the body, would have lessened. Unfortunately, a new project looking at conversations on Grindr — a social networking app for gay, bi, curious, and queer men — has shown that this stigma is very much present.