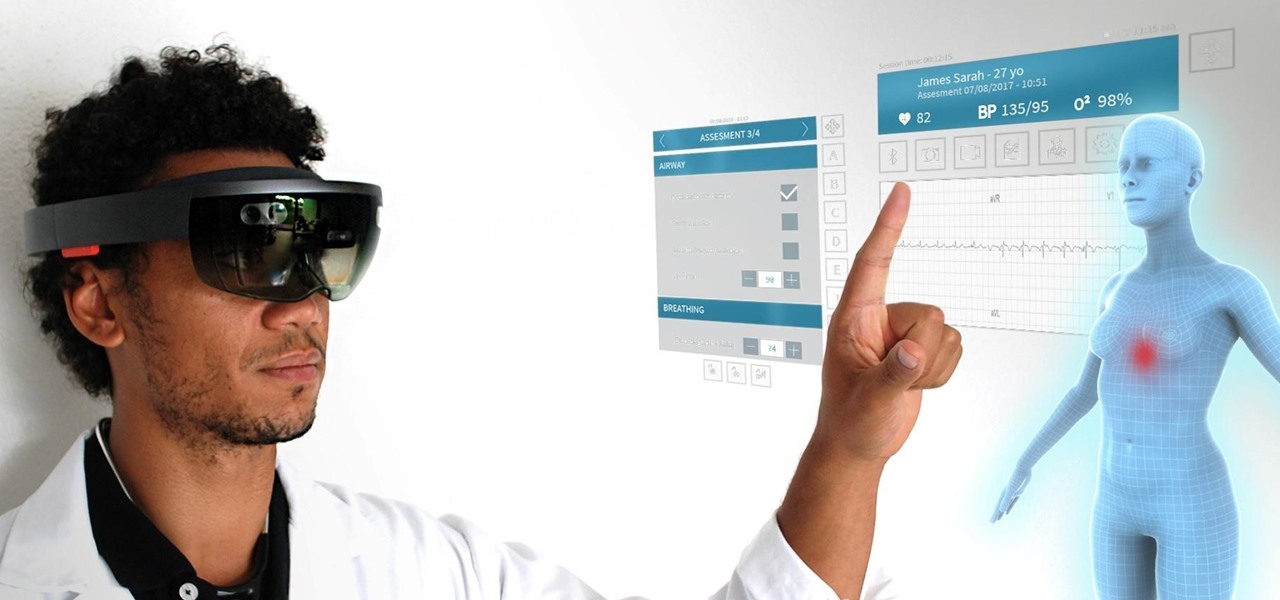
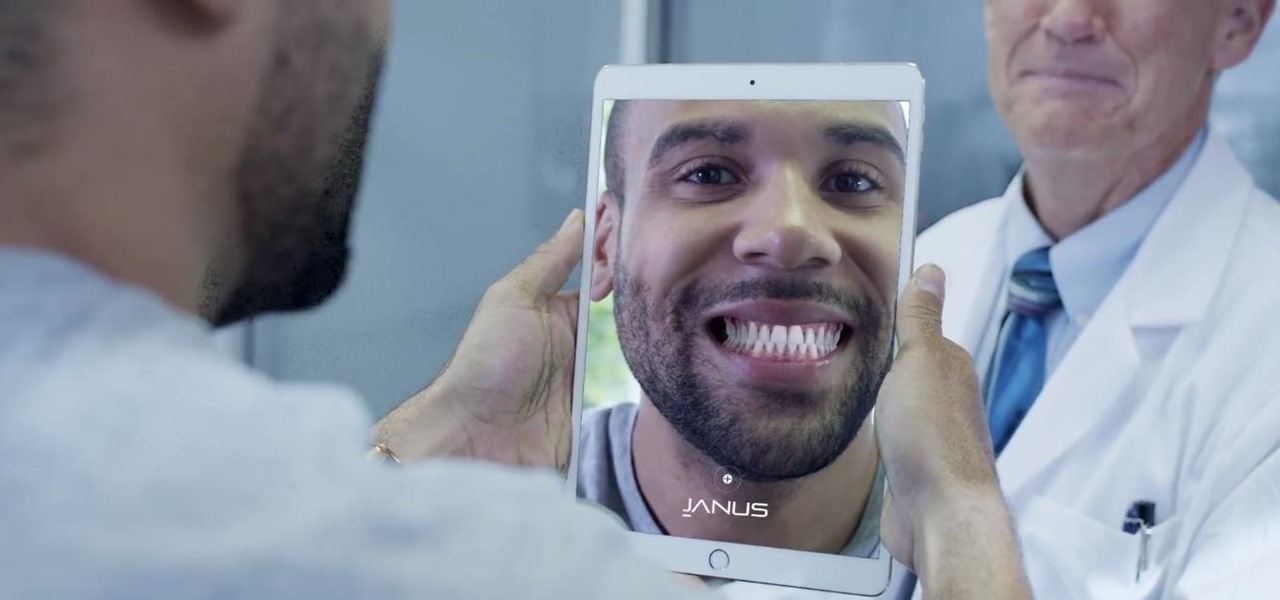
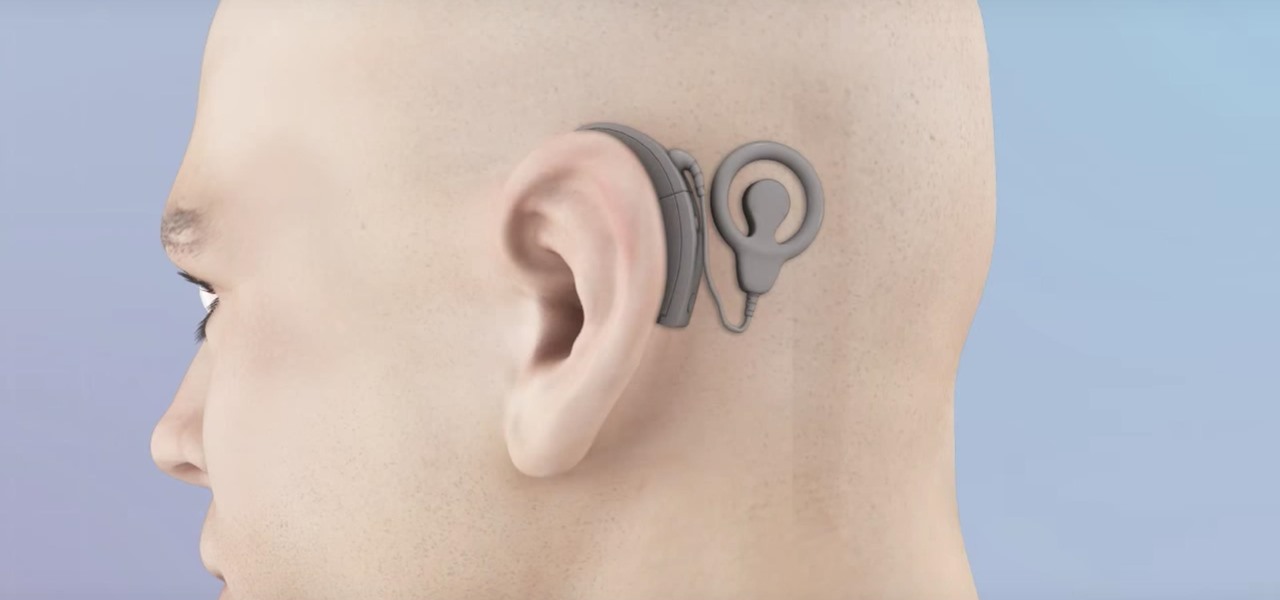
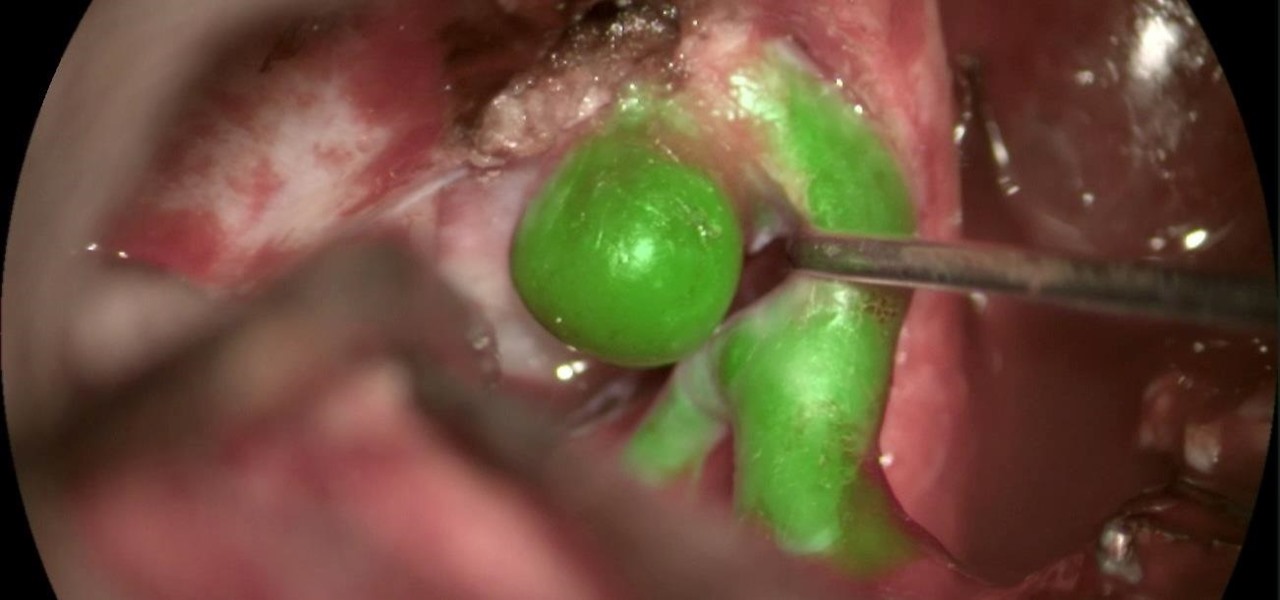
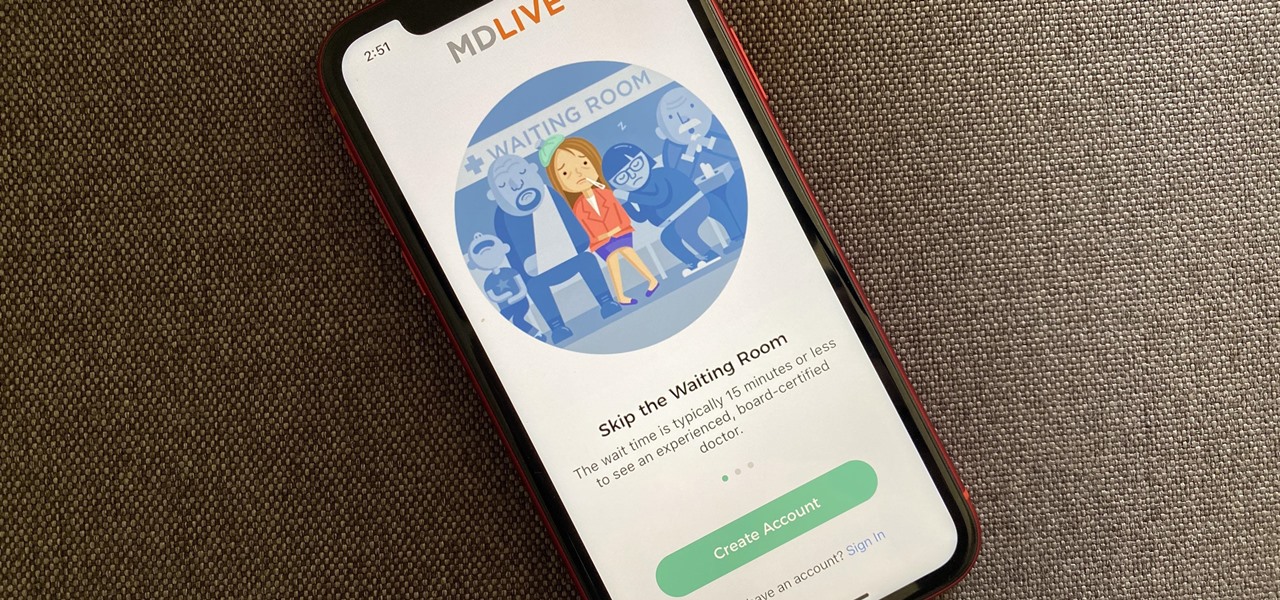
A new telemedicine application for the Microsoft HoloLens is promising paramedics and EMTs a new tool for diagnosis and treatment of patients in the field.

Phuket, the island in Thailand typically associated with paradise and most recently, illegally-run hotels, now has a different problem—a stray cat with the claws of death.
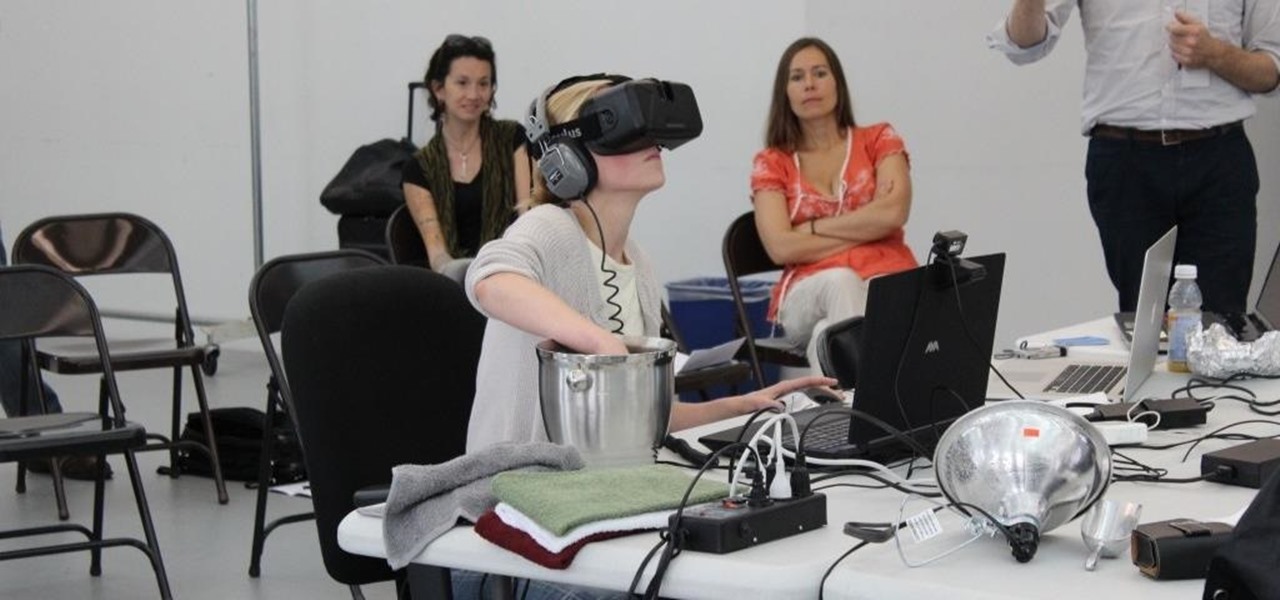

We've already seen how VR can have some therapeutic benefits, but not the dramatized version. A play called Ugly Lies the Bone emotionally examines how war veterans can heal (or at least treat) their PTSD using virtual reality.
As unappealing as it sounds, transplants with fecal material from healthy donors help treat tough Clostridium difficile gastrointestinal infections. Researchers credit the treatment's success to its ability to restore a healthy bacterial balance to the bowels, and new research has shown that the transplanted bacteria doesn't just do its job and leave. The good fecal bacteria and its benefits can persist for years.
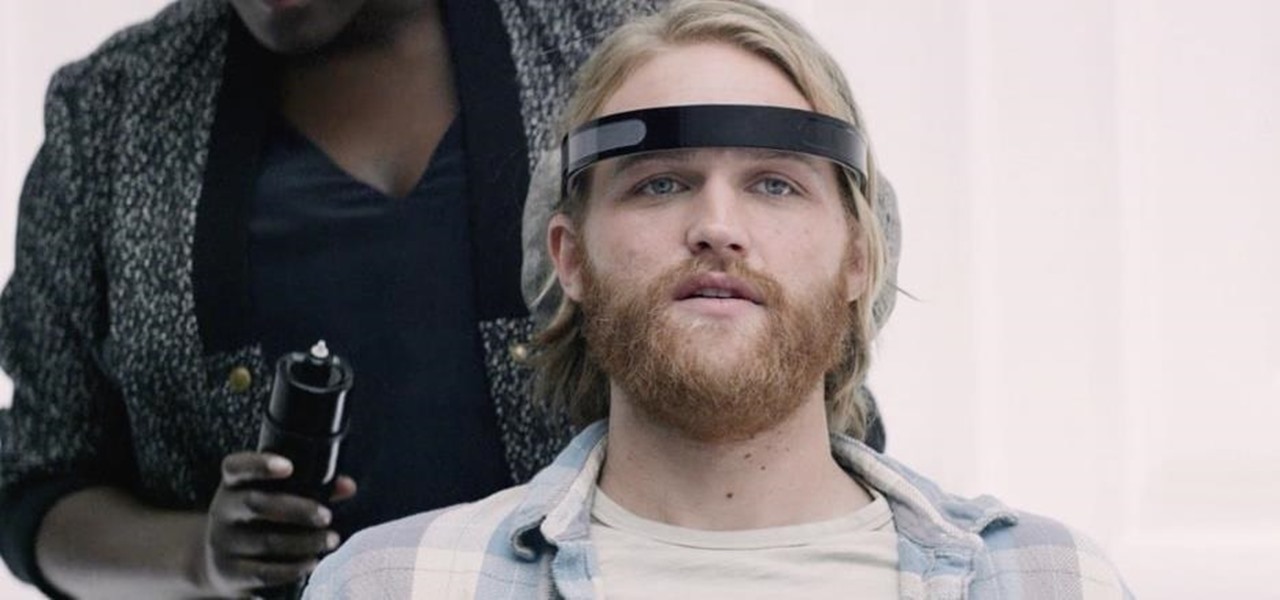

Black Mirror, Netflix's technology-horror anthology, never fails to provide thought-provoking entertainment centered around emerging and futuristic technologies, and the third season's second episode, "Playtest," delves deep into the worlds of mixed, augmented, and virtual reality. While designed to leave you haunted by the end, offering a more "evil" narrative than we'll likely see in our actual future, the episode explores possibilities that aren't as far off as one might think.
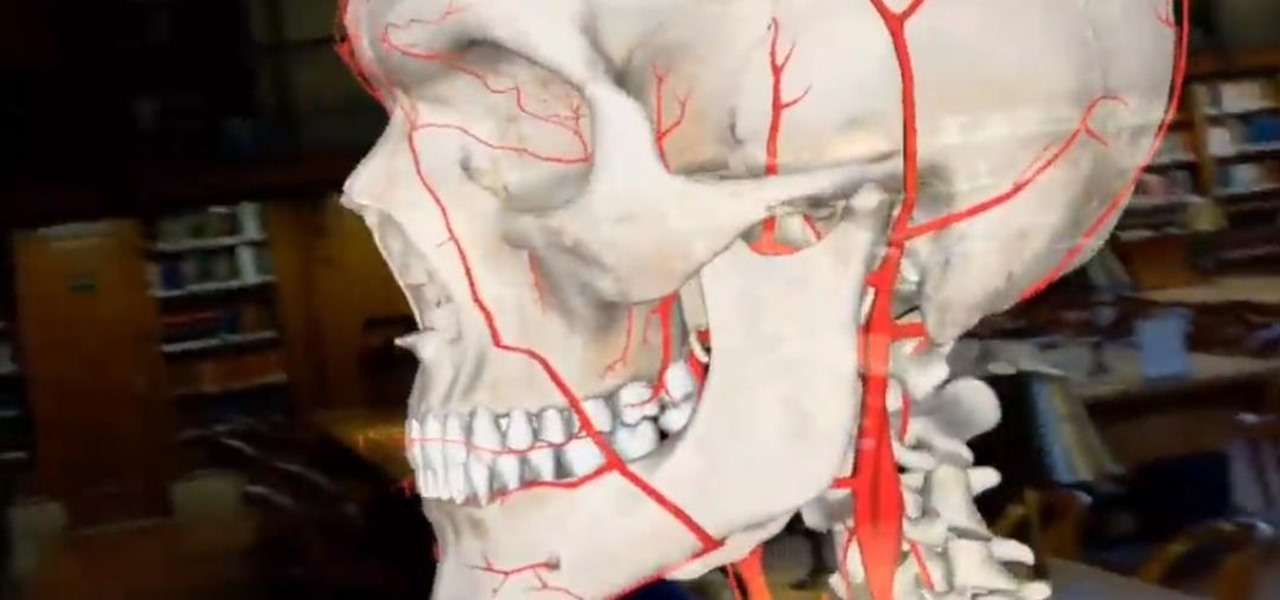
Not content to merely assist surgeons via the HoloLens, Medivis has expanded its augmented reality suite to Magic Leap One with an app for medical students.

For some, going to the dentist can be a terrifying experience, but a new use of augmented reality could go a long way toward making the trip feel more like it's worth the orthodontic angst.

Investors are ready to throw their money at augmented and virtual use cases that demonstrate a business purpose and a return on investment.

Despite mounting scientific evidence that viruses can cause changes in learning and memory, the reasons have remained elusive.

While many have their own strong opinions on Apple and their products, few have complaints about the way they embrace accessibility. Apple typically finds ways to make products functional to all customers, regardless of their situation. This philosophy can be seen in Apple's partnership with Cochlear, as the two develop a new cochlear implant sound processor for iPhone.

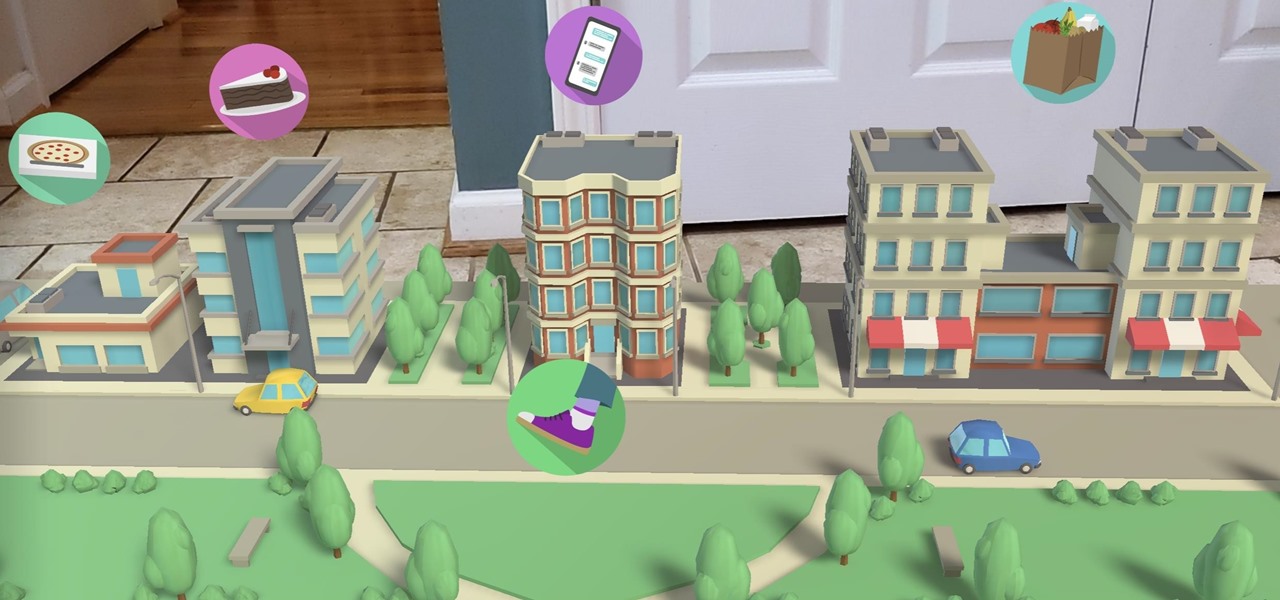
The common thread between this week's Brief Reality stories is that augmented reality is beginning to prove its worth as a technology that improves workflows and processes. From customer service to healthcare to manufacturing, augmented reality is helping companies improve productivity.

Sepsis is not only a gross sounding word but also a deceptively dangerous and fatal infection. Which is why more than 40 hospitals nationwide are coming together to a new collaboration to help reduce sepsis mortality, named Improving Pediatric Sepsis Outcomes (IPSO).

Every party has a pooper, and that's why you're reading this article. We don't mean to be a downer on such a fun day as 4/20, but it's important to make sure you know about the source of your pot, especially if you're one of the 2,299,016 people who use medical marijuana in the US.

Hey dolls! I have to share the secret of Copper peptides with you all. I don't know why it's taken me so long to jump on this band wagon because the science and studies behind the product are amazing!

Any living creature will die if deprived of sleep for long enough. The longest documented occurrence of a person not fully sleeping and surviving is only 11 days. There is a rare disease where deep sleep is never achieved, affecting roughly 100 people worldwide. Patients usually only survive between 6 to 18 months after the onset of chronic insomnia, and only 3 to 9 months in a parasomnia state without any real REM sleep.

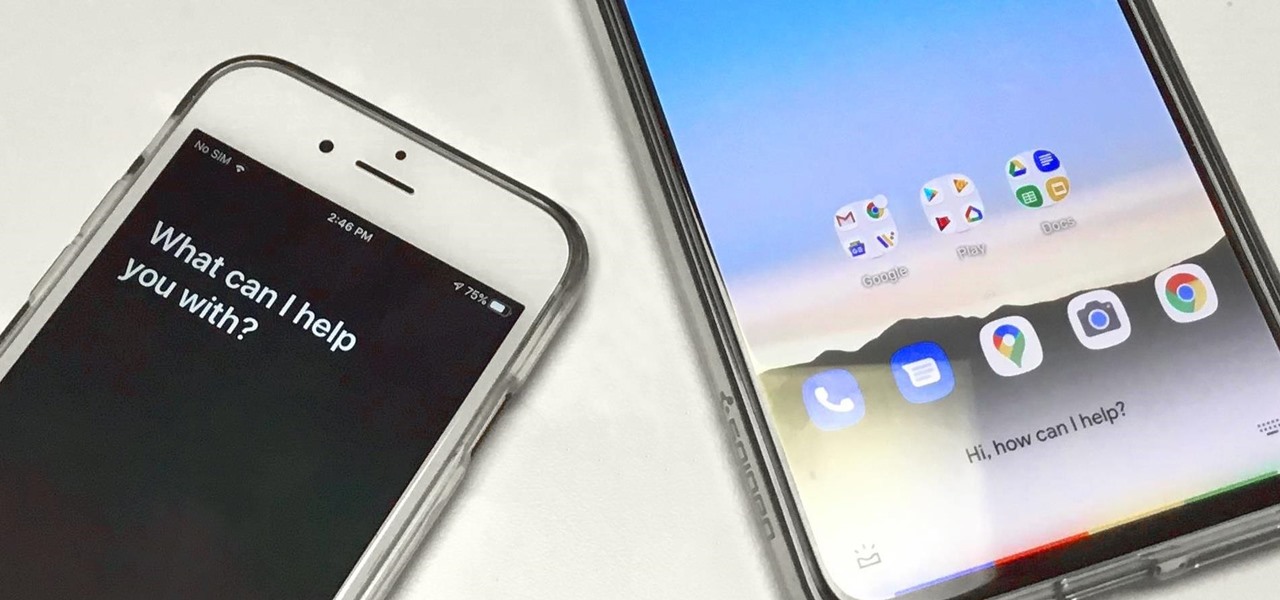
The COVID-19 pandemic has created a frenzy for news and information that is nearly unprecedented in the smartphone era, with a major side effect of misinformation. Now, major tech companies are making it easier to ask for advice about novel coronavirus from their respective digital assistants. Results may vary, but Apple and Google are the most useful at the moment.

I'm here at the annual AWE event in Santa Clara, California, and the venue is just as packed, if not more so, than last year.

With Microsoft taking direct aim at enterprises for its HoloLens 2 with a $3,500 price tag, one startup is betting that business will be willing to pony up for glasses-free 3D displays as well.

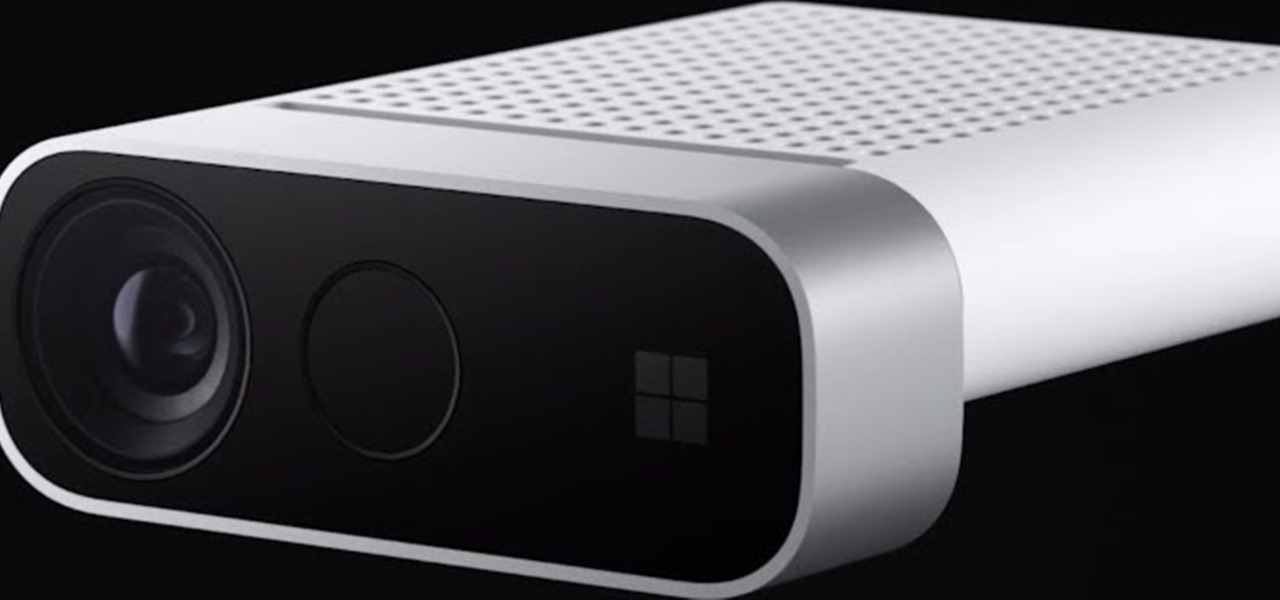
As the opening act to the grand unveiling of the long-awaited HoloLens 2 at Mobile World Congress Barcelona on Sunday, Microsoft showed off the standalone Azure Kinect time of flight sensor, which also happens to supply the improved human and environmental understanding capabilities of the next-generation augmented reality headset.

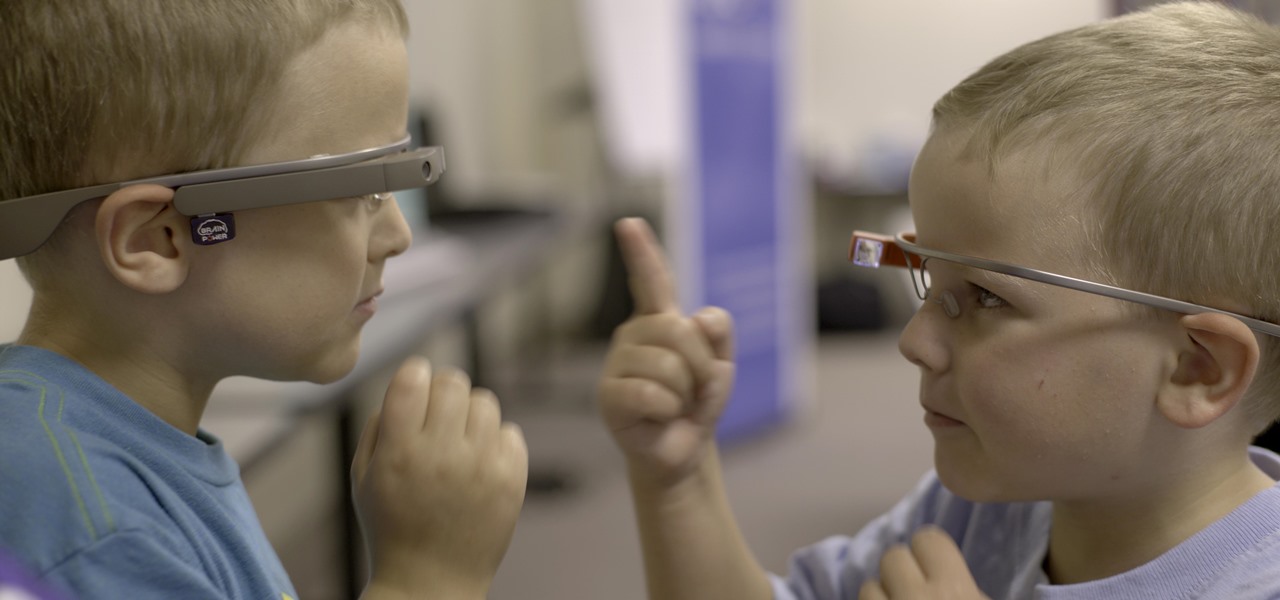
Considered by many (perhaps unfairly) to be a very public failure, Google Glass can add another plot point to its comeback story, this time as a tool to teach social skills to children and adults with autism.

The intestinal parasite Cyclospora cayetanensis has a dramatically increased infection rate this summer, and the source is still unknown, the CDC advised today. 2017 is a good year for Cyclospora looking for homes to start their families and a bad year for those of us who don't like food-stealing tenants living in our bodies.

Growing evidence suggests that neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's may develop in part due to environmental factors, including infections that can cause inflammation in the nervous system. New research from investigators from Jude Children's Research Hospital and Thomas Jefferson University has strengthened that connection.

In the race to outsmart "untreatable" antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea, one of the three new treatments on the track is about to enter Phase 3 clinical trials. Hopefully, it'll be widely accessible sooner rather than later, for the 78 million people who are diagnosed with gonorrhea each year.

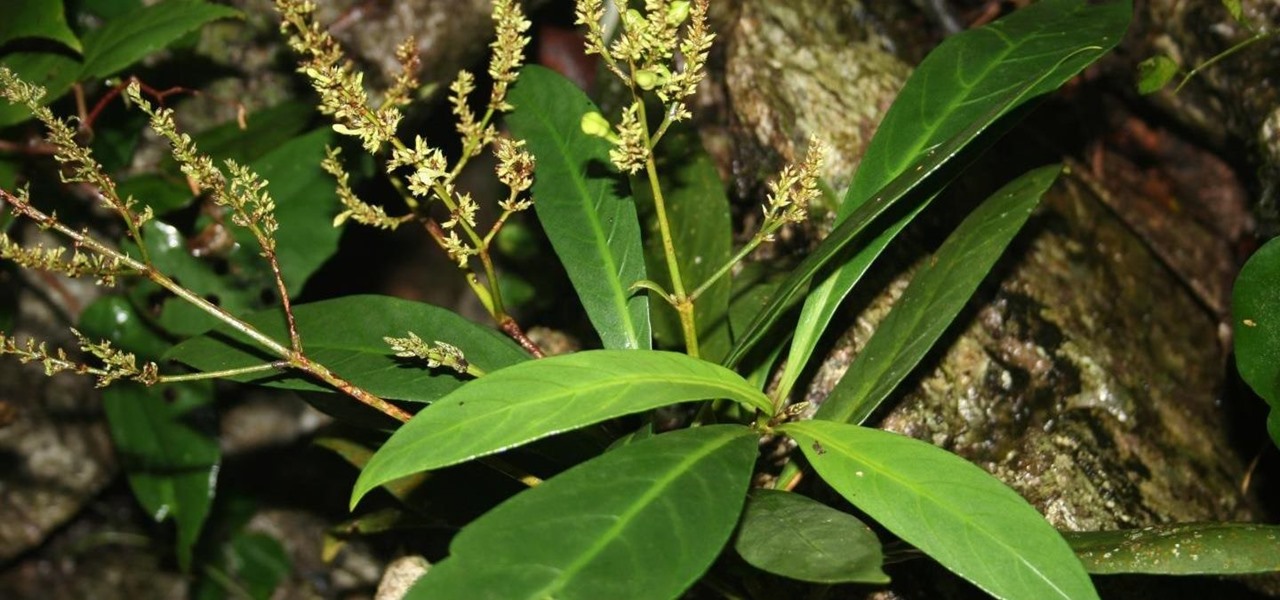
Natural remedies used through the ages abound, especially in Asian medicine. The willow-leaved justicia plant, found throughout Southeast Asia, has traditionally been used to treat arthritis, but scientists have just discovered it contains an anti-HIVcompound more potent than AZT. AZT was the first drug approved to treat HIV, and is still used in HIV combination therapy today.

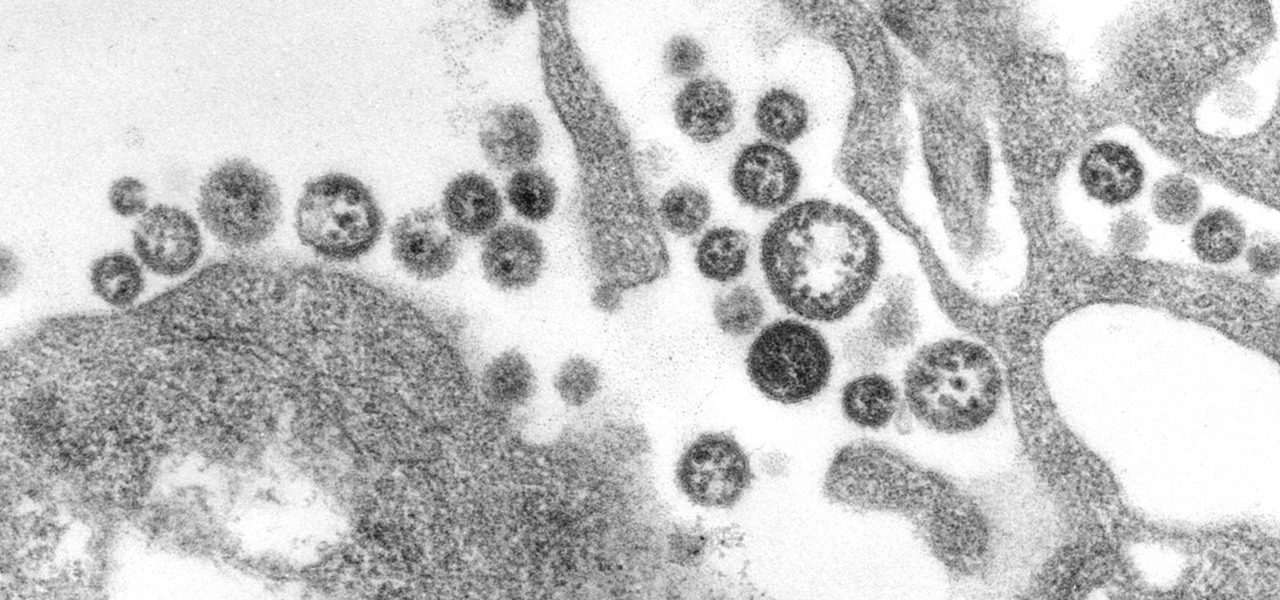
A new case of the still-mysterious Bourbon virus was confirmed in Missouri, likely originating within the state, local authorities said in a June 30 press release.

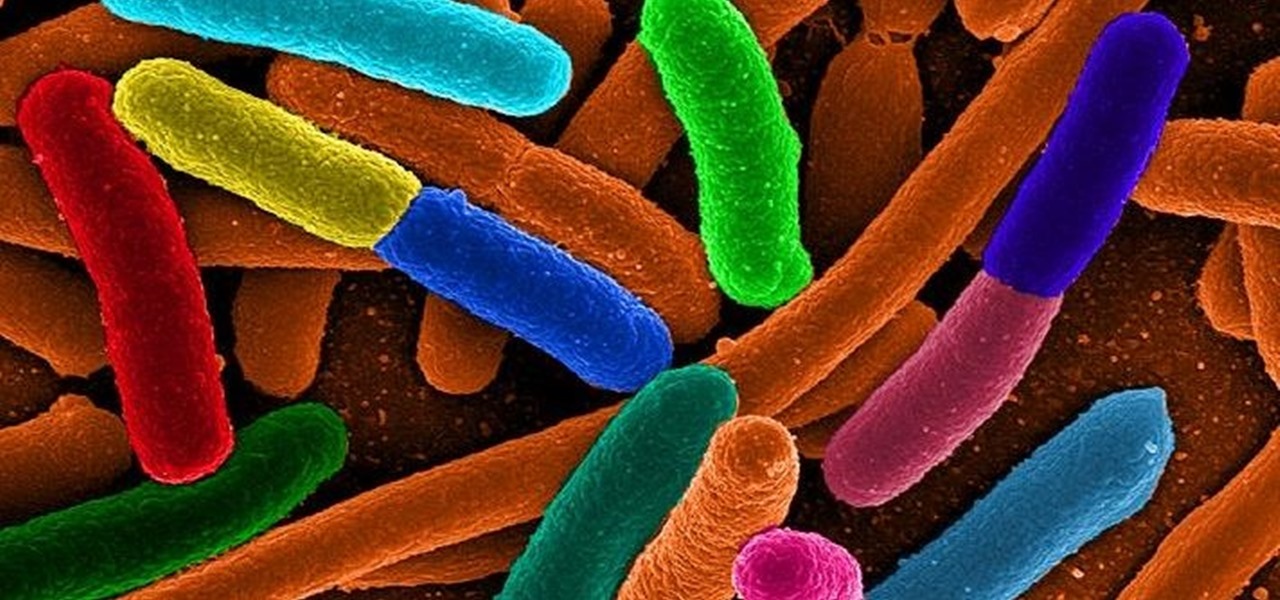
New research reveals how E. coli bacteria construct elaborate and effective tunnels to pump unwanted molecules like antibiotics and other toxins out of cells. The discovery could help us better understand how antibiotic resistance occurs and give us a leg-up to beat them at their own game.

The evidence is mounting and is becoming indisputable: Gut bacteria play a role in strokes and heart attacks. The link may seem a little far-fetched, but cardiovascular disease may have less to do with what we eat and more to do with what chemicals gut bacteria make from the food we eat.

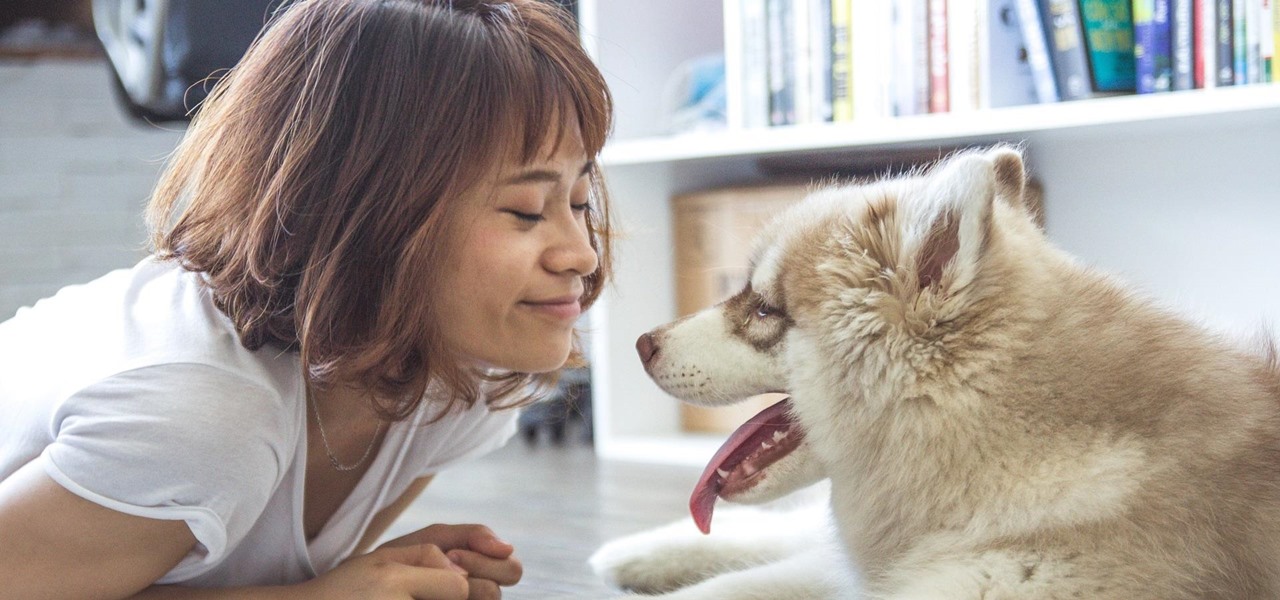
Our canine best friends could spread our bacterial worst nightmare, according to a recent study. The problem with drug-resistant bacteria is well known. Overused, poorly used, and naturally adaptive bacteria clearly have us outnumbered. As science drives hard to find alternative drugs, therapies, and options to treat increasingly resistant infections, humans are treading water, hoping our drugs of last resort work until we figure out better strategies.

In this Tuesday's Brief Reality report, there's a trio of stories from the healthcare world where augmented reality is helping out with surgical microscopes, asthma treatment, and other diagnostic and treatment tools. There's also something for all of you AR/VR storytellers out there.

As many as 700 species of bacteria live on our teeth and in our mouth, and just like the microbiomes inhabiting other parts of our bodies, they change in response to diseases and other health conditions.

Welcome back, my greenhorn hackers! Although we have focused primarily on technical hacks here, social engineering can sometimes be especially effective. This one requires a bit of technical skill, but not too much. In addition, it's limited by how specific a target you can choose—but it will work.

The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic caused by the novel coronavirus has practically guaranteed that the virus, along with the phrases "social distancing" and "flattening the curve," will rank among the top search terms of 2020. USA Today combined the phrases in its latest augmented reality experience, which quizzes your knowledge in the best practices of social distancing.

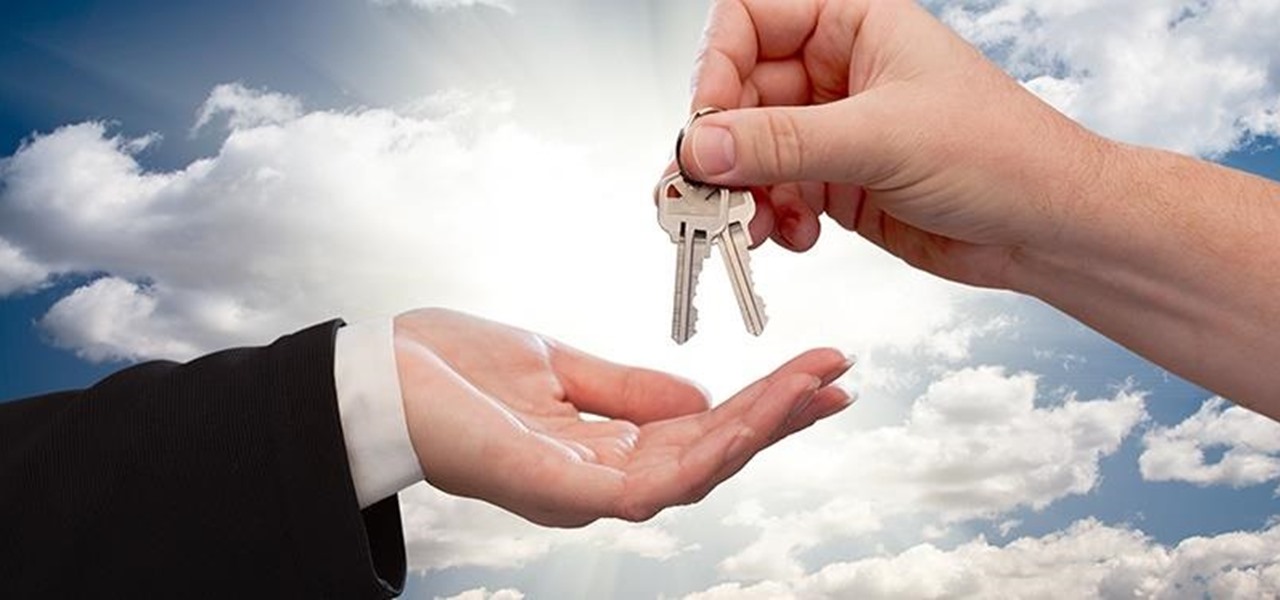
The World Health Organization has declared the new coronavirus a pandemic, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends video visits with a healthcare professional to reduce the risk of being exposed to the coronavirus that causes COVID-19. If you are experiencing mild flu-like symptoms, virtual doctor visits may also prevent you from endangering others.

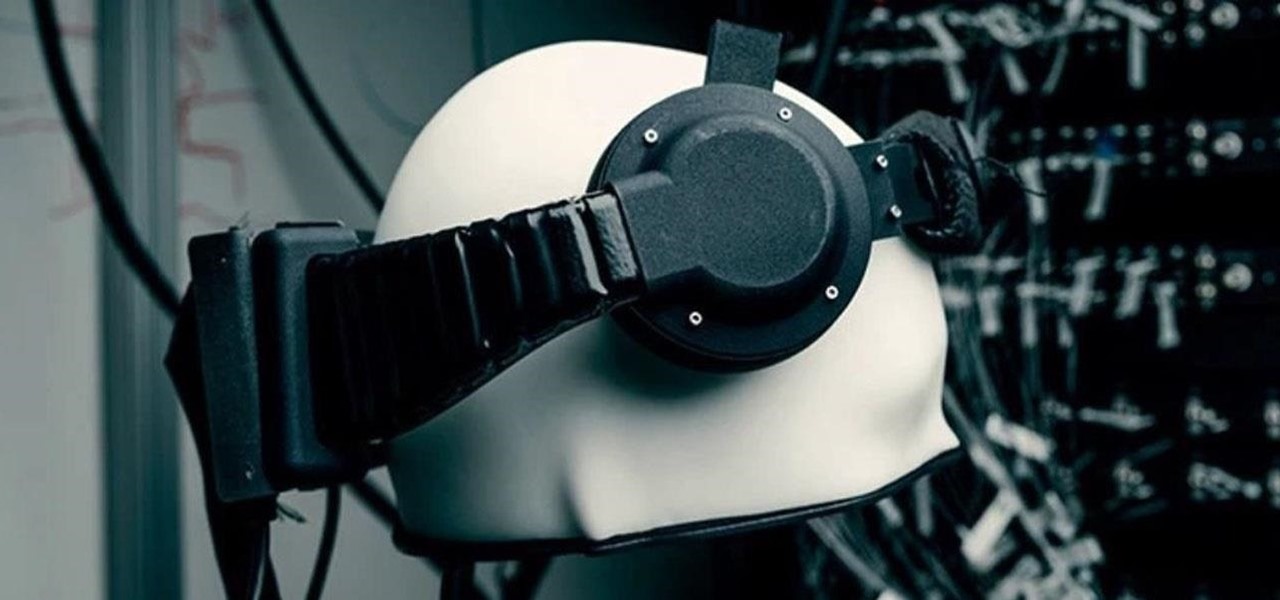
Who's ready to let future Facebook augmented reality smartglasses read their brain? Well, ready or not, the tech giant is making progress in the area of brain control interfaces (BCI) by funding research.

As Magic Leap prepares to ship the Magic Leap One later this year, the company is putting its focus on mentoring developers and creators to build a content ecosystem for the spatial computing platform.

This week, we're beginning to see the wide ranging impacts of some of the early iterations of augmented reality hardware and software.

A recent initiative by the Cherokee Nation American Indian Tribe delivers a success story for knocking out a silent killer — Hepatitis C.

A recent study offers information that might help combat a deadly virus that affects an estimated 300,000 people each year in West Africa.

Scientists know that bacteria create their own energy, get nutrients to run their cellular processes, and multiply. But, bacteria haven't been shown to respond to external mechanical stimulation or signals in a way that's similar to how our bodies respond to touch, until now.

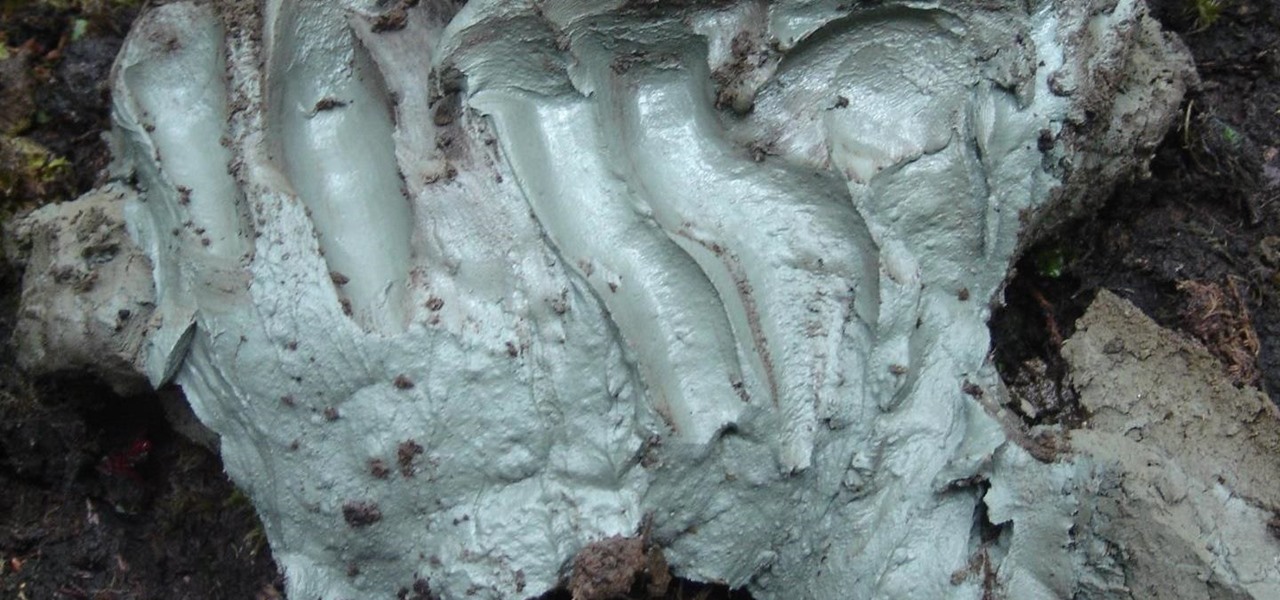
For as long as 14,000 years, the First Nations people of the Heitsuk Nation have made their home along the Central Coast of the Canadian province of British Columbia. Among the territory's inlets, islands, rivers, and valleys lie a clay deposit on the north side of Kisameet Bay, near King Island. For as long as most can remember, the tribe has used the clay as medicine. Now science says microbes that live in that clay may have important antibacterial properties.