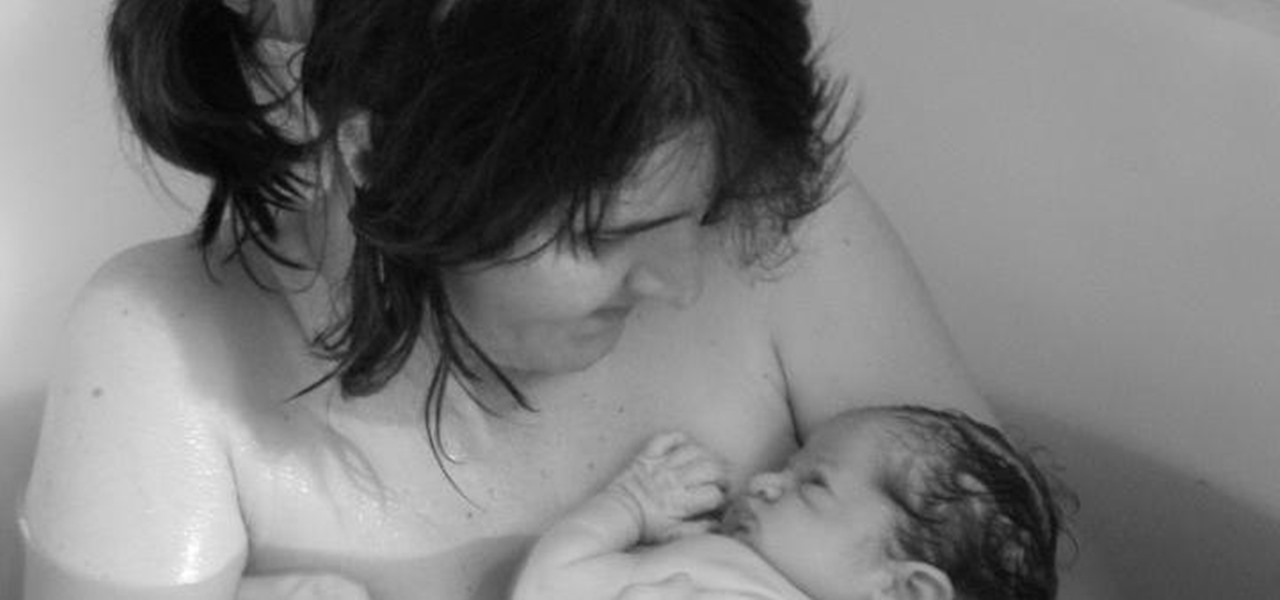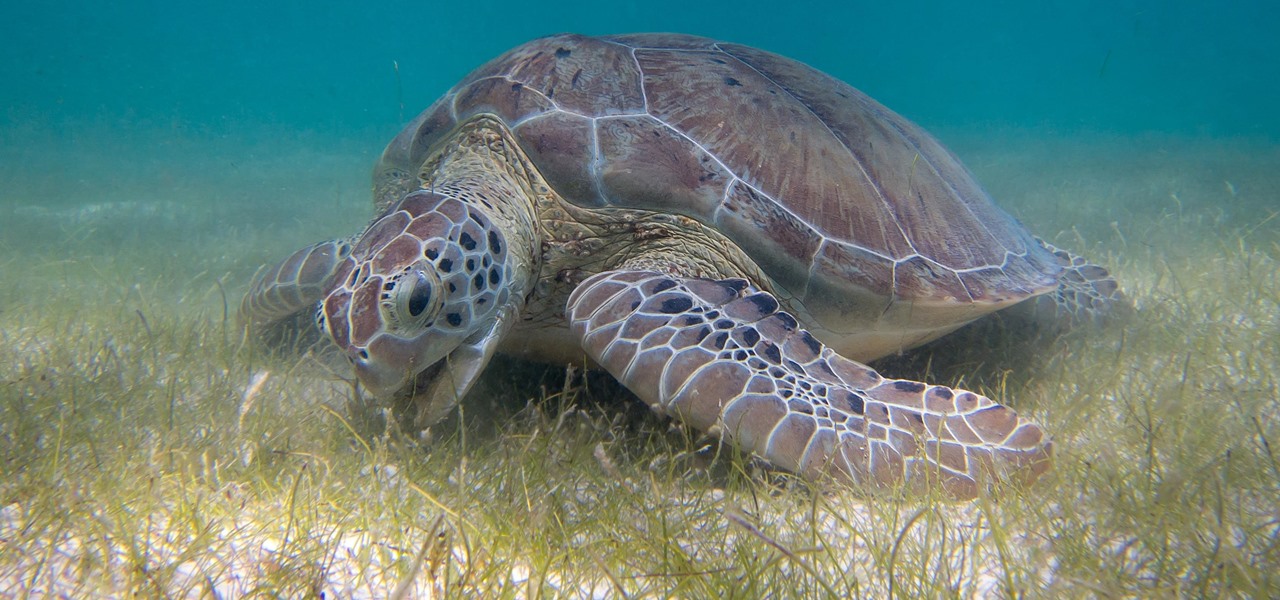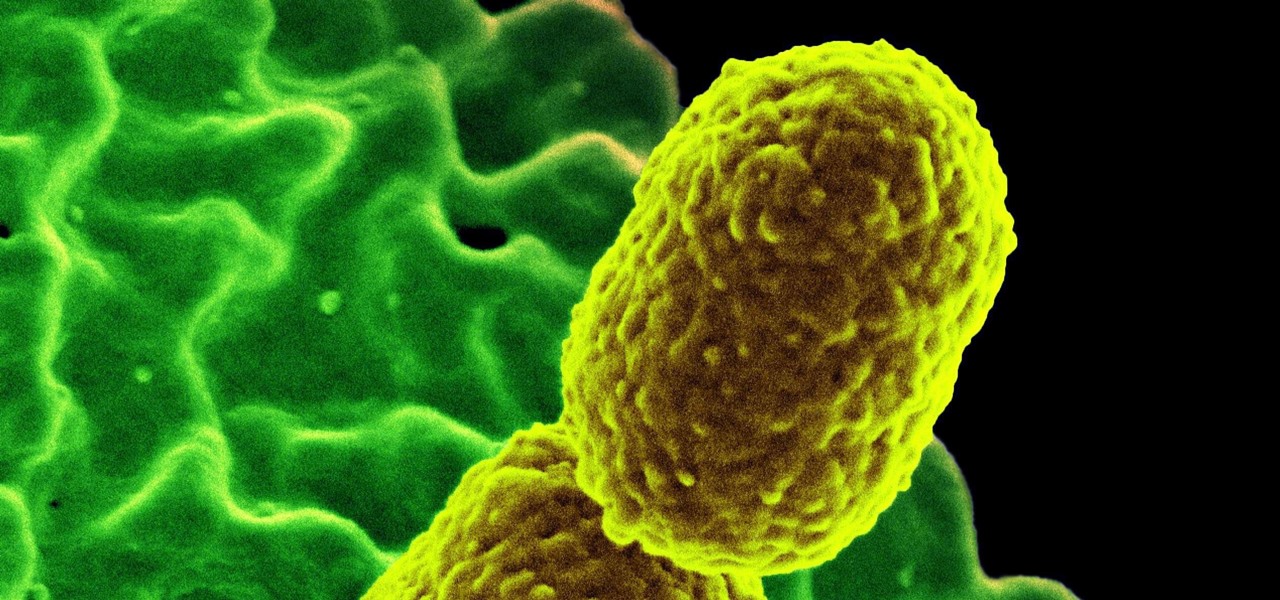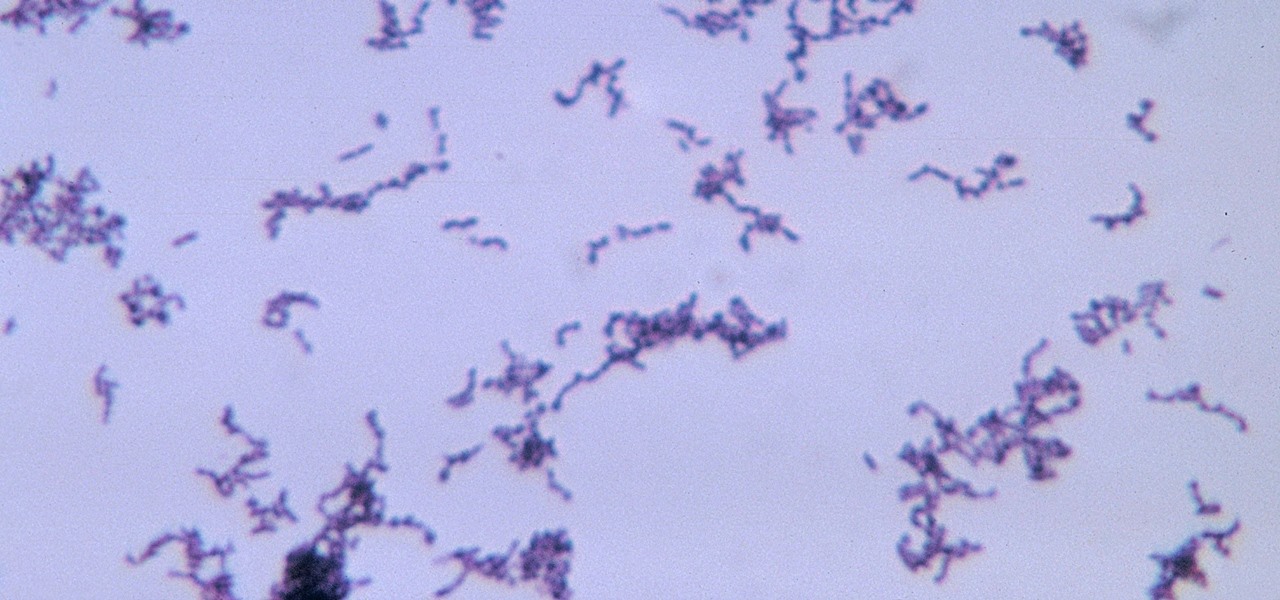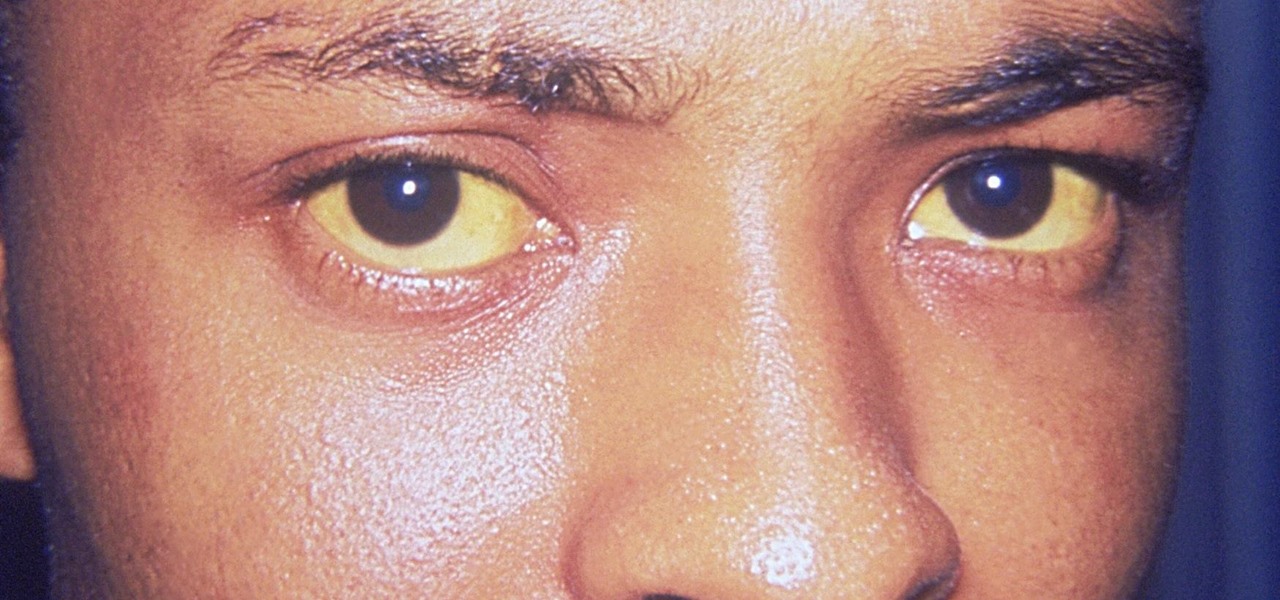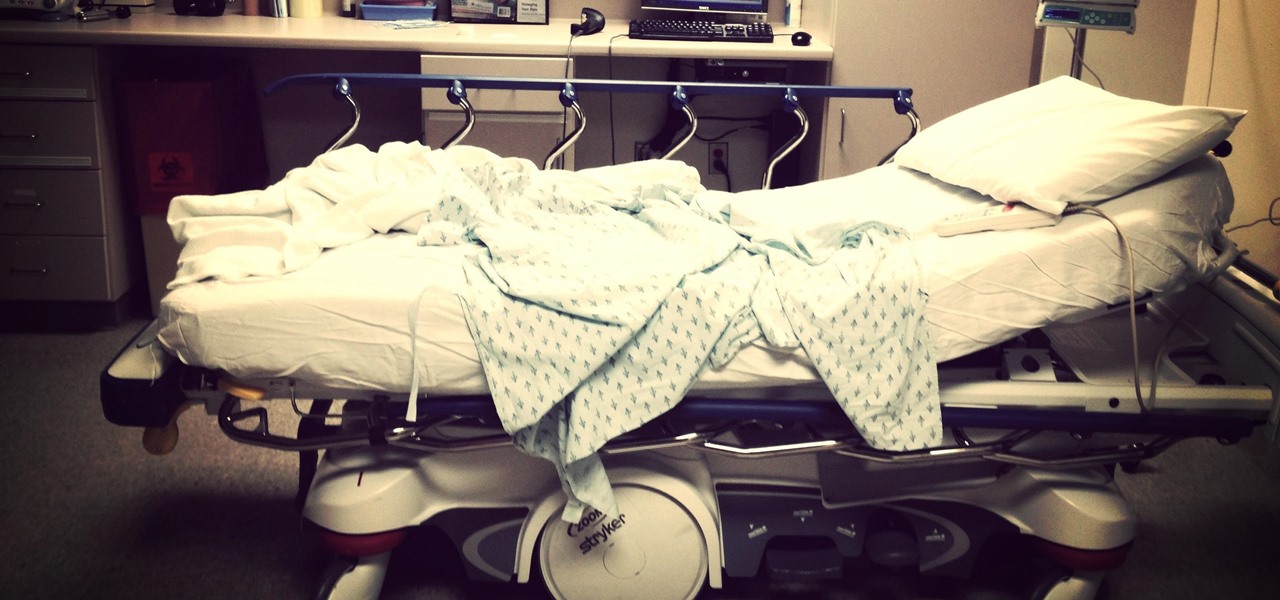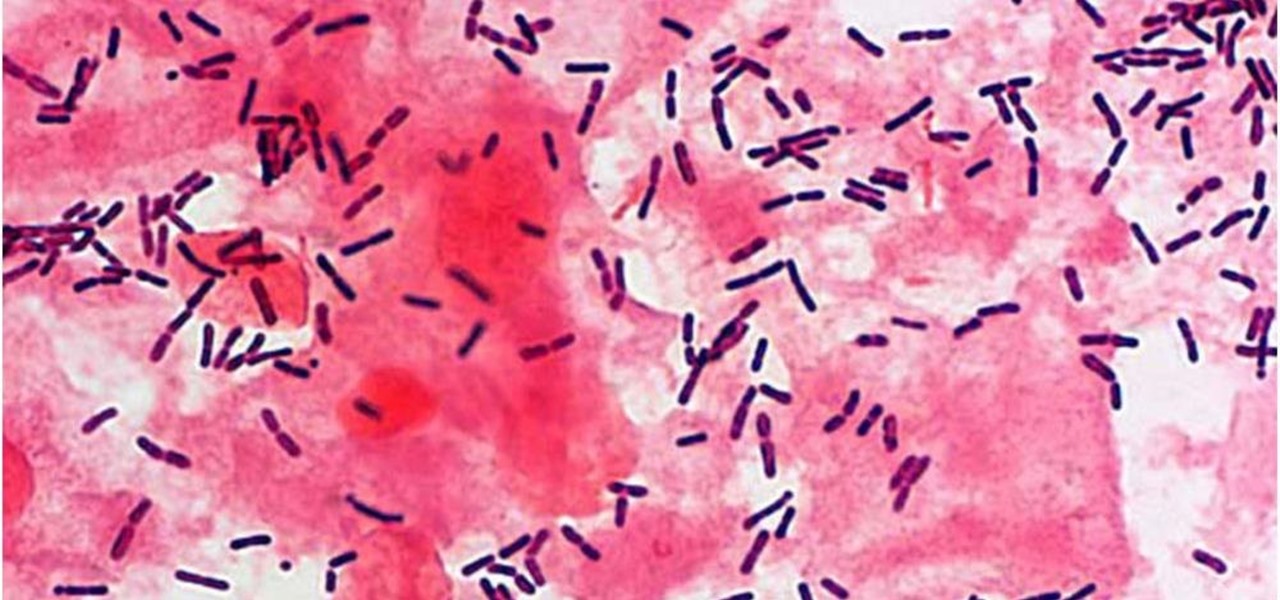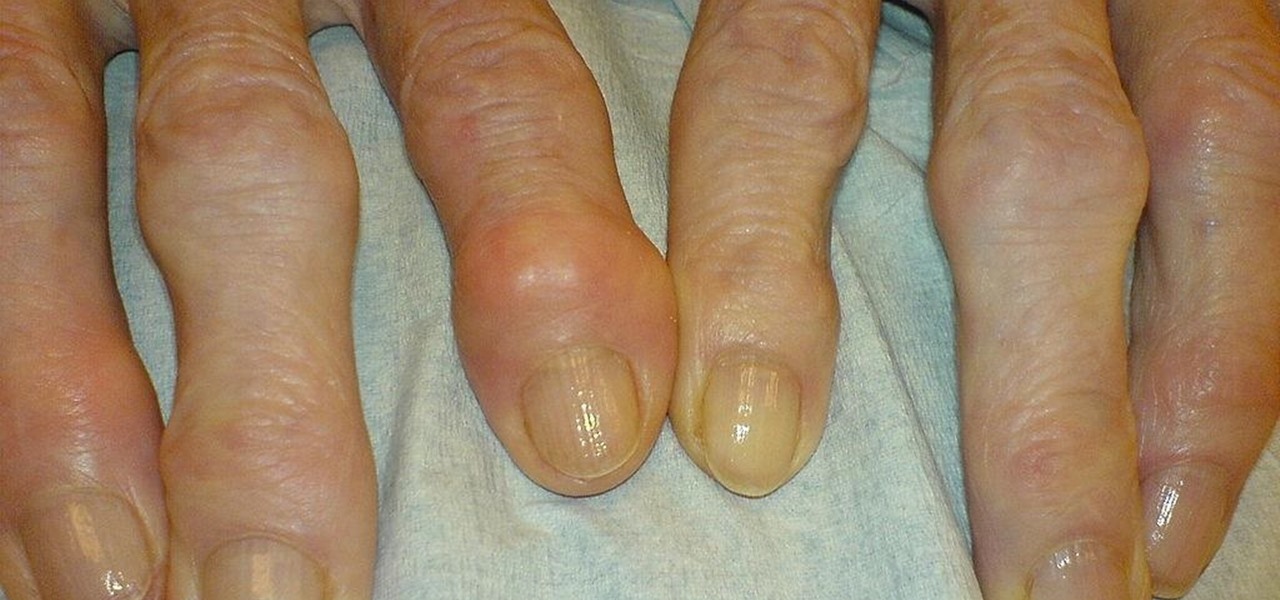
As if the swollen, painful joints of rheumatoid arthritis weren't enough, the disease is the result of our immune system turning against cells of our own body. Ever since this realization, scientists have worked to find the trigger that sets the immune system off. Scientists believe that gut bacteria may have a role in initiating the abnormal immune response. Now, a team of researchers from Boston has figured out how that might occur.
So while it is the weekend of San Diego Comic-Con, and it should not be a complete surprise — without a word of warning hitting my feed — the trailer for the upcoming film, Ready Player One was released today. And wow it looks amazing.
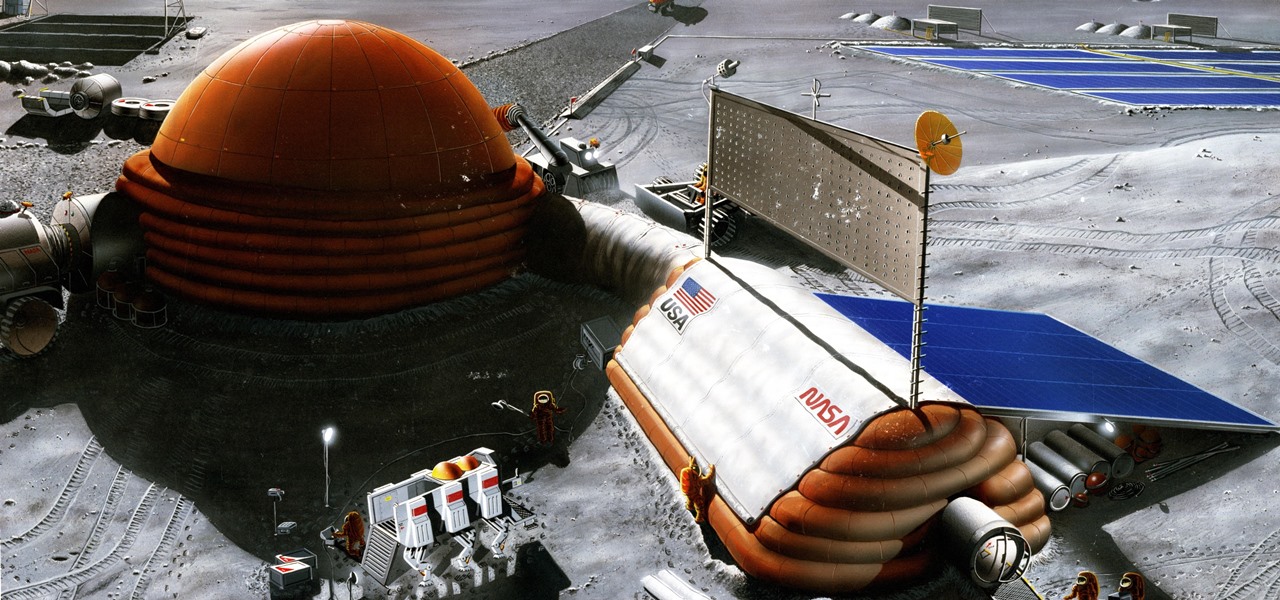

Wherever there are people, the party is sure to follow. Well, a party of microbes, at least. That is what scientists at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory have found after a 30-day microbial observation of the inflatable lunar/Mars analog habitat (IMAH).
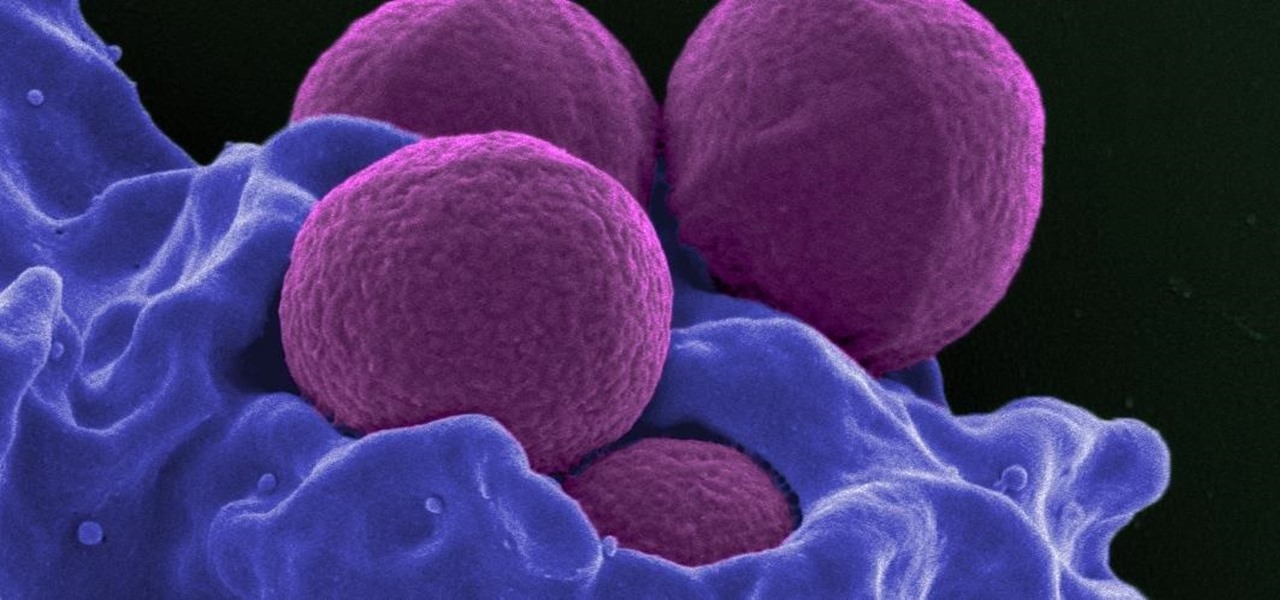
Staphylococcus aureus is a widespread bacteria — about a third of us have it on our body right now — usually in our nose or on our skin. And it probably isn't causing an infection. But, about 1% of people who have Staphylococcus aureus present have a type that is resistant to the antibiotic methicillin.
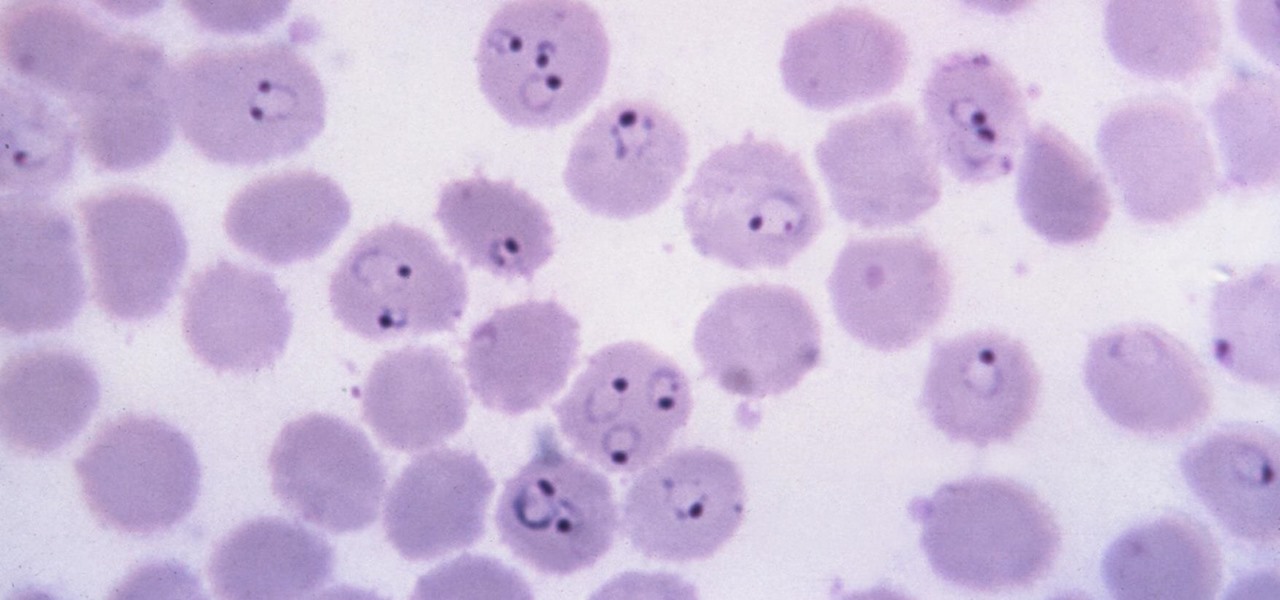
Malaria is a massive worldwide health problem. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate that 212 million cases of malaria occurred worldwide in 2015 and 429,000 of the infected people died.

Despite longer live spans, almost half a million people die of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) each year, many of them preventable.

The community of bacteria that lives in our gut has a lot to tell us. It can give clues to what we eat, the environment we live in, and diseases and disorders we may have. Now, scientists have linked these bacterial species to how we feel. A new research study found an association between women's gut bacteria and their emotions.

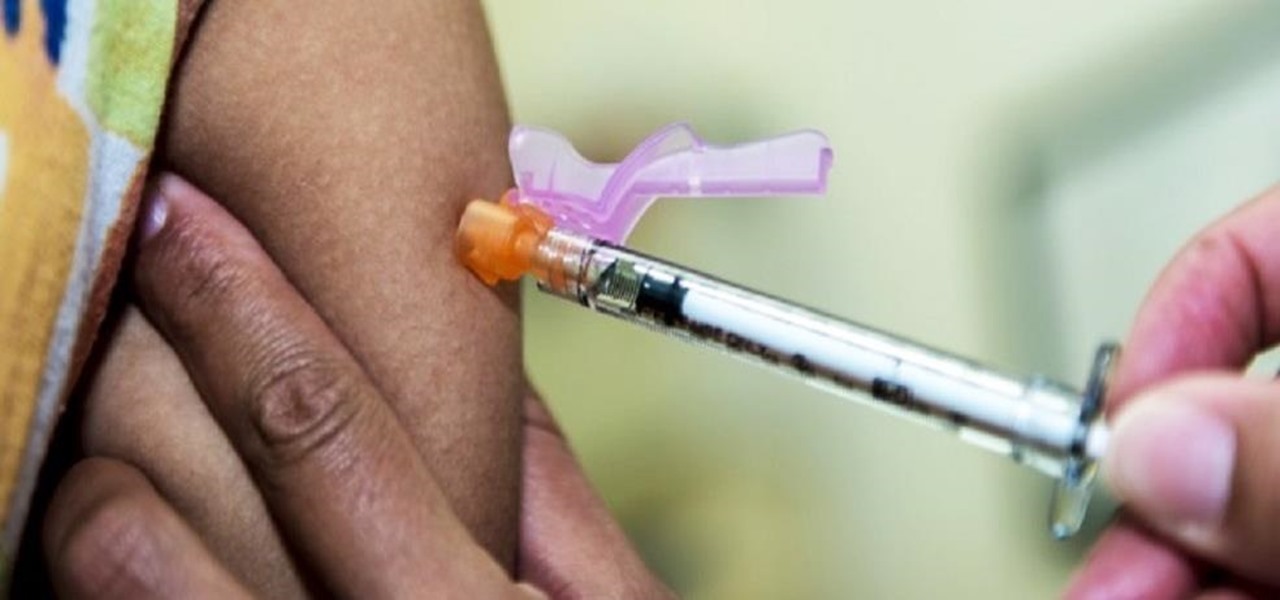
Sex makes the world go 'round, and when it does, so does gonorrhea. Finally some good news on the growing menace of drug-resistant gonorrhea — a large, long-term study shows a vaccine may work in reducing the incidence of an increasingly dangerous infection.

Tony Parisi, the global head of VR/AR at Unity Technologies, has been passionately working with virtual and immersive spaces for a long time. And while the internet world we live in now is very different than when Parisi was co-authoring VRML (Virtual Reality Modeling Language) — an early attempt at creating 3D environments that would work in a web browser — some of the questions that were assumed answered are being asked again.

Deadly rat lungworm parasites have found their way into Florida. The parasitic worm relies on snails and rats to complete its life cycle, but don't let this nematode's name fool you. This worm can cause meningitis and death in humans who inadvertently consume snails, frogs, or crustaceans harboring the infective parasite.

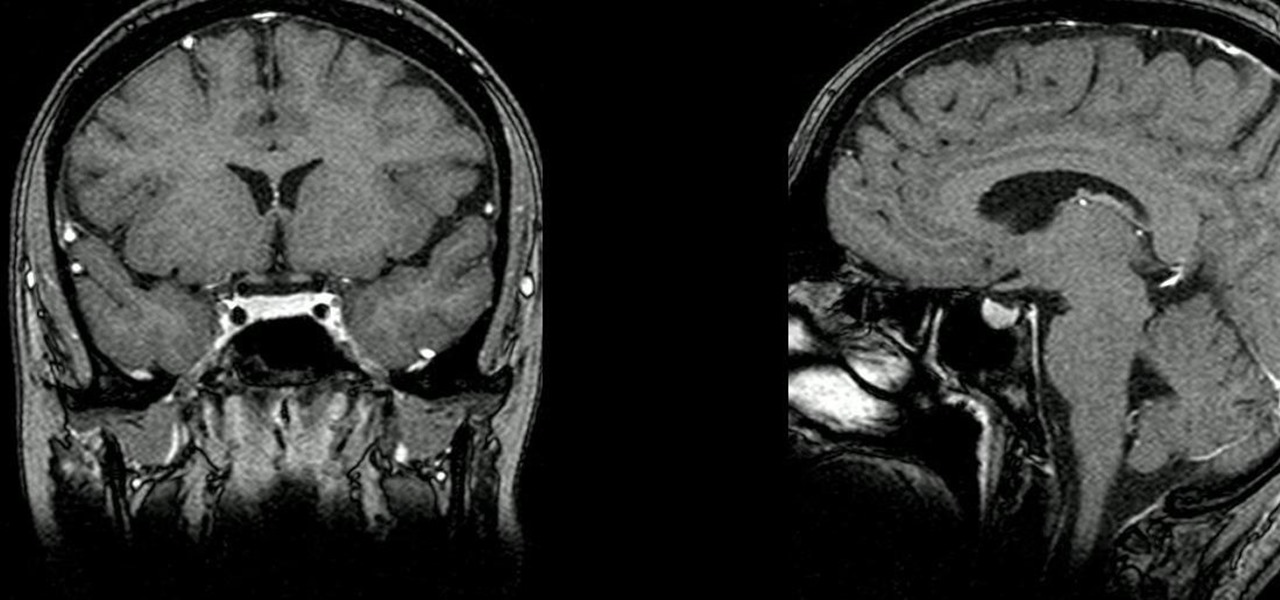
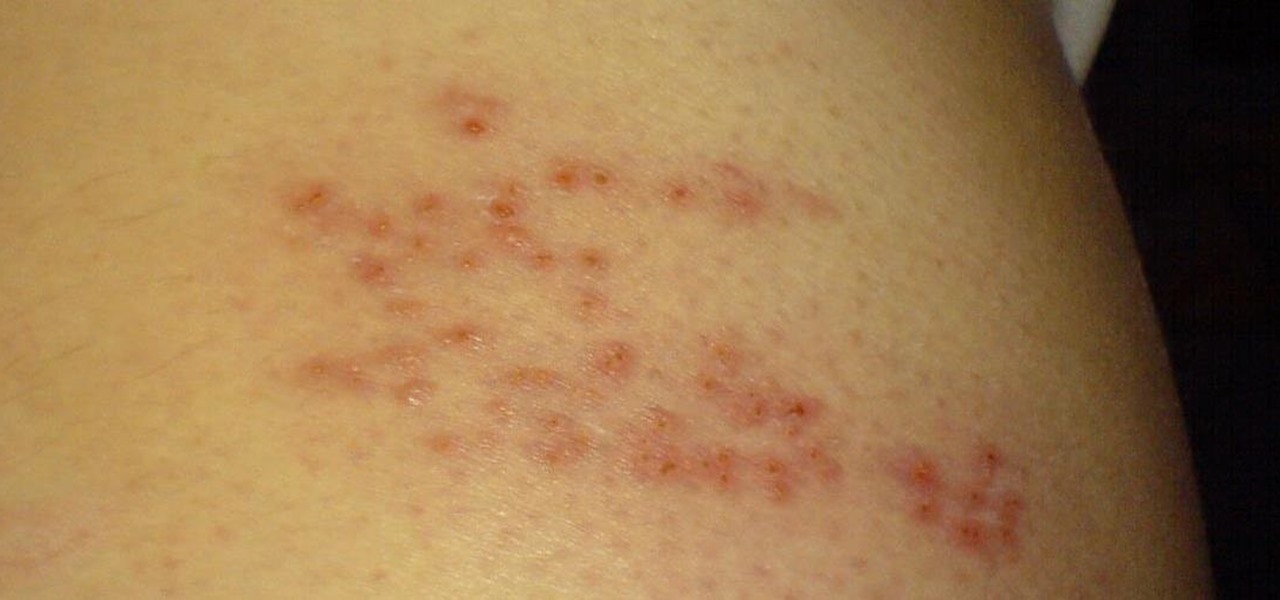
People who have heart disease get shingles more often than others, and the reason has eluded scientists since they first discovered the link. A new study has found a connection, and it lies in a defective white cell with a sweet tooth.

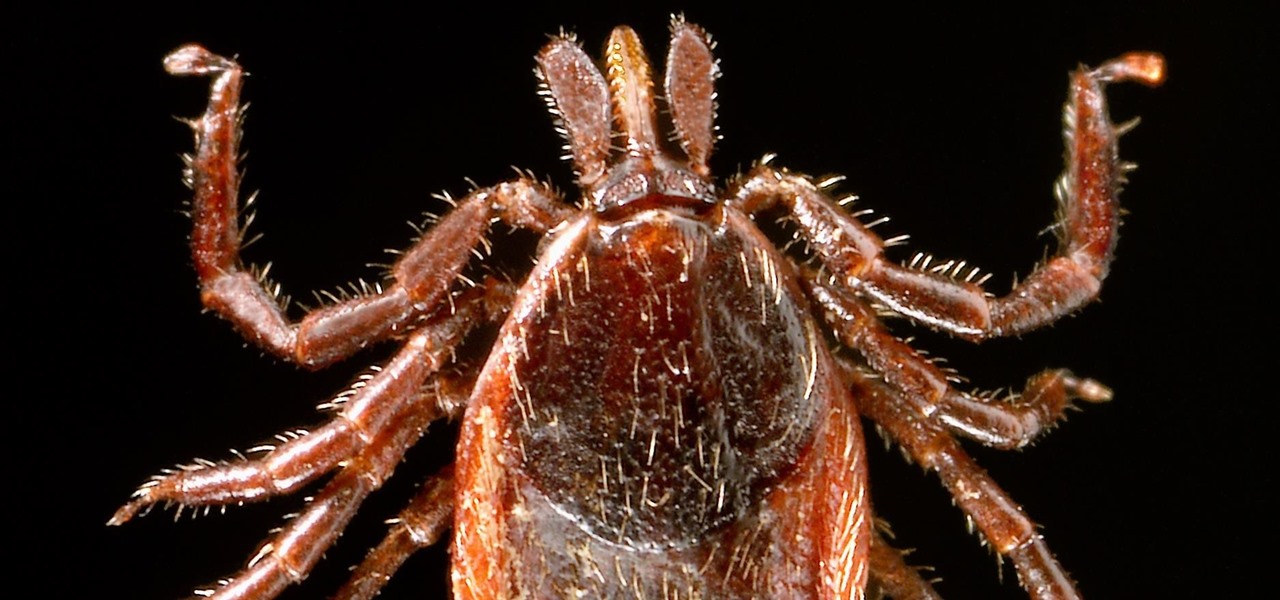
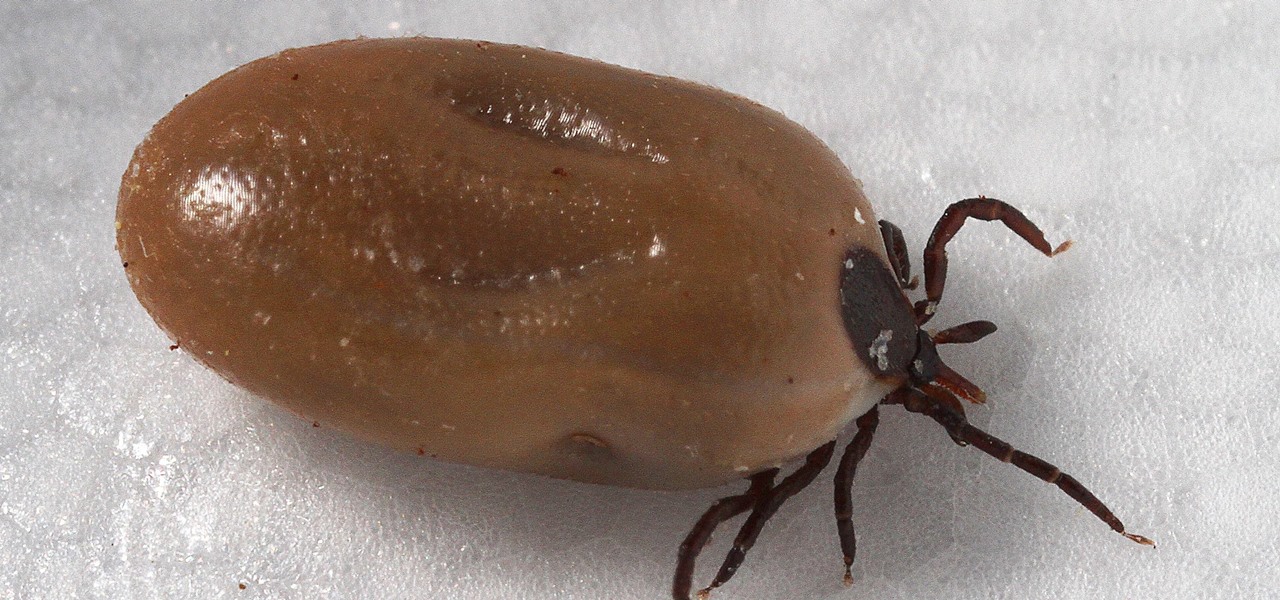
If you know that ticks spread Lyme disease, you may already know you might also catch a bunch of other infections from them. One of the lesser-known diseases spread by ticks is infection with the bacterium Anaplasma phagocytophilium, called anaplasmosis.

Legionnaires' disease is named after 1976 outbreak in Philadelphia that sickened 221 people and killed 34. More often striking adults over the age of 50, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently reported two cases where newborns contracted the often fatal disease — at their moment of birth.

As a part of the already crowded field of diseases transmitted by ticks, you may not know the disease babesiosis, a dangerous infection caused by a parasite that infiltrates blood cells.

Hey, all you Instagram lovers, haters, or people who have no choice but to submissively bow down to the social app giant for other reasons, you've come to the right place. Today, I'm going to walk you through a very simple marketing trick to start boosting traffic to your IG account.

Those of us who are actively developing for the HoloLens, and for the other augmented and mixed reality devices and platforms that currently exist, are constantly looking for the next bit of news or press conference about the space. Our one hope is to find any information about the road ahead, to know that the hours we spend slaving away above our keyboards, with the weight of a head-mounted display on our neck, will lead to something as amazing as we picture it.

Even though the Ebola virus was discovered as recently as 1976, over 30,000 people have been infected since, and half have died a horrible death. Since there's no way to cure the infection, the world desperately needs a way to prevent it — and the five similar viruses in its family, the ebolaviruses.

The bacteria Klebsiella pneumoniae is a bad actor known for being antibiotic-resistant and causing a variety of serious infections in hospitals, including pneumonia, surgical site wounds, and meningitis. K. pneumoniae is something you do not want to encounter if you have a compromised immune system.

Our quest to find new antibiotics has taken a turn — a turn down the road, that is. A team of scientists from the University of Oklahoma is scooping up roadkill and searching for bacteria on them that might yield the world's next antibiotic.

Antibiotics used to prevent diseases in livestock are creating a world of hurt for humans and the soil we depend on for food. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a global health issue. The overuse, underuse, and poor use of these life-saving drugs is rapidly removing them as a treatment option for serious infections in humans—plus bacteria are naturally adaptive.

The squiggly guys in this article's cover image are Propionibacterium acnes. These bacteria live in low-oxygen conditions at the base of hair follicles all over your body. They mind their own business, eating cellular debris and sebum, the oily stuff secreted by sebaceous glands that help keep things moisturized. Everybody has P. acnes bacteria—which are commonly blamed for causing acne—but researchers took a bigger view and discovered P. acnes may also play a part in keeping your skin clear.

An advance in the race to stop birth defects caused by Zika-infected mothers has been made by a team of researchers from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, New York. They have identified the process Zika uses to gain entry into the placenta, and published their findings in the journal Biochemistry.

Within the coming months, software startup Neurable plans to introduce the next paradigm in virtual and augmented reality: the brain–computer interface (BCI).

Yellow fever has emerged again in Brazil, causing death and disease to people unprepared for this mosquito-borne illness.

In the past, infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) commonly led to dementia as the virus made its way to the brain. Even in effectively treated people, HIV can hide out and replicate in places like the brain, where it's tough to detect. That's why it's very concerning that half of all HIV-infected patients still report cognitive problems.

The modern age of techno-dating has made an interesting landscape for social interactions when there is some modicum of romance (or lust). For those of us born before the internet evolved into the prolific monster it has become, we first met our love interests face to face. Today, however, apps like Tinder have changed the introductory stage, for better or worse.

Even as health authorities describe the symptoms of Zika infection in the general population as mild, a new surveillance study finds serious side effects are more common, and serious, than previously thought.

Hospitals are places we go to get well, and we don't expect to get sick or sicker there. But a study from researchers at the Cleveland Clinic, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, and Cleveland VA Medical Center in Ohio found that hospital floors in patient rooms were frequently contaminated with healthcare-associated pathogens—often dangerous multi-drug resistant bacteria.

Six people have died from fungal infections in Pittsburgh hospitals since 2014—that fact is indisputable. The rest of the situation is much vaguer. A lawsuit has been filed against the hospitals on behalf of some of the deceased patients, alleging that moldy hospital linens are to blame. While the lawyers argue over who's at fault, let's look at how this could have happened.

Seagrass may help your favorite beach stay a little less toxic. A new study, led by Joleah Lamb, a postdoctoral researcher in the Harvell Lab at Cornell University, found that coastal seagrasses reduce levels of pathogens dangerous to humans and marine organisms in near-shore waters.

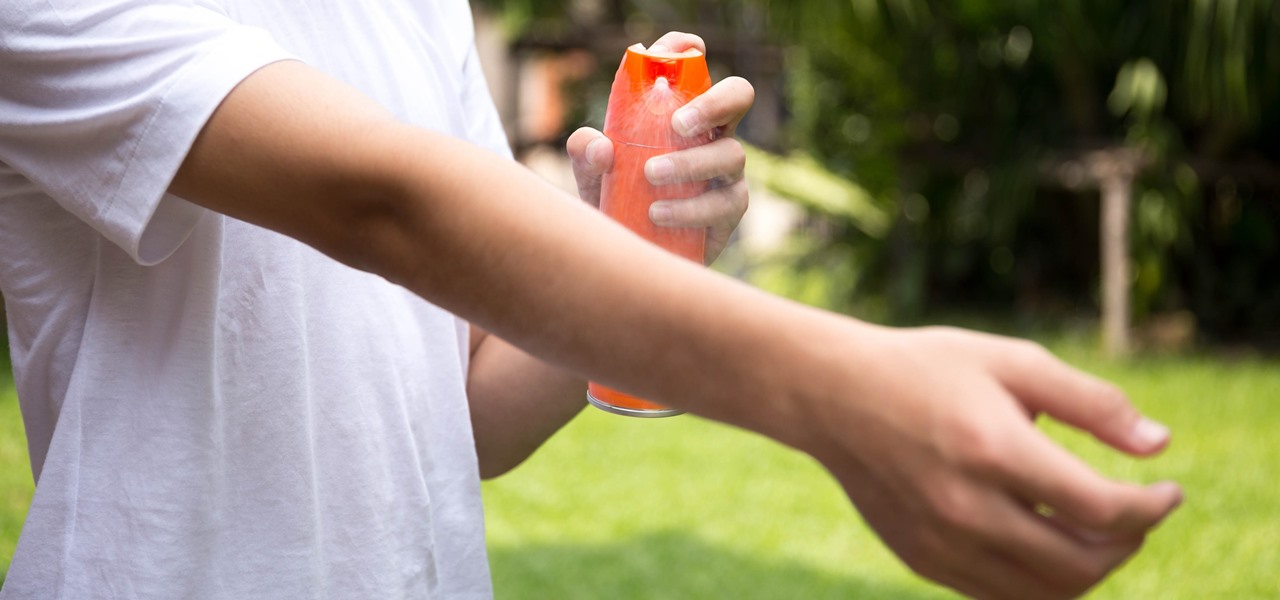
Responding to the emergence of Zika in the US, researchers investigated what type of repellent works best to reduce your odds of a mosquito bite from Aedes aegypti, the mosquito species that spreads the Zika virus.

We all know you are what you eat—or so the expression goes—but it's good to remember that what you are (at least intestinally) is mainly bacteria. A new study has shown that what you eat, and how your gut microbiome reacts to that food, might be a key player in your risk of developing a certain type of colon cancer—and changing your diet can help decrease your risk.

The presence of certain bacteria can indicate whether the vaginal tract is healthy or not. It could also impact the likelihood of acquiring certain sexually transmitted diseases, like HIV, a new study suggests.

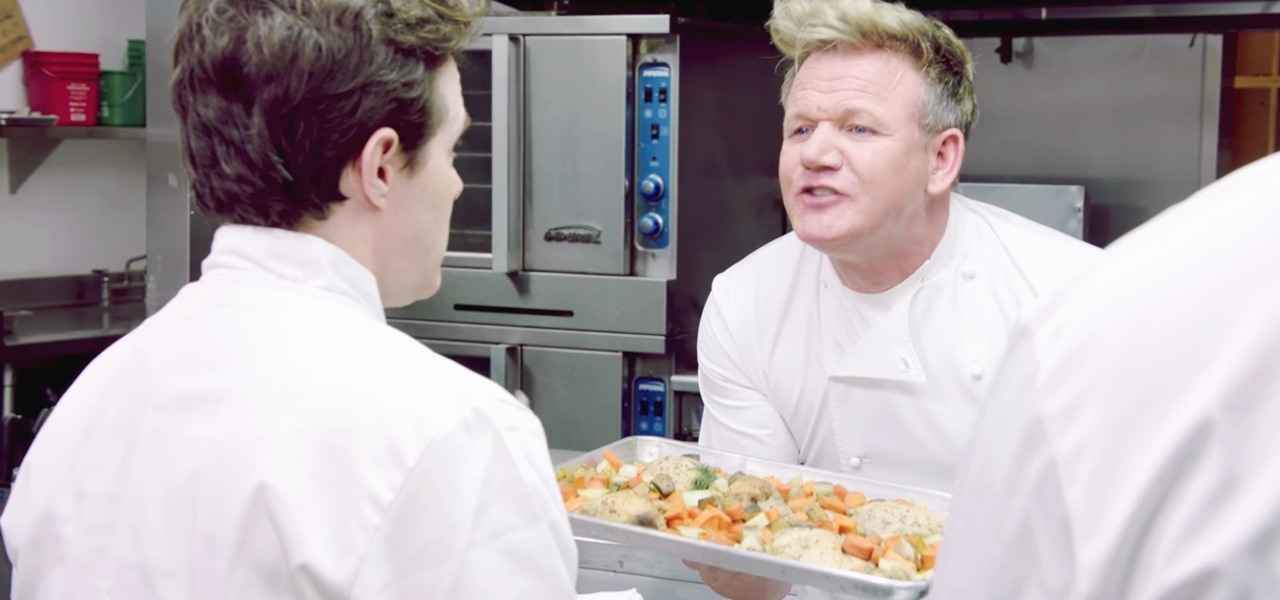
The food TV chefs prepare make our mouths water. From one scrumptious creation to another, they fly through preparation without frustration or error. They make us think we can do the same with similar ease and delectable, picture-perfect results. Some of us have noticed, though, that these TV chefs don't always adhere to the same safe food handling guidelines we've been taught to follow.

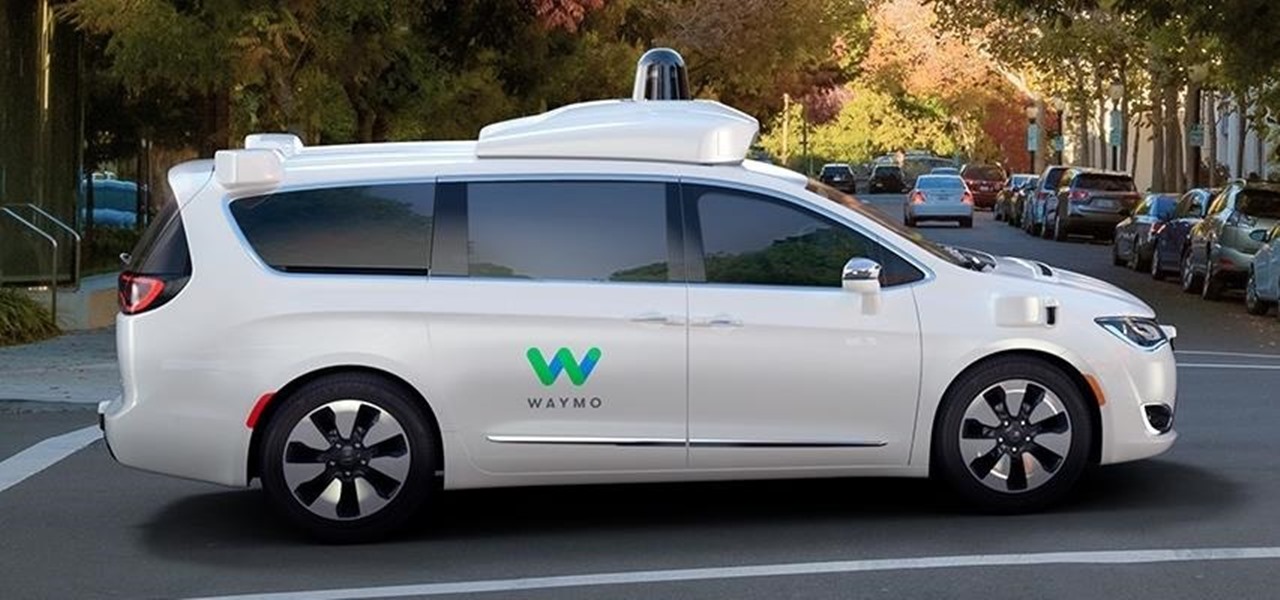
Last week it was announced that Waymo, the former Google Self-Driving Car project, had graduated from Alphabet's X innovation center. This graduation had been in the cards for many months with senior members of the project team and X hinting that it would be soon.

Breaking off a piece of that Kit Kat bar gets a lot more difficult when the whole thing weighs 13 pounds.

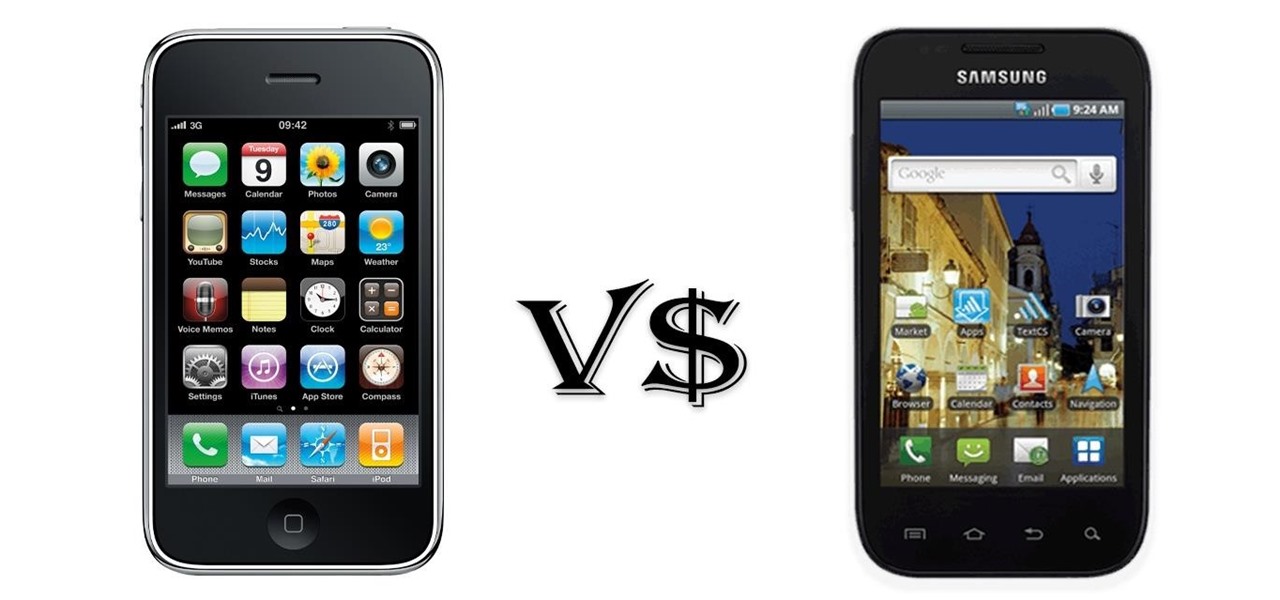
Samsung and Apple are back in court, but this time it's not just money at stake. The Supreme Court's decision could have a far reaching effect on patent law and innovation in design.

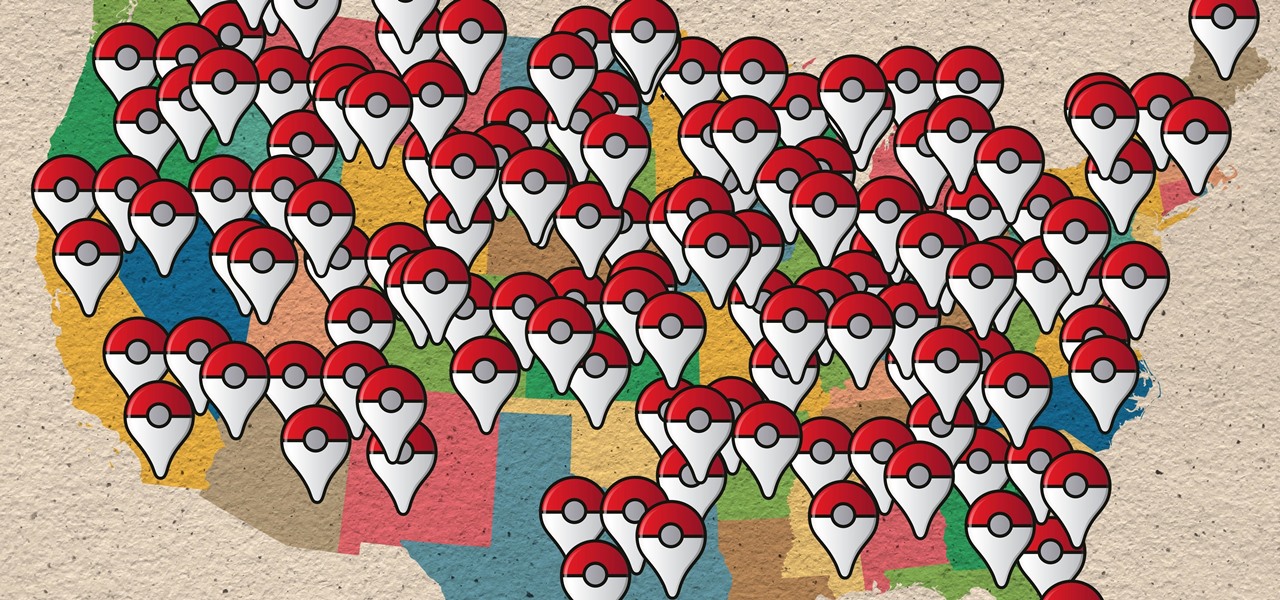
A strange thing is happening: there are people, groups of people even, walking the streets day and night staring wide-eyed at their mobile phones and laughing like manic children. What are these people doing? Are they taking pictures? Are they participating in some new social media craze? Is their activity an omen that the zombie apocalypse is upon us?

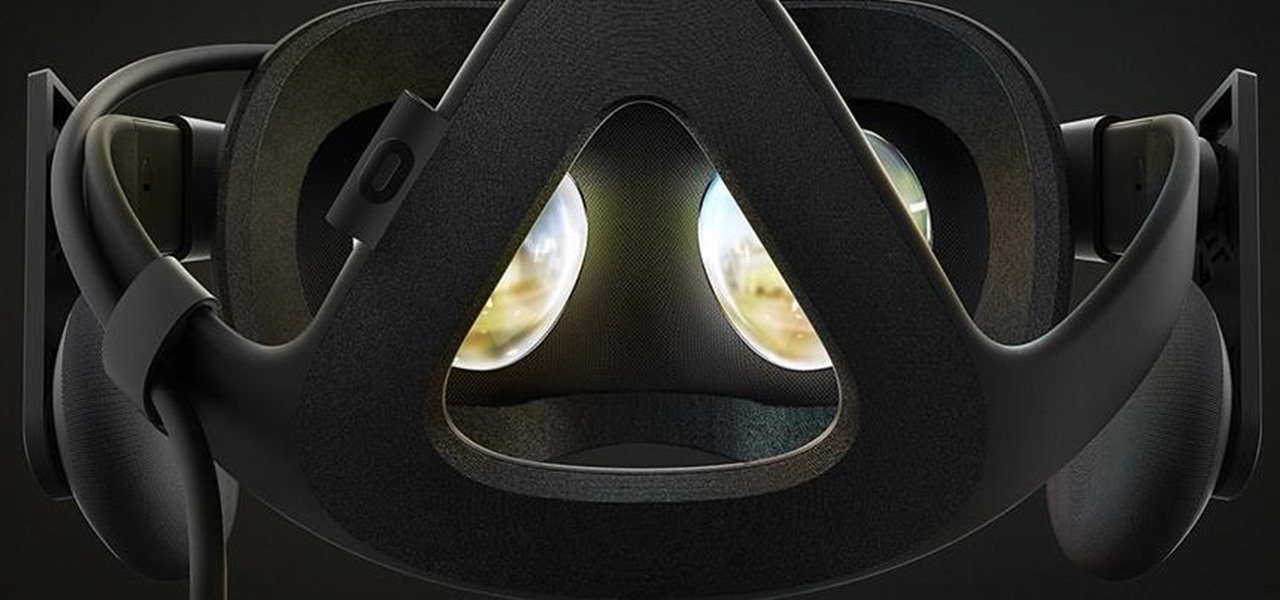
The Oculus Rift is finally shipping to customers in more than 20 countries, and we're getting a good idea of how the device holds up from the initial reviews. You'll see some common threads throughout: along with an impressive virtual reality experience, the device is very comfortable with a solid design.
If your company has already released some popular and addictive game and you're thinking about creation a sequel, this article is just what you need. We gathered the main tips and advices that will be useful for the building a strategy and a sequel itself. Check out the following instructions and recommendations that can lend you a hand in making a sequel for your game.