As headlines focus on melting glaciers and rising water levels caused by global warming, climate change is quietly taking its toll on the nearly invisible occupants of this planet, the microbes.
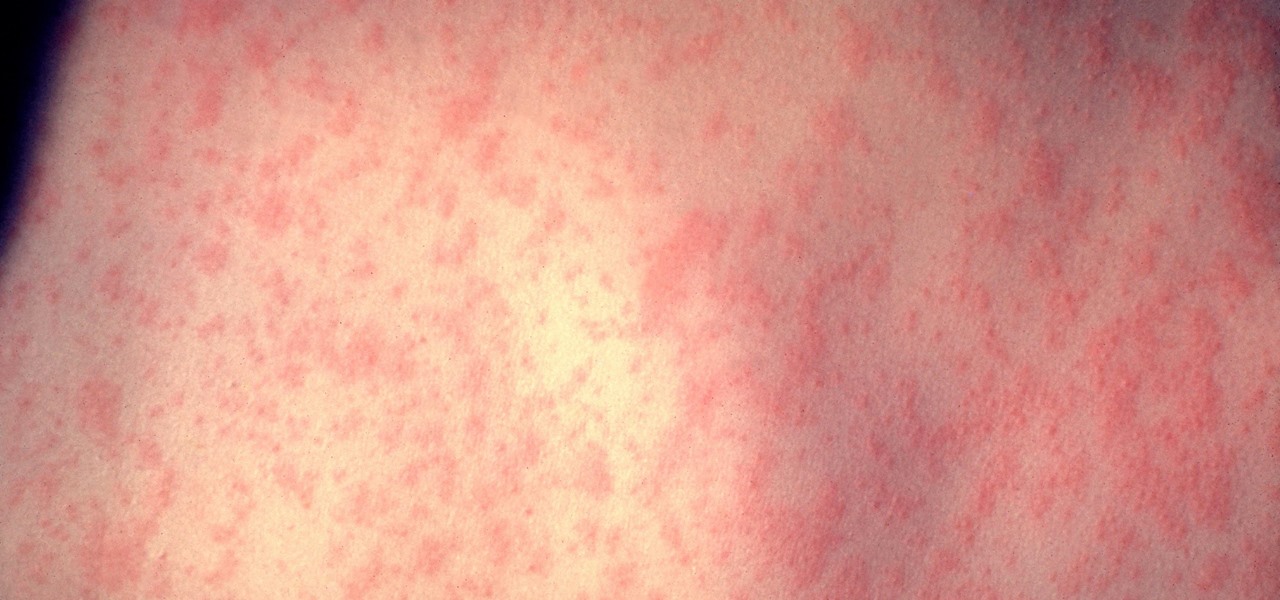
In the worst measles outbreak in the state since 1990, the Minneapolis Department of Heath races to contain the spread of an infection believed to have originated from an infected traveler. Mistaken attitudes and unvaccinated travelers are creating a world of hurt and disease for Americans. A recent study found that more than half of eligible travelers from the US are electing to skip their pre-trip measles vaccine.
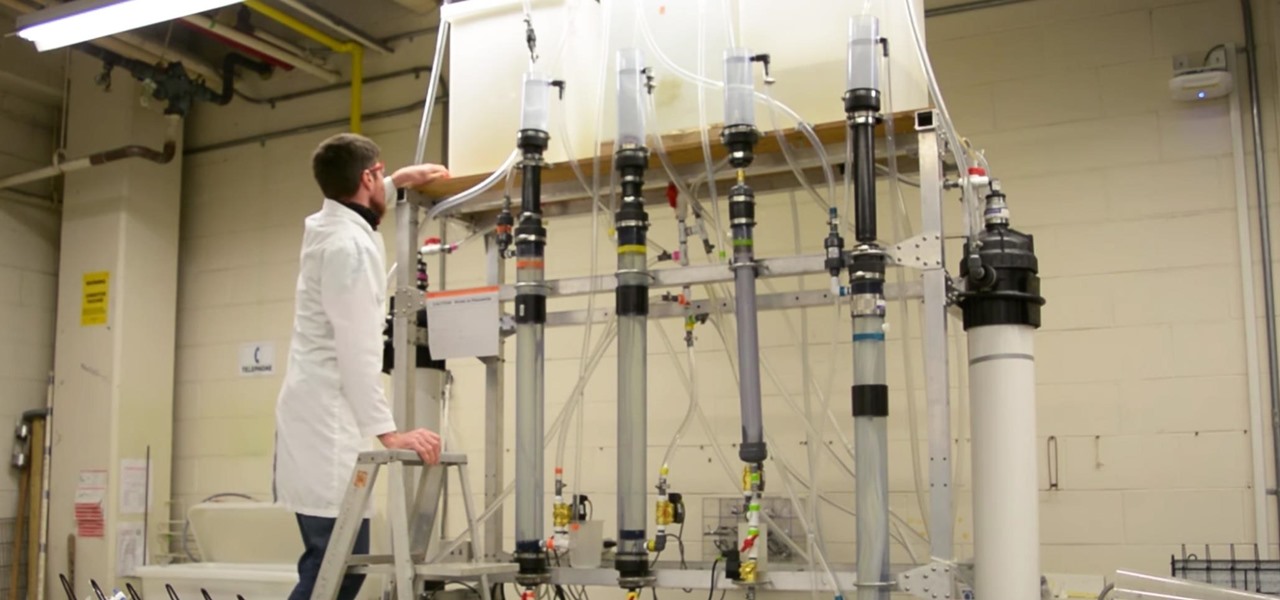

Water makes up about 60% of your body weight. Whether you like it plain, flavored, bubbly, or in beverages or food, we all need water daily to avoid dehydration and stay healthy. For communities in need of clean drinking water, new research using bacteria may offer a simplified, lower-cost method for boosting potable water supplies.
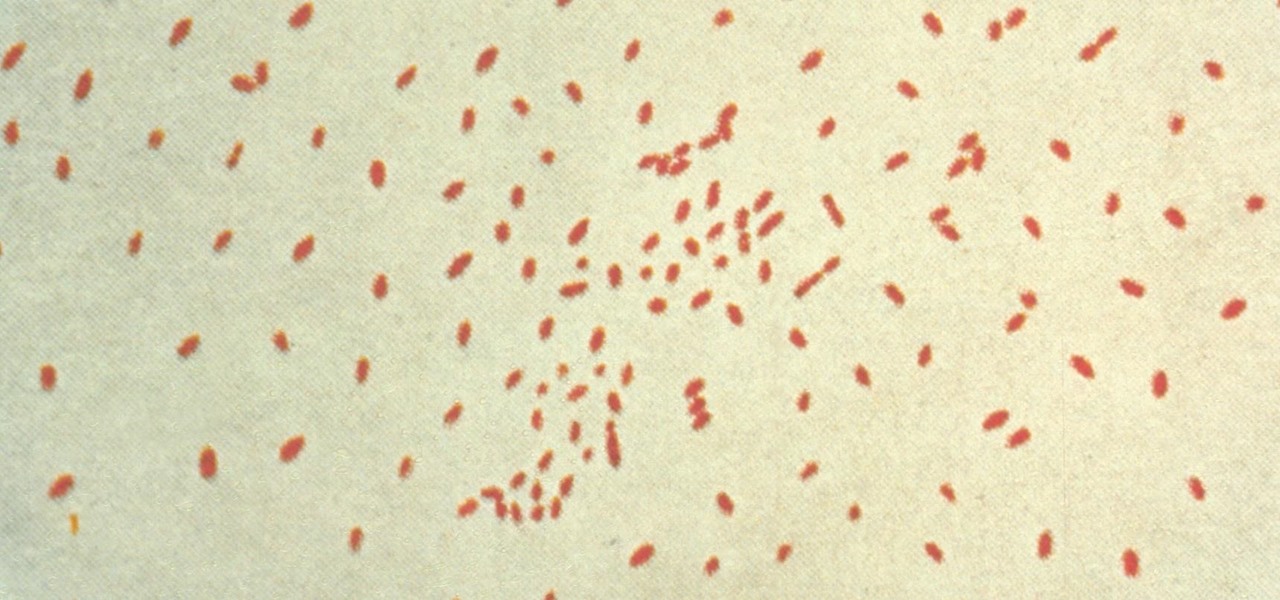
Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a highly contagious disease that can be life-threatening for young children. New research backs a recommendation that all pregnant women receive a pertussis booster with each pregnancy, as it can help their infants fight off the infection.
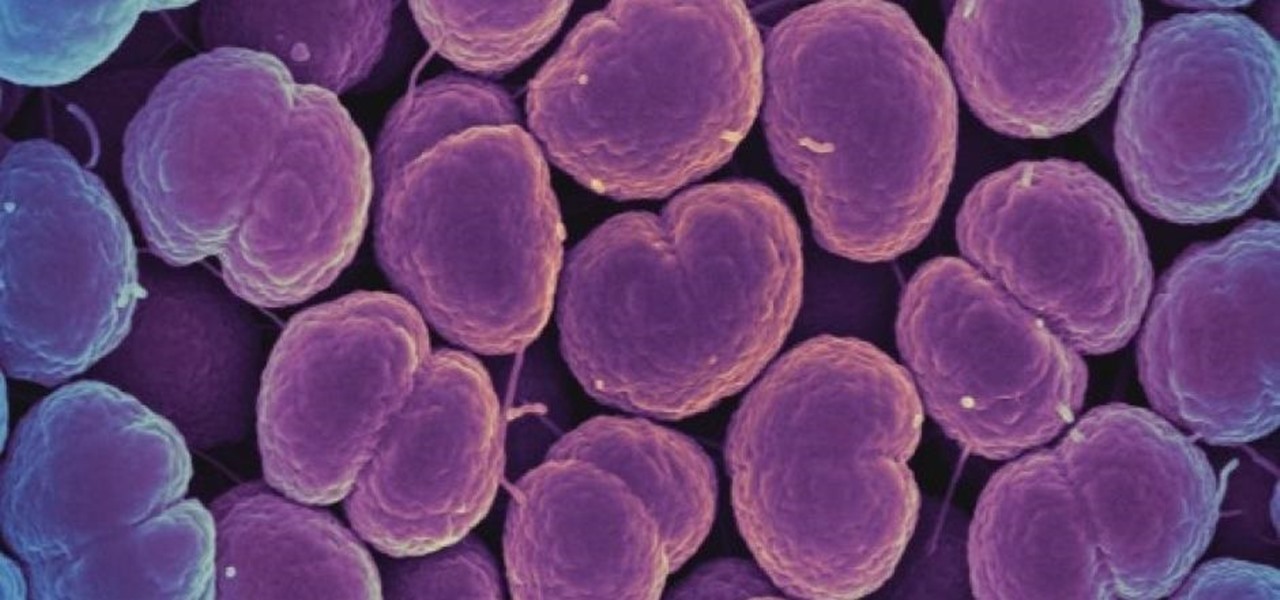
The ability of one microbe to adapt is giving it a whole new career as a sexually transmitted disease. Usually content with the back of the throat and nose of those who carry it, the dangerous pathogen Neisseria meningitidis has adapted to cause an illness that looks a lot like gonorrhea.

As summer mosquito season approaches, researchers are warning people with previous exposure to West Nile virus to take extra precautions against Zika. A new study found that animals with antibodies to West Nile in their blood have more dangerous infections with Zika than they would normally.

Antibiotics used to prevent diseases in livestock are creating a world of hurt for humans and the soil we depend on for food. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a global health issue. The overuse, underuse, and poor use of these life-saving drugs is rapidly removing them as a treatment option for serious infections in humans—plus bacteria are naturally adaptive.

Growing populations and higher temperatures put pressure on world food supplies. Naturally occurring soil bacteria may save crops in drought-stressed areas, put more land into crop production, and produce more food.

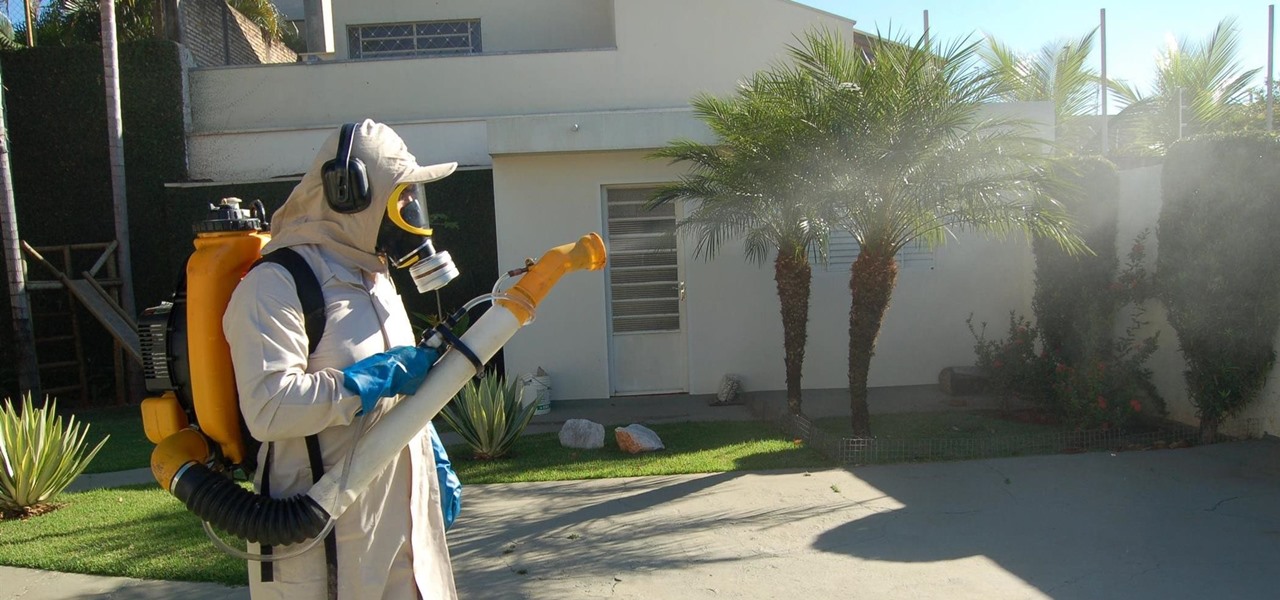
Yellow fever has emerged again in Brazil, causing death and disease to people unprepared for this mosquito-borne illness.

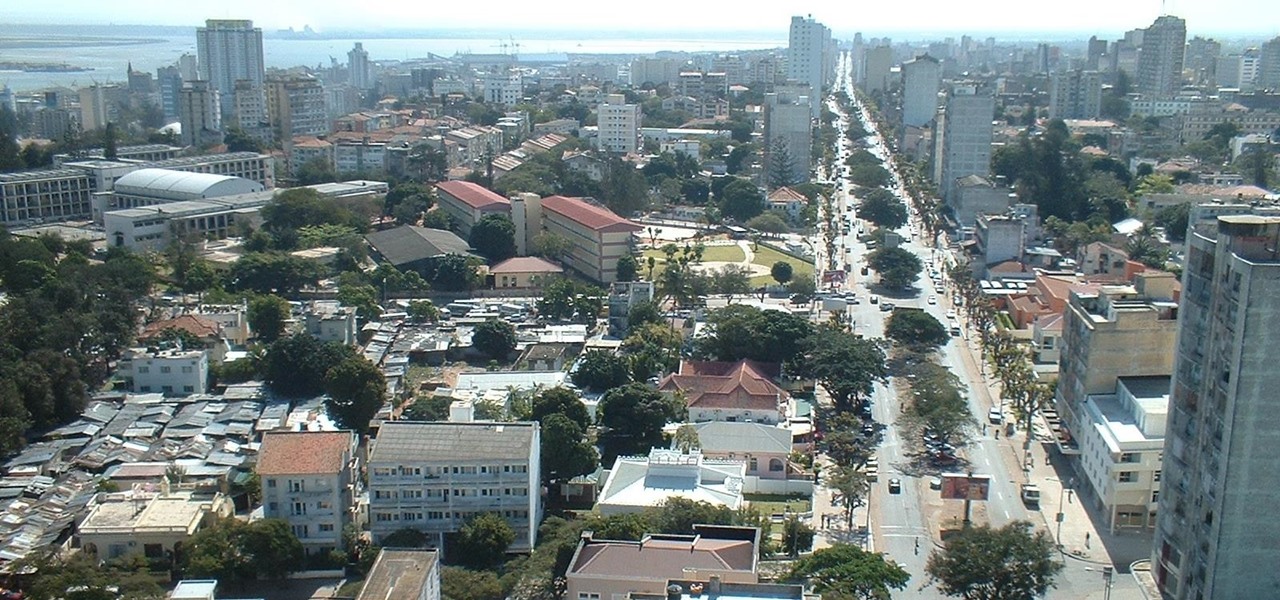
Cholera is rapidly spreading in Mozambique, with over 1,200 people infected. Since the outset of 2017, cholera has spread from the capital city of Maputo (pictured above) to three of its ten provinces. Health officials report other areas in the country are seeing case counts rise, and two deaths have been logged so far.

Even as health authorities describe the symptoms of Zika infection in the general population as mild, a new surveillance study finds serious side effects are more common, and serious, than previously thought.

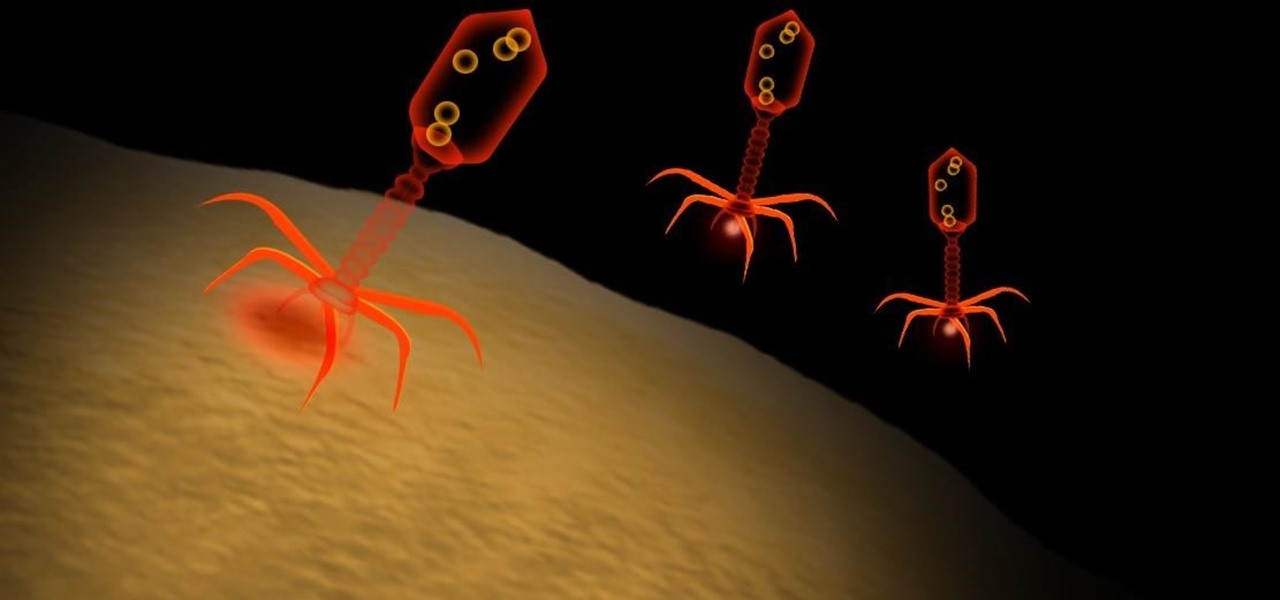
As drug-resistant bacteria become more commonplace, researchers are looking for new antibacterial strategies to disrupt disease-causing microbes. Some scientists are working to create new drugs, while others are trying out drug combinations. Another group, however, are ditching pharmaceuticals altogether and experimenting with non-drug alternatives.

As fun as it is to see Fido's face light up when you feed him table scraps, American dogs are getting fat. The good news is that research is homing in on nutritional strategies to boost canine capabilities to maintain a healthy weight.

Responding to the rapid emergence of dangerous pathogens around the world, a new initiative to prevent or contain pandemics was announced in Davos, Switzerland, yesterday. If you ever worried that a highly contagious pathogen could take down your community, or the country, this news is for you.

Bees are the key to pollination and healthy vegetation, and wasps may help by assisting in pest control, but despite their benefits in the world, they're still a real pain in the ass if they're in your face.

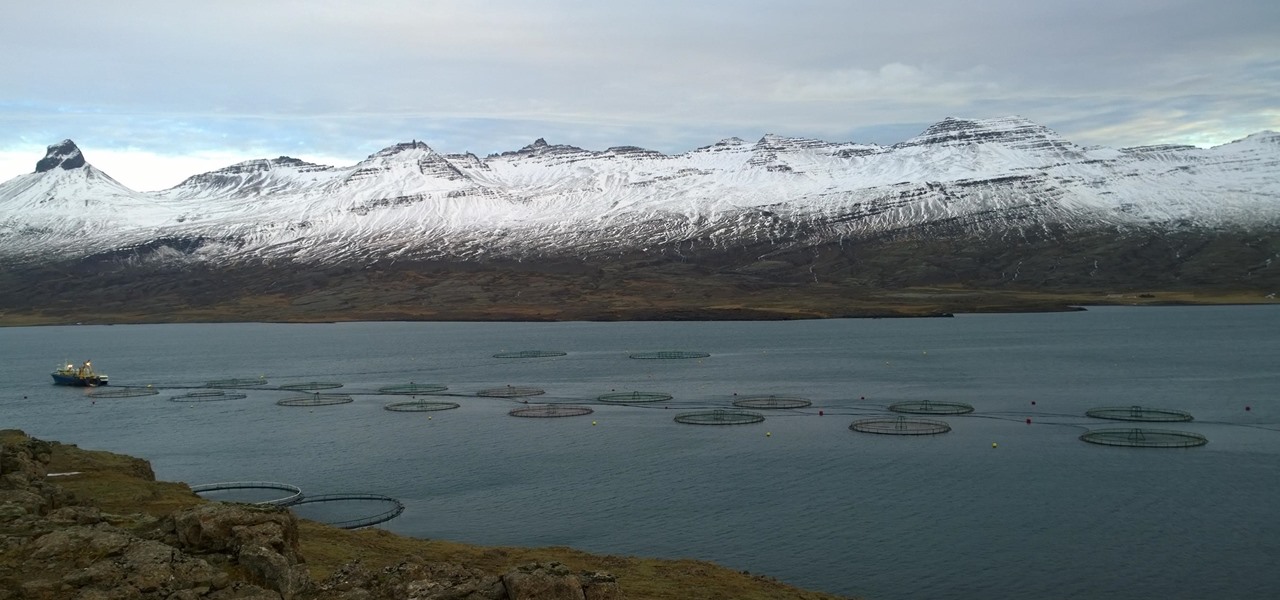
As the fish farming industry struggles to become more environmentally friendly, it just gained another problem. Fish food loaded with antibiotic-resistant genes.

The bacteria in our gut — a community called the gut microbiome — have been in the spotlight a lot lately. What we're learning about how our intestinal bacteria adapt and grow with our bodies could help athletes perform better, according to researchers starting a company focused on creating probiotics that mimic athletes' microbiomes.

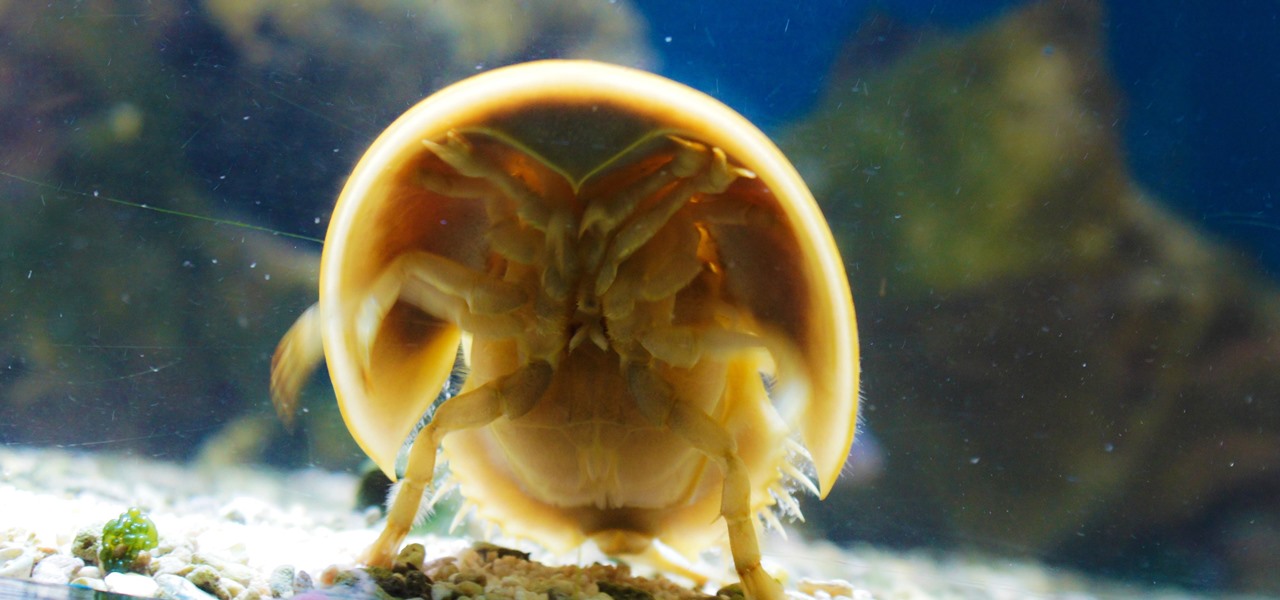
During the millions of years they've been on earth horseshoe crabs have developed a trick that can save our lives even now — and may be especially useful in the fight against healthcare-associated infections.

Type 1 diabetes is an attack on the body by the immune system — the body produces antibodies that attack insulin-secreting cells in the pancreas. Doctors often diagnose this type of diabetes in childhood and early adulthood. The trigger that causes the body to attack itself has been elusive; but many research studies have suggested viruses could be the root. The latest links that viruses that live in our intestines may yield clues as to which children might develop type 1 diabetes.

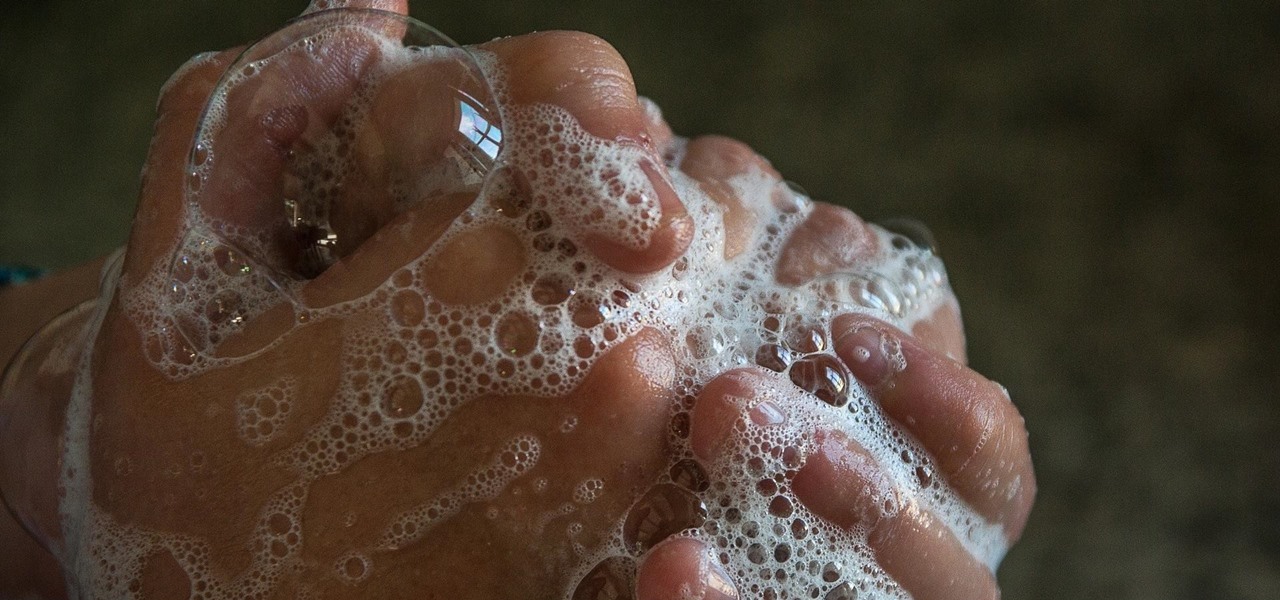
The best go-to method for reducing your risk of infection is to wash your hands. Next time you reach for the soap, here is some news you can use.

That soil under your feet is not just dirt. It is teeming with life that may not change as fast as we would like when challenged by global warming.

Like humans, cats can suffer infections caused by ticks, and too often, the disease is fatal. Learn about tickborne diseases that affect cats and what you can do to protect Fluffy from an untimely demise.

Bed bugs are brown and creepy. Could you spot one in your hotel room? A new study reveals most people are freaked out by bed bugs, but only about 35% could identify one.

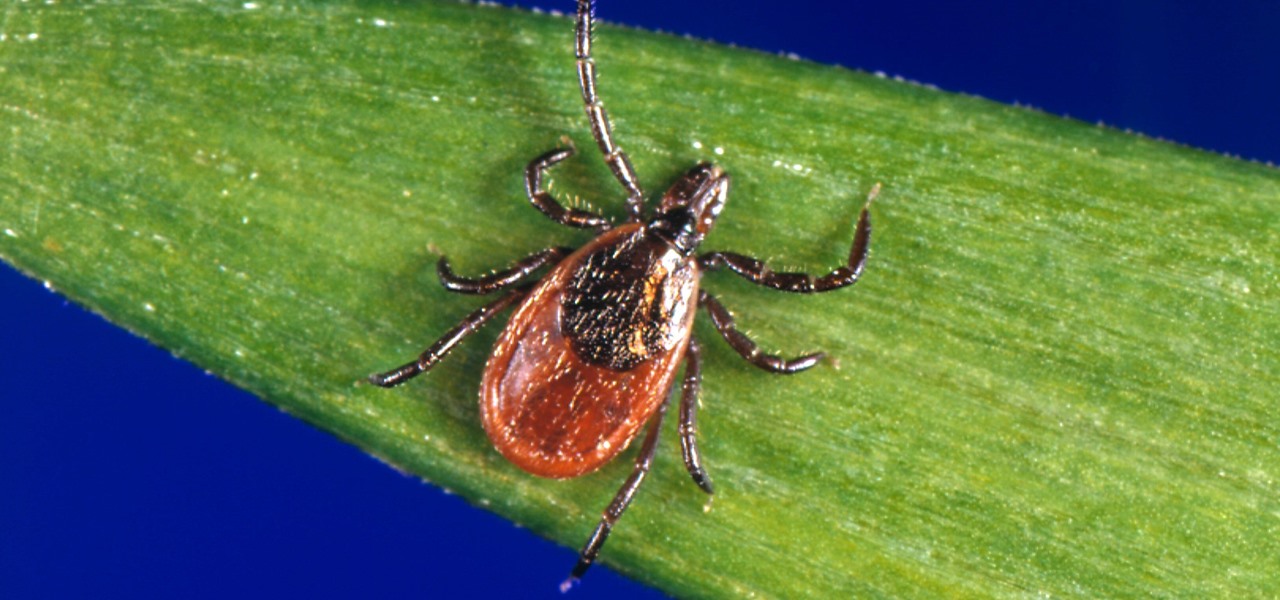
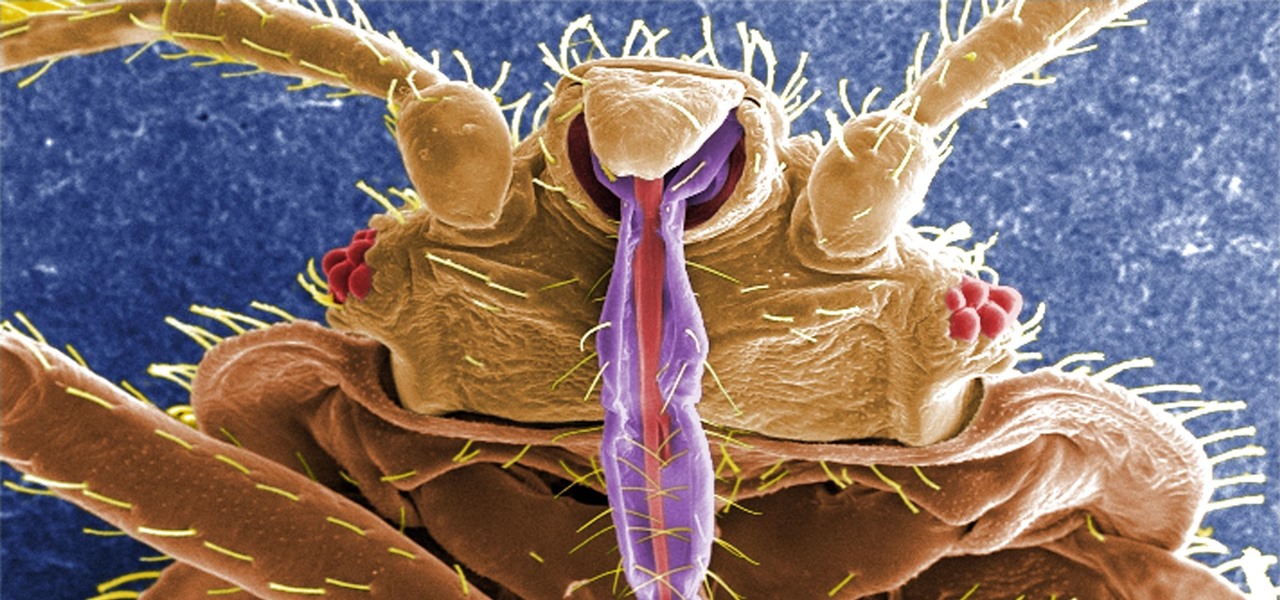
In the US, ticks can spread several pathogens in one bite. A new test offers physicians the ability to identify what infections ticks are carrying and can detect if one of the pathogens could be the spreading Powassan virus.

If you have encountered bed bugs lately, you are not alone. While the pesticides used to fight these pests are losing effectiveness, a fungus shows promise in knocking the bugs out of beds everywhere.

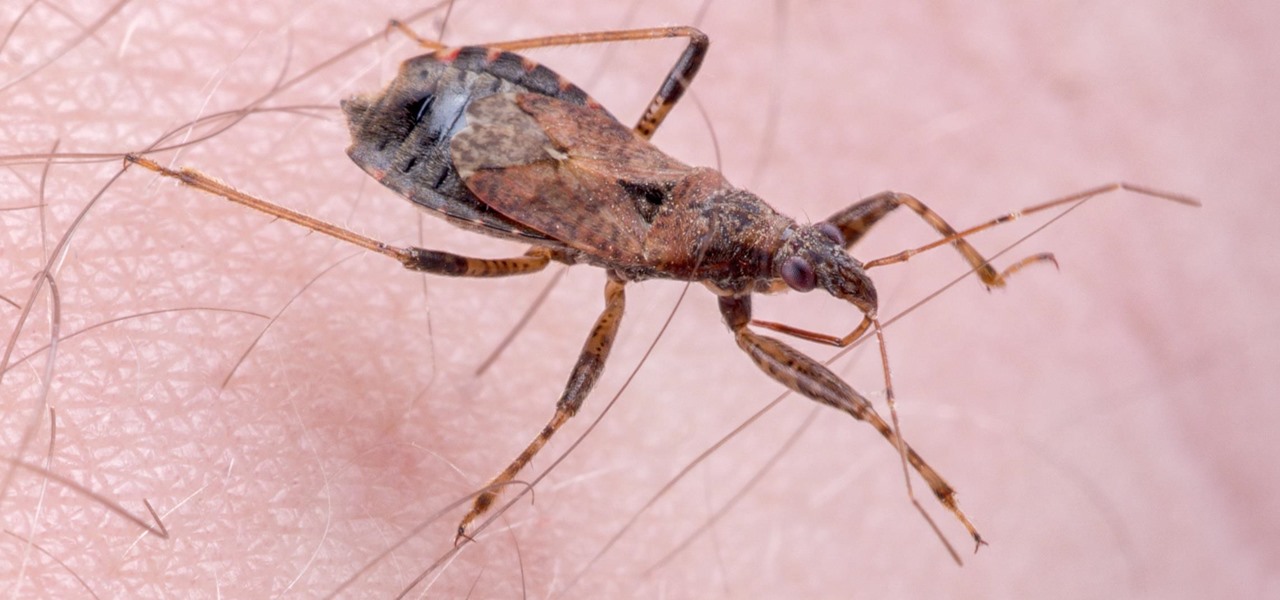
A sometimes serious disease spread by fleas is making inroads in Texas, quietly doubling case numbers since 2008, and beginning to encroach on larger metropolitan areas.

We can add one more health effect of our gut bacteria to the growing list. Researchers from the UK have just reported that the gut microbiota plays a role, both directly and indirectly, on the toxicity and efficacy of chemotherapy. Their findings are published online in the journal Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology.

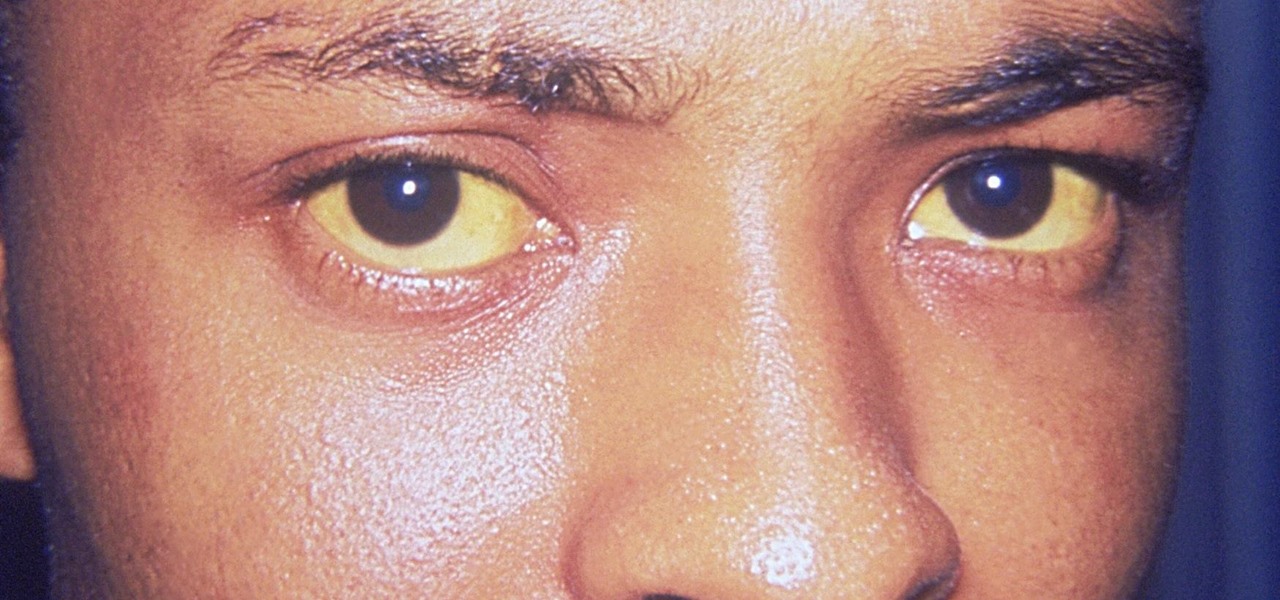
For some, drinking raw milk is a way to get back to nature, improve family nutrition, and hedge against asthma and allergies. However, according to public health authorities, drinking raw or unpasteurized milk is a big mistake—even fatal. So what's the story?

Six people have died from fungal infections in Pittsburgh hospitals since 2014—that fact is indisputable. The rest of the situation is much vaguer. A lawsuit has been filed against the hospitals on behalf of some of the deceased patients, alleging that moldy hospital linens are to blame. While the lawyers argue over who's at fault, let's look at how this could have happened.

Exposed to hormones, pharmaceuticals, and other chemicals, the beautiful wild fish in Canada's Grand River have taken on some pretty odd characteristics—they're turning into females. A long-term study suggests using bacteria to manage polluted water could turn the tide for feminized fish.

Bacteria gets a bad rap. Most headlines focus on the danger and discomfort posed by pathogens like bacteria, but many of the bacteria that live on and in us are vital to our health. Many products out there, called probiotics, are sold with the implication that they're supporting these healthy bacteria that share our bodies — but do they actually work?

To much of the United States, Zika seems like a tropical disease that causes horrible problems in other countries but is nothing to be worried about stateside. It may make you rethink your beach vacation abroad, but not much more than that. However, if you live in Florida or Texas, the possibility of getting a Zika infection where you live is real — and local outbreaks are more and more a possibility.

Joe McKenna died when he was 30 years old. A young married man with his future ahead of him, he was cleaning up the station where he worked as a fireman. Struck by a piece of equipment fallen from a shelf, Joe complained of a sore shoulder. Over the next week, Joe worsened and ended up in the hospital. Chilled, feverish, and delirious, his organs shut down from an infection we'd now call septic shock.

Only a handful of food products are impervious to spoilage—dried rice, salt, sugar—but even among those, honey is unique in that it remains edible without any preparation necessary. It's like this: if you came across honey in an Egyptian tomb, as archaeologists have, you could taste it and never guess it was thousands of years old.

You may not have heard of visceral leishmaniasis, onchocerciasis, or lymphatic filariasis, and there is a reason for that. These diseases, part of a group of infections called neglected tropical diseases (NTDs), impact more than a billion people on the planet in countries other than ours. Despite the consolation that these often grotesque illnesses are "out of sight, out of mind," some of these infections are quietly taking their toll in some southern communities of the US.

In a world increasingly regulated by computers, bugs are like real-life cheat codes. They give you the power to break the rules and do good or bad without ever leaving your seat. And government agencies around the world are discovering and stockpiling unreported bugs as cyberweapons to use against anybody they see fit.

Check out this science video tutorial on how to apply a C. elegans dopamine neuron degeneration assay for the validation of potential Parkinson's Disease genes.
Strange as it may seem to super urban people, certain animals, like coyotes, have high reproduction rates and can be a true menace to ranching. Even in the county where I live, which is home to Colorado Springs, there is a $30 bounty on coyotes. All you have to do is bring in both ears to the game warden, and you will be paid.

Thinking of planning a trip to India? Better wait 'til next year. Holi, the festival of colors, looks absolutely breathtaking.

If you have any little ones in your life (or you're simply a grown-up kid yourself), Just Bento has has posted Maki's Top 10 Bento Rules for Back-to-School. Rules listed below, click through for full explanations.