This video by the Food Standards Agency demonstrates the importance of good food hygiene and how to prevent the spread of bacteria. The beginning has a crazy and creative way of showing you how easy it is to spread bacteria. Eeeew! Prevent the spread of bacteria - shot CSI-style.
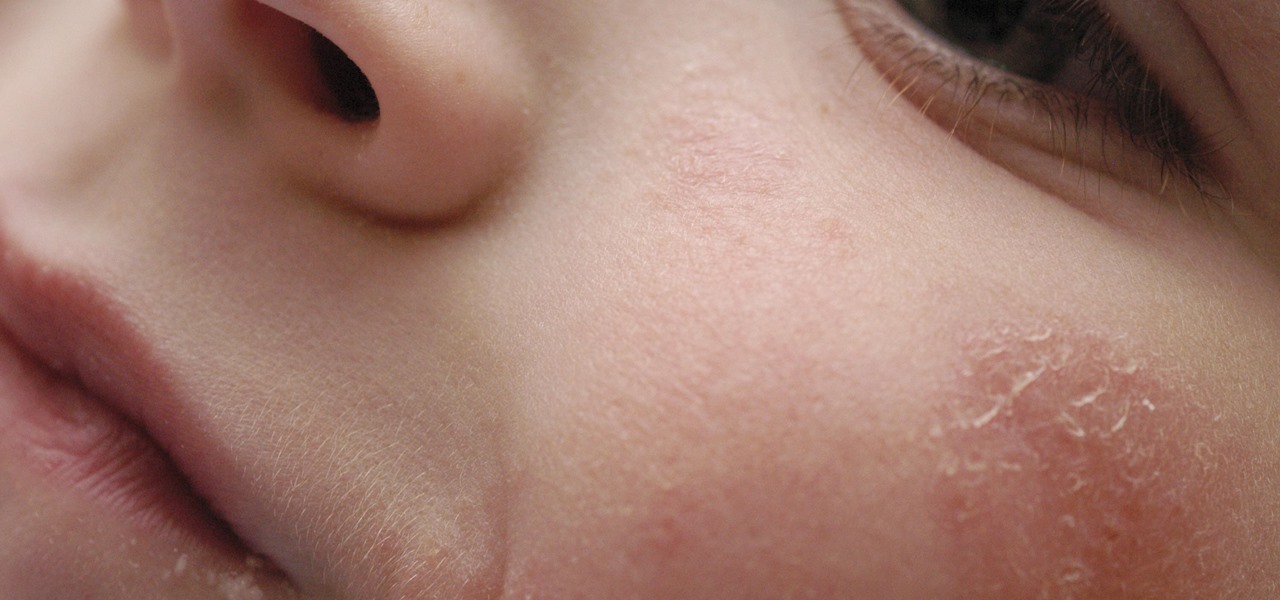
Most people know atopic dermatitis by its common name, eczema—that dry, flaky skin that itches incessantly. Along with the scratching comes frequent skin infections, often with Staphylococcus aureus.

Listeria monocytogenes bacteria don't play fair. Healthy people can usually handle the food-borne infection, but the bacterial infection hits pregnant women, fetuses and cancer patients very hard. Interestingly, a new study found that other bacteria may help prevent Listeria infections in those people.
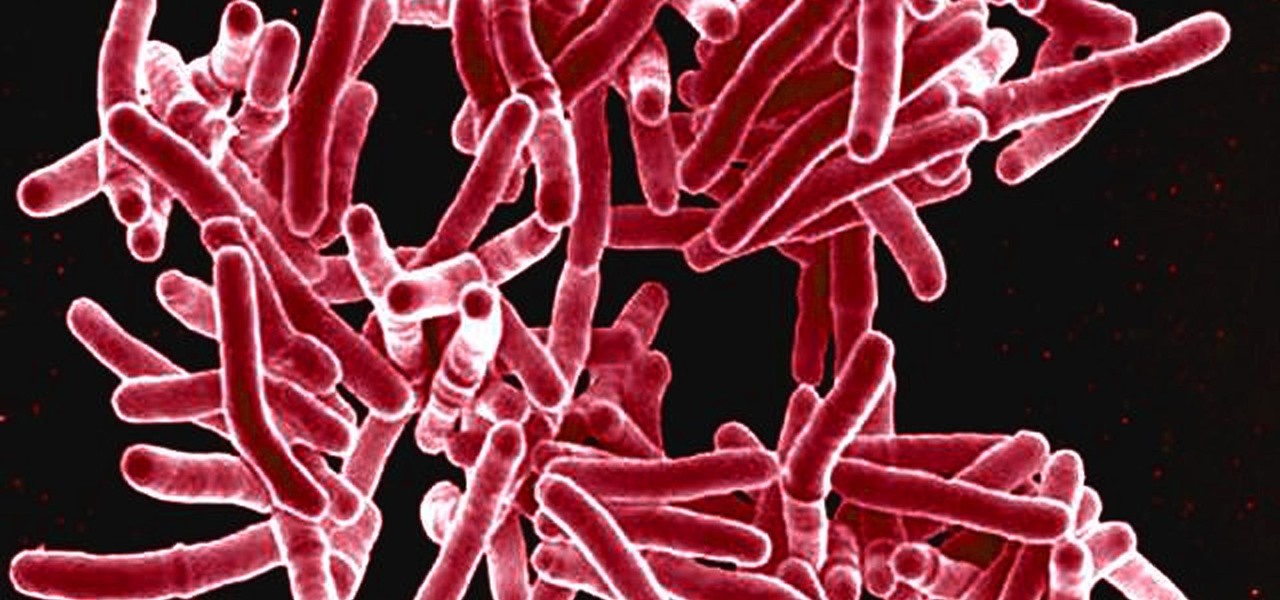
A promising new antibiotic has been discovered in, of all things, another bacteria. Burkholderia bacteria live in diverse habitats, including soil, plants, and humans where they thrive by knocking out other microbes that compete with them for resources or threaten their existence. Scientists have discovered they accomplish this by producing a very effective antibiotic.
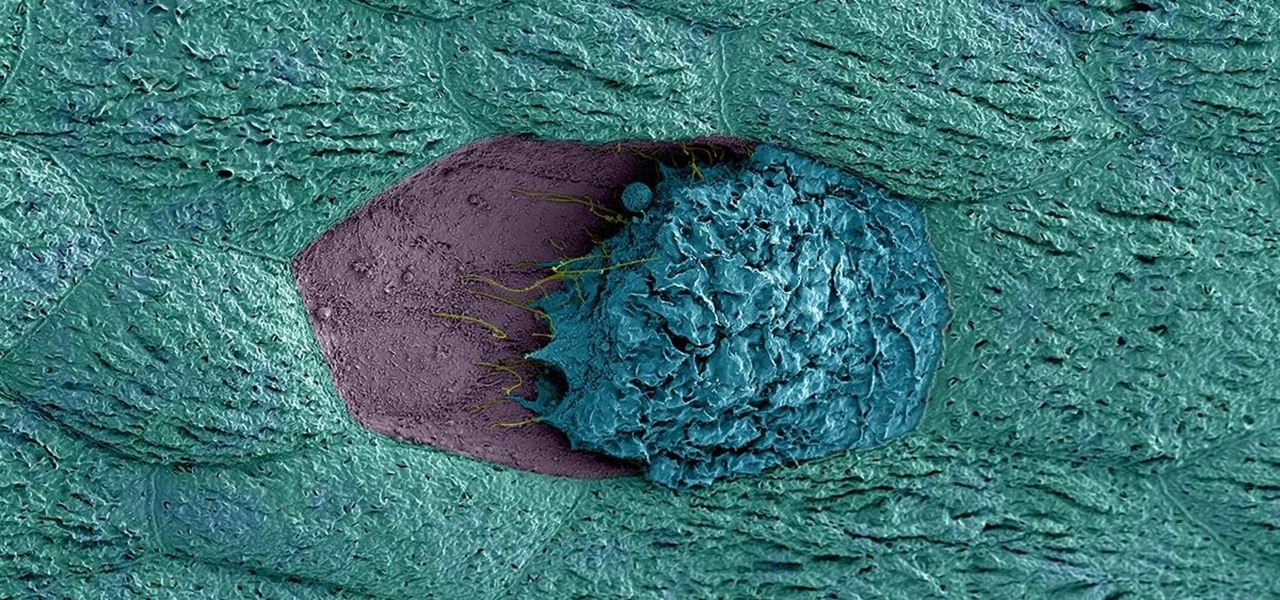
Most females have had at least one urinary tract infection in their lifetimes. Recurrent UTIs are particularly problematic in young, sexually active women, where about 80% of the infections are caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli, better known as E. coli.
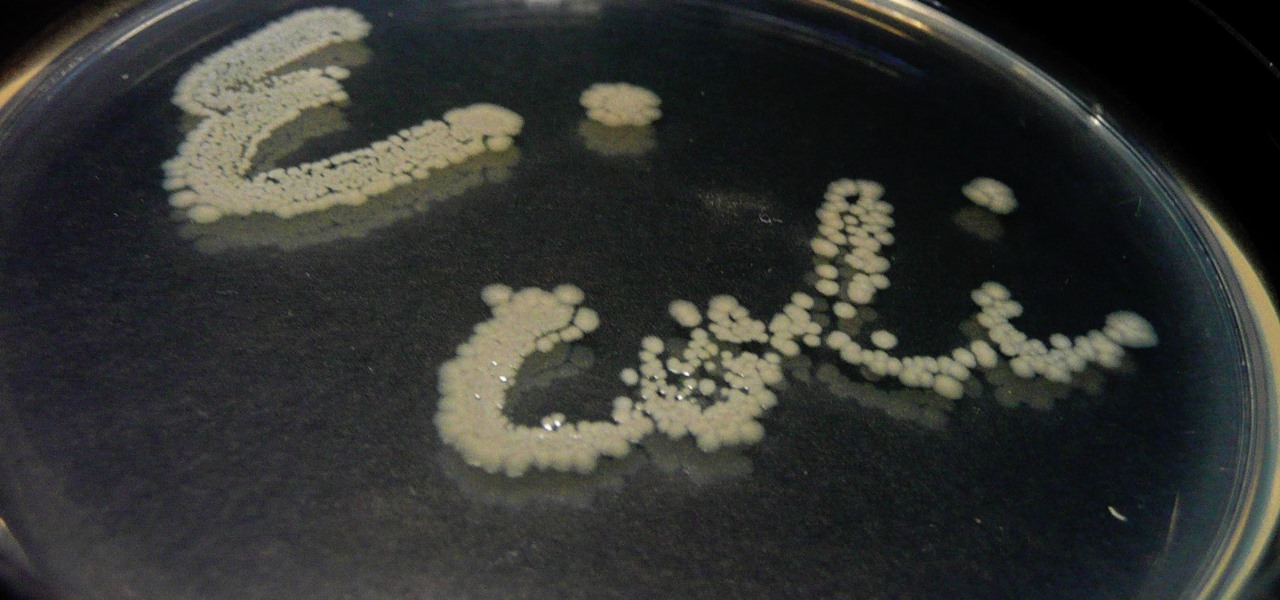
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) drive over eight million people to seek medical attention every year. Almost all — as many as 90% — of those infections are caused by Escherichia coli. Copper can kill bacteria, but E. coli has found a way to capture the copper, preventing its antibacterial action. Now, researchers have found that, in a cruel irony, the bacteria use the copper it grabs as a nutrient to feed its growth.

Next time you make dinner in your crockpot, be sure to follow these crockpot safety tips. The temperature should be at least 140 degrees. Food needs to cook at this temperature or higher to prevent the growth of bacteria. Do not put frozen foods into a crockpot. All foods should be defrosted before cooking, so the temperature can reach 140 degrees as quickly as possible. Do not lift the lid to stir, especially if you are cooking on the lowest setting. Each time you lift the lid, heat escapes ...

Peach trees and other related plants are susceptible to the devastation caused by fire blight, a contagious bacterial disease. Once contracted, infected trees have to be burned to contain the disease and prevent spread to nearby trees. Increasing resistance to antibiotic treatment has sent scientists in search of alternative ways to deal with the bacteria and prevent its catastrophic damage.

Cholera may be rare in the US, but cases of the disease have increased worldwide since 2005, particularly in Africa, southeast Asia, and Haiti. An estimated 3 to 5 million people are infected, and more than 100,000 die from the disease globally each year, mostly from dehydration.

Watch this video tutorial to learn how to prevent swimmer's ear. Don't let this painful infection of the ear canal keep you out of the water! A few simple precautions can combat the excessive moisture that causes bacteria to fester.

The search is on to find antibiotics that will work against superbugs — bacteria that are rapidly becoming resistant to many drugs in our antibiotic arsenal.

Wound infections don't usually enter the blood and become systemic, spreading the infection throughout our bodies, and there's a good reason for that: Our bodies actively work to prevent it, according to research that discovered a new use for a protein first discovered decades ago.

It's not the bacteria itself that takes lives and limbs during invasive flesh-eating bacteria infections. It's the toxins secreted by the group A Streptococcus bacteria invading the body that causes the most damage.

A rose by any other name may smell as sweet, but one annoying invasive weed may hold the answer to treating the superbug MRSA. Researchers from Emory University have found that the red berries of the Brazilian peppertree contain a compound that turns off a gene vital to the drug-resistance process.

We might think of Zika as a mosquito-borne virus that effects developing fetuses, but, it also can be passed through sex by either a man or a woman, just like herpes and other STD viruses. New research has shown that vaginal bacteria can inhibit sexually transmitted Zika virus and Herpes Simplex Virus-2 in women.

Where in the world did it come from? All of a sudden, one day, someone had an infection with flesh-eating bacteria. It captured headlines and worldwide attention because it was such a severe, strange, uncontrollable, and really disgusting condition.

In this tutorial, we learn how to prevent beach sand sickness. Sand has a ton of bacteria in it and can cause illness in your body right away. It will get on your hands, then when your hands go to your mouth, you will become sick. Don't bury yourself in sand, you are much more likely to have diarrhea after this occurs. Don't avoid the beach, just make sure you don't eat food after touching the sand. Keep hand sanitizer with you and wash your hands or take a shower after you get home from the ...

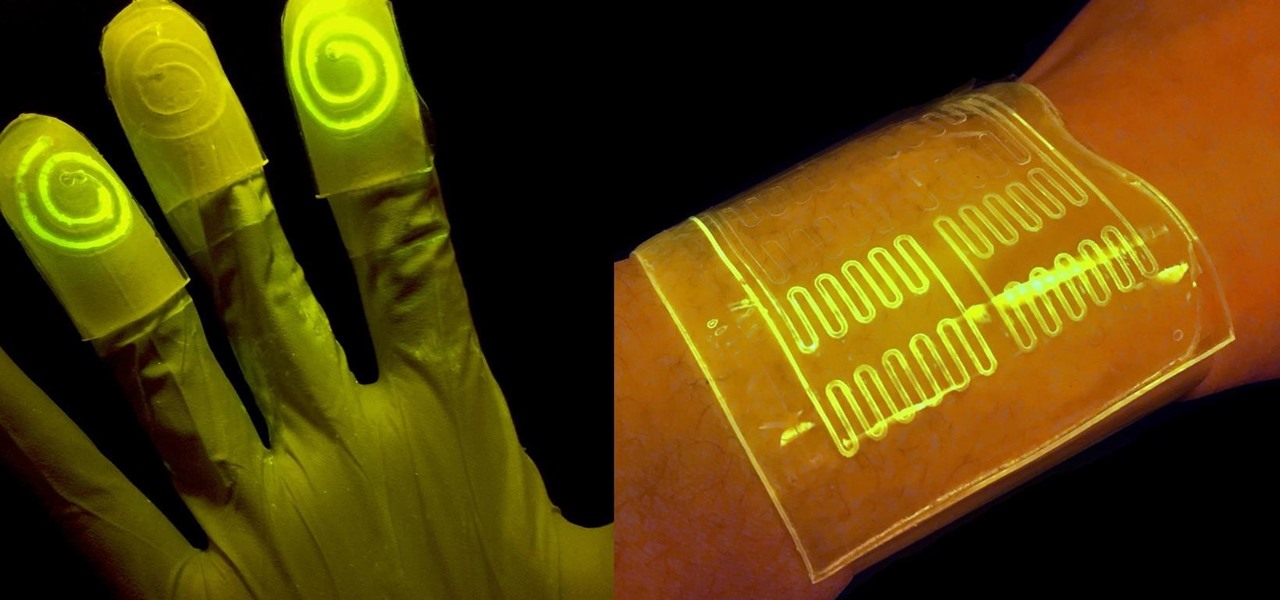
While at work, you notice your gloves changing color, and you know immediately that you've come in contact with dangerous chemicals. Bandages on a patient signal the presence of unseen, drug-resistant microbes. These are ideas that might have once seemed futuristic but are becoming a reality as researchers move forward with technology to use living bacteria in cloth to detect pathogens, pollutants, and particulates that endanger our lives.

The body's usual response to a bacterial infection in the blood — called sepsis — takes time. It requires a carefully orchestrated sequence of events that gets the body's immune system ramped up to deal with the invading bacteria.

We can add one more health effect of our gut bacteria to the growing list. Researchers from the UK have just reported that the gut microbiota plays a role, both directly and indirectly, on the toxicity and efficacy of chemotherapy. Their findings are published online in the journal Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology.

Colorectal cancer — cancer of the colon or rectum — is the third most commonly diagnosed cancer in the US. To reduce the chances of a diagnosis we are all urged to stop smoking, keep our weight down, decrease our intake of alcohol and red meat, keep active, and get screened for colon cancer. But, new research has found something that participates in the development of colorectal cancer that might not be as easy to control: A strep bacteria that promotes tumor growth.

Yogurt is more than an excellent source of protein, calcium, and gut-healthy probiotic bacteria. A protein isolated from probiotic lactobacillus bacteria in yogurt is capable of inhibiting drug-resistant bacteria.

Citrus greening disease — caused by a bacteria spread by psyllid insects — is threatening to wipe out Florida's citrus crop. Researchers have identified a small protein found in a second bacteria living in the insects that helps bacteria causing citrus greening disease survive and spread. They believe the discovery could result in a spray that could potentially help save the trees from the bacterial invasion.

Several recent research studies have pointed to the importance of the microbes that live in our gut to many aspects of our health. A recent finding shows how bacteria that penetrate the mucus lining of the colon could play a significant role in diabetes.

Drug-resistant bacteria have made curing some infections challenging, if not nearly impossible. By 2050, it's estimated that 10 million people will be dying annually from infections with antibiotic-resistant organisms.

In the summer of 1976, 4,000 American Legionnaires descended upon the Bellevue-Stratford Hotel in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, for a four-day convention. Several days later, many of the attendees experienced symptoms of severe pneumonia. By the beginning of August, 22 people had died. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimate that about 180 people were sickened and 29 people died before this mysterious outbreak burnt out.

Unfortunately, the very places we go to receive health care put us at risk for becoming infected with superbugs, bacteria exposed to so many antibiotics that they have become immune to their effects. Clostridium difficile (C. diff) is one such bacteria. It causes inflammation of the colon and rampant diarrhea that can have life-threatening consequences. Part of its virulence lies in the tough spores formed by the bacteria. They are responsible for starting infections in the colon and for spre...

Some types of bacterial infections are notoriously tough to treat — and it's not all due to antibiotic resistance. The bacteria themselves are rugged and hard to penetrate with drugs.

As researchers from Yale searched our environment for compounds to aid in the battle against drug-resistant bacteria, they got an unlikely assist from ticks.

How can bacteria that lives in the throat of 10%–35% of people—without causing an infection—cause life-threatening meningitis and sepsis in others?

The squiggly guys in this article's cover image are Propionibacterium acnes. These bacteria live in low-oxygen conditions at the base of hair follicles all over your body. They mind their own business, eating cellular debris and sebum, the oily stuff secreted by sebaceous glands that help keep things moisturized. Everybody has P. acnes bacteria—which are commonly blamed for causing acne—but researchers took a bigger view and discovered P. acnes may also play a part in keeping your skin clear.

Some bacteria can already do it—generate electric current, that is—and those microbes are called "electrogenic." Now, thanks to the work of a research group from the University of California, Santa Barbara, we know how to easily turn non-electrogenic bacteria into electricity producers.

New weapons are needed to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Instead of drugs, scientists have discovered in an animal study that they may be able to harness vampire bacteria to vanquish pneumonia.

Separate restroom hygiene fact from fiction – here's how. You Will Need

New research reveals how E. coli bacteria construct elaborate and effective tunnels to pump unwanted molecules like antibiotics and other toxins out of cells. The discovery could help us better understand how antibiotic resistance occurs and give us a leg-up to beat them at their own game.

The evidence is mounting and is becoming indisputable: Gut bacteria play a role in strokes and heart attacks. The link may seem a little far-fetched, but cardiovascular disease may have less to do with what we eat and more to do with what chemicals gut bacteria make from the food we eat.

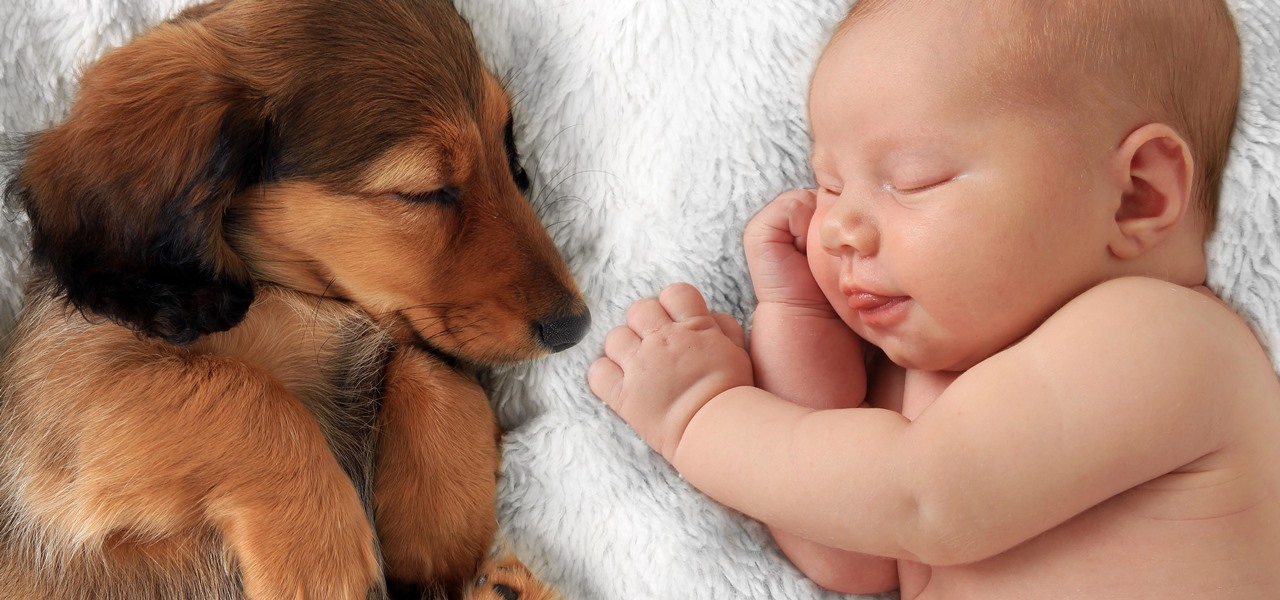
For many of us, pets are important family members. They give us loyalty, companionship, and comfort. Now, researchers have given us another reason to welcome them into the family: Babies from families with furry pets — the majority of which were dogs — had higher levels of two types of beneficial gut bacteria.

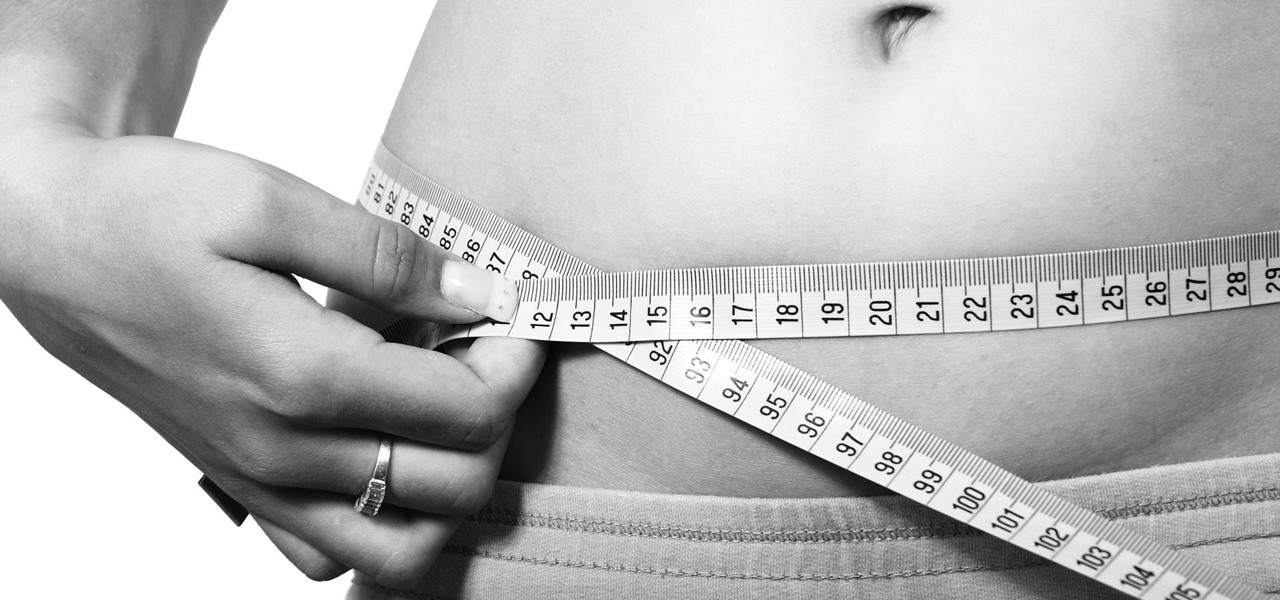
Potbellies don't have to happen as we age, according to two studies done on twins published online in the International Journal of Obesity.

As drug-resistant bacteria become more commonplace, researchers are looking for new antibacterial strategies to disrupt disease-causing microbes. Some scientists are working to create new drugs, while others are trying out drug combinations. Another group, however, are ditching pharmaceuticals altogether and experimenting with non-drug alternatives.

This video teaches the viewer how to cook 10-minute noodles. First, we are shown to slice an onion. Second, roughly chop some garlic. Heat up some oil in your skillet. While you're waiting, you can slice a pepper. Toss all the ingredients in and be sure to keep them moving in the skillet. Next, chop up some chicken. Flip the board over to prevent spreading bacteria, and then chop up some green beans. Toss the green beans into the skillet, along with any other chopped vegetables you choose. Co...