
News: Scientists Found an Antibody That Burns Belly Fat (In Mice)
Bone loss and belly fat may no longer be certain fates of menopause, thanks to new research from an international team of scientists.


Bone loss and belly fat may no longer be certain fates of menopause, thanks to new research from an international team of scientists.
Several recent research studies have pointed to the importance of the microbes that live in our gut to many aspects of our health. A recent finding shows how bacteria that penetrate the mucus lining of the colon could play a significant role in diabetes.
The story of Helicobacter pylori is a real testament to the tenacity of medical researchers to prove their hypothesis. It took decades before the scientific world would accept that the bacteria H. pylori caused ulcers.

Who doesn't enjoy sitting down to a nice dinner with a cocktail in hand? After a long day, a drink is a great way to unwind. Yet your favorite spirits can do more than just help you relax after work. By utilizing alcohol in the kitchen, you can enhance everything from how food tastes to your health.

Your entire life has been a lie. Mario does not hit blocks with his head, footlong subs are never really 12 inches long, and those paper ketchup cups at fast food joints aren't just little cups. And that's not the worst of it. What I'm about to tell you next is the revelation of all revelations.

With significant advancements in the treatment and prevention of HIV, you'd think the stigma surrounding the deadly virus and AIDS, the syndrome the infection causes in the body, would have lessened. Unfortunately, a new project looking at conversations on Grindr — a social networking app for gay, bi, curious, and queer men — has shown that this stigma is very much present.
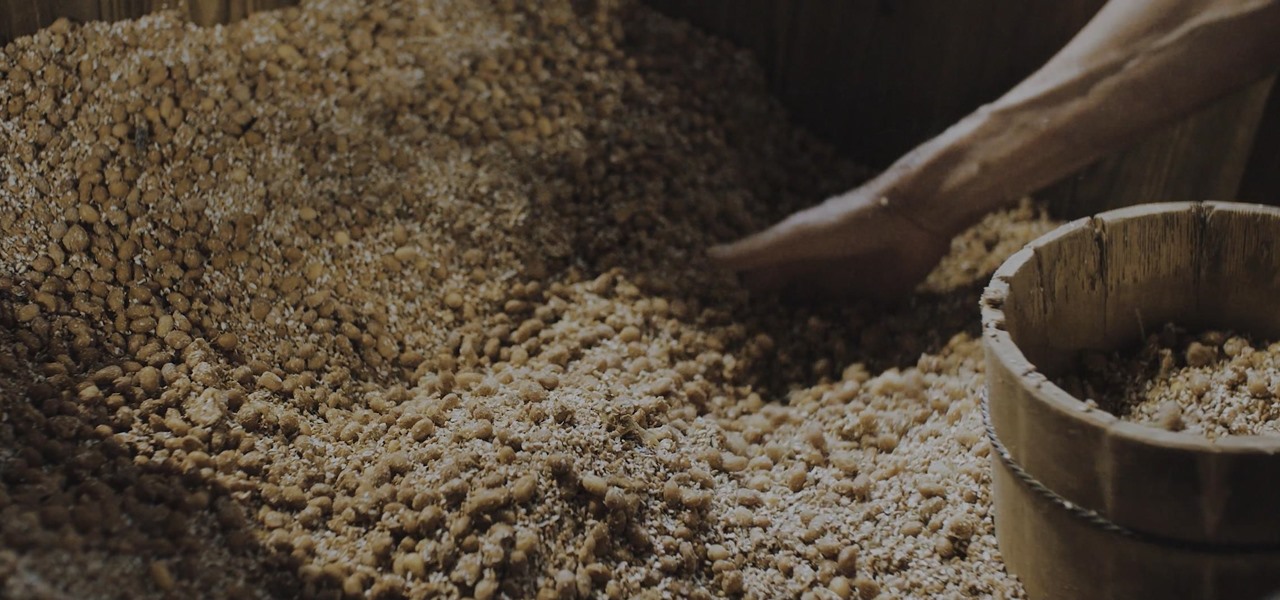

Soy sauce is a sushi essential for most Americans and we don't often consider its exact origins whilst chowing down on that tuna roll.

Biting into a perfectly ripe mango is living proof of nature's goodness. The flesh is at once creamy, smooth, tart, and sweet. Plus they're incredibly good for you.
"Millions of us have smartphones with the power to speed up research that will benefit billions of people around the world." - Professor Francois Grey

Remember those horrible, soul-crushing studies from a few years back linking grilled meats with cancer? Unfortunately, they're still true, but scientists have recently found that an unexpected ingredient can curb some of the harmful effects of high-temperature cooking.
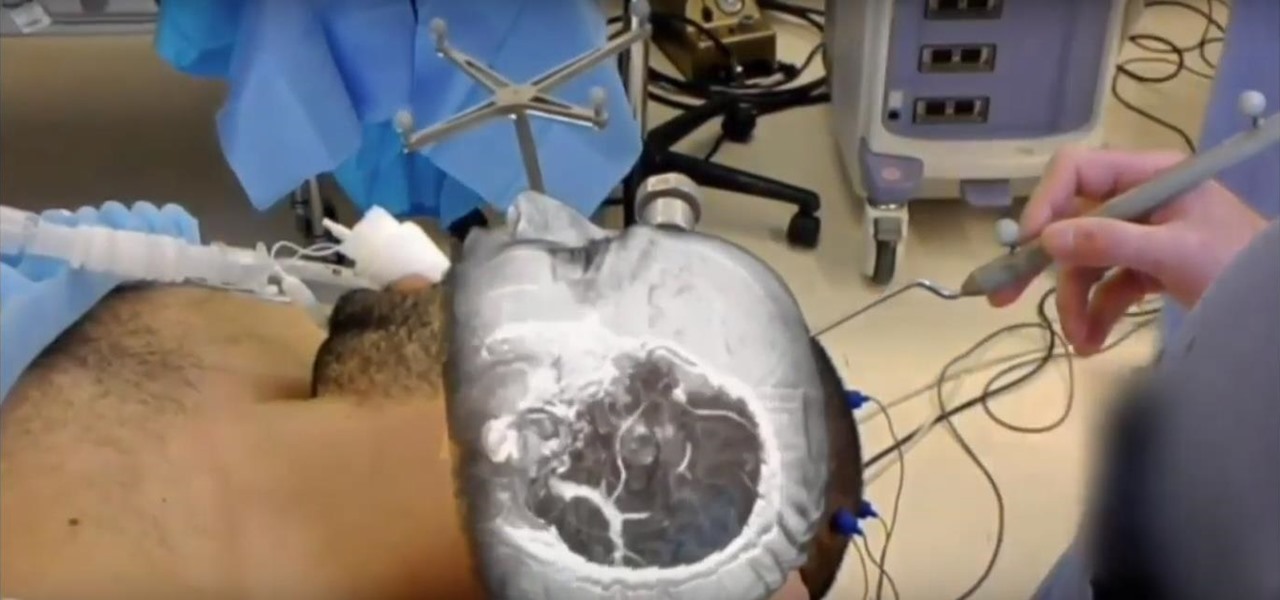
The HoloLens has made enough of an impact on the healthcare industry for Microsoft technology partner Medivis to convince investors to pledge $2.3 million in funding for its surgical platform.
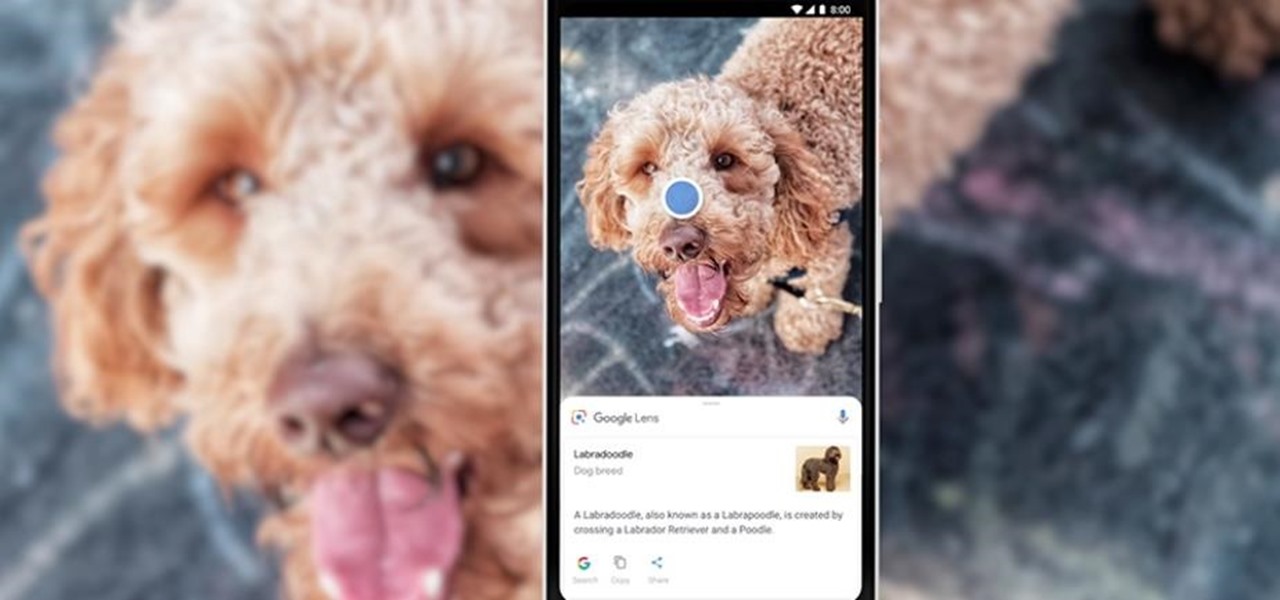
During Tuesday's keynote at the I/O developer conference, Google unveiled new capabilities for its Lens visual search engine and expanded the availability of the platform in smartphone camera apps.

The HoloLens has become a frequent sight in medical facilities around the world, but a new demonstration shows just how seamlessly it can be integrated into traditional medical procedures to improve the experience for physicians and patients alike.
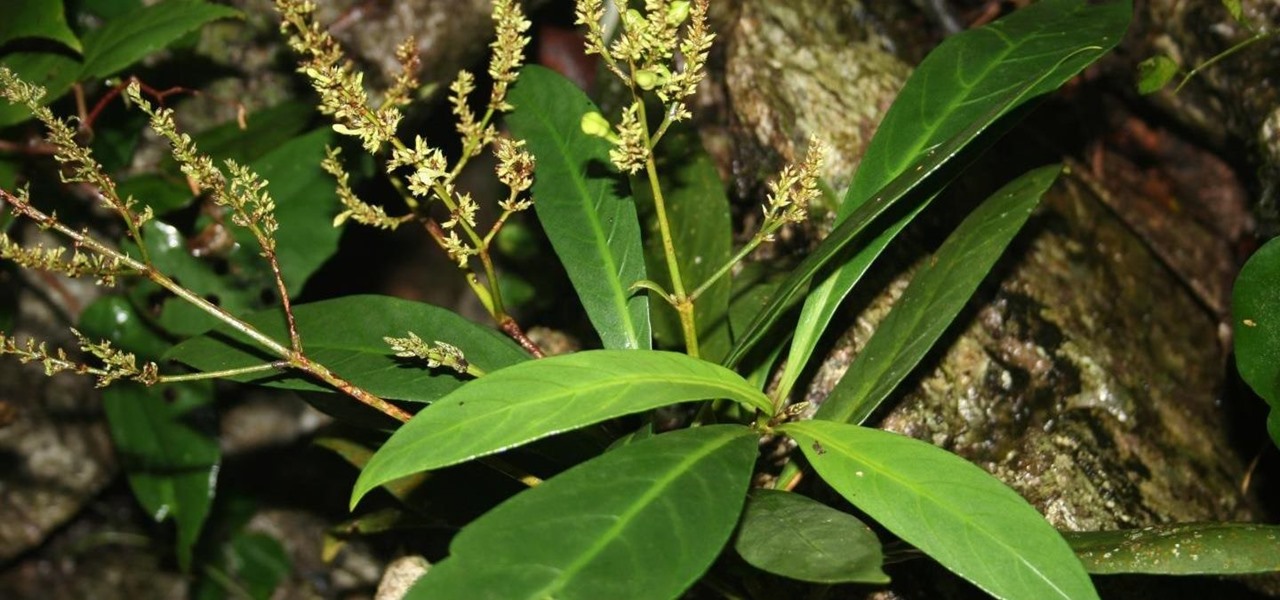

Natural remedies used through the ages abound, especially in Asian medicine. The willow-leaved justicia plant, found throughout Southeast Asia, has traditionally been used to treat arthritis, but scientists have just discovered it contains an anti-HIVcompound more potent than AZT. AZT was the first drug approved to treat HIV, and is still used in HIV combination therapy today.
Dramatic new research may change the fate of the hundreds of people who wait for a kidney transplant every year. The study hinged on the ability to cure hepatitis C infections, a possibility that became a reality in 2014.
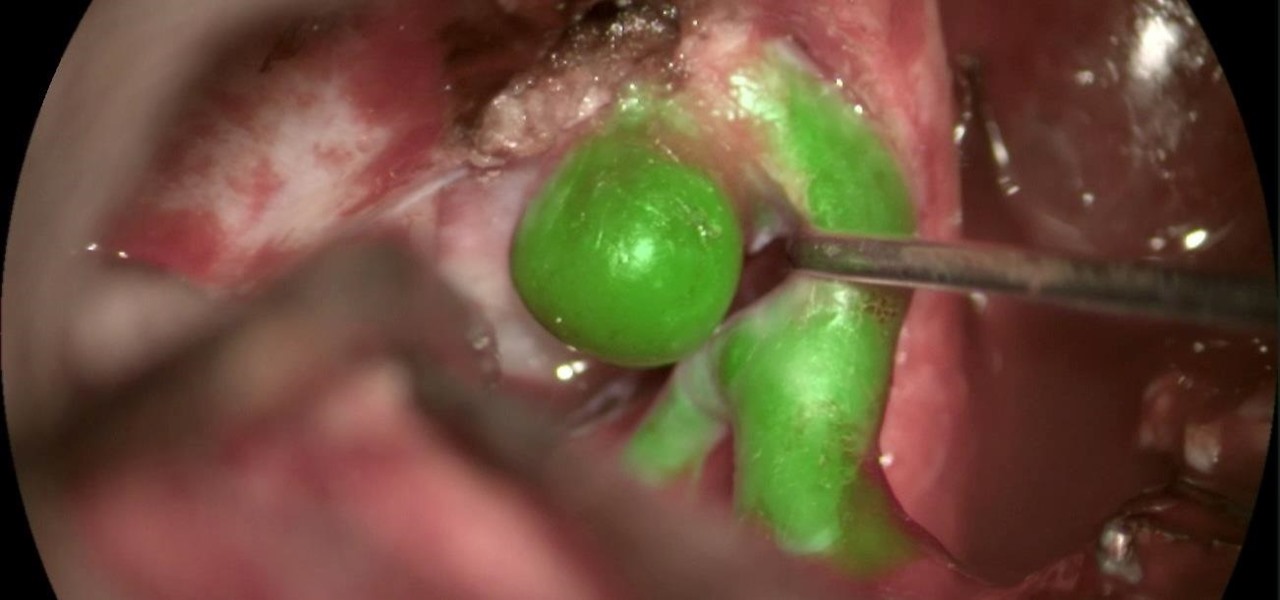
In this Tuesday's Brief Reality report, there's a trio of stories from the healthcare world where augmented reality is helping out with surgical microscopes, asthma treatment, and other diagnostic and treatment tools. There's also something for all of you AR/VR storytellers out there.

Usually, the mucus lining of the female genital tract presents a barrier that helps prevent infections. But, somehow, the bacteria that causes gonorrhea gets around and through that barrier to invade the female genital tract.

Overweight kids often become overweight adults. New research suggests a couple reasons why and suggested that there may be ways to intercept that fate.

Some studies have shown that vitamin D supplements help fight respiratory infections, but some haven't. A new study published in The BMJ clarified the confusion, and identified a group of people that might be better able to fight off colds and flu with vitamin D supplements.

Fish are delicate, flaky, and can be damn tricky to cook; more often than not, you end up with a hard, dry block of flesh that makes your taste buds sad. And the best ways to cook fish that you know of—c'mon, who doesn't love a fried fish—take way too much effort for you to bother with on a weeknight. Or maybe you're looking for a healthier way to enjoy fish that doesn't require batter or frying at all.

Koji is a culture made up of a certain fungus (mold) called Aspergillus oryzae, which has been used to ferment rice and soybeans in Japanese, Chinese, and Korean kitchens for centuries. Koji can actually have other involved fungi, but Aspergillus oryzae is the most common, and therefore the names can be used interchangeably. Its end purpose is to enhance the flavor of items like soy sauce, sake, and miso.
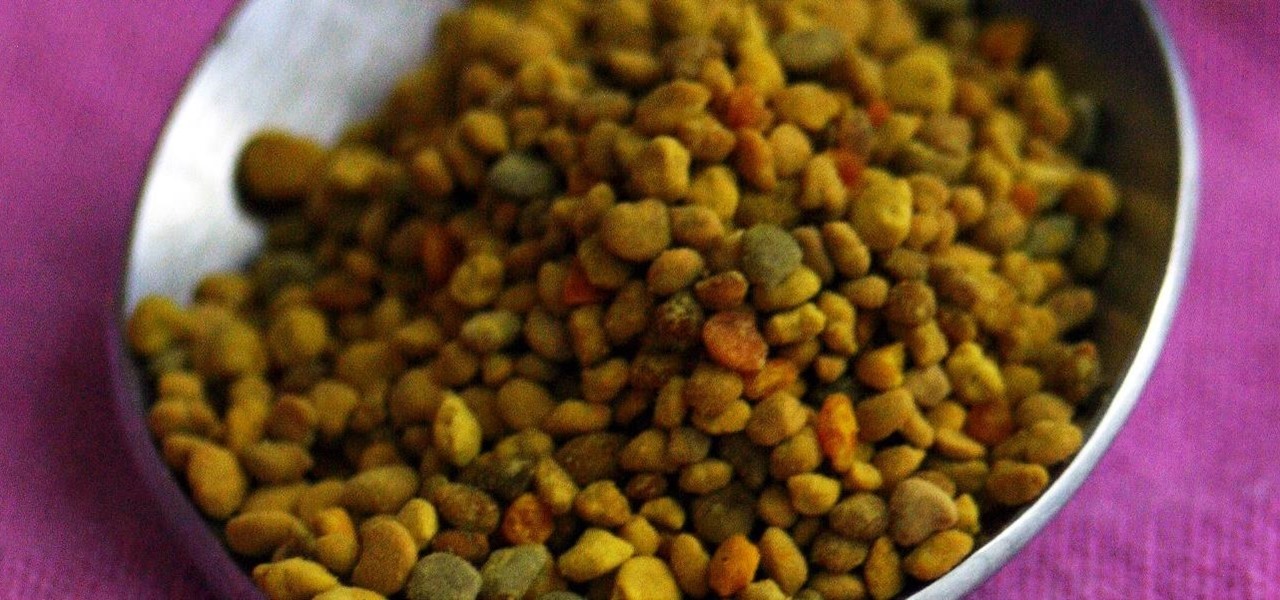

While honey is one of the most popular ingredients on kitchen shelves the world over, honeybee pollen is still a relatively rare find in most households. It's not hard to guess why: eating pollen just sounds weird... it would probably sell a lot better if it had a more appetizing name, like honey. Furthermore, it looks unlike any other common ingredient, and the smell can be off-putting to some. But it's good, it's healthy, and it's altogether pretty awesome!
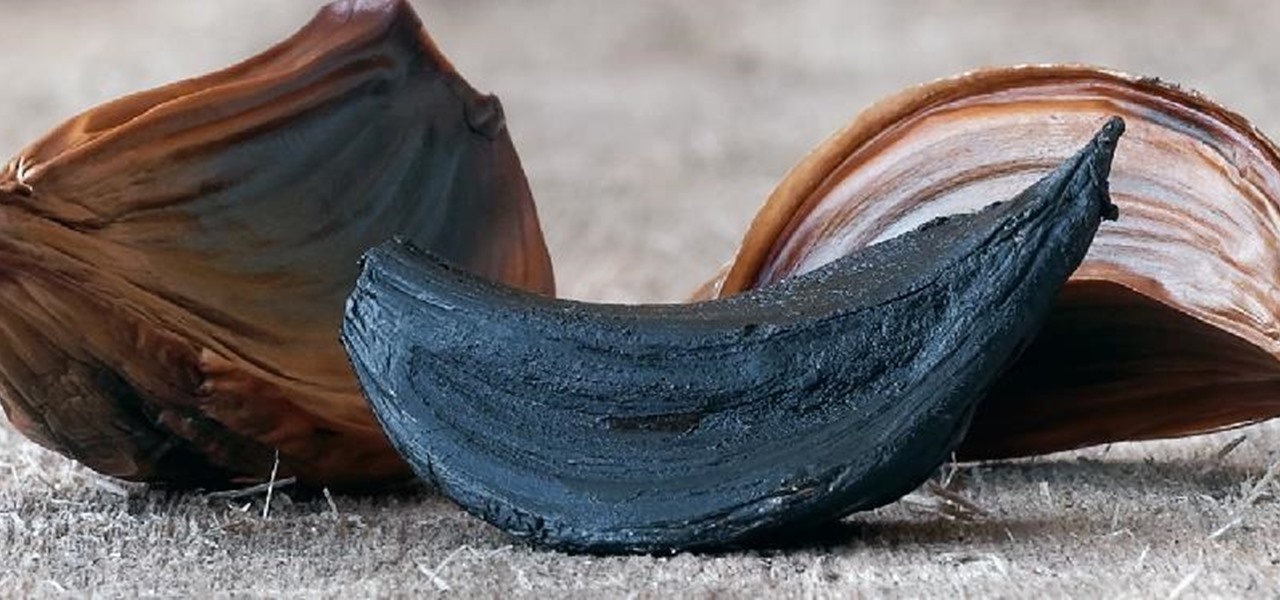

Garlic: almost every cuisine in the world considers it a staple, and for good reason. Its pungent flavor gives depth and character to food. Dishes made without it seem bland and forgettable. And on top of all that, it's been studied for its potential anti-cancer properties (and don't forget: it's been mythologized for warding off vampires).
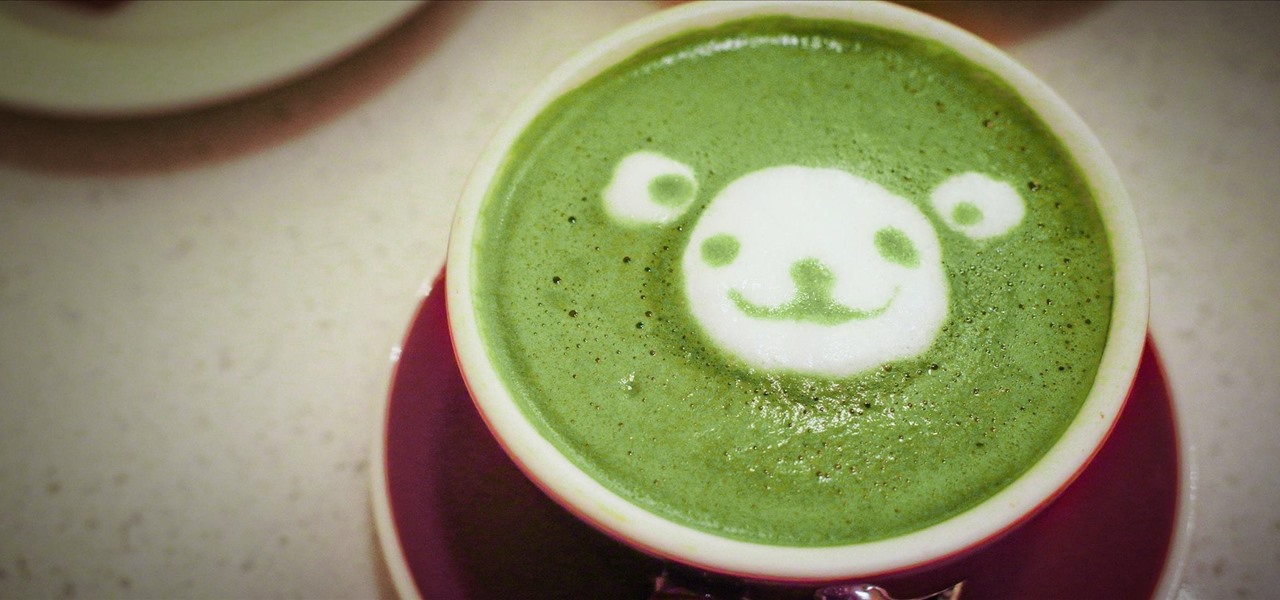

Many people drink green tea for health reasons, and it's no wonder. This beverage is a superstar when it comes to antioxidant levels, and is being studied for its potentially curative properties on multiple health concerns, whether it's staving off the aging process or fighting cancer.

You've got to be sick of it by now. Those meaningless and unsatisfying articles, lists, and videos you were duped into clicking on because their headline made them impossible to resist.
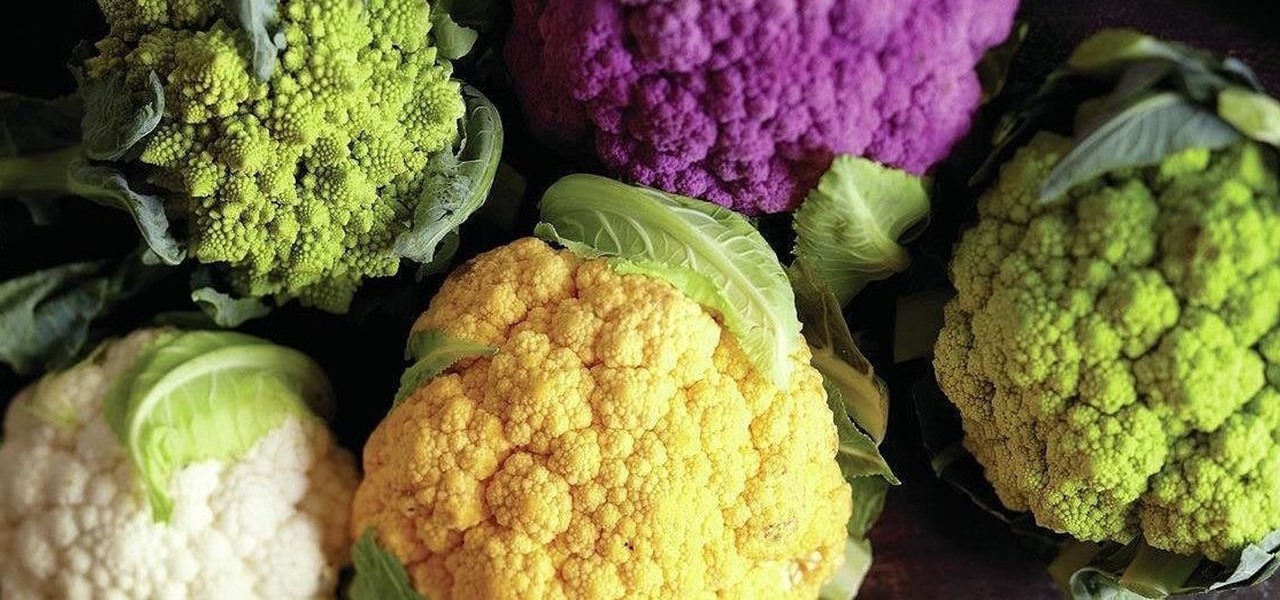

It's universally known that broccoli, kale, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, and all cruciferous vegetables (also known as brassicas) are good for you—but you probably don't know exactly how good they really are.

As a species, our cells are designed to use sugar for energy. Is it any wonder that as humans evolved, we grew to love the taste of sugar?

I grew up in a household where bacon was considered its own necessary food group. My mom saved the bacon fat in a jar and reused it in other dishes, which my friends considered vile, unless they were also from immigrant families or the American South, where saving bacon fat has never gone out of style.

About ten years ago, Western research figured out that green tea was a nutritional powerhouse. After all, in Asian countries where green tea is consumed throughout the day, cancer rates tend to be much lower, although there are probably other factors contributing to that fact, like less processed food and red meat in the standard Asian diet.

Today could mark the beginning of a new age in wireless charging. The FCC has certified the WattUp transmitter, a revolutionary technology that could shape the future of smartphone charging. This new tech addresses many of Qi charging's limitations, and if things go right, may lead to a truly wireless future.
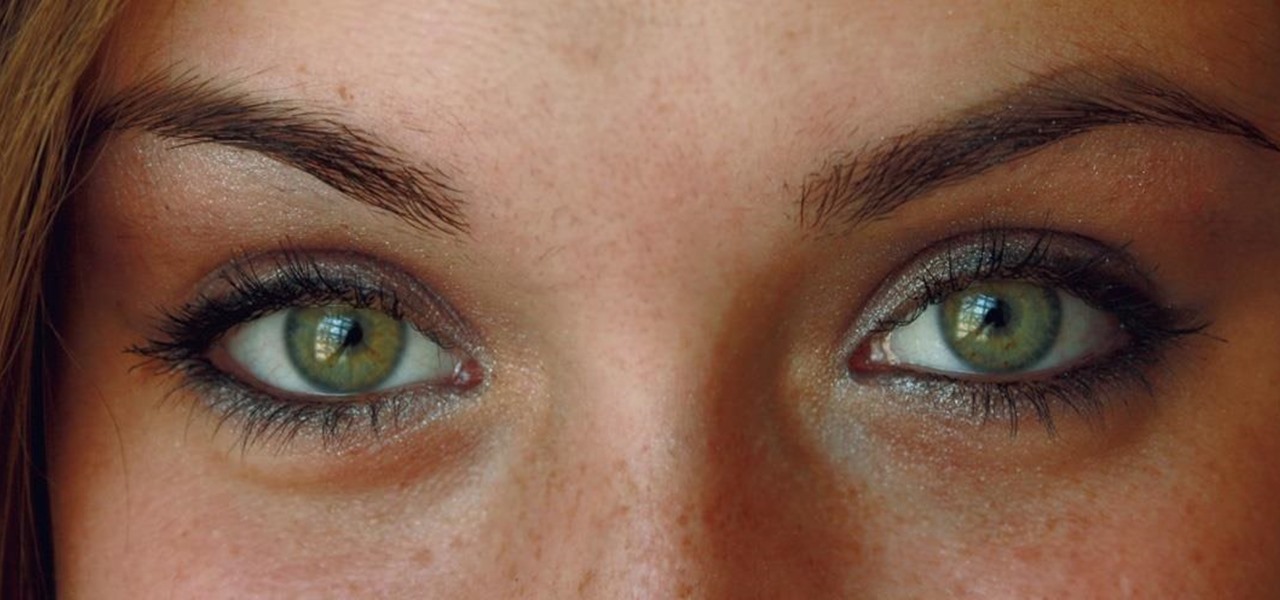
Not all bacteria in the eyes cause infection. A group of researchers from the National Eye Institue has shown that not only is there a population of bacteria on the eyes that reside there but they perform an important function. They help activate the immune system to get rid of bad, potentially infection-causing — pathogenic — bacteria there.
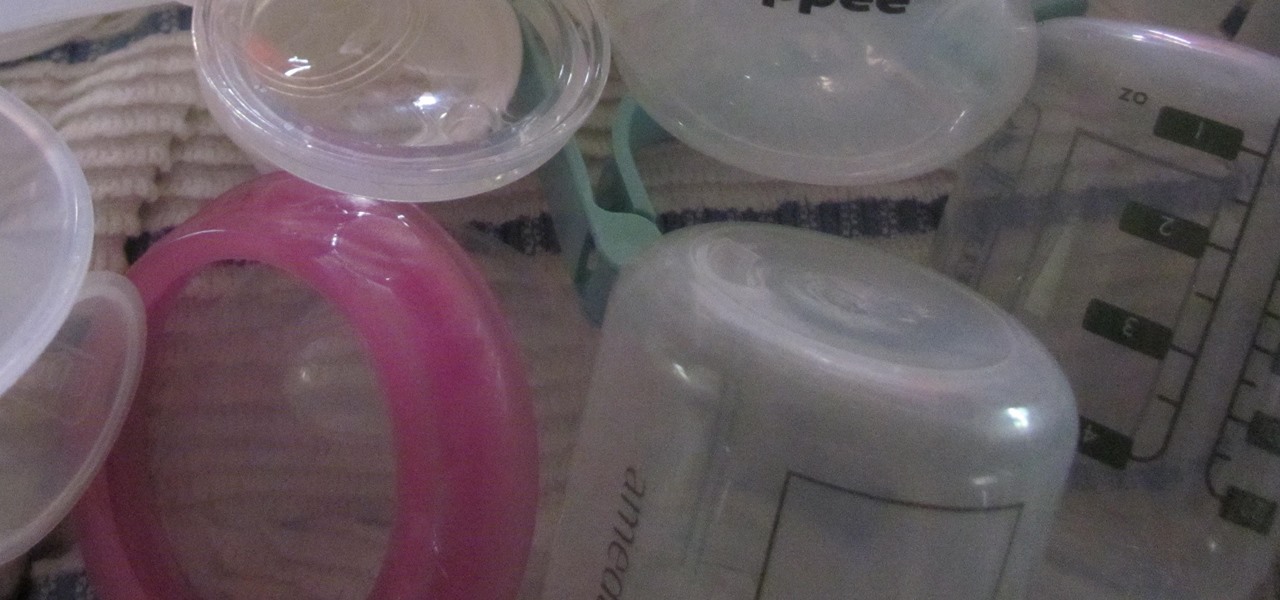

Foodborne infections often occur through the contamination of equipment, food-prep tools, and unsanitary surfaces. A recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reminds us that breast pump parts are part of the food-delivery chain — and they can become contaminated too.
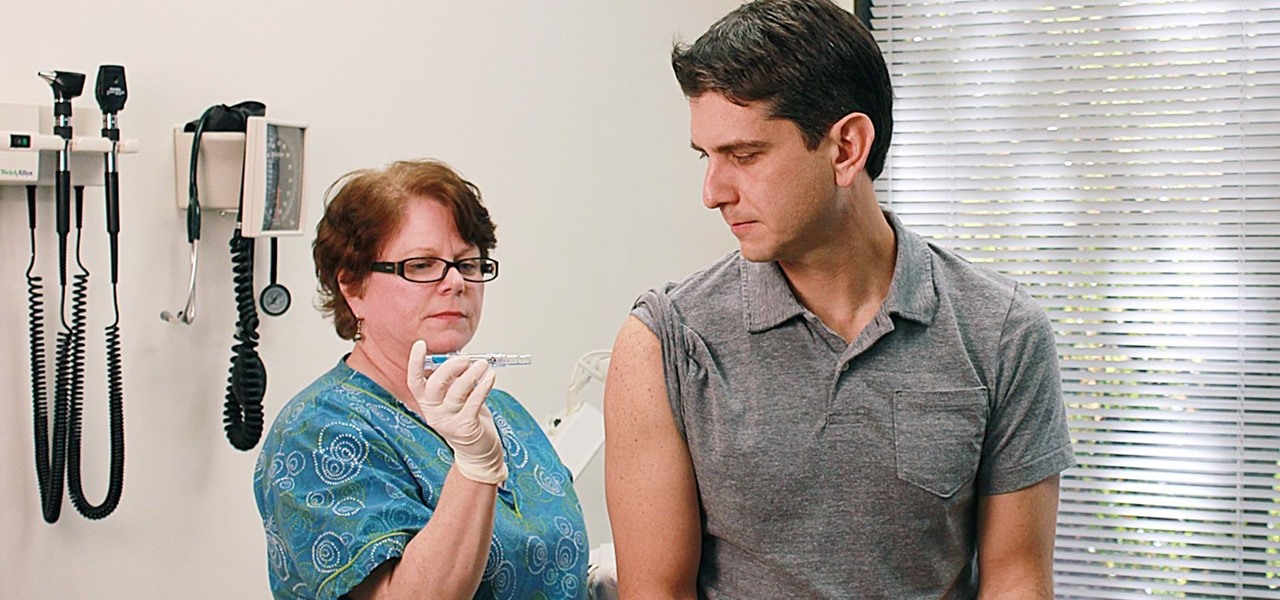
Flu vaccines can help prevent us from getting or suffering the most severe effects of the flu. But, each vaccine only protects us from three different strains of the flu. If we don't have a vaccine against all types of flu, it leaves us open for an epidemic with a flu virus we didn't expect.
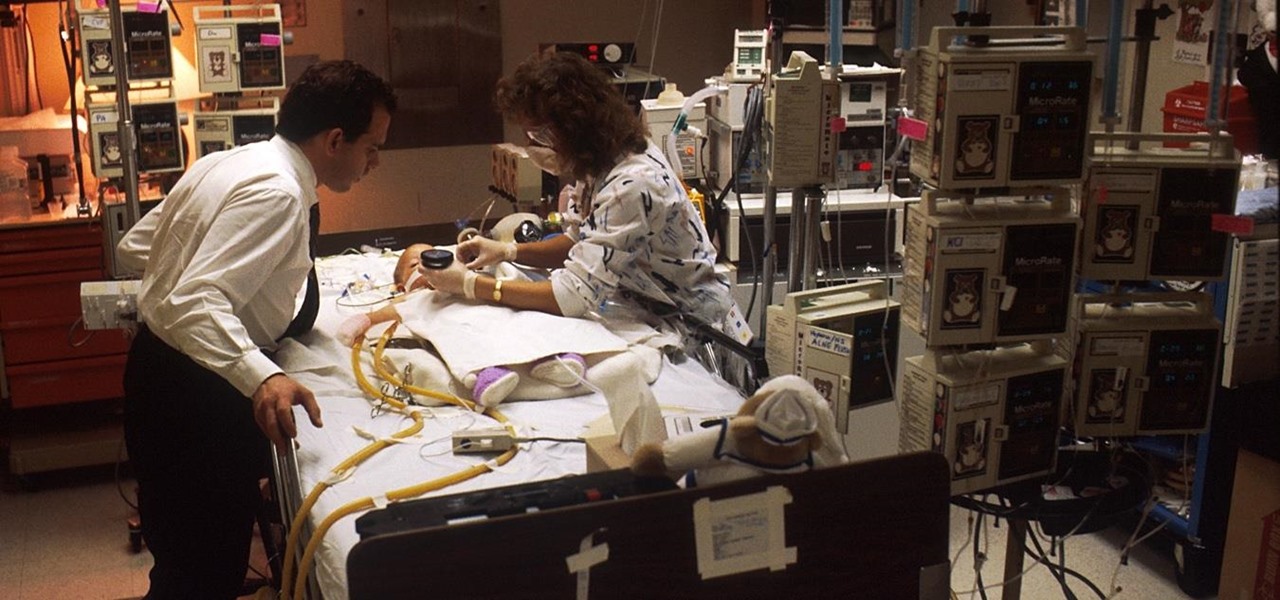
Twelve-year old Rory Staunton took a dive for a basketball during gym class and came up with a cut on his arm. The school nurse applied a couple of band-aids, without cleaning the cut, and off he went. In approximately three days, hospital physicians told his parents there was nothing else that they could do for their son; he was dead.
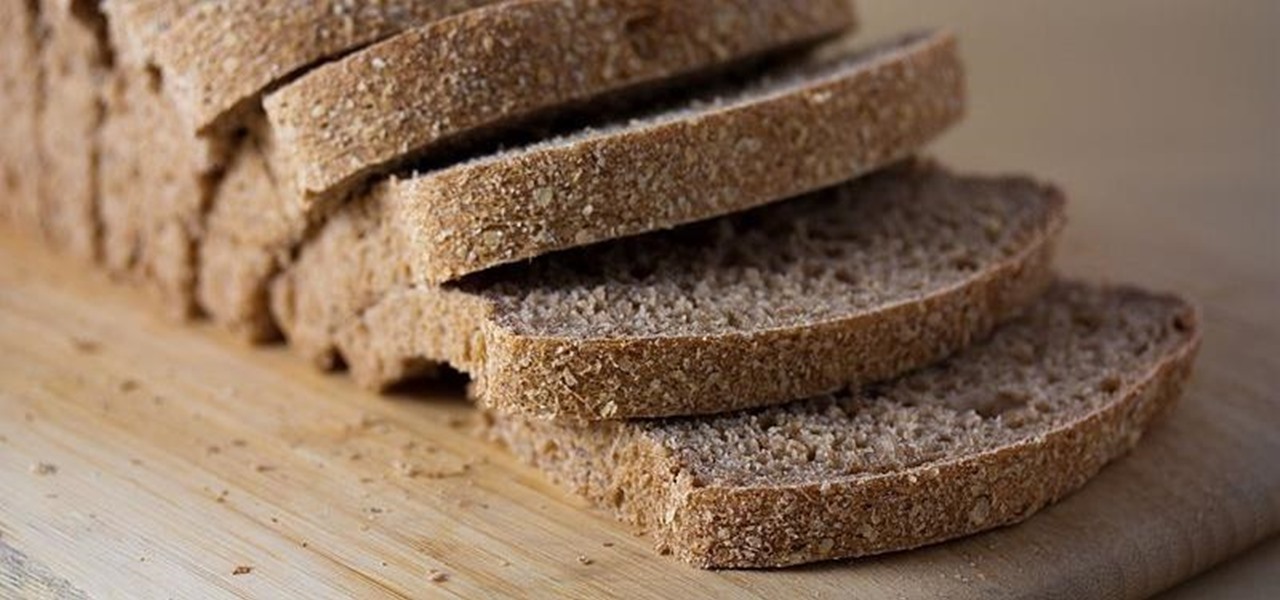

Move over whole wheat — white bread may be back in style after a new study shows that it may be your gut microbes that decide what kind of bread is best for you.
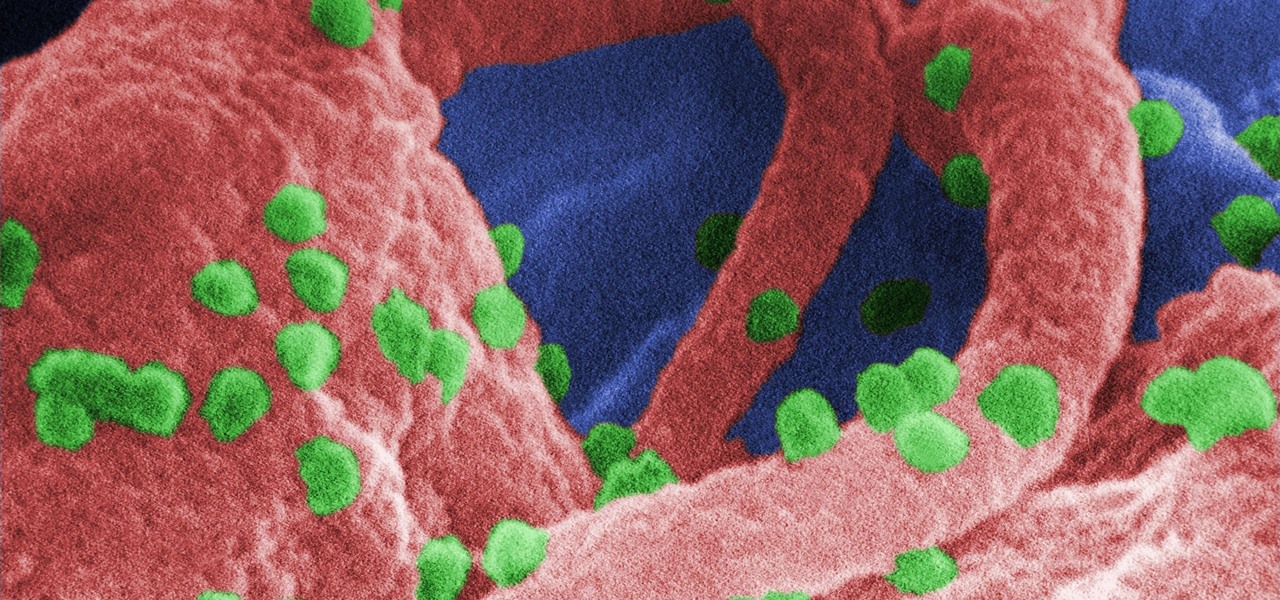
The problem with HIV is that it attacks and kills the very cells of the immune system that are supposed to protect us from infections — white blood cells. But a new technique, developed by scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) in La Jolla, California, offers a distinct HIV-killing advantage.
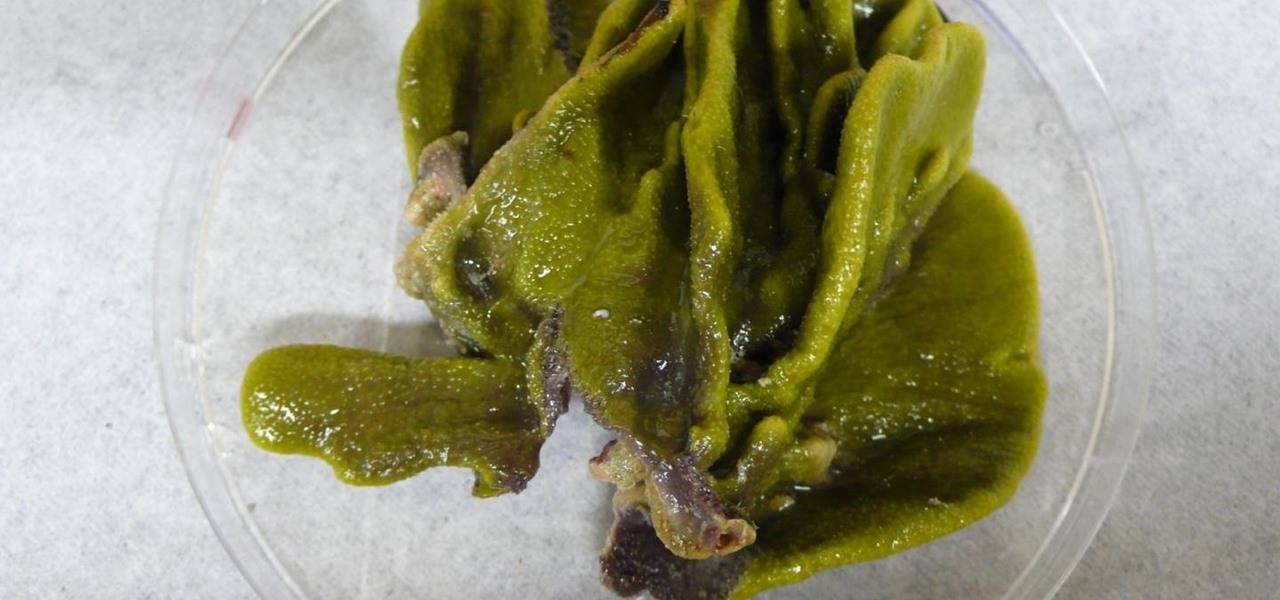

We've worked hard to reduce the flow of toxic chemicals into our waterways, which means no more DDT and other bad actors to pollute or destroy wildlife and our health. But one observation has been plaguing scientists for decades: Why are large quantities of one toxic chemical still found in the world's oceans?
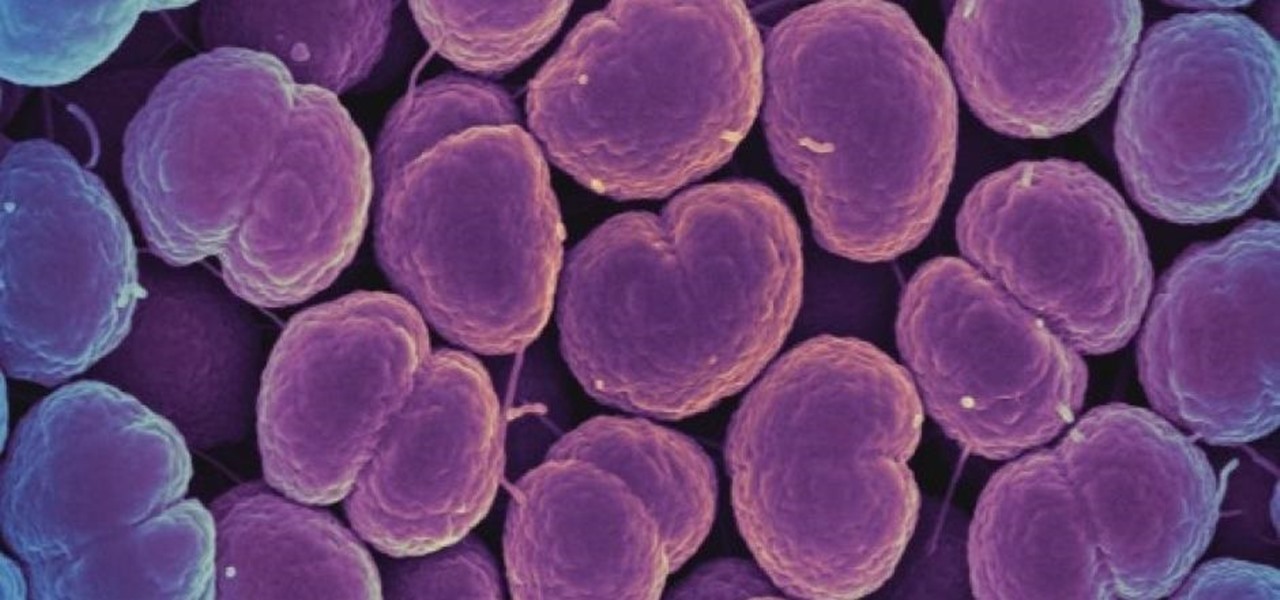
The ability of one microbe to adapt is giving it a whole new career as a sexually transmitted disease. Usually content with the back of the throat and nose of those who carry it, the dangerous pathogen Neisseria meningitidis has adapted to cause an illness that looks a lot like gonorrhea.
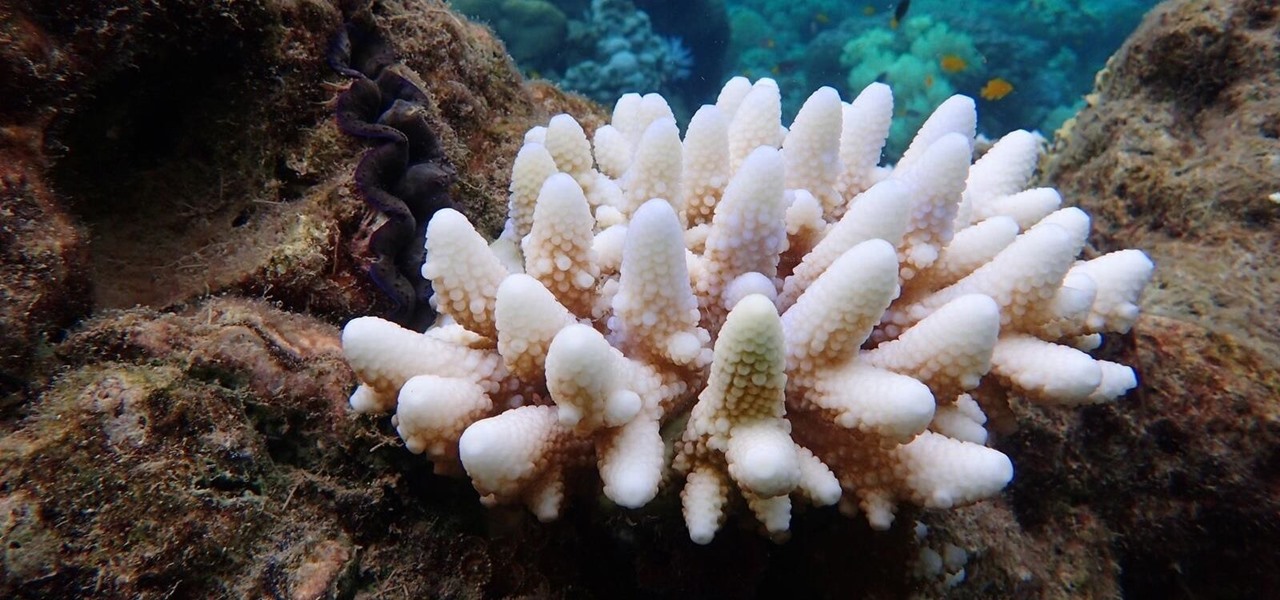

The Great Barrier Reef in Australia is the largest living system on the planet. Yet more than 90% of the reef is bleaching because of the loss of a tiny algae that lives within the coral.
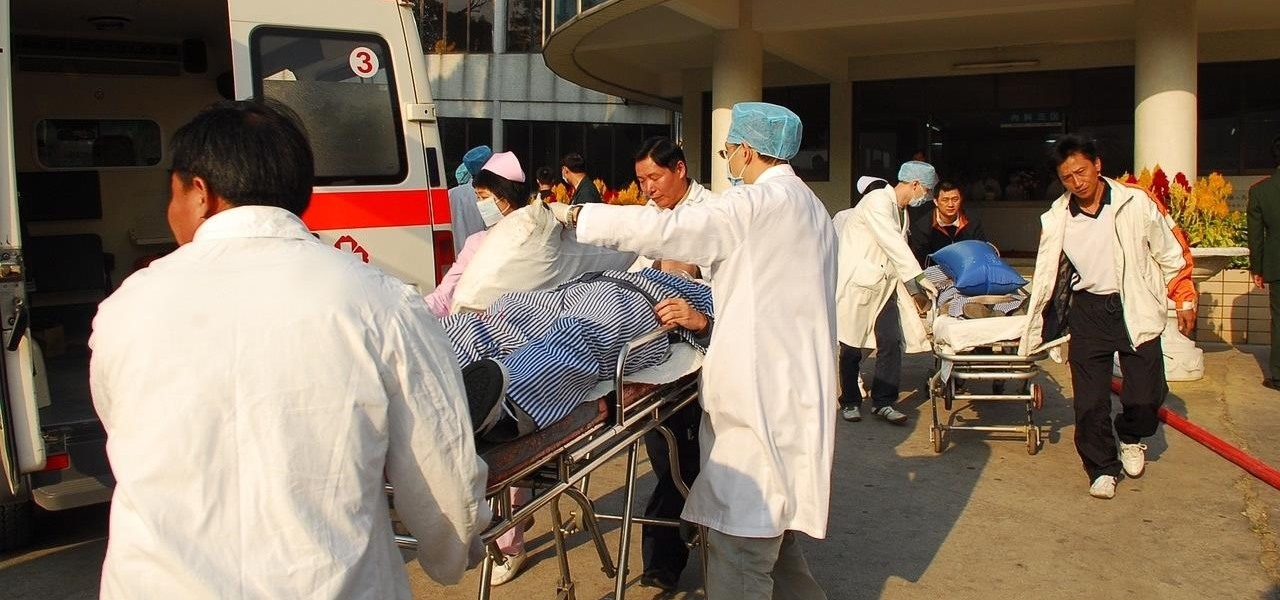

It hasn't even been eight years since Candida auris was discovered—cultured and identified from the ear canal of a patient in Japan—and now it's drug-resistant, setting up residence in hospitals, killing patients, and wreaking havoc across the globe.