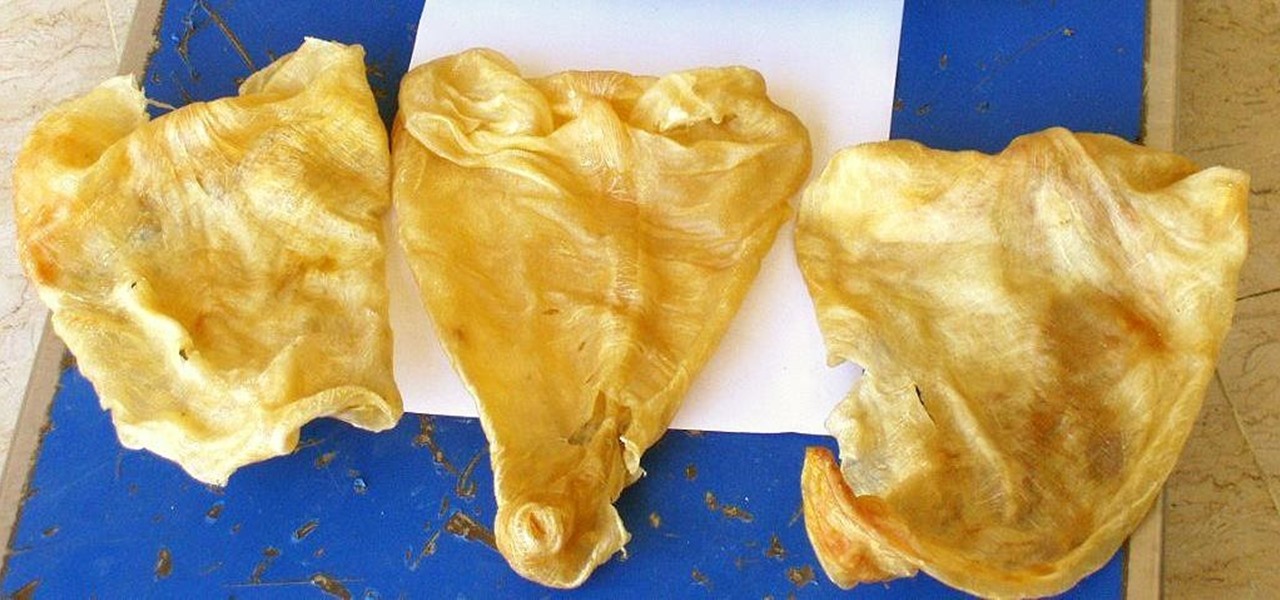
Fish is a remarkably useful ingredient, whether you eat it as is or use fish sauce to give your recipes extra depth and flavor. However, if you enjoy a glass of Guinness on occasion, you might be surprised to know that there's most likely fish in that beverage, too.

Hey dolls! I have to share the secret of Copper peptides with you all. I don't know why it's taken me so long to jump on this band wagon because the science and studies behind the product are amazing!

Cytochrome P450 (P450s) are proteins found in nearly all living organisms, which play roles that range from producing essential compounds and hormones to metabolizing drugs and toxins. We use some of the compounds synthesized by P450 in plants as medical treatments, but the slow growth and limited supply of these plants have put the drugs' availability in jeopardy and jacked up prices.

When Chan Mei Zhi Alcine chose her senior project, she thought outside the box by thinking inside the bottle. Along with a research team at her university, she found a way to combine health and enjoyment, while meeting a challenge not so definitively met before in alcoholic beverages. She and a research team at her university claim they've created the world's first probiotic sour beer.

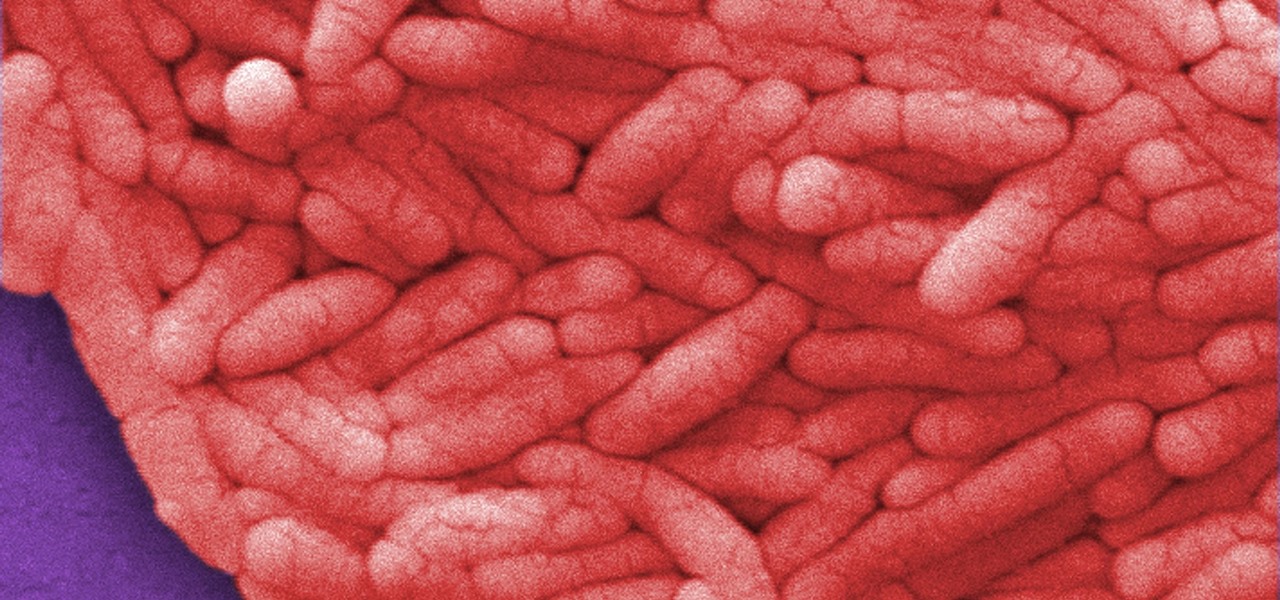
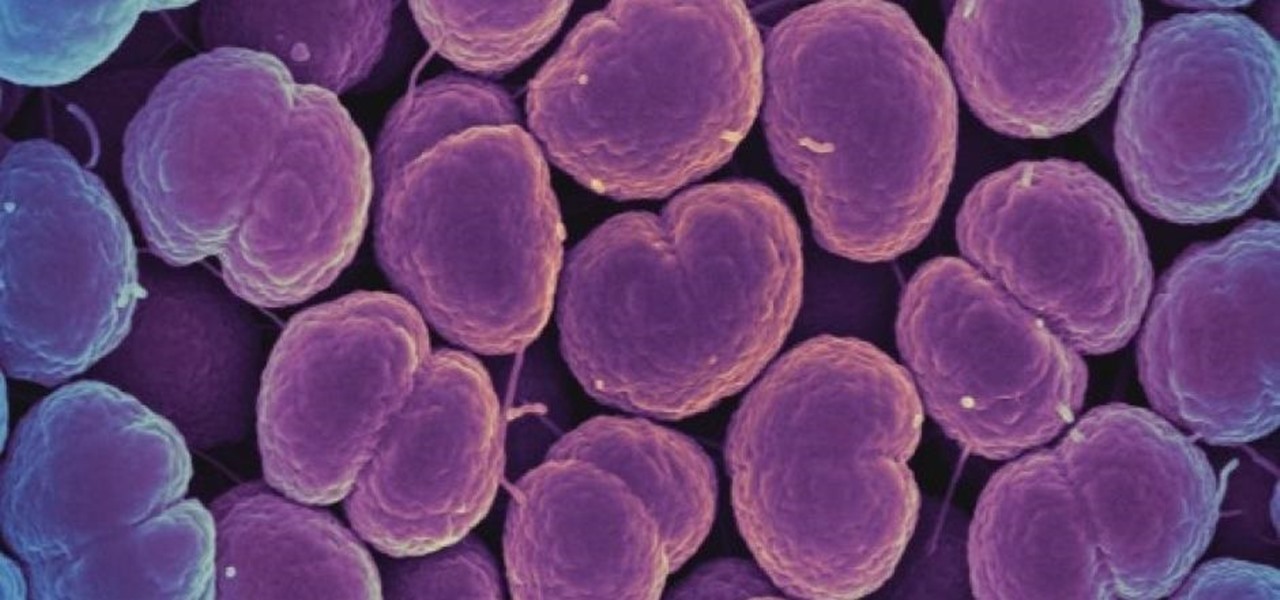
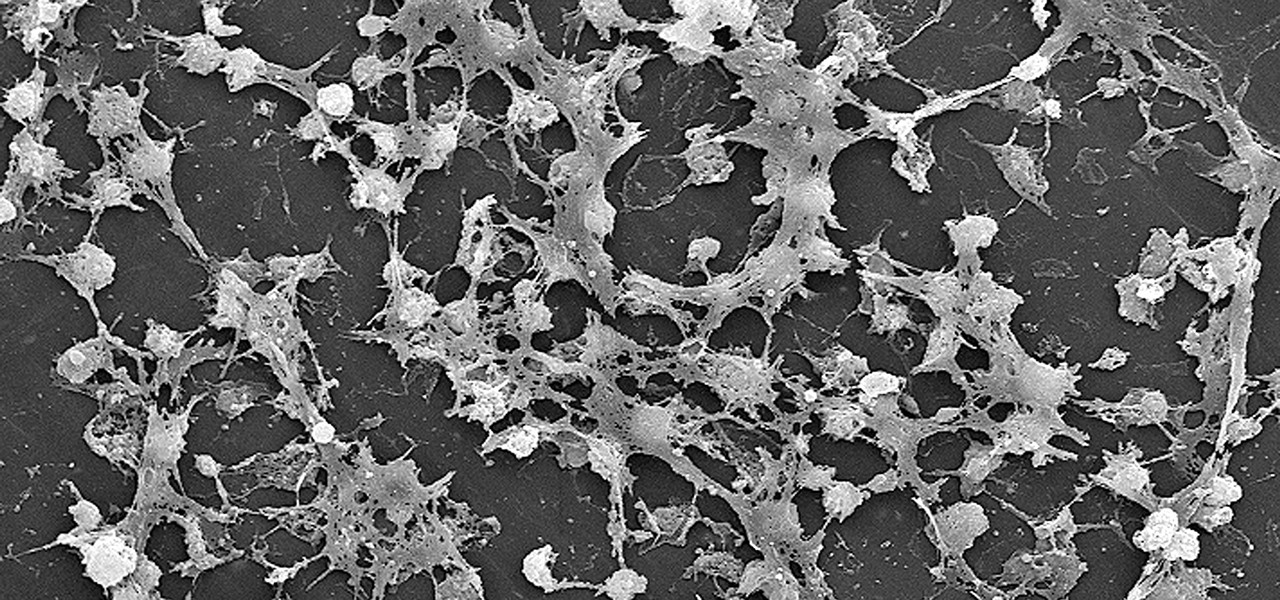
Some types of bacterial infections are notoriously tough to treat — and it's not all due to antibiotic resistance. The bacteria themselves are rugged and hard to penetrate with drugs.
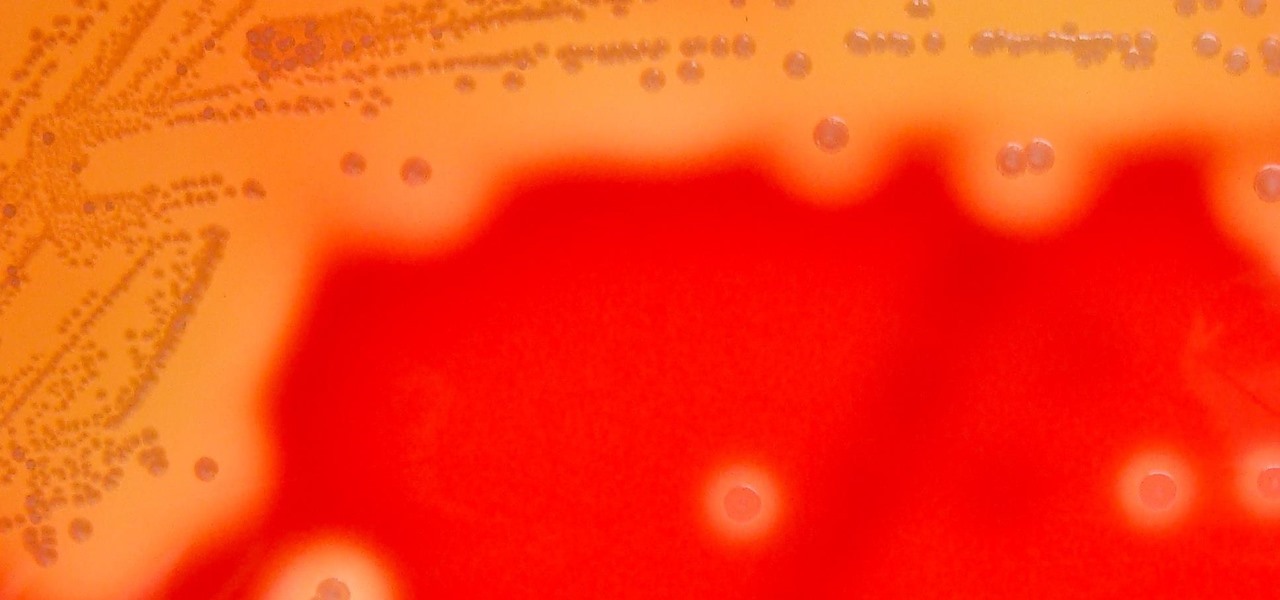
Streptococcus and staphylococcus bacteria produce toxins that can cause toxic shock syndrome.

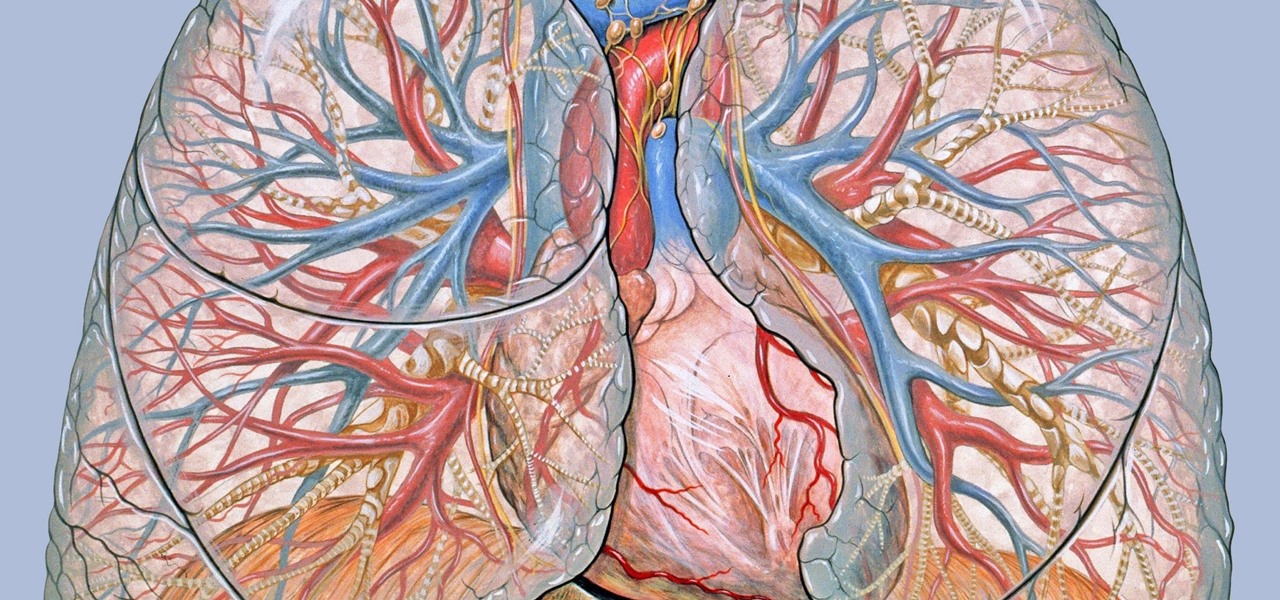
The body's usual response to a bacterial infection in the blood — called sepsis — takes time. It requires a carefully orchestrated sequence of events that gets the body's immune system ramped up to deal with the invading bacteria.

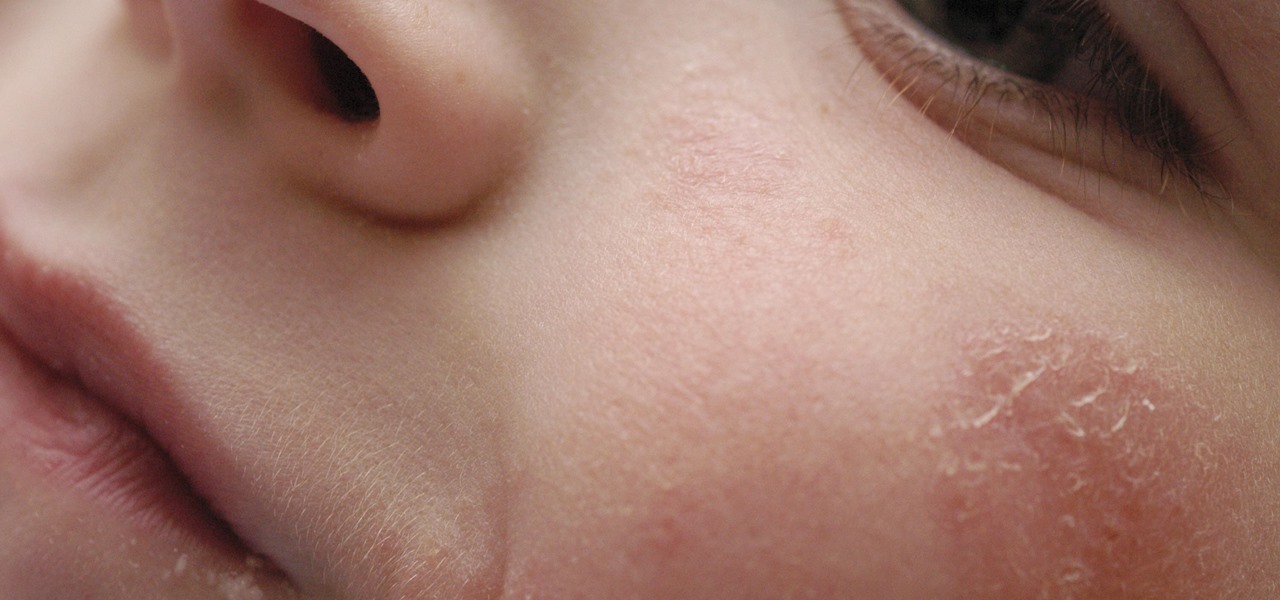
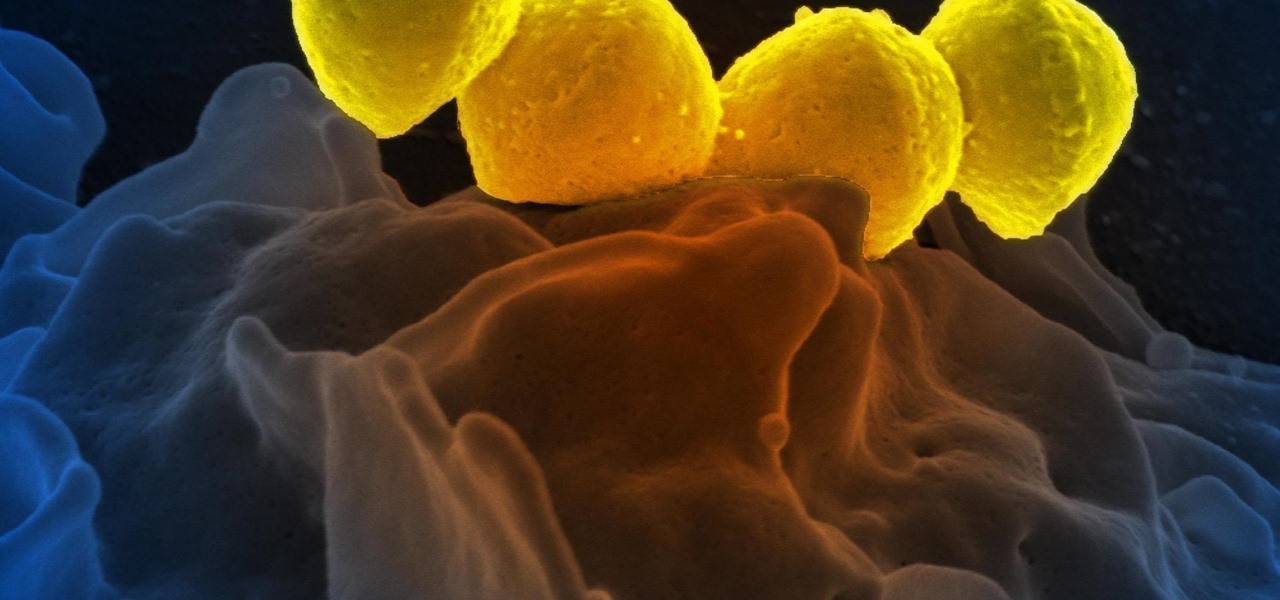
Most people know atopic dermatitis by its common name, eczema—that dry, flaky skin that itches incessantly. Along with the scratching comes frequent skin infections, often with Staphylococcus aureus.

Some studies have shown that vitamin D supplements help fight respiratory infections, but some haven't. A new study published in The BMJ clarified the confusion, and identified a group of people that might be better able to fight off colds and flu with vitamin D supplements.

Some bacteria can already do it—generate electric current, that is—and those microbes are called "electrogenic." Now, thanks to the work of a research group from the University of California, Santa Barbara, we know how to easily turn non-electrogenic bacteria into electricity producers.

We usually associate Salmonella bacteria with a dangerous type of food poisoning, but they actually are pretty good at seeking out tumors. That trait made the bacteria a great candidate to deliver a protein that would help knock tumors out.

Since the dawn of time—well, that maybe a slight exaggeration, but let's roll with it—sly entrepreneurs have been swindling the general public with inferior products for the sake of saving a few cents. Nothing is sacred when it comes to saving money: caviar, cheese, or even baby formula. Hell, there's even an entire book dedicated to the history of food swindling.

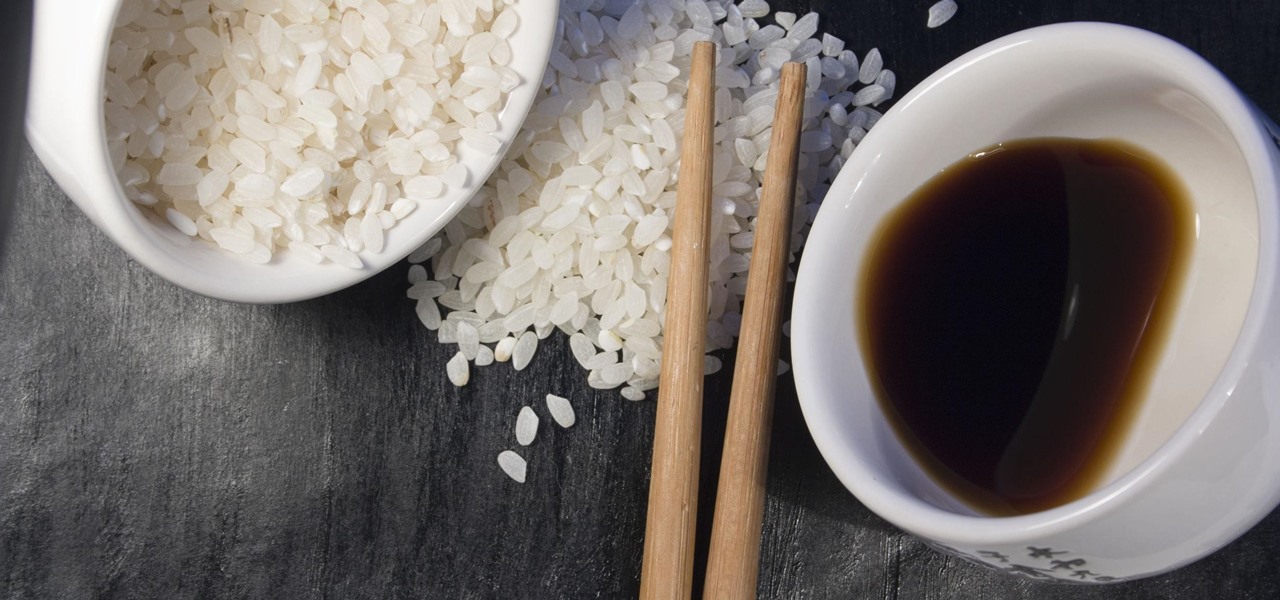
Koji is a culture made up of a certain fungus (mold) called Aspergillus oryzae, which has been used to ferment rice and soybeans in Japanese, Chinese, and Korean kitchens for centuries. Koji can actually have other involved fungi, but Aspergillus oryzae is the most common, and therefore the names can be used interchangeably. Its end purpose is to enhance the flavor of items like soy sauce, sake, and miso.

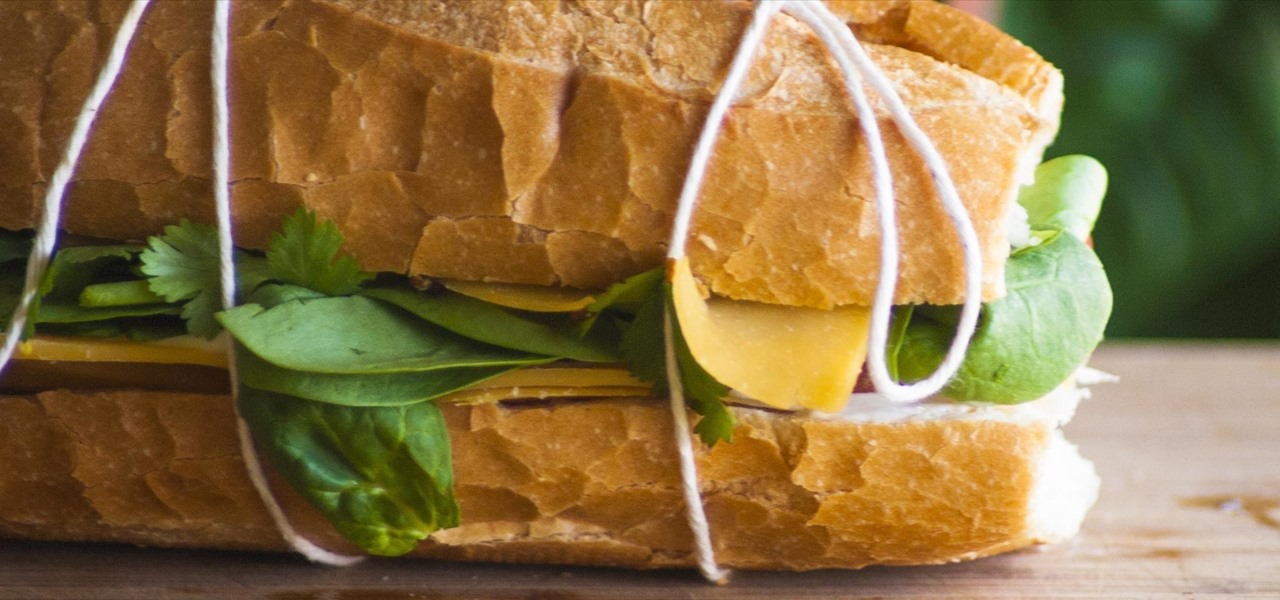
I'm a firm believer that a sandwich is the ultimate food. It's filling, but not heavy; it has carbs, protein, veggies, and sauces; and it's easily customizable. Add that all up and you've got the absolutely perfect lunch.

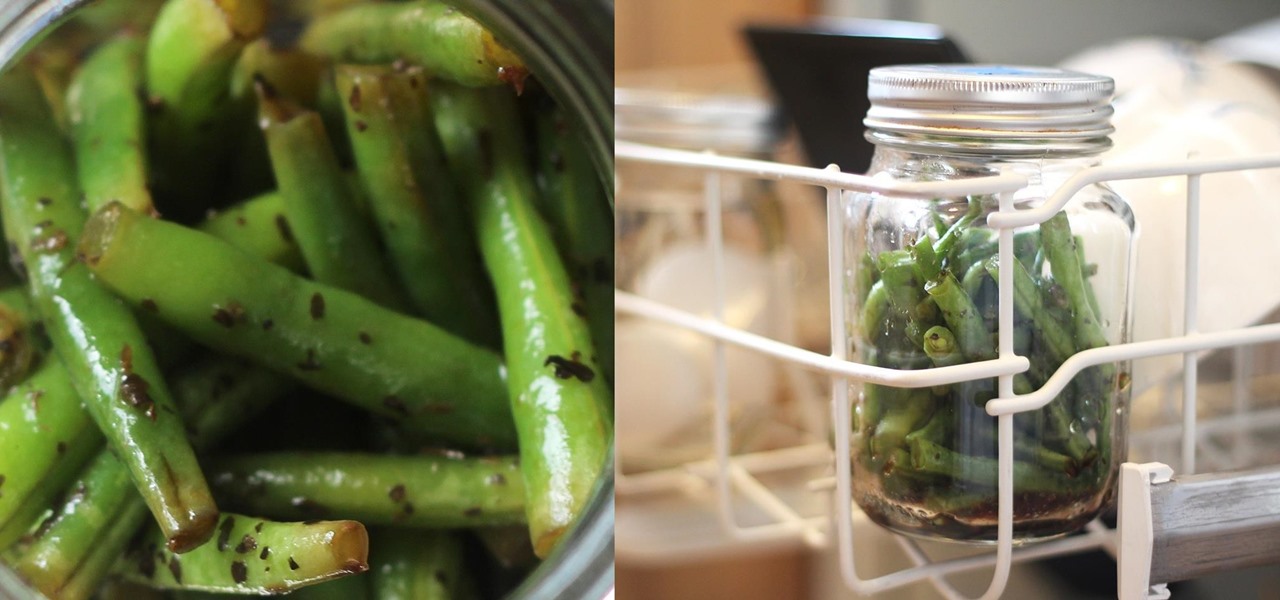
This sounds a little crazy, and it is—in a good way. Cooking food in the dishwasher while it cleans your dishes multitasks your appliance and saves time and energy. And who doesn't want to spend less time over a hot stove? How Dishwasher Cooking Works

Spills happen in the kitchen, and while every good cook knows to clean as you go, not every cook has an endless supply of cleaning materials. Besides, one spill can exhaust your entire stockpile of sponges, paper towels, and rags in a matter of minutes. Particularly egregious mishaps can make everything they touch feel sticky and gross.

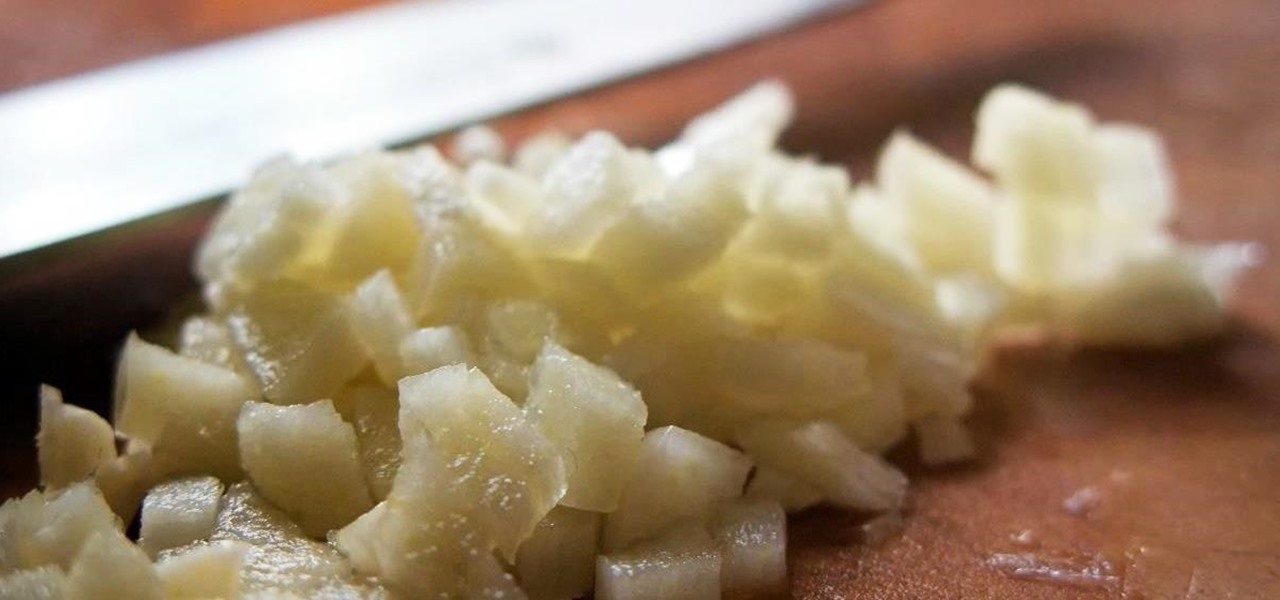
It's a shame that one of the world's tastiest foods can be such a pain to prep. Most cooks are familiar with this conundrum: chopping or crushing garlic releases a pungent liquid that causes bits of garlic to stick your knife and hands, creating a messy affair. So what is going on here? The common assumption is that the garlic is releasing some kind of oil, but the truth is that this liquid rinses away easily in water. Yet one of the basic precepts of chemistry is that oil and water don't mix.

How can a drug used to treat cancer be effective against viruses, too? The answer lies in the drug's shared target — specifically, cellular components that control the activity of genes. A new research study showed that one such type of drug, histone methyltransferase inhibitors used in cancer clinical trials, has activity against herpes simplex virus, too.

Colorectal cancer — cancer of the colon or rectum — is the third most commonly diagnosed cancer in the US. To reduce the chances of a diagnosis we are all urged to stop smoking, keep our weight down, decrease our intake of alcohol and red meat, keep active, and get screened for colon cancer. But, new research has found something that participates in the development of colorectal cancer that might not be as easy to control: A strep bacteria that promotes tumor growth.

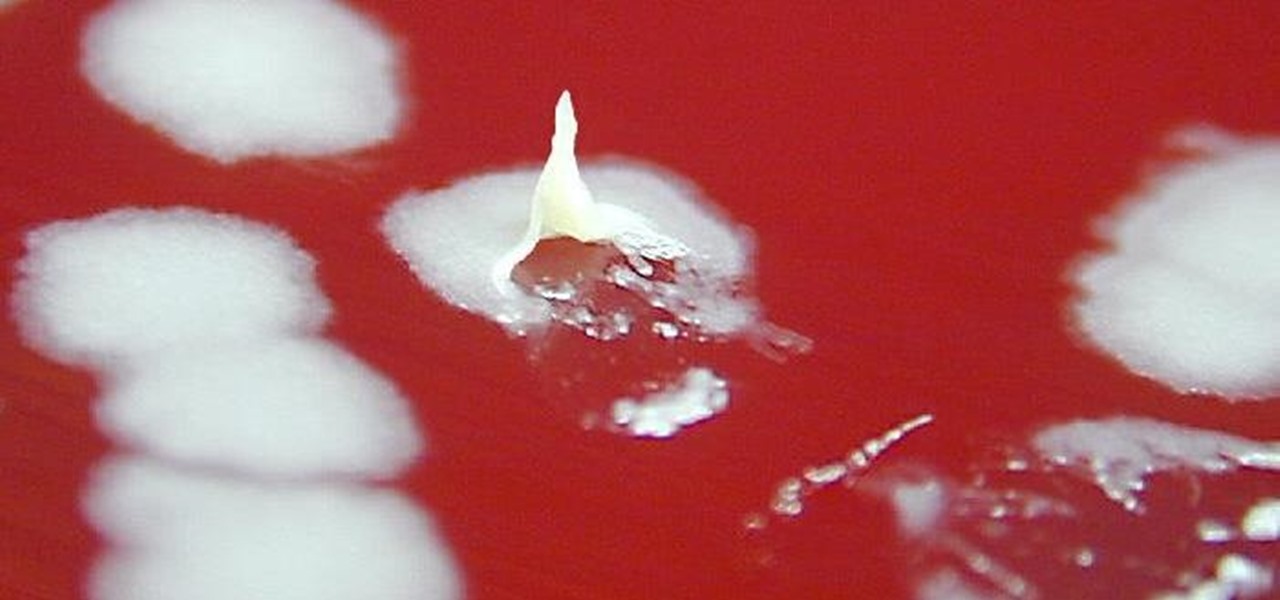
Significant strides have been in the race to find antibiotics to treat superbug infections — those caused by bacteria resistant to the antibiotics used to treat them. Now, an international team of scientists has discovered a new antibiotic produced by a microbe found in Italian soil.

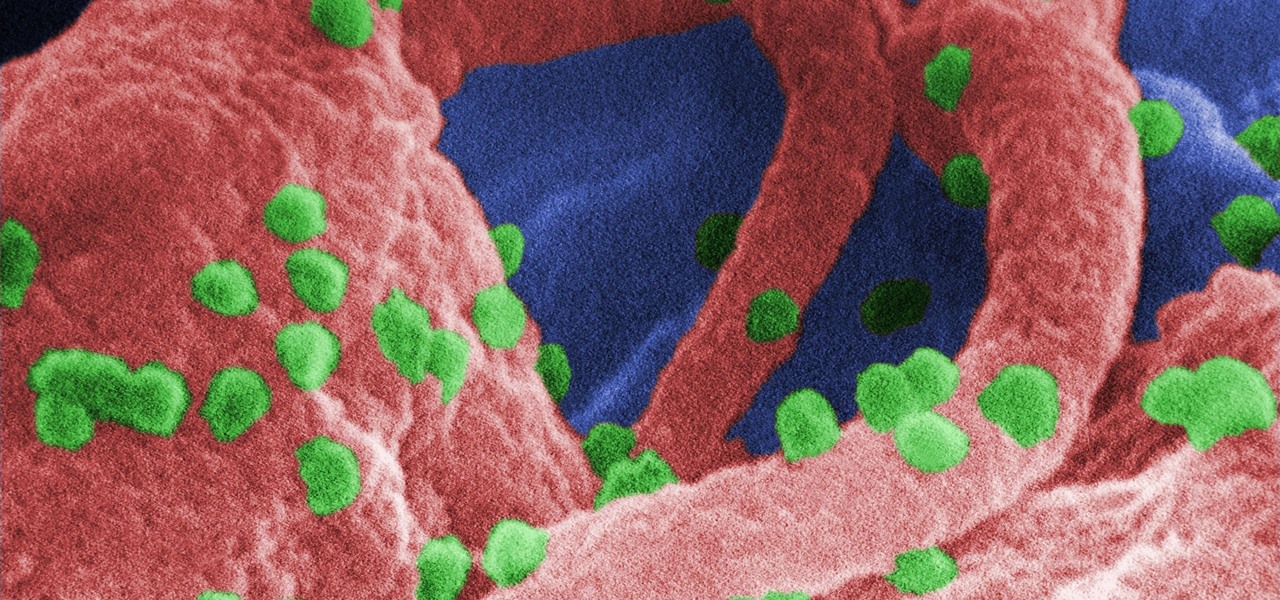
The problem with HIV is that it attacks and kills the very cells of the immune system that are supposed to protect us from infections — white blood cells. But a new technique, developed by scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) in La Jolla, California, offers a distinct HIV-killing advantage.

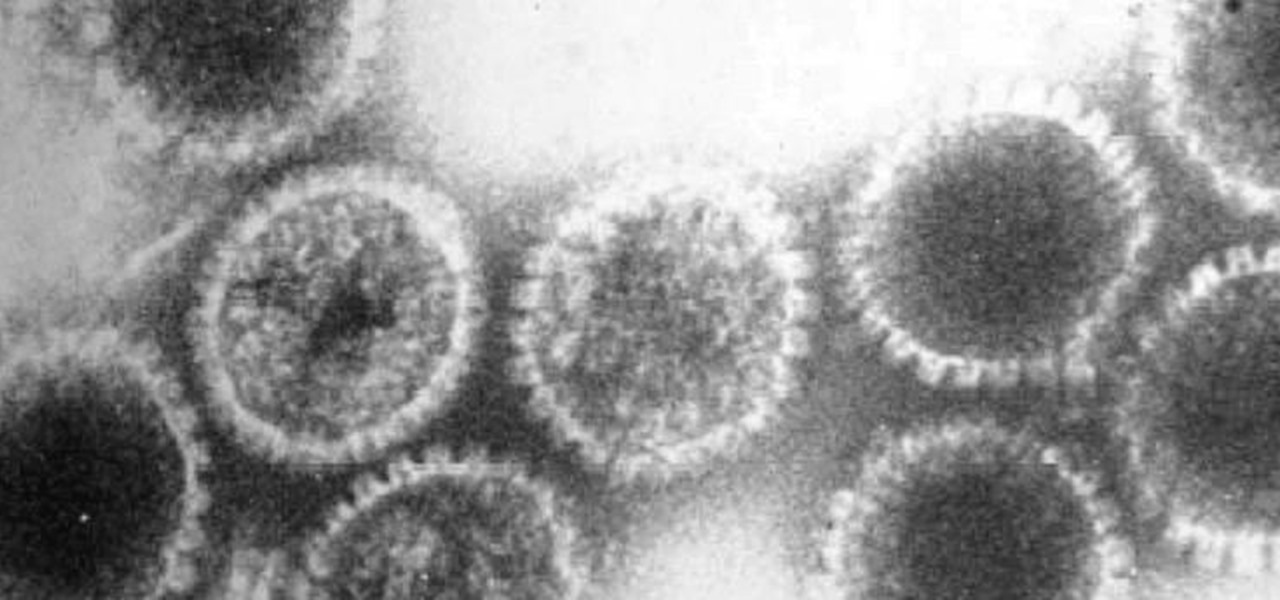
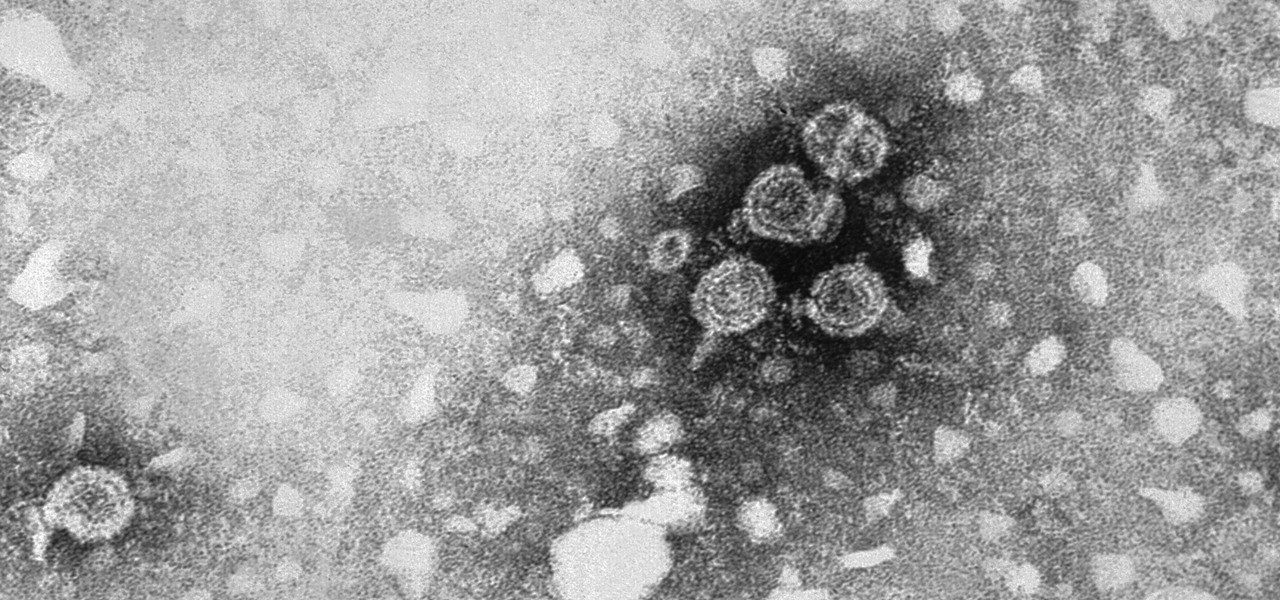
Could your fever, body aches, cough, and sore throat be the flu? Soon, finding out may not involve a trip to the doctor.

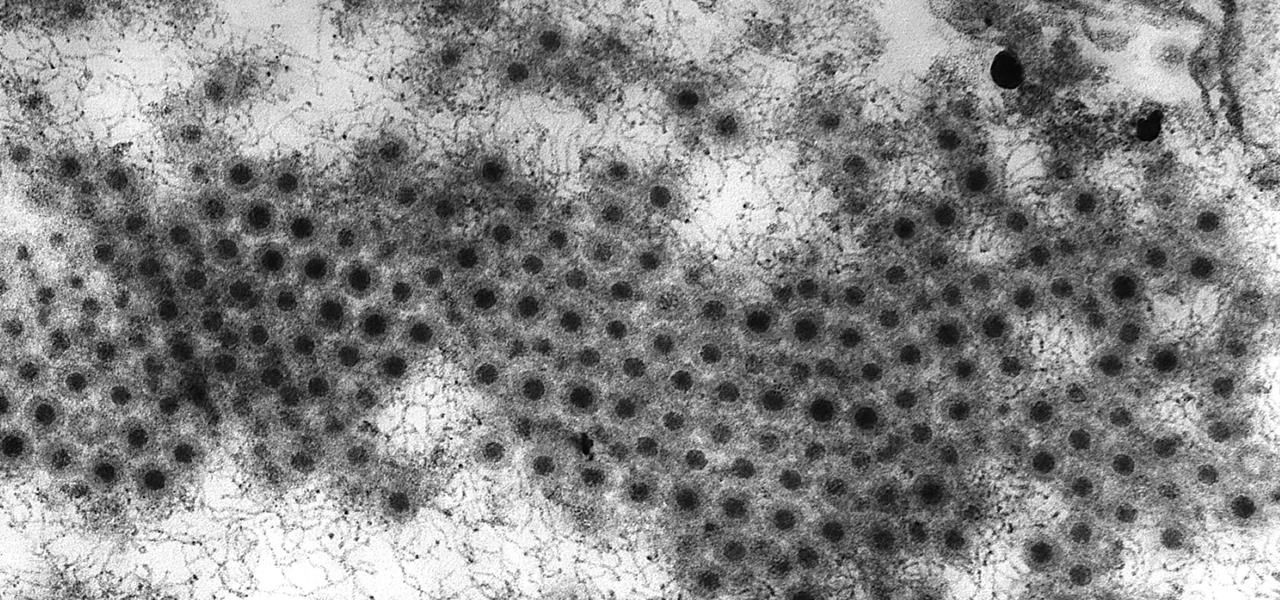
Even though the Ebola virus was discovered as recently as 1976, over 30,000 people have been infected since, and half have died a horrible death. Since there's no way to cure the infection, the world desperately needs a way to prevent it — and the five similar viruses in its family, the ebolaviruses.

The ability of one microbe to adapt is giving it a whole new career as a sexually transmitted disease. Usually content with the back of the throat and nose of those who carry it, the dangerous pathogen Neisseria meningitidis has adapted to cause an illness that looks a lot like gonorrhea.

Viral infections have been the focus of attention in the development of autoimmune diseases—diseases where the body's immune system reacts to the body's own cells—because they trigger the immune system into action.

An advance in the race to stop birth defects caused by Zika-infected mothers has been made by a team of researchers from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, New York. They have identified the process Zika uses to gain entry into the placenta, and published their findings in the journal Biochemistry.

Two viral liver diseases could help us find the path toward the cause of Parkinson's disease. Researchers from the University of Oxford and UCL Institute of Neurology in London have reported an association between hepatitis B and C infections and an increased risk of Parkinson's disease. Their findings were published early online in the journal Neurology.

An outbreak of anthrax from contaminated meat in Tanzania sickened dozens of people and moves the danger of this deadly bacteria back into focus.

Scientists are constantly on the search for new organisms, species, and other types of life. A special group of these researchers, calling themselves "bioprospectors," dive deep into mines to find unique lifeforms with special properties not found anywhere else.

Lighthouses and signal fires may have been the first social media. Without the ability to share language, a distant light meant "humans here." A new study from the University of California, San Diego, finds that bacteria can also send out a universal sign to attract the attention of their own, and other bacterial species.

If you could save the world by eating a burger, would you? Two companies, Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods, are on a mission to redefine veggie burgers and eliminate all of the downsides of animal farming on our planet. With over five years of research and product testing, they've finally figured out how to make a plant-based burger look, feel, and taste just like real meat.

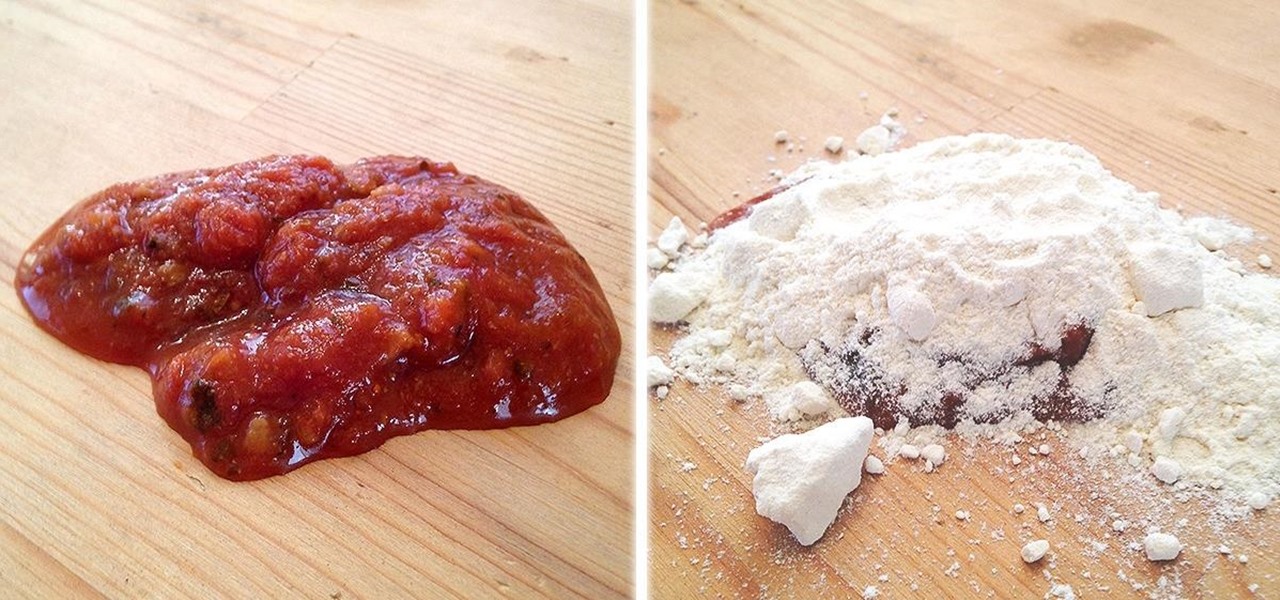
For those of you that prefer a soft-baked cookie that is fluffy in the middle, using cake flour instead of regular all-purpose (AP) flour is your secret baking weapon. "But I don't have cake flour," you protest. Fear not: if your kitchen is sans cake flour, you can easily whip some up by mixing together AP flour and a little bit of cornstarch for the same results.

It should come as no surprise that, according to Details Magazine, nearly half of all people who make New Year's resolutions pledge to lose weight, eat healthier, and/or get fit. There are innumerable companies out there that are ready and willing to take advantage of this momentum: from those hocking "magic bullet" pills that will increase your energy or reduce your belly fat to the myriad shake- and juice-based diets that put you at a near-starvation calorie input—and will probably have you...

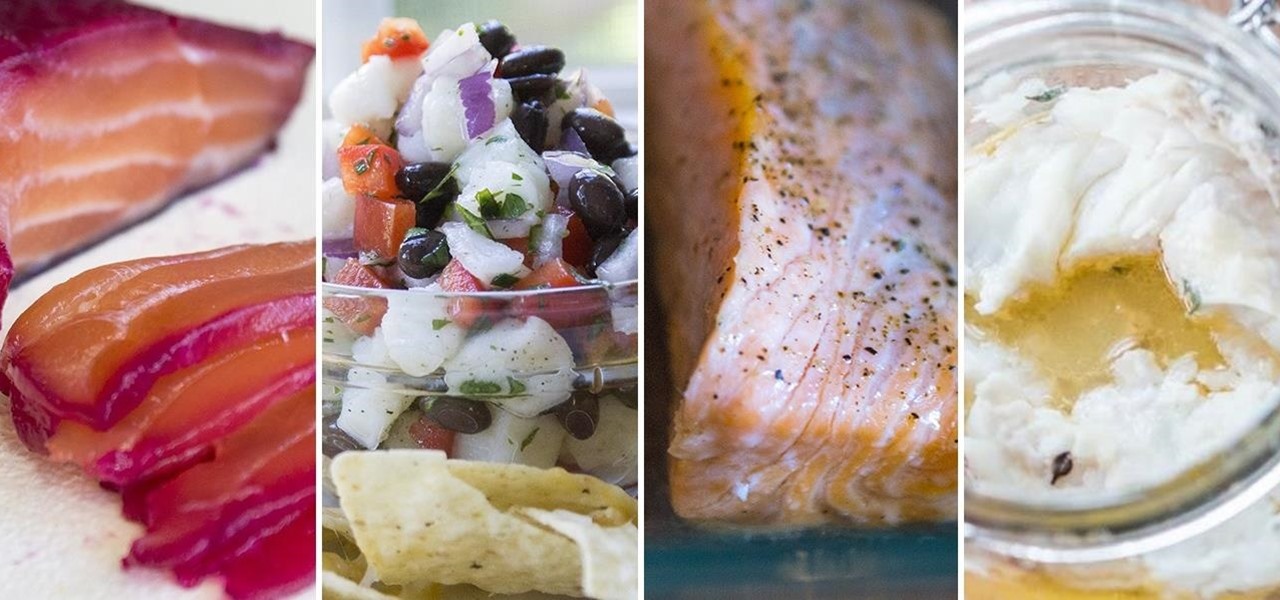
Preparing and serving seafood can be a daunting task. Fish is so delicate that one extra minute of heat can turn a juicy, flaky filet into a dried-out disaster. But that same fragility also allows us to use unconventional methods to chemically transform the fish into its cooked consistency.

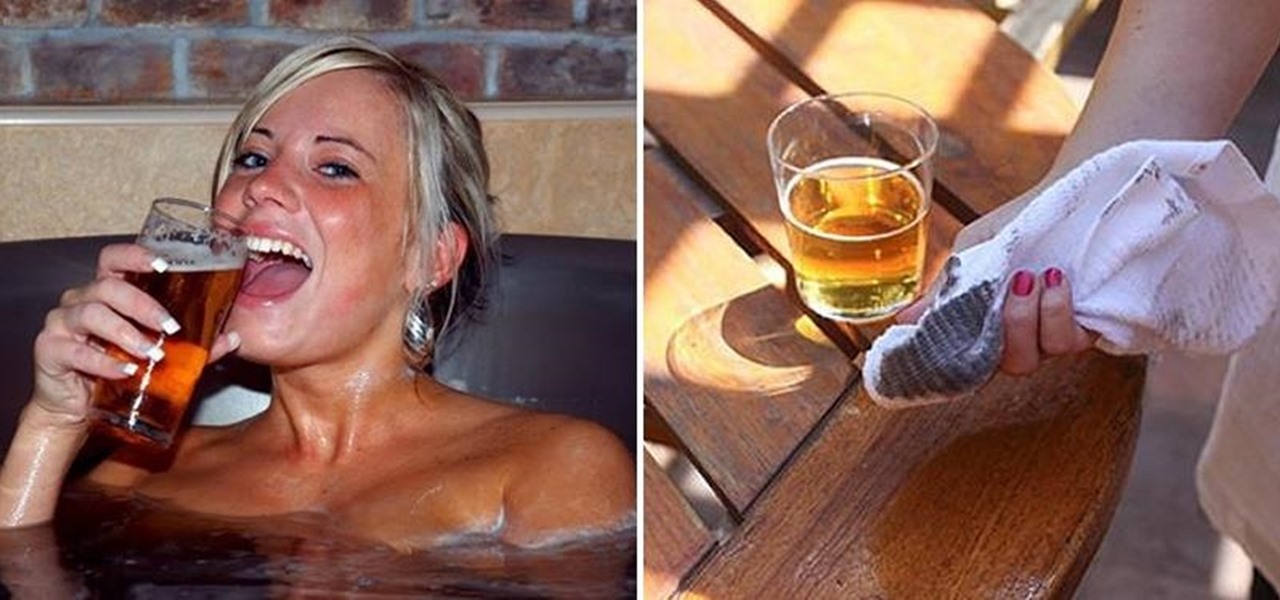
Beer isn't just for drinking anymore. There are many useful and surprising things that an ice-cold brewski can help you accomplish, from household chores to better-tasting food. It can even help you look and feel healthier.

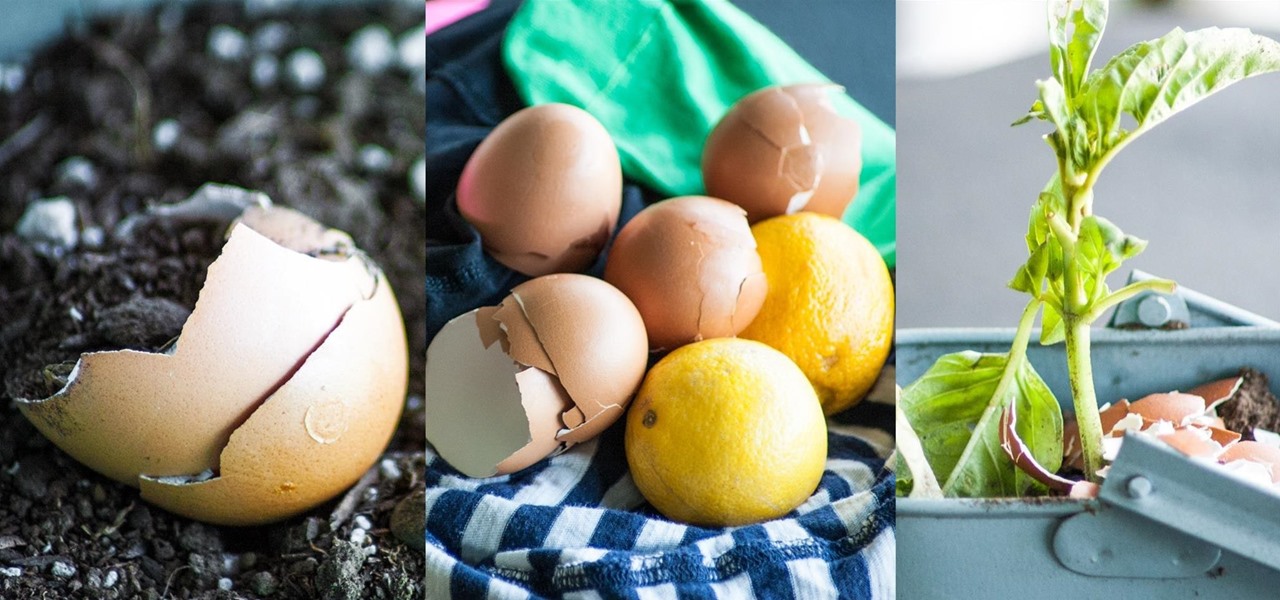
The other day I was doing the math on roughly how many eggs I eat each year. I estimated about 500. That's a lot of eggs. And, subsequently, that's a lot of eggshells to throw in the trash.

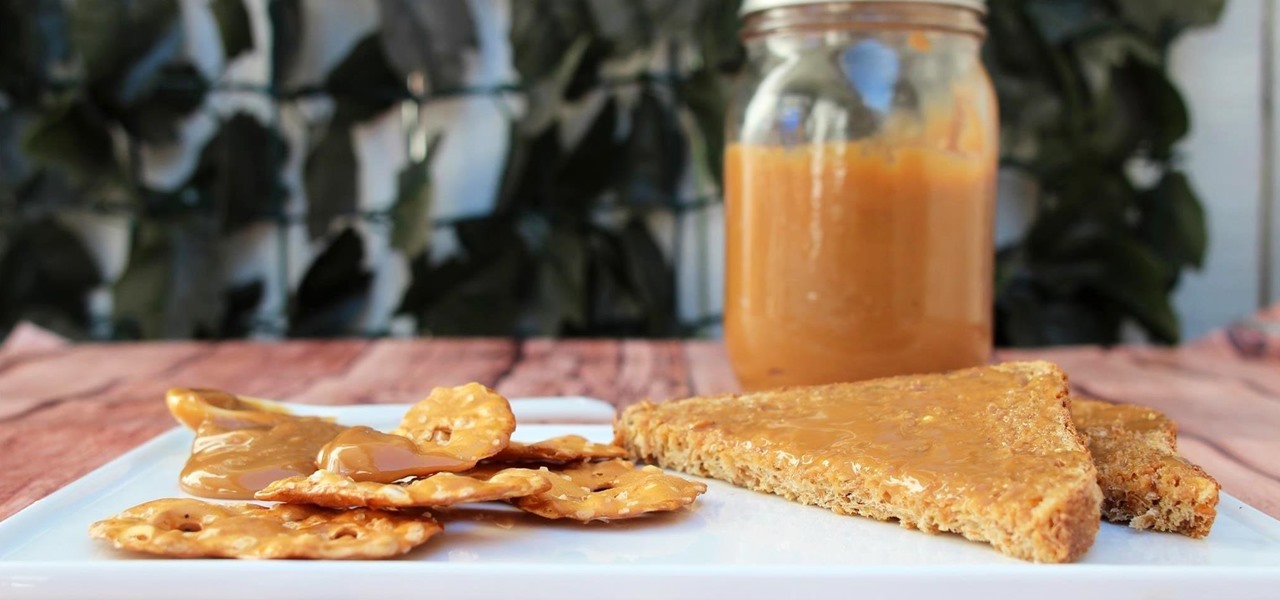
Dulce de leche is a beautiful, caramel-like spread that you can slather onto bread or use to flavor cakes, cookies, or flan. You can also use it as a drizzle for ice cream, chocolate candies, and pastries. It tastes like heavenly toffee, translates roughly to "milk candy," and is popular all over Latin and South America. A version of the confection is also popular in the Philippines, in Russia, and is known in France as "confiture de lait." The traditional way to make dulce de leche is to slo...

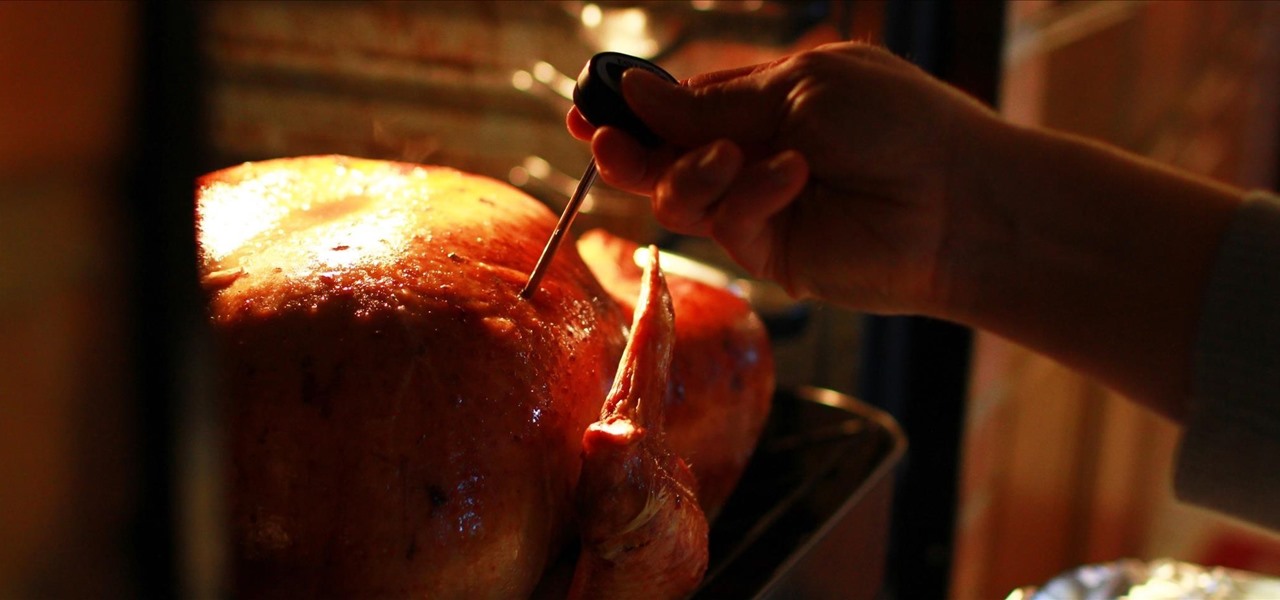
When I was 12, for some mysterious reason, my dad put my little brothers and me in charge of cooking the Thanksgiving turkey. Naturally, my brothers and I spent the rest of the day playing hide-in-seek in the backyard and forgot all about the humble bird defrosting in the sink.

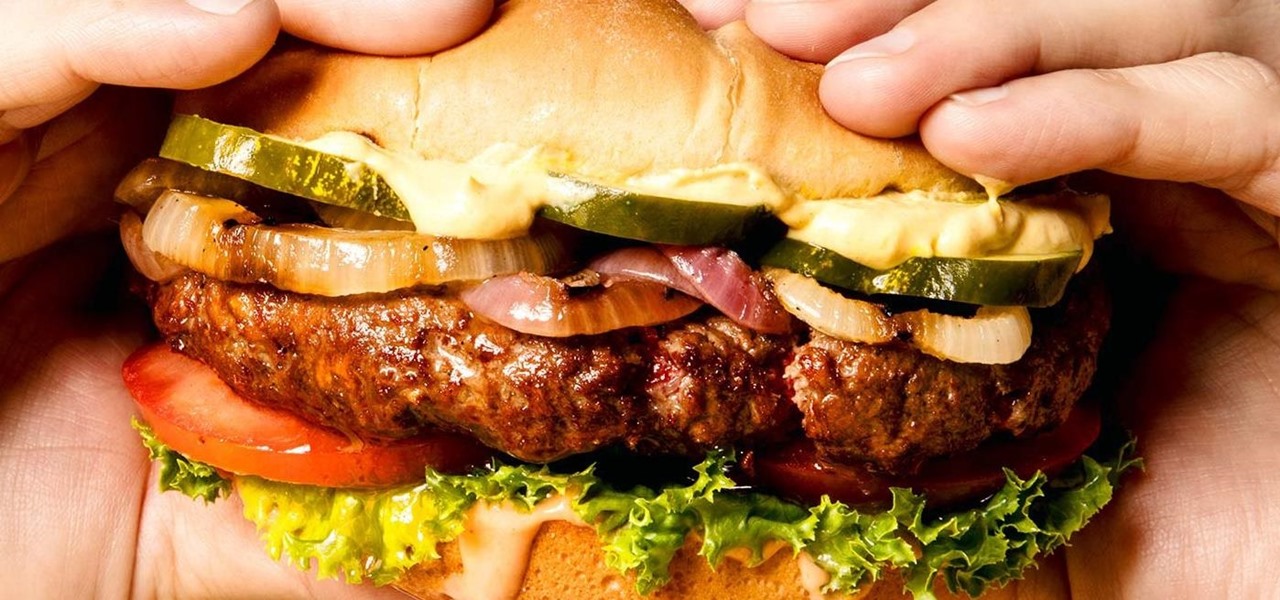
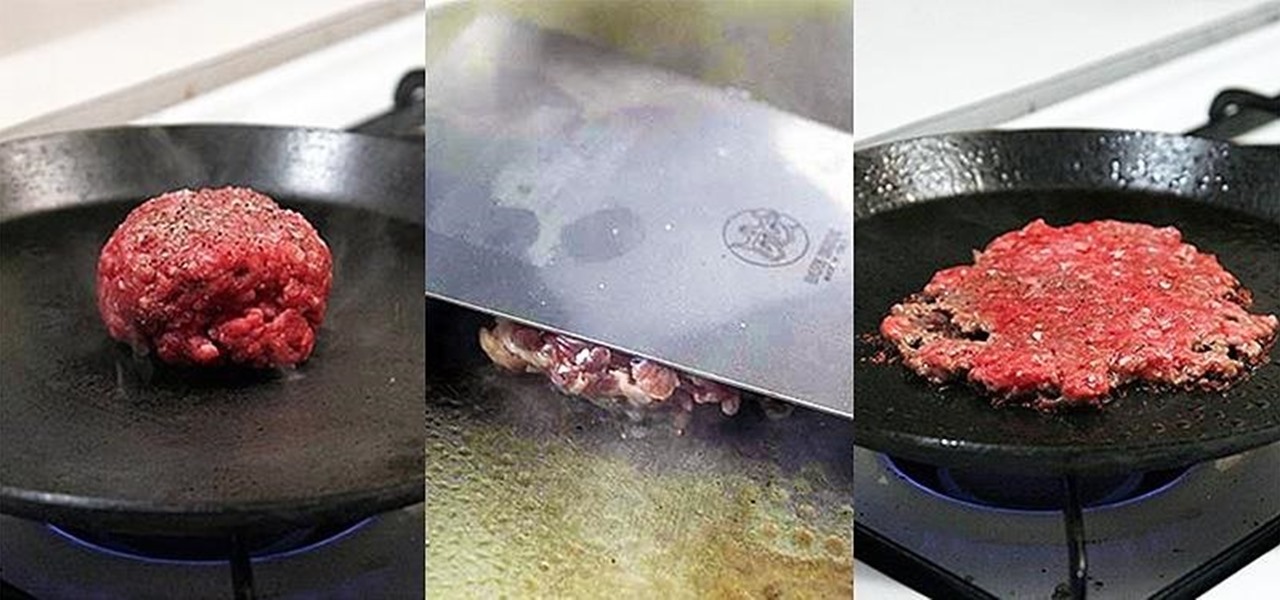
Many home cooks were taught never to press down on a burger as it cooks since that would ruin your all-beef patty by getting it to release the juices it needs to stay tender and moist.

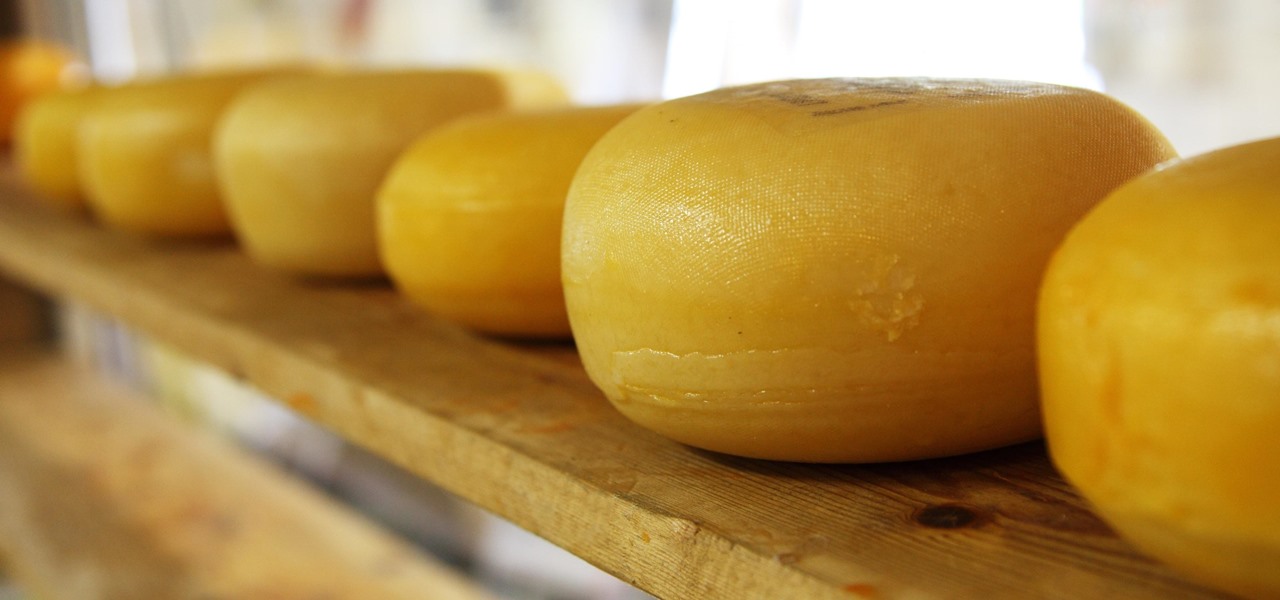
Whether your palate runs to domestic or imported, a piece of cheese can be a real treat for the senses. Its smell, taste, and texture are all parts of its appeal. A big part of what makes that savory wonderfulness comes from the microbes in and on the cheese. Thanks to a team of researchers dedicated to studying those microbes, we have a better understanding of their importance to cheese and us.