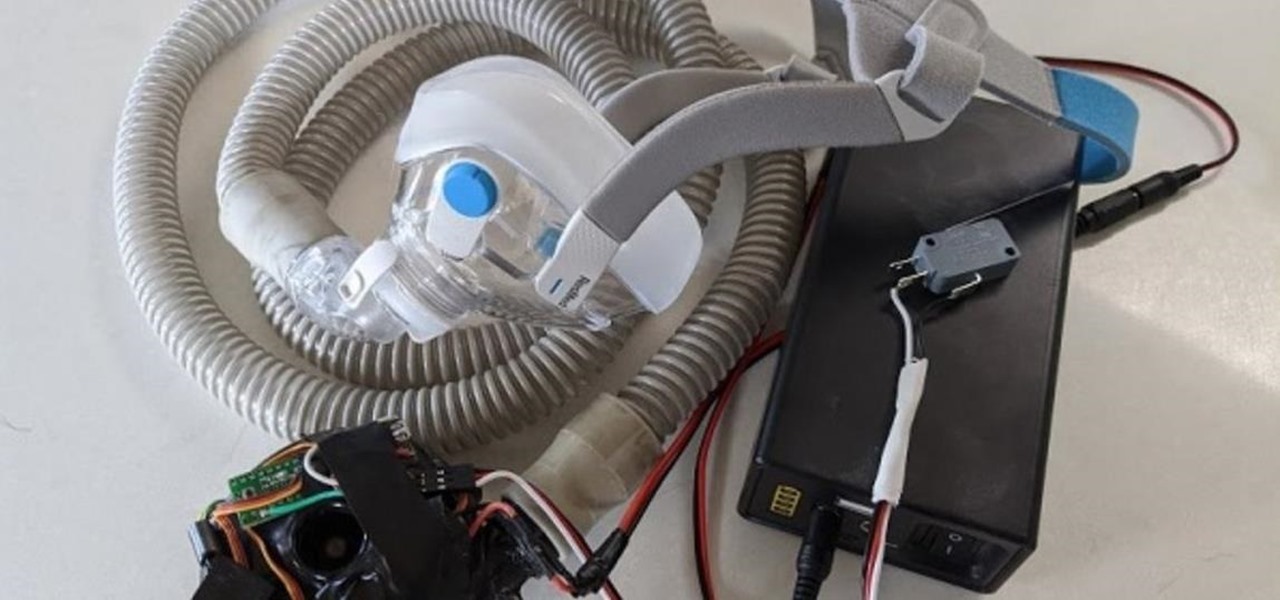
With the nation facing a shortage of ventilators for COVID-19 patients and no apparent ramp-up in the production of new ones, engineers, medical resistents, and do-it-yourselfers are sharing plans for homemade versions.
The Massachusetts Department of Public Health (DPH) issued a health alert for a Boston mumps outbreak, on Monday, June 5th, to healthcare providers and local boards of health. There have been 12 reported cases of mumps during the recent outbreak. The affected residents' symptoms occurred between March 24th and May 31st, and 10 of the 12 had symptoms after May 9th. There have been 35 confirmed cases of mumps in 2017 in Massachusetts, and "nearly 300" suspected cases in the continuing outbreak.
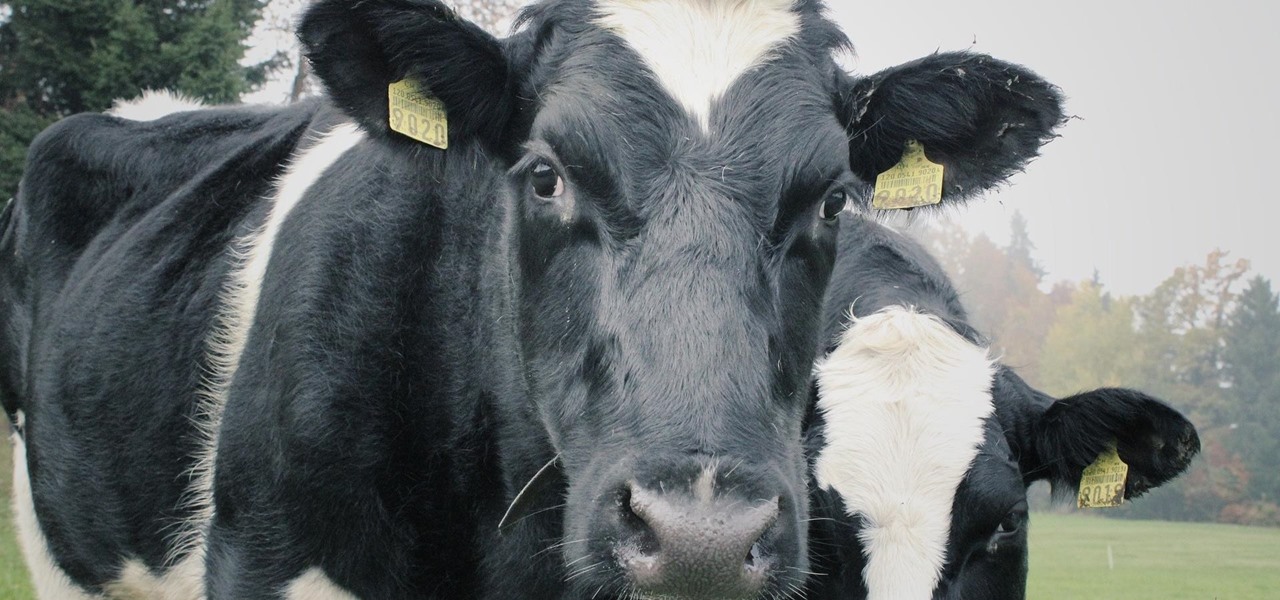

Antibiotics used to prevent diseases in livestock are creating a world of hurt for humans and the soil we depend on for food. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a global health issue. The overuse, underuse, and poor use of these life-saving drugs is rapidly removing them as a treatment option for serious infections in humans—plus bacteria are naturally adaptive.
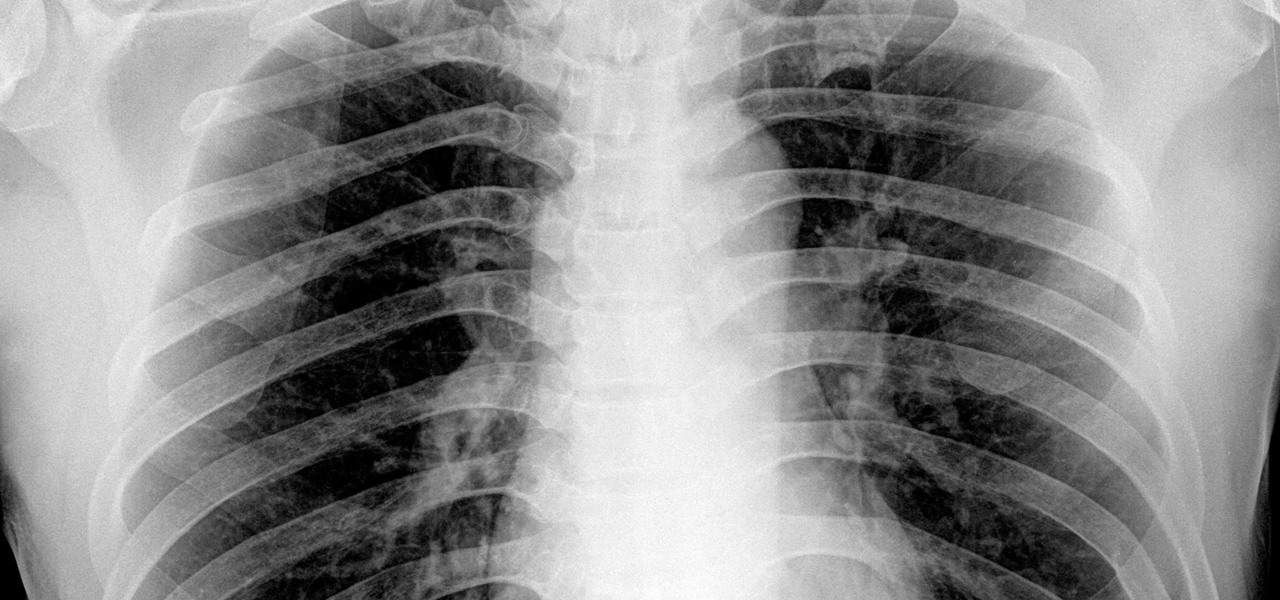
By looking for the mechanism that allows influenza A to invade lung cells, scientists also discovered a treatment that might block the virus from taking hold there.
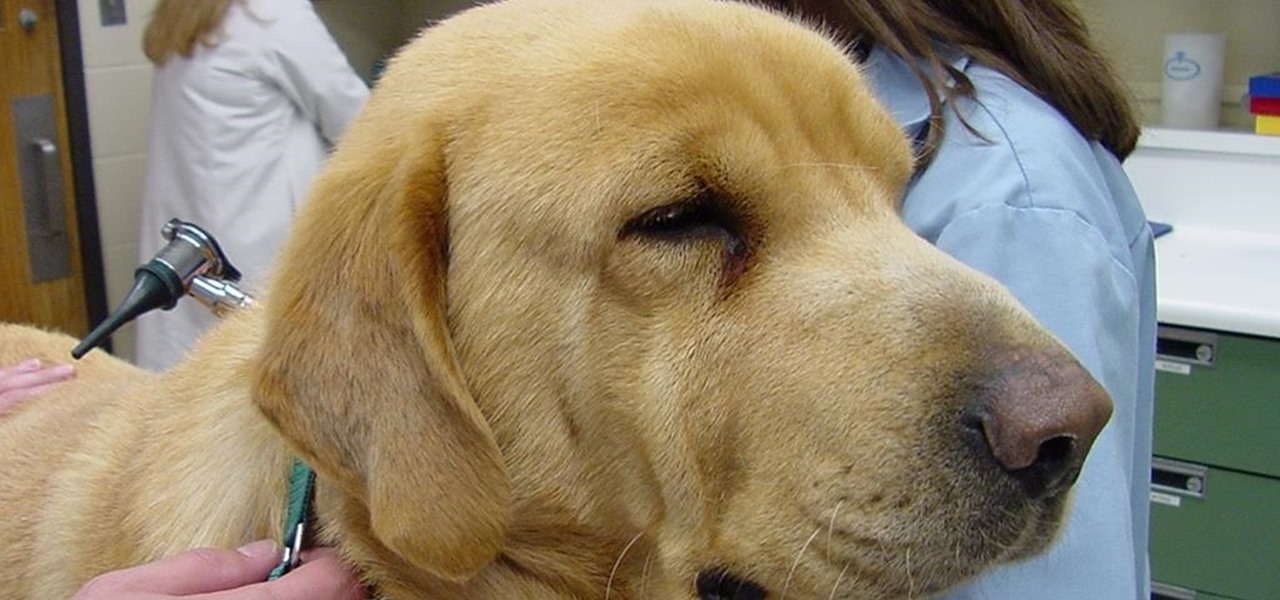

You know the signs—sneezing, fever, nagging cough, no energy, no appetite. It's the flu, but this time, it's your dog who's down and out. Yes, dogs get the flu, too. However, a team from the University of Rochester Medical Center and their collaborators have developed a new vaccine that may make the doggy flu a thing of the past.

All fields of study have their own language. For people interested in learning about microbes, the language can sometimes be downright difficult — but it doesn't need to be. From antibiotics to xerophiles, we have you covered in an easy-to-understand glossary.

On June 11, 2016, an Arizona woman died from what appeared to be several infections, including pneumonia. She likely caught at least one of these from her dog.

Tell the truth. The bat picture creeps you out. You are not alone. But in reality, bats truly are some of our best friends. They gobble thousands of disease-spreading bugs a night. But they also carry viruses that can be deadly to humans. So, bats — friend or foe?

Jostled in the airport, someone is coughing in line. The air looks empty but it is loaded with microbes that make their way into your body. You get sick. You give it to your family, and that's pretty much it. But what if you were so contagious that you spread it to your entire community and beyond?

A bacterium which triggers respiratory disease has been detected in the water systems of two Pennsylvania nursing facilities.

In their first head-to-head major contract clash, Microsoft has emerged victorious over Magic Leap, as the US Army has awarded a $480 million contract to the HoloLens maker.

The worldwide health crisis around the coronavirus has gripped the live events industry, particularly in the tech sector, with the cancellations of Mobile World Congress, the Game Developers Conference, Facebook's F8, Google I/O and now South by Southwest.

For once there is good news — surprising news, but good news — in the fight against antibiotic-resistant organisms. A recent study found that Staphylococcus aureus bacteria is becoming more sensitive to some key drugs used to treat it.

A recent case of Powassan virus has been reported in Saratoga County and may have been the cause of the infected patient's death. It's the 24th case in New York State since 2000, and will be reported to the CDC tomorrow, the NY Department of Health told Invisiverse. The tick-borne illness has no vaccine or specific treatments and can damage the nervous system.

Despite what you may have heard, sleep is NOT for the weak. It's essential, not to mention it makes us feel a hell of a lot better in general. But for some, getting to sleep is easier said than done. In fact, about 50 million to 70 million people in the US have a sleep or wakefulness disorder, according to the CDC.

A state of emergency has been declared in Malaysia's northeastern Kelantan state after an outbreak of avian influenza virus H5N1.

Editor's Note: The claims by Vani Hari which were originally detailed in the article below about azodicarbonamide were unscientific in nature. This article has been updated to reflect that and provide more scientific context on the issue.

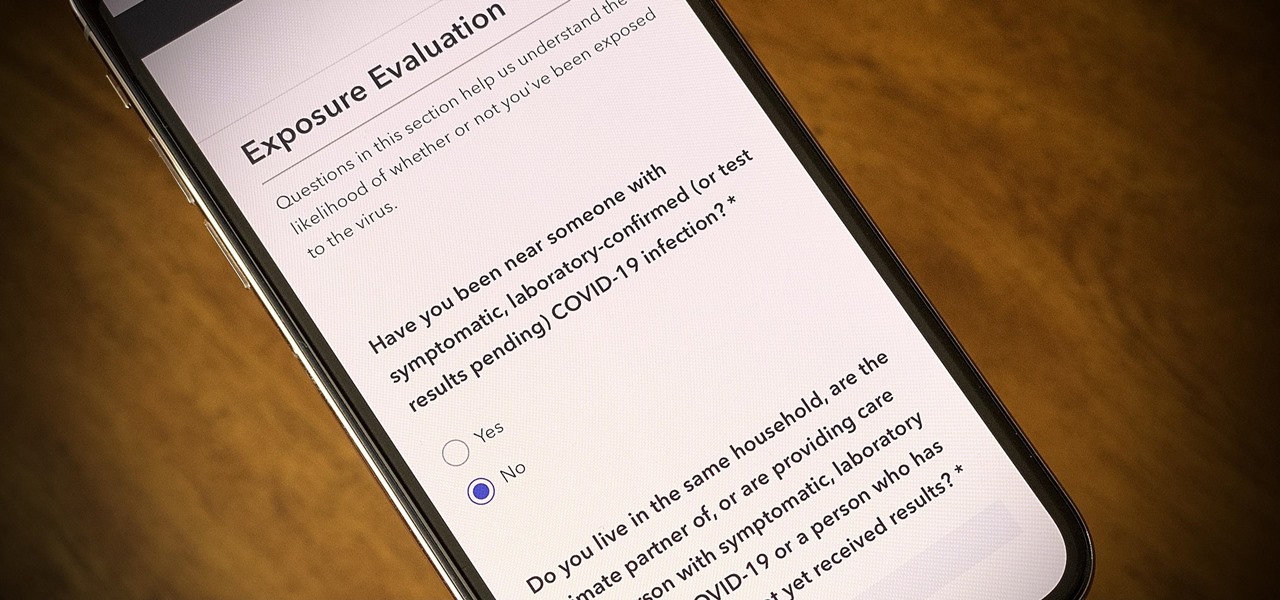
One of the scariest things about the COVID-19 virus is that you can show no symptoms but still be infected (and contagious). Naturally, we all want to know whether we're carrying the new coronavirus, but if you're showing signs of COVID-19, how can you be tested to know for sure? Websites are popping up to help with that, screening for symptoms, and directing you to a testing site if needed.

Despite longer live spans, almost half a million people die of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) each year, many of them preventable.

Add breathing in your house as another possible danger to your health. If your home is sick, it's possible you could get sick too.

Maine reported their first measles case in 20 years yesterday, June 27, in a press release from the Maine CDC. Many other people may have been exposed and could show signs of infection soon, with the potential for outbreak brewing. The last measles case in Maine was in 1997.

It's not always easy to get to the root of an infection outbreak. Epidemiologists study infected people, contacts, and carefully examine where the infections happened and when. In the case of a 2012 outbreak of pertussis — whooping cough — in Oregon, scientists just published an analysis of how vaccination status affected when a child became infected during the outbreak.

Despite the threat of superbugs, physicians continue to prescribe antibiotics when they might not be needed, and patients are suffering.

With summer just ahead, you, or your children, may be looking forward to some pool time or the water park. When planning water-based fun this year, keep a heads-up for microbes.

In the worst measles outbreak in the state since 1990, the Minneapolis Department of Heath races to contain the spread of an infection believed to have originated from an infected traveler. Mistaken attitudes and unvaccinated travelers are creating a world of hurt and disease for Americans. A recent study found that more than half of eligible travelers from the US are electing to skip their pre-trip measles vaccine.

As if being pregnant did not come with enough worry, a new study found that certain antibiotics are linked to an increased risk of spontaneous abortion, or miscarriage — a terrifying finding for any expectant mother.

Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a highly contagious disease that can be life-threatening for young children. New research backs a recommendation that all pregnant women receive a pertussis booster with each pregnancy, as it can help their infants fight off the infection.

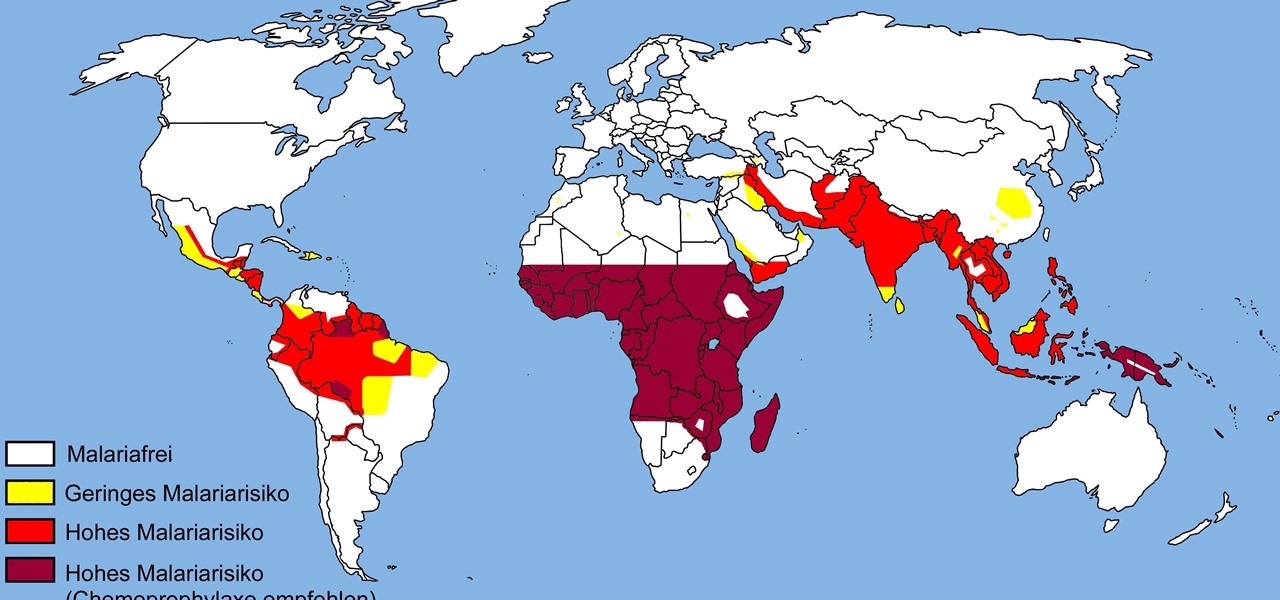
The theme for 2017's World Malaria Day, which is today, April 25, is "End Malaria for Good." For many Americans, this might seem like an odd plea. Especially since Malaria is seemingly an obsolete problem here. However, on World Malaria Day, it's important to remember the danger of malaria is still very much present in the US. And around the world, the disease is at the epicenter of a global crisis.

An outbreak of anthrax from contaminated meat in Tanzania sickened dozens of people and moves the danger of this deadly bacteria back into focus.

Have you ever had the stomach flu, aka the 24-hour flu? Well, chances are high that you never had influenza, but an intestinal infection called gastroenteritis.

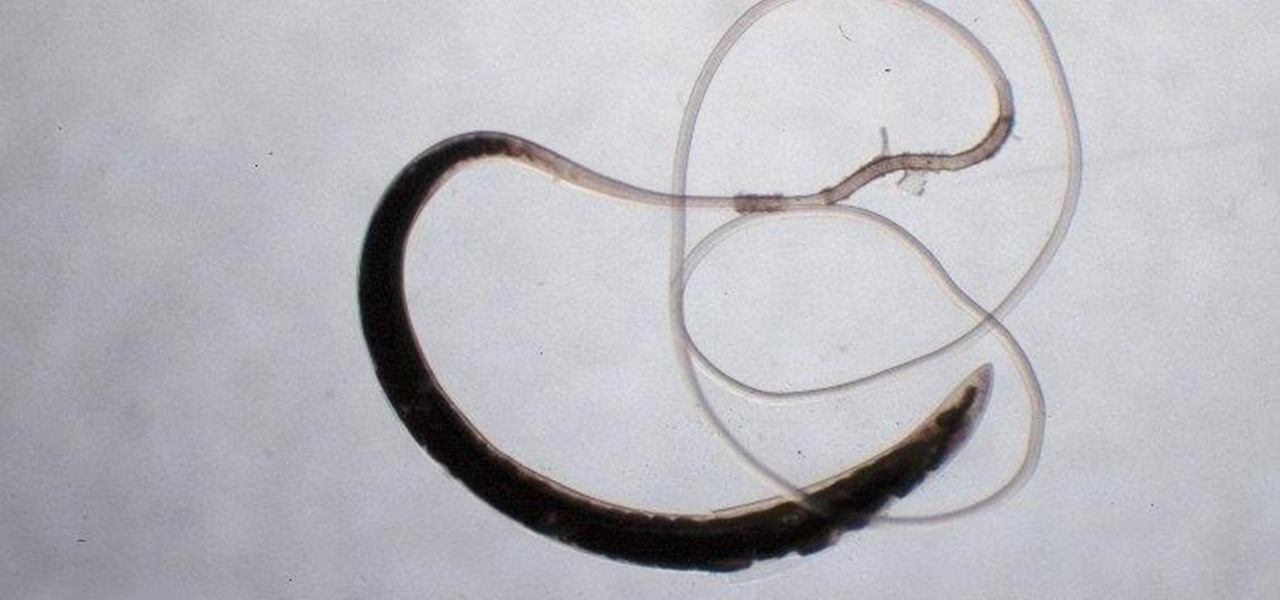
Somewhere around 600–800 million people in the world are infected with whipworm (Trichuris trichiura), an infection they got from ingesting soil or water contaminated with feces of infected animals or people containing the parasite's eggs.

A rose by any other name may smell as sweet, but one annoying invasive weed may hold the answer to treating the superbug MRSA. Researchers from Emory University have found that the red berries of the Brazilian peppertree contain a compound that turns off a gene vital to the drug-resistance process.

A new study just out reveals that HIV takes hold in the human body with the help of cells that usually work to heal, not kill.

Avian flu is making the news again with new human cases in China reported in January. What does "avian flu" mean to you—and how dangerous is it?

As fun as it is to see Fido's face light up when you feed him table scraps, American dogs are getting fat. The good news is that research is homing in on nutritional strategies to boost canine capabilities to maintain a healthy weight.

In the summer of 1976, 4,000 American Legionnaires descended upon the Bellevue-Stratford Hotel in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, for a four-day convention. Several days later, many of the attendees experienced symptoms of severe pneumonia. By the beginning of August, 22 people had died. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimate that about 180 people were sickened and 29 people died before this mysterious outbreak burnt out.

Despite the availability of a vaccine against it, almost 50% of men aged 18-59 in the US are infected with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Why?

Specialized cells in the lining of the gut may provide a key to preventing an infectious brain disease caused by misfolded proteins.

New weapons are needed to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Instead of drugs, scientists have discovered in an animal study that they may be able to harness vampire bacteria to vanquish pneumonia.

With the height of the flu season ahead, there are some good reasons to keep a flu vaccination in mind.