
News: Fighting Nightmare Bacteria Is Like a Game of Whack-a-Mole—It Keeps Popping Up in Unexpected Places
The pathogen referred to as a "nightmare bacteria" is quietly adapting and spreading faster than anticipated.


The pathogen referred to as a "nightmare bacteria" is quietly adapting and spreading faster than anticipated.
Using extreme time-lapse microscopy, scientists watched a virus take over a bacteria to create a cell that looked and functioned more like a plant or animal cell. True story.
You might feel the bite, you might not, but an infected mosquito has injected you with a parasite named Plasmodium falciparum, a single-cell protozoa that quickly takes up residence in your body.
Using mathematical modeling, researchers suggest weather and warming created the "perfect storm" that drove the Zika outbreak in 2016.
Despite mounting scientific evidence that viruses can cause changes in learning and memory, the reasons have remained elusive.
While some researchers look for drugs to treat HIV, other scientists delve deep into the virus itself for answers on how it causes infections.

During the millions of years they've been on earth horseshoe crabs have developed a trick that can save our lives even now — and may be especially useful in the fight against healthcare-associated infections.

With significant advancements in the treatment and prevention of HIV, you'd think the stigma surrounding the deadly virus and AIDS, the syndrome the infection causes in the body, would have lessened. Unfortunately, a new project looking at conversations on Grindr — a social networking app for gay, bi, curious, and queer men — has shown that this stigma is very much present.

Just like your gastrointestinal tract, and the soil we walk on — a dust storm has a collection of bacteria, fungi, and viruses all its own called a "dust microbiome."

Earlier this year, NASA reported on findings that might point to water, and microbial life, on moons orbiting Jupiter and Saturn. Named Europa and Enceladus, those moons contain large oceans under their icy surfaces, which many speculate could hold microbial life.

The future of forests looks dreary in the face of a warming climate, but scientists are exploring the relationship between soil microbes and the ability of trees to move to higher altitudes, a key component of their survival.

Augmented reality upstart DAQRI announced today that it has strengthened their in-house talent by recruiting renowned physicist Seamus Blackley and acquiring a team of 15 engineers and scientists from Heat Engine, LLC.

Cats give us so much—companionship, loyalty, love... and now the bird flu. Several weeks ago, a veterinarian from the Animal Care Centers of New York City's Manhattan shelter caught H7N2 from a sick cat. According to a press release from the NYC Health Department on December 22, "The illness was mild, short-lived, and has resolved." This isn't the first time cats have passed infections on to humans, but it is the first time they passed on the bird flu—avian flu H7N2, to be exact.

Remember those horrible, soul-crushing studies from a few years back linking grilled meats with cancer? Unfortunately, they're still true, but scientists have recently found that an unexpected ingredient can curb some of the harmful effects of high-temperature cooking.

Rumors are swirling today that NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) may have shown us the first public glimpse of the next-generation HoloLens. Are they real? Or just a prototype? We've been digging in all day to find the answers.

A new study shows the Zika virus is present in saliva — but it may not be enough to make you sick. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention notes there is "no evidence that Zika can be transmitted through saliva during deep kissing." Given the results of research published in the journal, Nature Communications," the agency may need to revise its guidance.
Results of an early-stage clinical trial of an HIV vaccine could mean a hoped-for breakthrough in the battle against AIDS.
Growing evidence suggests that neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's may develop in part due to environmental factors, including infections that can cause inflammation in the nervous system. New research from investigators from Jude Children's Research Hospital and Thomas Jefferson University has strengthened that connection.

Cytochrome P450 (P450s) are proteins found in nearly all living organisms, which play roles that range from producing essential compounds and hormones to metabolizing drugs and toxins. We use some of the compounds synthesized by P450 in plants as medical treatments, but the slow growth and limited supply of these plants have put the drugs' availability in jeopardy and jacked up prices.
As our cells age, they eventually mature and die. As they die, they alert nearby cells to grow and multiply to replace them. Using a special imaging process that combines video and microscopy, scientists have observed the cellular communication between dying and neighboring cells for the first time, and think they may be able to use their new-found information against cancer cells, whose damaged genomes let them escape the normal dying process.
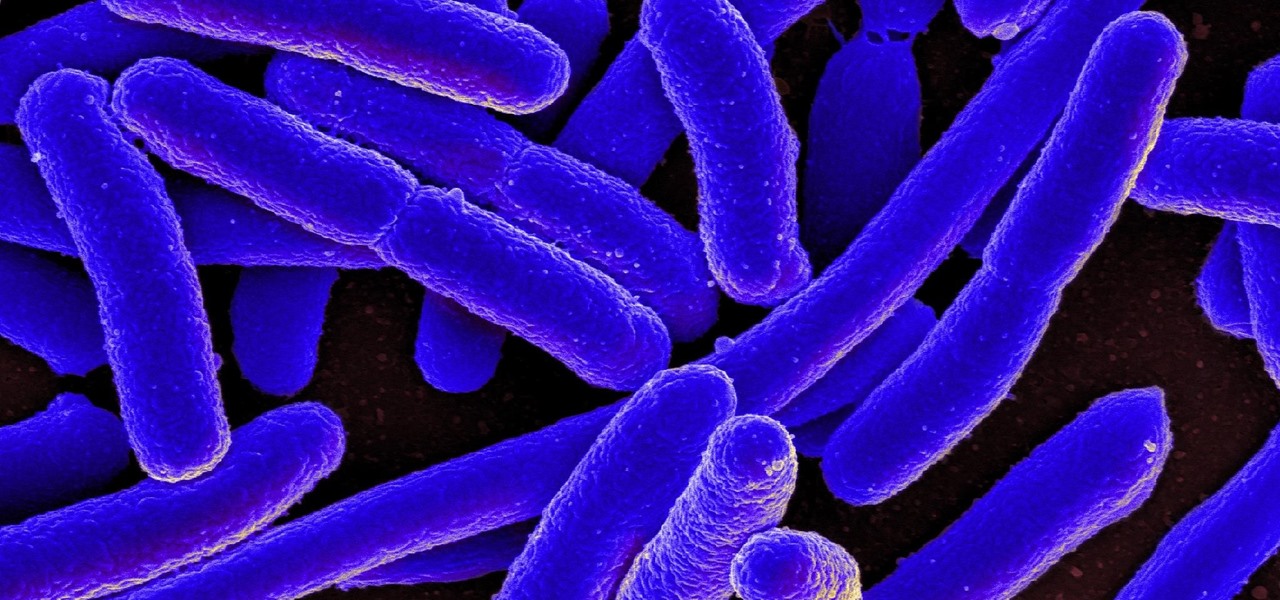
New research reveals how E. coli bacteria construct elaborate and effective tunnels to pump unwanted molecules like antibiotics and other toxins out of cells. The discovery could help us better understand how antibiotic resistance occurs and give us a leg-up to beat them at their own game.

Our canine best friends could spread our bacterial worst nightmare, according to a recent study. The problem with drug-resistant bacteria is well known. Overused, poorly used, and naturally adaptive bacteria clearly have us outnumbered. As science drives hard to find alternative drugs, therapies, and options to treat increasingly resistant infections, humans are treading water, hoping our drugs of last resort work until we figure out better strategies.
The body's usual response to a bacterial infection in the blood — called sepsis — takes time. It requires a carefully orchestrated sequence of events that gets the body's immune system ramped up to deal with the invading bacteria.
How can bacteria that lives in the throat of 10%–35% of people—without causing an infection—cause life-threatening meningitis and sepsis in others?

One booze hack that's been making the rounds for years is that inserting a spoon by the handle in a champagne bottle's neck will preserve its carbonation. This is one of those tips that I wish were true. Champagne is a great thing to have around on a special occasion, and it seems a shame to pour any leftovers down the drain once its lost its fizz. While there's lots of anecdotal evidence surrounding this trick, Harold McGee and Stanford University chemist Richard Zare debunked this myth as d...

You've got to be sick of it by now. Those meaningless and unsatisfying articles, lists, and videos you were duped into clicking on because their headline made them impossible to resist.
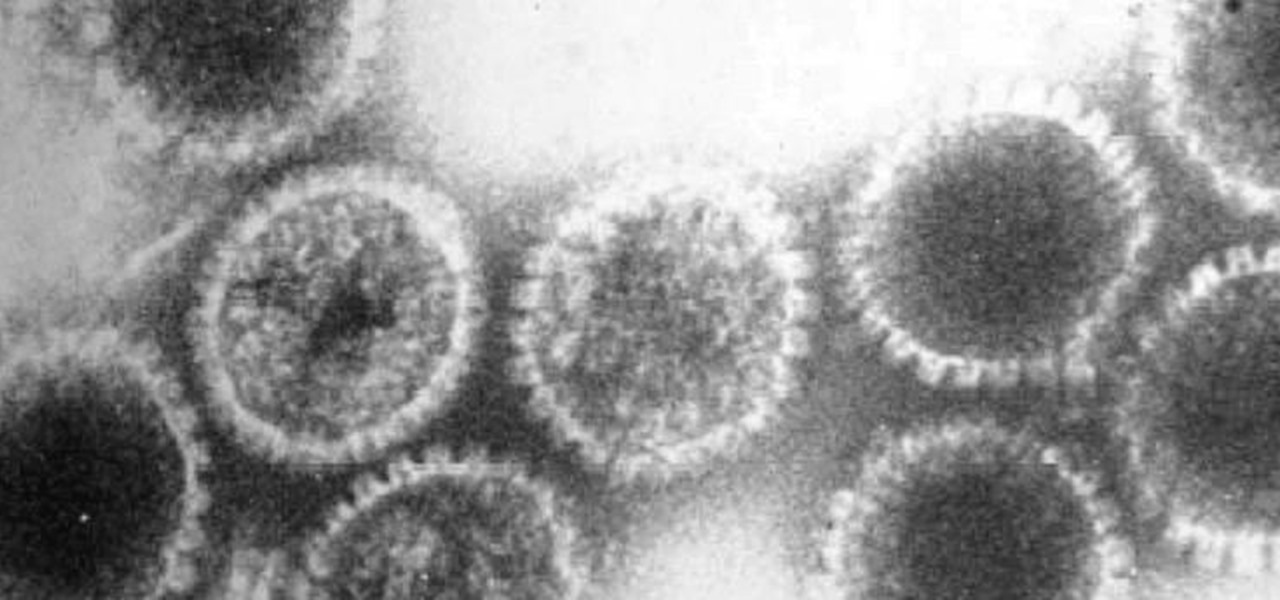
How can a drug used to treat cancer be effective against viruses, too? The answer lies in the drug's shared target — specifically, cellular components that control the activity of genes. A new research study showed that one such type of drug, histone methyltransferase inhibitors used in cancer clinical trials, has activity against herpes simplex virus, too.

While not cuddly to most, bats are shy, skilled flyers that fill an important role in their environments. A new study reveals a deadly disease decimating North American bat populations has stepped up its attack on vulnerable bat populations in the summer months.
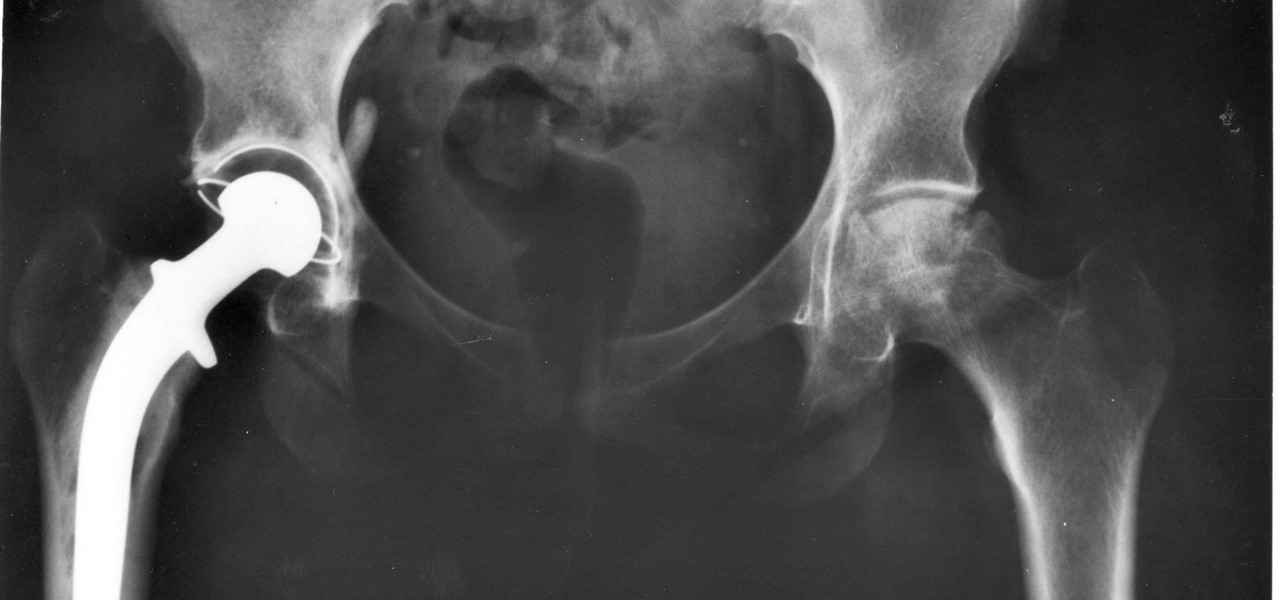
For about a million Americans each year, a joint replacement brings relief from pain and restored mobility. But, 5–10% of those people have to endure another surgery within seven years, and most of those are due to an infection in their new joint. If doctors could treat infections more effectively, patients could avoid a second surgery, more pain, and another rehabilitation.

More than one in ten people in the US have type 2 diabetes — that's over 29 million people. It's characterized by excessive sugar (glucose) in the blood due to the development of resistance to insulin, the hormone that normally metabolizes glucose.
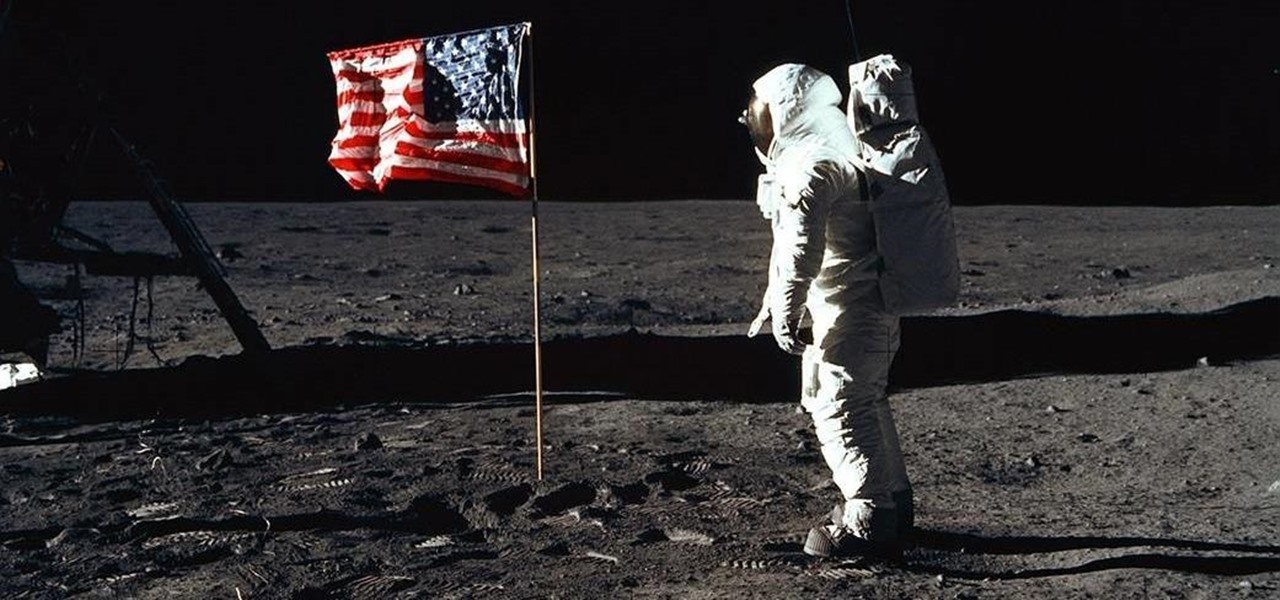

On July 20, 1969, humans set foot on the moon for the first time. But some say our microbes beat us there. With the Space Age came new questions about microscopic invaders from outer space and concern about where we are leaving our microbial footprints. The questions are even more relevant today.
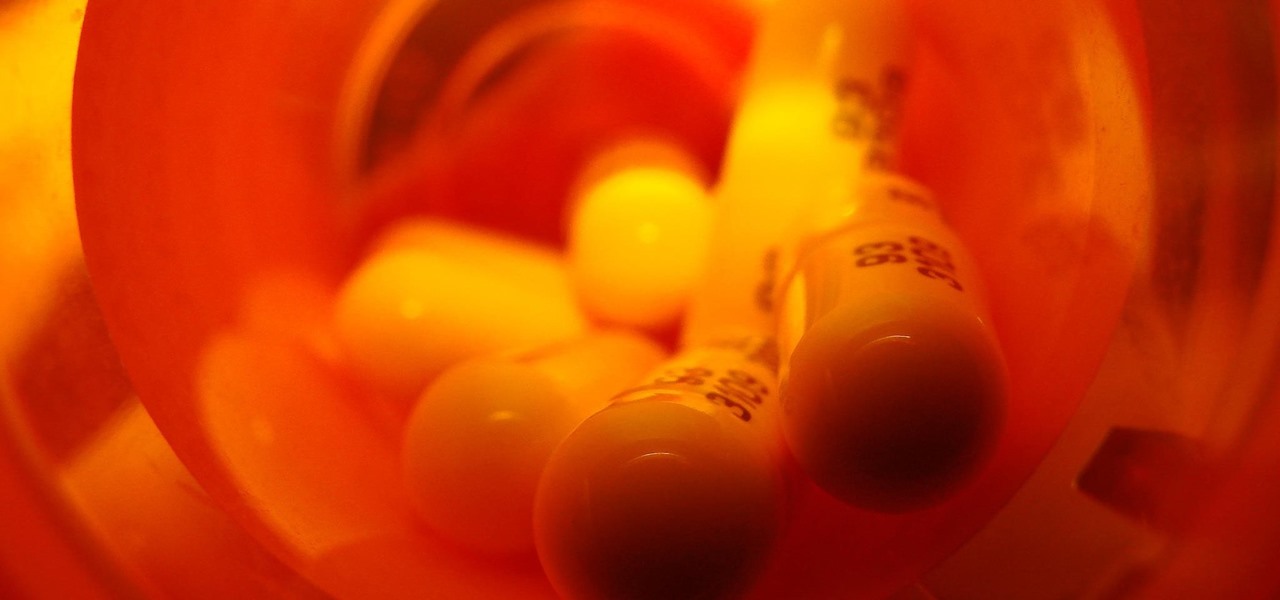
After years of telling patients to finish any prescribed course of antibiotics completely, a group of researchers in the UK say it is no longer necessary, and could even be harmful if we want to preserve the antibiotics we can still use.
Once we recover from the respiratory infection pneumonia, our lungs are better equipped to deal with the next infection — thanks to some special cells that take up residence there.
Not all bacteria in the eyes cause infection. A group of researchers from the National Eye Institue has shown that not only is there a population of bacteria on the eyes that reside there but they perform an important function. They help activate the immune system to get rid of bad, potentially infection-causing — pathogenic — bacteria there.
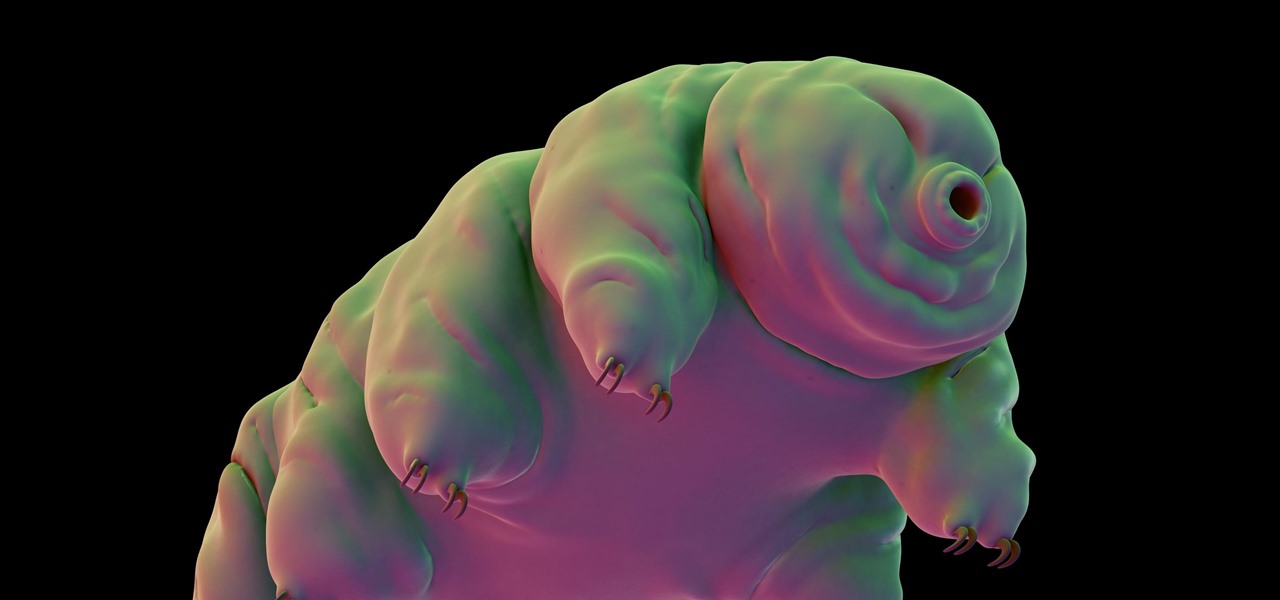
Forget the rise of the machines. Tardigrades are set to outlive everything — even the bots. When the last echo of a whisper in a cell phone has long dissipated into space, the water bears will still be hanging out.
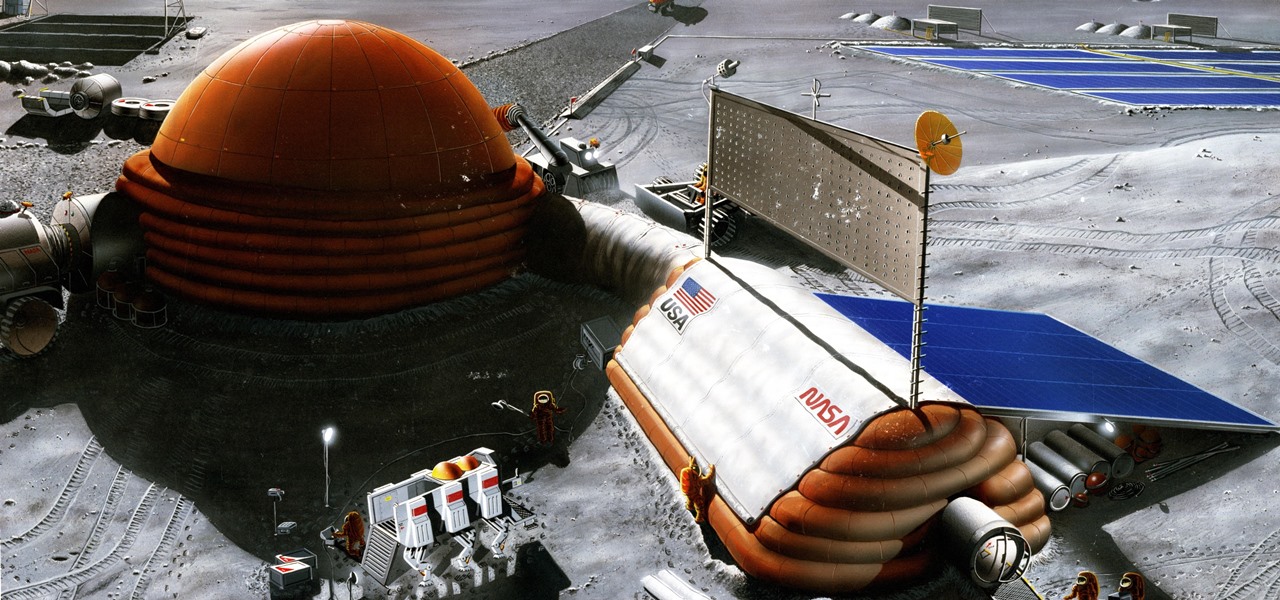

Wherever there are people, the party is sure to follow. Well, a party of microbes, at least. That is what scientists at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory have found after a 30-day microbial observation of the inflatable lunar/Mars analog habitat (IMAH).
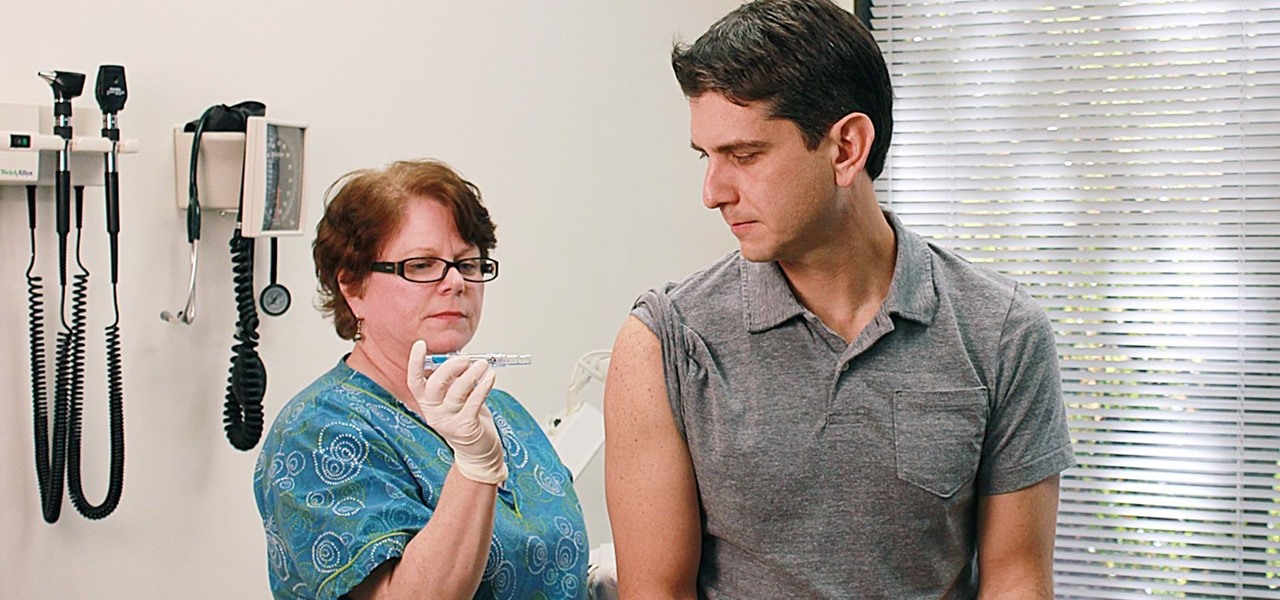
Flu vaccines can help prevent us from getting or suffering the most severe effects of the flu. But, each vaccine only protects us from three different strains of the flu. If we don't have a vaccine against all types of flu, it leaves us open for an epidemic with a flu virus we didn't expect.

About a third of the methane released into the environment comes from the production and transport of natural gas. The gas leaks as it moves along the transport chain from gas wellheads to market.
The community of bacteria that lives in our gut has a lot to tell us. It can give clues to what we eat, the environment we live in, and diseases and disorders we may have. Now, scientists have linked these bacterial species to how we feel. A new research study found an association between women's gut bacteria and their emotions.

The herpes simplex virus (HSV) can cause devastating complications for infected newborns whose mothers have genital herpes. Understanding risk and research can help you, and your baby, when the time comes.