Those of us with modern smartphones know that 4G LTE networks have provided us with a phenomenal experience. One light years beyond what we had access to before. For some time, AT&T has been teasing its dive into the next iteration of network speeds, agonizingly doing so without any specific dates for when they would actually deliver. But today, AT&T confirmed what they call the "5G Evolution," and it's available now.
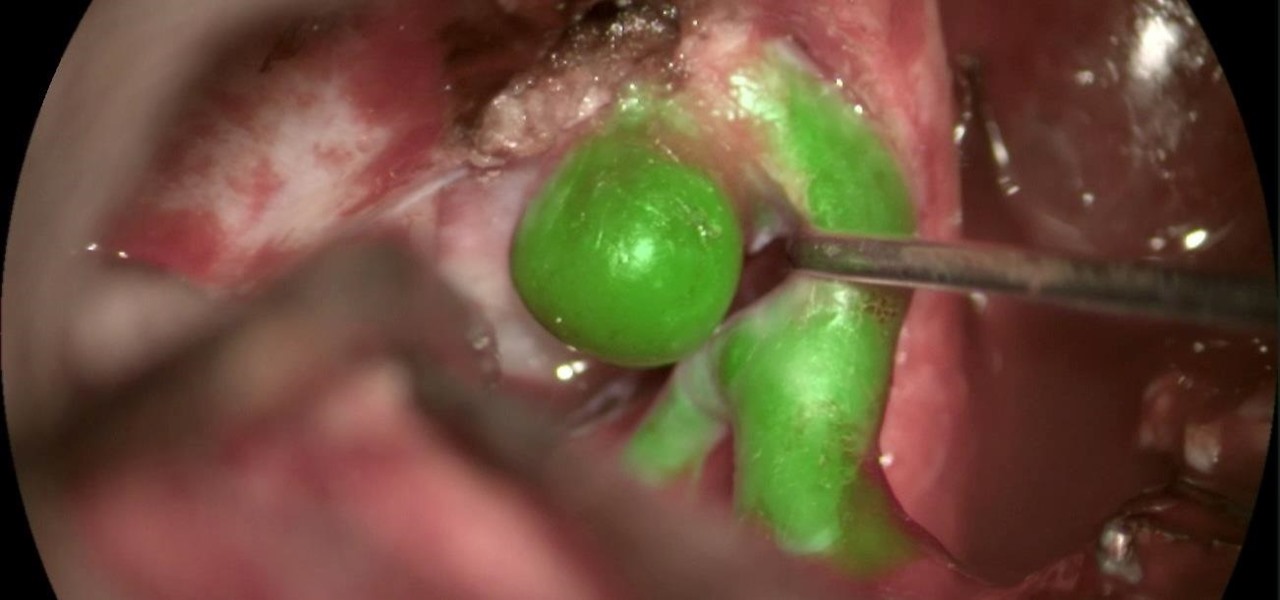
In this Tuesday's Brief Reality report, there's a trio of stories from the healthcare world where augmented reality is helping out with surgical microscopes, asthma treatment, and other diagnostic and treatment tools. There's also something for all of you AR/VR storytellers out there.
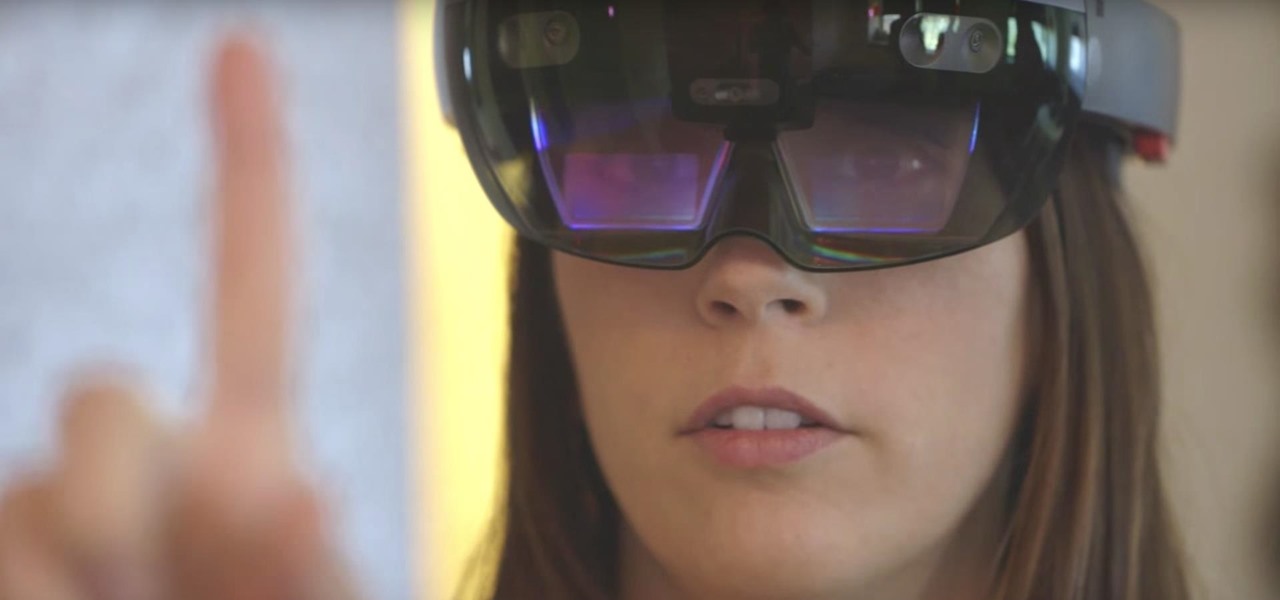

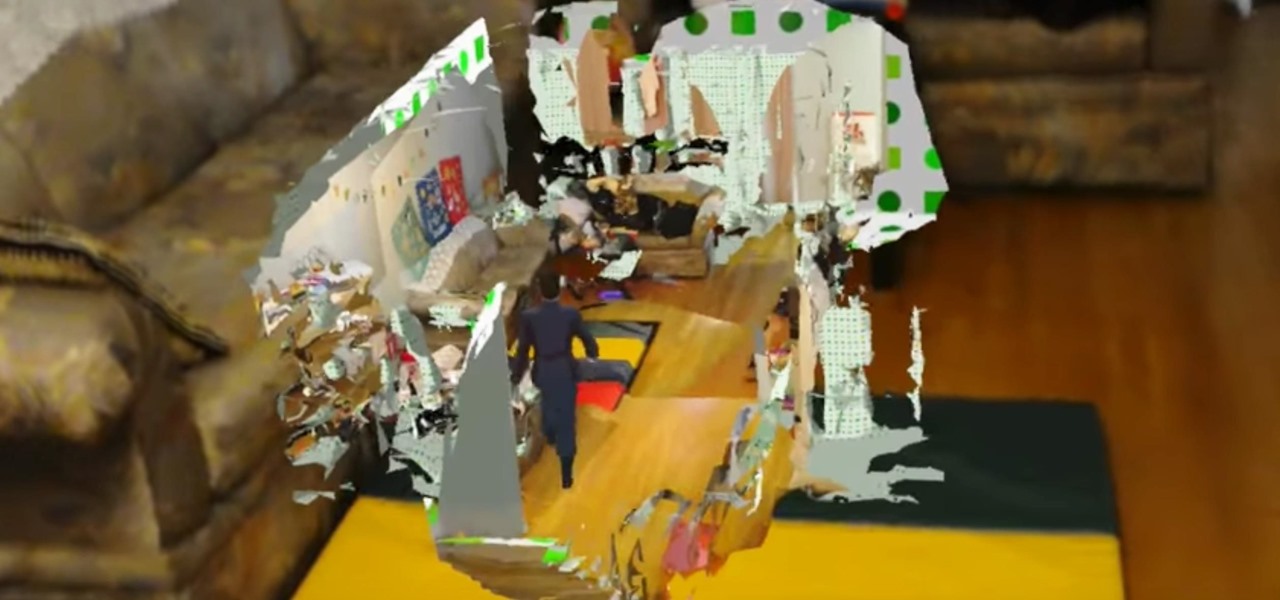
In the nascent AR/VR race, any release news is big news. For augmented reality, those invested in the new technology eagerly await the release of Microsoft's Hololens and any inkling of information that comes with it. If you're one of those folks, you're in luck, as new information has just been disclosed about one of Microsoft's partners on the project, Lenovo, and their Hololens; including its release date and price.
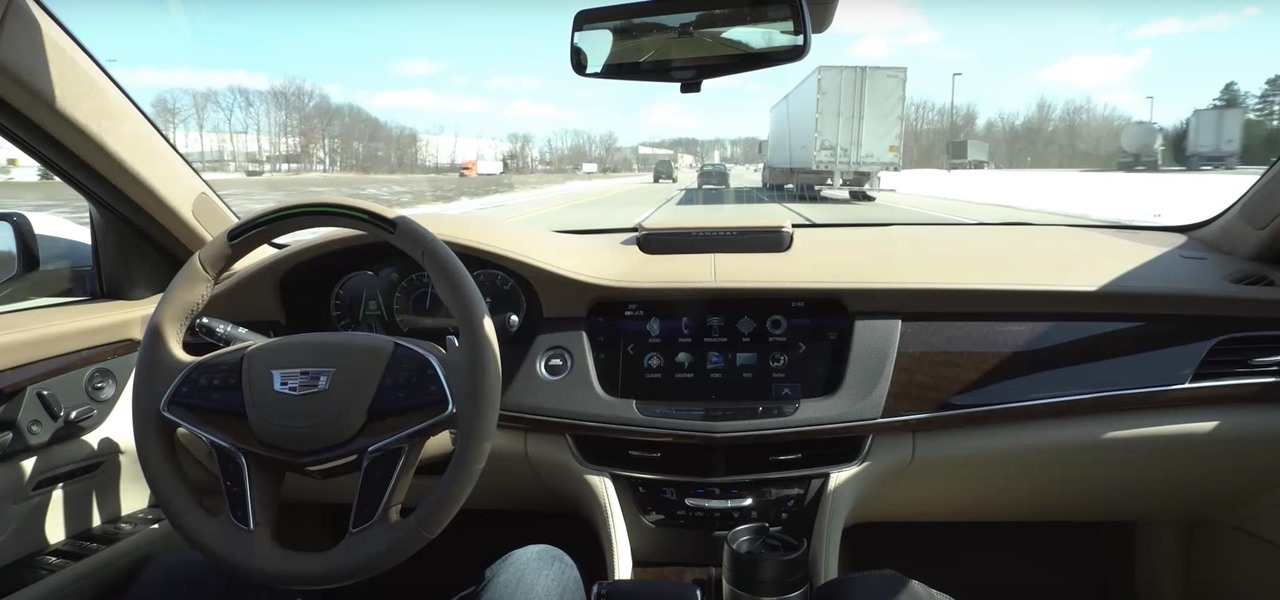

It be would the ideal morning commute—sit back, drink some coffee, and read the news as your car drives you to your destination. That reality isn't quite here yet, but Cadillac is offering something close with "Super Cruise" on the CT6.
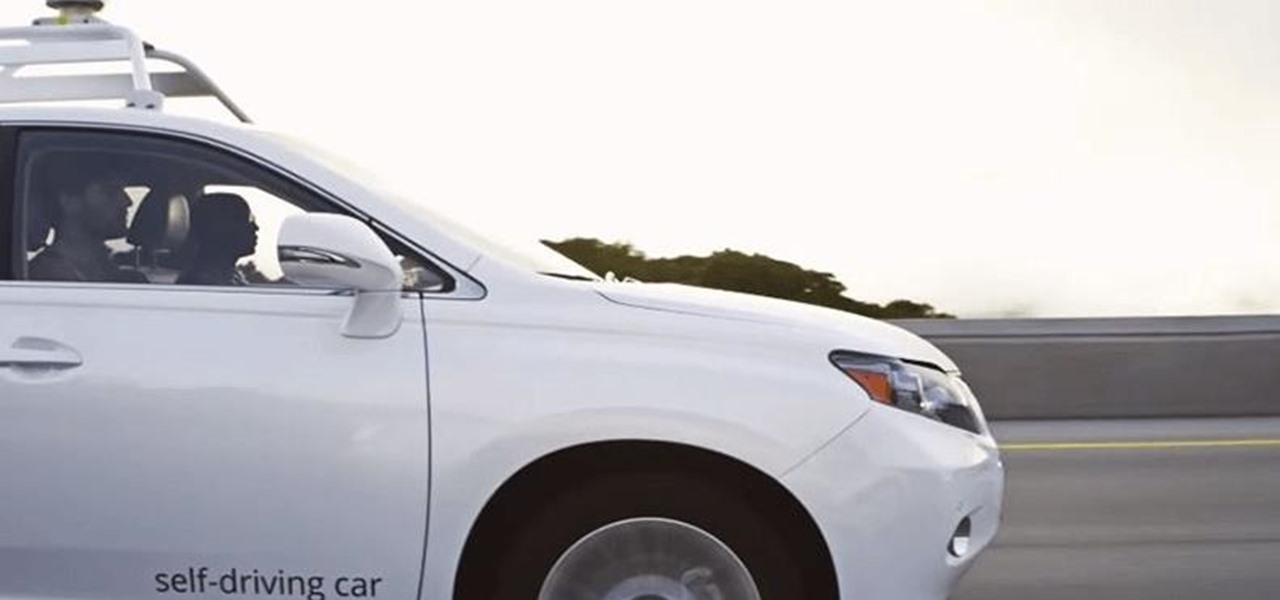

It may seem strange to find the director of engineering at a question-and-answer site all of a sudden pick up and lead a new driverless startup, but to Kah Seng Tay, both engineering tasks require building the right infrastructure to handle large amounts of AI data.

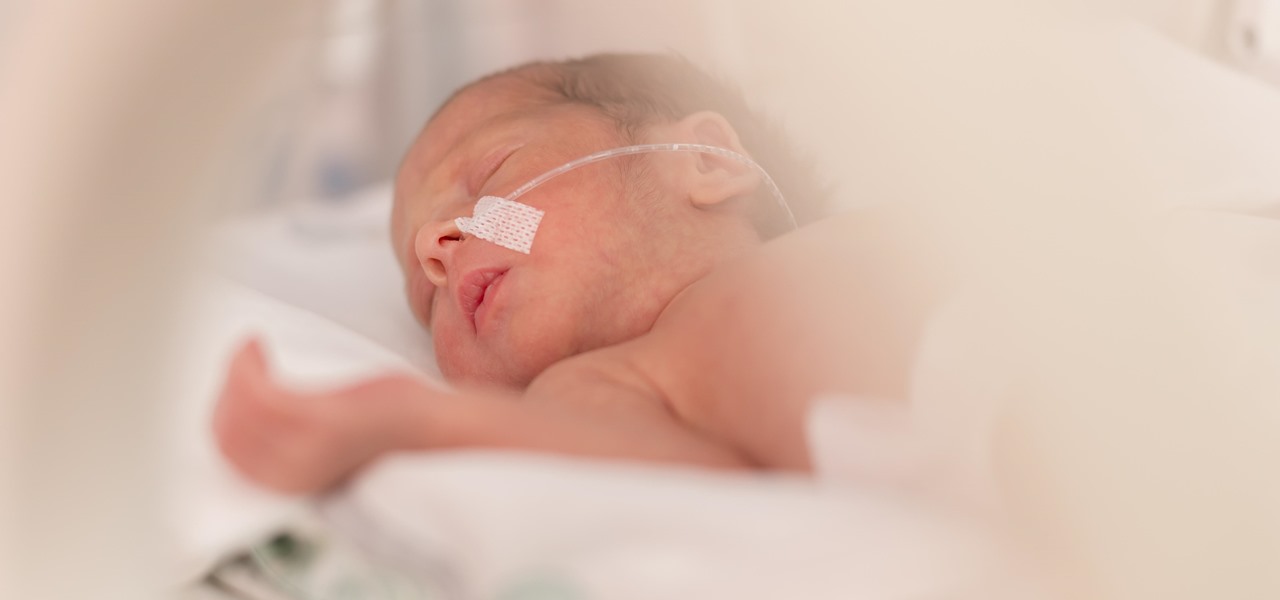
After a brief reprieve, Zika fear is back with a vengeance as the US mosquito population booms. And we're just now seeing the true impact of this devastating virus, as babies of mothers infected with the virus are being born.

For all of its drama, Uber's driverless program has states like Arizona excited for the future of self-driving vehicles. But it's not Arizona alone that supports the driverless craze; the Illinois House of Representatives will hear a bill that would allow driverless cars on the road with or without human operators.

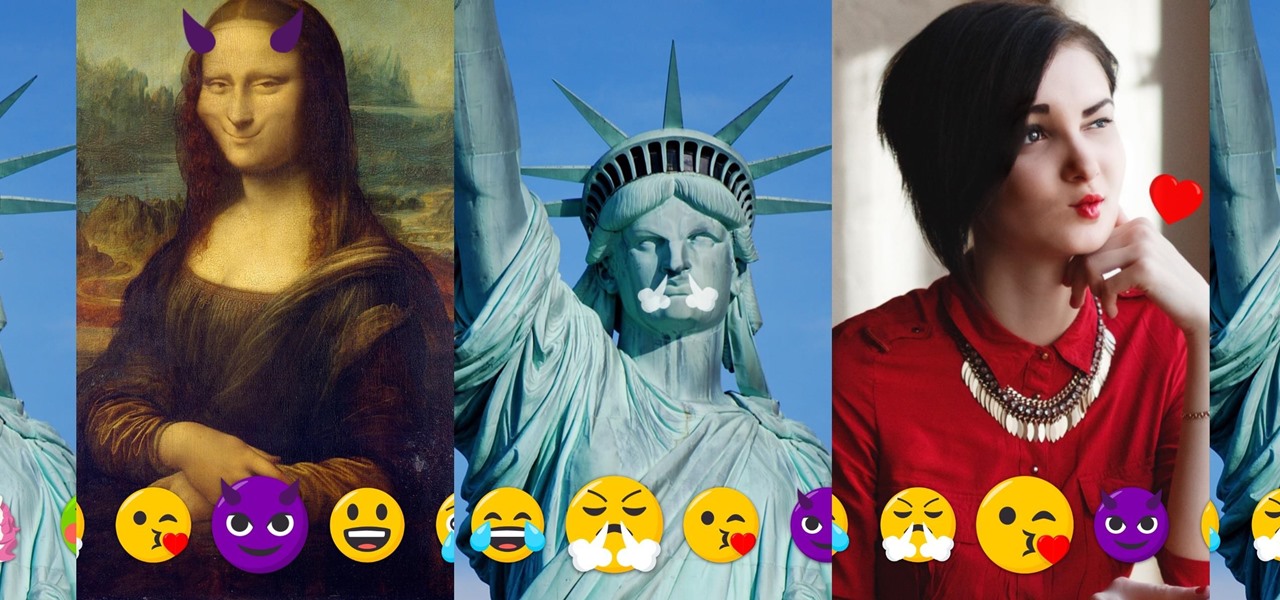
As a society, we seem to be moving backwards toward communicating by pictures only. Emojis and GIFs are today's cave paintings, and I, for one, am totally okay with that. To make this transition even more amazing, photo-editing app Facetune created a tool that lets us change our very own faces into moving emojis.

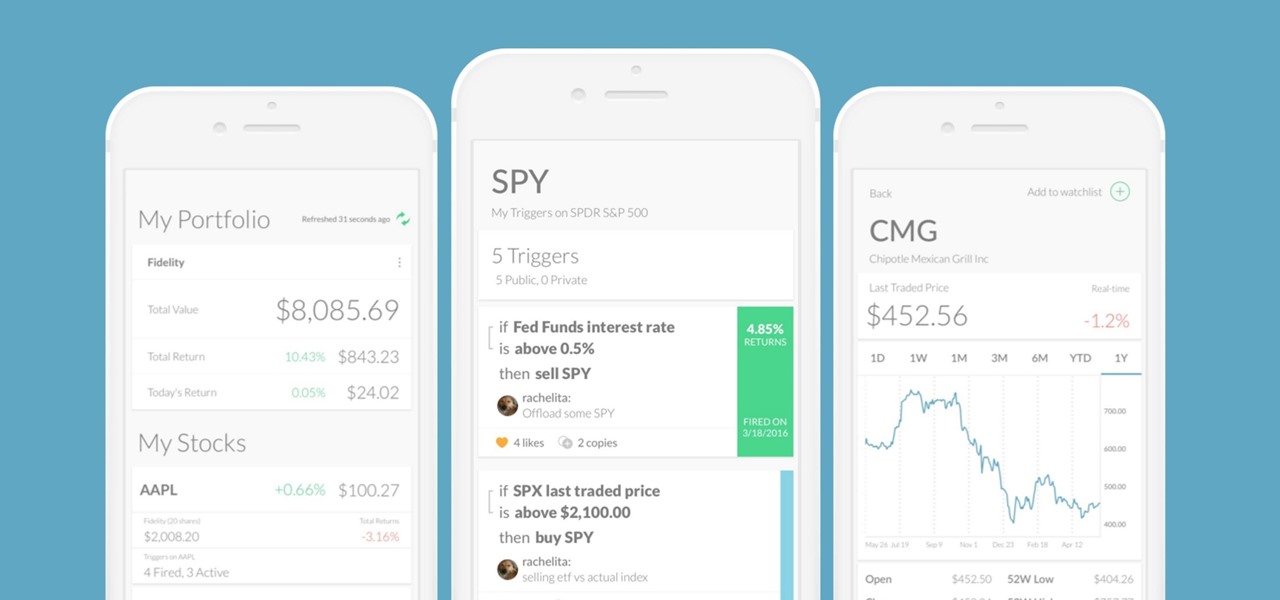
Every time Donald Trump tweets about a stock you own, Trigger Finance, or just Trigger—the app founded on the "if this, then that" rule to track and invest in the stock market—alerts you with a notification for real-time analysis of financial data.

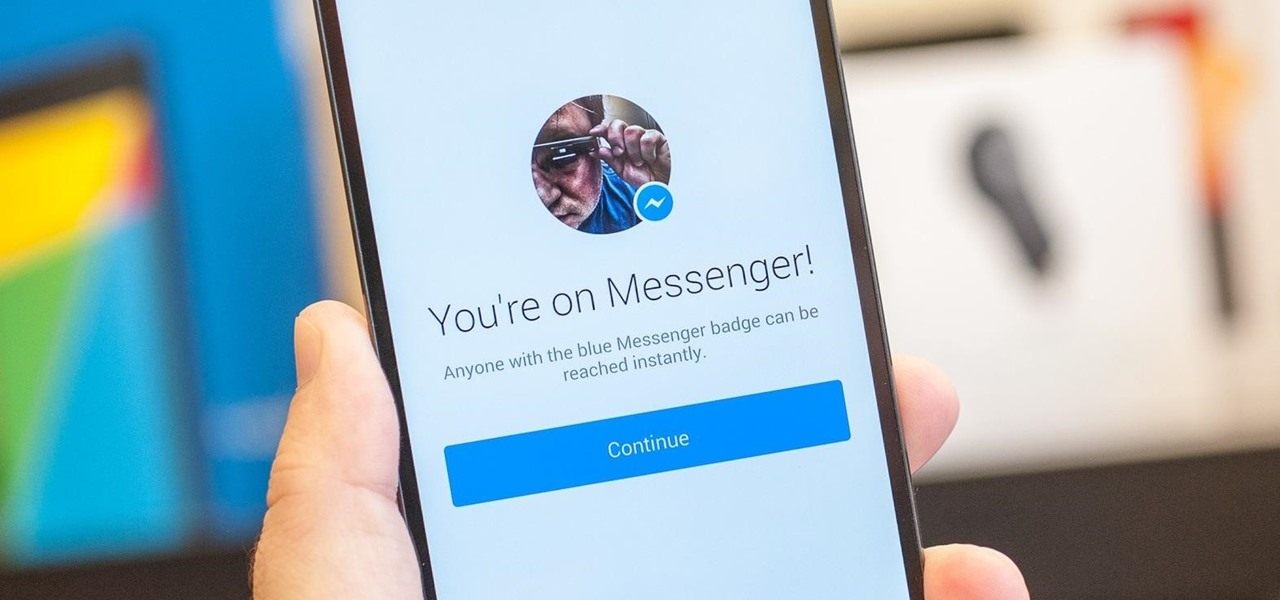
Facebook Messenger has now incorporated a live location sharing feature, one week after Google Maps revealed its own real-time location tool. On Monday, the social media giant announced the new feature, which will allow users to share their live whereabouts with friends at the press of a button.

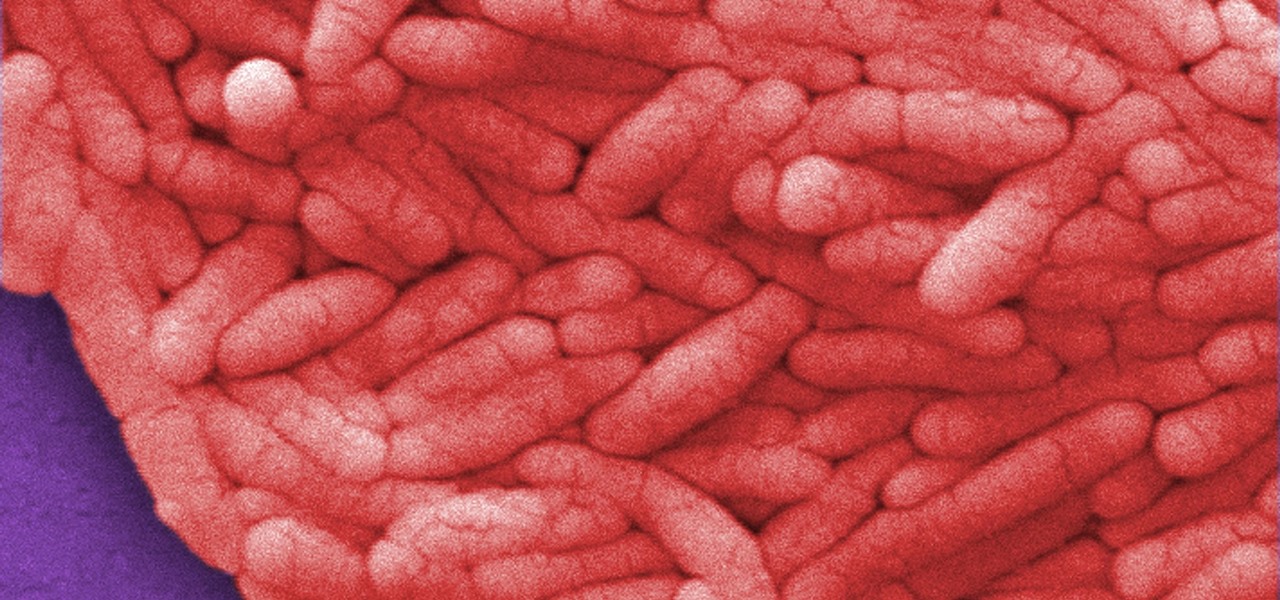
There have been seven more people sickened from four states since the I.M. SoyNut Butter E. coli outbreak was announced earlier this month. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Washington Department of Health have confirmed the I.M. Healthy SoyNut Butter was the cause of the outbreak in an update today.

Baidu Inc, the "Chinese Google" search engine and technology company, which has been actively pursuing self-driving cars, reported that a gang of hackers recently attempted to steal its driverless car technology.

A state of emergency has been declared in Malaysia's northeastern Kelantan state after an outbreak of avian influenza virus H5N1.

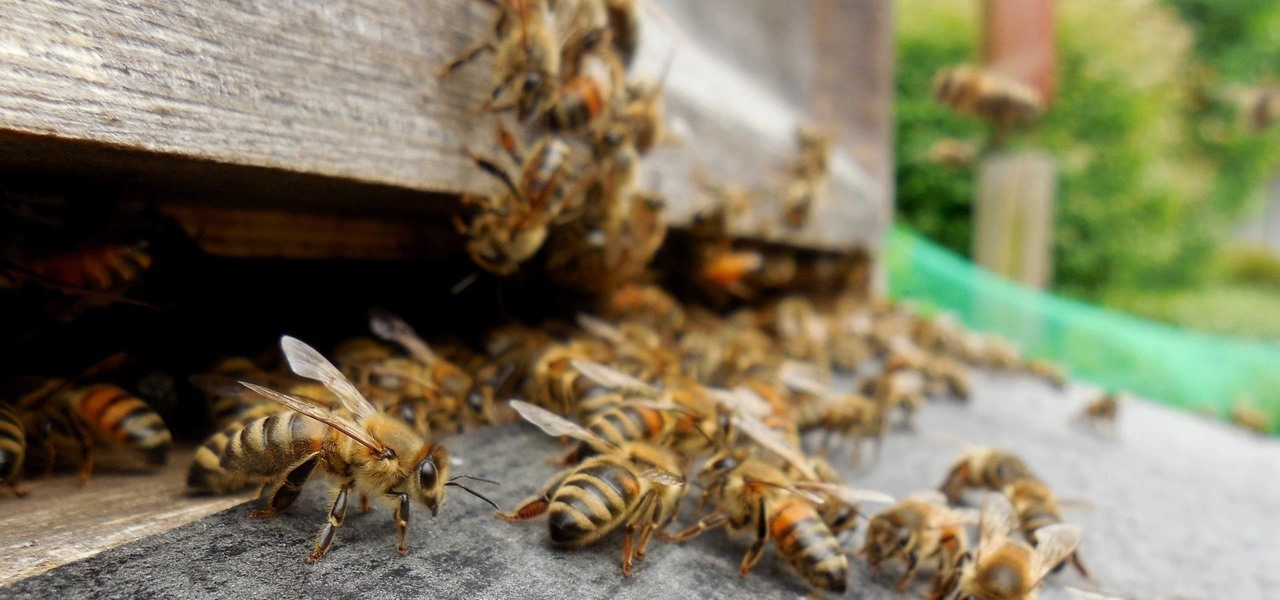
Add antibiotics to the possible list of culprits responsible for honeybee decline around the world. While it may come as a surprise, antibiotics are commonly mixed into feed used by commercial beekeepers to maintain their hives. In a recent study published in PLOS Biology, researchers from the University of Texas at Austin found antibiotics used to treat honeybees may be a contributing factor in individual bee death and colony collapse.

In a press event this past week at the Game Developers Conference in San Francisco, California, Unity Labs, the experimental and forward thinking arm of Unity, announced an upcoming toolset for developers in the augmented, mixed, and virtual reality space called the XR Foundation Toolkit (XRFT).

Yes, bubonic plague—the Black Death that killed millions in the Middle Ages— is still out there. It even infects and kills people in the United States. Without treatment, half the people infected die, but the Food and Drug Administration approved ciprofloxacin in 2015 to treat plague, and it has just successfully been used to stop the infection in five people.

Norovirus outbreaks occur all year long, but peak in the winter months, which means we are in the middle of norovirus season. But there's still time to protect yourself from the highly infectious bug.

Antibiotic-resistant infections that usually occur only in hospital settings are spreading in communities, increasing hospital stays—and danger—for young children.

Antibiotic use in infants has been associated with a host of childhood conditions later in life. Yet when an infection is suspected in a newborn, usually a sample of their blood is drawn to check for the presence of bacteria and 5 to 8 percent of them receive antibiotics while the diagnosis is pending.

Sky Zhou, also know as Matrix Inception on YouTube, is no stranger here on NextReality. We loved his Pokémon concept game for HoloLens, as well as his D3D Keyboard that lets HoloLens users leave notes around the house. He just can't seem to stop creating cool mixed reality apps, and he's already got another one in the works.

We usually associate Salmonella bacteria with a dangerous type of food poisoning, but they actually are pretty good at seeking out tumors. That trait made the bacteria a great candidate to deliver a protein that would help knock tumors out.

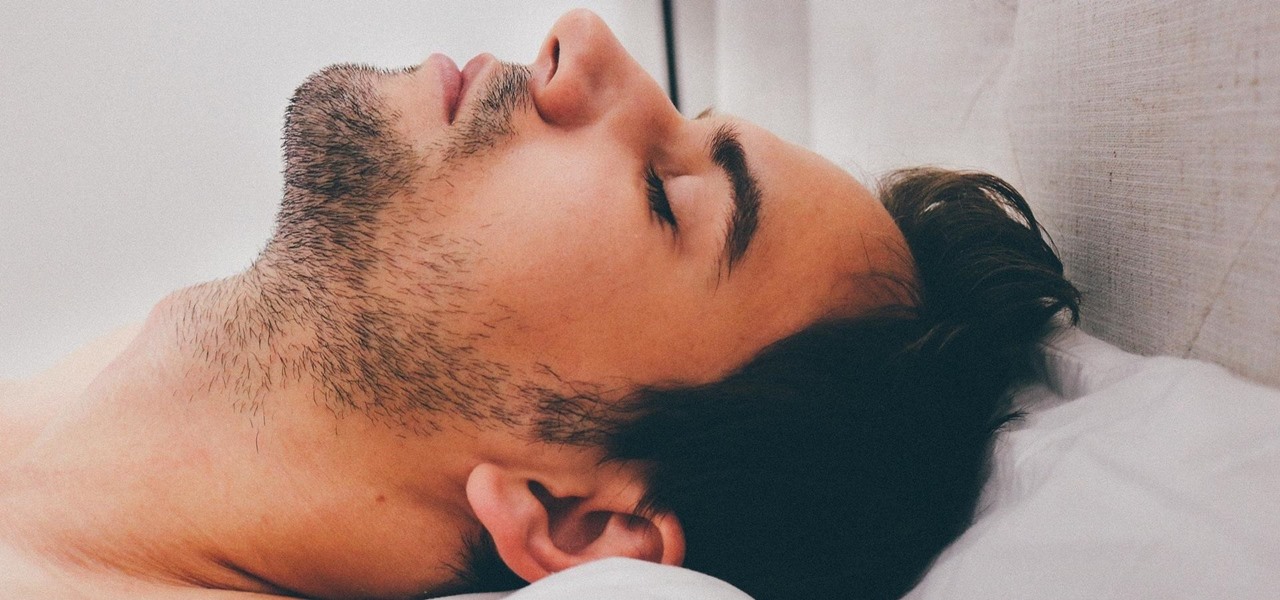
Sleep lets our body processes rest and restores us for the next day, so a bad night's sleep can ruin the following twenty-four hours and even make us feel sick. Now, new research published in the journal Sleep cements the idea that loss of sleep actually leaves us vulnerable to sickness.

To shine light on the future of the relationship between humans and viruses, a team of researchers from the University of Oxford looked into the dim and distant past.

If you're in the Windows Holographic community of developers, make sure to mark your calendar and set your alarms for February 8, 2017 because it's Windows Developer Day.

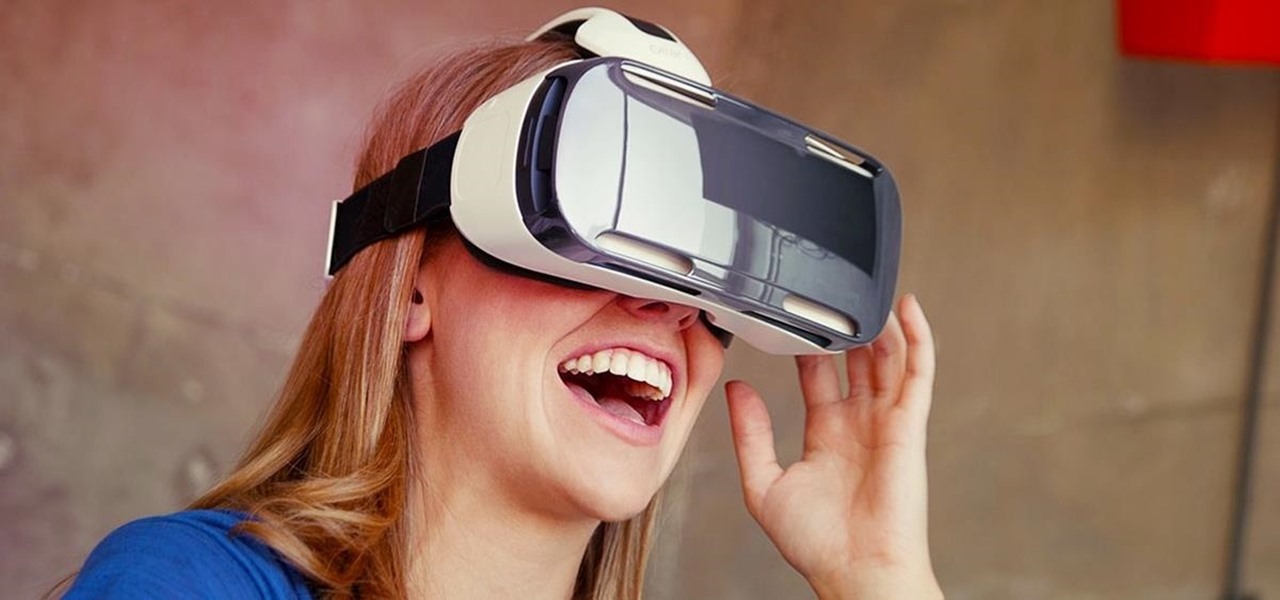
Last month, Dr. Sung-Hoon Hong, Vice President of Samsung Electronics, announced at the Virtual Reality Summit in San Diego that Samsung would be moving into the augmented reality market. According to a recently published patent application, that move has begun.

Remember back in 2011–2012 when "Little Talks" by Of Monsters and Men was the bumping new single being played everywhere? Well, thanks to this robot created from a LEGO Mindstorm EV3 kit, and an acoustic guitar, you get to get the iconic "hey!" stuck in your head for the rest of 2017. You're welcome.

When a dead body is discovered, finding out when the person died is just as important as finding out how the person died. Determining the time of death has always involved lots of complicated scientific detective work and less-than-reliable methods. However, a study by Nathan H. Lents, a molecular biologist at the John Jay College of Criminal Justice in New York, is the first of its kind to show how microbes colonize a body's ears and nose after death.

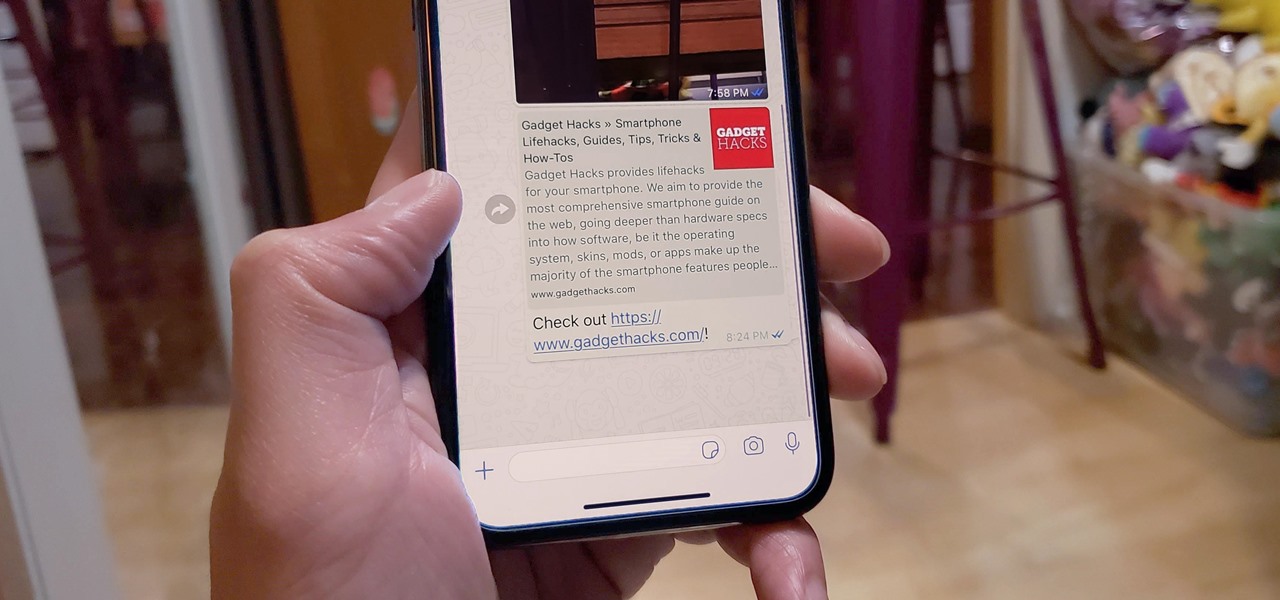
When WhatsApp first came out in 2010, it quickly gained notoriety as a great way to meet new people all over the world thanks to group chats, which allow multiple admins for each group that can all add participants from their own contacts lists.

People have been transforming mud into art, aka pottery, for thousands of years. This is not a new phenomenon, but often the finished product has a certain utilitarian aesthetic, such as a bowl or vase.

You're all kale-d out, you've had it up to here with golden milk, and you're on the prowl for the next superfood. Well, get ready for some unicellular goodness: the next superfood is an algae named Spirulina, also known as Blue Majik. (Kudos to the marketing exec that came up with that, am I right?)

Halloween is this weekend, so if you're looking for a last-minute big batch cocktail that will keep your guests properly hydrated—and might turn them into mutants—look no further! (Note: This will not actually hydrate anyone, just so we're clear. Priorities, people!)

Blue light (like that from our smartphone) tricks the human brain into thinking it's still daytime, even if it's coming from something as small as a screen. So while you're playing around with your new Pixel or Pixel XL after dark, subconscious signals to be awake are preventing you from getting to sleep as early as you should.

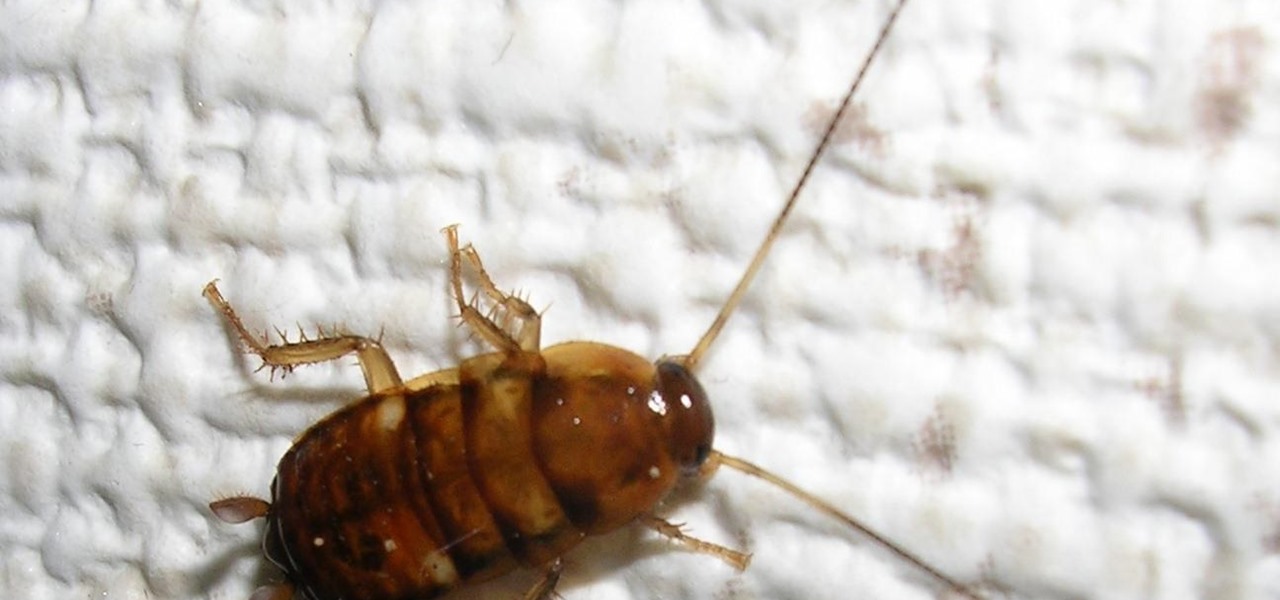
In the Western world, the only time you'd associate food with cockroaches is health code violations. And while other cultures and countries are more open to cooking with and eating these and other little buggers, insects are probably not a food trend that will be adopted by the West anytime soon.

Some of the best Android apps are not hosted on the Google Play Store, and that means you have to sideload them if you want to get their awesome functionality. But without the Play Store, these APKs are never automatically updated, so your only choice has been to scour the internet for a newer version when you need a bugfix.

When it comes to hacking guides, most are written from the perspective of a Linux user. There are a few outliers, but it's mainly Linux, which leads to the idea that Linux is the only OS that's viable for hacking. This couldn't be further from the truth. A properly set up Apple machine can do quite a bit of heavy lifting.

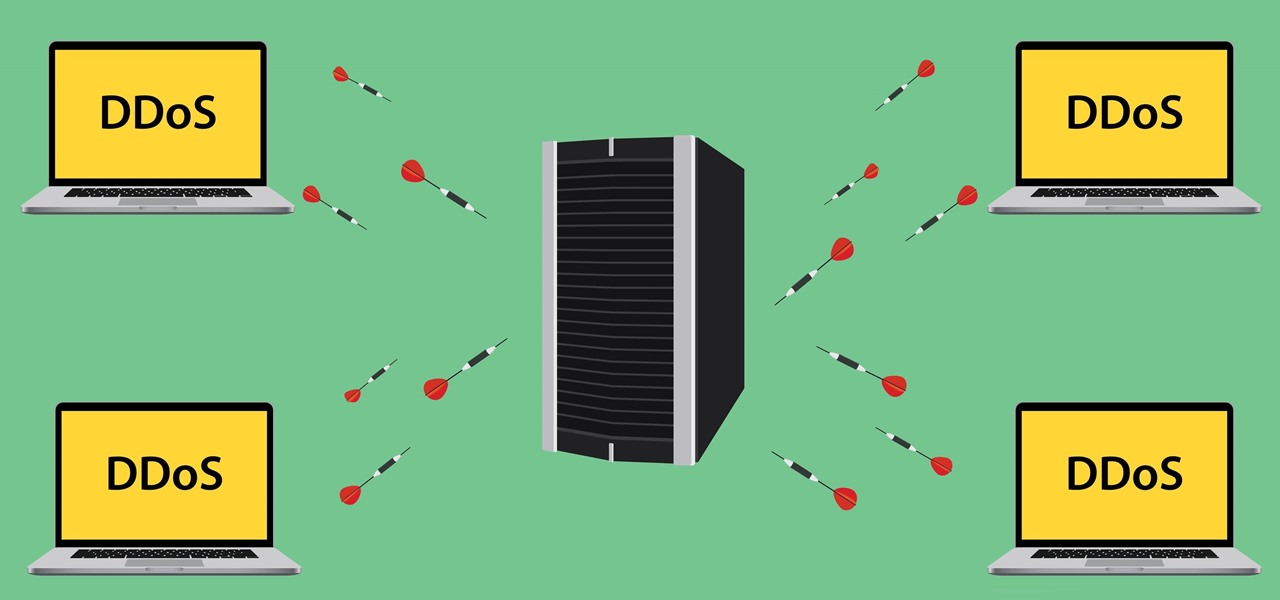
Security journalist Brian Krebs recently suffered a record-breaking DDoS attack to his his website, clocking in at or near a whopping 620 Gbps of traffic. Krebs' site was down for over 24 hours, and it resulted in him having to leave his CDN behind.

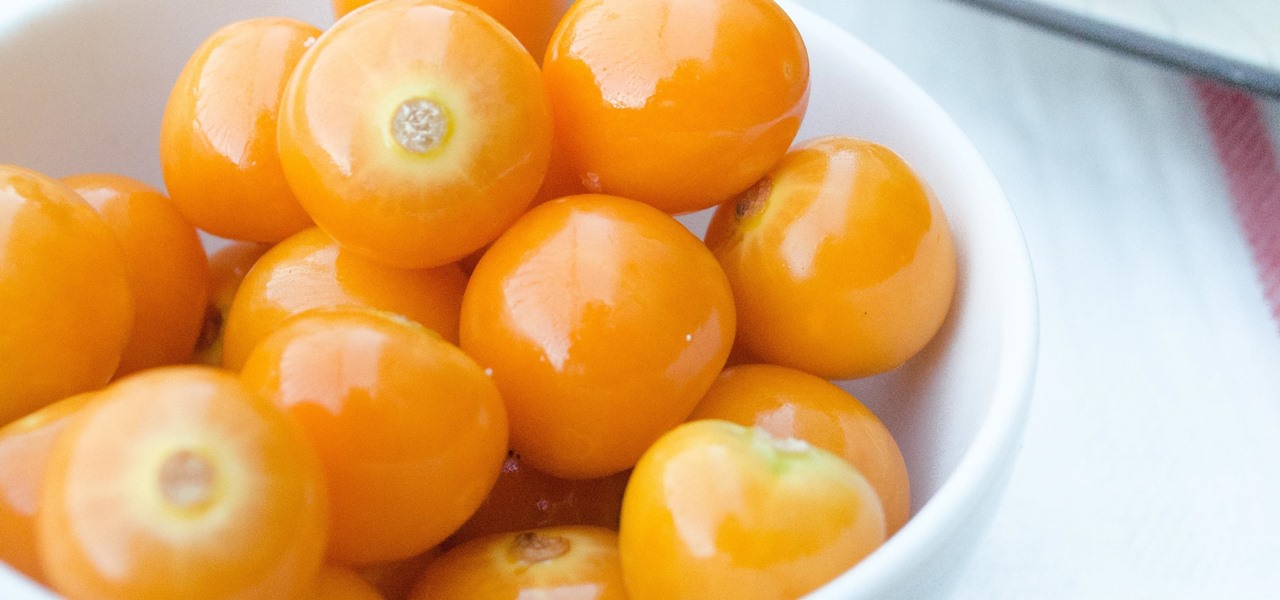
Whenever I went to the grocery store on a mission for blueberries, I'd inevitably find myself staring at these weird little tomato-looking berries... and wondering what the hell they really were. Tomatoes? Berries? A weird science experiment? Then, I'd set a pint of blueberries in my cart and carry on, forgetting about them for the time being.

Fall is here, and it's time for warm, filling meals... that don't involve a lot of effort, because it is getting cold outside and you spent a full day at work wishing you were on the couch with a blanket over your head, dammit.

When Facebook purchased WhatsApp for $19.3 billion back in 2014, we all knew this was coming—it just took longer than we thought. But starting today, the data mining became official, and now, information from your favorite messaging app is no longer out of reach for the world's biggest social media site.

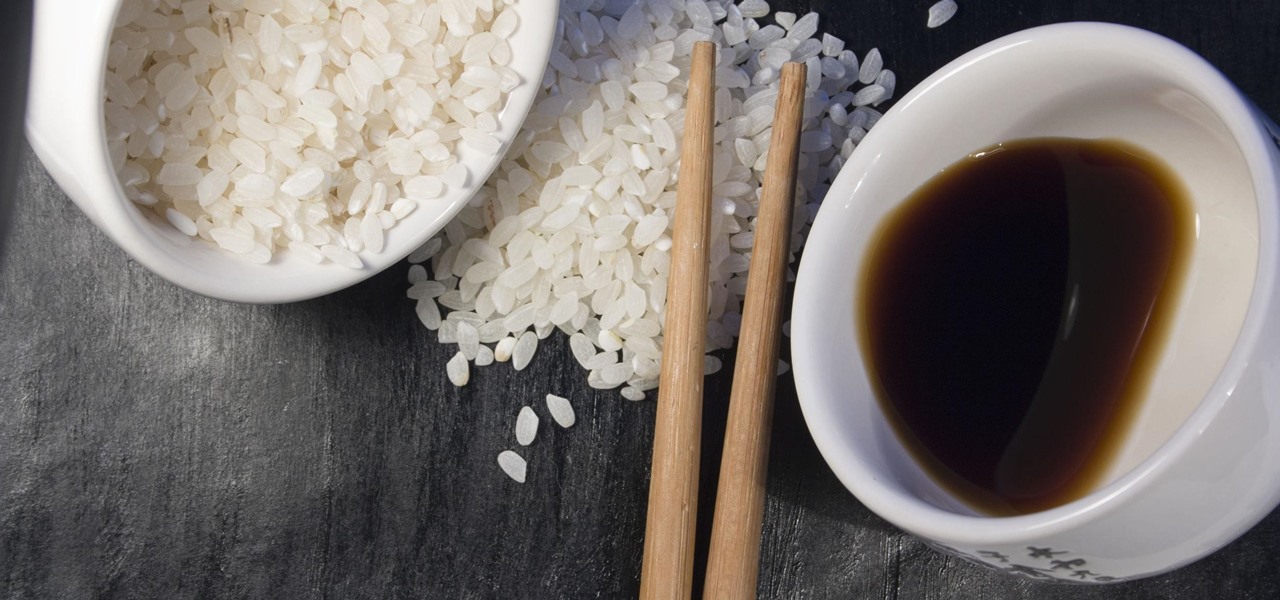
Koji is a culture made up of a certain fungus (mold) called Aspergillus oryzae, which has been used to ferment rice and soybeans in Japanese, Chinese, and Korean kitchens for centuries. Koji can actually have other involved fungi, but Aspergillus oryzae is the most common, and therefore the names can be used interchangeably. Its end purpose is to enhance the flavor of items like soy sauce, sake, and miso.