
How To: Use color theory when decorating your home
Do you want your house to look dull or colorful? If the latter, then be sure to check out this video to learn how to best utilize the color theory.


Do you want your house to look dull or colorful? If the latter, then be sure to check out this video to learn how to best utilize the color theory.

Getting splinters is no fun, but making them can be if you've got the right tools and the proper technique.

If your blood pressure is 140/90 or higher, you need to get it down! The good news is that many of the steps you can take are painless, and some are downright enjoyable.

Why sweat through a boring exercise routine when you can achieve the same results while having fun? You Will Need

It's the most frustrating thing in the world: You're in the middle of a story and can't think of the word or name you need. Retrieve it fast with these tricks.

A better body image in six steps, and dieting isn't one of them. This video will show you how to build a better body image.

Save yourself back pain and injury by learning the correct way to pick up heavy objects. Watch this video to learn how to lift a heavy object.

Do you write down everything you hear—then get overwhelmed when it’s time to study? Save time—and improve your grades—with this note-taking system. Learn how to take good notes in class with this Howcast guide.

Is your child a gimme monster? Put a lid on demands and tantrums with these tips. You Will Need
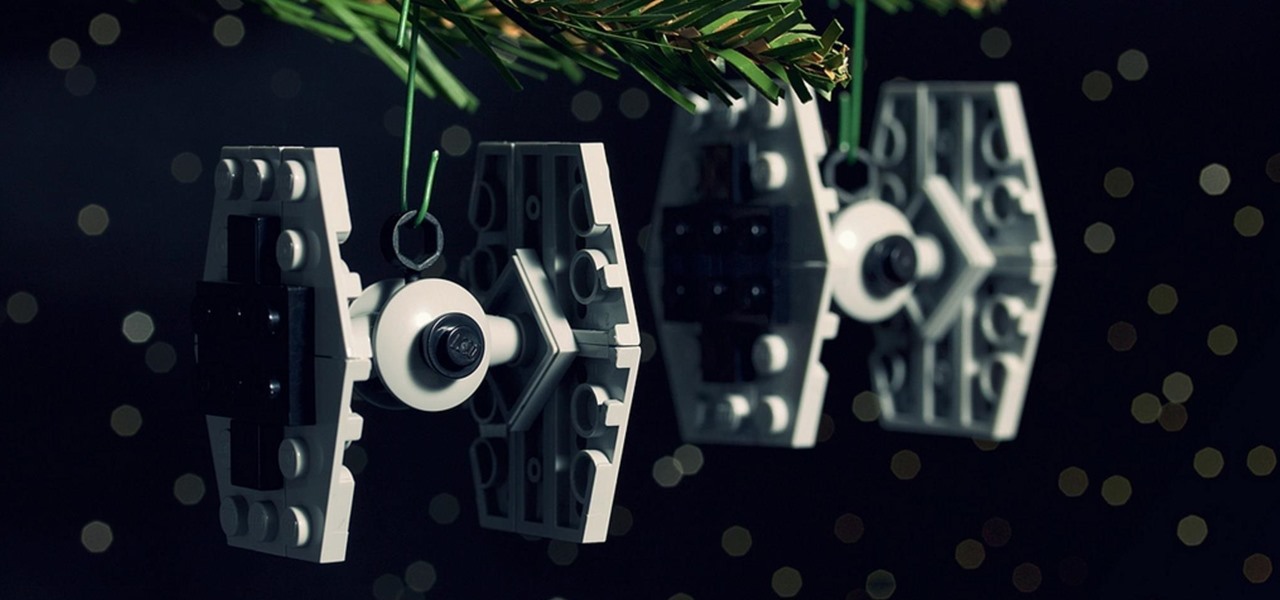

LEGOs are more than just a toy for young children— it's an emerging art form combining photography, stop-motion (i.e., brickfilms), and imitative models that portray today's pop culture as it is. It's something visual culture analysts are sure to be studying over the next decade, and Chris McVeigh, from Halifax, Nova Scotia, is sure to be studied for his LEGO mastery.
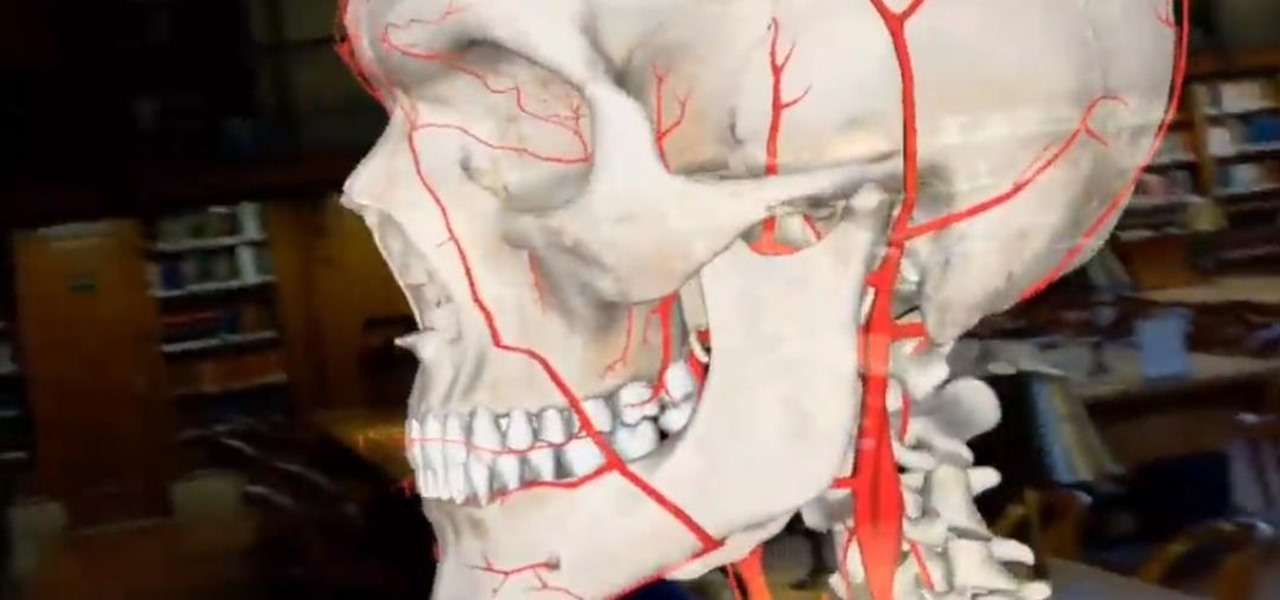
Not content to merely assist surgeons via the HoloLens, Medivis has expanded its augmented reality suite to Magic Leap One with an app for medical students.

The bacteria in our gut — a community called the gut microbiome — have been in the spotlight a lot lately. What we're learning about how our intestinal bacteria adapt and grow with our bodies could help athletes perform better, according to researchers starting a company focused on creating probiotics that mimic athletes' microbiomes.
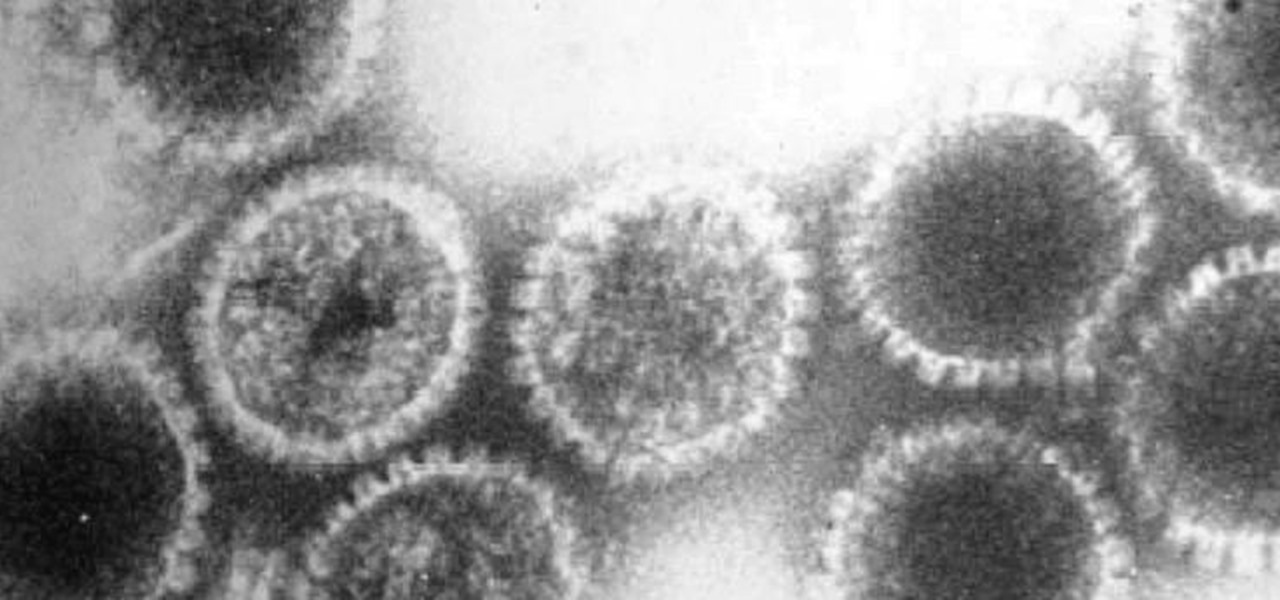
How can a drug used to treat cancer be effective against viruses, too? The answer lies in the drug's shared target — specifically, cellular components that control the activity of genes. A new research study showed that one such type of drug, histone methyltransferase inhibitors used in cancer clinical trials, has activity against herpes simplex virus, too.

Regarding foodborne pathogens, eating fish is not as hazardous as it was a few years ago — but if fins are on the menu, it's good to have a heads-up about what's good and what's bad these days.

For a company more associated with debugging computer programs, Google's parent company, Alphabet, is making a name for itself by taking on the real thing — mosquitoes.
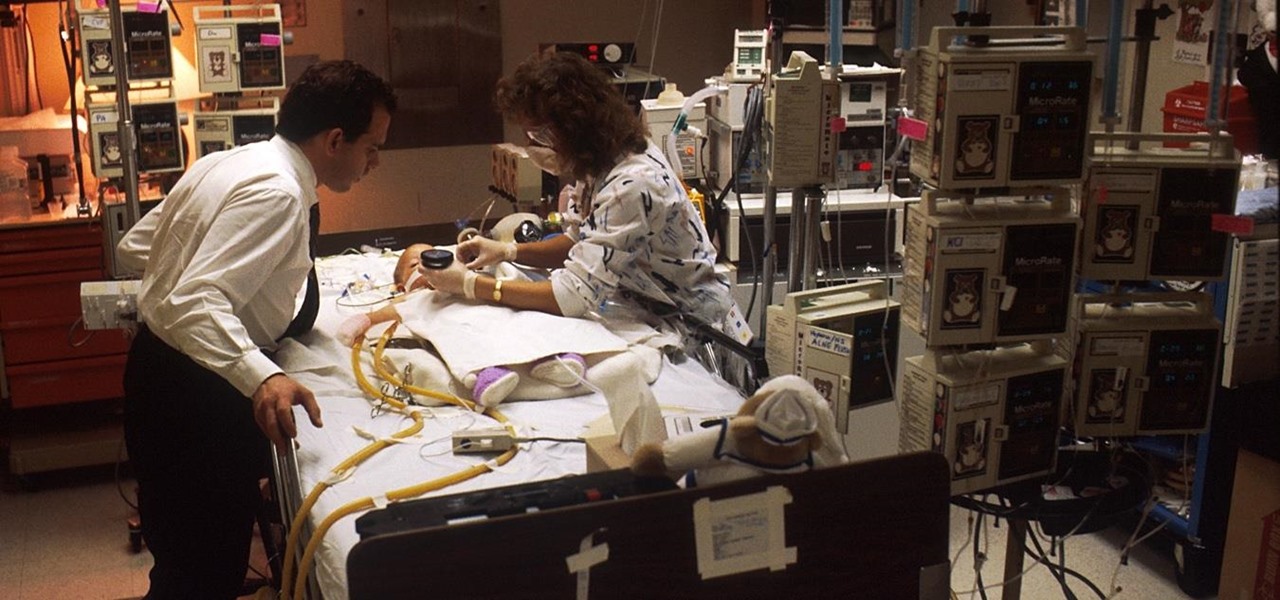
Twelve-year old Rory Staunton took a dive for a basketball during gym class and came up with a cut on his arm. The school nurse applied a couple of band-aids, without cleaning the cut, and off he went. In approximately three days, hospital physicians told his parents there was nothing else that they could do for their son; he was dead.

Montezuma's revenge, the runs, the trots, or just diarrhea — everyone gets it sooner or later. What exactly is diarrhea good for, if anything?

Alzheimer's disease — an irreversible, progressive brain disorder — is the sixth leading cause of death in the US and more than afflicts 5 million Americans. As if those numbers aren't scary enough, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention expect that number to nearly triple by 2050.
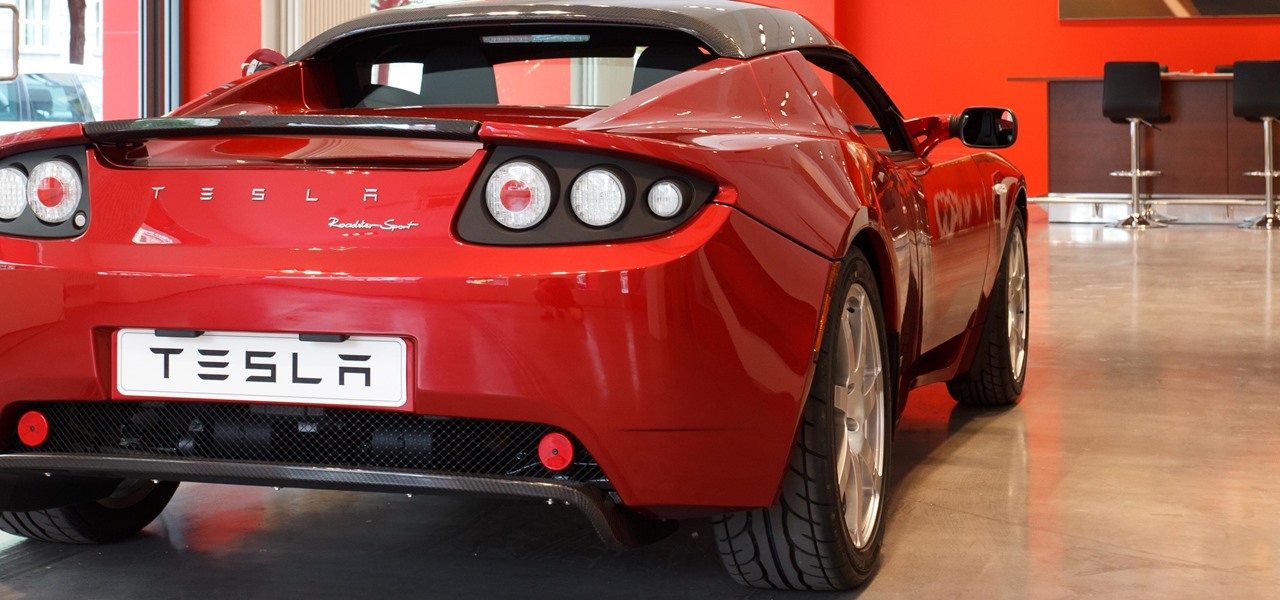

Demand for Tesla's driverless features as well as its ultra-long battery ranges and a reputation for offering the best-in-class electric car driving experience helped Tesla see a 32% surge in its value as a brand, topping out at $5.9 billion in the BrandZ Top 100 Most Valuable Global Brands study, released June 5.
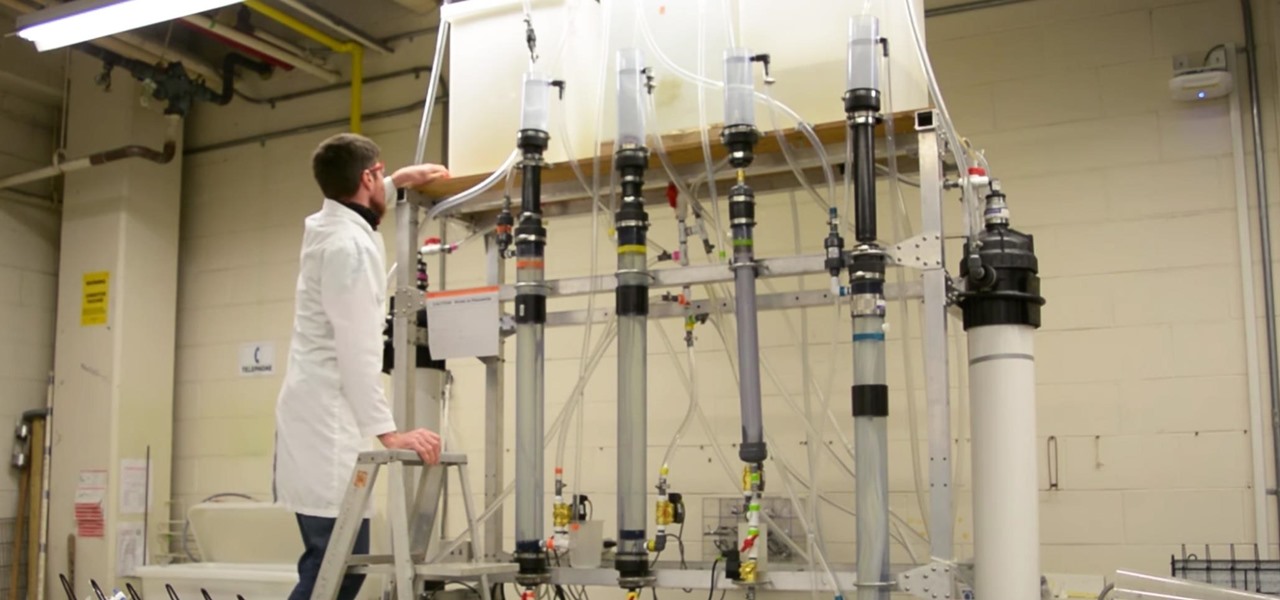

Water makes up about 60% of your body weight. Whether you like it plain, flavored, bubbly, or in beverages or food, we all need water daily to avoid dehydration and stay healthy. For communities in need of clean drinking water, new research using bacteria may offer a simplified, lower-cost method for boosting potable water supplies.

As summer mosquito season approaches, researchers are warning people with previous exposure to West Nile virus to take extra precautions against Zika. A new study found that animals with antibodies to West Nile in their blood have more dangerous infections with Zika than they would normally.
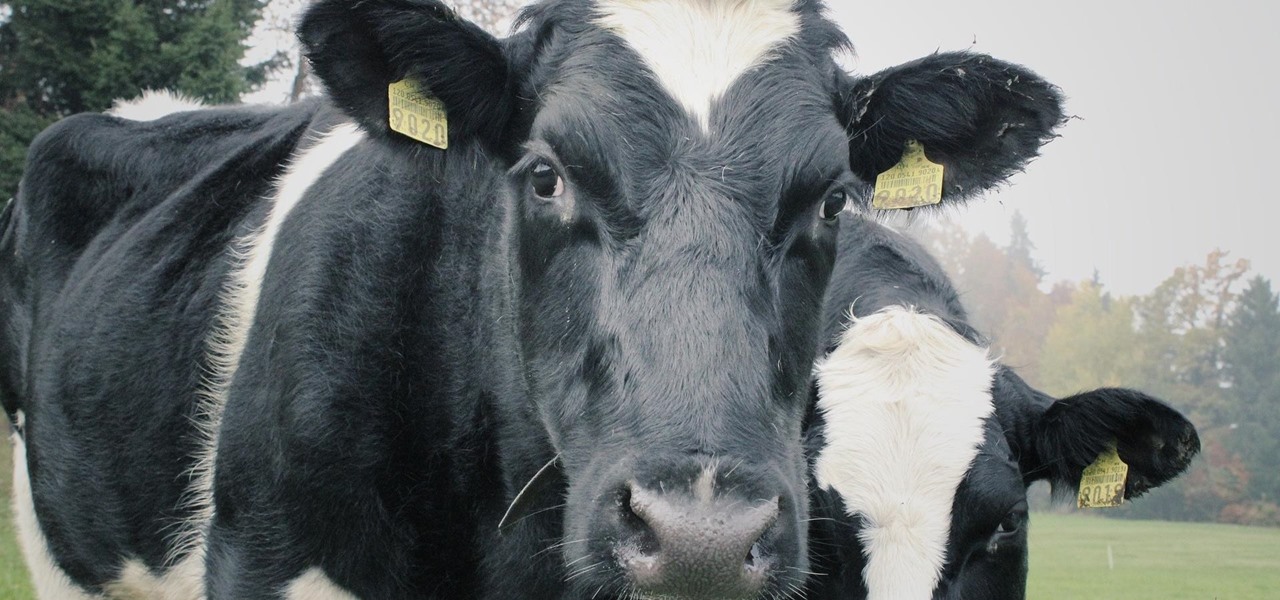

Antibiotics used to prevent diseases in livestock are creating a world of hurt for humans and the soil we depend on for food. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics is a global health issue. The overuse, underuse, and poor use of these life-saving drugs is rapidly removing them as a treatment option for serious infections in humans—plus bacteria are naturally adaptive.
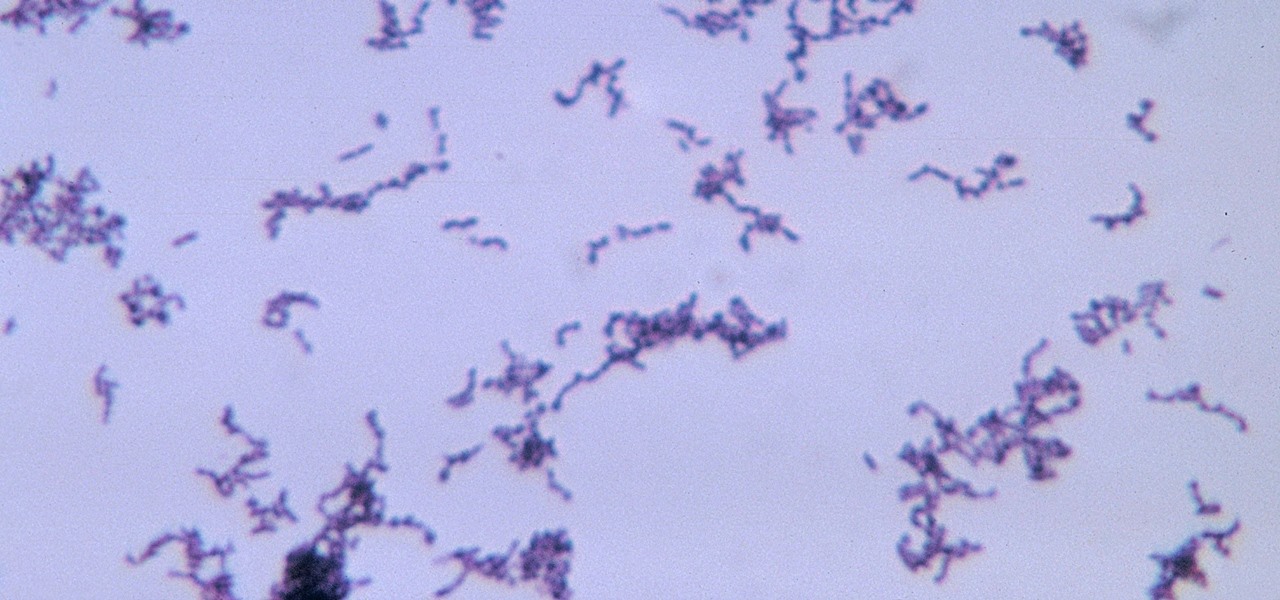
The squiggly guys in this article's cover image are Propionibacterium acnes. These bacteria live in low-oxygen conditions at the base of hair follicles all over your body. They mind their own business, eating cellular debris and sebum, the oily stuff secreted by sebaceous glands that help keep things moisturized. Everybody has P. acnes bacteria—which are commonly blamed for causing acne—but researchers took a bigger view and discovered P. acnes may also play a part in keeping your skin clear.

To keep fungal pathogens at bay in their crowded homes, wood ants mix potions to create powerful protection for their nest and their young.
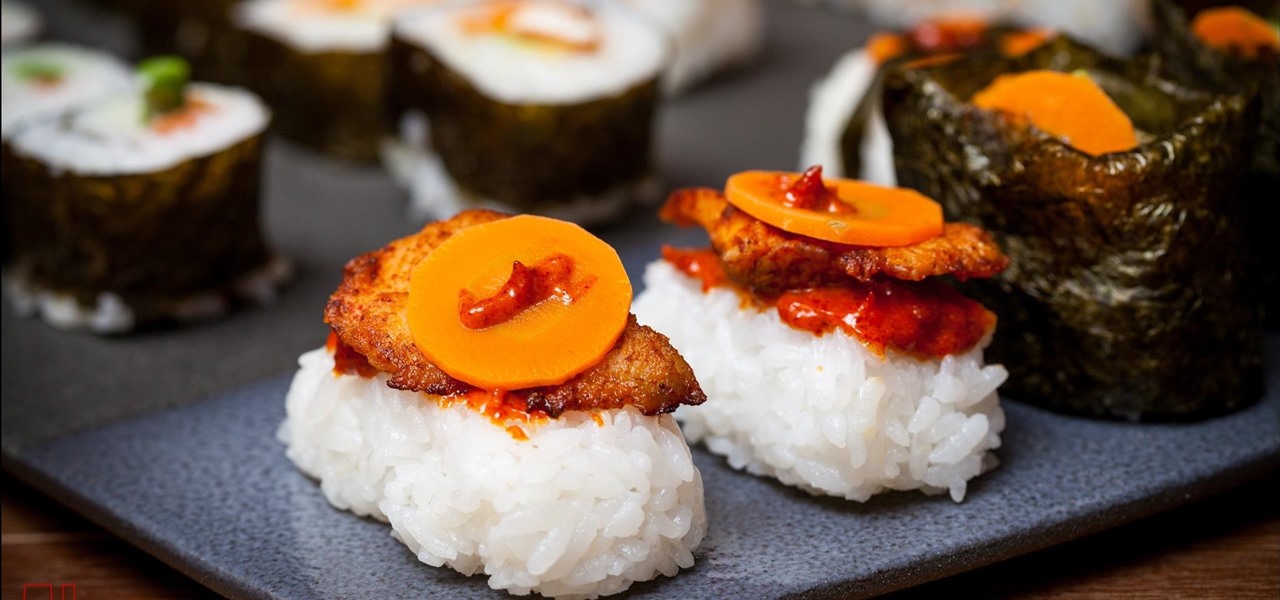

Augmented reality seems to be the talk of the town lately, with everything from glasses to furniture stores prepping to implement exciting, new AR technology. Well now, it looks like even our food is getting a makeover for the augmented reality future.

In the past, infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) commonly led to dementia as the virus made its way to the brain. Even in effectively treated people, HIV can hide out and replicate in places like the brain, where it's tough to detect. That's why it's very concerning that half of all HIV-infected patients still report cognitive problems.
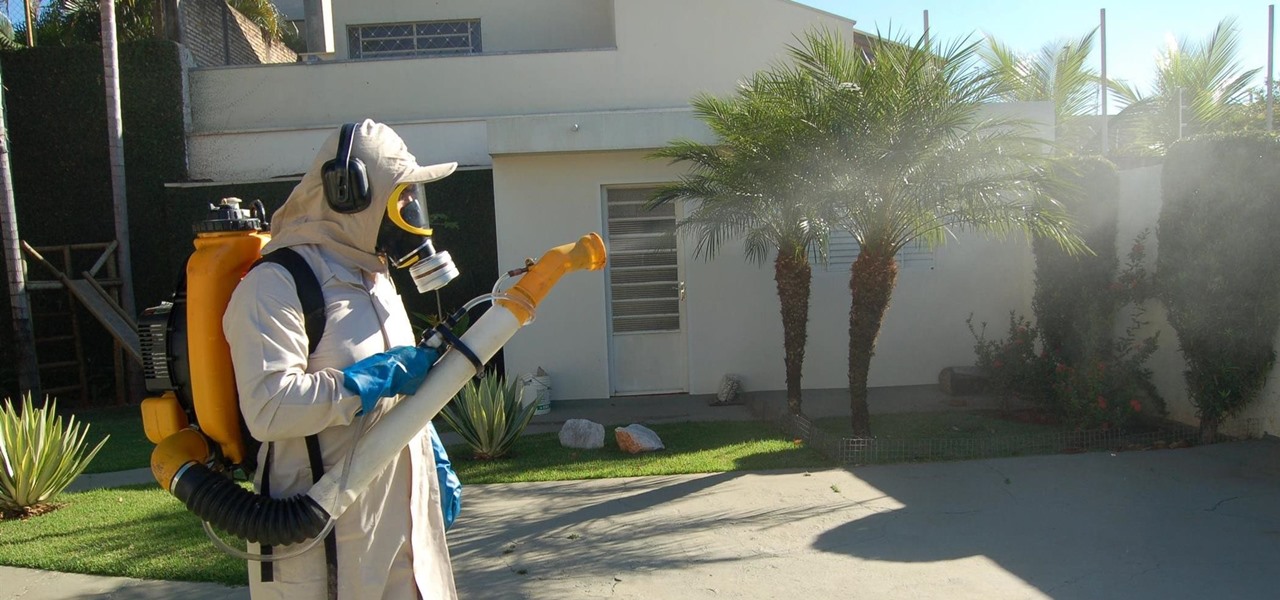

Even as health authorities describe the symptoms of Zika infection in the general population as mild, a new surveillance study finds serious side effects are more common, and serious, than previously thought.
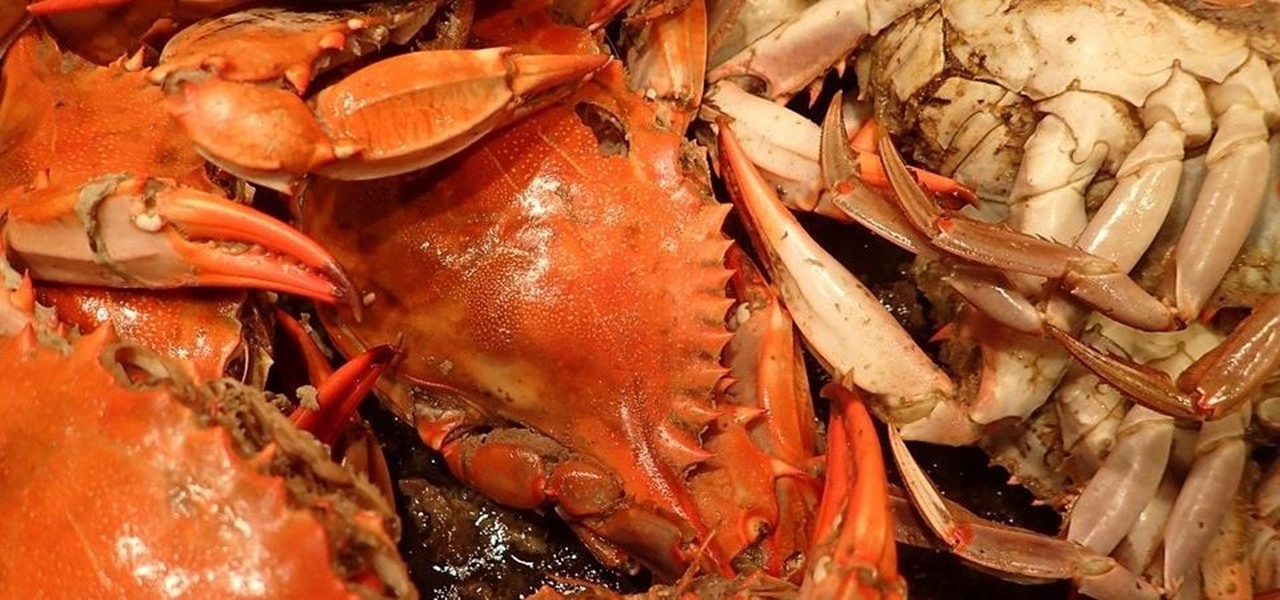

A robust appetite for imported foods is leading to increased disease outbreak in the US. Despite the locovore and slow food movements, America's demand for foreign foods is picking up. According to a study published in the journal of Emerging Infectious Diseases, demand for imported fresh fruits, vegetables, and seafoods has jumped in recent years.
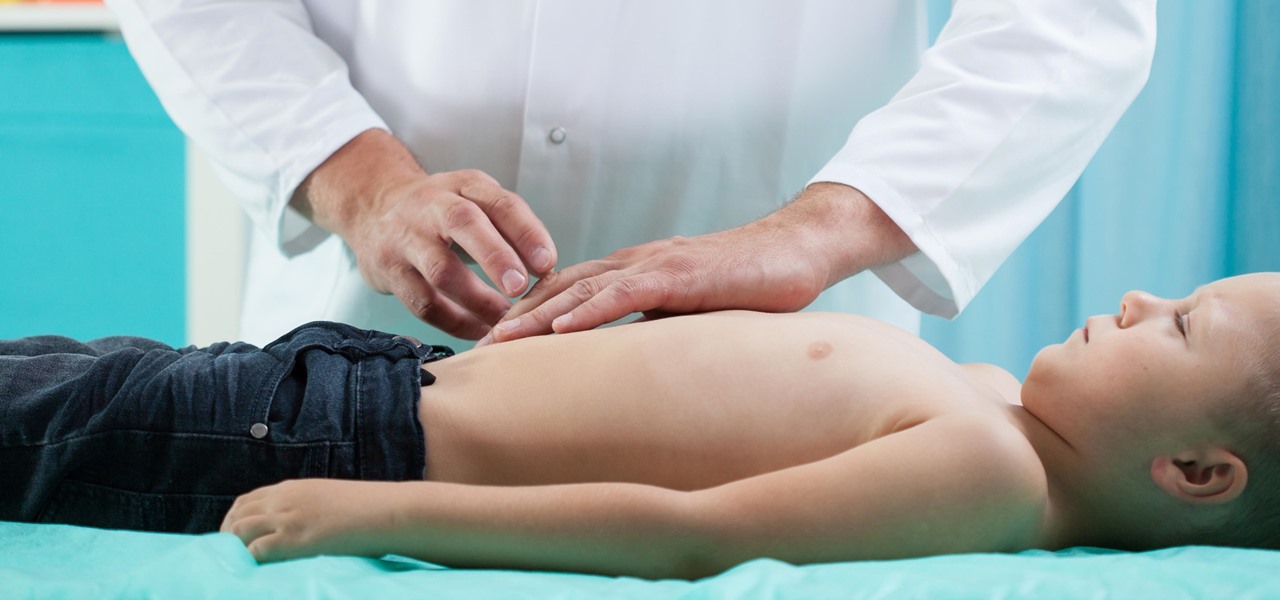
A new study confirms that antibiotics can prevent surgical intervention if your child's appendix becomes inflamed, potentially saving his or her life.
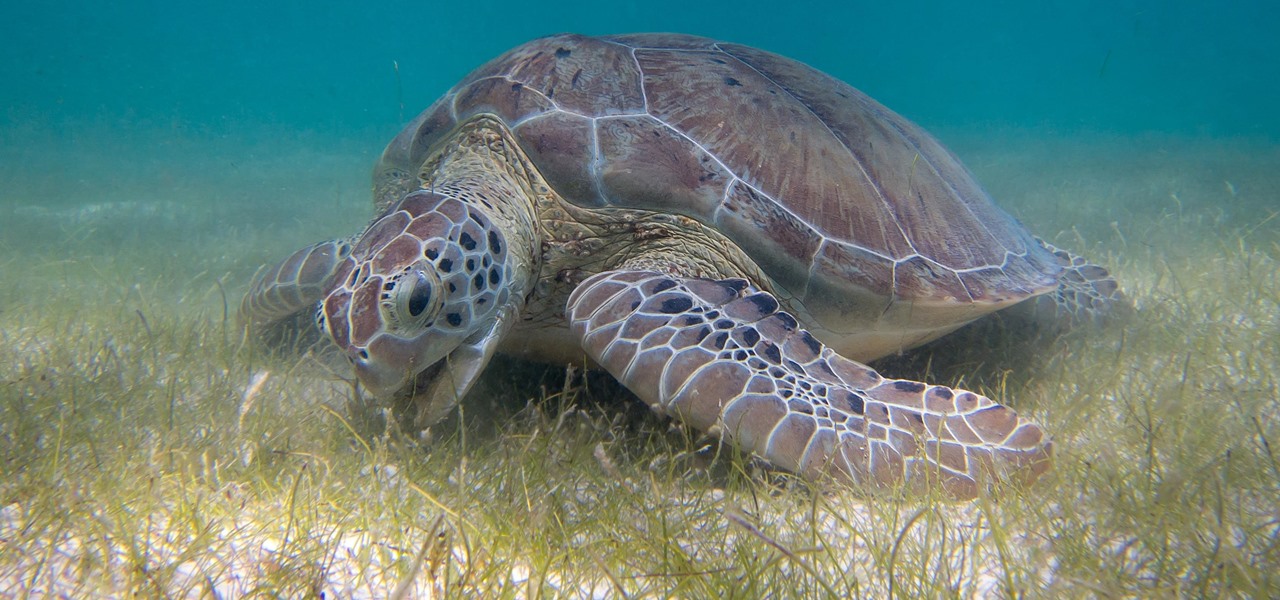

Seagrass may help your favorite beach stay a little less toxic. A new study, led by Joleah Lamb, a postdoctoral researcher in the Harvell Lab at Cornell University, found that coastal seagrasses reduce levels of pathogens dangerous to humans and marine organisms in near-shore waters.
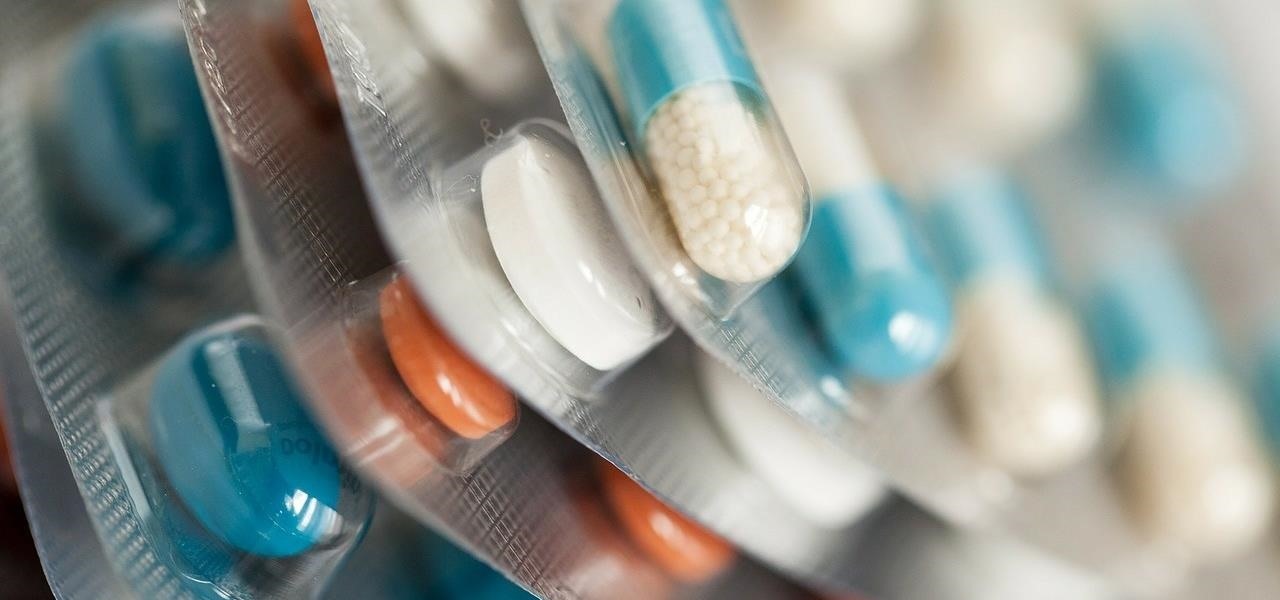
Although their effectiveness is waning, antibiotics remain a front-line defense against many infections. However, new science reveals using the wrong antibiotic for an infection could makes things much worse.
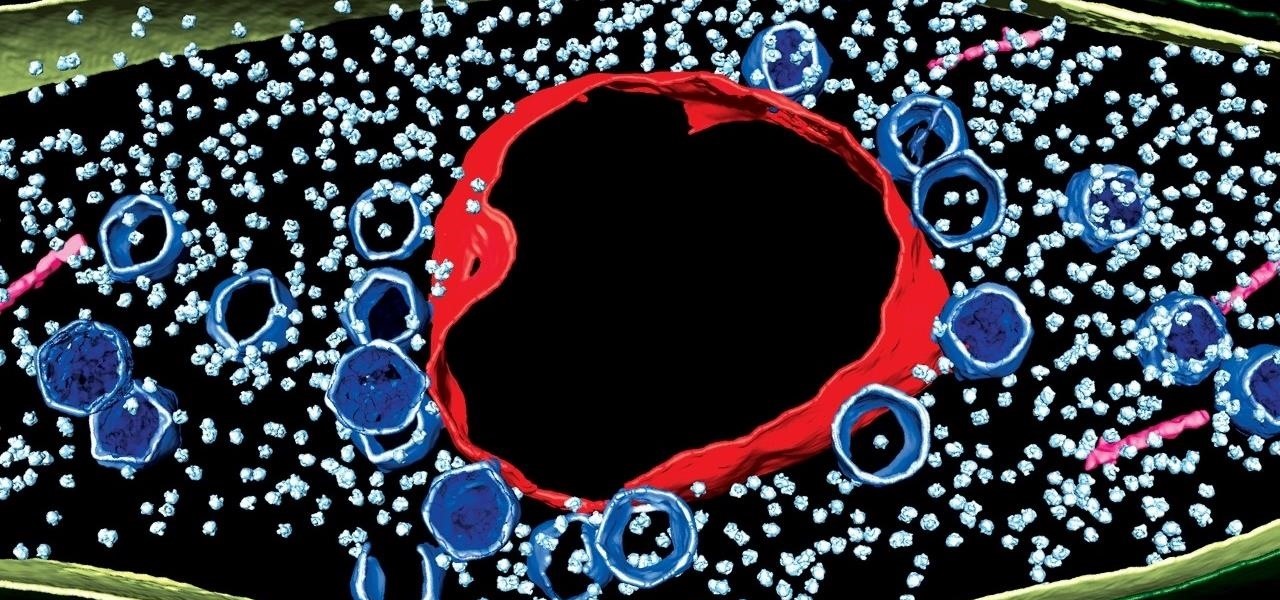
Using extreme time-lapse microscopy, scientists watched a virus take over a bacteria to create a cell that looked and functioned more like a plant or animal cell. True story.

Despite the availability of a vaccine against it, almost 50% of men aged 18-59 in the US are infected with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Why?
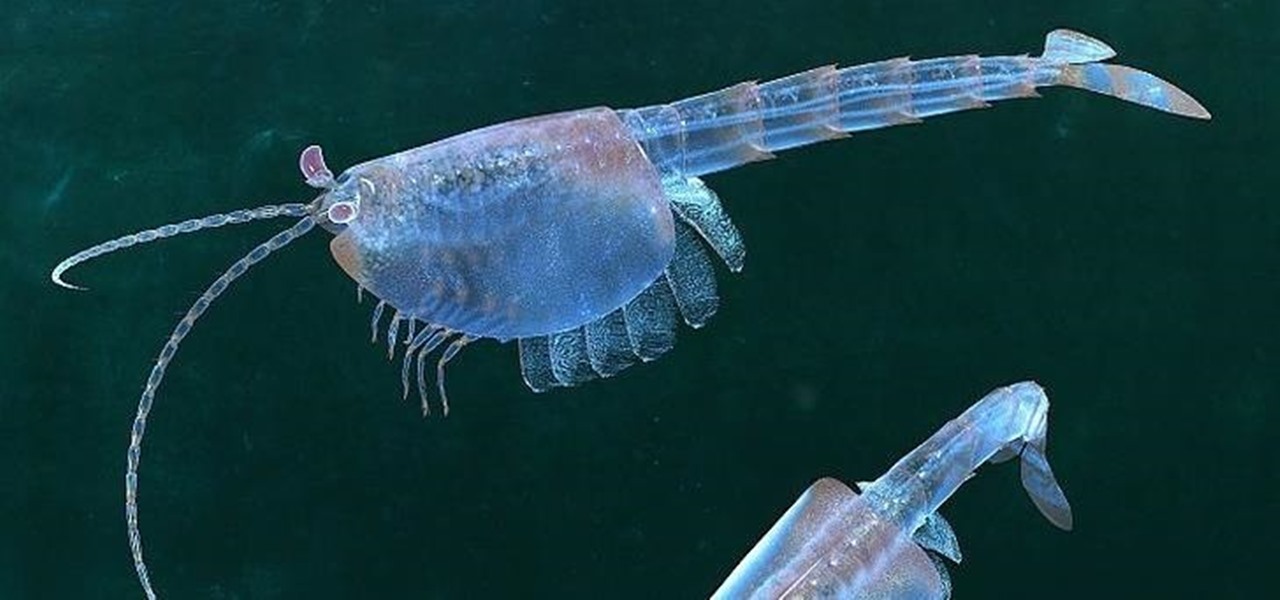

To shine light on the future of the relationship between humans and viruses, a team of researchers from the University of Oxford looked into the dim and distant past.

Specialized cells in the lining of the gut may provide a key to preventing an infectious brain disease caused by misfolded proteins.
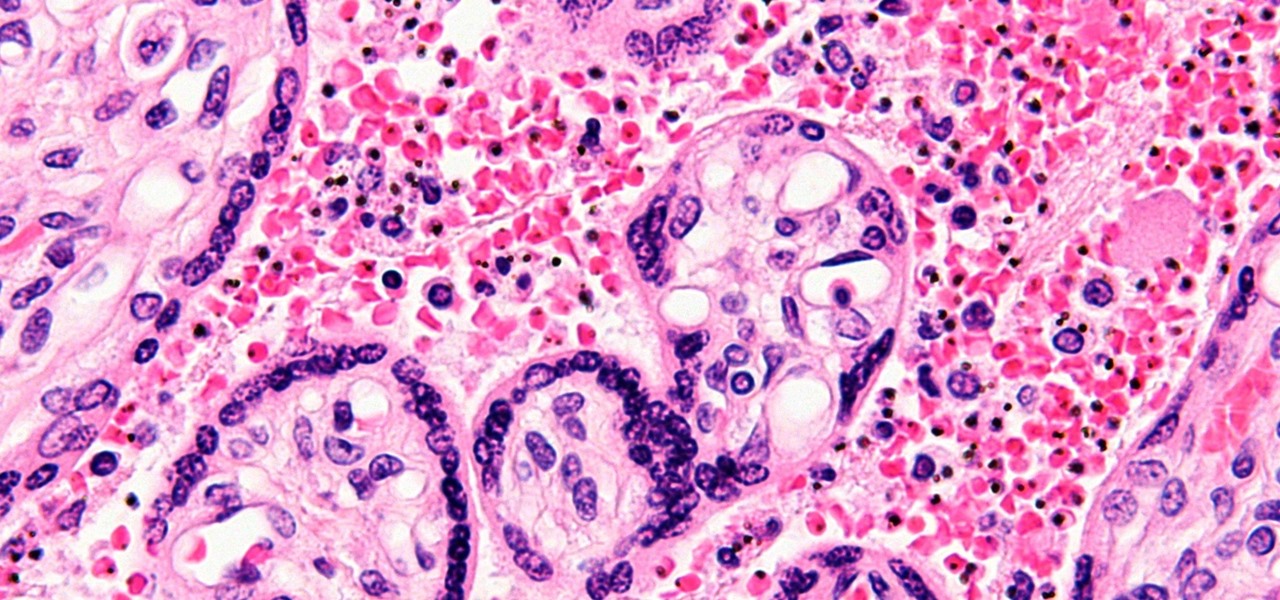
You might feel the bite, you might not, but an infected mosquito has injected you with a parasite named Plasmodium falciparum, a single-cell protozoa that quickly takes up residence in your body.

As many of you know, I have been running a couple of series here on Null Byte about digital forensics called Digital Forensics for the Aspiring Hacker and Digital Forensics Using Kali. Although many readers have seemed to enjoy these series, just as many seem to be pondering, "Why should I study digital forensics?"

From day to day, it can be difficult to remember everything that's required of you. I tend to forget exactly where it is I'm supposed to be during my busiest moments, and it's even easier to delete each day's events out of your brain when there's so much else that dominates your mind. Yet taking the time to remember exactly what it is that happens during each of our days can be a vital part of our memory—and with nothing more than 15 minutes, we can strengthen our brains and remember more tha...

Whether you're a serious, sweating athlete or just need to recover after a night of drinking, chances are you've replenished your body's fluids with a sports drink at some point. Those electrolytes aren't the only thing entering your systems, though. Sports drinks are sugary, sweet, and loaded with calories—but there's a way you can still recharge your body without ingesting the unhealthy additives.

We tend to assume that eating is mostly a physical act, but the mind has so much to do with the choices we make.