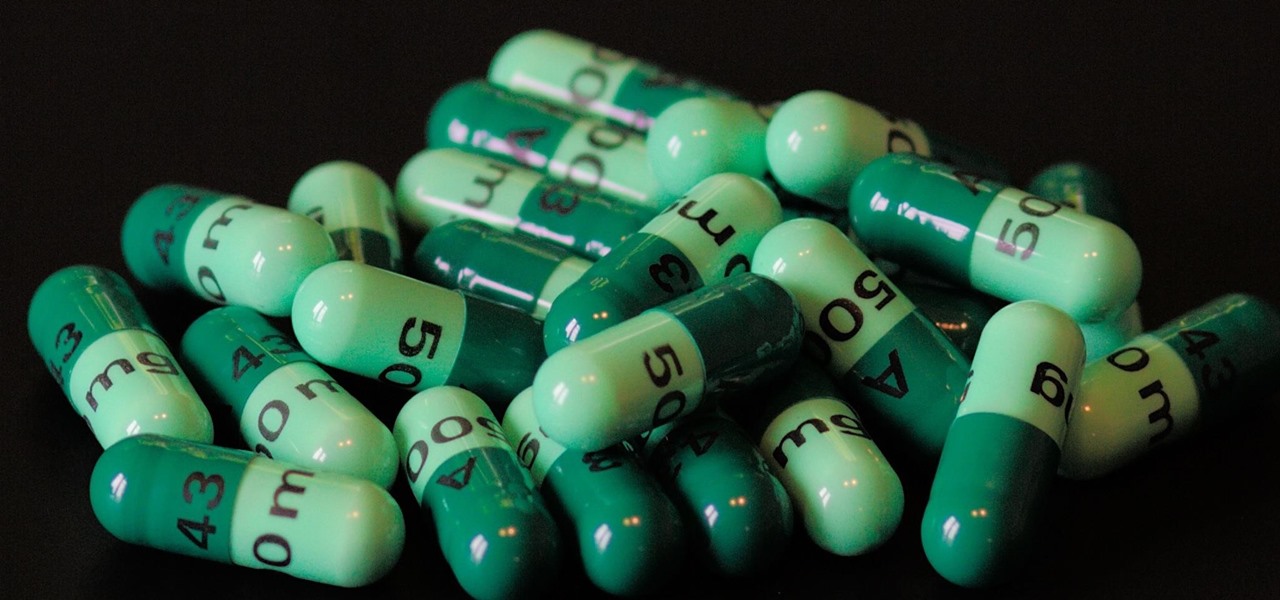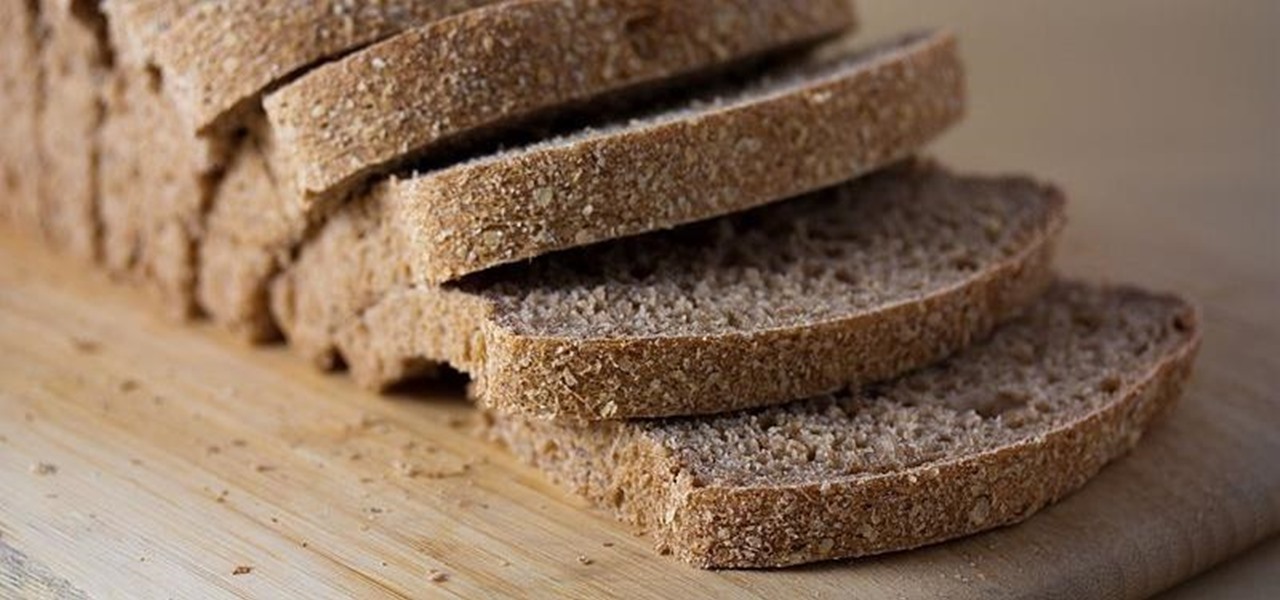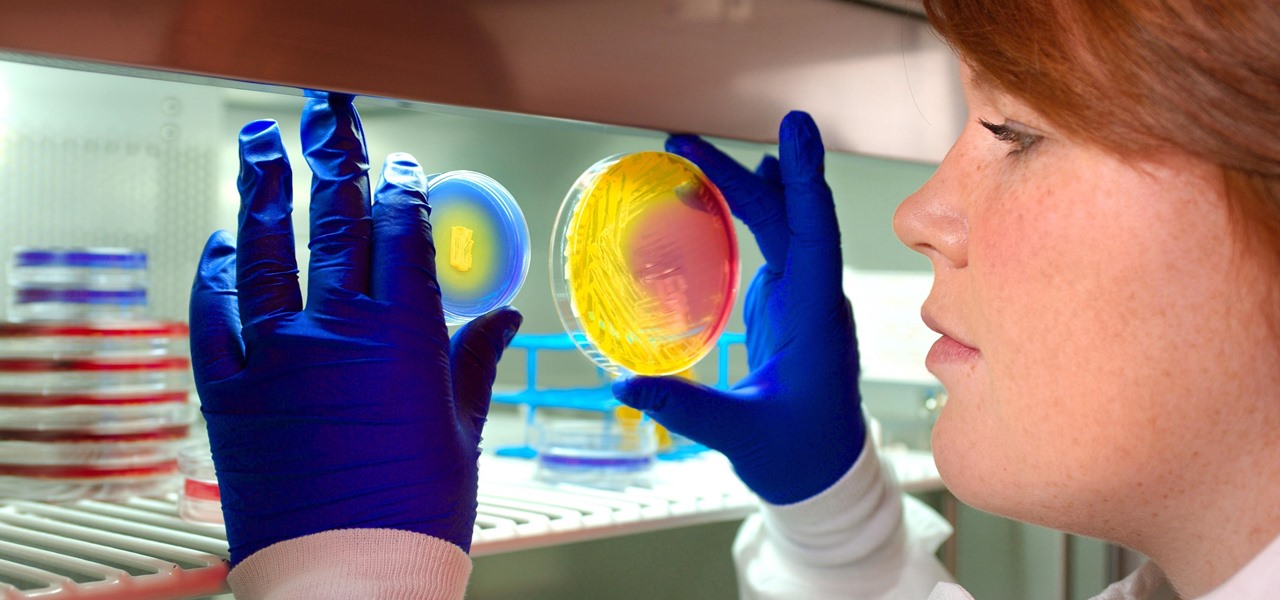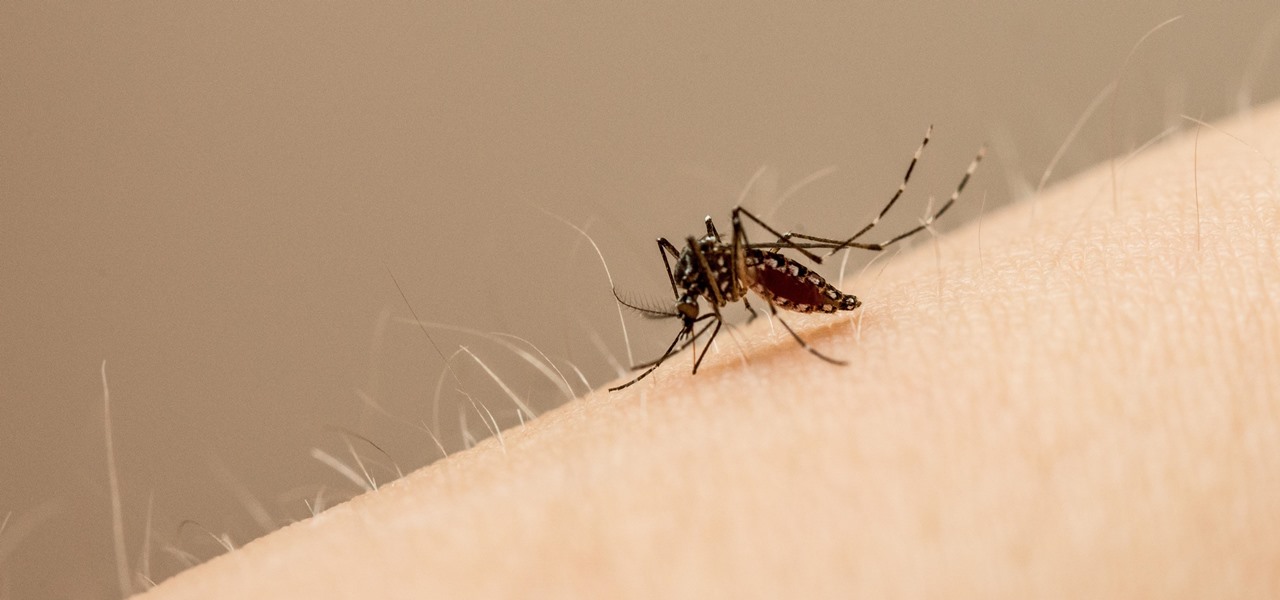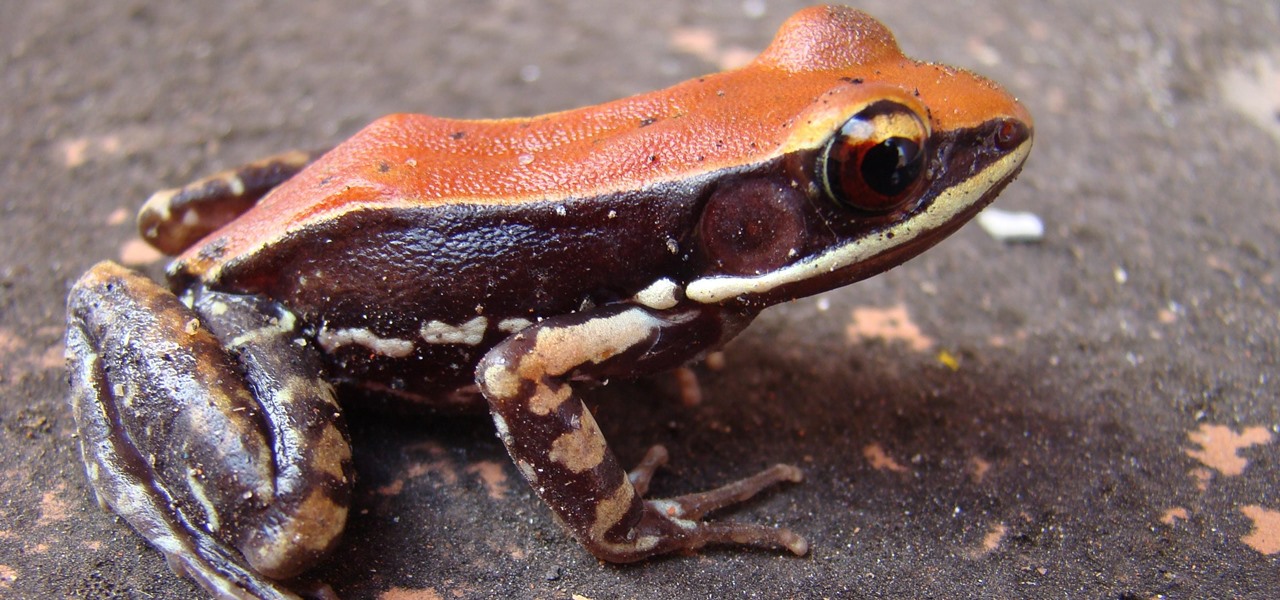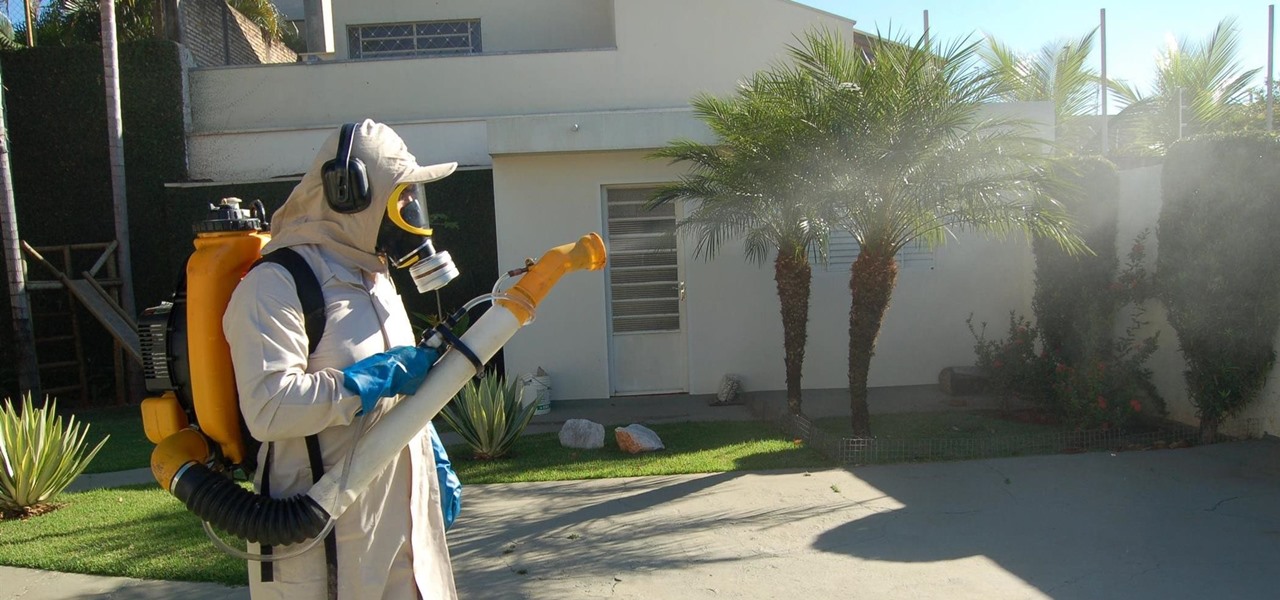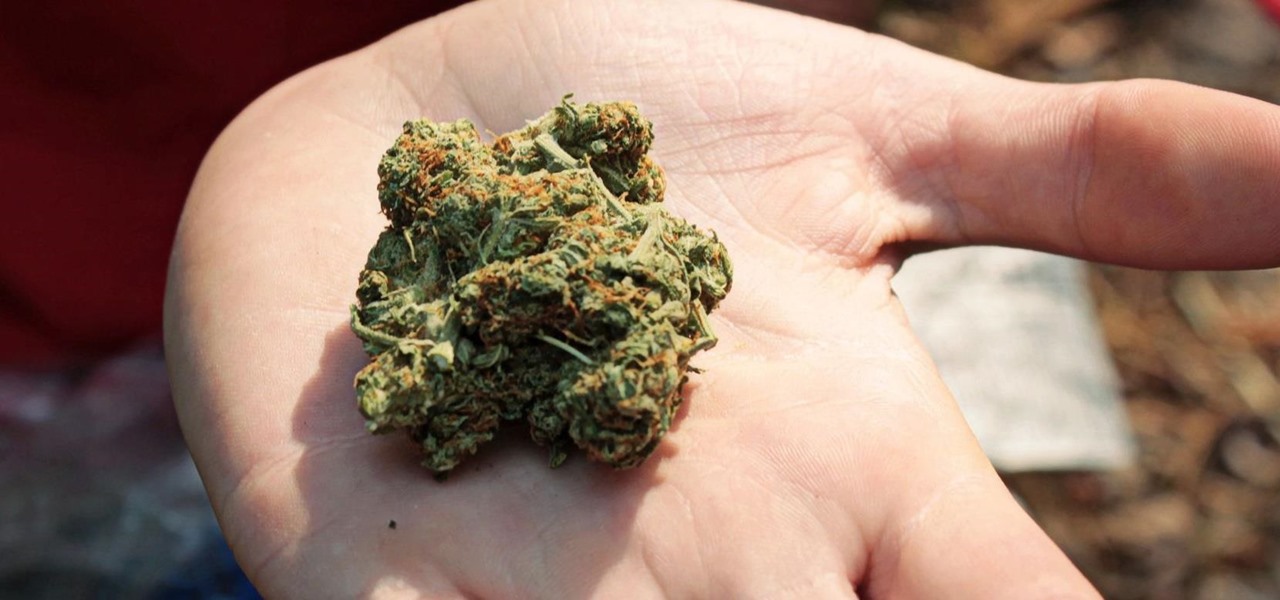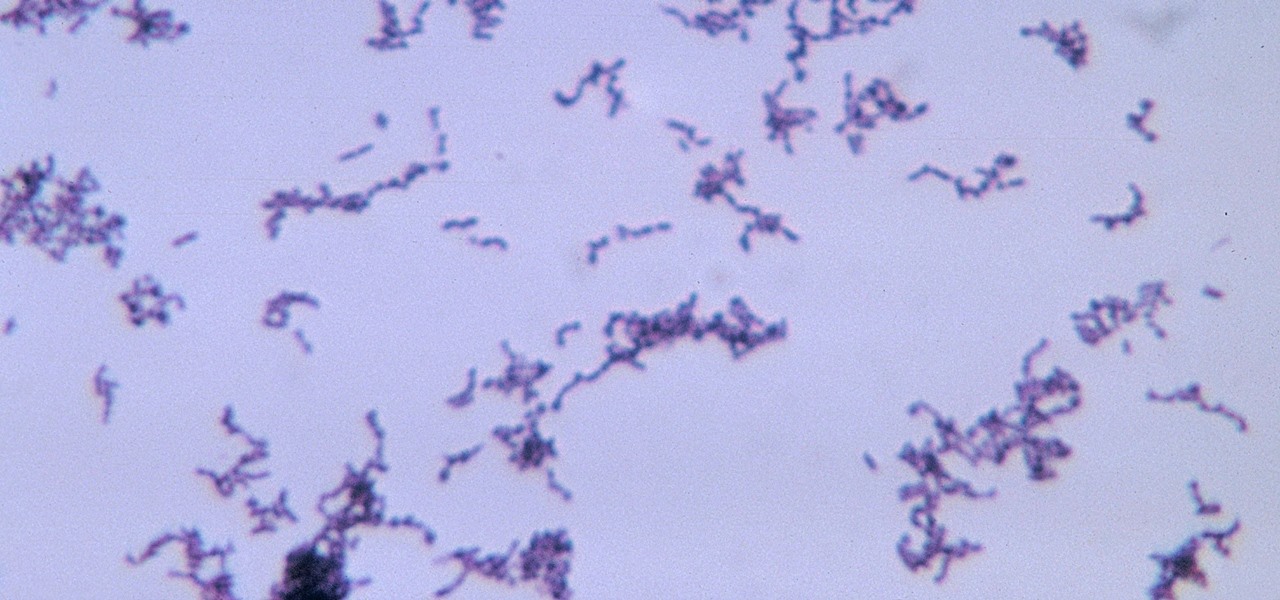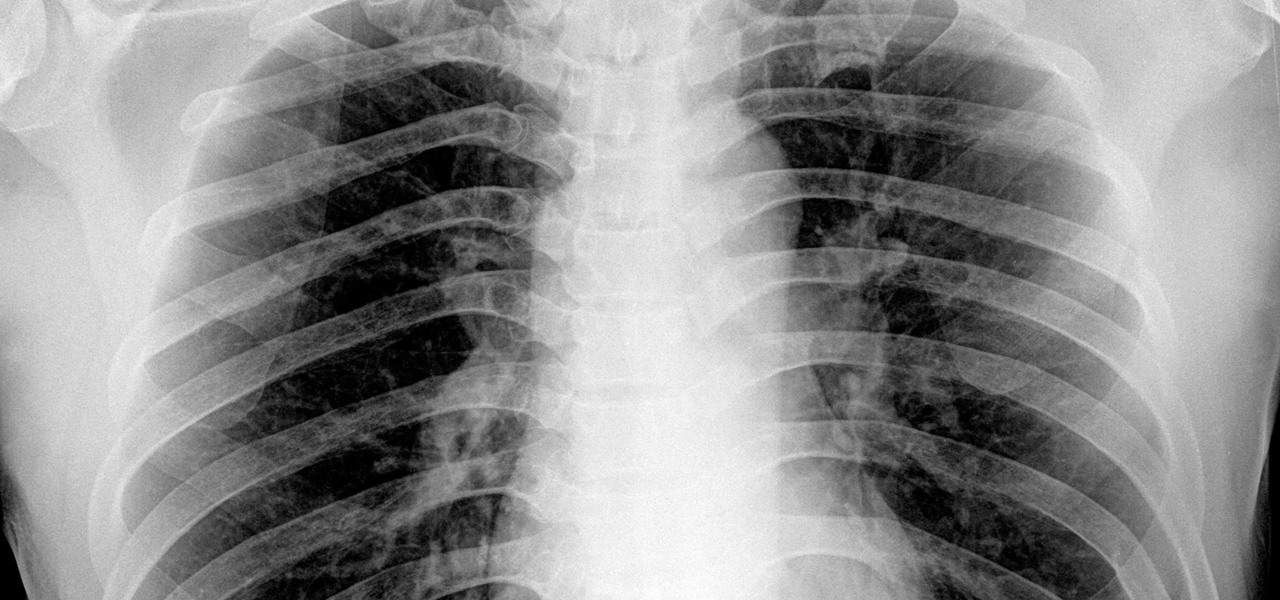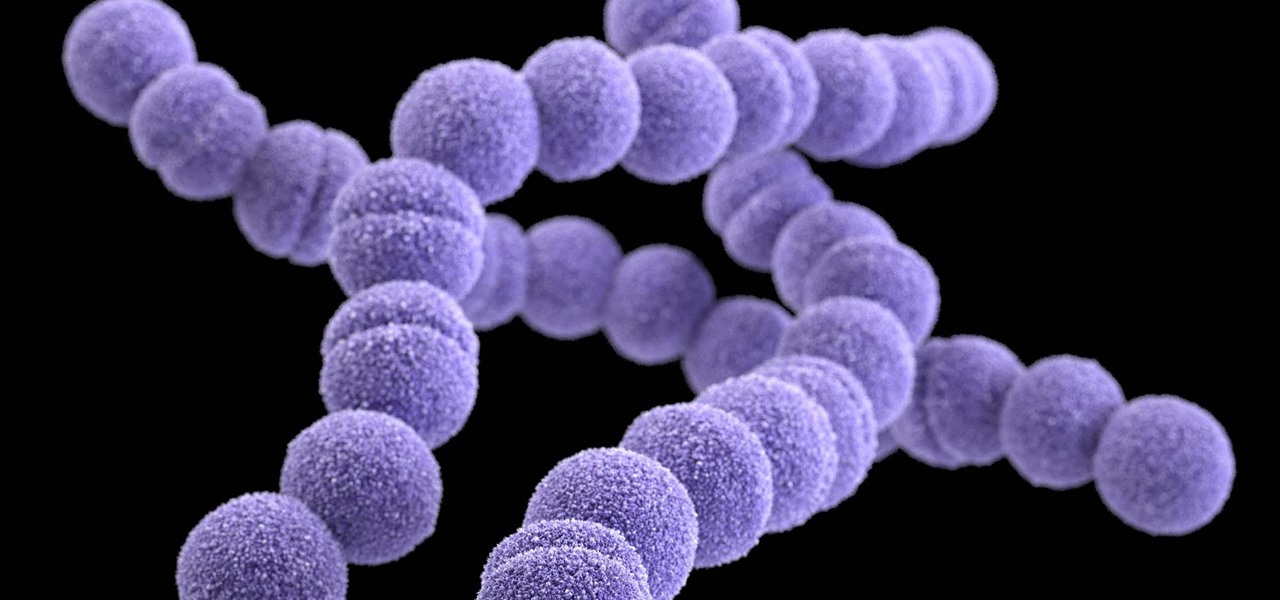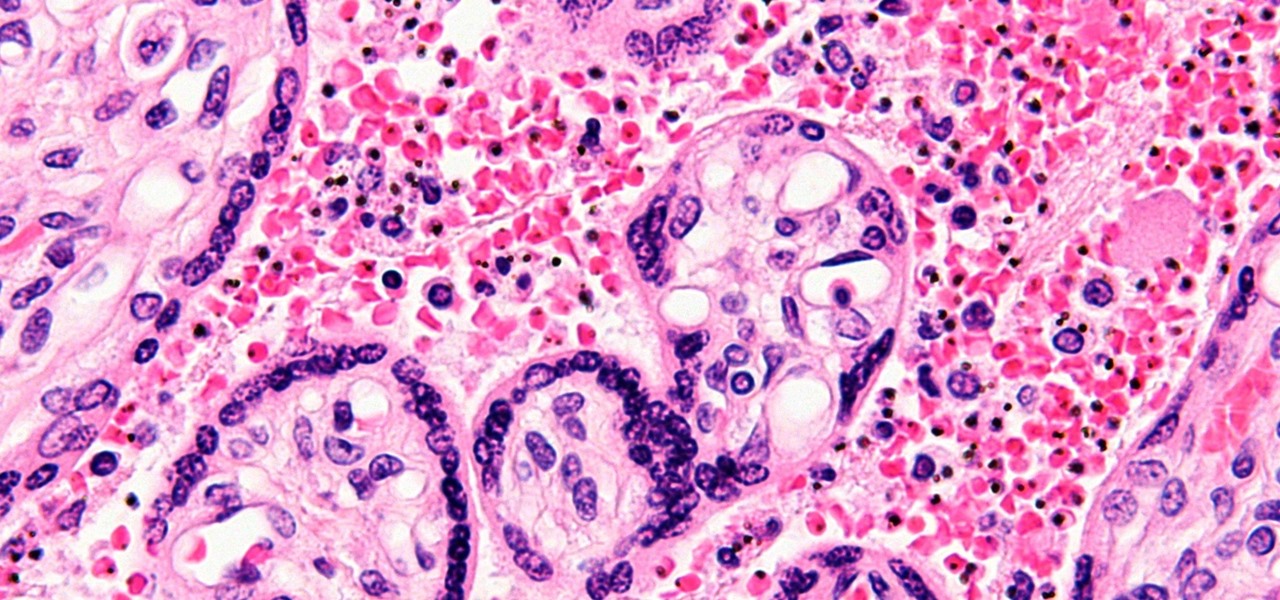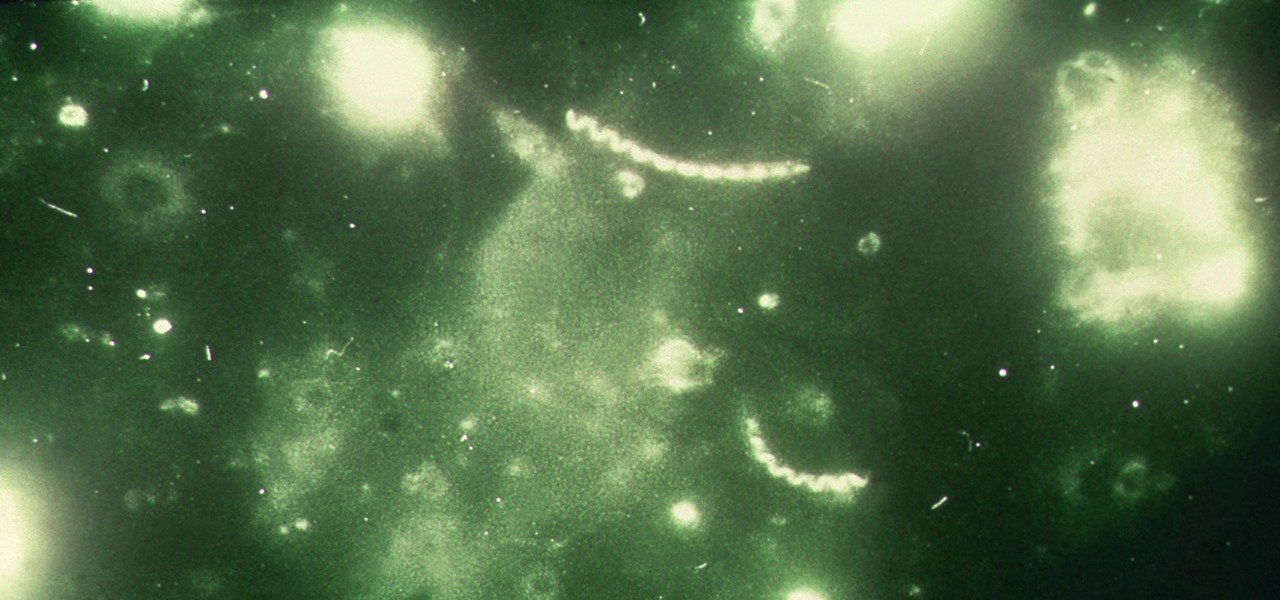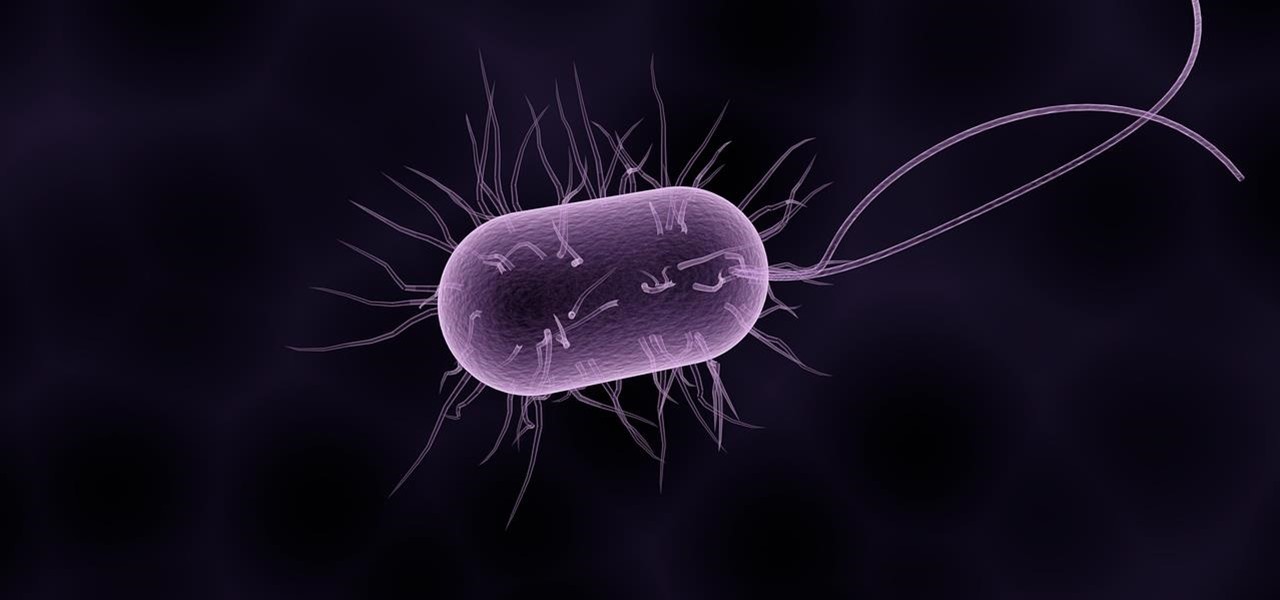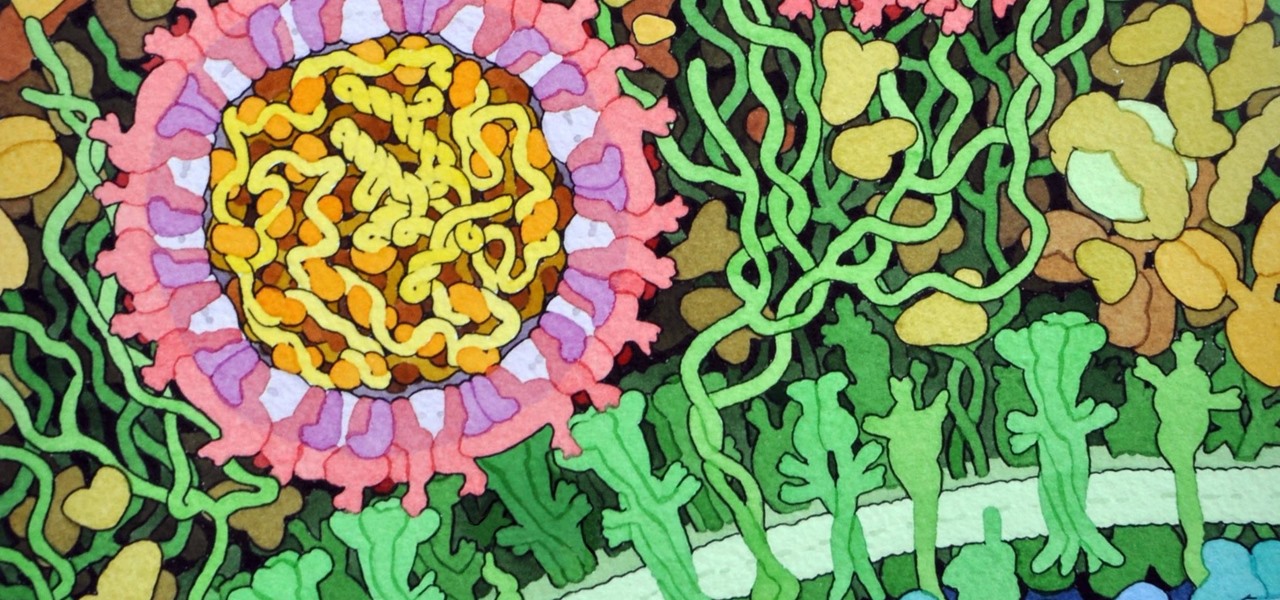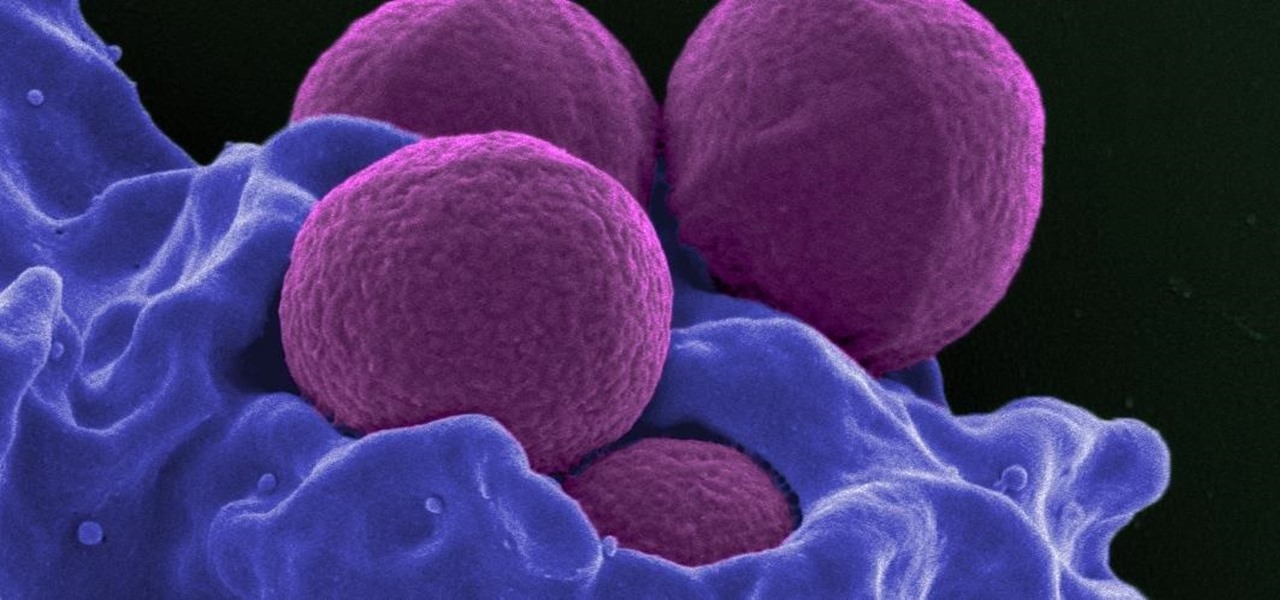
Staphylococcus aureus is a widespread bacteria — about a third of us have it on our body right now — usually in our nose or on our skin. And it probably isn't causing an infection. But, about 1% of people who have Staphylococcus aureus present have a type that is resistant to the antibiotic methicillin.

When you think about preparing for an internship, I'm sure your first thought is to go shopping for professional outfits or to brush up on technical skills. While that's all important, there's so much more for you to think about.

The herpes simplex virus (HSV) can cause devastating complications for infected newborns whose mothers have genital herpes. Understanding risk and research can help you, and your baby, when the time comes.
More bad news for patients who have undergone heart surgery in the past five years. A new study suggests about one-third of heater-cooler units used in cardiac procedures remain contaminated with a slow-growing, potentially fatal bacteria.
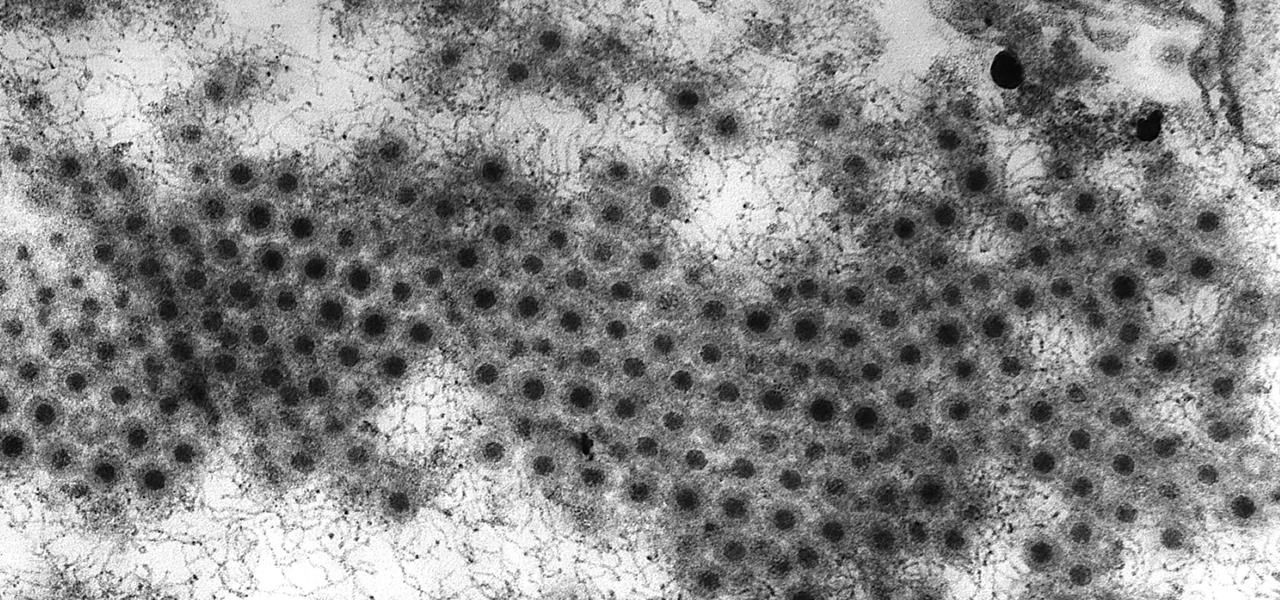
Coronaviruses are common viruses, and most of us catch one at some point — they cause about 30% of all common colds. A new accidental discovery could help fight these viruses, even the deadlier, emerging ones.

Bone loss and belly fat may no longer be certain fates of menopause, thanks to new research from an international team of scientists.

Despite the threat of superbugs, physicians continue to prescribe antibiotics when they might not be needed, and patients are suffering.

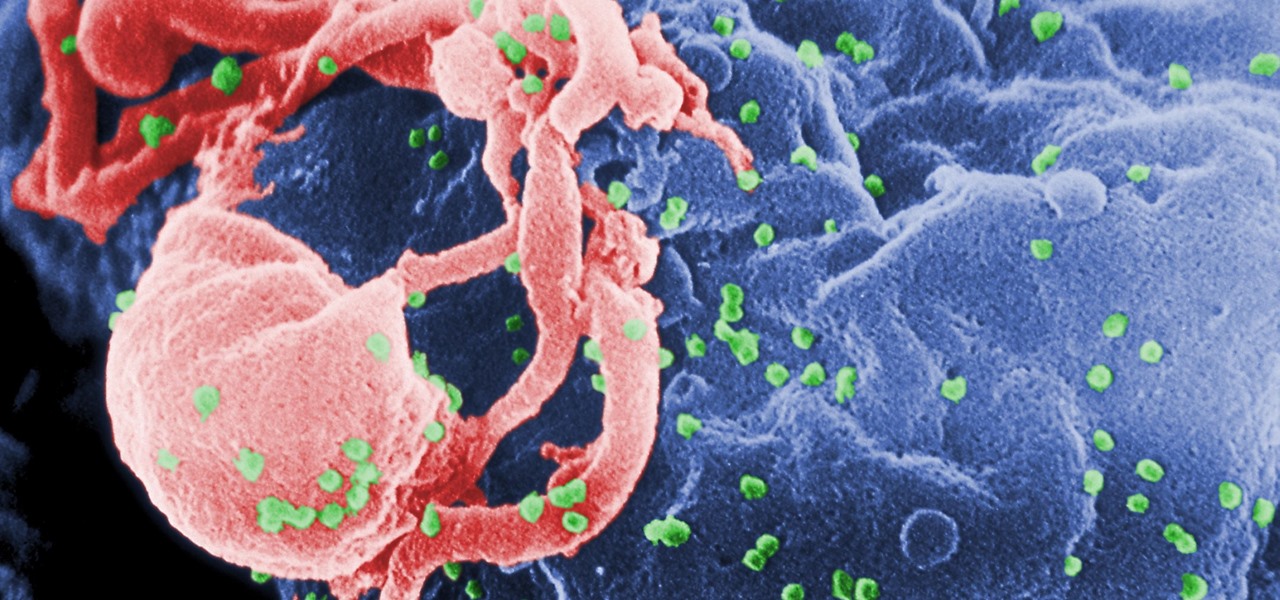
HIV infections persist despite treatment that successfully decreases viral blood levels to the point where doctors can't detect the virus. But that doesn't mean the person is cured. The virus hides in the body, not replicating, just waiting for a chance to jump out of the shadows and reemerge.

Move over whole wheat — white bread may be back in style after a new study shows that it may be your gut microbes that decide what kind of bread is best for you.

Listeria monocytogenes bacteria don't play fair. Healthy people can usually handle the food-borne infection, but the bacterial infection hits pregnant women, fetuses and cancer patients very hard. Interestingly, a new study found that other bacteria may help prevent Listeria infections in those people.

Most of us have already had an encounter with the Epstein-Barr virus, or EBV, for short. As part of the herpes family, it's one of the most common disease-causing viruses in humans. We get the disease with (or without) some nasty symptoms, then we recover. However, EBV stays in our body after the illness has ended, and it's one of the few viruses known to cause cancer.

As researchers from Yale searched our environment for compounds to aid in the battle against drug-resistant bacteria, they got an unlikely assist from ticks.

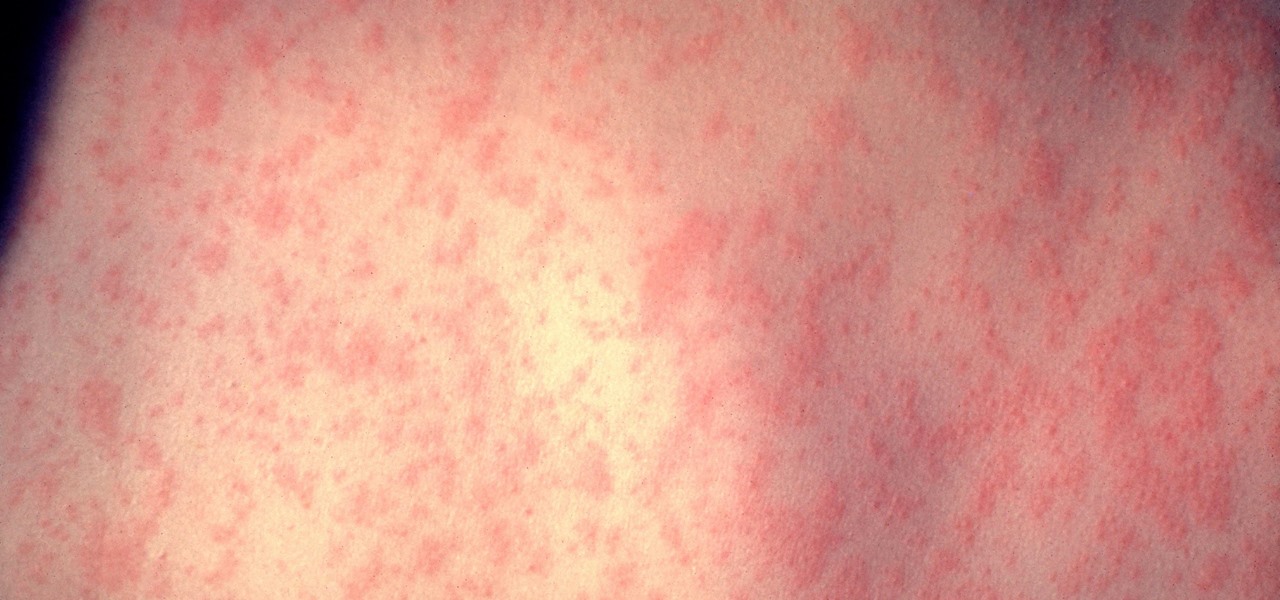
In the worst measles outbreak in the state since 1990, the Minneapolis Department of Heath races to contain the spread of an infection believed to have originated from an infected traveler. Mistaken attitudes and unvaccinated travelers are creating a world of hurt and disease for Americans. A recent study found that more than half of eligible travelers from the US are electing to skip their pre-trip measles vaccine.

Being infected with HIV means a lifetime of antiviral therapy. We can control the infection with those drugs, but we haven't been able to cure people by ridding the body completely of the virus. But thanks to a new study published in Molecular Therapy by scientists at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine (LKSOM) at Temple University and the University of Pittsburgh, all that may change.

Colorado State University scientists have developed new tech that quickly identifies the presence of Zika virus in mosquito populations — and in human body fluid.

Our quest to find novel compounds in nature that we can use against human diseases —a process called bioprospecting — has led a research team to a small frog found in India. From the skin slime of the colorful Hydrophylax bahuvistara, researchers reported finding a peptide — a small piece of protein — that can destroy many strains of human flu and can even protect mice against the flu.

Viral infections have been the focus of attention in the development of autoimmune diseases—diseases where the body's immune system reacts to the body's own cells—because they trigger the immune system into action.

The squiggly guys in this article's cover image are Propionibacterium acnes. These bacteria live in low-oxygen conditions at the base of hair follicles all over your body. They mind their own business, eating cellular debris and sebum, the oily stuff secreted by sebaceous glands that help keep things moisturized. Everybody has P. acnes bacteria—which are commonly blamed for causing acne—but researchers took a bigger view and discovered P. acnes may also play a part in keeping your skin clear.

To keep fungal pathogens at bay in their crowded homes, wood ants mix potions to create powerful protection for their nest and their young.

Most females have had at least one urinary tract infection in their lifetimes. Recurrent UTIs are particularly problematic in young, sexually active women, where about 80% of the infections are caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli, better known as E. coli.

Yellow fever has emerged again in Brazil, causing death and disease to people unprepared for this mosquito-borne illness.

In the past, infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) commonly led to dementia as the virus made its way to the brain. Even in effectively treated people, HIV can hide out and replicate in places like the brain, where it's tough to detect. That's why it's very concerning that half of all HIV-infected patients still report cognitive problems.

Even as health authorities describe the symptoms of Zika infection in the general population as mild, a new surveillance study finds serious side effects are more common, and serious, than previously thought.

Hospitals are places we go to get well, and we don't expect to get sick or sicker there. But a study from researchers at the Cleveland Clinic, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, and Cleveland VA Medical Center in Ohio found that hospital floors in patient rooms were frequently contaminated with healthcare-associated pathogens—often dangerous multi-drug resistant bacteria.

By looking for the mechanism that allows influenza A to invade lung cells, scientists also discovered a treatment that might block the virus from taking hold there.

Marijuana is legal to use for medical purposes in 28 states and the District of Columbia, but the quick development of this new industry could have left some regulation issues in the lurch.

Even if your cat drives you a little nuts, don't worry, because a new study says that cats pose no risk to your mental health.

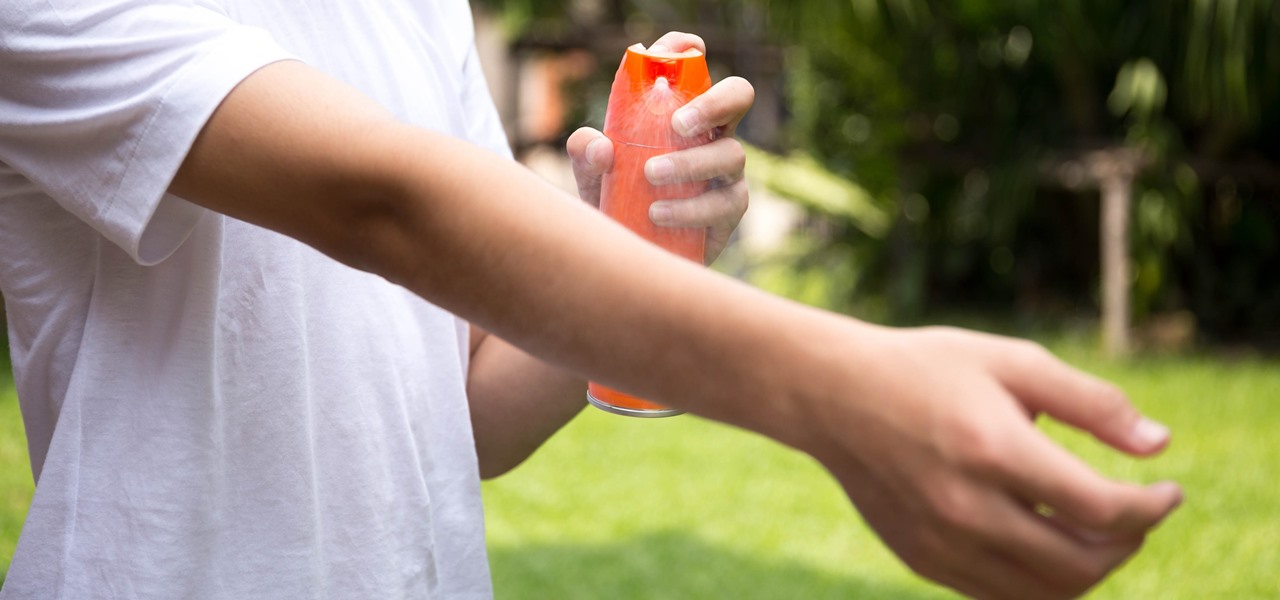
Responding to the emergence of Zika in the US, researchers investigated what type of repellent works best to reduce your odds of a mosquito bite from Aedes aegypti, the mosquito species that spreads the Zika virus.

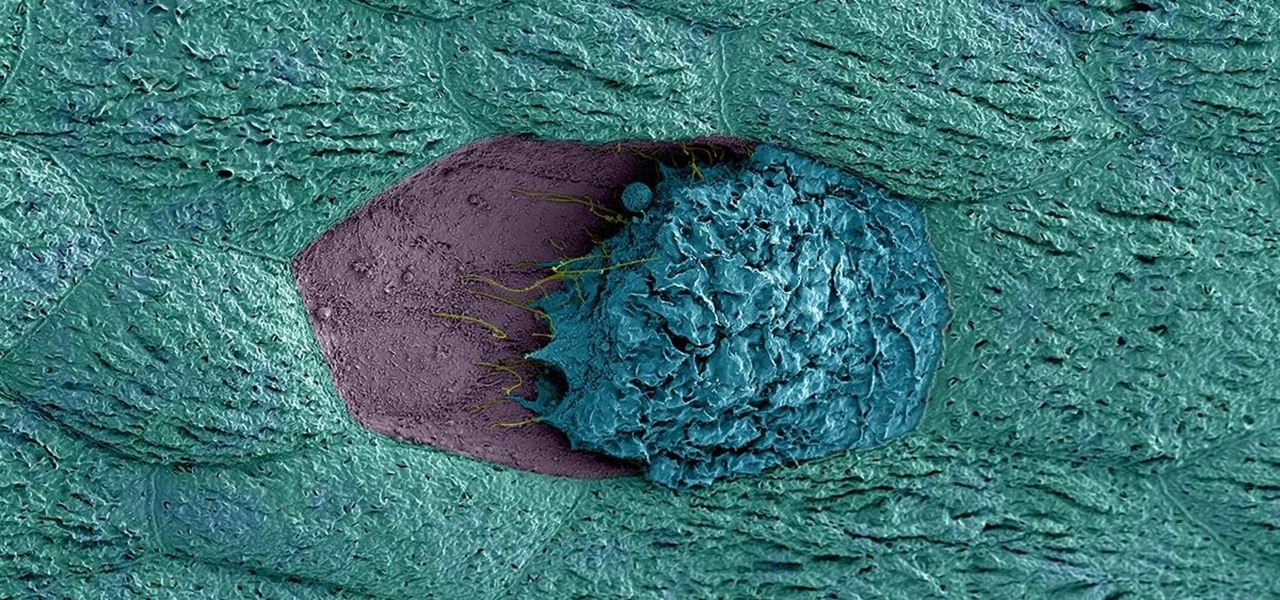
Where in the world did it come from? All of a sudden, one day, someone had an infection with flesh-eating bacteria. It captured headlines and worldwide attention because it was such a severe, strange, uncontrollable, and really disgusting condition.

There are all kinds of theories—many supported by science—about what causes Alzheimer's disease. Tangles of protein called ß-amyloid (pronounced beta amyloid) plaques are prominently on the list of possible causes or, at least, contributors. An emerging theory of the disease suggests that those plaques aren't the problem, but are actually our brains' defenders. They show up to help fight an infection, and decades later, they become the problem.

Responding to the rapid emergence of dangerous pathogens around the world, a new initiative to prevent or contain pandemics was announced in Davos, Switzerland, yesterday. If you ever worried that a highly contagious pathogen could take down your community, or the country, this news is for you.

You might feel the bite, you might not, but an infected mosquito has injected you with a parasite named Plasmodium falciparum, a single-cell protozoa that quickly takes up residence in your body.

What do Leo Tolstoy (writer), Beethoven (composer), Paul Gaugin (artist), and Adolf Hitler (politician) have in common? They are all considered to have suffered from the sexually transmitted disease syphilis.

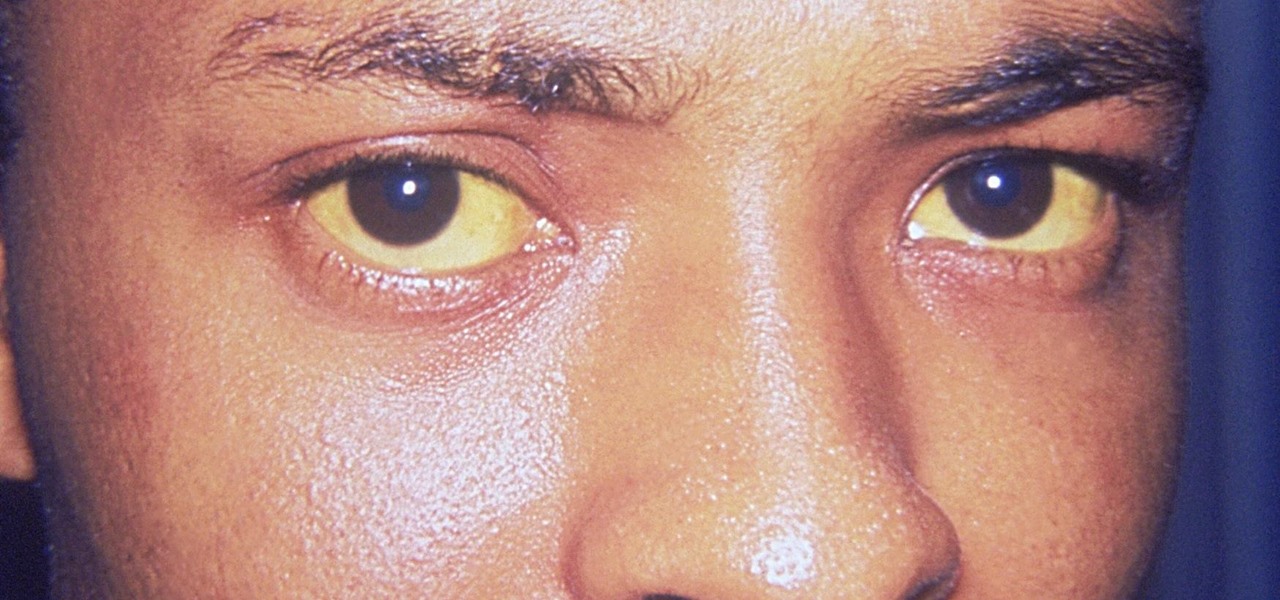
The story of Helicobacter pylori is a real testament to the tenacity of medical researchers to prove their hypothesis. It took decades before the scientific world would accept that the bacteria H. pylori caused ulcers.

Findings from a mouse study suggest that the Zika virus infection may have serious reproductive consequences for men.

I don't know about you, but visions of pumpkin pie and cornbread stuffing and big, juicy turkeys are constantly dancing through my head right now. I'm sorry, healthy eating habits, but it's Thanksgiving week, and all I can do is think about food.

YouTube has gotten so big over the years that it is now viewed by more 18-49 year-olds than any cable network in the United States. But even though online video platforms continue to gain ground on traditional TV stations, there's one aspect to the viewing experience that live TV still does better—it lets you tune into a channel, then just sit back and watch indefinitely.

I'm sure I'm not the only one on here that has googled "Why am I always tired?"... and I'm definitely not alone when I say that all of the advice I've found so far is useless:

Most of us work with a single monitor, but even with one or two extras, they still offer a rather confined workspace. Virtual reality, however, doesn't have such boundaries. As a result, VR headsets can work as excellent productivity tools. Windows can't just adapt on its own, however, so Envelop VR stepped in and created a new working environment to allow the desktop to expand beyond its traditional, rectangular bounds.

We admit it: we are ranch dressing fanatics. We like to put it on our simple salads, spread it across our chicken wings, and dip homemade sweet potato fries in it. Plus, since childhood, neither of us can eat pizza without ranch dressing to accompany it.