
How To: Recognize OCD symptoms
If you have habits that are repetitive, time-consuming, and don't seem to make sense, and they interfere with daily functioning, you may have Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder.


If you have habits that are repetitive, time-consuming, and don't seem to make sense, and they interfere with daily functioning, you may have Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder.

Walk right past that pricey salon and head to the grocery store instead. Tame your frizz for less at home! This video will show you how to make a banana hair mask to combat frizz.

Though most warts disappear eventually without treatment, it's still useful to know how to prevent these unsightly marks from ever popping up. Watch this video to learn how to reduce your chances of warts.

It’s easy to make those telltale sweat spots disappear if you know what to use on them. Don't throw away those white shirts, learn how to get rid of sweat stains instead.
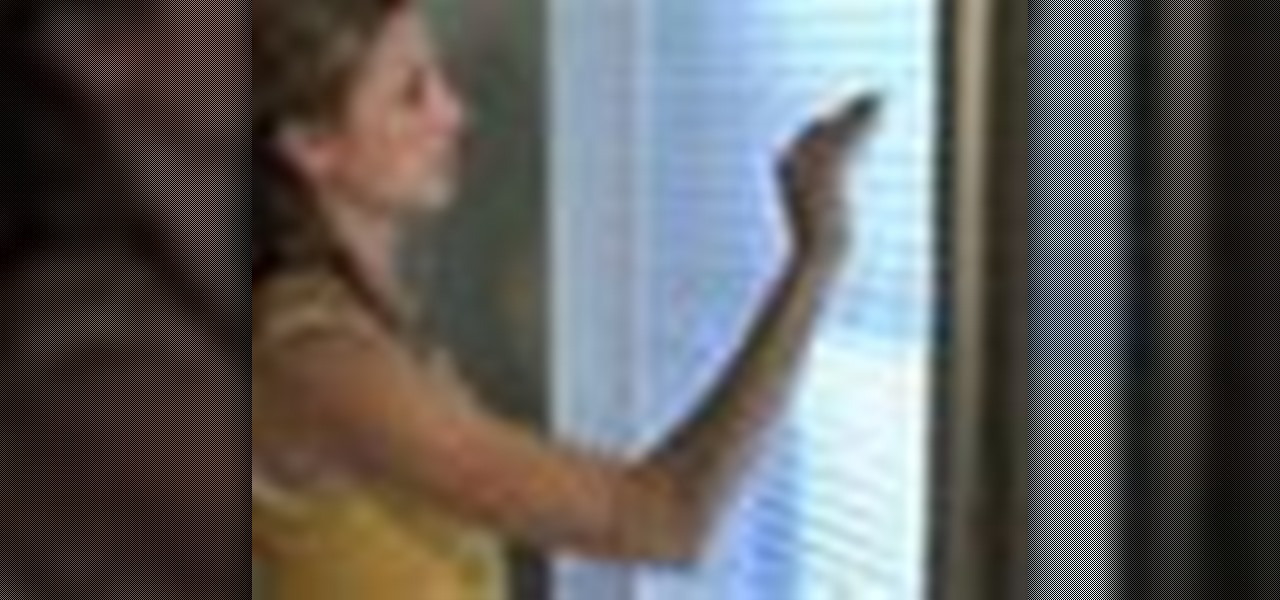

Wash your window blinds with a minimum of mess. Howcast presents you with tips on how to effectively clean your window blinds. Blinds can be tricky to clean, so pay attention.

Get luscious, pillowy, kissable lips—with or without injections. You Will Need

Stop bemoaning your blotchy complexion and start evening it out instead, no matter your specific skin complaint.

Food poisoning, also referred to as food-borne illness, is a gastrointestinal disorder that results from eating contaminated food. . Who is at risk? Anyone can get food poisoning, especially travellers and those who live in tropical climates. Infants, elderly people, and those with serious medical conditions have the greatest risk if they get food poisoning. Pregnant and breastfeeding women also need to be especially careful. Learn about the different causes, symptoms, and treatments of food ...
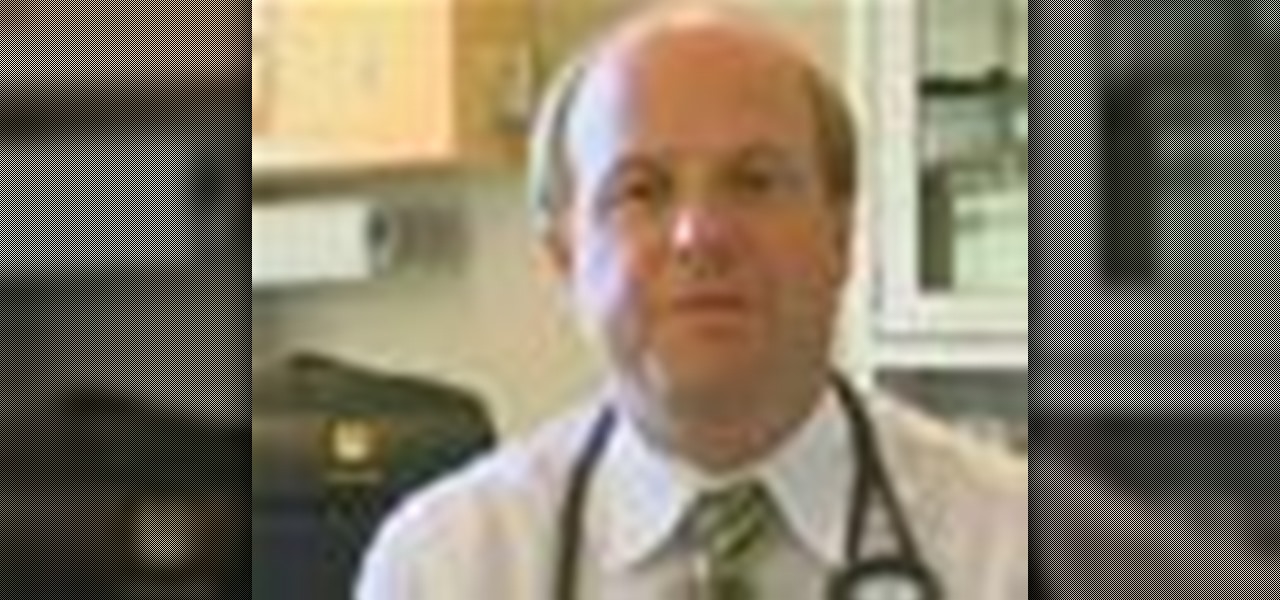

Nosebleed or the official term is epistaxis is bleeding from the nasal cavity. Nose bleeds are very common and are often caused by dry air, illness, or trauma. Learn more about the causes, symptoms and treatments of nose bleeds in this medical how-to video.
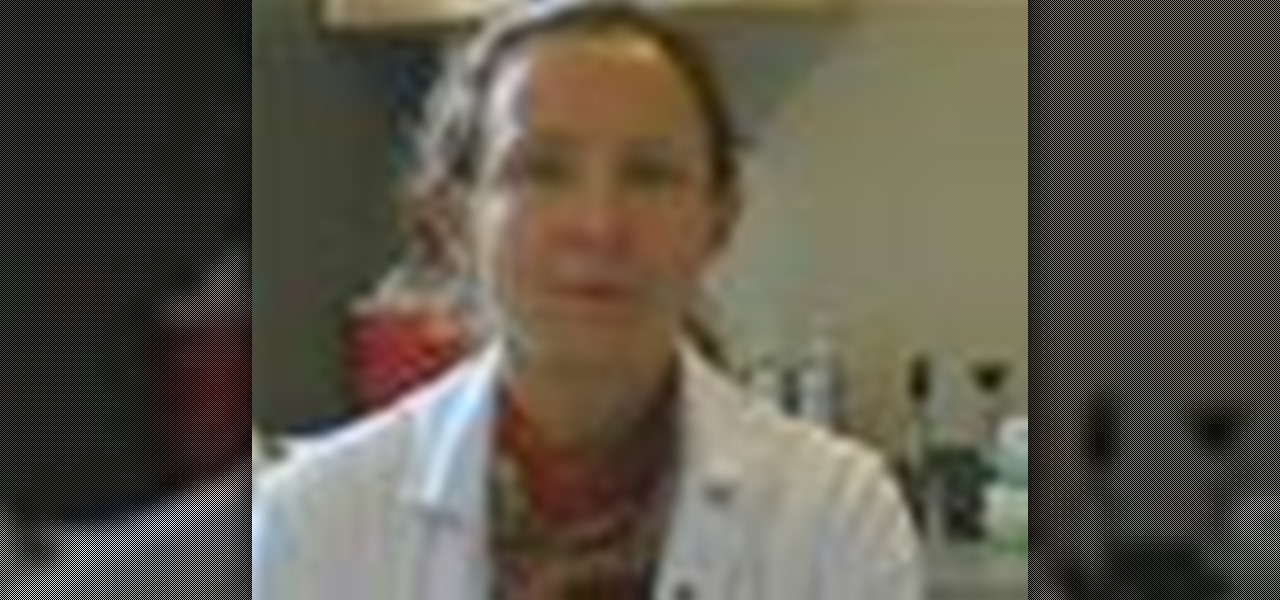

The MCL or the medial collateral ligament is a thick fibrous tissue that spans the distance between the bottom of the thigh bone and the top of the tibia on the inside of the knee joint. A MCL injury is caused by stretching or tearing of the MCL ligament in the knee. Learn more about the causes, symptoms and treatments for a MCL injury in this medical how-to video.
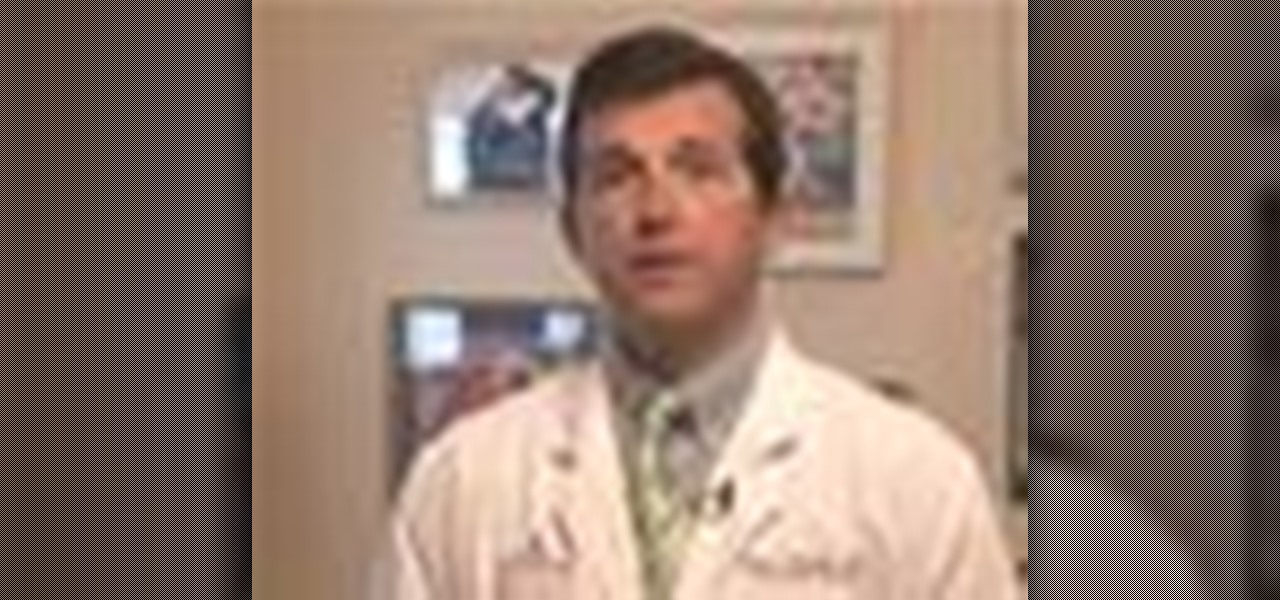

The biceps tendon attaches the biceps muscle to the radius. Learn how to diagnose and treat a biceps tendon tear in this medical how-to video. Usually the area is painful, swollen and bruised.
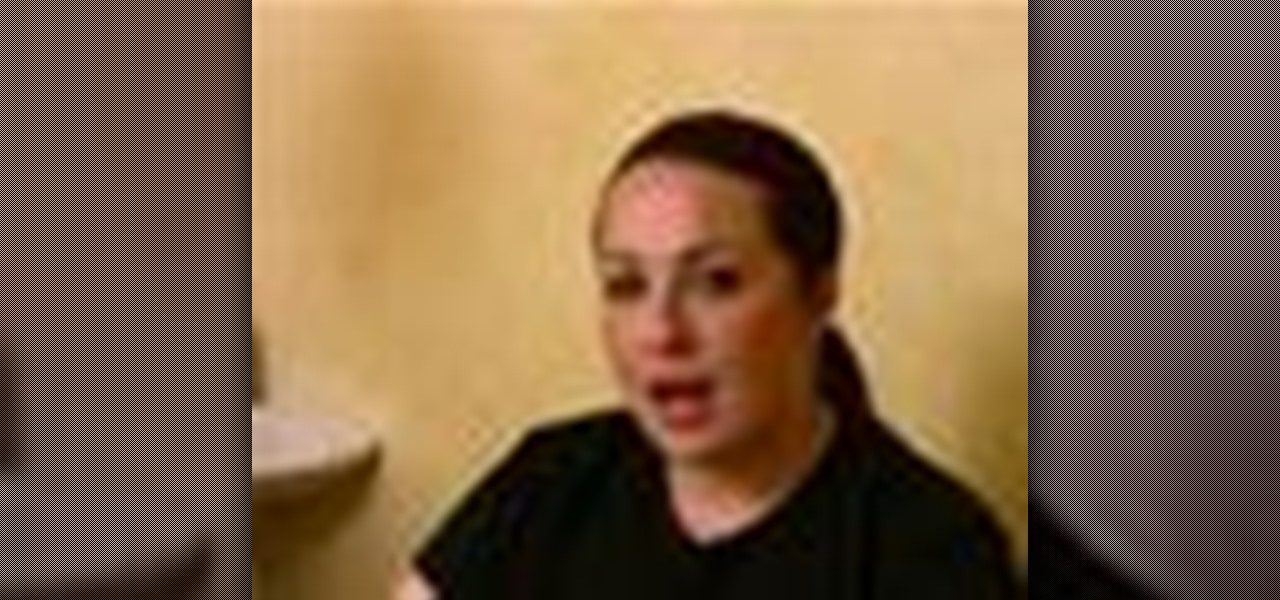

Scrubs are abrasive creams that exfoliate skin, removing the upper, dead layer of skin for a healthy glow. Learn tips for giving face scrubs from an esthetician in this free spa treatment video.
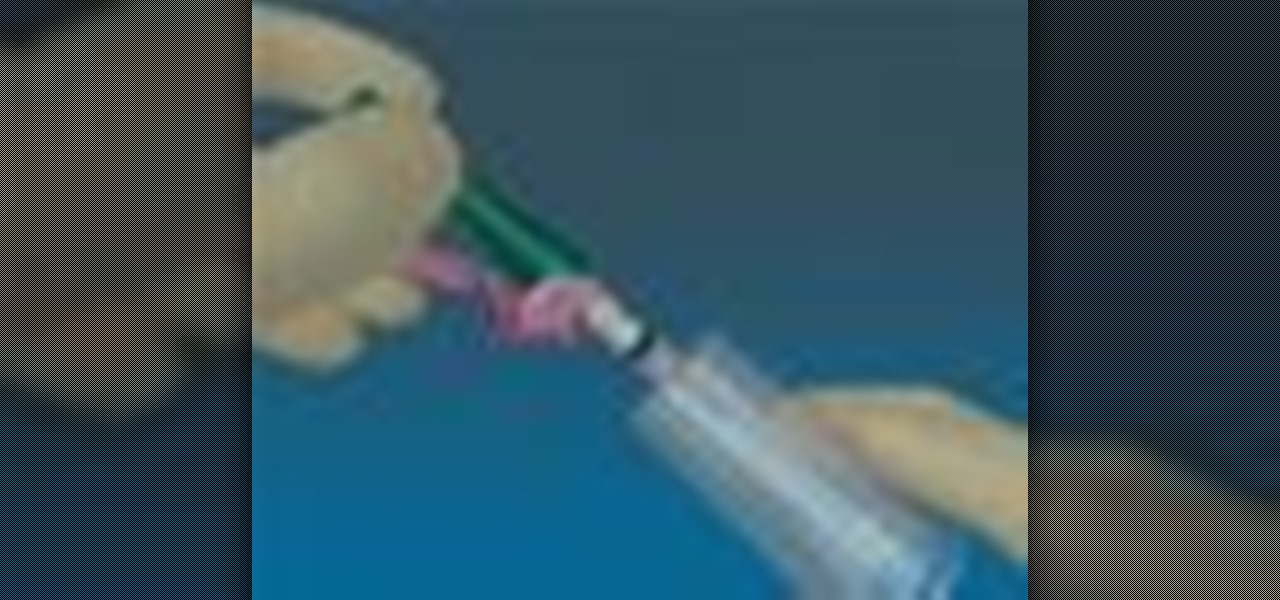
Check out this video to see how to collect blood with the BD Vacutainer Eclipse Blood Collection Needle.
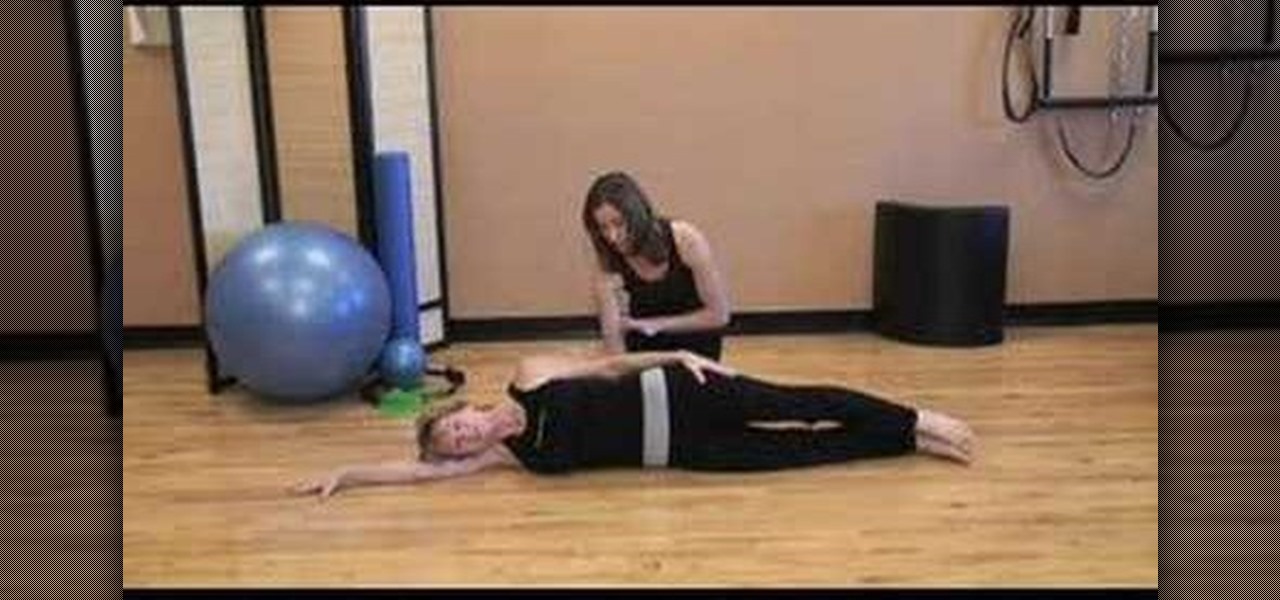

This pilates how-to video illustrates the Lateral Flexion exercise of the Side Leg Series. It is obviously a great exercise for lateral flexion and balance.

It's just a fact that hairy legs on women are not the most attractive. From razors to lasers, hairy legs can be a thing of the past. Hairy legs are some of the hardest parts to deal with because they're so visible all the time. Whether you want to rid yourself of prickly leg hair or just simply hide it, there are always solutions for your hairy legs. Shaving is of course the most common way of removing leg hair. It's relatively quick and easy, and once it's built into your routine you don't e...

No one can escape the wrath of fire. Eery living person will experience some sort of burn during their lifespan, from scalds to third degree burns. Burns and scalds are among the most common injuries requiring emergency treatment in hospitals, but would you know what to do if a friend or family member, maybe even a stranger, burned themselves badly? Could you help?

On June 11, 2016, an Arizona woman died from what appeared to be several infections, including pneumonia. She likely caught at least one of these from her dog.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) drive over eight million people to seek medical attention every year. Almost all — as many as 90% — of those infections are caused by Escherichia coli. Copper can kill bacteria, but E. coli has found a way to capture the copper, preventing its antibacterial action. Now, researchers have found that, in a cruel irony, the bacteria use the copper it grabs as a nutrient to feed its growth.
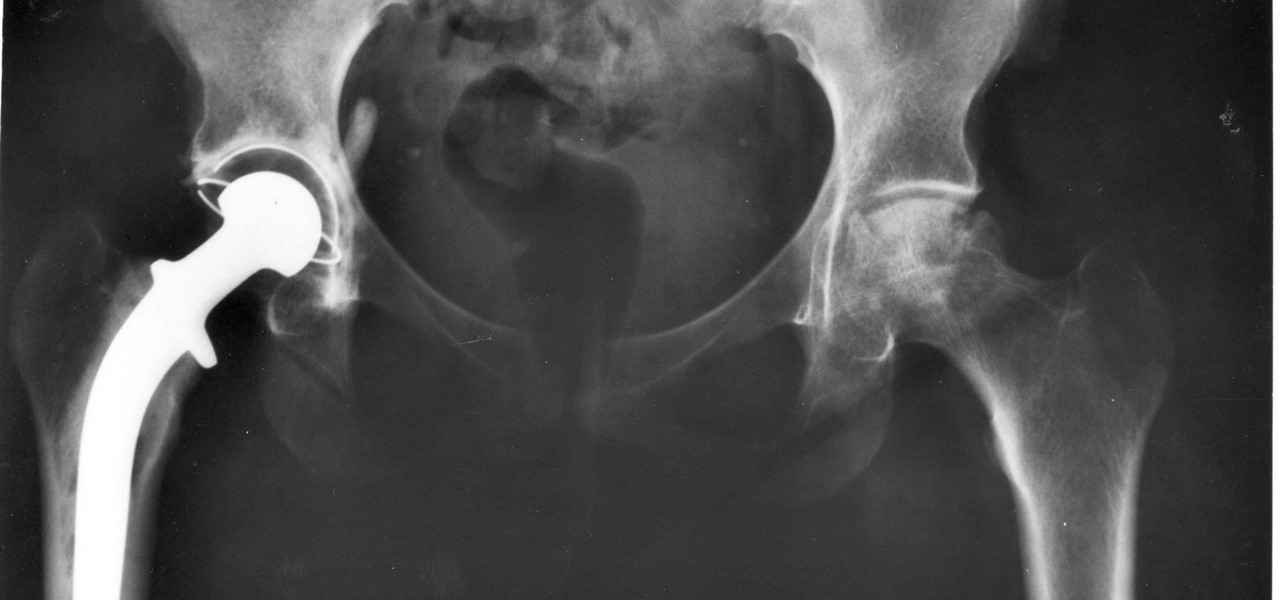
For about a million Americans each year, a joint replacement brings relief from pain and restored mobility. But, 5–10% of those people have to endure another surgery within seven years, and most of those are due to an infection in their new joint. If doctors could treat infections more effectively, patients could avoid a second surgery, more pain, and another rehabilitation.

Sex makes the world go 'round, and when it does, so does gonorrhea. Finally some good news on the growing menace of drug-resistant gonorrhea — a large, long-term study shows a vaccine may work in reducing the incidence of an increasingly dangerous infection.

The noses of kids who live in areas of intense pig farming may harbor antibiotic-resistant bacteria, presumably acquired from the animals, according to a new study by scientists at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, UNC Gillings School of Global Public Health, and Statens Serum Institut in Denmark, published in Environmental Health Perspectives.
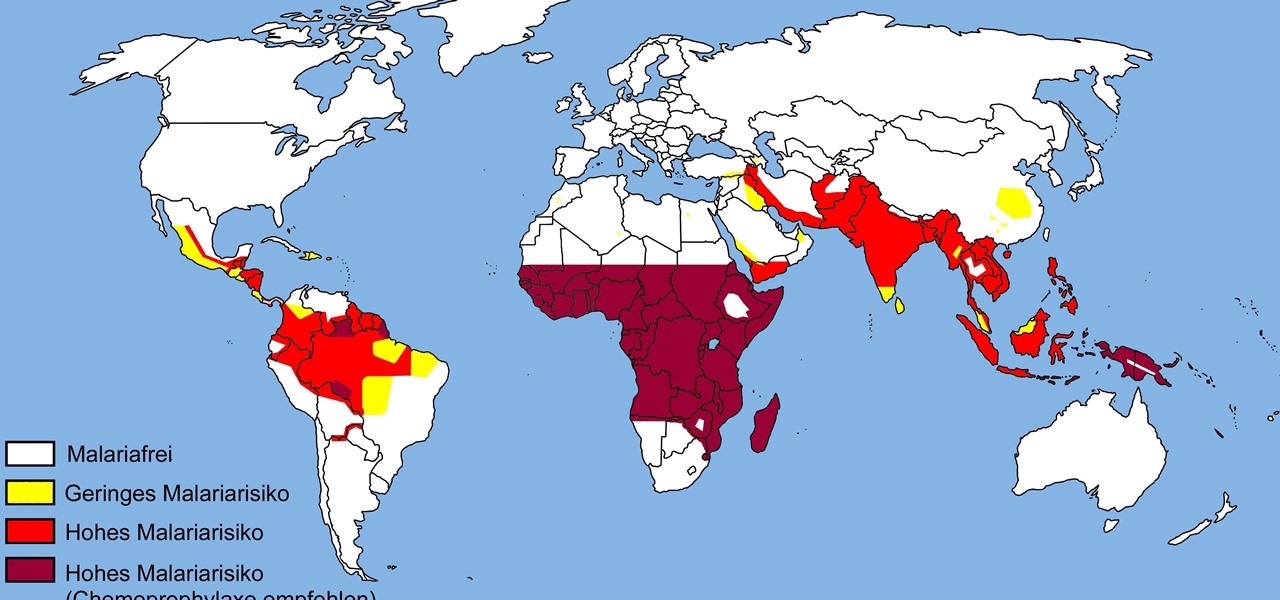
The theme for 2017's World Malaria Day, which is today, April 25, is "End Malaria for Good." For many Americans, this might seem like an odd plea. Especially since Malaria is seemingly an obsolete problem here. However, on World Malaria Day, it's important to remember the danger of malaria is still very much present in the US. And around the world, the disease is at the epicenter of a global crisis.
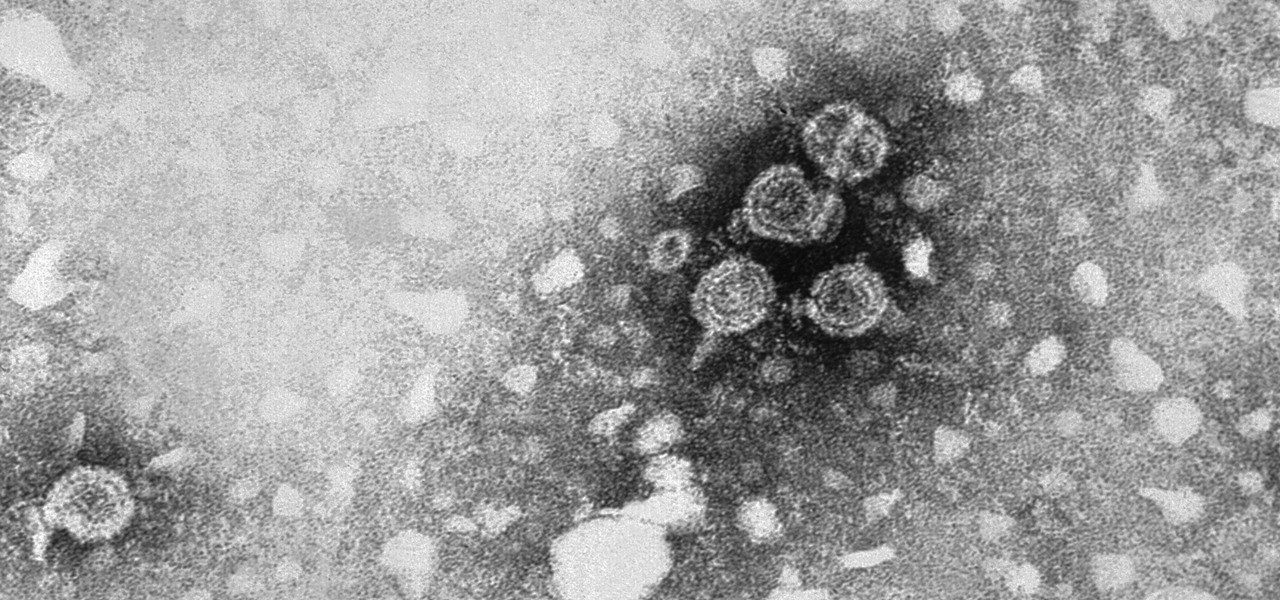
Two viral liver diseases could help us find the path toward the cause of Parkinson's disease. Researchers from the University of Oxford and UCL Institute of Neurology in London have reported an association between hepatitis B and C infections and an increased risk of Parkinson's disease. Their findings were published early online in the journal Neurology.
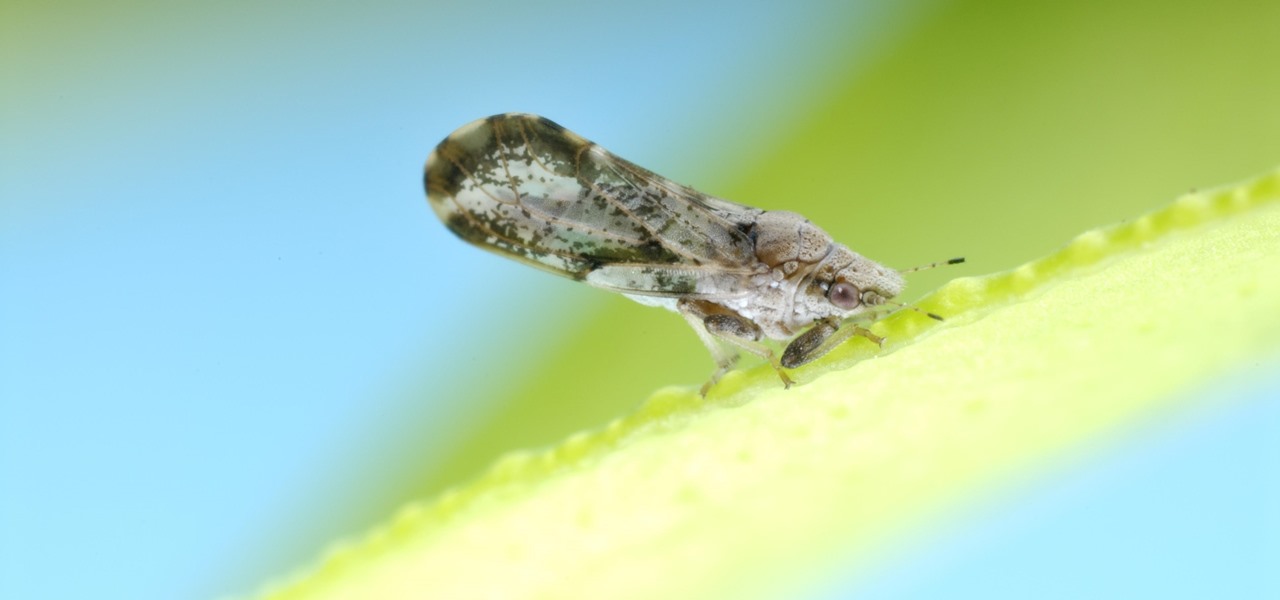

A tiny louse is responsible for decimating the citrus industry. Diaphorina citri, the louse in question, better known as the Asian citrus psyllid, harbors and spreads the "Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus" bacteria that causes citrus greening disease.
Although their effectiveness is waning, antibiotics remain a front-line defense against many infections. However, new science reveals using the wrong antibiotic for an infection could makes things much worse.

We all know you are what you eat—or so the expression goes—but it's good to remember that what you are (at least intestinally) is mainly bacteria. A new study has shown that what you eat, and how your gut microbiome reacts to that food, might be a key player in your risk of developing a certain type of colon cancer—and changing your diet can help decrease your risk.
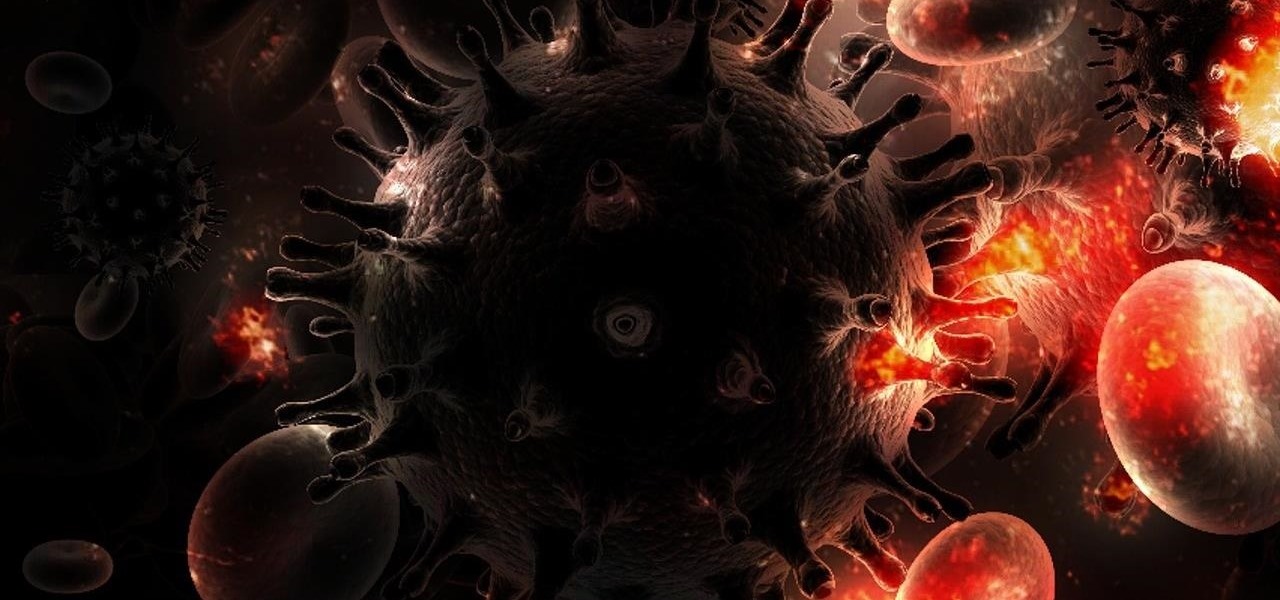
Over 1.2 million people in the US are infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)—and one out of eight of them don't know it. Even after decades of intense research into the virus, there's still no cure for it. One of the big problems is that the virus hides out in certain cells of the body, resisting treatments that kill it.

Pharmacist Sherry Torkos recommends natural treatments for arthritis and inflammation conditions.

Facing mixed reviews for the Magic Leap One, Magic Leap has already returned to the lab to improve on the device's successor.

Microsoft is adding another important piece to its growing immersive computing arsenal by putting its newest Mixed Reality Capture Studio in the center of the movie business: Hollywood.

Microsoft's latest move to further secure its hold on the emerging mixed reality space comes in the form of two new Mixed Reality Capture Studios in San Francisco (the flagship studio) and London.
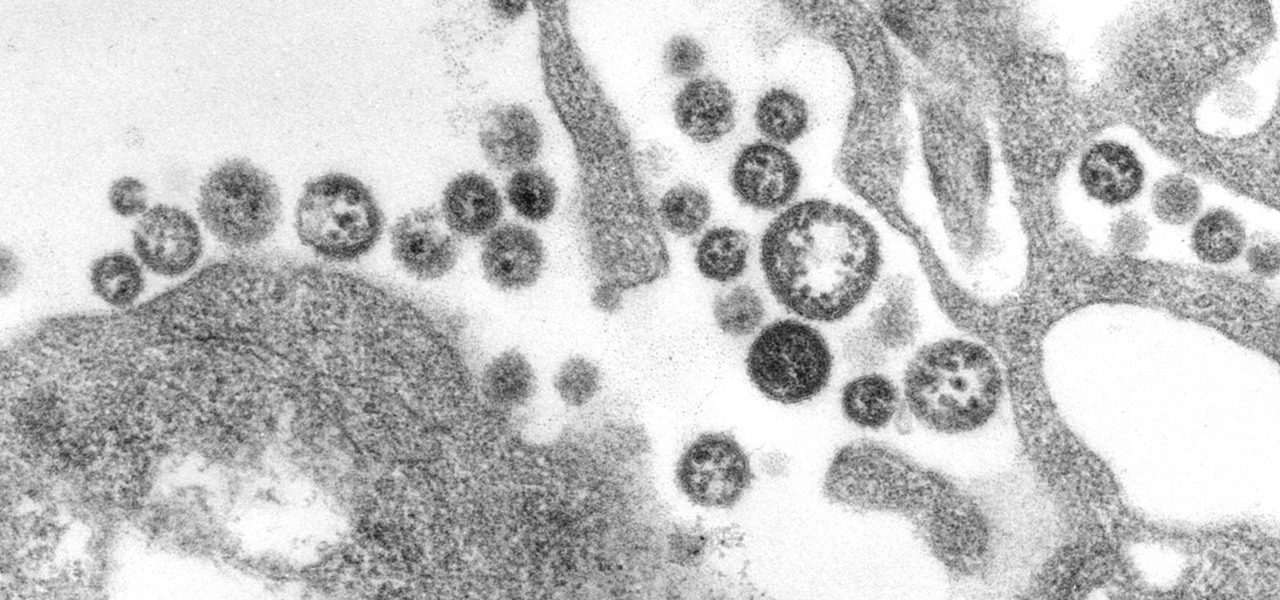
A recent study offers information that might help combat a deadly virus that affects an estimated 300,000 people each year in West Africa.
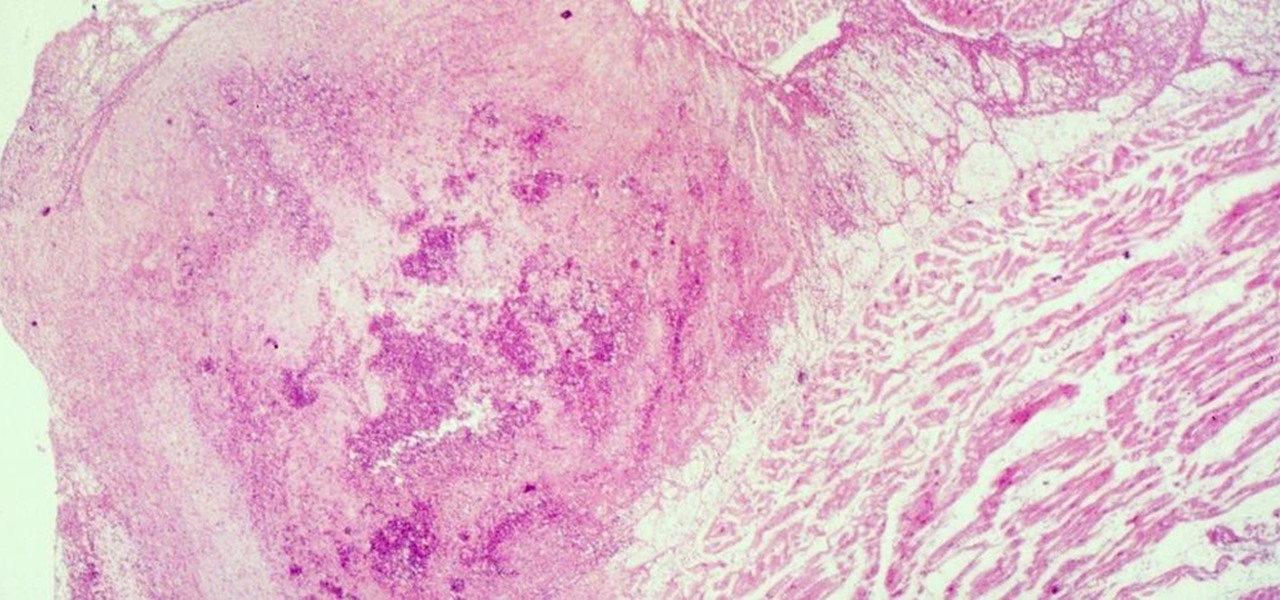
Four million Americans misused prescription opioid painkillers in 2014. Those who do are 40 times more likely to inject heroin or other drugs than other people. Now, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) are blaming that misuse for a 12-fold increase in endocarditis, an infection of the heart valves.

Cytochrome P450 (P450s) are proteins found in nearly all living organisms, which play roles that range from producing essential compounds and hormones to metabolizing drugs and toxins. We use some of the compounds synthesized by P450 in plants as medical treatments, but the slow growth and limited supply of these plants have put the drugs' availability in jeopardy and jacked up prices.
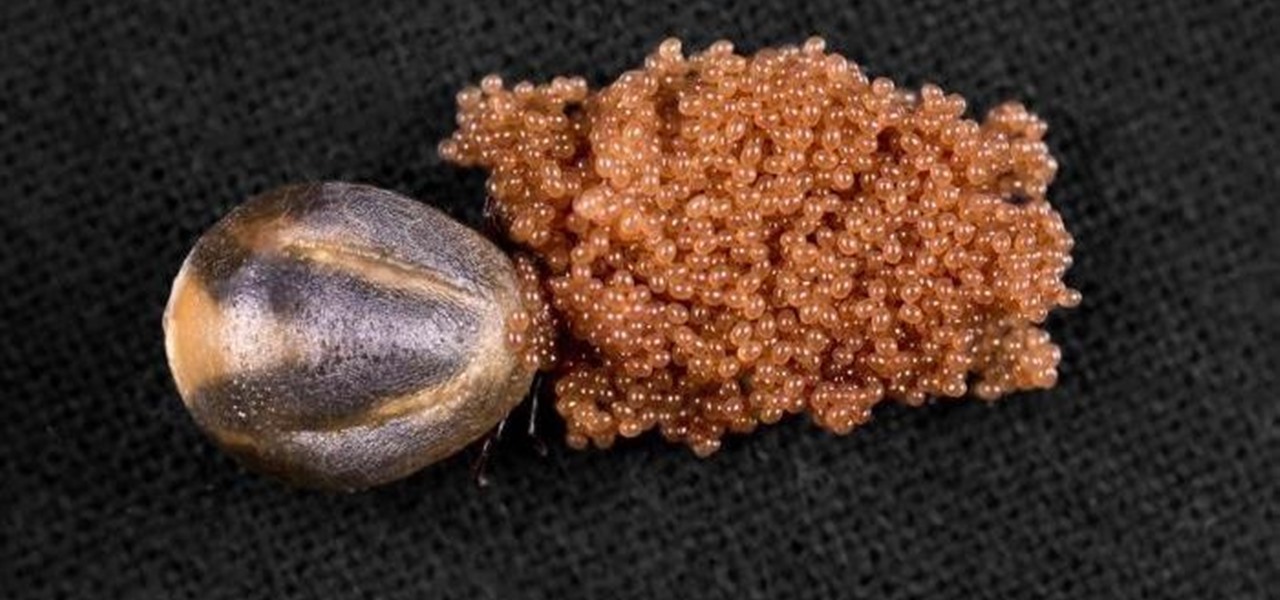

A recent case of Powassan virus has been reported in Saratoga County and may have been the cause of the infected patient's death. It's the 24th case in New York State since 2000, and will be reported to the CDC tomorrow, the NY Department of Health told Invisiverse. The tick-borne illness has no vaccine or specific treatments and can damage the nervous system.
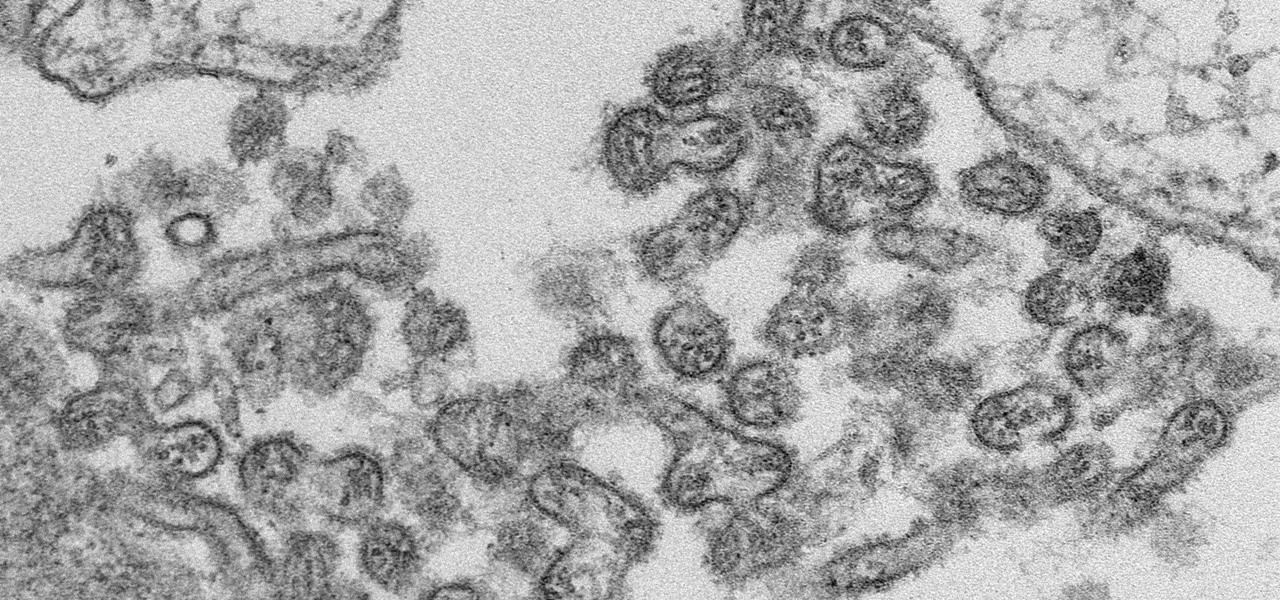
A new case of the still-mysterious Bourbon virus was confirmed in Missouri, likely originating within the state, local authorities said in a June 30 press release.
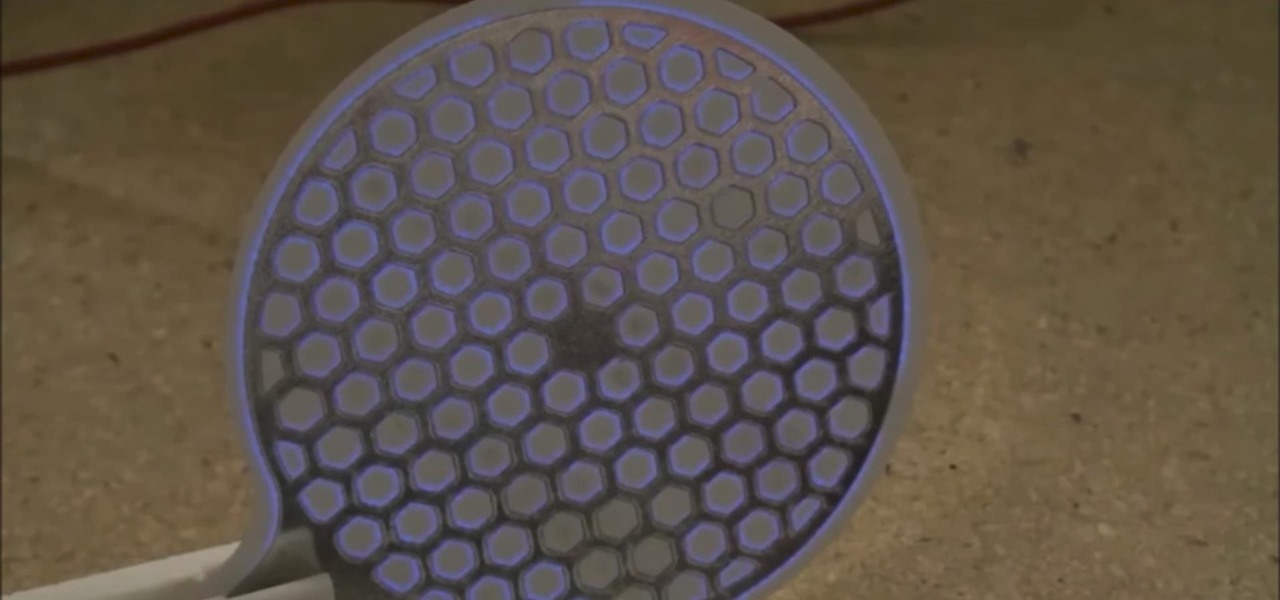

What would it be like to have clothing that killed microbes? Or paper that repelled pathogens? A research team from Rutgers University has developed a prototype out of metalized paper to zap the bad guys without being super expensive. Sound good? Read on.
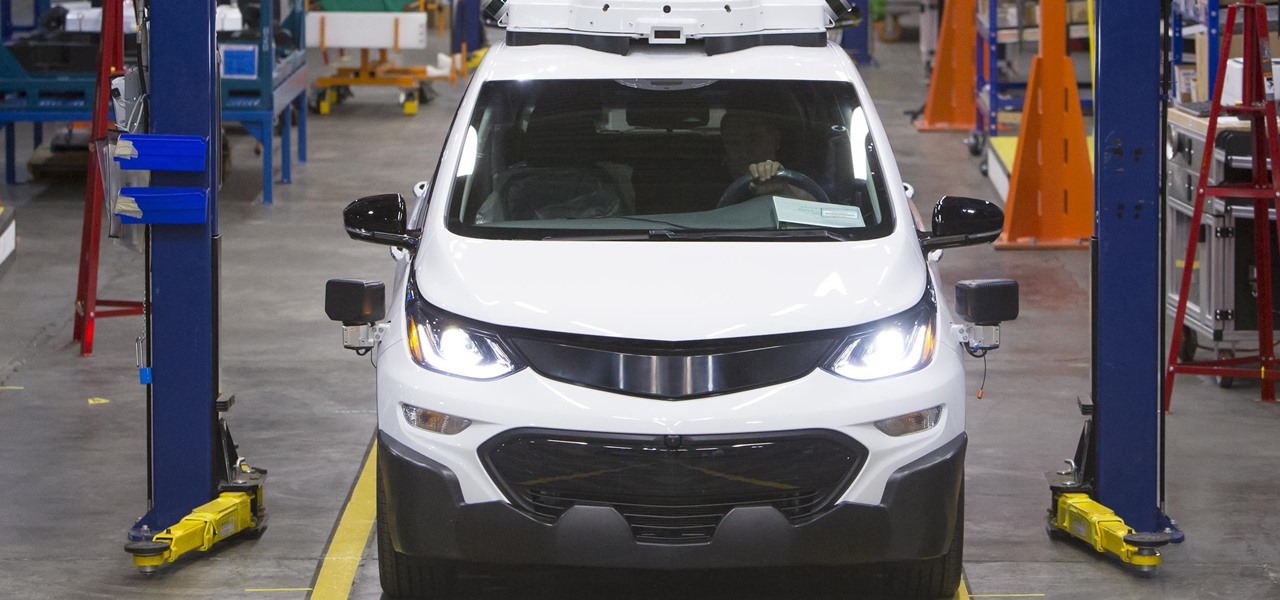

General Motors (GM) has begun production of 130 Chevrolet Bolt EV driverless test vehicles at its Orion Township, Mich. plant as it expands its fleet to total 180 models deployed in San Francisco; Scottsdale, Arizona; and Detroit.

With summer just ahead, you, or your children, may be looking forward to some pool time or the water park. When planning water-based fun this year, keep a heads-up for microbes.
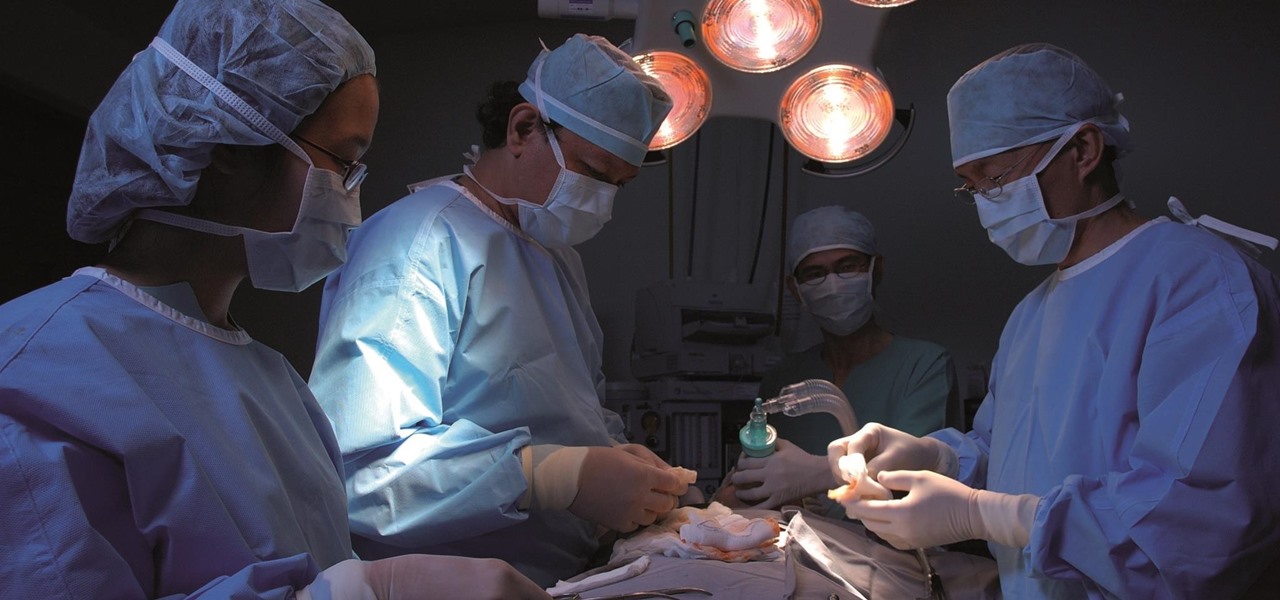
Dramatic new research may change the fate of the hundreds of people who wait for a kidney transplant every year. The study hinged on the ability to cure hepatitis C infections, a possibility that became a reality in 2014.