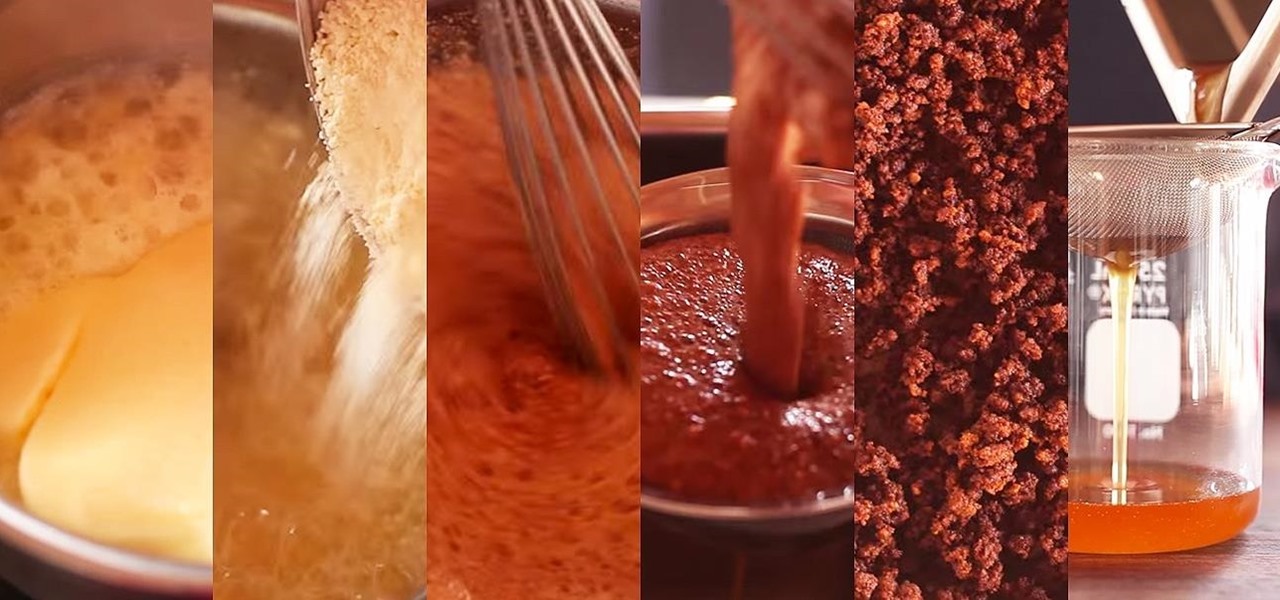
Butter can be even more delicious than it already is. While that may be a shocking claim, it's most definitely true. Many new cooks and even seasoned chefs don't realize this, but the few minutes it takes to do these things will pay you back exponentially when it comes to that buttery taste.

I have a theory that chocolate chip cookies are the gateway drug to cooking. The recipe is easy, no special equipment is required, and at the end, you get warm, fresh-from-the-oven cookies that are simply irresistible. It's how I got hooked on baking and cooking, and anecdotal evidence (i.e. me asking my other kitchen-obsessed friends and a few culinary students) supports me.
Whether you call 'em soda, pop, fizz, or coke, carbonated soft drinks are among the least healthy beverages out there, yet they're consumed by millions of Americans every day. For those of you worried about your health, there are diet and zero-calorie options available, but are they really better for you?

It's no surprise that Costco has great deals, and that's why millions pay annual fees for the privilege to shop in their wholesale outlets. Just take their hotdog and soda combo for $1.50—it's the same price now as it was 27 years ago.

While Siri has never been my favorite, after using her in the new iOS 7, I have definitely become a fan. If you want to know why, check out the newest cool features that Siri has to offer!
We don't generally think of medicine as being very relevant to Steampunk, but it was a big part of Victorian science fiction. Notable examples that you may be familiar with would be Frankenstein and The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde.

Every year the fine folks at Row Three do a post-TIFF mega-wrap up, collecting the micro-blurbs of a bunch of attendees into a giant meta-analysis of what everyone liked, loved, hated, etc. etc.. We'll link to that post when it goes up on the weekend, but in the mean time, here's my contribution:

There is something special about a secret knock. It gets you into secret super villain meetings and is a surefire way to test for rotating bookcase passages. Secret knocks usually work with an intimidating drug lord and for policeman listening at the door for the correct pattern of raps.

Awakening the female energy that resides in the base of your spine is not a process that can be done in an afternoon but is something you work towards though lots of work in kundalini yoga and work toward an enlightened state of being.

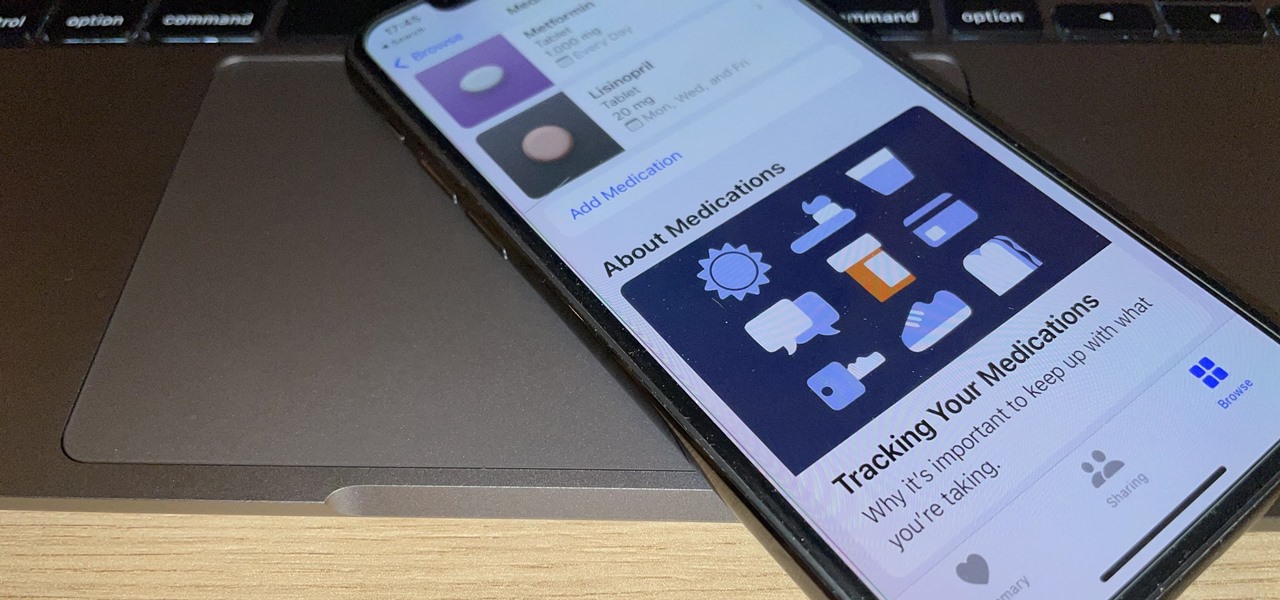
You've probably already been using iOS 16 on your iPhone for months, but there's a good chance you haven't found or explored everything the new software has to offer. Health-related features are usually the first to be ignored or go unnoticed, but they're essential to know about even if you don't plan on using them right away.

Your iPhone's Health app has a new medications hub that can be a one-stop destination for all the medicine, vitamins, and supplements you're taking. Adding new entries is easy and well worth the effort to get reminders to take your meds, learn about drug interactions, easily share your routine, and track your history to see what is and isn't working for you.

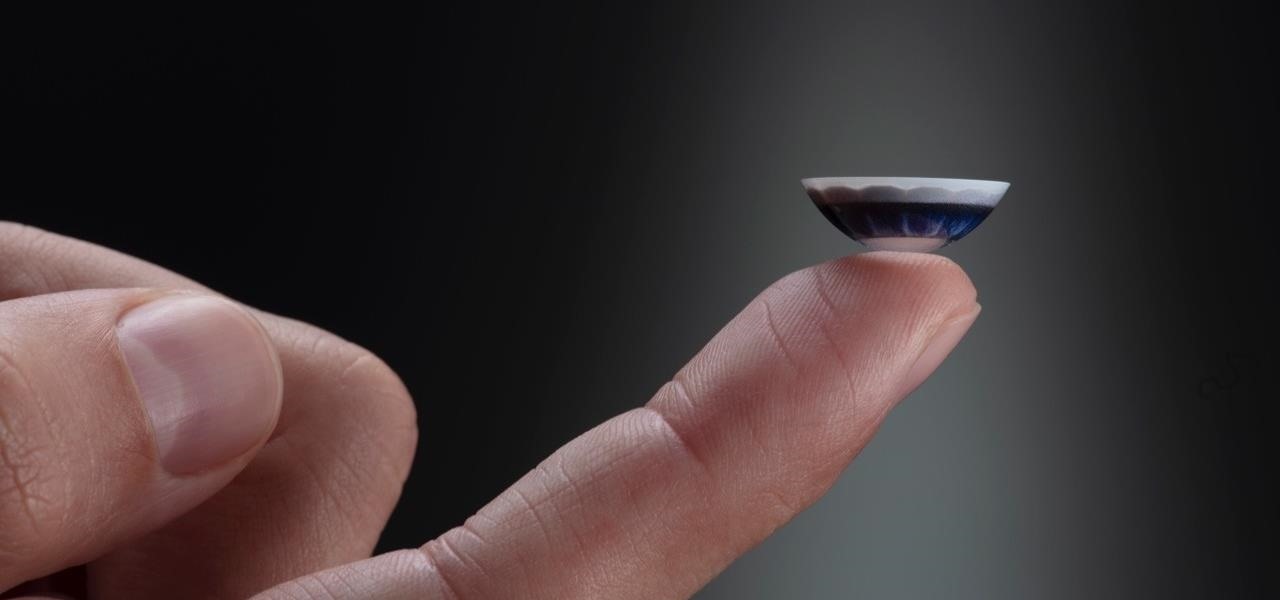
After more than two years of teasing, augmented reality startup Mojo Vision has confirmed that "invisible computing" means what we've suspected all along.

Cross-site scripting is one of the most common vulnerabilities found on the web today, with repercussions of this type of flaw ranging from harmless defacement to sensitive data exposure. Probing for XSS can be tedious and time-consuming for an attacker, but luckily there are tools available to make things a little easier, including Burp Suite, Wfuzz, and XSStrike.

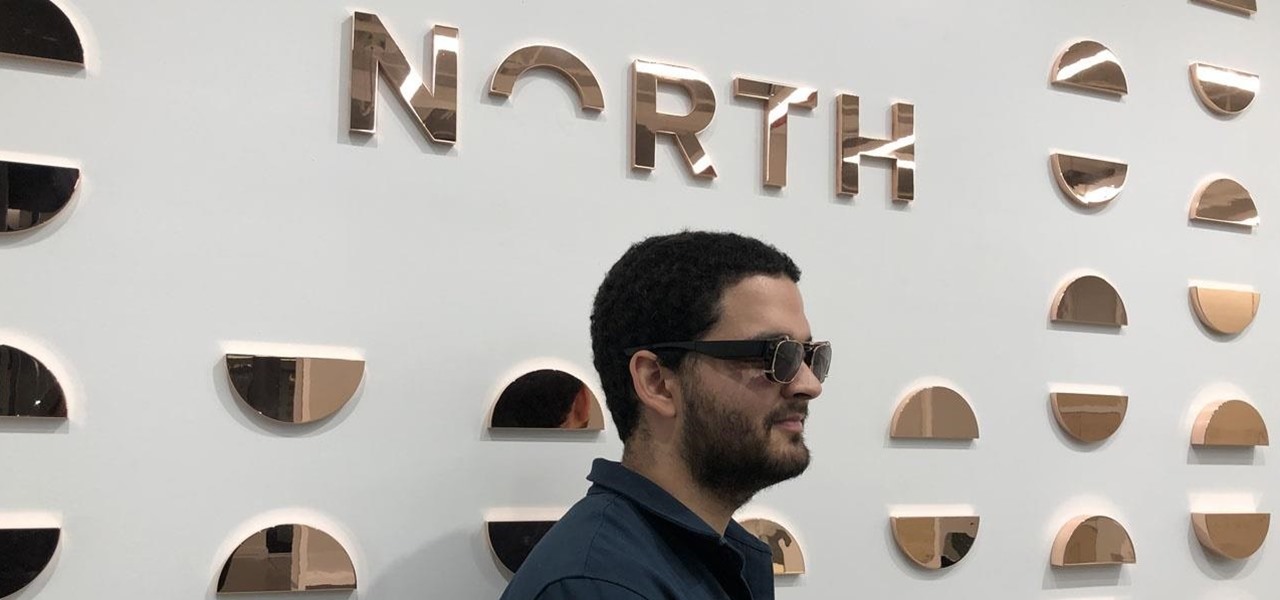
On Tuesday, the smartglasses startup known as North finally took the wraps off its Focals product, but in a very unique way: The team simply opened a couple of stores and invited the public in.

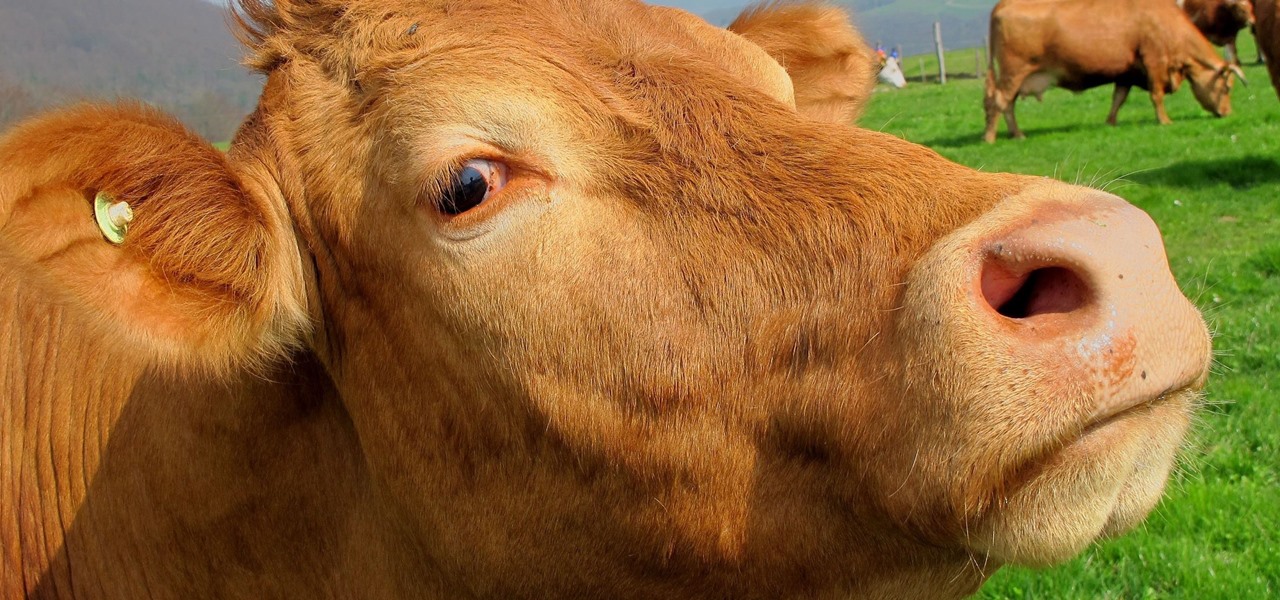
A vaccine against HIV might prevent the disease that we can't seem to cure. Some HIV patients make antibodies that can take down the virus, much the way a vaccine might. But, scientists haven't been able to provoke that type of response in other people. However, in a process that might work in humans, a group of researchers has successfully generated antibodies in cows that neutralize multiple strains of HIV.

A recent study offers information that might help combat a deadly virus that affects an estimated 300,000 people each year in West Africa.

Scientists know that bacteria create their own energy, get nutrients to run their cellular processes, and multiply. But, bacteria haven't been shown to respond to external mechanical stimulation or signals in a way that's similar to how our bodies respond to touch, until now.

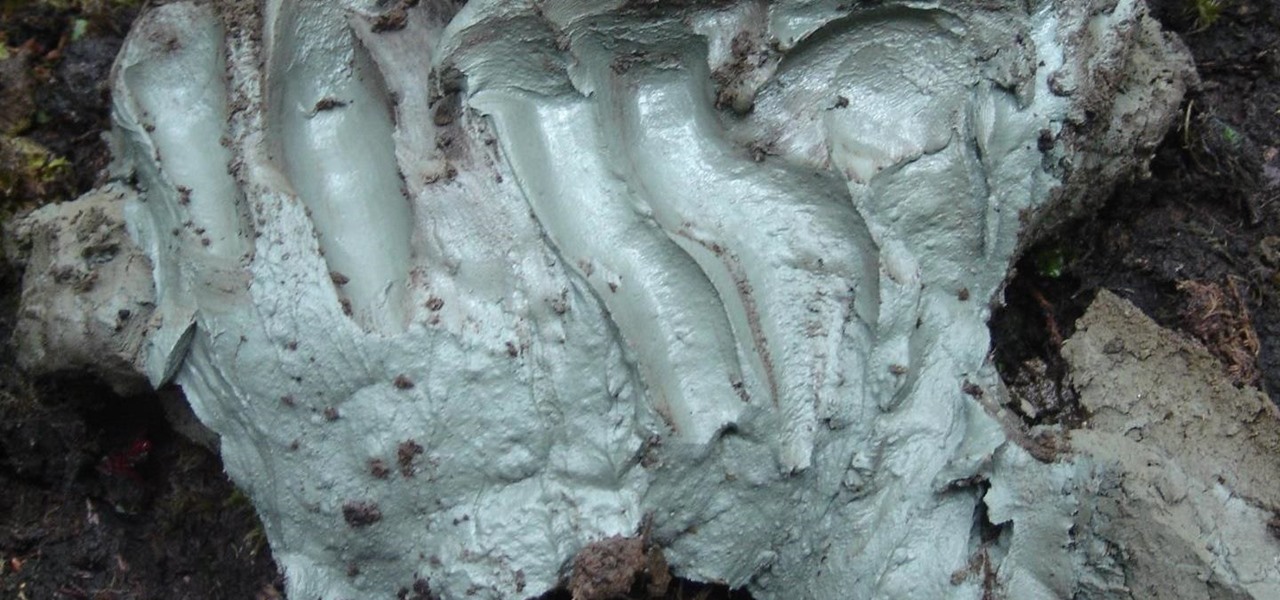
For as long as 14,000 years, the First Nations people of the Heitsuk Nation have made their home along the Central Coast of the Canadian province of British Columbia. Among the territory's inlets, islands, rivers, and valleys lie a clay deposit on the north side of Kisameet Bay, near King Island. For as long as most can remember, the tribe has used the clay as medicine. Now science says microbes that live in that clay may have important antibacterial properties.

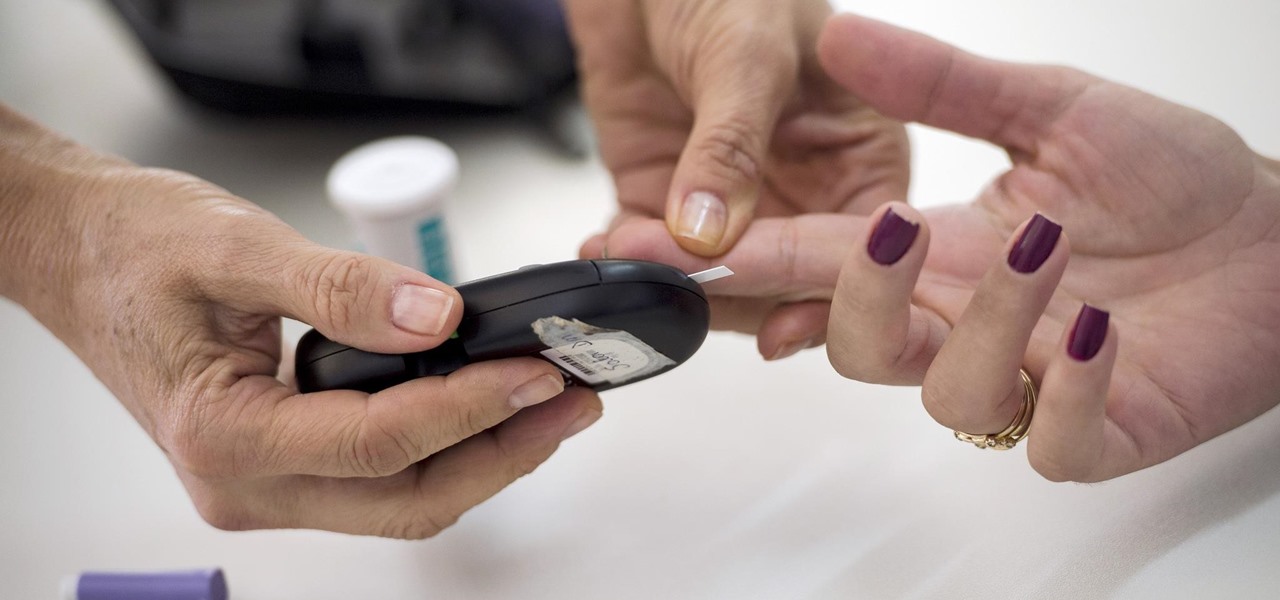
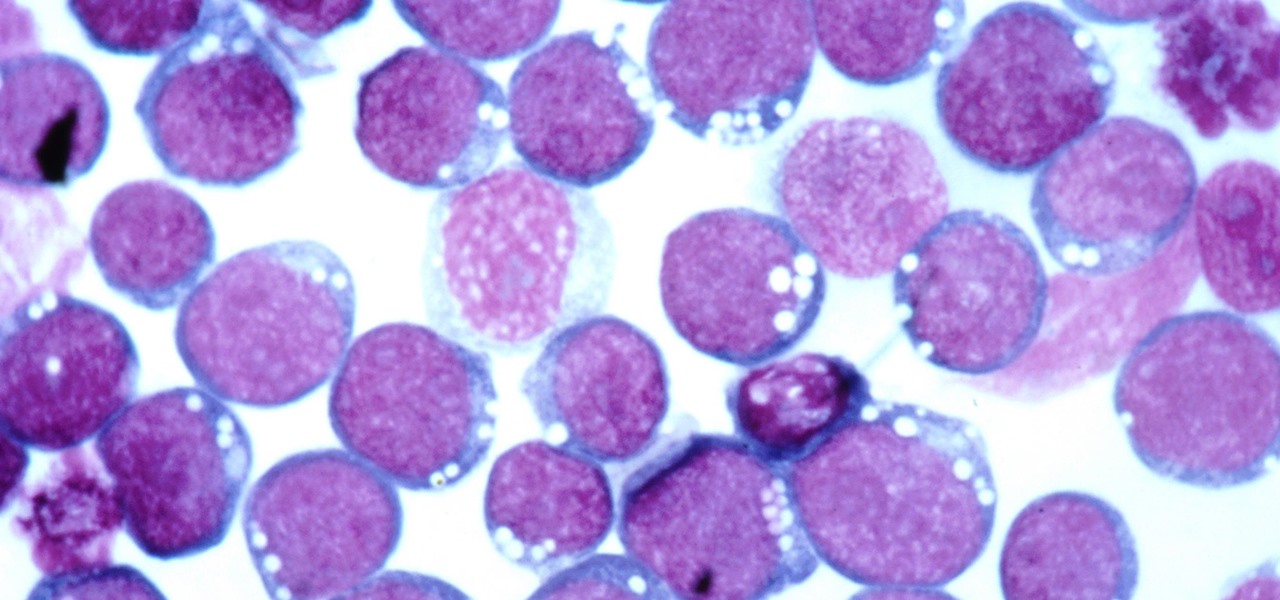
More than one in ten people in the US have type 2 diabetes — that's over 29 million people. It's characterized by excessive sugar (glucose) in the blood due to the development of resistance to insulin, the hormone that normally metabolizes glucose.

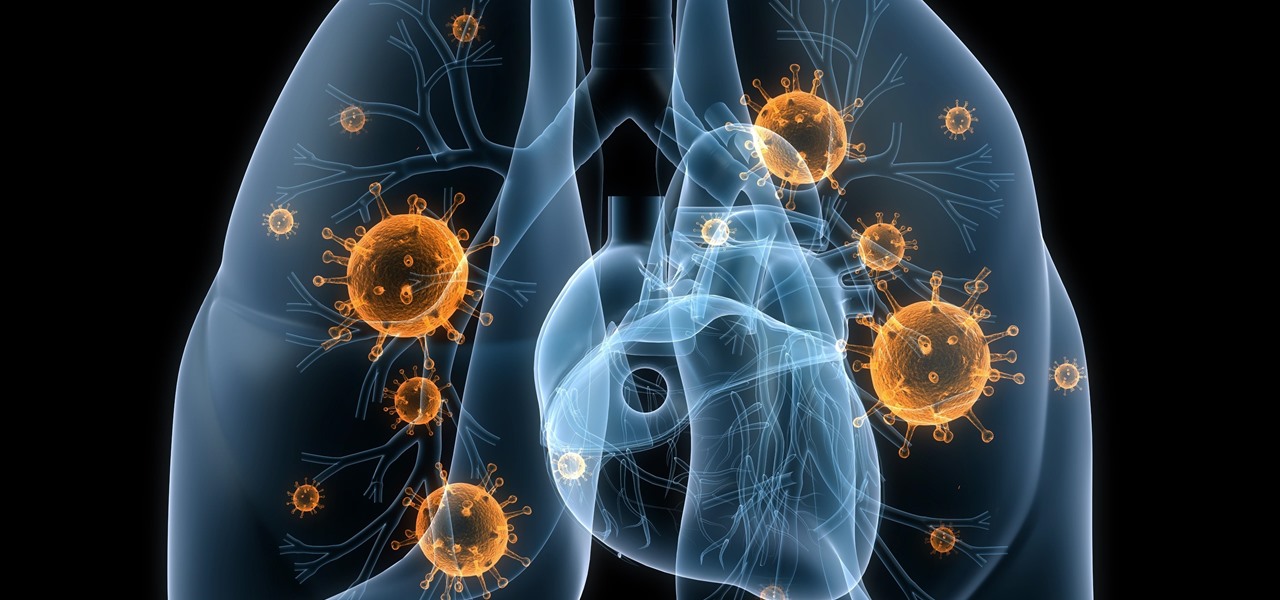
Once we recover from the respiratory infection pneumonia, our lungs are better equipped to deal with the next infection — thanks to some special cells that take up residence there.

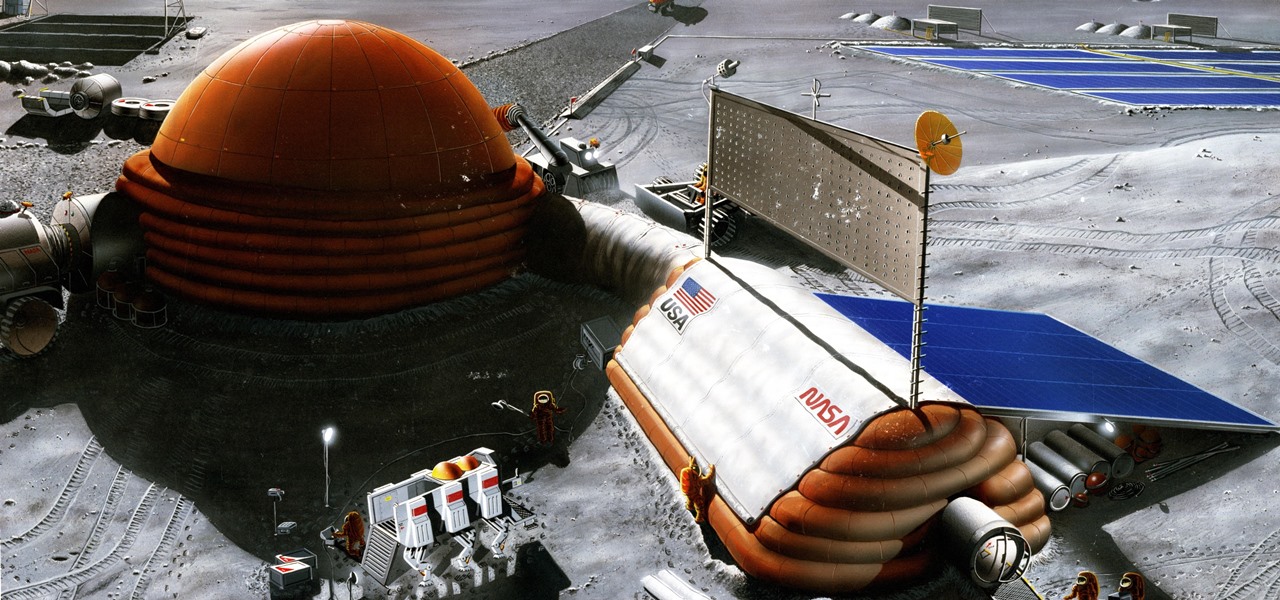
Wherever there are people, the party is sure to follow. Well, a party of microbes, at least. That is what scientists at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory have found after a 30-day microbial observation of the inflatable lunar/Mars analog habitat (IMAH).

Despite longer live spans, almost half a million people die of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) each year, many of them preventable.

Peach trees and other related plants are susceptible to the devastation caused by fire blight, a contagious bacterial disease. Once contracted, infected trees have to be burned to contain the disease and prevent spread to nearby trees. Increasing resistance to antibiotic treatment has sent scientists in search of alternative ways to deal with the bacteria and prevent its catastrophic damage.

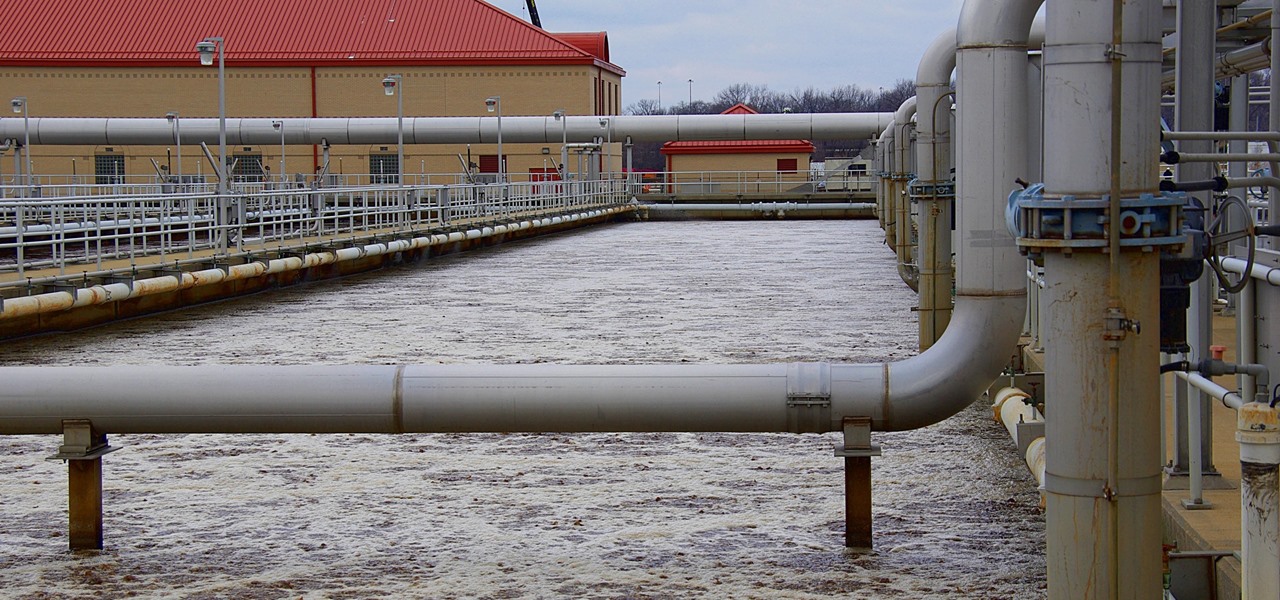
Everything from disposed of drugs to hormones and disease-causing bacteria — anything that is rinsed or flushed down the drain — can contaminate wastewater.

Add breathing in your house as another possible danger to your health. If your home is sick, it's possible you could get sick too.

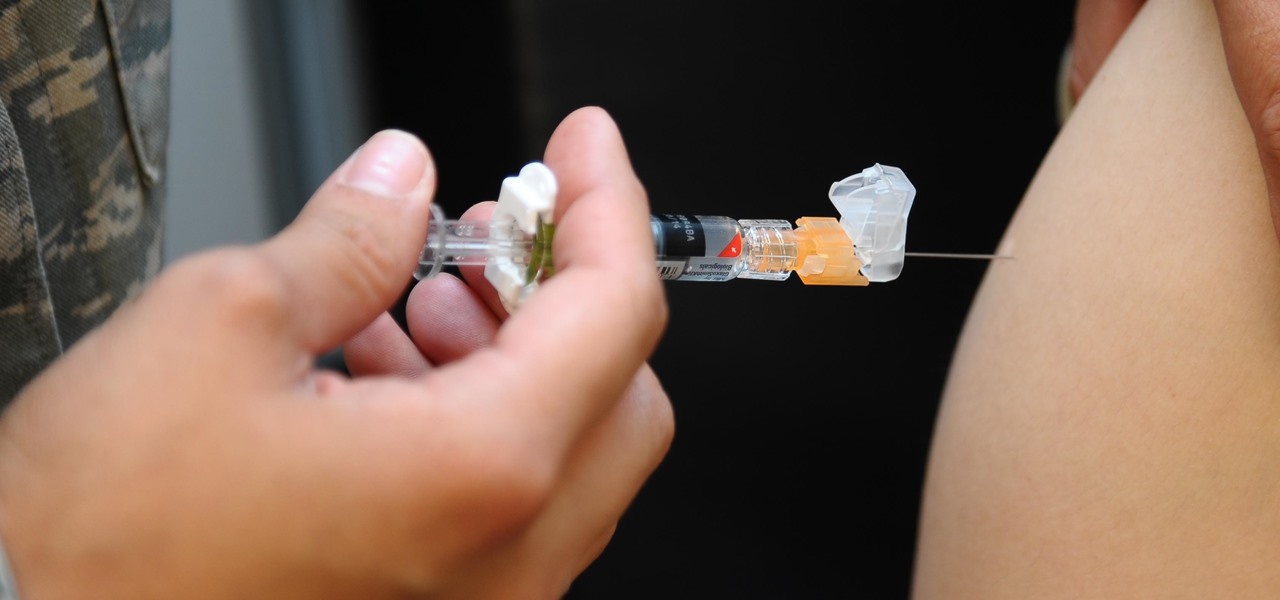
A new medical development is going to change the way many of us look at getting the flu vaccine. A painless flu vaccine skin patch is making needles and vials a thing of the past. Researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University have shown that a flu vaccine can be administered safely and comfortably with this new patch, which delivers the vaccine through a matrix of tiny dissolving microneedles.

Listeria monocytogenes bacteria don't play fair. Healthy people can usually handle the food-borne infection, but the bacterial infection hits pregnant women, fetuses and cancer patients very hard. Interestingly, a new study found that other bacteria may help prevent Listeria infections in those people.

With summer just ahead, you, or your children, may be looking forward to some pool time or the water park. When planning water-based fun this year, keep a heads-up for microbes.

Most of us have already had an encounter with the Epstein-Barr virus, or EBV, for short. As part of the herpes family, it's one of the most common disease-causing viruses in humans. We get the disease with (or without) some nasty symptoms, then we recover. However, EBV stays in our body after the illness has ended, and it's one of the few viruses known to cause cancer.

Drug-resistant bacteria have made curing some infections challenging, if not nearly impossible. By 2050, it's estimated that 10 million people will be dying annually from infections with antibiotic-resistant organisms.

Long admired for their active and cooperative community behavior, some types of ants also wear a gardening hat. Nurturing underground fungus gardens, these ants have a win-win relationship that provides food for both ants and fungi. If we humans understand it better, it may just help us out, too.

As if being pregnant did not come with enough worry, a new study found that certain antibiotics are linked to an increased risk of spontaneous abortion, or miscarriage — a terrifying finding for any expectant mother.

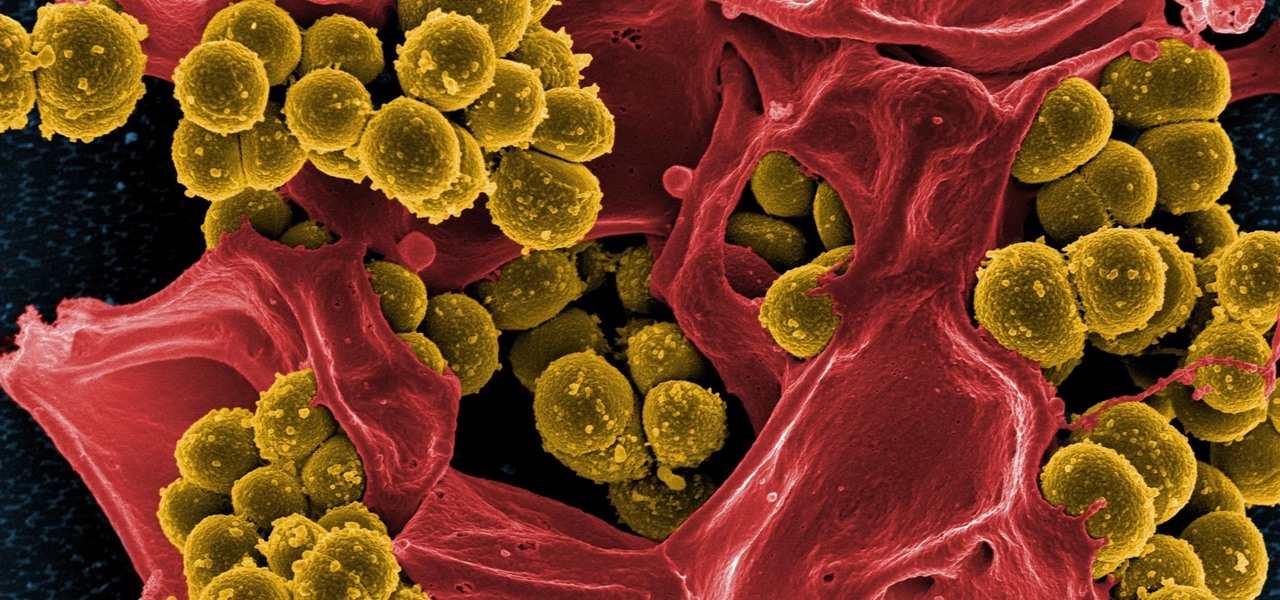
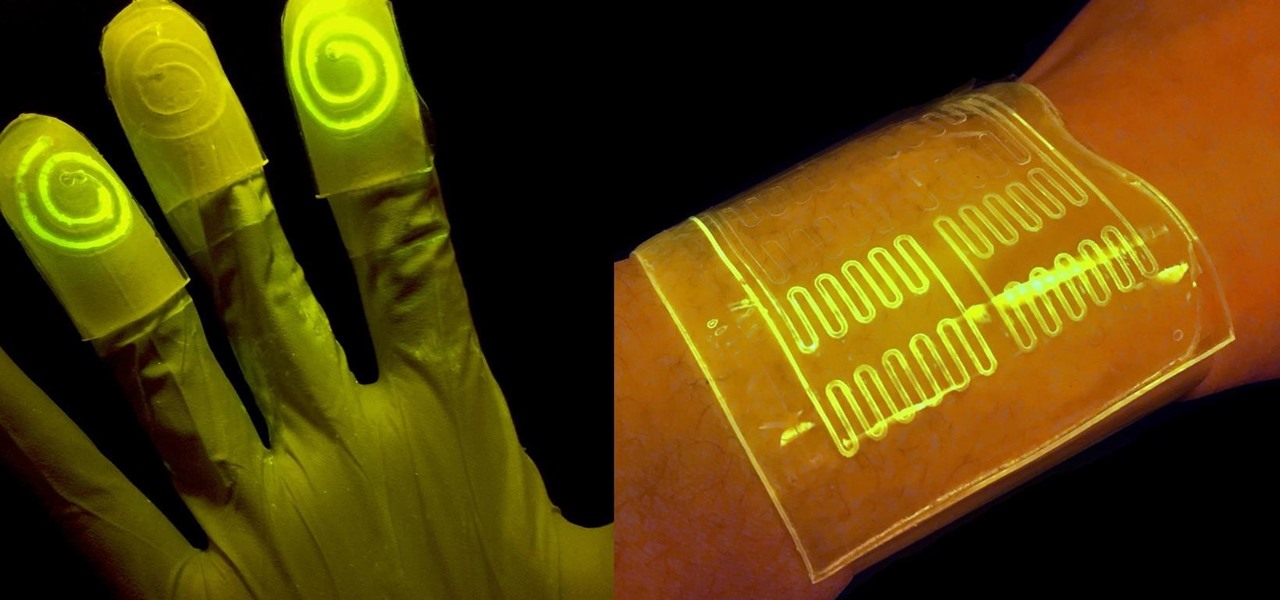
While at work, you notice your gloves changing color, and you know immediately that you've come in contact with dangerous chemicals. Bandages on a patient signal the presence of unseen, drug-resistant microbes. These are ideas that might have once seemed futuristic but are becoming a reality as researchers move forward with technology to use living bacteria in cloth to detect pathogens, pollutants, and particulates that endanger our lives.

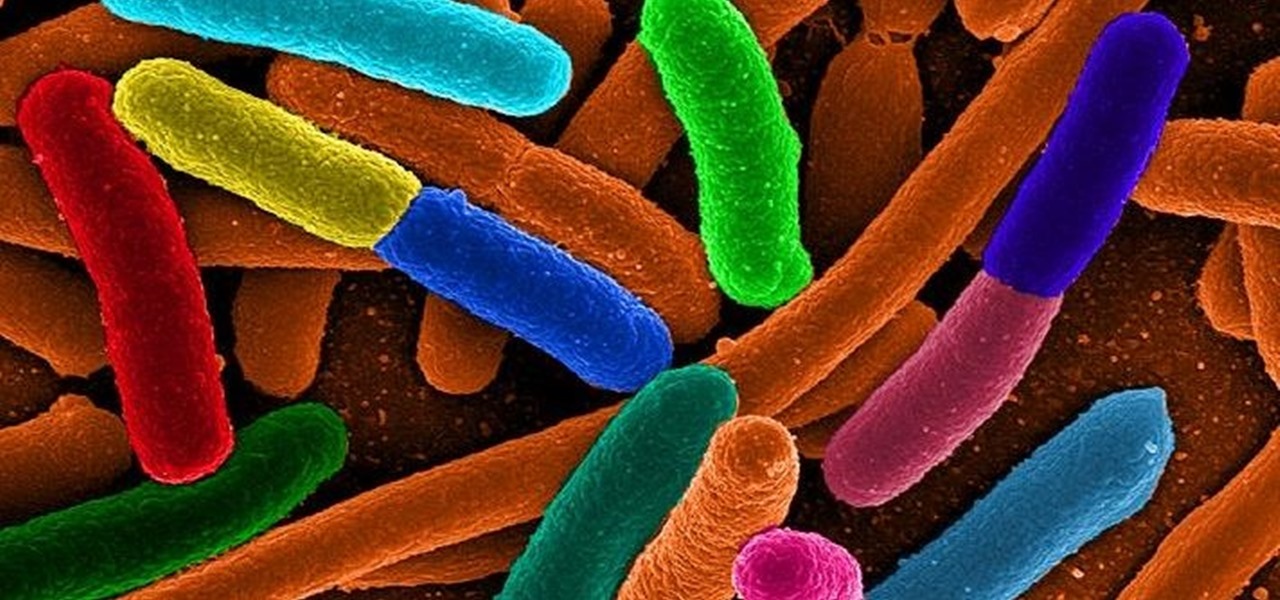
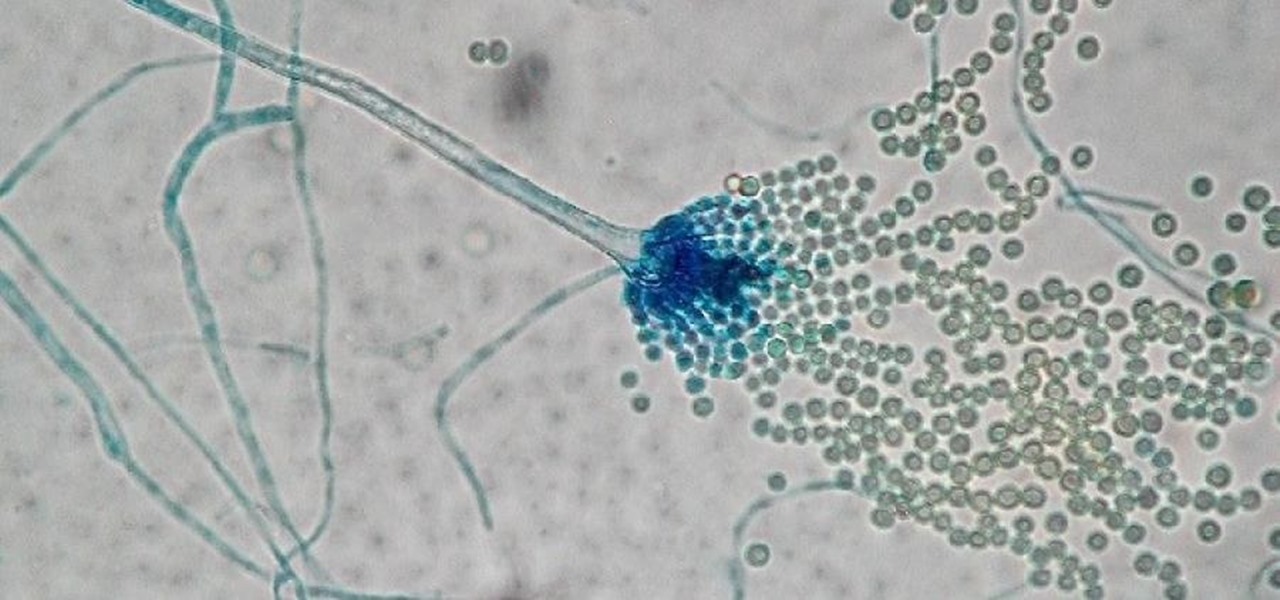
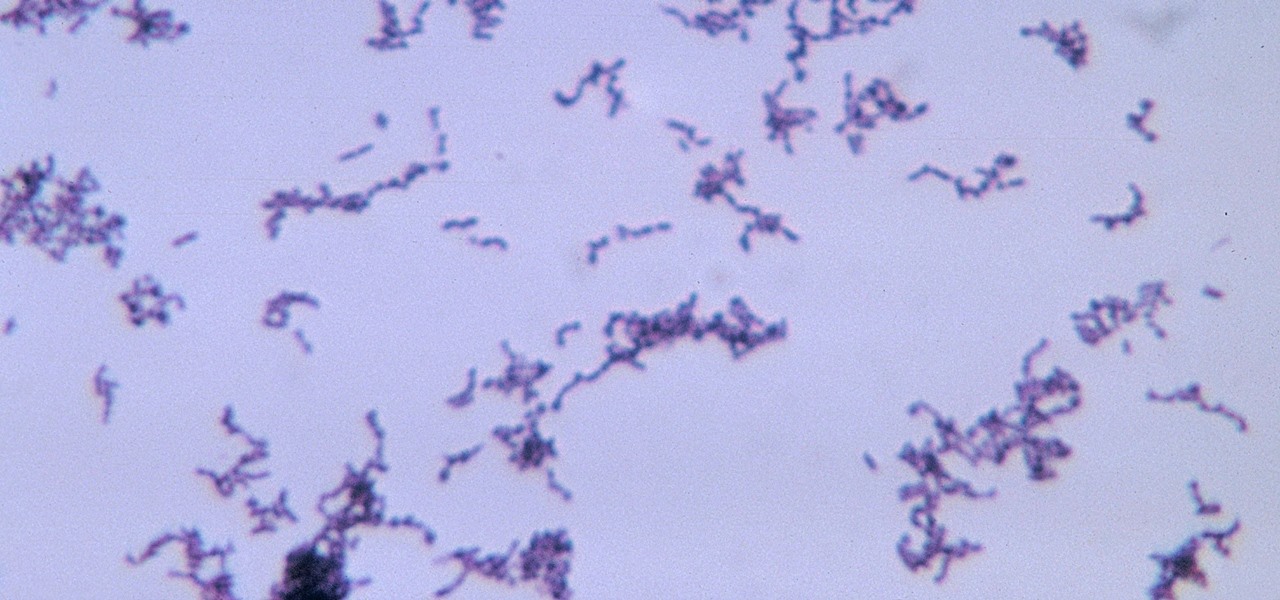
The squiggly guys in this article's cover image are Propionibacterium acnes. These bacteria live in low-oxygen conditions at the base of hair follicles all over your body. They mind their own business, eating cellular debris and sebum, the oily stuff secreted by sebaceous glands that help keep things moisturized. Everybody has P. acnes bacteria—which are commonly blamed for causing acne—but researchers took a bigger view and discovered P. acnes may also play a part in keeping your skin clear.

Yellow fever has emerged again in Brazil, causing death and disease to people unprepared for this mosquito-borne illness.

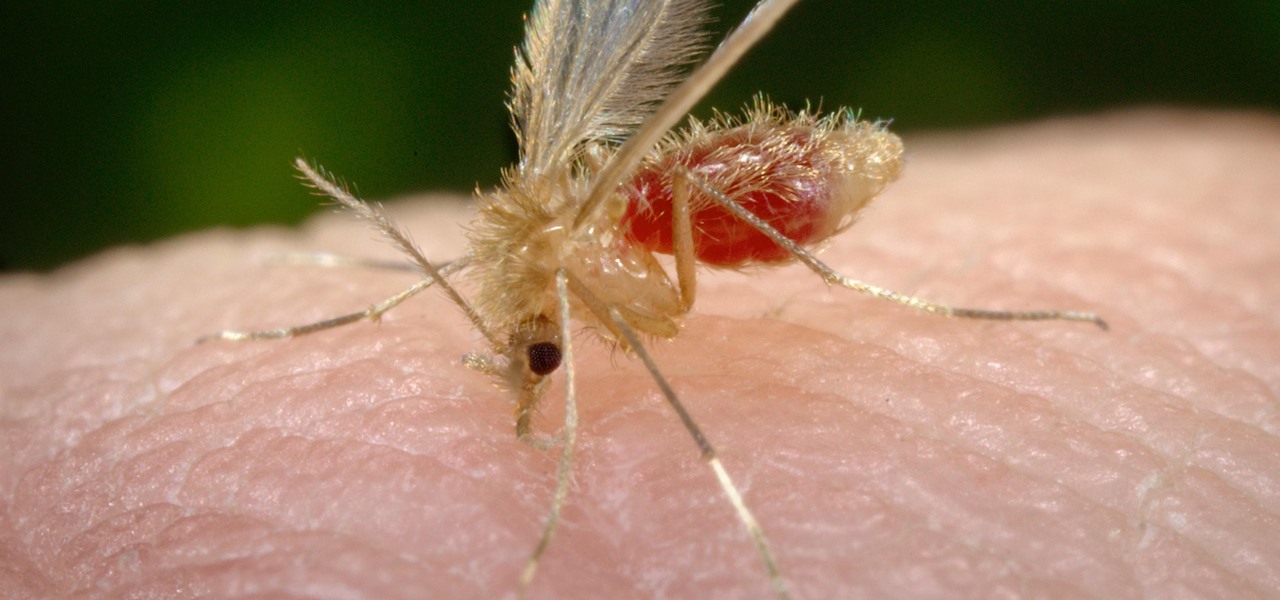
Transmitted by a sandfly one-third the size of a mosquito, parasitic Leishmania protozoa are responsible for a flesh-destroying disease that kills an estimated 20,000 people per year. Two new studies offer understanding of how the parasite provides immunity through persistence and why some people suffer more virulent forms of the disease.

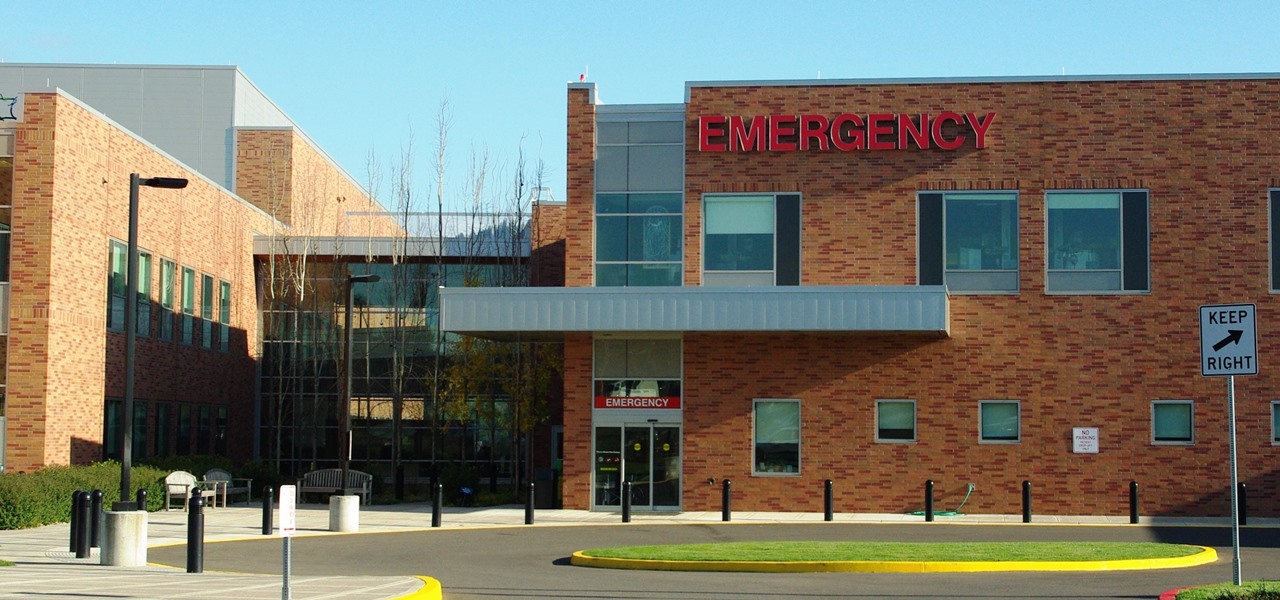
It feels like someone reached into your chest and squeezed. Your head throbs in unison with your heartbeat. Clammy dread coats your body in sweat. Whether you call 911 or someone does it for you, the ER is your next stop.

Lighthouses and signal fires may have been the first social media. Without the ability to share language, a distant light meant "humans here." A new study from the University of California, San Diego, finds that bacteria can also send out a universal sign to attract the attention of their own, and other bacterial species.

All fields of study have their own language. For people interested in learning about microbes, the language can sometimes be downright difficult — but it doesn't need to be. From antibiotics to xerophiles, we have you covered in an easy-to-understand glossary.

Specialized cells in the lining of the gut may provide a key to preventing an infectious brain disease caused by misfolded proteins.