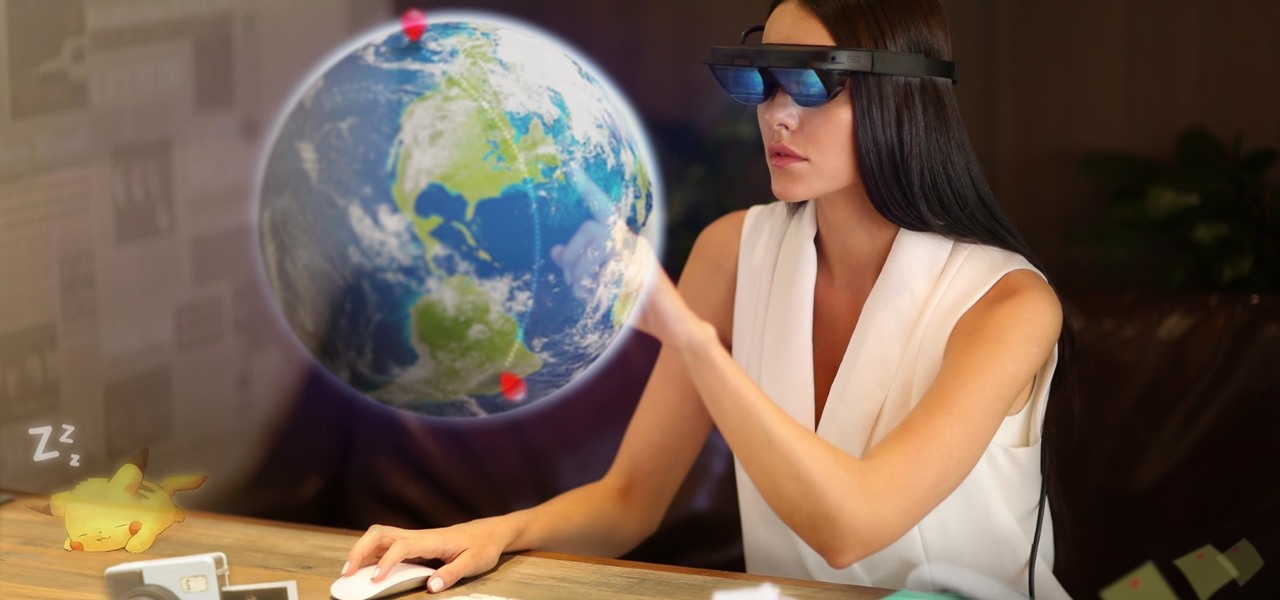
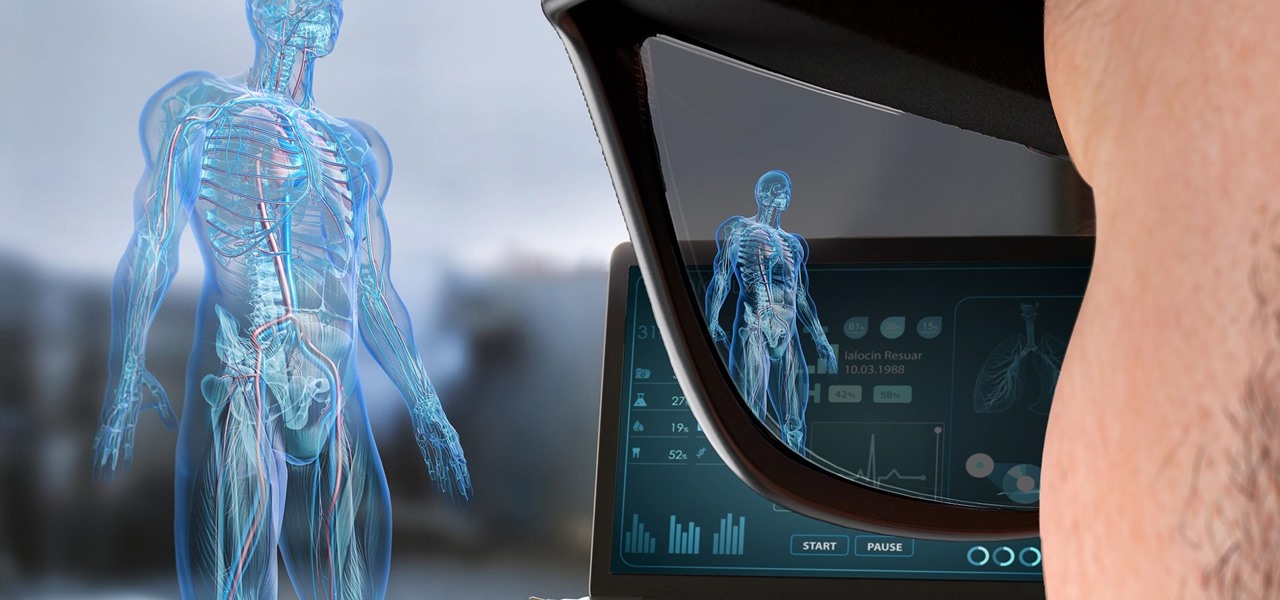
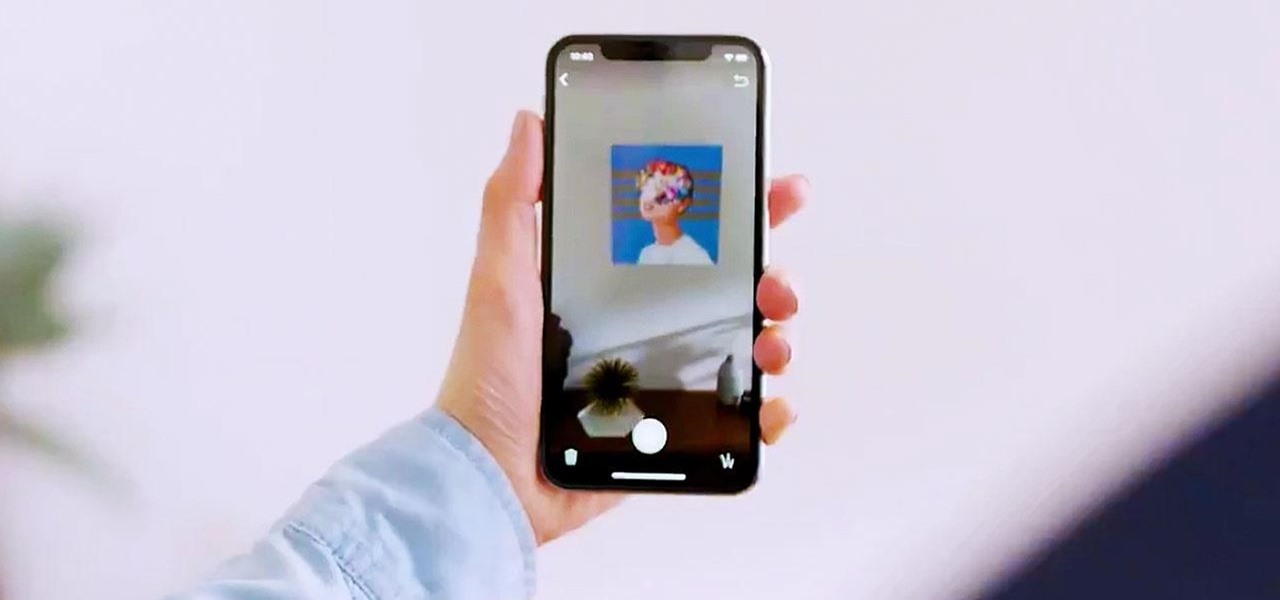
The mainstreaming of augmented reality won't happen overnight, but it's becoming increasingly clear that traditional media is leading the charge in the effort to introduce the public to immersive computing. A recent example came from none other than USA Today via its 321 Launch app.

OnePlus pulled out almost all the stops with their latest flagship, but there are a few areas where the phone falls just short of perfect. The single bottom-firing speaker leaves a lot to be desired, for instance, but thanks to the awesome development community for the OnePlus 6, you can already give your phone true stereo speakers with a software mod.
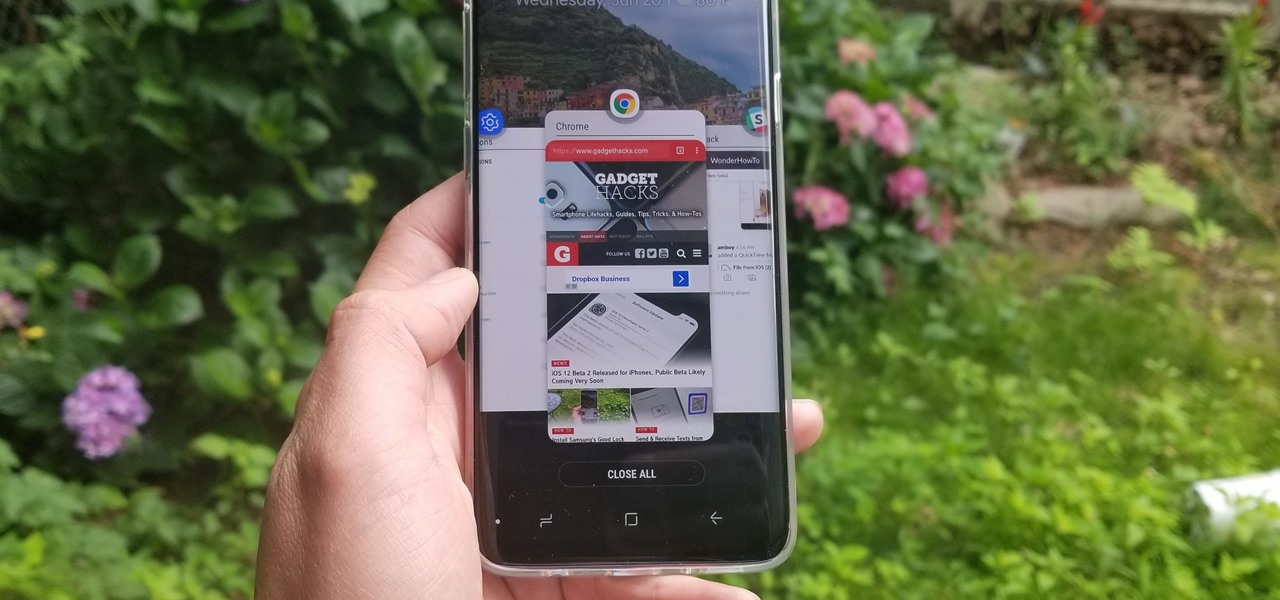
A revamped Recent Apps overview is one of the most significant changes set to arrive with Android P when it touches down later this year. Incredibly, Samsung has beaten Google to the punch, and has made this feature available for all its Oreo-based Galaxy handsets courtesy of its Good Locks app.
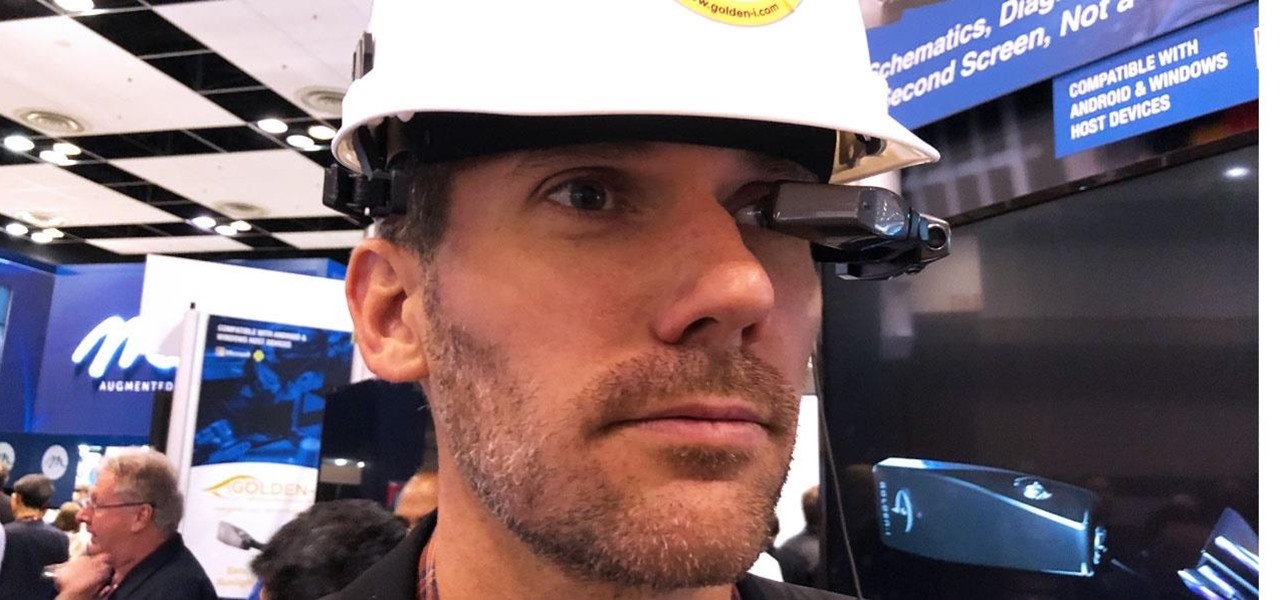

If you cover a particular area in tech long enough, you develop certain pet peeves, and one of mine happens to be devices that attempt to keep us wed to the Google Glass style of augmented reality. And while I remain mostly uninterested in such devices, one of these products recently earned my admiration and might work for you, too, under the right circumstances. It's called the Golden-i Infinity.
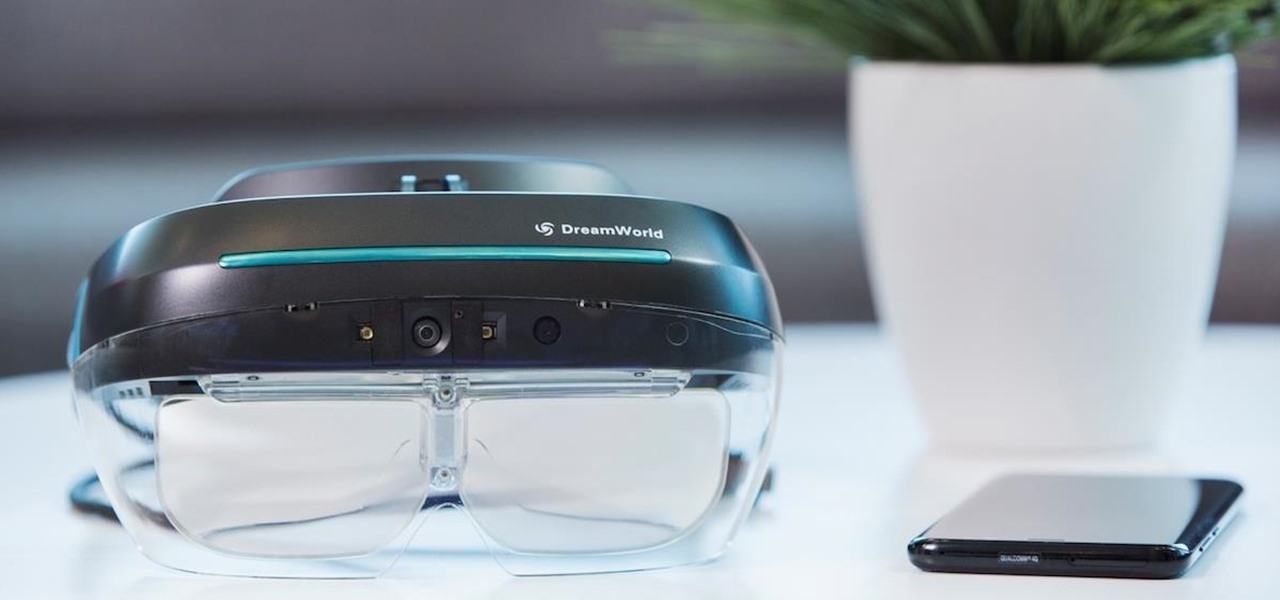

Just a year after facing trade secret theft allegations from his former employer, ex-Meta Company employee Kevin Zhong and his new company are ready to ship the product that triggered the lawsuit.

Google's ARCore has expanded its support to include the Galaxy S9 and S9+, which means you get access to all the cool new apps that can sense the world around them. But one of ARCore's coolest uses so far is still Pixel-exclusive: AR stickers built right into the Google Camera app. Thankfully, XDA user lofass33 has an ingenious workaround for using these stickers on your S9.

The pending union between Prince Harry and American actress Meghan Markle is almost guaranteed to set the internet ablaze as millions tune in to experience the spectacle and pageantry of such a momentous event. If you've cut the cord and are wondering where you can stream the royal wedding for free, we've got you covered.

China-based virtual reality headset maker ANTVR has decided to enter the augmented reality space, and to do so it's launching its headset on Kickstarter. The company claims that its new Mix AR device has a field of view that surpasses the Meta 2, the HoloLens, and others within a smaller form factor and at a fraction of the price. But there's a catch.

With all the recent activity around augmented reality, the possibilities involving immersive computing and commerce are quickly becoming obvious, and digital payments giant PayPal has no plans to sit on the sidelines

The price tag for the Microsoft HoloLens might be out of range for the average consumer's budget, but for enterprises, like BAE Systems, adopting the AR headset is yielding a return on the investment. And for those with even slimmer wallets, Best Buy just made the Lenovo Mirage, part of the Star Wars: Jedi Challenges package, more affordable.

It appears we're in the midst of an augmented reality art boom, because in the same month that the famed Christie's auction house launched its mobile AR app, leading art gallery and art seller Saatchi Art has also announced its entry into the AR space.

Contrary to popular belief, augmented reality apps have been available for a while now. I remember using the Layar app (still available for iOS and Android) to explore nearby businesses and landmarks with varying success via an early-generation Android handset.

If you've unlocked your iPhone lately and noticed some apps aren't fully installed anymore, you're not alone. After updating my device recently to a newer version of iOS 11, I didn't immediately understand what caused a few of my games to uninstall themselves. It turns out, there's a simple setting that explains what's going on.

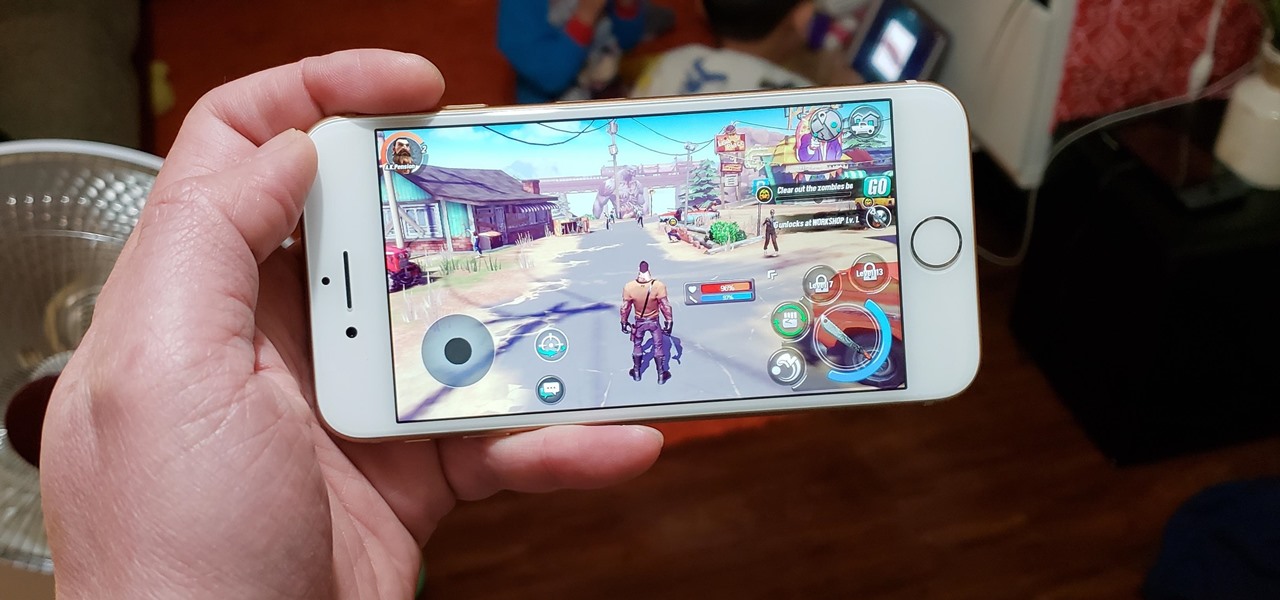
Mobile gamers are well aware of this, but zombie shooters have become pretty stagnant and unimaginative in recent years. Too many entries in this genre feature the same cookie-cutter gameplay, but thankfully, Gameloft aims to change this. The company has soft-launched Dead Rivals in a few countries, and with a little work, you can try the game yourself right now.

One odd change found in the Android Pie update is that the "Battery" menu no longer lets you see apps that are draining your battery, nor gives access to usage details. However, one quick menu tweak will bring the Battery menu back in line with Android Oreo's, only there's a hidden setting you have to unlock first.

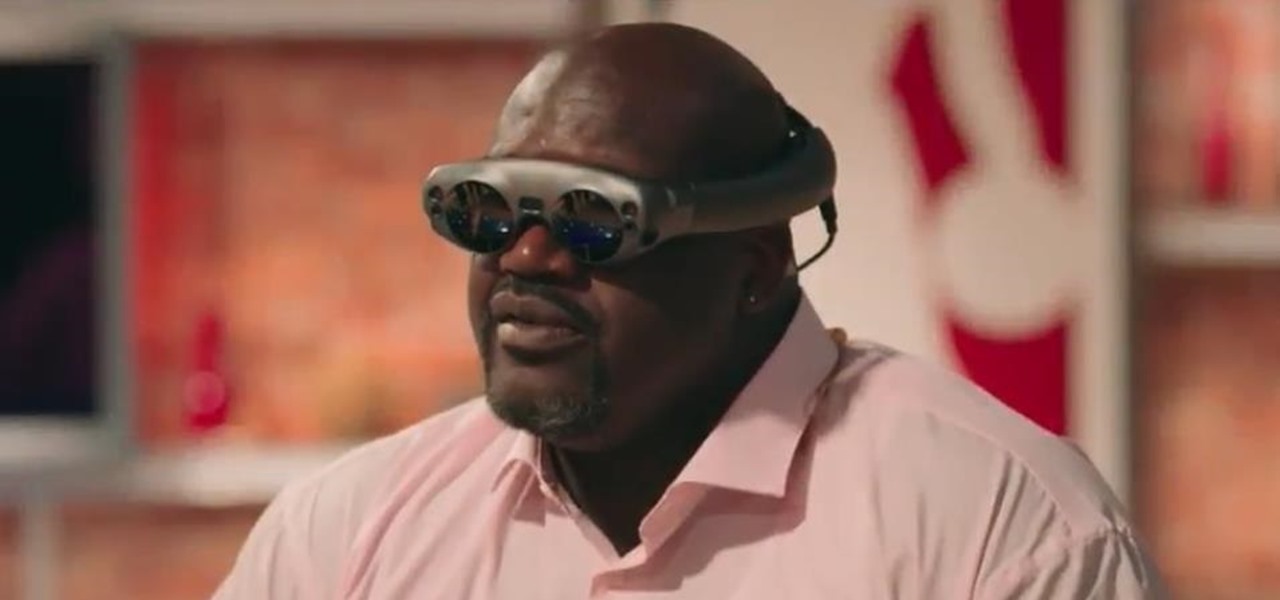
On Tuesday, NBA Commissioner Adam Silver joined Magic Leap CEO Rony Abovitz on stage to unveil a partnership between the two companies.

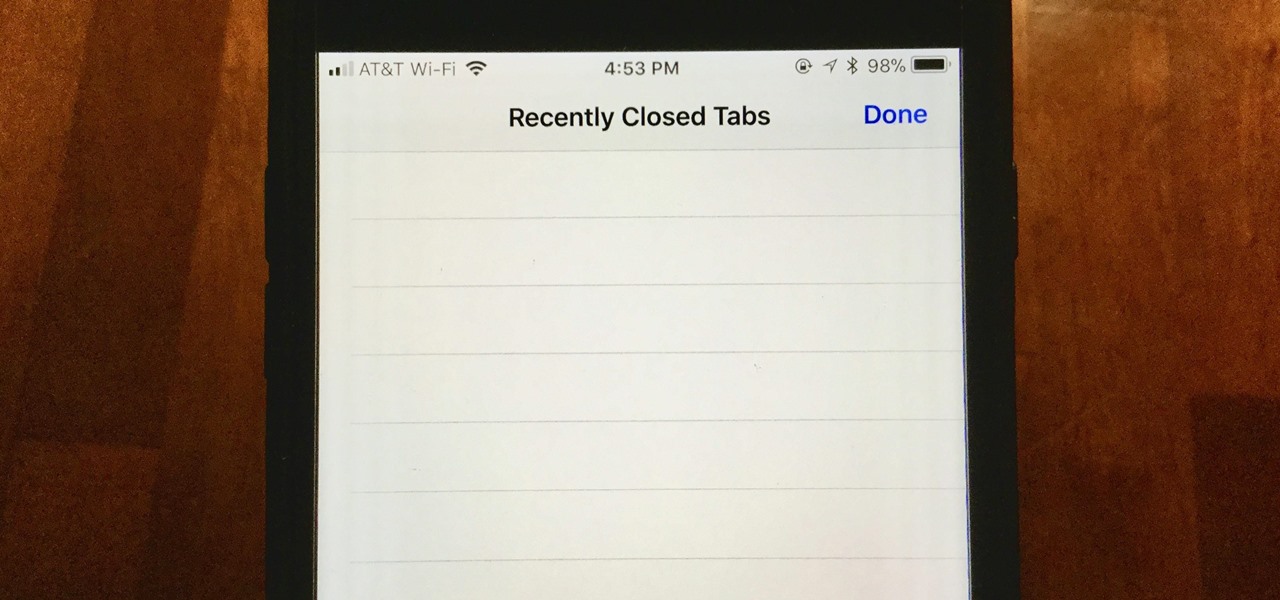
When you accidentally close out of an important tab on your iPhone, Safari's "Recently Closed Tabs" list really comes in handy. However, when it comes time to clear the list, things get a bit complicated. There's no "Delete" or "Erase" button on this page, but don't let that fool you — there are three easy ways to clear your recently closed tabs list.

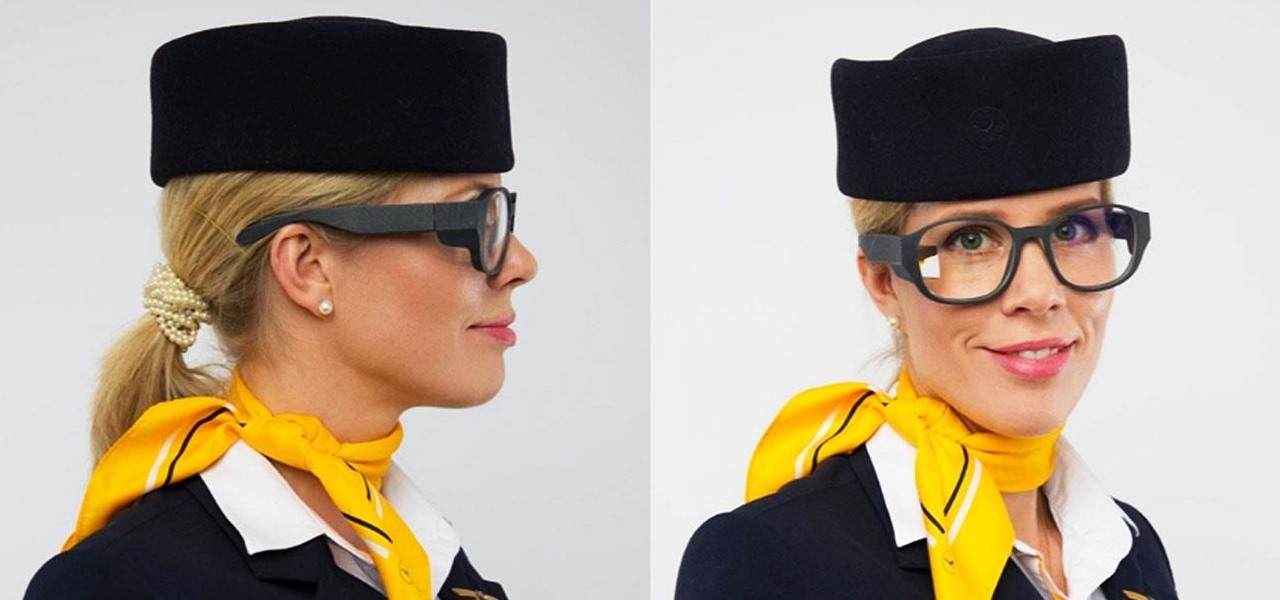
A new smartglasses powerhouse is rising in Europe, led by two of the region's leading brands, optical systems company Zeiss (also known as Carl Zeiss) and telecommunications giant Deutsche Telekom.

Google, Facebook, and Huawei have made an investment in nurturing the future of augmented and virtual reality through $6 million in contributions to the opening of a new center at the University of Washington.

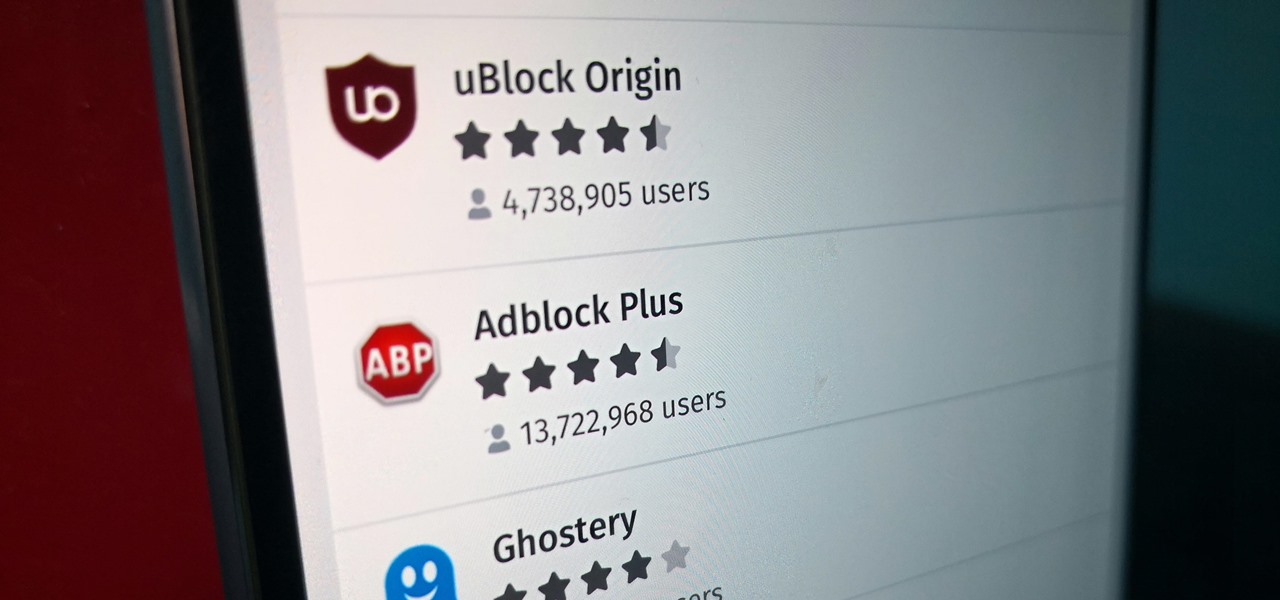
Features like themes and a tab queue make Firefox an extremely versatile mobile browser. Mozilla is constantly adding bonus functionality like this to Firefox, but a long-time staple is perhaps the most powerful feature: Extensions. This system gives you the ability to add features without having to upgrade the entire app.

It recently came to light that a number of Android phones are unable to stream HD video through services like Netflix, Google Play Movies, and Amazon Prime Video. If you're worried that your phone may be affected, there's a simple tool you can use to find out for sure if you can actually stream video in 720p or higher.

Between Renault Truck's testing of the HoloLens in factories and BMW promoting its newest model through Snapchat, the auto industry is hot for augmented reality to improve internal operations and engage consumers.

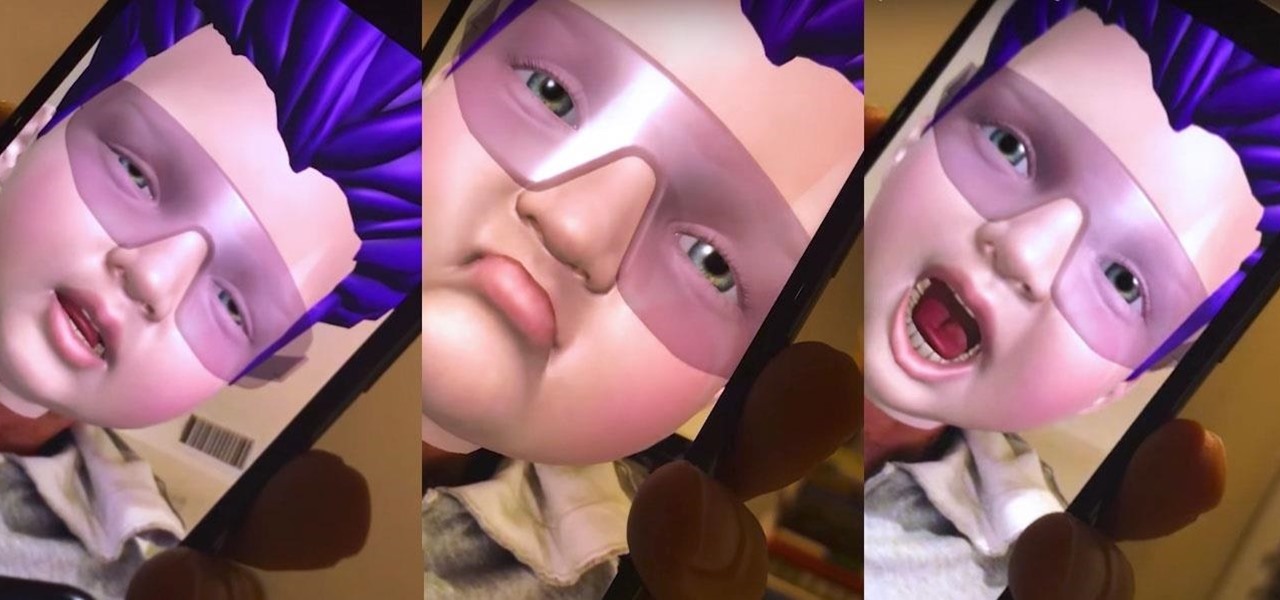
Since the very first moment I saw the iPhone X track a human face and display the results in real-time on an Animoji character, I've been waiting for the first great hack of this new iPhone feature.

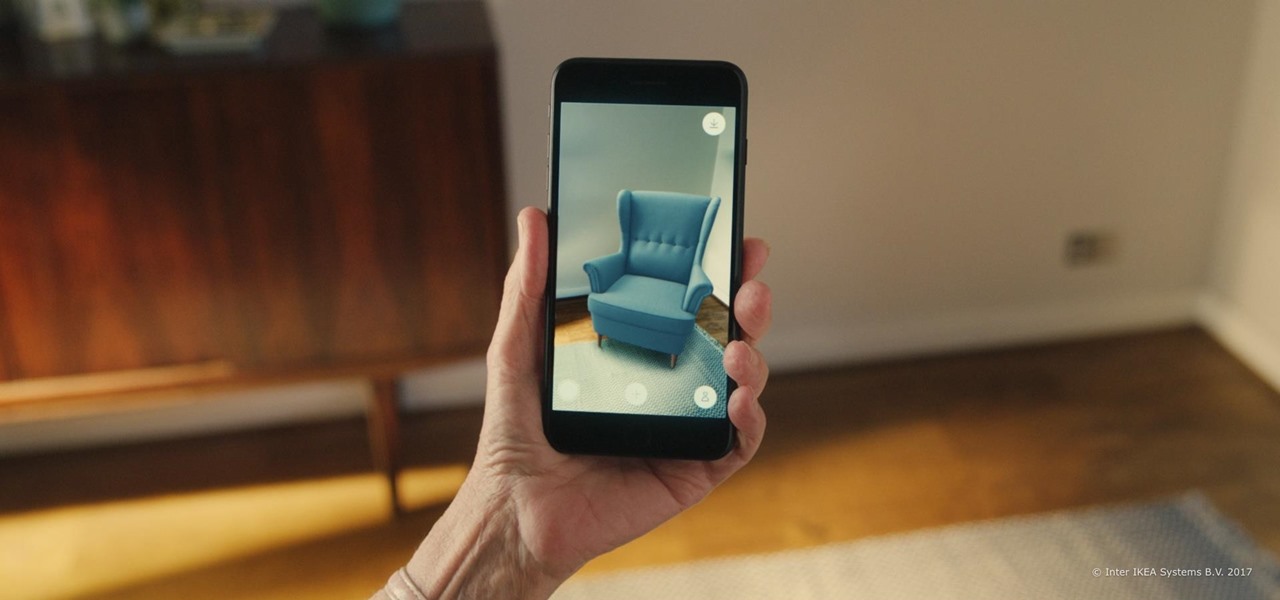
In case you didn't already know, augmented reality is here. It's no longer just an idea in a cyberpunk novel. And while augmented reality has been around for a long time, the actual technology is finally catching up to the idea.

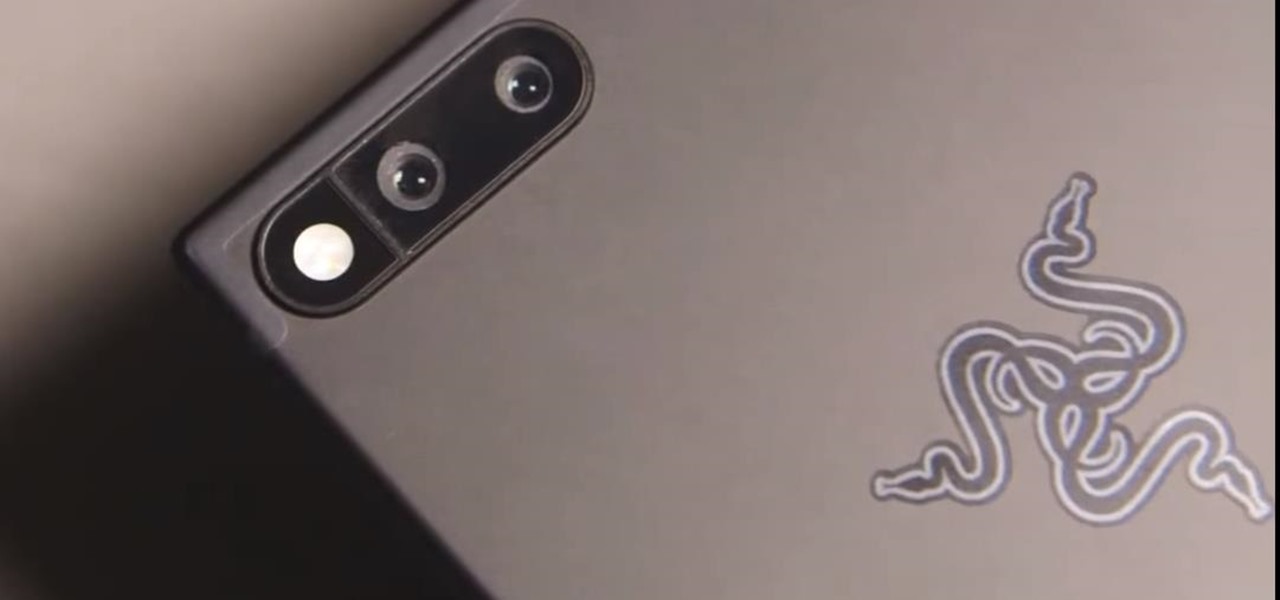
Razer, the company known for PC peripherals and laptops, is joining the smartphone industry with a new device. Rumors have been swirling since they announced an event on November 1 at 4 PM EDT, but now, we have our best look yet with a leaked promotional video before the actual announcement.

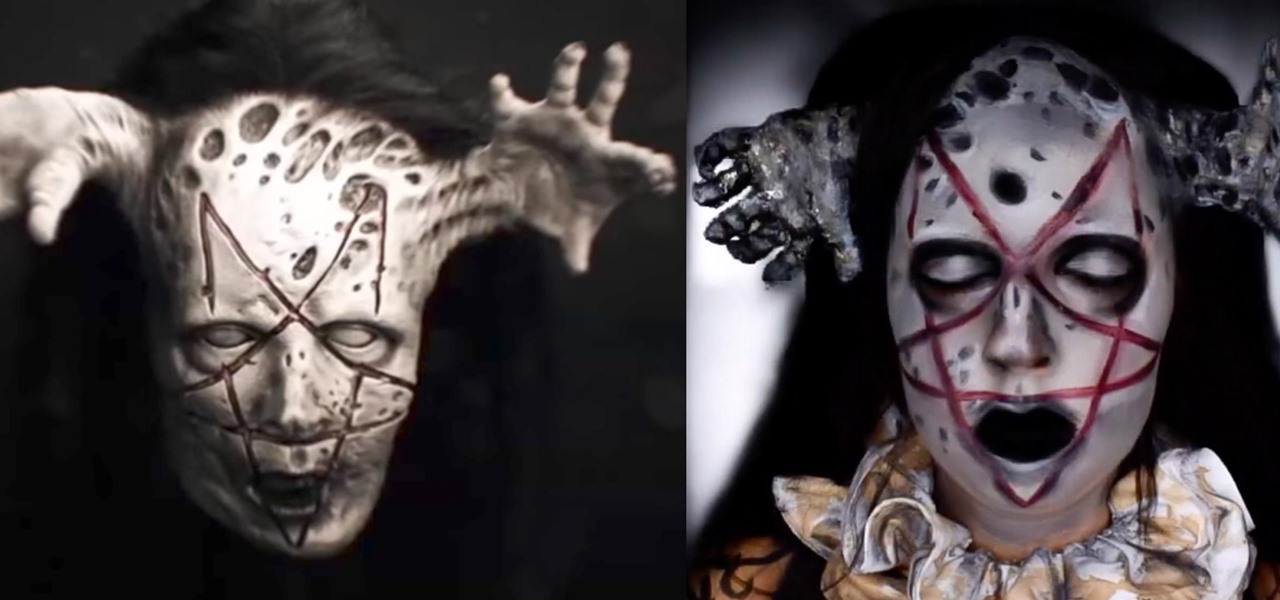
Pentagram has to be one of the most nightmarish creations on American Horror Story (even though she has some pretty tough competition to fend off). Can you think of anything much worse than a pair of hands wriggling their way out of your temples?

The first wave of iPhone X preorders, the ones with a delivery date of Nov. 3, sold out in ten minutes. You can still preorder one and skip the lines next week at Apple Stores across the country, but if you want that bezel-less beauty in your hands ASAP, brick and mortar might be the way to go.

The highly anticipated iPhone X is finally up for preorder, and it's been almost as exciting as we expected. With the dual cameras, bezel-less display, and high-tech facial recognition, there's almost nothing on the iPhone X that won't be liked. But around the same time as the iPhone X's announcement, another phone was revealed, and almost everyone seems to have forgotten about it. We didn't.

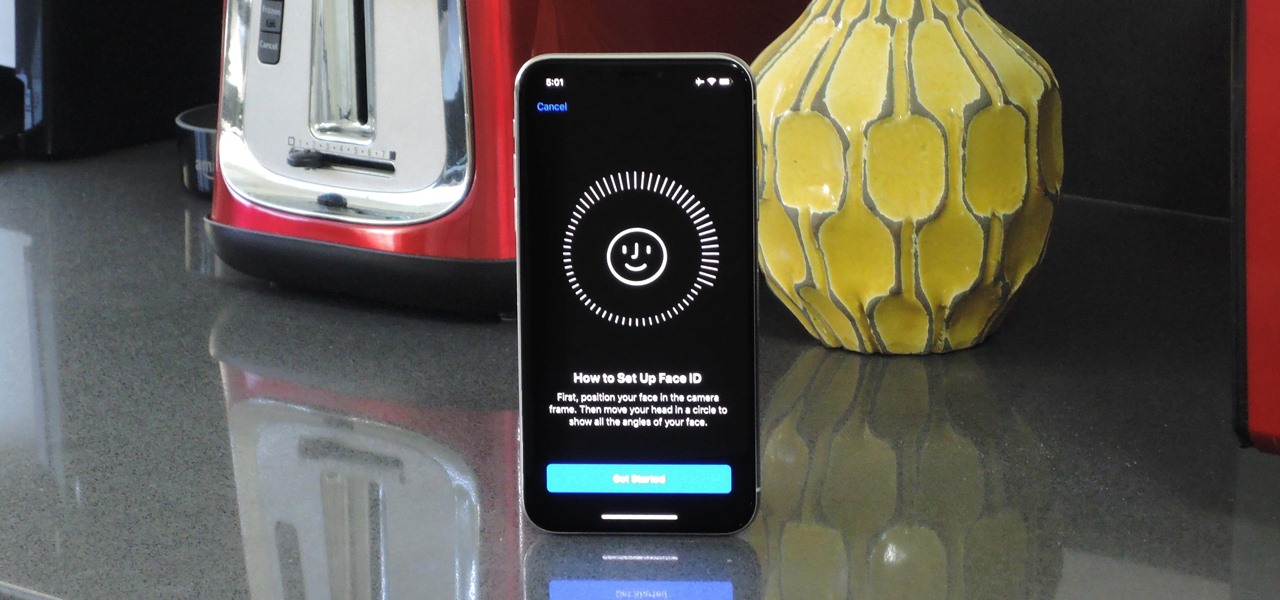
The cutting-edge iPhone X, XS, XS Max, and XR have one-upped their Android competitors when it comes to facial recognition. Apple packed these flagships with an array of front-facing sensors to complement its selfie camera, which allows the new device to more accurately analyze faces, which you need for Face ID, Touch ID's replacement.

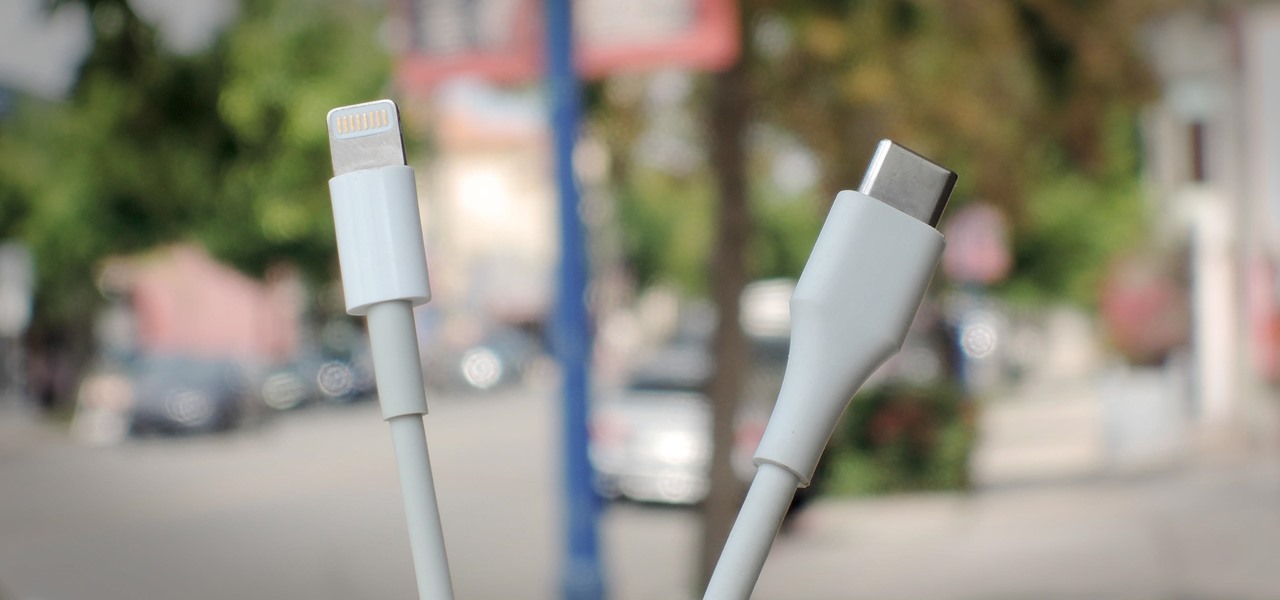
After learning that you'll need to spend at least $74 on a special charger and a USB Type-C Lightning cable to enable fast charging on the new iPhone X and iPhone 8 models, you may be wondering why you can't just use the standard Lightning cable. While we can't answer why Apple didn't include the USB-C cable in the box with their new phones, we can explain why you need USB-C to enable fast charging.

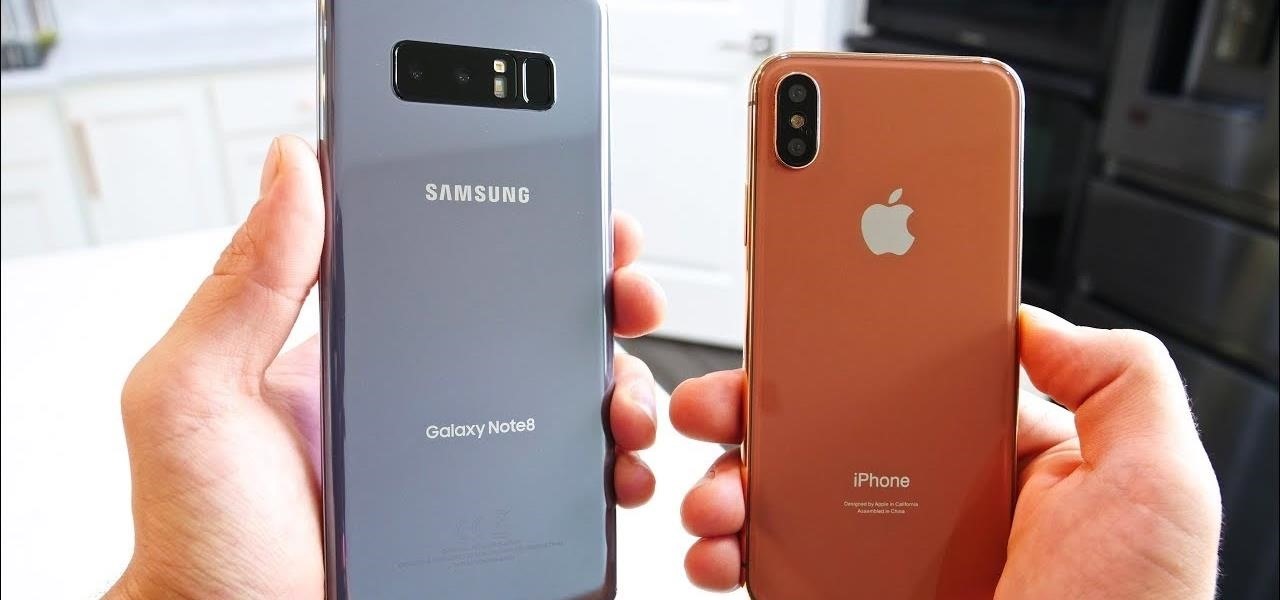
Now that the cutting-edge iPhone X is up for preorder, everyone is excited to see how the new device will compare to offerings from Apple's competitors. Namely the Galaxy Note 8, which is a beast of a phone in its own right.

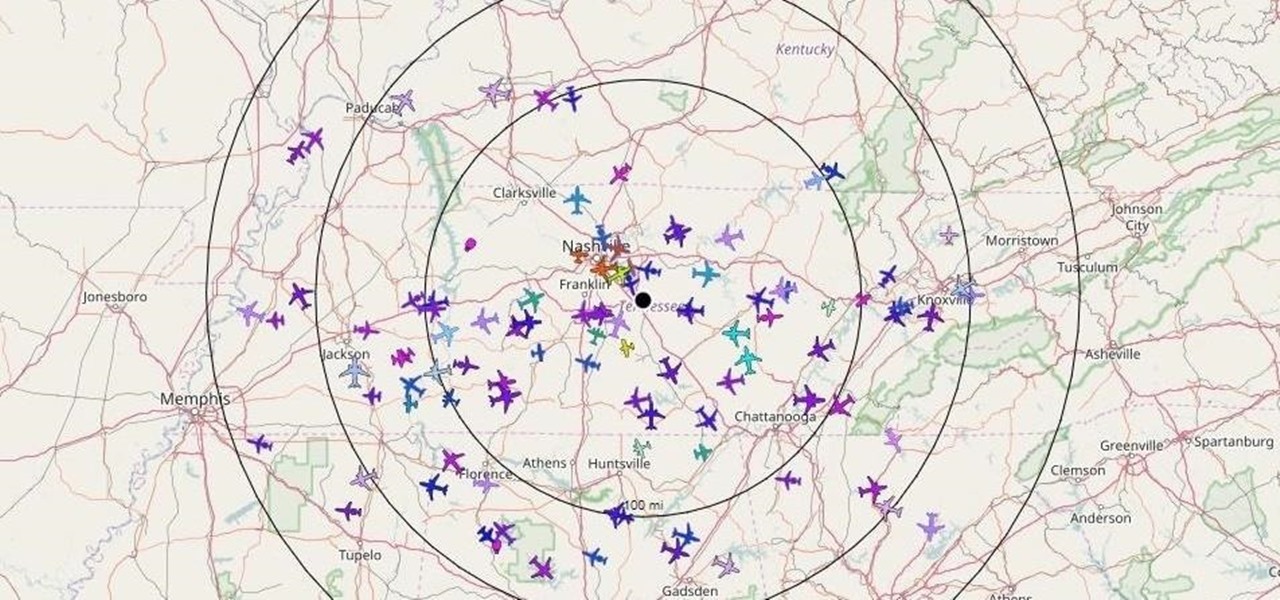
Aircraft equipped with ADS-B are constantly shouting their location into the radio void, along with other useful unauthenticated and unencrypted data. In this guide, we will make an ADS-B receiver using a Raspberry Pi with a software-defined radio (SDR) dongle, which we can use to track aircraft anywhere in real time.

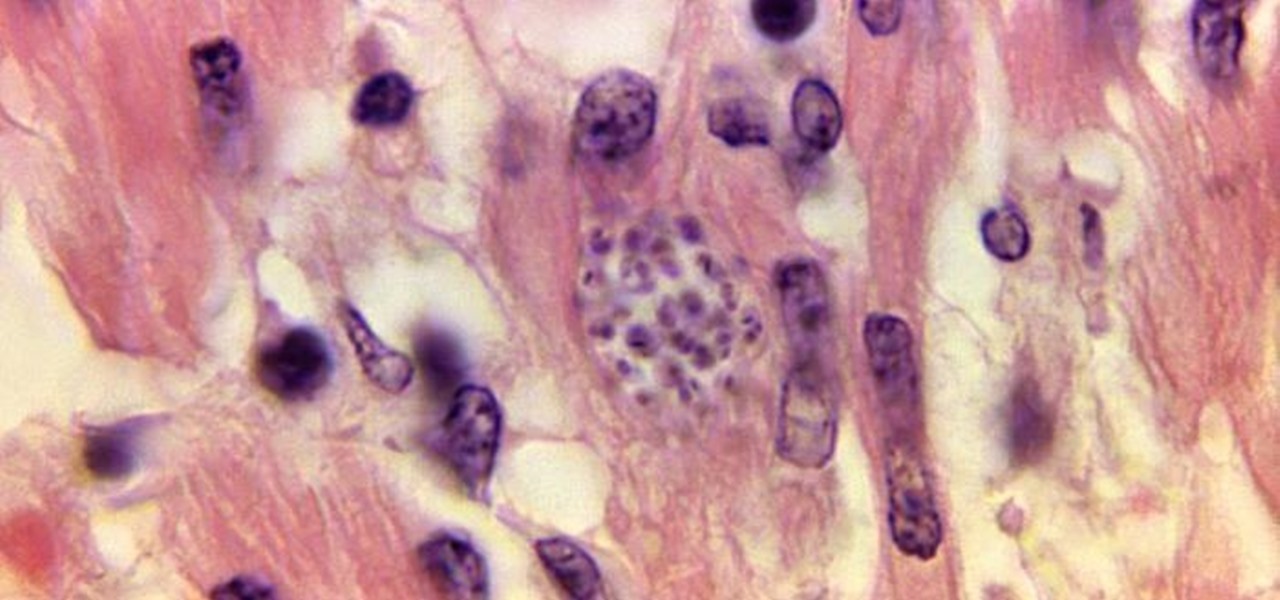
For the first time, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved medication to treat children with a serious infection called Chagas disease, which stealthily infects and damages the hearts of millions of victims a year.

Plants all around us capture sunlight every day and convert it to energy, making them a model of solar energy production. And while the energy they make may serve the needs of a plant, the process isn't efficient enough to generate power on a larger scale. So, scientists from the University of California found a way to treat bacteria with chemicals that turned them into photosynthesis machines, capable of generating products we can convert into food, fuels, and plastics.

This morning Google announced ARCore, an SDK for Android devices that will allow augmented reality developers to add new functionality to Android 7.0 and up, all without any special hardware other than the camera of a phone.

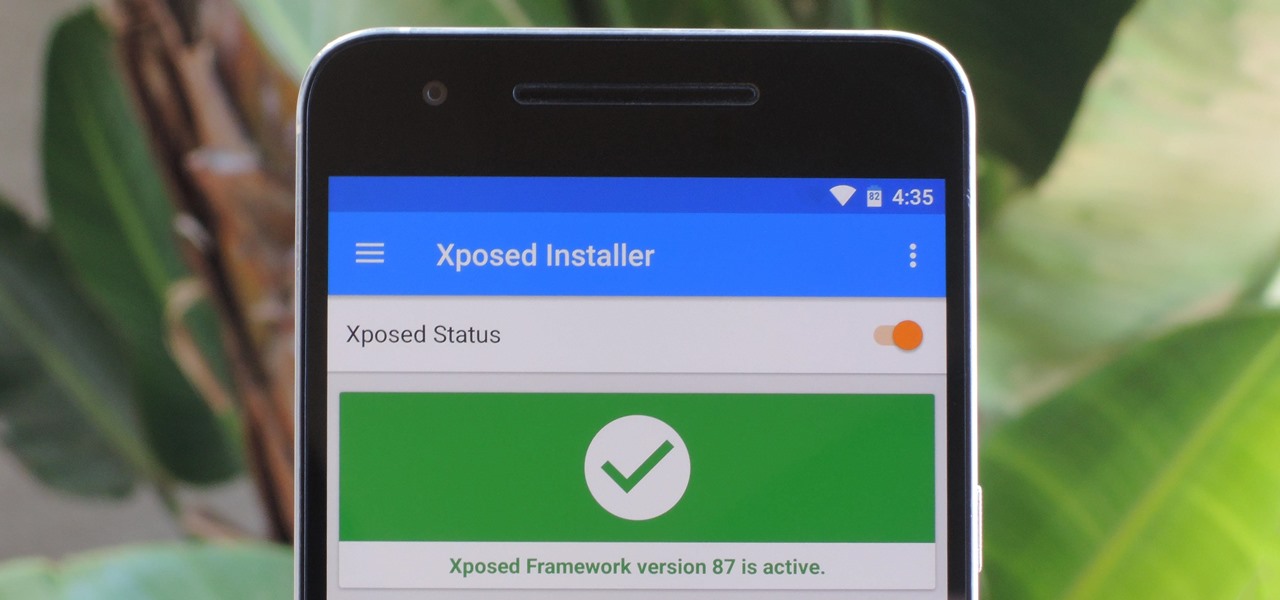
The Xposed Framework lets you modify your phone's software like nothing else. But because of how powerful this tool can be, it seems like things are always in development. This is certainly the case with many Xposed modules, to the point where some have several alpha and beta releases before they go mainstream.

The Xposed Framework is still alive and kicking despite the fact that development has slowed down a bit lately. Rovo89 is the only true developer behind Xposed, so it's really a one-man show. This means the popular root mod doesn't typically support the latest Android version, but it's usually only one version number behind.

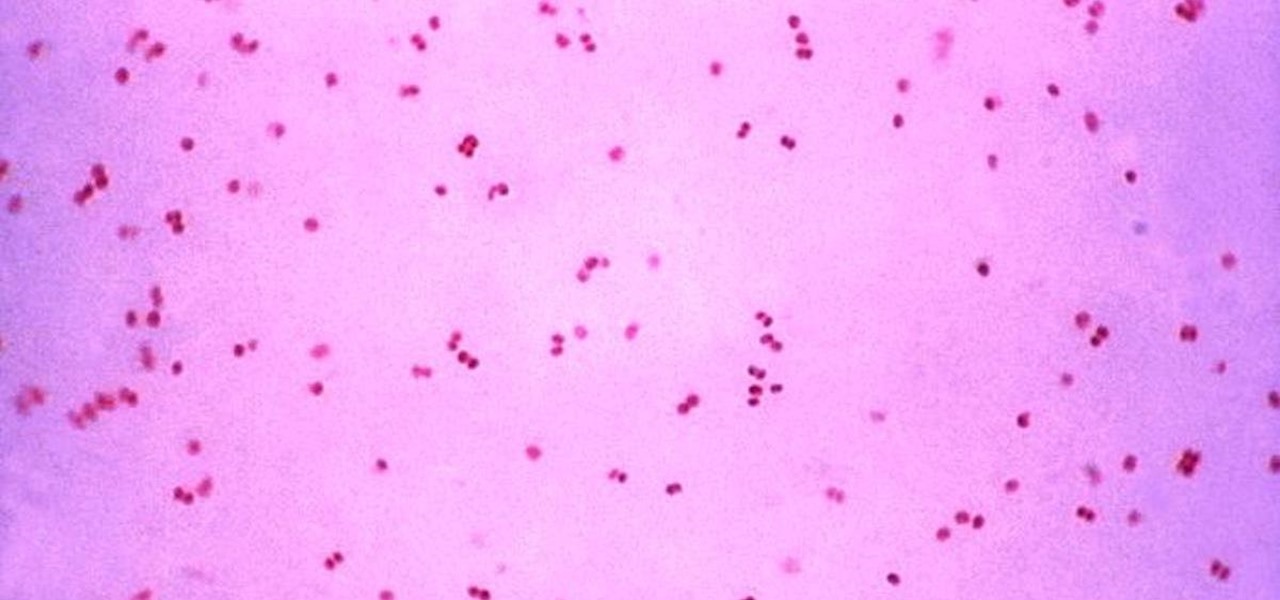
Gonorrhea infections reached a peak in 1975, then decreased until 2009, when infection rate started rising and has increased each year since. With the rise of antibiotic resistance, those numbers are only going to get worse — unless we find new treatments against the bacteria.

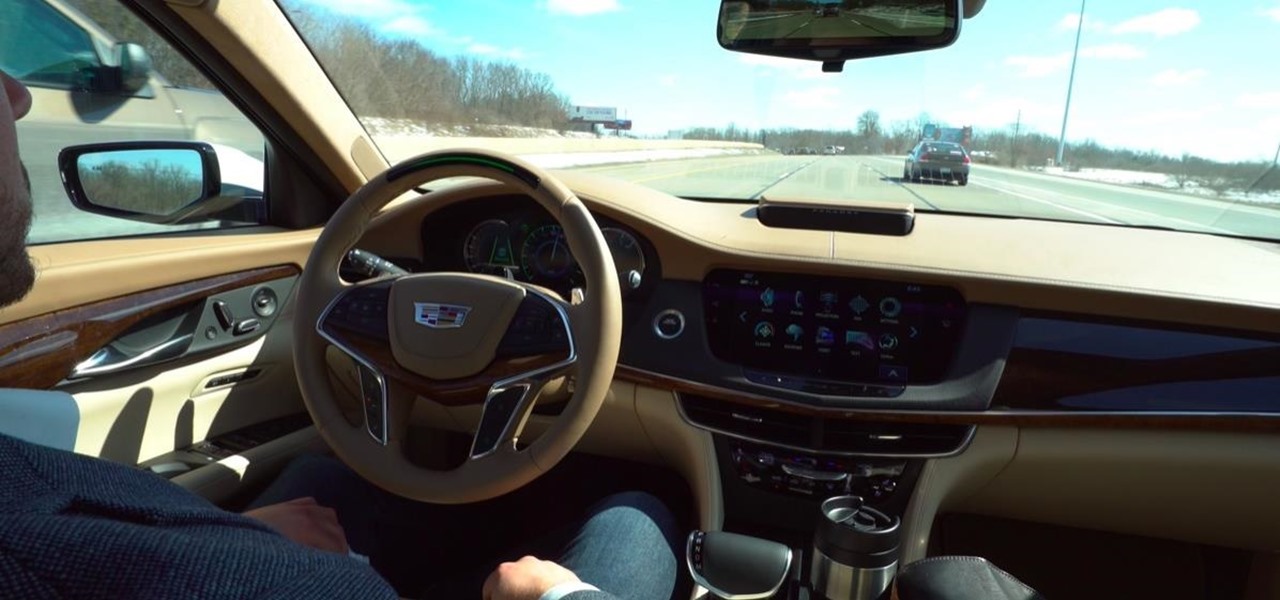
General Motors (GM) seems to have gone to great lengths to avoid lawsuits as it launches its first hands-off driving system in its soon-to-be-launched Cadillac CT6.

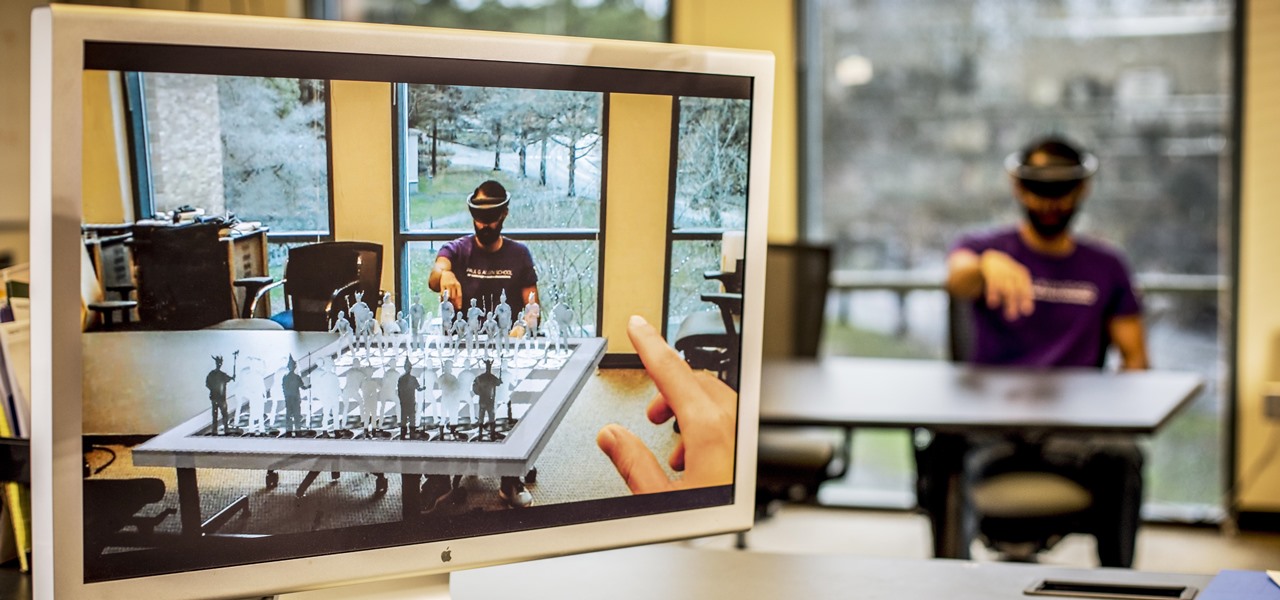
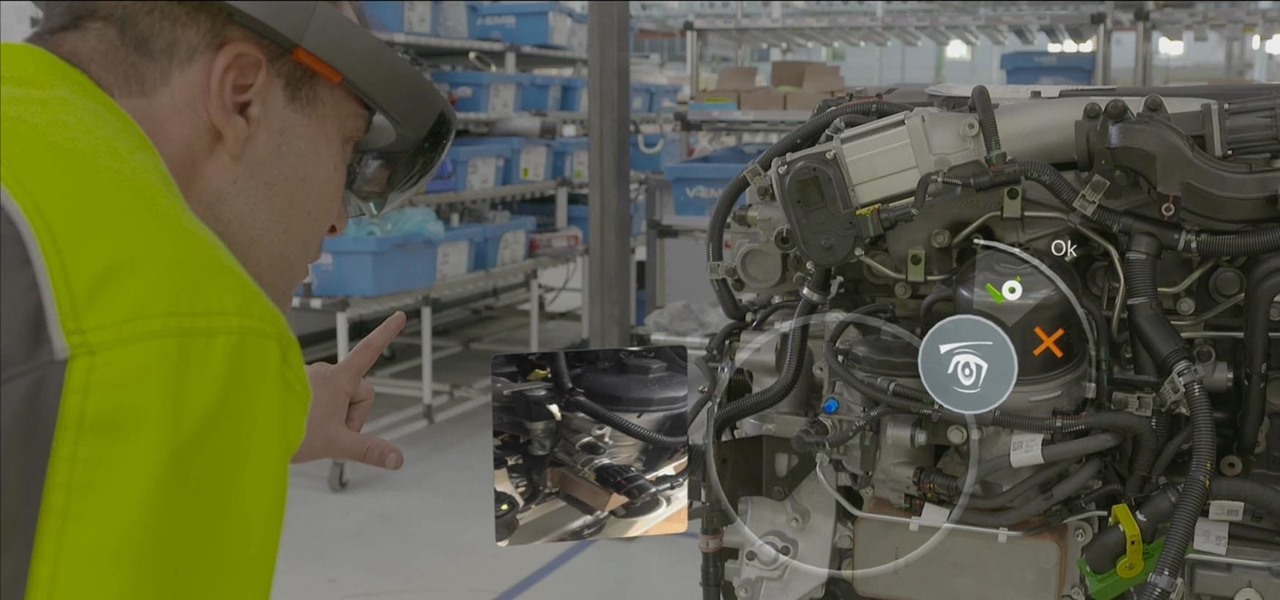
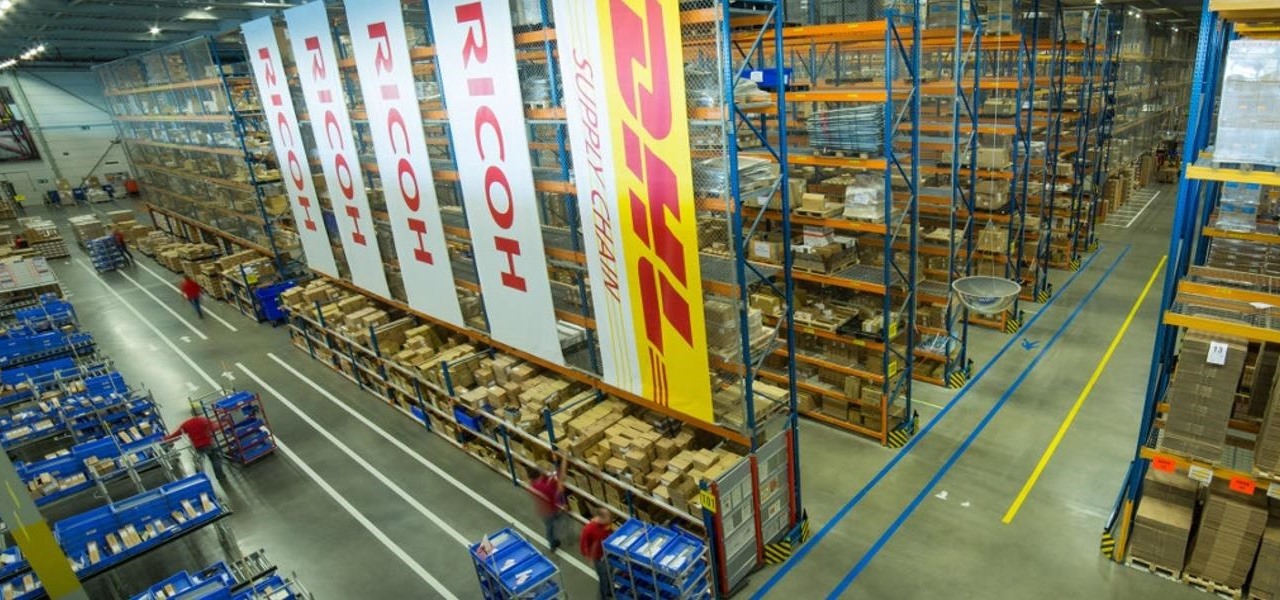
Augmented reality can be used to fascinate and entertain, but it can be applied in the workplace. While companies on the entertainment end received their votes of confidence via funding, two companies working with enterprises demonstrated their worth by teaming up to pursue customers.