
How To: Make rye bread
In this video series, our expert will show you how to make homemade rye bread. You will learn how to activate the yeast, work that rye bread dough and add the flour for this homemade bread recipe.


In this video series, our expert will show you how to make homemade rye bread. You will learn how to activate the yeast, work that rye bread dough and add the flour for this homemade bread recipe.
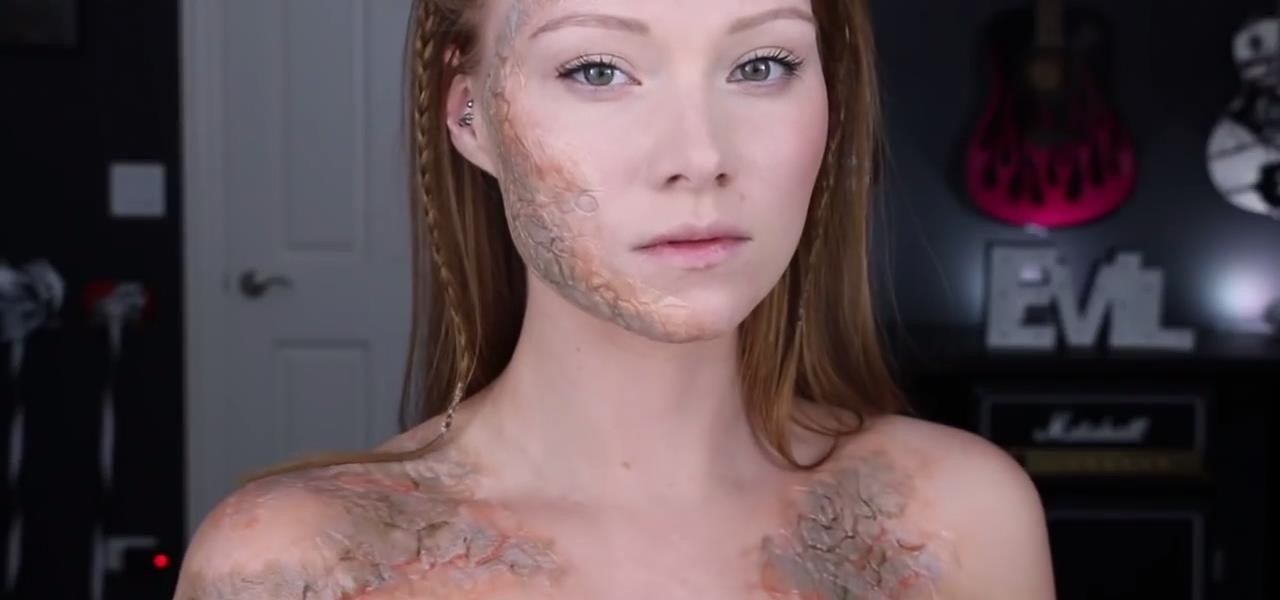

There aren't many people who will believe that a prosthetic zipper face or gunshot wound to the eye (disgusting as they are) are real, but greyscale from Game of Thrones? That'll really unsettle people for awhile because it totally looks like an actual, honest-to-God infection that someone in 2017 could conceivably have. Which makes it very effective come Halloween, whether it's for a full-on Princess Shireen, Jorah Mormont, or Stone Man costume, or to just infect a completely different chara...
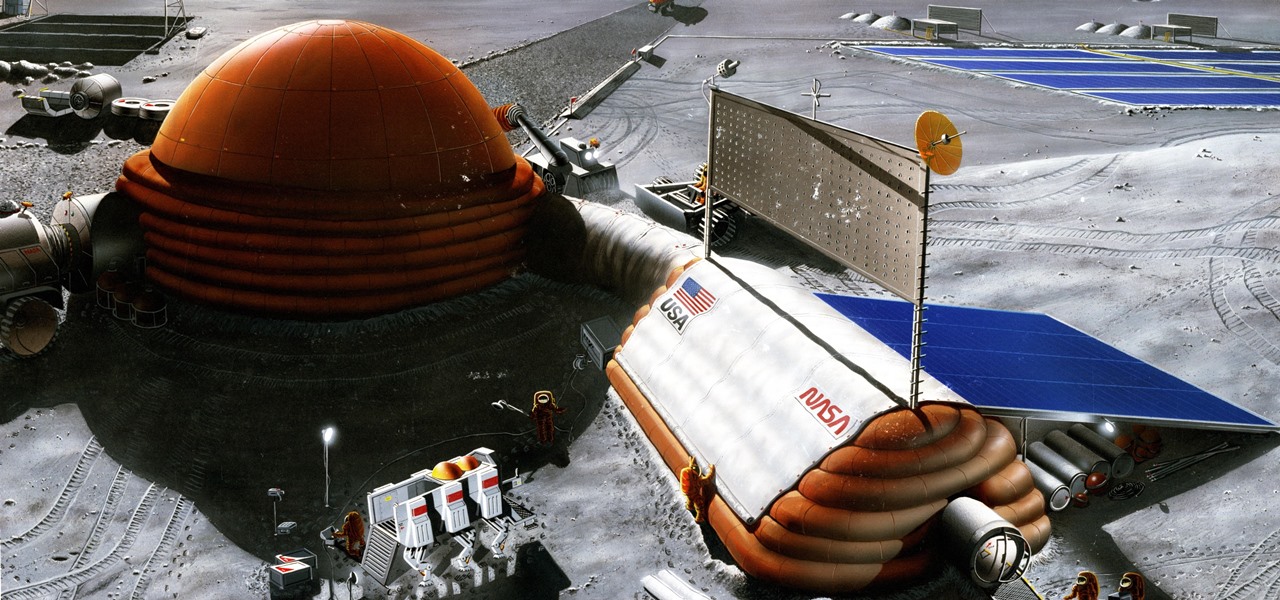

Wherever there are people, the party is sure to follow. Well, a party of microbes, at least. That is what scientists at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory have found after a 30-day microbial observation of the inflatable lunar/Mars analog habitat (IMAH).
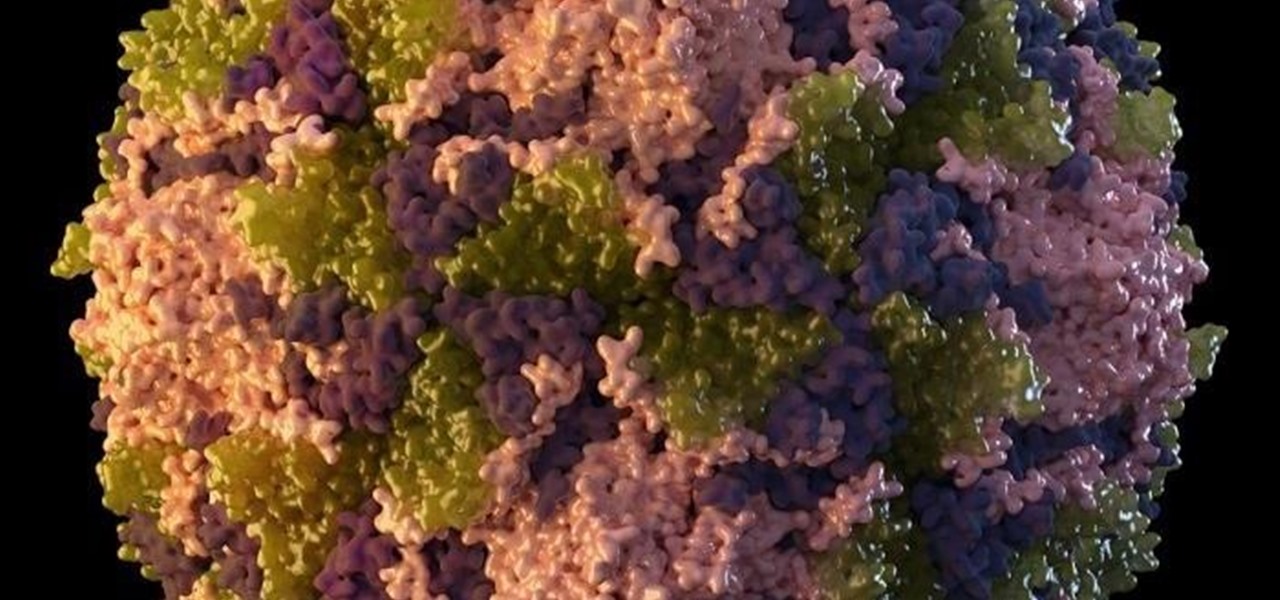

A recently confirmed polio outbreak in Syria is connected to low levels of vaccination, worsened by conflict. It is the first confirmed incidence of polio in Syria since 2014. Before 2013, the last case of polio in Syria was in 1999.
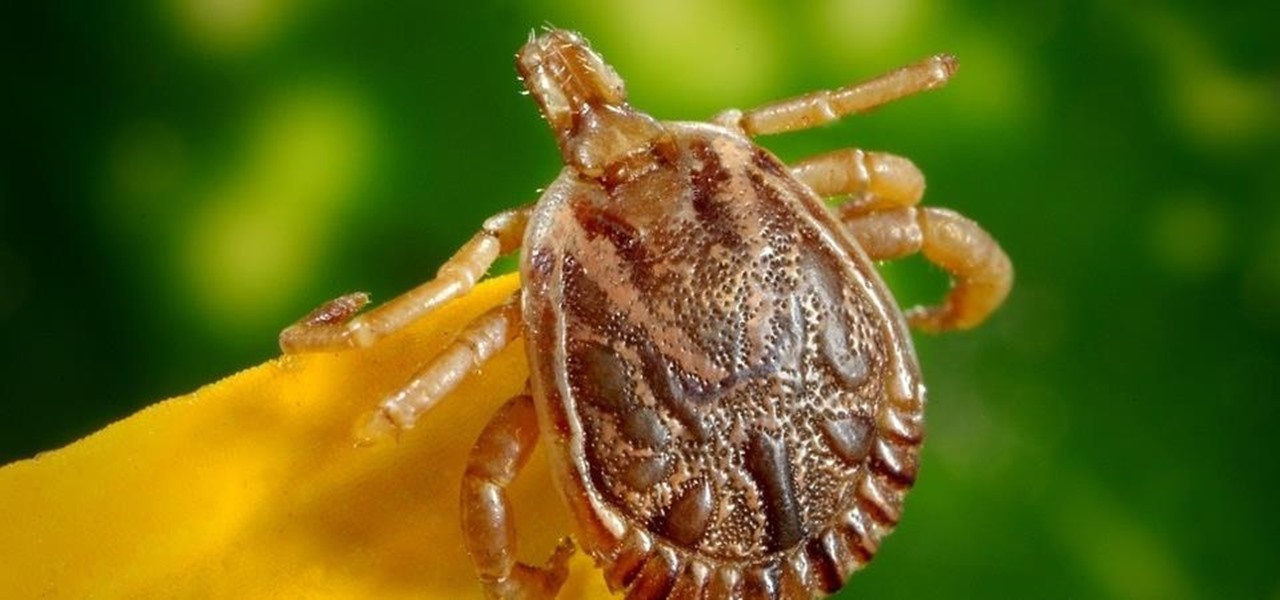

In Indianapolis, two-year-old Kenley Ratliff has passed away from what is suspected to be Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF), a tick-borne illness. The young girl fell ill with a fever, and just a week later, passed away. Now her family and doctors are looking into the cause of her death and warning others to check themselves for ticks this summer.
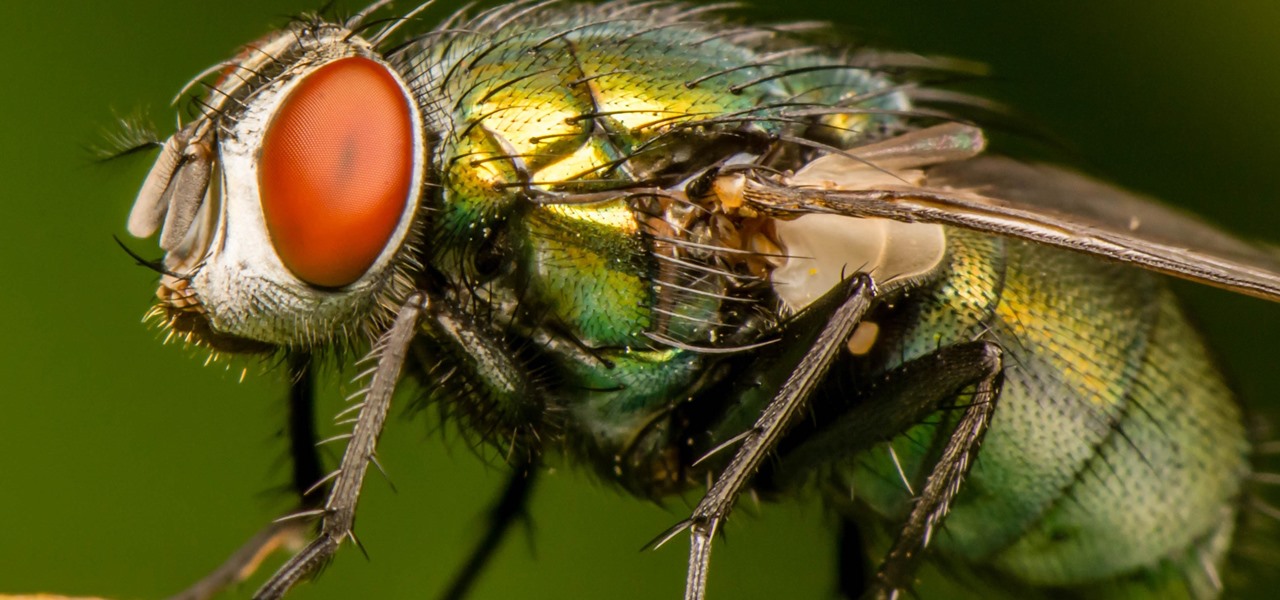

Researchers have been studying the blood meals of flies to understand the flow of infectious pathogens in wild animals.
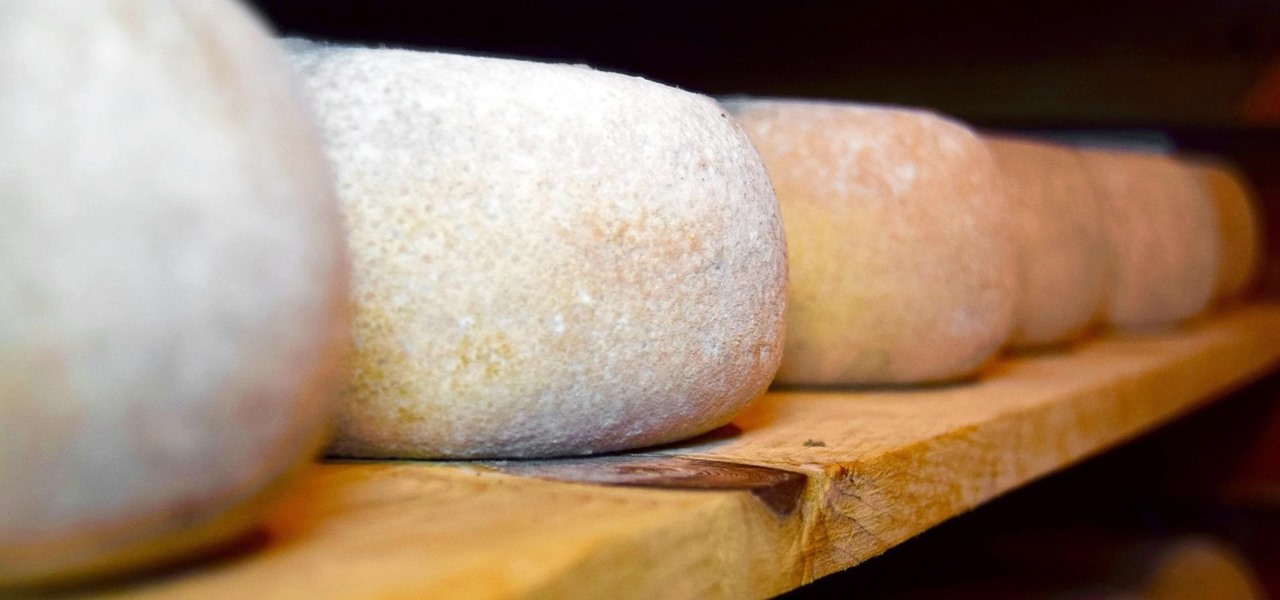

If you want to appreciate the value of microbes, look no further than a chunk of cheese. Because cheese roughly traces back to the Neolithic Era, we might say the earliest cheesemakers were the first humans to manipulate microbes—without even knowing it. Now, thanks to microbiologists and the long tradition of cheesemaking, we know a lot more about the microbes that make our favorite types of cheese possible.
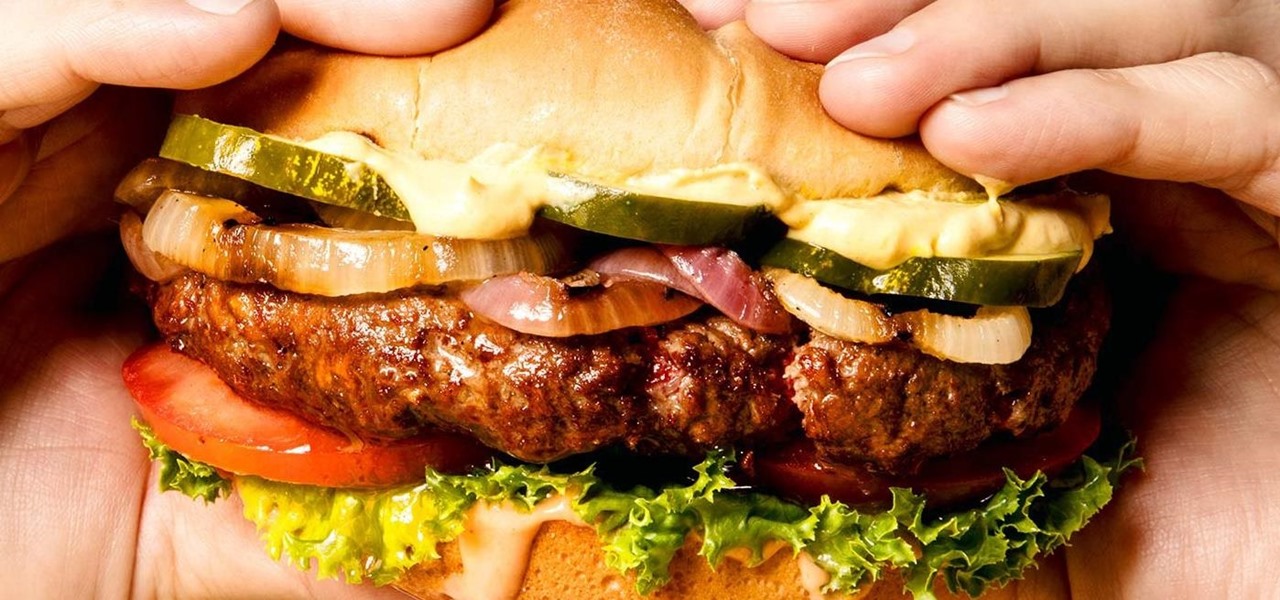

If you could save the world by eating a burger, would you? Two companies, Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods, are on a mission to redefine veggie burgers and eliminate all of the downsides of animal farming on our planet. With over five years of research and product testing, they've finally figured out how to make a plant-based burger look, feel, and taste just like real meat.
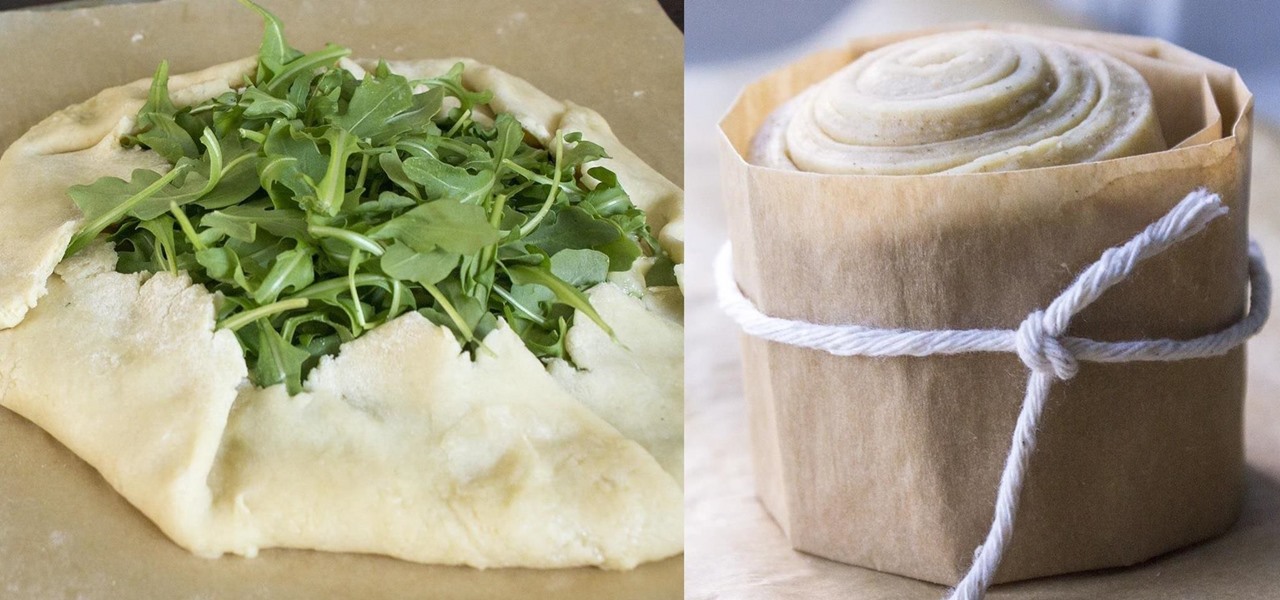

If you're anything like me, the urge to bake comes in waves. Winter constitutes an especially large wave; when I need to put on a few extra pounds for insulation, I go a bit carb crazy and take any opportunity to make breads, pies, and cakes.

Most people's fascination with social media these days is the instant gratification that can come with it. Whether you post an image on Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat, or Twitter, a minute or two later your phone will receive a notification informing you of a buddy or two who liked it.
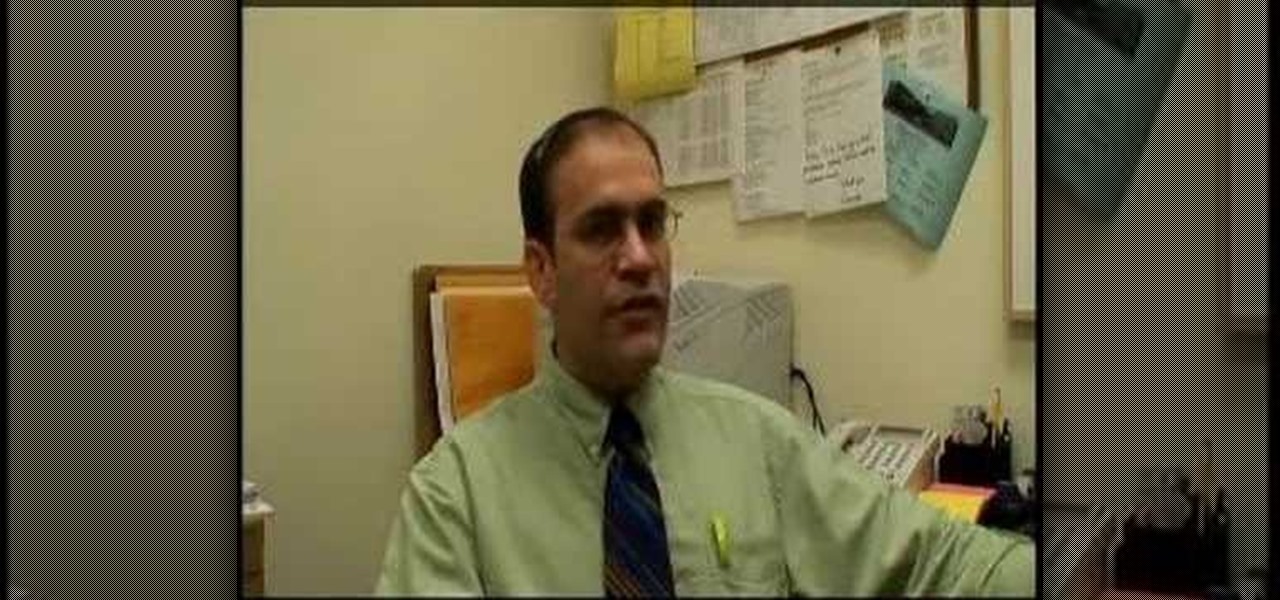

Dr. Ari Goldsmith discusses the diagnosis of swimmers ear and a few common treatments.
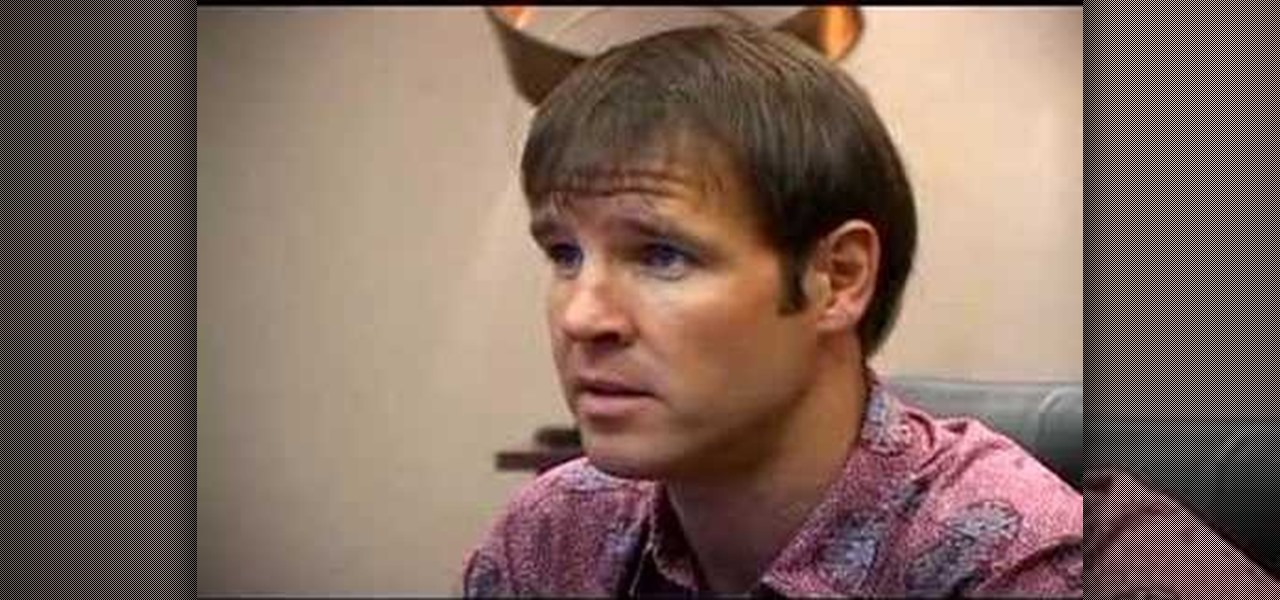

Dr. Christopher Lepisto shares how different forms of Kolorex, made from the horopito plant, can naturally fight off forms of Candida Infections.

In this video, we learn how to pierce your lip at home. Start off by numbing the area with ice cubes, then grab a clean and sharp object and poke it through the area. When it's inside, leave for a couple of minutes, then use a piece of ice to keep the swelling down. After this, grab the jewelry and place it through the lip after you clean it. Make sure you don't give the piercing any time to close in between when you pierce it and when you place the jewelry in. When you're done, remember to k...
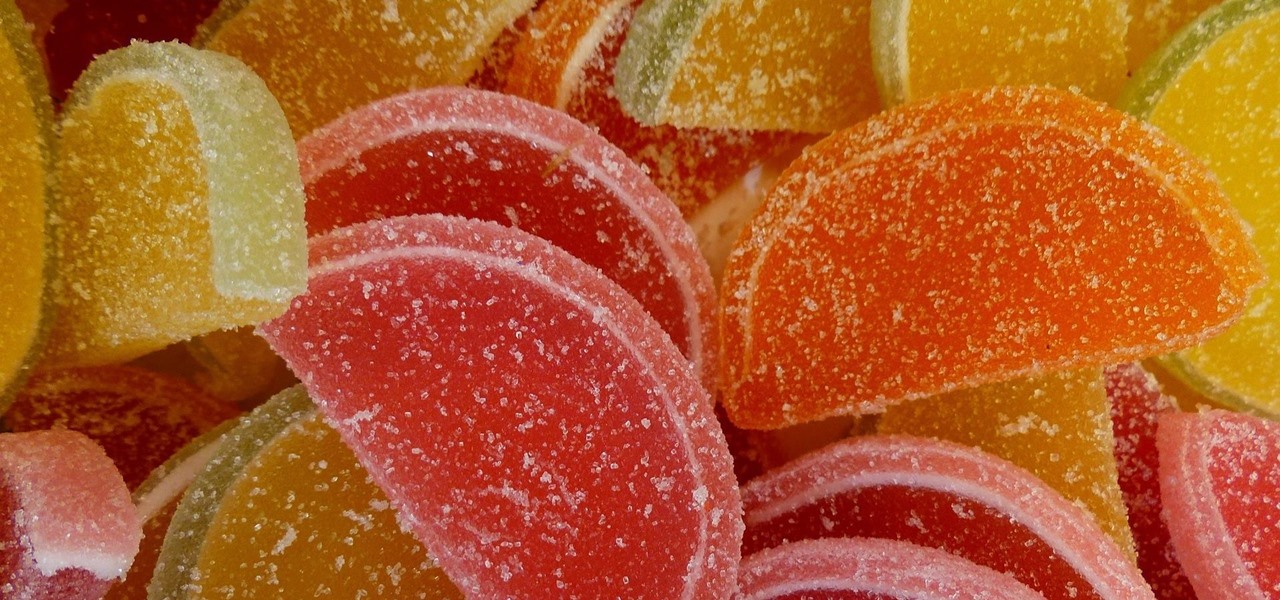

If you have a taste for sweets, you have at least one thing in common with mosquitoes. While too much sugar is unhealthy for humans, a new product makes sweets deadly to mosquitoes.
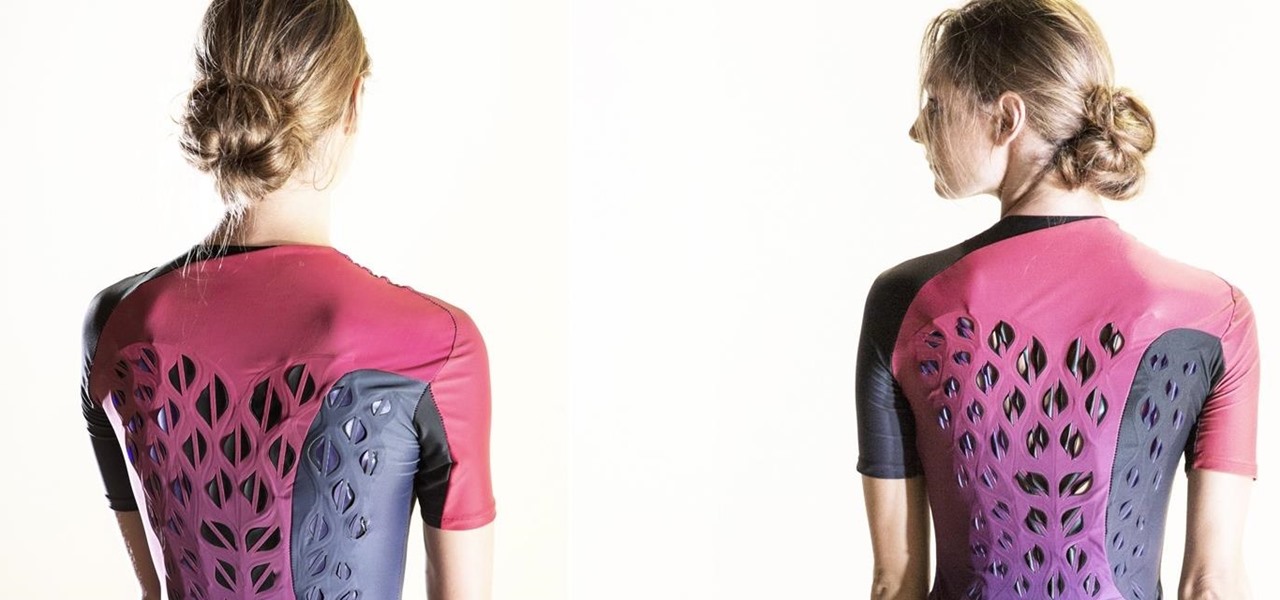

Microbial cells can improve the functionality of clothes in creative and useful ways, including cooling us down during a workout or making clothing glow for better visibility.
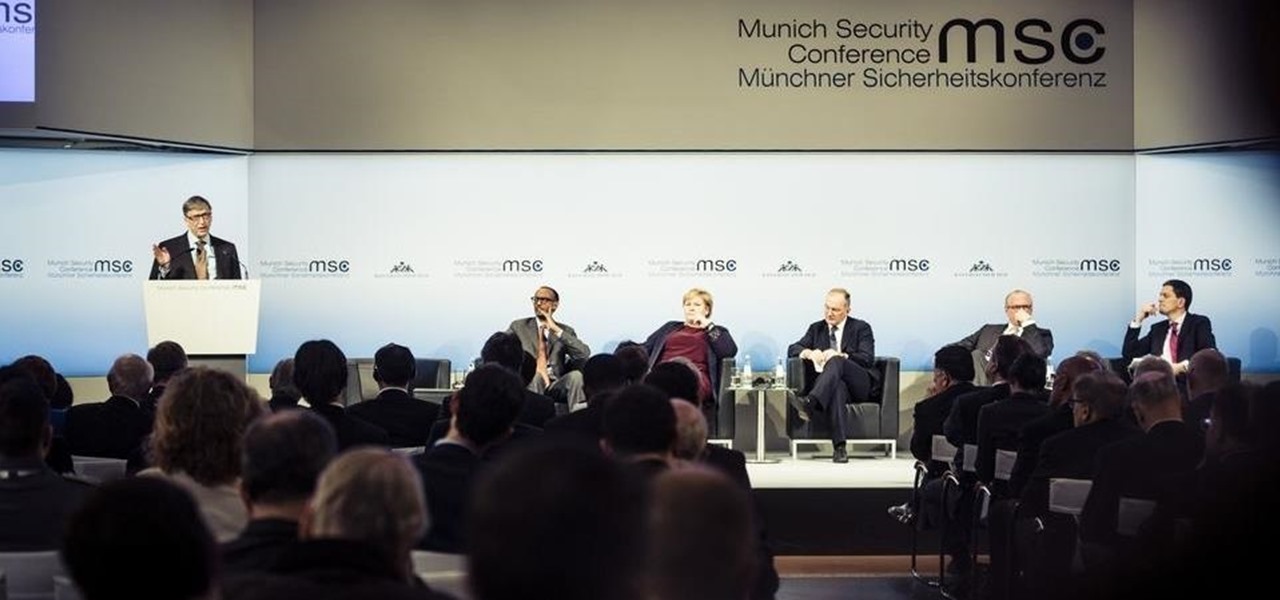

At a global security conference in Munich, philanthropist and businessman Bill Gates spoke about the next pandemic and a dire lack of global readiness. Here's how his statement could come true—and how to be ready when it does.
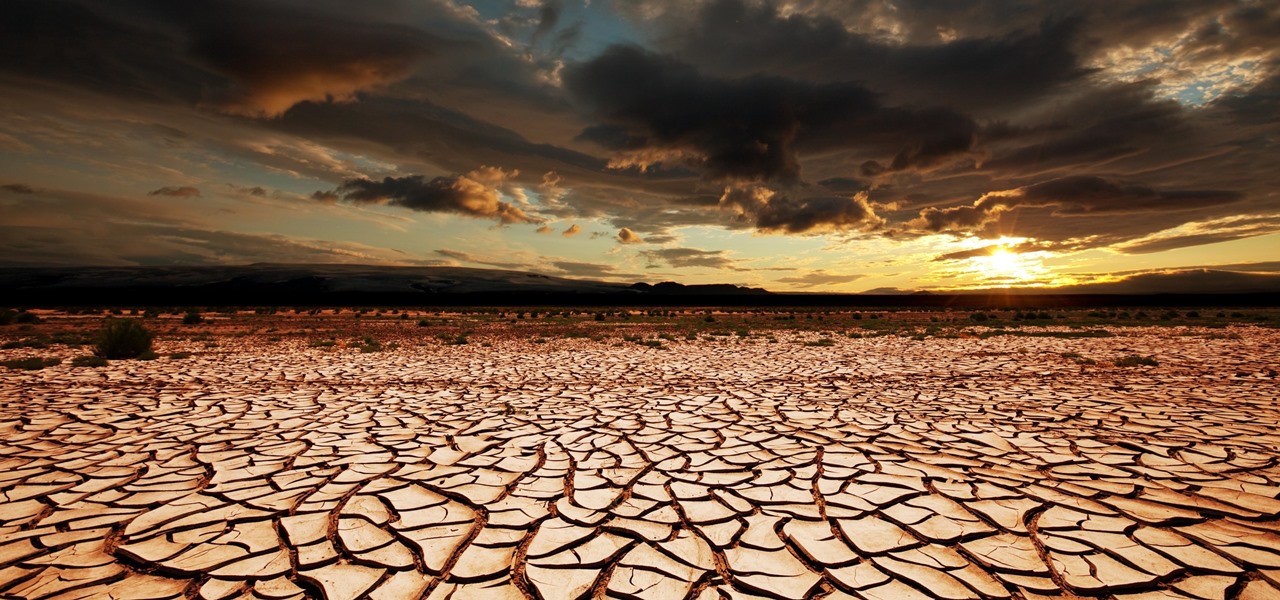

A recent study underscores a connection between climate change and infectious disease, raising concerns about our quickly warming planet.
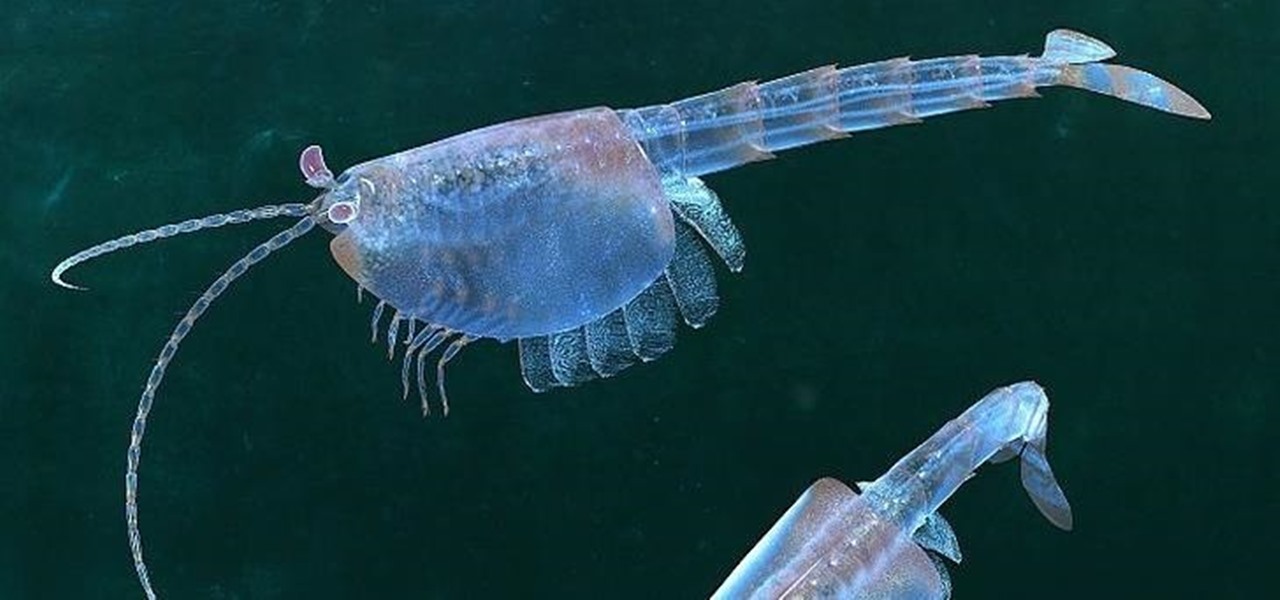

To shine light on the future of the relationship between humans and viruses, a team of researchers from the University of Oxford looked into the dim and distant past.
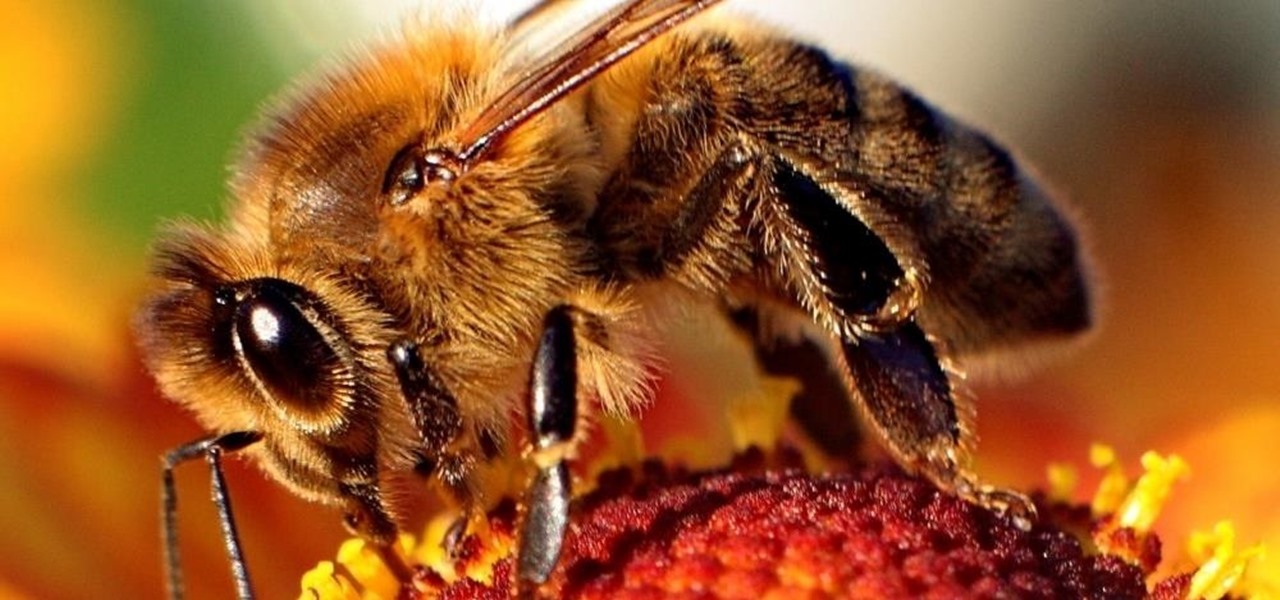

The search for the causative agent of colony collapse—the mass die off of honey bees throughout the US and Europe—has escalated with increasing confusion lately. Everything from pesticides and stress to viruses and mites have been implicated, and some researchers think that many of these environmental factors work together to take down hives.

As researchers learn more and more about our intestinal bacteria—also called the gut microbiome—we're finding out that these microbes aren't just influencing our health and wellness, they're a useful tool for improving it, too.
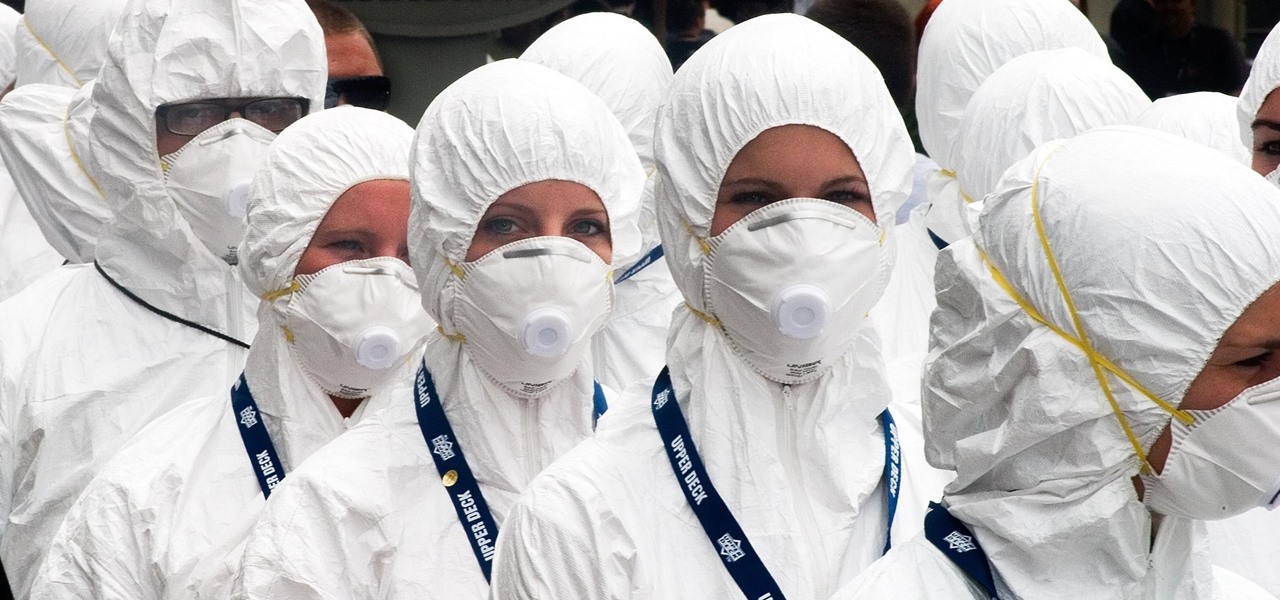

When Kaci Hickox, a Doctors Without Borders nurse, returned to New Jersey from working with Ebola patients in West Africa in 2014, she was surprised by her reception. Instead of a quiet return to her home in Maine after four weeks on the front line of Ebola treatment, she was quarantined by the State of New Jersey in Newark. She later filed a lawsuit in U.S. District Court for violation of her civil rights, false imprisonment, and invasion of privacy.
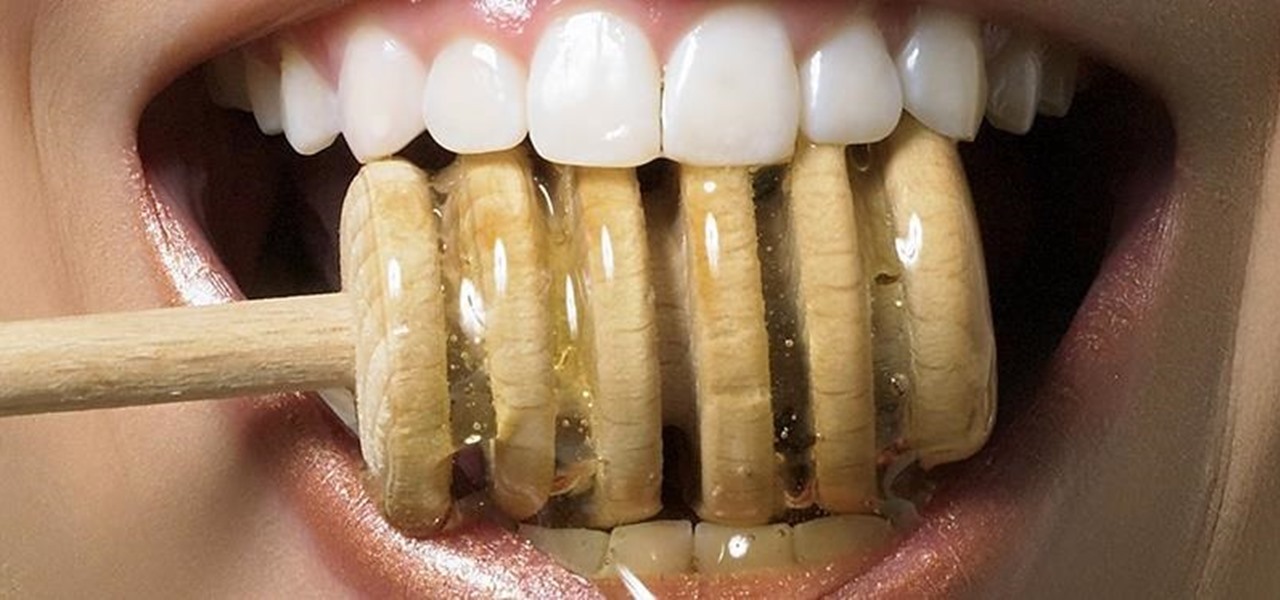
Only a handful of food products are impervious to spoilage—dried rice, salt, sugar—but even among those, honey is unique in that it remains edible without any preparation necessary. It's like this: if you came across honey in an Egyptian tomb, as archaeologists have, you could taste it and never guess it was thousands of years old.
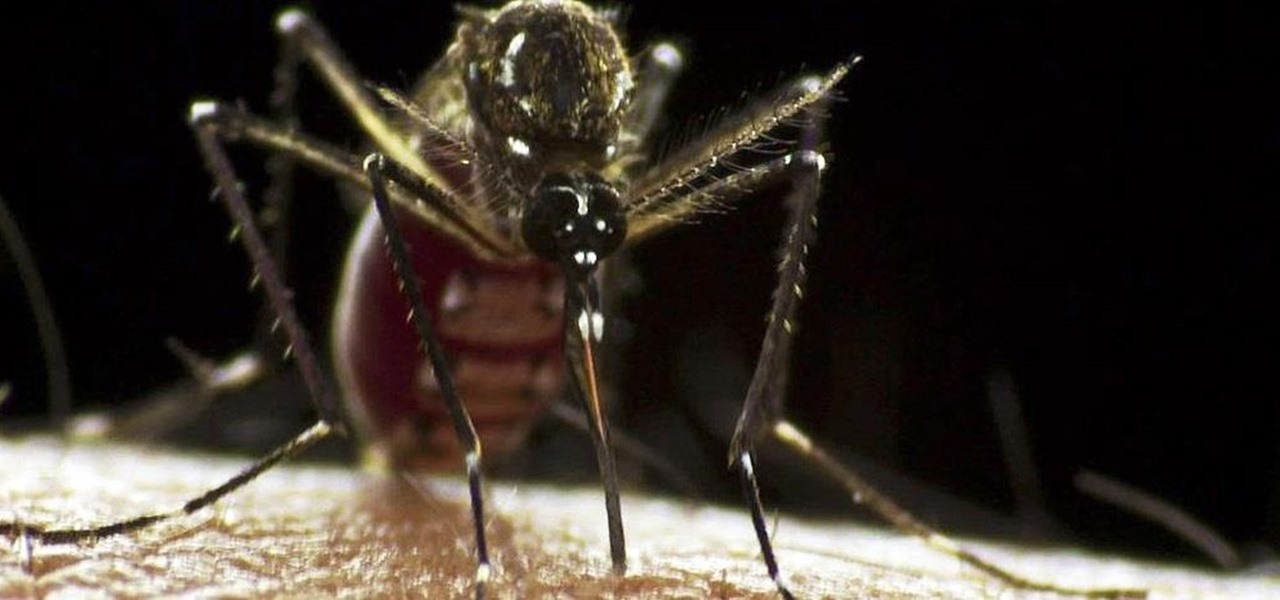
With warm weather comes bugs, and with bugs come bites, and with bites come itches. From ticks and spiders to mosquitoes and bees, insect bites come in sundry shapes and sizes, but they all commonly pull an itchy, red reaction out of our bodies.

In this video series, our expert Mark Emily will show you how to brew your own black lager, he will tell you about hops and malts, yeast, and Irish moss. Mr. Emily will also teach you about brewing equipment, different styles of beers, recipes, and ingredients, and equipment cleaners.

In this online video series learn how to culture fruit flies from fruit fly culture expert Richard Reavis. Watch these videos to learn about the different types of fruit flies. And learn fruit fly culturing essentials such as what materials and supplies you need to culture; how to select fruit flies; how to clean the culture area; how to measure and properly mix the media, water, and yeast for the culture; how to add flies to the culture; how to prevent infestation and contamination of mites ...
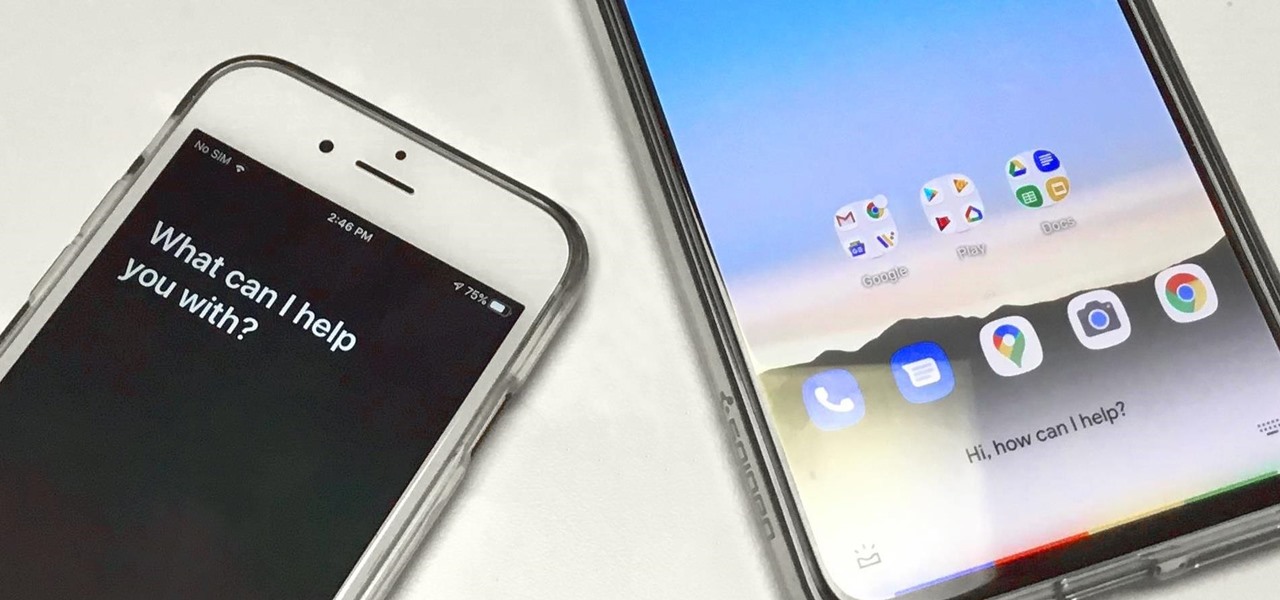

The COVID-19 pandemic has created a frenzy for news and information that is nearly unprecedented in the smartphone era, with a major side effect of misinformation. Now, major tech companies are making it easier to ask for advice about novel coronavirus from their respective digital assistants. Results may vary, but Apple and Google are the most useful at the moment.
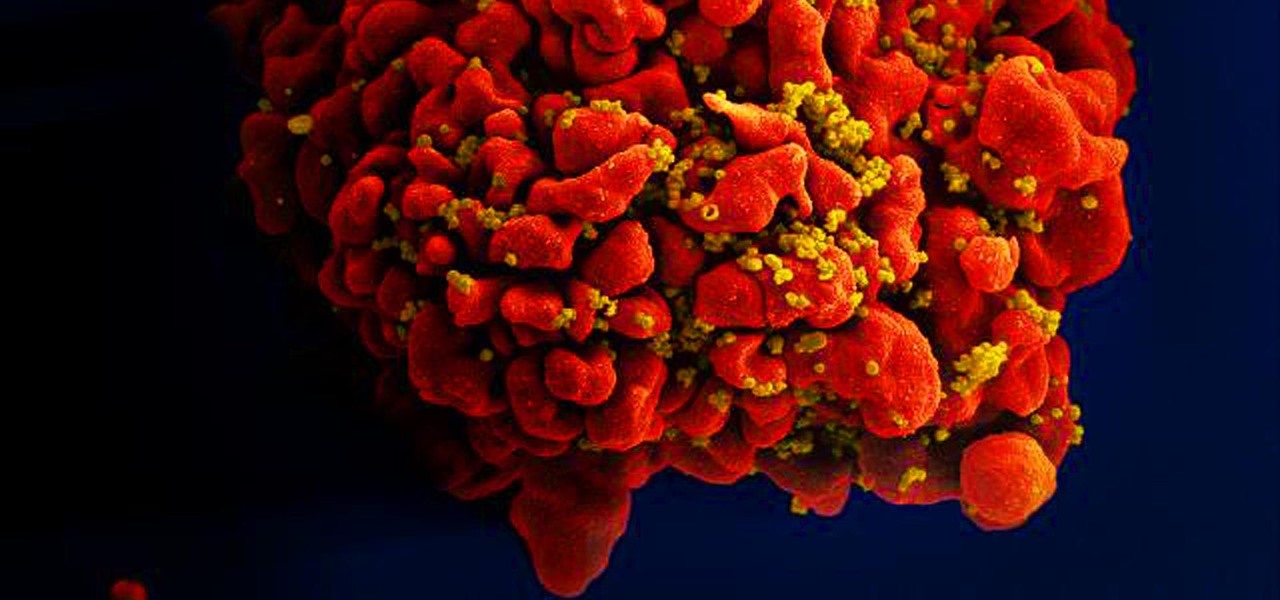
Results of an early-stage clinical trial of an HIV vaccine could mean a hoped-for breakthrough in the battle against AIDS.
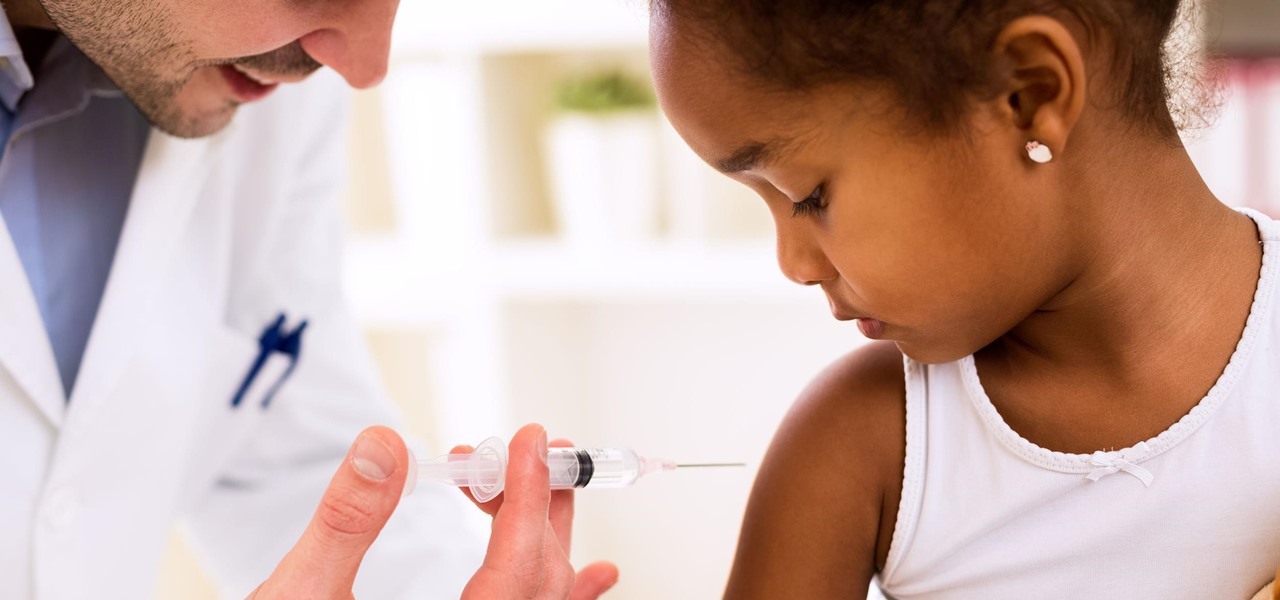
In late June, the biggest measles outbreak to strike Minnesota since 1990 seemed to be winding down. Today, public health officials announced a new confirmed measles case in the area.

Cytochrome P450 (P450s) are proteins found in nearly all living organisms, which play roles that range from producing essential compounds and hormones to metabolizing drugs and toxins. We use some of the compounds synthesized by P450 in plants as medical treatments, but the slow growth and limited supply of these plants have put the drugs' availability in jeopardy and jacked up prices.

Some types of bacterial infections are notoriously tough to treat — and it's not all due to antibiotic resistance. The bacteria themselves are rugged and hard to penetrate with drugs.
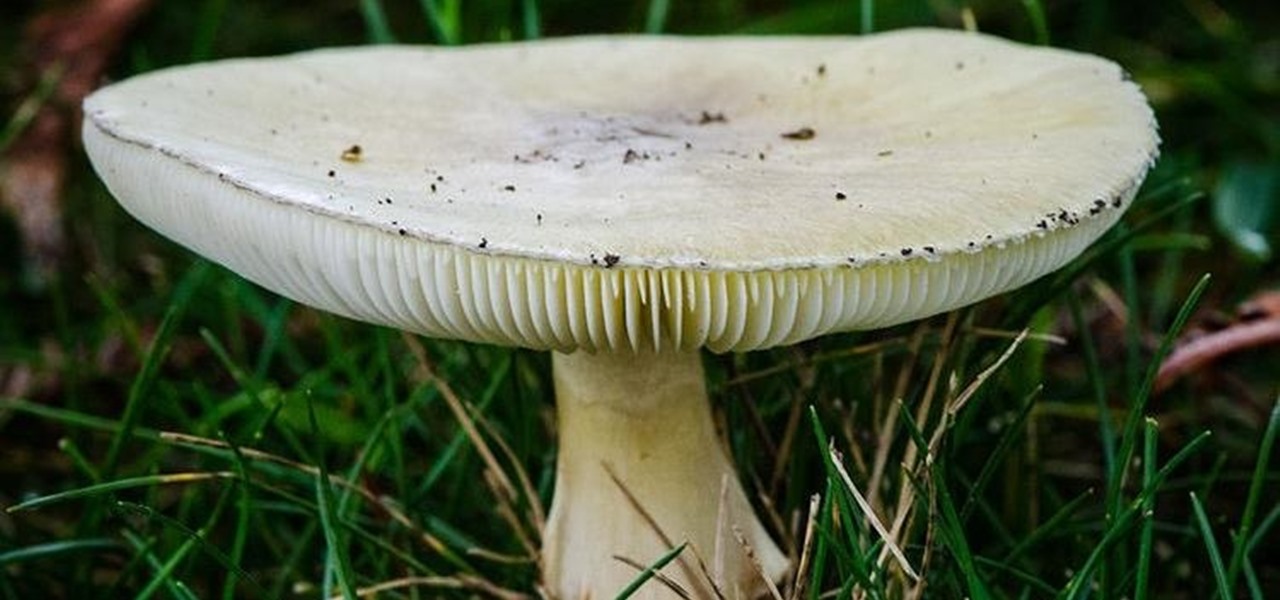

There is a reason the Amanita phalloides mushroom is called the "Death Cap." It can kill you. Mushrooms are a type of fungi, an organism that produces thread-like mycelia that often produce spores. Spores allow the fungi to reproduce. Molds, lichens, and yeast are all fungi, but the most visible fungi are mushrooms. Some fungi are delicious, but others can cause disease or, and still others, like Penicillium, can cure it.
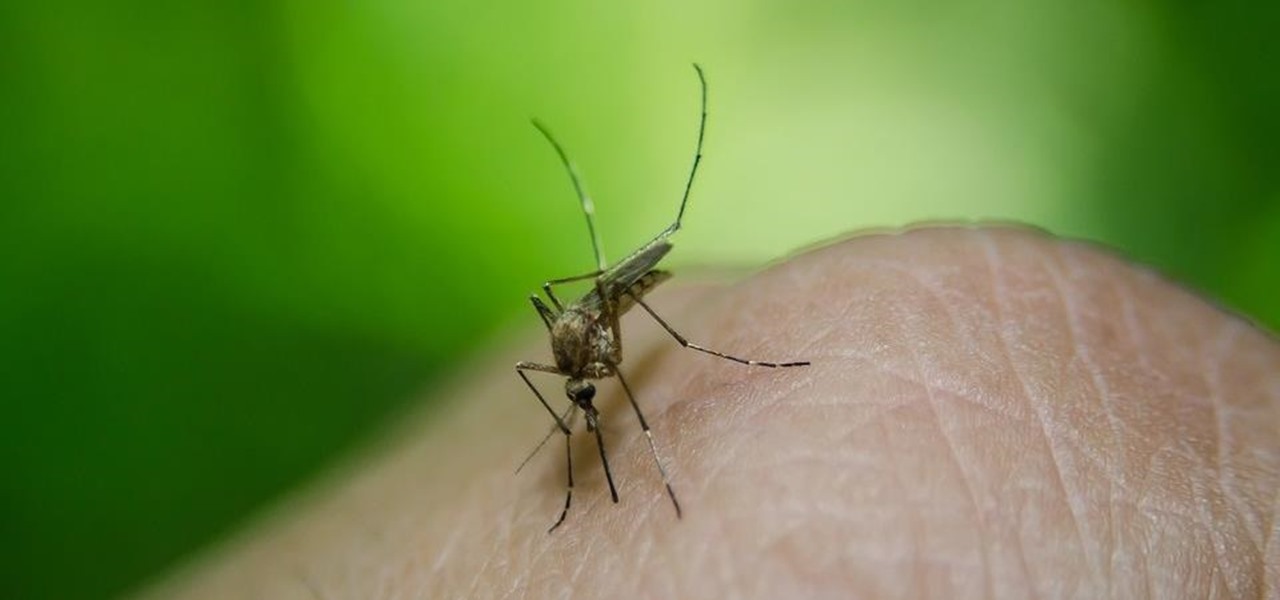

A case of West Nile virus recently confirmed in a person in Barton County, is the first human case of 2017 in Kansas. State health officials confirmed the appearance of West Nile this year in a press release on June 9th.
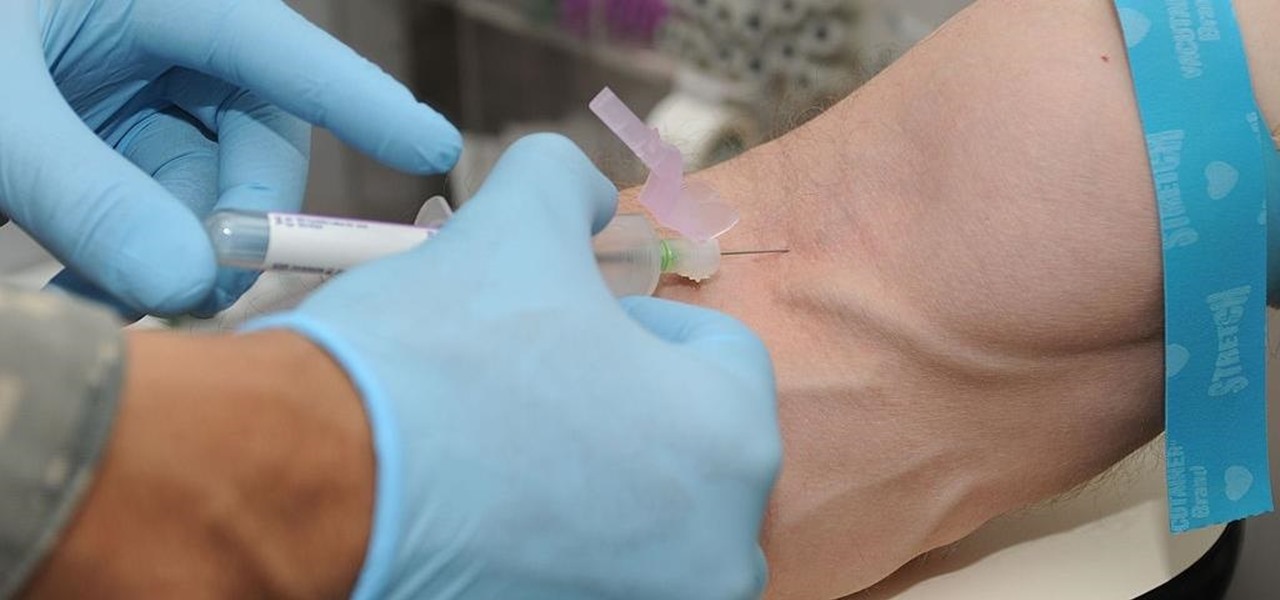
US blood banks have assured the American public that they have the tools to prevent a Zika contamination, despite the rapid spread of the disease.
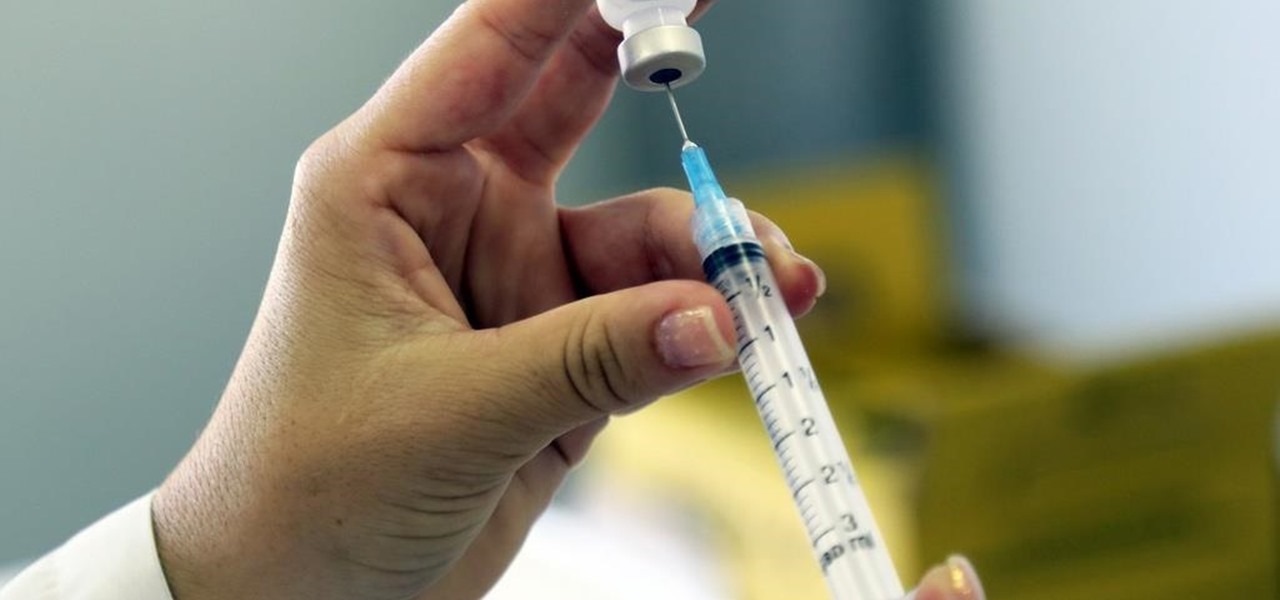
Officials in Colorado are concerned as 61 cases of the mumps were reported so far this year, a significant increase in the prevalence of the contagious disease in the state.
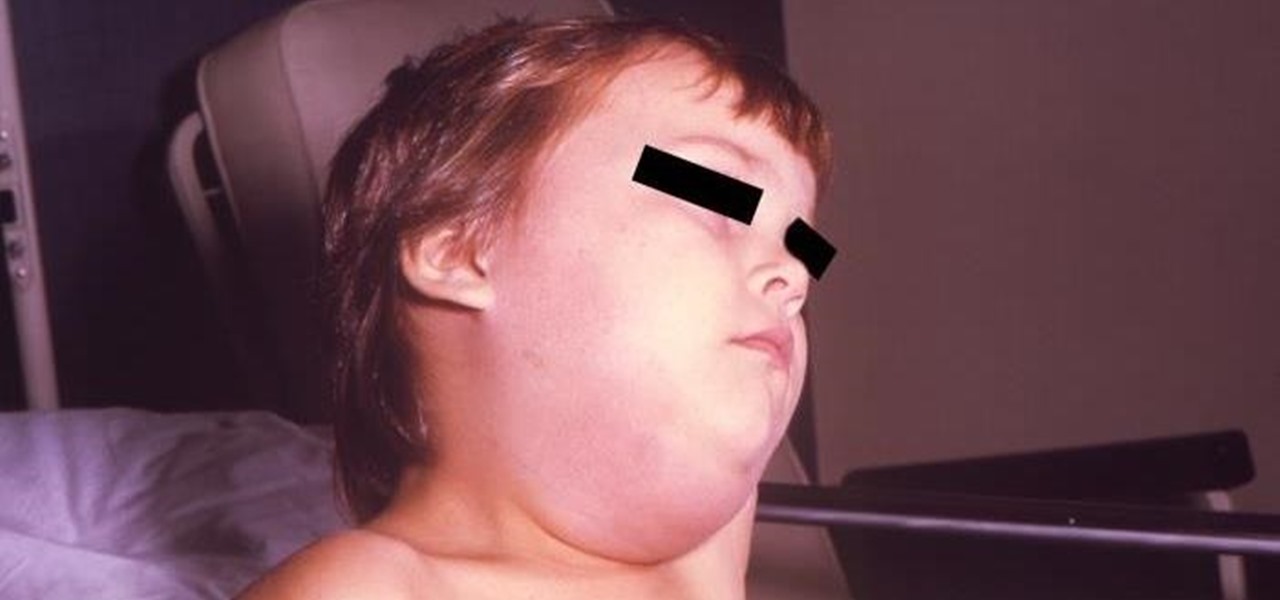
Obstetric tetanus in an unvaccinated Amish woman after a home birth has emphasized the need for preventative healthcare.
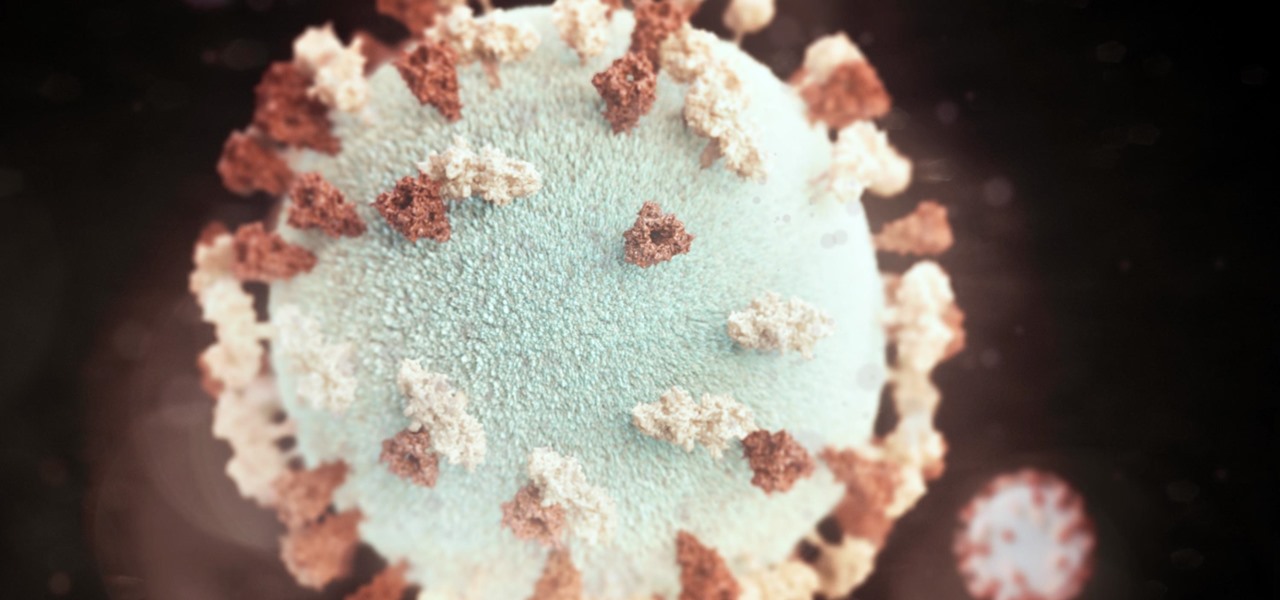
There have been mumps outbreaks in three different US colleges so far this year as instances of the illness are on the rise, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
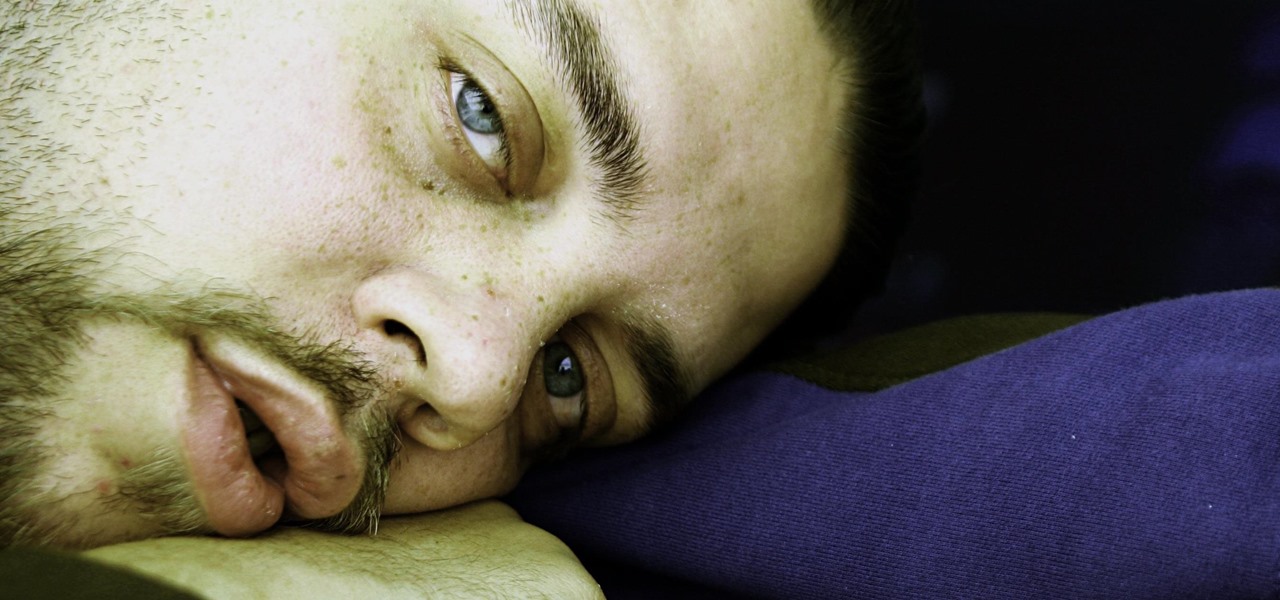

There's now more reasons to make sick workers stay home—a new game theory study suggests adequate hand washing and other illness-aversion tactics aren't as useful as we thought to keep you from getting infected when a virus or bacteria is circulating.
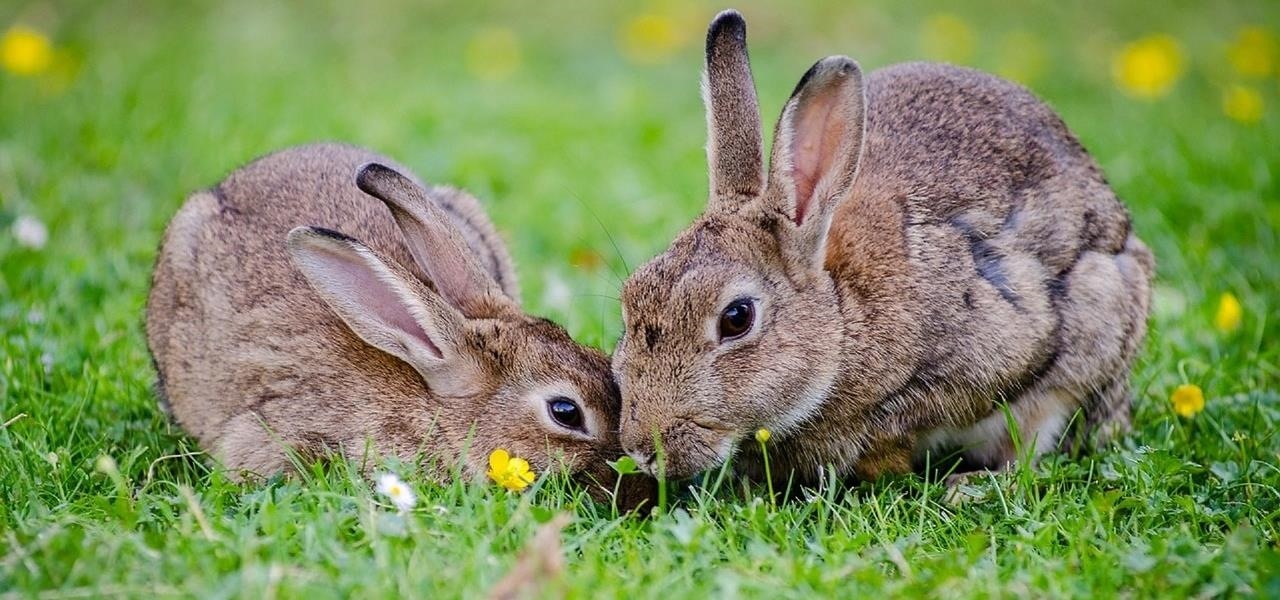

Rabbits have been a persistent problem in Australia for over 150 years. Now the Peel Harvey Catchment Council (PHCC) and Peel-Harvey Biosecurity Group have released a strain of the rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV), called RHDV1 K5, to reduce the number of pests in the Murray region of New South Wales.
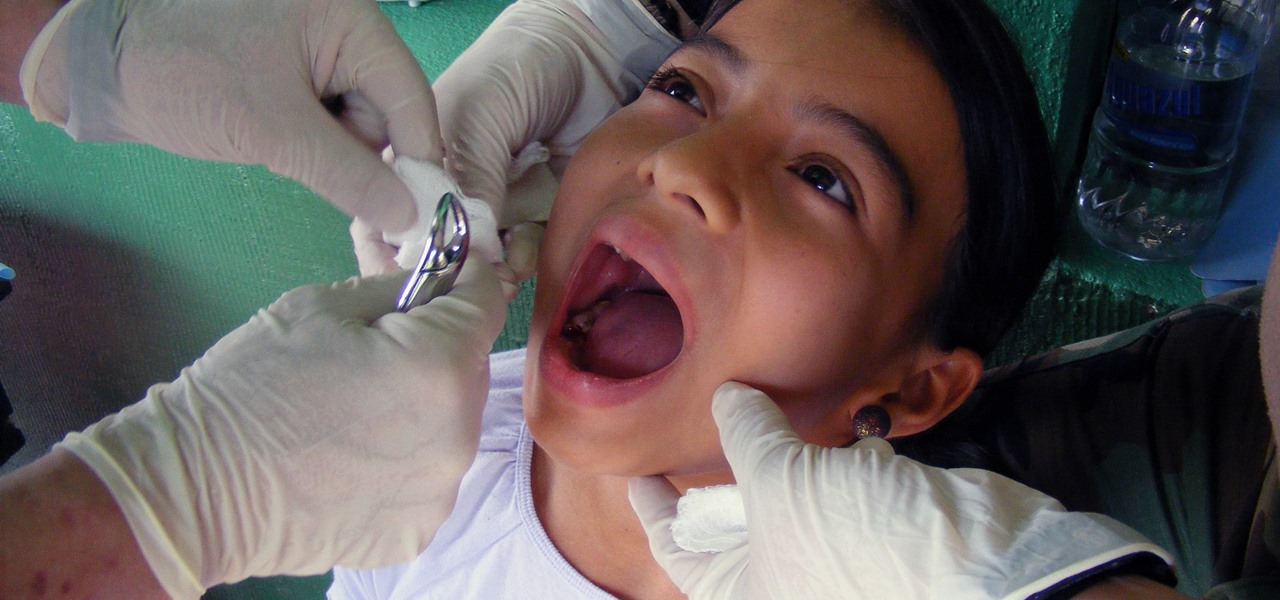
As many as 700 species of bacteria live on our teeth and in our mouth, and just like the microbiomes inhabiting other parts of our bodies, they change in response to diseases and other health conditions.
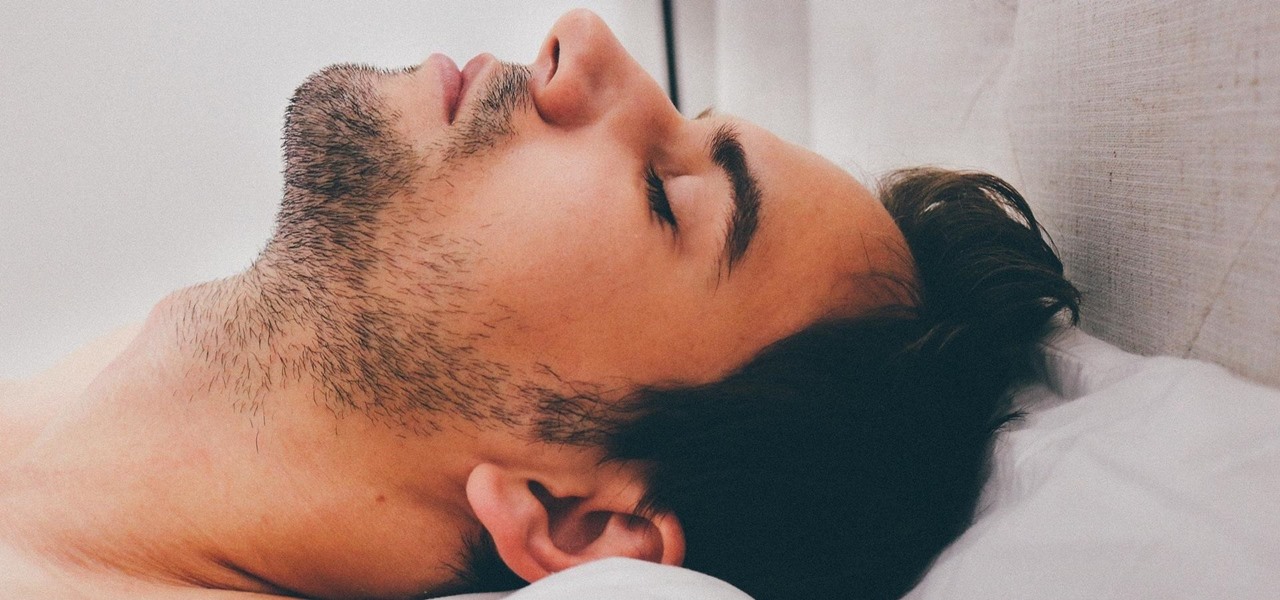

Sleep lets our body processes rest and restores us for the next day, so a bad night's sleep can ruin the following twenty-four hours and even make us feel sick. Now, new research published in the journal Sleep cements the idea that loss of sleep actually leaves us vulnerable to sickness.